International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Kaleeswari S1, Rajalakshmi T2, Dr. Jai Ruby3, Mrs. J. Steffi4
1, 2PG Scholar, Department of Computer Applications and Research Centre, Sarah Tucker College (Autonomous), Tirunelveli, Tamil Nadu, India
3Associate Professor, Department of Computer Applications and Research Centre, Sarah Tucker College (Autonomous), Tirunelveli, Tamil Nadu, India
4Assistant Professor, Department of Computer Applications and Research Centre, Sarah Tucker College (Autonomous), Tirunelveli, Tamil Nadu, India ***
Abstract eLearning has a huge cost hurdle in increasing its services as technology becomes more available in higher education. Artificial intelligence based deep learning is becoming more popular, anditisinfluencingmanyelementsof eLearning. It delivers straightforward algorithms and automated eLearning content delivery through current LMS systems to future online learners. This paper will look at a range of deep learning applications for producing eLearning platform resources, including how to leverage predictions, algorithms, and analytics to create more personalized future eLearning experiences. There are also deep learning models for creating the contents of the eLearning platform, as well as a deep learning framework for integrating deep learning systems into eLearning and its development. Deep learning models for developing eLearning platform contents, deep learning frameworks that enable deep learning systems into eLearning and their development,benefitsandfuturetrendsof deep learning in eLearning, and relevant deep learning based artificial intelligence tools such as CNN, Logistic Regression, and KNN a platform that allows developers and learners to quickly reuse resources are also summarized. As a consequence, deeplearninghasevolvedtoincludedetermining ways to recycle existing resources in order to save money on future eLearning development.
Key Words: eLearning, Deep Learning (DL), Learning ManagementSystem(LMS),ArtificialIntelligence,Machine Learning
TherehavebeenseveralapplicationsinHigherEducationas aresultoftheemergenceofinformationandcommunication technology (ICT) in the current age (HE). In this environment, eLearning was introduced as a means of meeting new educational expectations. Learning managementsoftwaresystemsthatsynthesisthefeaturesof computer mediated communications software and online meansofprovidingcoursematerialshavebeendescribedas eLearning [7]. One of the most compelling arguments for investing heavily in web based technology is its ability to improveteachingandlearning[22],aswellasstimulatethe developmentofstudent centered,autonomouslearning[30] and nurture a more in depth approach to learning [12].
According to [9], the time spent developing eLearning materialforonehourrangedfrom49to125hours.Although thescalabilityoftheeLearningenvironmentpromisesmore flexibleandautonomouslearning,itmightstillbeabarrier forschoolswhocannotaffordtheinitialexpenditure.
AsAIadvances,newapproachessuchasdeeplearningand artificialneuralnetworksarecreatedtoincreasetheefficacy ofmachinelearningandmakeAIapplicationsfar reaching andmeaningful.
Machine learning aims to model the world, while deep learning aims to mimic the human brain in order to constructandmaintainitsownrepresentationsoftheworld. Deeplearningreferstoalgorithmsthatanticipateprobable outcomes based on user input, allowing a machine to demonstrate taught behaviours rather than human interactions.Itfacilitatesautomationbyallowingcomputers to learn from data and generate predictions. The deep learningmodelbecomesmoreintuitivewitheachnewpiece ofdataitgets.
It'sdifficulttoindexandutilizeexistingmaterialontheweb duetotremendousinformationoverload.Thechallengeof indexing and reusability might be solved by classifying information according to domain specific concept hierarchies. As a consequence of the challenges in human categorization, automated classifiers are in great demand. Deep learning may help with eLearning development by enhancingthecategorizationofcontentpieces,sincedigital learners want material to be available in a number of formats and platforms. The deep learning process takes occurautonomouslyintheeLearningarena,fromobtaining and assessing data sets from the LMS to forecasting what onlinelearnersneedbasedontheirpriorperformance.
ThisstudydiscusseshowdeeplearningwillaffecteLearning in the future and analyses its implications on resource management in eLearning. We examine four important elements from the viewpoints of both learners and developers.:
• Motivationsofapplyingdeeplearning
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
• Deep Learning Framework for developing the contentsofeLearningplatform
• Tools and platforms that enable deep learning systemsintoeLearninganditsdevelopment
• Benefits&futuretrendsofeLearning
Therestofthepaperisplannedasfollows:Section2focuses onasurveyrelatedtodeeplearningineLearning.Section3 describes deep learningtechniquesinthe development of eLearning platform. Section 4 covers the benefits of DL in eLearning. Tools, platforms and Future trends of DL in eLearningisdiscussedinsection5andsection6concludes thesummary.
Deep learning models the hierarchical organization of the human brain by processing input from a lower level to a higher one and eventually assembling growing semantic notions.Deeplearningisbecomingmoreusedasamethod formassivedataanalysis[40]andartificialintelligence[40]. Artificial intelligence has made significant progress in numerousdomains,includingfacerecognition[40],image processing[3],andvoicerecognition[2].Inspirebythis,a surveyontheeffectofdeeplearninginaneLearningsetting wasconducted.
