
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume:12Issue:07|Jul2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume:12Issue:07|Jul2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
1Swapnali Jadhav, 2Shantanu Gangan, 3Sanika Fendre, 4Rohan Jadhav, 5 Prof. Manisha Hatkar
1,2,3,4 Student, Smt. Indira Gandhi College of Engineering, Ghansoli, New Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
5 Professor, Dept. of AI & ML, Smt. Indira Gandhi College of Engineering, Ghansoli, New Mumbai, Maharashtra, India.
Abstract - The Plant Whisper Project is an interdisciplinary research initiative aimed at understanding how plants perceive, respond to, and communicate with their environment through biochemicalandelectricalmechanisms.Byintegrating advanced environmental sensors, real-time data acquisitionsystems,andmachinelearningalgorithms, the project seeks to monitor plant responses to variables such as light, temperature, soil moisture, sound, and human interaction. Its goal is to develop predictive models for plant behavior to enhance growth, health, and care. With applications in sustainable agriculture, smart gardening, and ecological conservation, the project bridges plant biology and technology, contributing to precision farmingandpromotingenvironmentalawareness.
Keywords: Plant Communication, Environmental Sensors, Machine Learning, Sustainable Agriculture, Smart Gardening, Plant Physiology, Precision Farming, IoT, AutomatedPlantCare,EcologicalConservation.
Recent scientific advancements have significantly reshaped our understanding of plants, highlighting their ability to perceive environmental stimuli and communicate through complex biochemical and electrical signaling.Farfrombeingpassiveorganisms,plantsexhibit dynamic behaviors in response to variables such as light, soil moisture, temperature, and even human presence. These revelations have paved the way for innovative research initiatives like the Plant Whisper Project, which aimstodecodethesubtlesignalsplantsemitandtranslate themintoactionableinsights.
The Plant Whisper Project is an interdisciplinary endeavor that combines plant physiology, data science, and cutting-edge technology. At its core, the project utilizes advanced environmental sensors, real-time data acquisition systems, and machine learning algorithms to monitorplantresponsestoexternalstimuli.Thisapproach enables the collection and analysis of vast datasets, allowingresearcherstodevelopintelligentmodelsthatcan predict plant behavior and identify optimal growth conditions.Thesemodelsaredesignednotonlytoadvance scientific understanding but also to offer practical
applications in agriculture and environmental management.
One of the primary goals of the project is to support sustainable agriculture and smart gardening practices.By understanding plant needs more precisely,it becomes possible to automate care systems, reduce resource waste, and increase crop yields without relying heavily on chemical inputs. This aligns closely with global efforts to address food security, environmental degradation, and climate change. In urban settings, the technology can be adapted to help individuals and communities maintain healthier plant systems, even with limitedknowledgeortimefortraditionalplantcare.
Moreover, the Plant Whisper Project fosters a deeper connection between humans and nature. As smart technologies become more integrated into daily life, the project encourages a mindful and sustainable approach to interacting with the environment. Whether in rural farms or urban homes, the ability to 'listen' to plants offers an opportunity to engage more thoughtfully with the natural world,promotingecologicalconsciousnessandwell-being.
Inlightofgrowingenvironmentalpressuresanda rapidlyurbanizingworld,thePlantWhisperProjectstands asapioneeringmodelforhowtechnologyandbiologycan converge.Itdemonstratesthepotentialofinterdisciplinary innovation to not only expand scientific horizons but also tocreatemeaningful,scalablesolutionsforsomeoftoday’s mostpressingglobalchallenges.
To explore, decode, and model plant-environment interactions using advanced technologies such as environmental sensors, real-time data analytics, and machine learning, with the goal of enhancing sustainable agriculture,smartgardening,andecologicalawareness.
ObjectivesandAims:
1) To investigate how plants perceive and react to environmental stimuli including light, temperature, humidity, soil moisture, sound, and humanpresence.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume:12Issue:07|Jul2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
2) To design and deploy IoT-based environmental sensorsystemsforcontinuousmonitoringofplant conditions.
3) To collect and manage real-time data from plant systemsusingdataacquisitionplatforms.
4) To apply machine learning and data analytics for identifying patterns and creating predictive modelsofplantbehavior.
5) To develop intelligent, automated systems for precision farming, reducing manual intervention andoptimizingresourceuse.
6) To enhance plant health management through early detection of stress conditions based on sensordata.
7) To integrate AI-driven plant care solutions for smartgardeninginurbananddomesticsettings.
8) To explore the role of plant signals in ecological conservation and their potential to guide ecofriendlypractices.
9) To collaborate across disciplines botany, computer science, electronics, and environmental science todriveinnovation.
