
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Vaishnavi Gadhave1, Rupesh Ukey2, Natasha Lanjewar3, Mr. Laximikant Tibude4
1Student, Department of Civil Engineering, Kavikuluru Institute of Technology & Science, Ramtek.
2 Student, Department of Civil Engineering, Kavikuluru Institute of Technology & Science, Ramtek
3 Student, Department of Civil Engineering, Kavikuluru Institute of Technology & Science, Ramtek
4Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Kavikuluru institute of Technology & Science, Ramtek.
Abstract
Thispaperinvestigatessolidwastemanagementstrategies in Gadchiroli, a region experiencing significant challenges due to escalating waste generation driven by population growthandevolvinglifestyles.Improperwastedisposalhas led to adverse health and environmental impacts, underscoring the urgent need for effective waste managementsystems.Throughacomprehensivereviewof existingliteratureandcasestudiesfromIndiancitiessuchas Sholapur,Indore,Nagpur,SaltLakeCity,andKhamgaon,the studyidentifiescommonissues,includingillegaldumping, inadequate infrastructure, and low public awareness. To address these challenges, the study proposes actionable recommendations, such as enhancing community engagement, adopting the 4R principles (Reduce, Reuse, Recycle,Recover),and improvinginfrastructureforwaste collectionandrecycling.Thesemeasuresaimtomitigatethe detrimental effects of improper waste management, safeguardpublichealth,andfostersustainableurbanliving conditions in Gadchiroli and similar regions. The findings contribute valuable insights into developing robust and scalablewastemanagementsolutionsforrapidlyurbanizing areas.
Key Words: Municipal Solid waste management, 4R principles
Populationisincreasingdaybyday,andwithit,solidwaste generationisalsograduallyincreasing.Themanagementof solidwasteisoneofthemostsignificantissuesforahealthy lifestyle and a safer environment. In many cases of solid wastemanagement,ithasbeenobservedthatthereispublic apathy and a lack of coordination between different civic bodies.
Modern and unorganized lifestyles are putting great pressure on natural resources. To cater to the needs of people, various products are created. The specialized productsmadebyindustriesdemandcarefulhandlingand treatment.Disposalofsolidwastewithoutpropertreatment negatively impacts soil, water, air, human health, and aesthetic value. Uncollected waste accumulates on the
streets,publicareas,andvacantlots,leadingtothecreation of illegal open dumps. Residents may simply throw their wasteintotheneareststreamorburnit.
Thecourseformsthebasisforhelpingstudentsunderstand solid waste management, health theories, concepts, and practices.Italsoequipsstudentswiththeknowledge,skills, andattitudesneededtomanagehazardousandelectronic waste. The main solid waste generators are households, commercial areas, public areas, RWAs (Residents Welfare Associations), public and community toilets, offices, and schools.Thesegeneratelargequantitiesofsolidwastedaily, whichmustbeprocessedanddisposedofproperly.
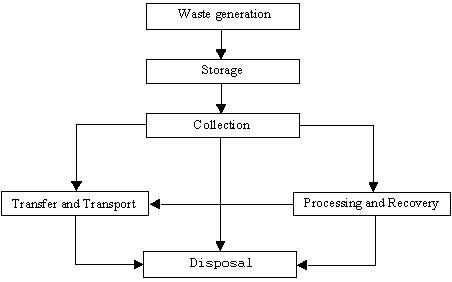
Wastemanagementinvolvesthecollection,transportation, processing, recycling, disposal, and monitoring of waste materials. It relates to discarded materials produced by humanactivityandisgenerallyundertakentoreducetheir impact on health, the environment, and aesthetics. Waste managementisalsocarriedouttorecoverresourcesfrom waste. It involves the use of solid, liquid, gaseous, or radioactivesubstances,withdifferentmethodsandfieldsof expertiseappliedtoeach.
