• 3 phases
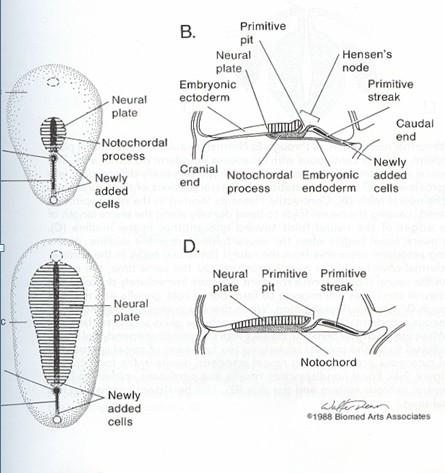
• Gastrulation/Notocord Integration 2 nd-3rd weeks
• Two layer embryonic plate divides into three laters (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm)
• Notocordal cells enter and extend cranially
• Neuroenteric canal forms temporarily
• Primary Neurulation 3rd-4th weeks
• Notochord interacts with overlying ectoderm, fusion to form the neural tube
• Secondary Neurulation 5th-6th weeks
• Cells of Hensen’s node migrate caudally to presacral region
• Retrogressive differentiation & Canalisation
EMBRYOLOGY
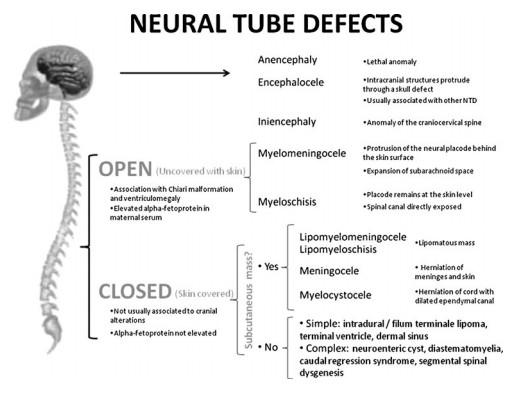
PRIMARY NEURULATION DEFECT
OPEN SPINAL DEFECT OSD MYELOCELE, MYELOSCHISIS
The placode remains “flat” and meninges are deep to the bony defect
OPEN DEFECT, CHIARI II MYELOMENINGOCELE
MMC
Placodr extends beyond the spinal defect, into a dilated cyst
• Theories:
• Anomaly of Primary Neurulation with Premature Disjunction
LIPOMA WITH DORSAL DEFECT
CSD WITH (OR W/O) SUB Q MASS
Lipomyelocele Lipomyelomeningocele
Key: The intrathecal fat associated with the low cord must be contiguous with the subcutaneous fat!
CSD WITHOUT MASS INTRADURAL/INTRASPINAL LIPOMA
• INTACT DURA
• Fat is NOT contiguous with the subQ fat
• Dorsal surface cord 75%
• Subpial, filling placode
• normal skin
• 2% syrinx