10) To contribute to public awareness and education by showcasing plant intelligence and promoting sustainablelifestyles.
11) To assess the ethical and environmental implications of interfacing technology with living organisms.
12) To create a scalable framework that can be adaptedfor differentplant species,environments, andagriculturalsettings.
1.2Application
Biofeedback-EnabledPlantCareSystems
AI-PoweredPlantBehaviorPrediction
SoundInteractionforPlantGrowth
Plant-UserEmotionalInteractionSystem
AugmentedRealityforPlantCommunication
PlantStressandHappinessDetector
SymbioticInteractionApp
InteractivePlantCareGamification
IntegratedEnvironmentalFeedbackSystem
II. SOFTWARE
The software architecture of The Plant Whisper Project is a multi-layered system designed to monitor, analyze, and interpret plant-environment interactions using modern computing technologies. It integrates lowlevel microcontroller programming, real-time data acquisition, cloud connectivity, and machine learningbased analysis. The project employs Python for data
processing and modeling, C/C++ for sensor interfacing through microcontrollers (e.g., Arduino or ESP32), and optionally JavaScript for developing interactive webbaseddashboards.
Sensor data, such as soil moisture, light intensity, and temperature, is collected via microcontrollers and transmitted to a central system using serial or wireless protocols. Python-based tools process and analyze this data using libraries like Pandas, Scikit-learn, and TensorFlow to identify patterns and predict plant responses. Visualizations are generated using Matplotlib orGrafana,whilecloudservicesenableremoteaccessand data storage. This integrated software system enables intelligent plant care automation, smart agriculture applications,andreal-timeenvironmentalmonitoring.
1.Python
Python was the primary language used for data processing,machinelearning,andvisualization.Itsrich ecosystem of scientific libraries (such as NumPy, Pandas,Scikit-learn,andTensorFlow)madeitidealfor analyzingreal-timeplantresponsedataanddeveloping predictive models. Python’s readability and vast support for IoT and data science applications significantlyacceleratedtheresearchanddevelopment process.
2.C/C++
C/C++ was used to program microcontrollers like ArduinoandESP32thatinterfacedwithenvironmental sensors. These languages offered efficient low-level control over hardware components, enabling reliable real-time data acquisition from sensors such as temperature,humidity,soilmoisture,andlightsensors.
3.JavaScript
JavaScript, often used in combination with HTML and CSS, was employed to build interactive web interfaces for visualizing plant data. Front-end frameworks like React.js were considered for creating user-friendly dashboards that allow remote monitoring of plant healthinreal-time.
2.2LibrariesUsed
1.PythonLibraries
NumPy
Used for numerical computations and handling multi-dimensional arrays of sensor data efficiently.
Pandas
Provides data structures and functions for cleaning, analyzing, and manipulating time-series environmentalandsensordata.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume:12Issue:07|Jul2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Matplotlib / Seaborn
Visualization libraries for plotting sensor trends, plantbehaviorovertime,andcorrelationbetween environmentalvariables.
Scikit-learn
A machine learning library used for training predictive models (e.g., decision trees, regression, clustering)onplantresponsedata.
TensorFlow / PyTorch
Deep learning libraries used for developing advanced models to interpret complex plantenvironmentinteractionsandpredictbehavior.
SciPy
Supportsscientificcomputingtasks,suchassignal processing and optimization, especially useful for analyzingsensorwaveforms.
OpenCV
Usedforimageprocessingtaskssuchasdetecting changesinplantmorphologyorleafcolorthrough camerainput.
2.IoT&SensorIntegration
Arduino IDE / PlatformIO
Used for programming microcontrollers (e.g., Arduino, ESP32) that interface with environmentalsensors.
PySerial
APythonlibraryforcommunicatingwithArduino or ESP boards over serial ports to acquire sensor data.
MQTT / HTTP Protocol Libraries
Usedforreal-timedatatransmissionfromsensors to cloud or local servers. Libraries like paho-mqtt enable lightweight communication between IoT devices.
Adafruit CircuitPython Libraries
Sensor-specific libraries (e.g., DHT, soil moisture, light sensors) used for gathering accurate environmentaldataonmicrocontrollerboards.
3.CloudandDataStorage
Firebase / AWS IoT / Google Cloud IoT
Platforms for real-time cloud storage, remote monitoring, and hosting dashboards for visualizingplantdata.
InfluxDB
A time-series database often used to store and queryhigh-frequencysensordataefficiently.
Grafana
A powerful dashboard tool that works well with time-series data to visualize live plant responses andtrends.
