150
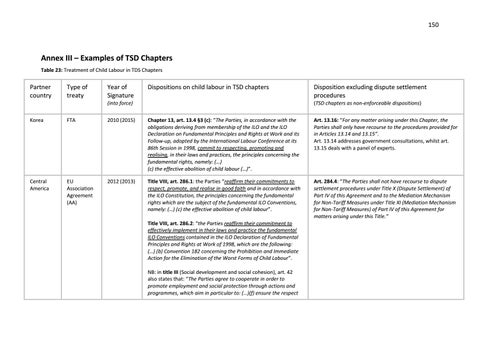
Annex III – Examples of TSD Chapters Table 23: Treatment of Child Labour in TDS Chapters
Partner country
Type of treaty
Year of Signature
Dispositions on child labour in TSD chapters
(into force)
Disposition excluding dispute settlement procedures (TSD chapters as non-enforceable dispositions)
Korea
FTA
2010 (2015)
Chapter 13, art. 13.4 §3 (c): “The Parties, in accordance with the obligations deriving from membership of the ILO and the ILO Declaration on Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work and its Follow-up, adopted by the International Labour Conference at its 86th Session in 1998, commit to respecting, promoting and realising, in their laws and practices, the principles concerning the fundamental rights, namely: (…) (c) the effective abolition of child labour (…)”.
Art. 13.16: “For any matter arising under this Chapter, the Parties shall only have recourse to the procedures provided for in Articles 13.14 and 13.15”. Art. 13.14 addresses government consultations, whilst art. 13.15 deals with a panel of experts.
Central America
EU Association Agreement (AA)
2012 (2013)
Title VIII, art. 286.1: the Parties “reaffirm their commitments to respect, promote, and realise in good faith and in accordance with the ILO Constitution, the principles concerning the fundamental rights which are the subject of the fundamental ILO Conventions, namely: (…) (c) the effective abolition of child labour”.
Art. 284.4: “The Parties shall not have recourse to dispute settlement procedures under Title X (Dispute Settlement) of Part IV of this Agreement and to the Mediation Mechanism for Non-Tariff Measures under Title XI (Mediation Mechanism for Non-Tariff Measures) of Part IV of this Agreement for matters arising under this Title.”
Title VIII, art. 286.2: “the Parties reaffirm their commitment to effectively implement in their laws and practice the fundamental ILO Conventions contained in the ILO Declaration of Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work of 1998, which are the following: (…) (b) Convention 182 concerning the Prohibition and Immediate Action for the Elimination of the Worst Forms of Child Labour”. NB: in title III (Social development and social cohesion), art. 42 also states that: “The Parties agree to cooperate in order to promote employment and social protection through actions and programmes, which aim in particular to: (…)(f) ensure the respect