Theprimarysourcesofmunicipalsolidwasteincludewaste generated from domestic, institutional, and commercial activities,aswellasgardenandmunicipalservices.Domestic wasteisproducedinlargequantitiesandvarieswithtime andseason.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
ThestudyisbeingconductedinGadchirolicity.Inancient times the region was ruled by the Rashtrakutas, the Chalukyas, the Yadavas of Deogiri and later theGondsof Gadchiroli.Gadchirolidistrictwascarvedoutonthe26thof August 1982 by the division of erstwhile Chandrapur district. Total population of the district is 10, 72,942 The SurjagarhregionofGadchiroliisamongthelargestreserves ofironoreinMaharashtra.
Sanket Talewar & Anurag K. Gahalod (2023) studiedon solidwastemanagementforkanhancity.Itpointsoutthata lot of waste comes from homes, businesses, and public places. The paper highlights problems with the current waste management system, such as illegal dumping and ineffective collection methods, which can harm people's healthandtheenvironment.Toimprovethesituation,the study suggests better waste management strategies, like recycling, proper disposal, and recovering energy from waste.Itrecommendsactionssuchasstoppingopenwaste storage,makingsurewasteiscollectedfrompeople'shomes, andusingbetterdisposalmethods.
Joy Karmakar (2023) workedonchallengesofMunicipal SolidWastemanagementinKolkata ThesituationinKolkata MetropolitanArea(KMA)reflectsbroadertrendsobserved inurbanwastemanagementacrossIndiancities.Addressing thesechallengesrequirestargetedimprovementsinwaste segregationpractices,infrastructuredevelopment,andthe expansion of waste processing facilities to ensure sustainable waste management in the face of increasing urbanization.Abetterwastecollectionsystemisneededto savemoneyandworkmoreefficiently. Thepapercallsfor better infrastructure, funding, and strategies to address theseissues.Thepaperreferencesvariousstudiesonwaste management in India and globally, highlighting ongoing challengesandsolutions.
Rasmeet Singh et. al. (2021) studied on solid waste management in Indore city aims to analyze the current situationofwastegeneration,collection,transportation,and disposal. This study provides readers with a clear understanding of the existing Municipal Solid Waste Management (MSWM) system in Indore. The plan is developed by closely monitoring key parameters such as populationdensity,roadconnectivity,wastegenerationand disposal capacity, and the transportation of waste from collection sites to disposal sites. The study highlights the complexitiesofmunicipalsolidwastemanagementinurban areasandunderscorestheneedforintegrated,inclusive,and innovativeapproachestoaddressthesechallenges.Italso emphasizes the importance of public awareness, institutional capacity, and technological advancements in achievingeffectivewastemanagement.Thestudyincludes the implementation of centralized composting plants and
bio-methanationfacilitiesforgeneratingBio-CNG.Indorehas achieved 100% door-to-door waste collection and source segregation,settinganexampleforothercitiestofollow.
R. Gajalakshmi & S. K. Manivannan (2020)studiedfocuses onsolidwastemanagementinChennai,India,anditseffects onhealthandtheenvironment.Itexaminesthevolumeof wastegeneratedandtherisksfacedbywastecollectors.The studyhighlightshealthandenvironmentalissuescausedby improper waste disposal, such as harmful gases and contaminated water. The paper emphasizes the need for improvedwastemanagementpracticesandincreasedpublic awareness.Itsuggestspromotingrecycling,composting,and adoptingthe5Rprinciples(Recycle,Reduce,Reuse,Refuse, andRecover).
V.N. Patil & R.S. Patil (2018) focused on solid waste management(SWM)inIchalkaranjicity,Maharashtra.The paperexaminesthecurrentscenarioofSWMinIchalkaranji, highlighting its pros and cons, and discusses the need for treatment facilities in the future, along with some environmentalimplications.Thestudyevaluateshowsolid waste is managed in Ichalkaranji, where current waste management practices are insufficient, with much of the waste not being treated properly. The amount of waste is increasingduetothecity'sgrowthandrisingconsumption.