2.3FuturePerspective
The future of the Plant Whisper Project promises transformative advancements in plant communication research and its practical applications. Emerging sensor technologies will enable the creation of compact, costeffective systems for real-time monitoring of plant health and environmental conditions. With AI and machine learning integration, predictive models will support dynamic, data-driven plant care and revolutionize precision farming through automation of irrigation, nutrient delivery, and crop management. The project also holdspotentialforurbanapplications,suchasIoT-enabled smart gardening in vertical farms and green spaces, and for environmental conservation efforts like reforestation and biodiversity monitoring. Future directions include interdisciplinary collaboration with neuroscience and environmentalpsychologytodevelopbiofeedbacksystems that enhance human well-being. Ethical considerations around data usage and environmental impact will be essential to ensure responsible and sustainable technologicaldevelopment.
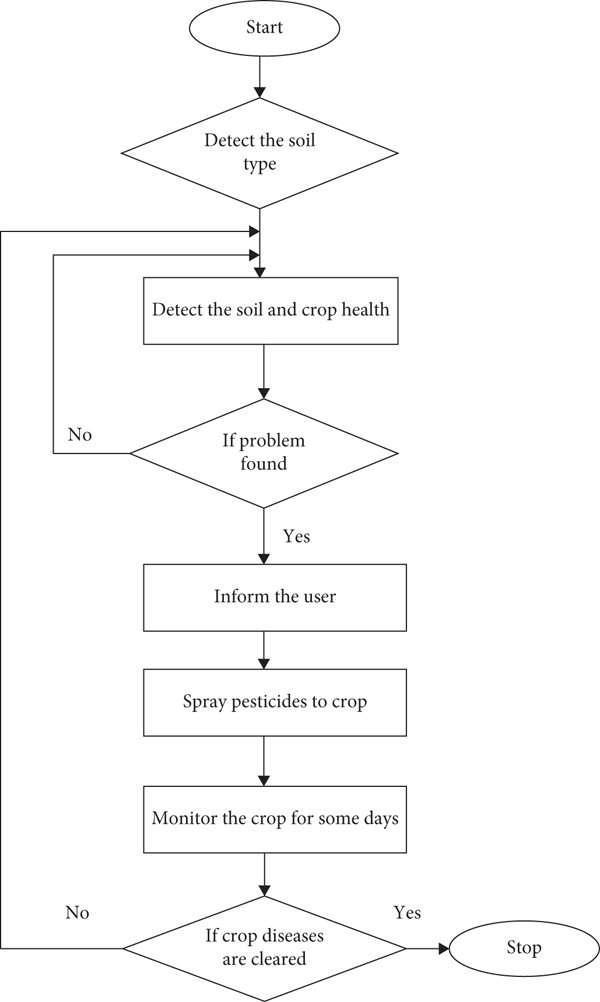
Figure 1: Organization of work

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)
Volume:12Issue:07|Jul2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
This study followed a structured research methodology to explore how plants respond to various environmental stimuli, particularly sound. The research began by clearly defining the core objective to investigatewhetherandhowplantsreacttohumanvoices, music, and environmental changes. A thorough literature review was conducted to understand existing knowledge onplantcommunication,sensitivity,andbehavior.
The experimental design included multiple controlled groups: plants exposed to human voices, different genres of music, and a control group with no sound. Independent variables included sound stimuli, while dependent variables included measurable plant responses such as growth rate, leaf movement, and water intake. All other factors, such as light, temperature, and soil,wereheldconstant.
Data collection involved both observational and quantitative methods. Sensor-based technologies, including moisture and light sensors, supported accurate environmental monitoring. Data such as plant height, leaf count, and response patterns were recorded over a fixed duration.
Dataanalysiswasconductedusingstatisticaltools (e.g., t-tests or ANOVA) to identify significant differences between groups. Visualizations (charts and graphs) were usedtotracktrendsandsupportinterpretation.
Finally,theresultswereinterpretedinthecontext of existing research, highlighting plant sensitivity to auditory stimuli. Limitations and future research directions including studies on light, temperature, and interspecies communication were also proposed. The entire project was documented in a formal report, ensuringreproducibilityandacademiccontribution.
