4
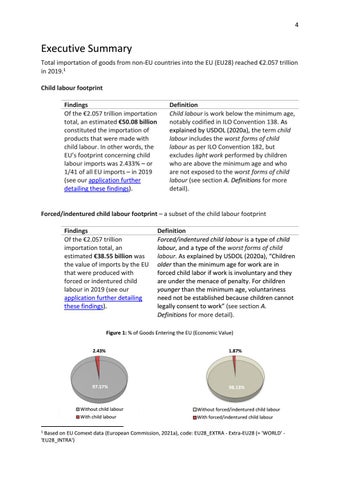
Executive Summary Total importation of goods from non-EU countries into the EU (EU28) reached €2.057 trillion in 2019.1 Child labour footprint Findings Of the €2.057 trillion importation total, an estimated €50.08 billion constituted the importation of products that were made with child labour. In other words, the EU’s footprint concerning child labour imports was 2.433% – or 1/41 of all EU imports – in 2019 (see our application further detailing these findings).
Definition Child labour is work below the minimum age, notably codified in ILO Convention 138. As explained by USDOL (2020a), the term child labour includes the worst forms of child labour as per ILO Convention 182, but excludes light work performed by children who are above the minimum age and who are not exposed to the worst forms of child labour (see section A. Definitions for more detail).
Forced/indentured child labour footprint – a subset of the child labour footprint Findings Of the €2.057 trillion importation total, an estimated €38.55 billion was the value of imports by the EU that were produced with forced or indentured child labour in 2019 (see our application further detailing these findings).
Definition Forced/indentured child labour is a type of child labour, and a type of the worst forms of child labour. As explained by USDOL (2020a), “Children older than the minimum age for work are in forced child labor if work is involuntary and they are under the menace of penalty. For children younger than the minimum age, voluntariness need not be established because children cannot legally consent to work” (see section A. Definitions for more detail).
Figure 1: % of Goods Entering the EU (Economic Value)
1
2.43%
1.87%
97.57%
98.13%
Without child labour
Without forced/indentured child labour
With child labour
With forced/indentured child labour
Based on EU Comext data (European Commission, 2021a), code: EU28_EXTRA - Extra-EU28 (= 'WORLD' 'EU28_INTRA')