International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS AND EFFICIENCY IMPROVEMENT OF COOLING TOWER AT MTPS-I
Mr. N.THIRU SENTHIL ADHIBAN1 , M.SUKEL AHAMED2 , S.SUGUMAR3 , P.NETHAJI41Head of the Department, 2,3,4 UG Scholar 1,2,3,4 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Sengunthar Engineering College (Autonomus), Tiruchengode, Namakkal, India. ***
Abstract In thermal power station one of the main part is condenser which cools the hot water. When cooling the hot water, it becomes cold water. The how water temperature is reduced by the cooling tower. When hot water enters into the cross flow induced draft cooling tower and sprayed by the nozzle, so that hot water is converted into cold water. The effective cooling water is depends upon wet bulb temperature, dry bulb temperature, size and height. This project deals with analysis of cooling tower which is one of the deciding factors used for the power plant efficiency.
Key Words: Wet bulb temperature, dry bulb temperature, cooling water range, cooling water approach, inlet air and water temperature, outlet air and water temperature etc.
1.INTRODUCTION
The Mettur thermal power station is the Tamilnadu electrical board's inland thermal power facility. Industrial development iscritical to thecountry's economicsuccess. The facility is on Stanley reservoir's left edge, on the Ellis Surplusroute.Themajorgoalofthe840MWMetturThermal ElectricityStationistomeetthepowerneedsofthestateof Tamilnadu'sindustrialcenters.Workontheprojectbeganin 1981,andthefirstunitwascommissionedin1987.Thelast threeunitswereputintoservicein1987,1989,and1990, respectively
1.1 SCOPE OF THE PROJECT
Thescopeoftheprojectistofindtheenergyconservation opportunitiesinMetturThermalPowerStationbyfollowing methods:
Tofindthevariousopportunitiesincoolingtower casing,fanbladematerialandfanbladeangle.
Throughreplacementofmotorstoreducethe currentandhorsepower.
2.COOLING TOWER
The cooling system conjointly includes any machinery accustomedoperatethetowerandanytanks,pipesorvalves. A cooling is instrumentality accustomed cut back the temperatureofthewaterbyextractingheatfromwaterand emittingtotheatmosphere.coolingbuildusetoevaporation whereverbyanumberofthewaterisgaseousintoamoving airstreamandafterwarddischargedintotheatmosphere.As a results the reminder of the water is cooled down considerably.coolingsquaremeasureabletolowerthewater temperatureoverdevicesthatusesolelyairtorejectheatjust liketheradiatorwithintheautomobileandsquaremeasure thus most value effective and energy economical. cooling squaremeasureemployedinairconsystemforrefrigeration or to cool down materials in industrial processes. cooling squaremeasuredevicesthatusecloseairtocooldownwater. Acoolingsystemmightcontainoneoralotofcoolingthatuse identicalrecirculatingwater
2.1 HOW DOES A COOLING TOWER WORKS?
Inacoolingtowersystem,thefanpushesorattractsairfrom the atmosphere into the tower to cool down recirculating water.Warmwater,thathasremovedheatfromassociate air con, refrigeration or process, enters the highest of the tower.becausethewaterfallsthroughthetowerrecentairis forcedthroughit.Thisrecentaircoolsthewater.Thecooled waterthenfallstoastoragebasinbeforebeingrecirculates throughsystemoncemore.
2.2 TYPES OF COOLING TOWER
Thesectiondescribesaboutthetypesofcoolingtower theyare:
Typesofdraftincoolingtower
Naturaldraftcoolingtower
Mechanicaldraftcoolingtower
Tooptimizetheblowdownrate.
Torestrictflowsthroughthelargeloadstodesign values.
Toincreasethecoolingtowerefficiency.
Forceddraftcoolingtower
Induceddraftcoolingtower
Typesofwaterandairflowincoolingtower
Crossflow
CounterFlow
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page378

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
2.3 NATURAL DRAFT COOLING TOWER
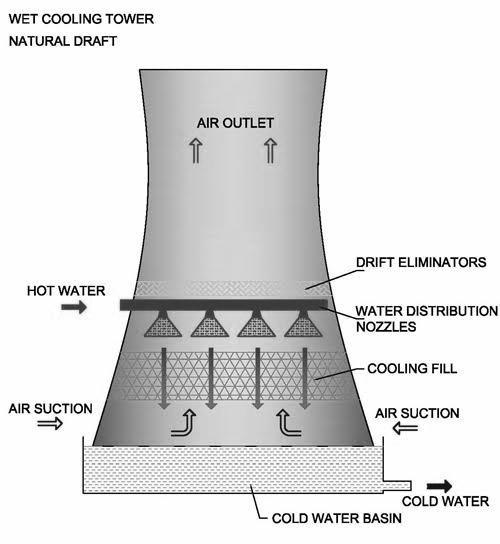
This type of tower is incredibly common. It are often knownbythefanatthehighestofthetower.Thefanpulls airupthroughthetowerwithinthewrongwaytothatthe waterisfalling.Theairsometimesentersthetowerthrough bodyofwaterlouversontheperimetersofthetower.This typeoftowerasshowninFig. 1.