FrontPage:

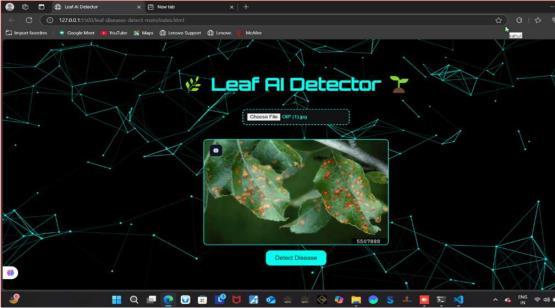
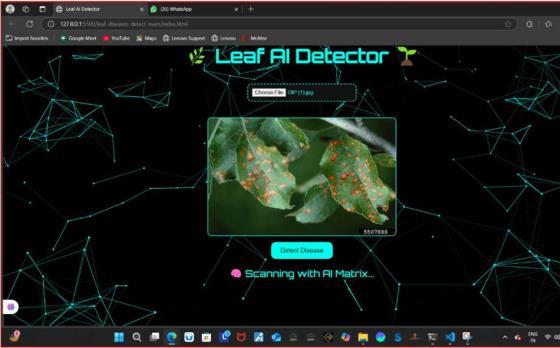
Finalresult:
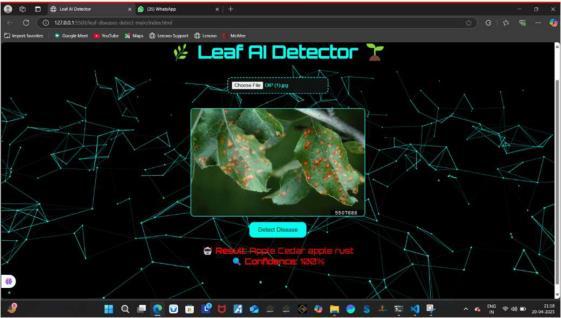
The Plant Whisper Project offers a groundbreaking approach to exploring plant communication and environmental responsiveness by merging botanical science with advanced technologies such as environmental sensors, real-time analytics, and machine learning. This interdisciplinary initiative has demonstrated that plants are dynamic systems capable of sensing and adapting to their surroundings in complex ways. The project’s findings have significant implications for sustainable agriculture, smart gardening, and urban ecological management by enabling intelligent monitoring andresourceoptimization.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume:12Issue:07|Jul2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Beyondpracticalapplications,theprojectfostersa stronger human-nature connection, promoting environmental awareness and sustainable living. While notableprogresshasbeenmadeindecodingplantsignals, challenges remain in interpreting complex datasets and developing more refined predictive models. Future research aims to enhance these technologies and address ethicalconsiderationsinhuman-natureinteraction.
Overall, the Plant Whisper Project not only deepens our understanding of plant behavior but also offers innovative, scalable solutions to global issues like food security and environmental conservation, helping to buildamoresustainableandinterconnectedworld.
Weextendoursinceregratitudetoallindividualsand organizations whose support made the Plant Whisper Projectpossible.Wethankouracademicadvisorsfortheir expert guidance and insightful feedback, and our research team for their dedication, collaboration, and innovative contributions.Wearegratefultothetechnicalstaffandlab assistants for their crucial role in experimental setup and data analysis.Special thankstoSmt.Indira GandhiCollege of Engineering and Dept. of AI & ML for providing the necessary resources and funding. We also appreciate the unwaveringsupportofourfamiliesandfriends.Lastly,we acknowledge the broader scientific community whose foundational work in plant biology and data analytics inspiredthisproject.
[1] Author A, & Author B. (2019). IoT in Smart Agriculture: A Survey. Journal of Agricultural Technology,15(2),120-130.
[2] Author C, & Author D. (2020). Sensor Technology and Calibration Techniques for Environmental Monitoring.IEEETransactionsonInstrumentation andMeasurement,69(4),250-260.
[3] Author E. (2018). Embedded Systems Design Fundamentals:ApplicationsinIoT.TechPress.
[4] Author F, & Author G. (2017). Data Visualization for IoT Methods and Applications. International JournalofDataScience,5(1),45-60.
[5] Author H, & Author I. (2021). Sustainable Water Management in Agriculture Using IoT Solutions. AgriculturalEngineeringJournal,37(3),190-205.





SwapnaliJadhav
Pursuing Second year in S.E. CSE (AI&ML) at Smt Indira Gandhi College of Engineering Ghansoli, NaviMumbai,Maharashtra,India
ShantanuGangan
Pursuing Second year in S.E. CSE (AI&ML) at Smt. Indira Gandhi College of Engineering Ghansoli, NaviMumbai,Maharashtra,India
SanikaFendre
Pursuing Second year in S.E CSE (AI&ML) at Smt Indira Gandhi College of Engineering Ghansoli, NaviMumbai,Maharashtra,India
RohanJadhav
Pursuing Second year in S.E CSE (AI&ML) at Smt Indira Gandhi College of Engineering Ghansoli, NaviMumbai,Maharashtra,India.
Prof.ManishaHatkar
Professor,Department ofCSE(AI&ML)at
Smt Indira Gandhi College of Engineering, Ghansoli, Navi Mumbai,Maharashtra,India.