• “Lipoma with Dorsal Defect”
• Bony spine may or may not be intact
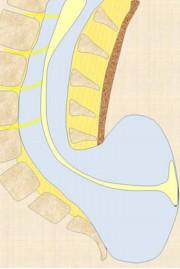
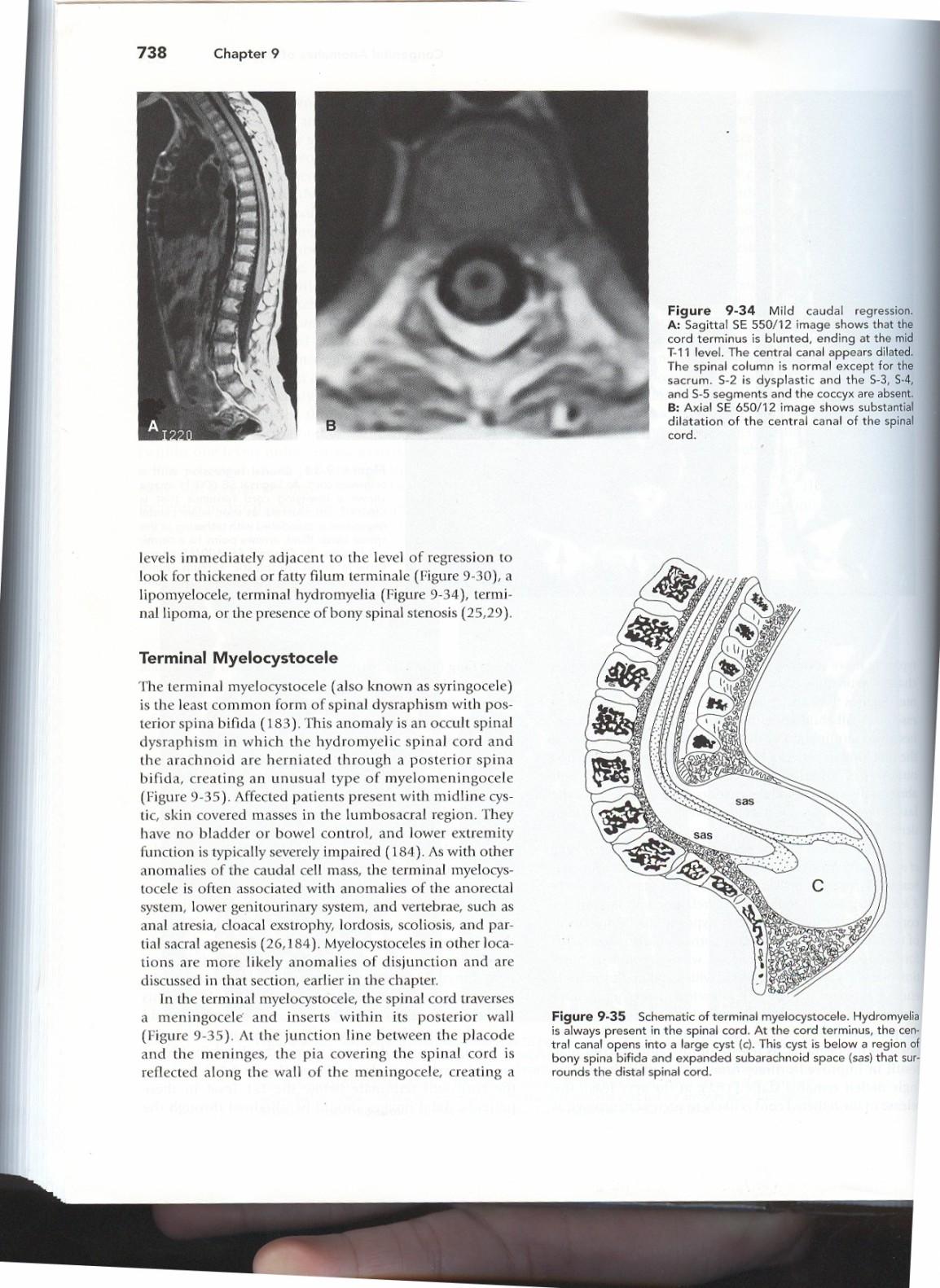
TERMINAL MYELOCYSTOCELE
CSD WITH SUBQ MASS
• Rare, = Syringocele
• Central cord canal expands thru spinal defect
• Asstd terminal lipoma
• more rarely, in association with a LMC/LMMC or Teratoma
• Associated anomalies:
• Imperforate, anus, ambiguous genitalia, vertebral segmentation anomalies
• Hydrocephalus uncommon
• poorer prognosis
SECONDARY NEURULATION
CAUDAL DEDIFFERENTIATION
• Normal Conus Position:
• Conus ascends in canal due to faster spinal bone growth
• 24 weeks L3
• 40 weeks inferior L2
• 3 months mid L2 >90%
Sacrococcygeal hypogenesis= caudal regression
GASTRULATION & NOTOCHORDAL FORMATION AND INTEGRATION
Intercalation: notochord fuses with endoderm > primitive neurenteric canal (communication between the central canal of notochord and the yolk sac)
SECONDARY NEURULATION CAUDAL DEDIFFERENTIATION CAUDAL REGRESSION ANOMALIES
VACTERL
• Vertebral anomalies
• Anorectal atresia
• Cardiac
• TE fistula
• Renal
• Limb anomalies
SC TERATOMA
• Classification
– Type I
• External 47%
– Type II
• External>Internal 35%
– Type III
• Internal>External 8%
– Type IV
• Presacral 10%
• Better prognosis (decreased incidence of malignancy) if:
• Extrapelvic
• Cystic