2.5.1 INDUCED DRAFT COUNTER FLOW COOLING TOWER
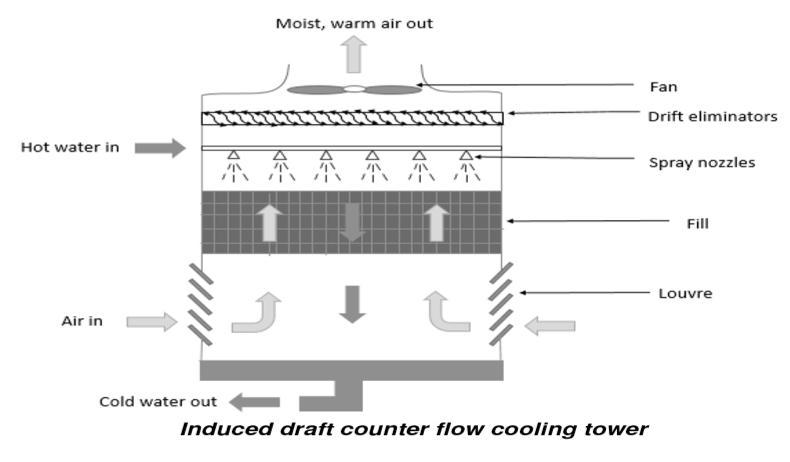
Thisisarelativelypopularformoftower.Thefanatthetop of the tower can be used to identify it. In the opposite directionfromwherethewaterisfalling,thefandrawsairup throughthetower.Normally,airentersthetowerthrough intake louvers on the tower's sides. This type of tower as showninFig. 2.
Fig 1:NaturalDraftCoolingTower
2.4 MECHANICAL DRAFT COOLING TOWERS
Mechanicaldraftcoolingtowershavegiantfanstoforceor draw air through circulated water. The water falls downward over fill surface that facilitate increase the contact time between the water and therefore the air this helpsmaximizeheattransferbetweenthe2coolingratesof mechanical draft towers rely upon numerous parameters like fan diameter and speed of operation, fill for system resistanceetc
2.4.1
COUNTER FLOW TOWERS
Counterflowcoolingtowerairisdrawnthroughthefalling waterandthefillthereforelocatedinsidethetoweralthough designdependsonspecificsiteconditions
2.4.2 CROSS FLOW TOWERS
Crossflowtowerairisdrawnthefallingwaterandthefill islocatedoutsidethewater
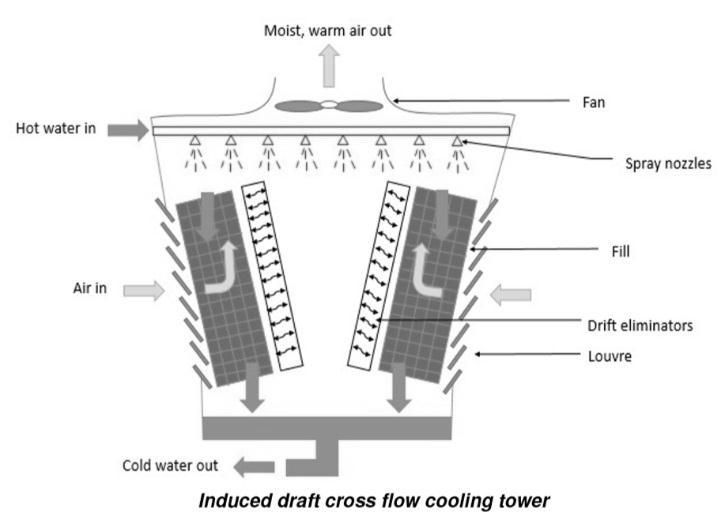
2.5 INDUCED DRAFT COOLING TOWER
Type of mechanical draft cooling tower with a fan at the discharge(atthetop)whichpullsairupthroughthetower. Thefaninduceshotmoistairoutthedischarge
Fig 2:InducedDraftCounterFlowCoolingTower
2.5.2 INDUCED DRAFT CROSS FLOW COOLING TOWER
The fan is also mounted onthe top ofa cross flow cooling towerwithinduceddraught.Inthistypeoftower,thefan,on the other hand, pulls or induces atmosphericair over the waterfallingfromthetopofthetowertothebasinThistype oftowerasshowninFig. 3.