Thepapersuggeststhatadoptingthe4Rtechnique(Reduce, Reuse,RecycleandRecover)incurrentpracticescouldsave costsandimprovetheadministration'spotentialforeffective SWM. The investigation reveals that the current waste management processes need to be coupled with a refusederivedenergyrecoverysystem,whichwouldaddeconomic value and lead to more effective waste management practices.Thestudyalsosuggeststhatwastemanagement canbeimprovedthroughbetterpracticesandgreaterpublic awareness. Sustainable waste management in the city requires better facilities and community involvement. Additionally, the study identifies different types of waste, includingmunicipal(household),industrial,andbiomedical waste.
D.S. Salgude (2017) conducted a review on solid waste management and recycling to understand the waste generation rate and the corresponding management approach using qualitative techniques in Nashik city, Maharashtra. Both qualitative and quantitative data were collectedthroughafeedbackassessmenttest.Approximately 350 tons of waste are generated in the city each day. The simplestwaytoreducewasteistotreatitasaresourcethat can be reused or recycled. This approach helps conserve resources, reduce pollution, save energy, and assists the Earthincopingwithhumandemands.
Inthefuture,therecouldbeadrasticreductioninwasteif moremanufacturersdesignandproducedurablegoodsthat areeasytodisassemble,repair,reuse,orrecycle.Solidwaste isfirstsortedandthenprocessedthroughvariousrecycling

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
methods, such as biomethanization, inert processing, windrowprocessing,andrefuse-derivedfuel(RDF)plants. The non-recyclable waste is sent to sanitary landfills. The reprocessingandreuseofwasteplasticshelpreducetheuse of natural materials and energy, leading to a decrease in carbondioxideemissions.
Nashikhastakenaleadingroleinthescientificmanagement of municipal solid waste, in line with the Municipal Solid Waste(ManagementandHandling)Rules,2000.
Ashwini S. Bhagat (2017) conductedastudyonsolidwaste managementinKhamgaonCity,withaparticularfocuson children,ragpickers,andemployeesworkinginthewaste managementsector.Solidwasteisgeneratedfromvarious sources, including domestic households, commercial establishments,industrial activities,medical facilities,and institutions.Asignificantpercentageofworkerswhohandle refuse,aswellasindividualslivingnearorondisposalsites, areatriskofinfectionscausedbygastrointestinalparasites, worms, and other related organisms. Contamination is prevalent at all stages where waste is handled. Gases are produced in landfills through anaerobic digestion by microbes,commonlyknownas"landfillgases."Thesegases consist of approximately 45-55% methane, which can be captured through a network of gas collection pipes and convertedintoasourceofenergy.Giventheexpansivearea around Khamgaon City, the process of sanitary landfilling can be easily adopted and proven to be one of the most effectivemethodsofwastedisposal.
Bhushan R. Ambade et.al. (2015)studiedonOpportunities andChallengesinMunicipalNagpurhasapopulationofover 2.8millionandgeneratesapproximately905tonsofwaste perdayover100tonsofthedailygeneratedwastearesent tothelandfillwithoutprocessingduetolimitedprocessing plant capacity. additional issues include inefficient waste segregation, unscientific dumping practices, and unauthorizedaccessbyanimalsandragpickers,enhancing wastesegregationatthesource,Increasingtheprocessing plant's capacity, implementing daily compaction and coveringofwaste,ensuringpropermonitoringoflandfillgas and leachate to prevent environmental contamination, Conductingregularhealthchecksforworkers.
B.L. Chavan and N.S. Zambare (2014) conductedastudy onMunicipalSolidWasteManagement(MSWM)inSolapur city. The study primarily focused on investigating the presentstatus of MSWM.A detailed study wasconducted, covering the methods and practices associated with the generated quantityofwaste,itscollection,transportation, treatment,anddisposalinthecity.Ananaerobicdigestion treatmentplantisunderdevelopmenttoextractenergyfrom organicwastebygeneratingbiogas.Thecombinedeffectsof uncollectedwaste,poorhandling,andinadequatedisposal safeguardsformunicipalwastehavesignificantimplications forpublichealth,increasingtheriskofdiseasetransmission,
thespreadofepidemics,andthelossofahealthy,urban,and amenableenvironment.
