The Converging Technology Revolution and Human Capital l 19
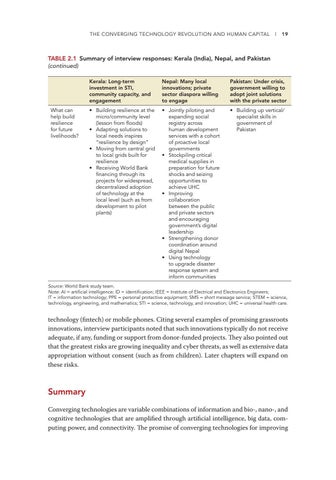
TABLE 2.1 Summary of interview responses: Kerala (India), Nepal, and Pakistan (continued)
What can help build resilience for future livelihoods?
Kerala: Long-term investment in STI, community capacity, and engagement
Nepal: Many local innovations; private sector diaspora willing to engage
Pakistan: Under crisis, government willing to adopt joint solutions with the private sector
• Building resilience at the micro/community level (lesson from floods) • Adapting solutions to local needs inspires “resilience by design” • Moving from central grid to local grids built for resilience • Receiving World Bank financing through its projects for widespread, decentralized adoption of technology at the local level (such as from development to pilot plants)
• Jointly piloting and expanding social registry across human development services with a cohort of proactive local governments • Stockpiling critical medical supplies in preparation for future shocks and seizing opportunities to achieve UHC • Improving collaboration between the public and private sectors and encouraging government’s digital leadership • Strengthening donor coordination around digital Nepal • Using technology to upgrade disaster response system and inform communities
• Building up vertical/ specialist skills in government of Pakistan
Source: World Bank study team. Note: AI = artificial intelligence; ID = identification; IEEE = Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers; IT = information technology; PPE = personal protective equipment; SMS = short message service; STEM = science, technology, engineering, and mathematics; STI = science, technology, and innovation; UHC = universal health care.
technology (fintech) or mobile phones. Citing several examples of promising grassroots innovations, interview participants noted that such innovations typically do not receive adequate, if any, funding or support from donor-funded projects. They also pointed out that the greatest risks are growing inequality and cyber threats, as well as extensive data appropriation without consent (such as from children). Later chapters will expand on these risks.
Summary Converging technologies are variable combinations of information and bio-, nano-, and cognitive technologies that are amplified through artificial intelligence, big data, computing power, and connectivity. The promise of converging technologies for improving