Fig 3:InducedDraftCrossFlowCoolingTower
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
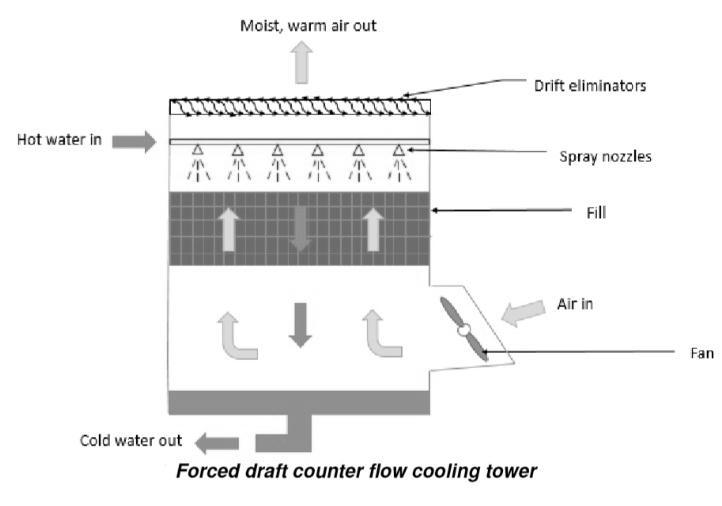
2.6 FORCED DRAFT COOLING TOWER
Typeofmechanical drafttowerinwhichoneormorefans locatedattheairinlettoforceairintothecoolingtower
2.6.1 FORCED DRAFT COUNETER FLOW COOLING TOWER
Thewaterinaforceddraughtcounterflowcoolingtoweris cooledbyairdriventhroughthetopofthewaterandinto thefallingwater.ThistypeoftowerasshowninFig. 4
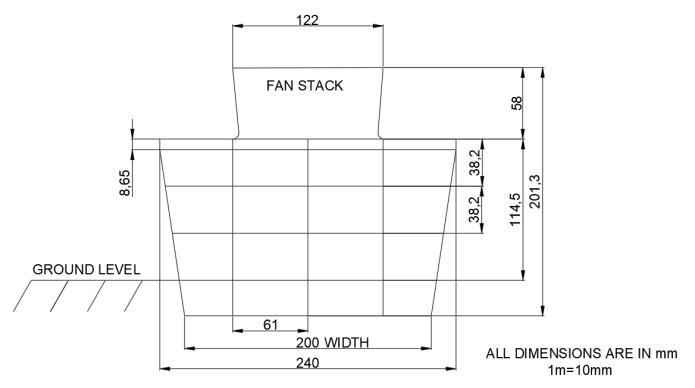
3. DESIGN OF INDUCED DRAFT COOLING TOWER
IDCTFAN :11Noperunit
Totally22Noforstage(unitI&II)
Flowcontrolvalves :22Nperunit
Totally44Noforstage(unitI&II)
Totalheightofcooling :20.13m tower
Depthofcoolingtower :2.88m sump
Heightfromgroundlevel:(11.45+5.8)=17.25m
Fanstackheight :5.80m
Heightfromgroundleveltotop :11.45m
Fig 4:ForcedDraftCounterFlowCoolingTower
2.6.2 FORCED DRAFT CROSS FLOW COOLING TOWER
Thefanismountedononeordoublesideofthetowerina forced draught cross flow cooling tower. This fan forces atmosphericairtothefill.Thisfanishorizontallyacrossthe tower,passingthroughthewaterdroppingfromthetopof theforceddraftcoolingtower'stoptothebasinthrough the fill.ThistypeoftowerasshowninFig. 5.