B.K. Bhattacharyya et al. (2011) conducted a study on Municipal Solid Waste Management (MSWM) in Salt Lake City,WestBengal.Thestudy,undertakenin2011,aimedto understandthechallengesandperspectivesassociatedwith solid waste management in the city. It focused on the collection and disposal of municipal solid waste, an issue exacerbatedbyrisingconsumptionlevels.
Theinvestigationincludedadetailedanalysisofthemethods and practices related to the sources, quantity of waste generated,collection,transportation,storage,treatment,and disposalofmunicipalsolidwasteinSaltLakeCity.Thecity comprisesatotalof78blocks.Greaterprioritymustbegiven to municipal solid waste management by the local authorities, with a systematic approach being essential to optimize the entire SWM process. This approach should include segregation of waste at the source, timely and efficientcollection,optimizationoftransportationroutesand vehicle types, as well as the development and proper managementofasanitarylandfillsite.
Theresearchhighlightsthatcitiesarefacingbig problems with waste management due to growing populations and changingconsumerhabits.Adetailedstudycomprisingthe methodofpracticesassociatedwithgeneratedquantityof waste,collection,transportation,treatmentanddisposalof (MSW)incitywasconducted.Toimprovethesituation,the study suggests better waste management strategies, like recycling, proper disposal, and recovering energy from waste. The complexities of municipal solid waste management in urban areas and the need for integrated, inclusive, and innovative approaches to address the challenges. The paper also encourages following the 4R’s principle:Reduce,Reuse,RecycleandResourcesRecoveryto improve waste management in the city. Many cities have trouble collecting and transporting waste properly, which canharmhealthandtheenvironment. Wasteworkersare especiallyatriskbecauseofpoorworkingconditions.The paper suggests that cities need to improve their waste managementpractices,raisepublicawareness,sortwasteat the source, recycle more, recover energy from waste, and buildbetterinfrastructure.Overall,thereisanurgentneed for better waste management strategies to protect public healthandtheenvironment.
[1] SanketTalewar&AnuragK.Gahalod“Casestudyon solid waste management for kanhan city” InternationalResearchJournalofModernizationin EngineeringTechnologyandScience(2023)e-ISSN 2582-5208

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[2] Dr.JoyKarmakar“AnOverviewandChallengesof Municipal Solid waste Management in Kolkata MetropolitanArea”JournalofIndianAssociationfor Environmental Management (2023)e-ISSN No.: 2582-4228
[3] Rasmeetsingh“Municipalsolidwastemanagement in the city of Indor A case study” Journal of civil engineering and environmental science (2021) ISSN:2455-488X
[4] R.Gajalakshmi&Dr.S.K.Manivannan“SolidWaste Management–ACaseStudy”TESTEngineeringand Management(2020)ISSN:0193-4120
[5] PatilV.N.&PatilR.S.“acasestudyofsolidwaste management in ichalkaranji city of maharashtra,india”https://www.researchgate.net/ publication/326534244 (2018) ,ISSN No 2277 –8179
[6] D.S.Salgude“AreviewonSolidwastemanagement and it’s recycling.” International journals of scientificandresearch(2017)ISSN2250-3153
[7] BhushanR.Ambade’,Dr.D.K.Parbat,VivekB.Dhait “Opportunities and Challenges in Municipal Solid Waste Management in Nagpur City, Maharashtra” International Journal of Modern Trends in EngineeringandResearch(2015)ISSN:2349-9745, P-ISSN:2393-8161
[8] B.L.Chavan, N.S. Zambare “A Case Study on MunicipalSolidWasteManagementinSolapurCity, Maharashtra, India” International Journal of ResearchinCivilEngineering,Architecture&Design (2013)ISSNOnline2347-1855.
[9] SK. Maity, BK Bhattacharyay, B Bhattacharyya “A CaseStudyonMunicipalSolidWasteManagement in Salt Lake City” International Journal of EngineeringScienceandTechnology(UEST)(2011).
[10] Ashwini S. Bhagat “Study of Solid Waste Management:CaseStudyforKhamgaonCity”UCRT Publish Paper record is available at DOI: http://doi.one/10.1727/JCRT.17123(2017).