Fig 6:DesignofInducedDraftCoolingTower
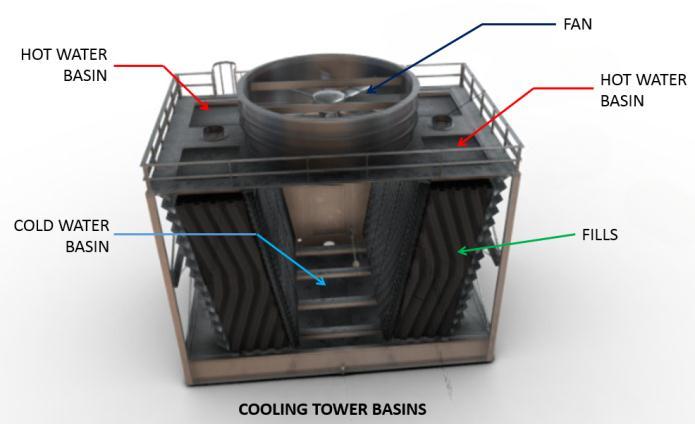
3.1. COMPONENTS OF COOLING TOWER
Basiccomponentsofcoolingtowerisgivenbelow
Frameandcasing
Fills
Hotwarerbasin
Coldwaterbasin
Drifteliminator
Louvers
Nozzles
Fans
Fig 5:ForcedDraftCrossFlowCoolingTower
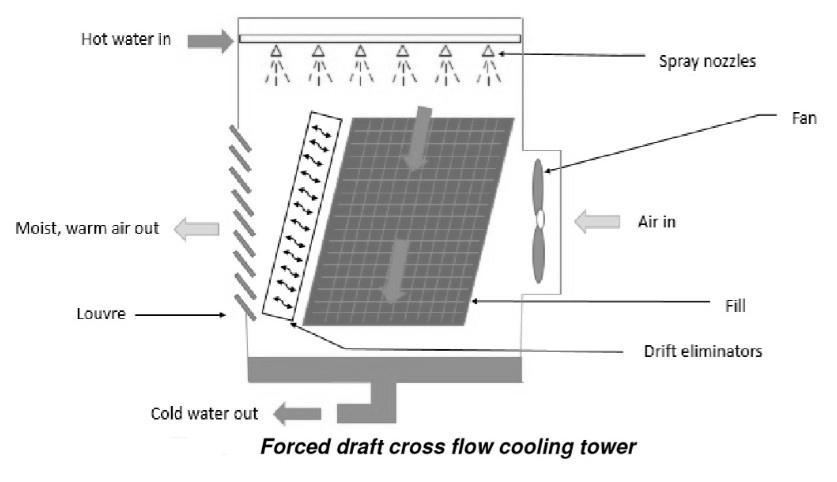
Fig 7:CoolingTowerBasins
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
3.2 PERFORMANCE OF COOLING TOWER
During the performance evaluation, portable monitoring instrumentsareusedtomeasurethefollowingparameters.
Wetbulbtemperature
Drybulbtemperature
Coolingtowerinletwatertemperature
Coolingwateroutlettemperature
InletandExhaustairtemperature
RangeandApproach
Airandwaterflowrate
4. PROBLEM IDENTIFICATION IN INDUCED DRAFT COOLING TOWER
Thecoolingtowersefficiencyandperformanceisreduced duetotheseproblemstheyaregivenbelow
Algae grows fastly due to sunlight falling on coolingtowerhotwaterbasin.Algaeblocksthe coolingtowernozzle.Ifalgaegrowscontionously theseleadstostopthewaterflowtothecooling tower.
The temperature of the hot water doesn’t maintainevenlyonallcellsofthecoolingtower. Uneventemperaturecauseefficiencydrop
Dustandgarbagesareblocksthecoolingtower nozzle.
Tosolvetheseproblemscoverthecootingtowerbyusing GIroofsheets.
4.1 FACTORS AFFECTING THE COOLING TOWER
Capacity
Range
Headload
Algaegrowth.
5. ALGAE GROWTH IN COOLING TOWER
5.1 HOW ALGAE IS FORMED IN COOLING TOWER
Moisture,sunshine,andnutrientsarerequiredforalgaeto flourish.Becausecoolingtowersareexposedtotheoutside air,theyfrequentlyenableoutsidebacteria(algalnutrients) andsunlighttoenterthewater.Asaresult,ifleftuntreated, algaemaysoongrowoutofcontrol.
5.2 PROBLEM OF ALGAE GROWTH IN COOLING TOWER

If algae are growing continuously, they block the coolingtowerspraynozzleandreducesthewater flow
Theymakemoremaintenancecostthenregular maintenance.
Thismakesmorewaterloss
5.3 REDUCTION OF ALGAE GROWTH IN COOLING TOWER
Tocontrolthealgaegrowth,preventsunlightfalling onhotwaterbasinofthecoolingtowerbyusingGI roofsheets.
Periodicwaterchemicaldosingreducesthewater nutrientsandalgaegrowth
Periodic maintenance and cleaning excess algae improvesthecoolingtowerperformance.
Fig 8:AlgaeGrowthCoolingTower
6. PROVIDING GI ROOF SHEET ONCOOLINGTOWER HOT WATER BASIN
6.1 PURPOSE OF PROVIDINGGI SHEET ONCOOLING TOWER HOT WATER BASIN
Toreducealgaegrowthincoolingtower
To maintain hot water temperature evenly on all cellsofthecoolingtower
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 06 | June 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072