ELearningisaformofremoteeducationdeliverysystem that allows for synchronous and asynchronous resource sharing through a communication network [23]. It is a technological and social framework that surrounds the learnerandtheteacherandencouragescommunicationand cooperationbetweenstudentsandinstructors[24].Distance learning, sometimes known as e learning, is a systematic teaching and learning framework designed to be done remotelyviaelectroniccorrespondence[11].Manycolleges and universities have begun to use course management software(suchasBlackboard,LMS,WebCT,andMoodle)to supplementconventionalclassroomeducation.Accordingto authorsintheliterature[32]and[1],eLearningprovidesa balance between technological enablers and acceptability issues.In[32],Rosenberg provideda significant blueprint for maintaining e learning in a sustainable and ongoing expansion by displaying a twenty year timeline of e Learningprogression.
Incorporating modern technology Web 2.0 into the learning process is difficult, but it has the potential to transform the learning and training paradigm. Podcasts, weblogs, wikis, and other online sharing tools have prompted the emergence of e Learning 2.0 [16]. The emphasisintheE Learning2.0environmentisoninvolving studentsinthelearningprocess.
Thefeatureengineeringprocess,whichinvolvesdomain knowledgeandistime consuming,isthemajordistinction between classical machine learning and deep learning algorithms(Fig.1).Deeplearningtechniquesuseautomated feature engineering, while typical machine learning algorithmsneedustocreatethefeatures.Tolearnintricate patterns in vast volumes of data, deep learning combines increasesinprocessingpowerwithneuralnet workswith multiplelayers(Fig.2).It'savariationonastandardneural network that employs extra hidden layers to allow algorithms to handle complicated input with a variety of structures[14].
• Deeplearningusesfourbasicalgorithmstopredict future events and identify patterns based on individualuserdata.
• A supervised learning system predicts outcomes basedonpreviousinstancesandfreshdatasets.To trainthesoftware,thesystembeginswithspecified inputs and outputs. The system may then create outputs or goals for new datasets automatically overtime.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
• There are no labels or data classifications in unsupervisedlearningalgorithms.
• The system analyses data to find patterns and provideconclusionsorpredictions.
• A semi supervised learning method combines unlabelled data with human based training, in whichlabelledwebresourcesareusedtoaccurately mapoutcertaininputsandoutputs.
• A particular objective or goal for the system is includedinthereinforcementlearningalgorithm.It getsinputduringtheprocessinordertolearnthe necessary behaviours for the most effective approachviareinforcementsignals.
Personalized learning route [10]: This is an eLearning technique that highlights the learner's unique goals and objectives, as well as preferences for course mapping. A learning path is defined by a series of courses or learning resources that enable learners to gradually expand their knowledge.Itisdynamicallycreatedandaltereddepending on learner employment responsibilities, areas of interest, progress, learning preferences, demographic data, competences or knowledge levels, and so on. A learner modelisoftenconstructedinthebackendtodetect,gather, andupdatevariablesinordertocustomisedistinctmaterial foreachuniquelearner.
Chatbots [34]: They operate as a virtual assistant, providingconversationalreplies,servingasafastreference guide,andasaknowledgemanagementtool,they maytap intoavarietyofsourcesofinformationspreadaroundthe business. An intelligent tutoring system introduces a learningideaviaaseriesofdialoguesthatprovidecoaching andperformanceassistance.
Itisutilizedtodiscoveraspecificlearningpattern,such as substantial changes in course shortcomings, so that instructorsmaycounselstudentsbeforeitistoolate.Itwill also allow for a more efficient analysis of student engagementdataandtheidentificationoftrends.Asaresult, thecontentredesignrecommendationwillgiveextrahelpto learnerswhoarestrugglingtofinishacourseoralearning activity.
Georgia Institute of Technology developed the virtual teaching assistant [35] to online classrooms to answer problemswithuniqueandobviousreplies.Studentsmayask the same questions again and over, which will help them expandtheirknowledgebaseinvariouscircumstances.
Therearefivewidespreadkindsofinformation[17]:
• Sequences
• Association
• Classifications
• Clusters
• Prediction
Similarly,thegeneralpurposeofdeeplearningmodelisto provide powerful solutions to associations, classifications, clusters and predictions problems. In the eLearning applications, the commonly used deep learning models include:
1. Convolution Neural Network (CNN):[26]designed and implemented the CNN for high dimensional imageprocessingforthefirsttime.Itismadeupof convolutionalfiltersthatconvert2Dto3D.
2. Recurrent Neural Network (RNN): It is a neural networkdesignthatfeaturesrecurrentconnections betweenhiddenstatesandcanlearnsequencesand represent temporal dependencies. The recurrent connections are utilized to identify relationships acrosstimeaswellasbetweeninputs.Asaresult,it's ideally suited to health issues that often entail modellingclinicaldatachangesovertime[41].
3. Deep Belief Network (DBN):Thismodelfeaturesa two layerunidirectionallinkatthetopofthelayers. Eachsub hiddennetwork'slayersserveasavisible layerforthefollowinglayer.
4. Deep Neural Network (DNN):Itcontainsmorethan two layers, allowing for a complex non linear interaction.
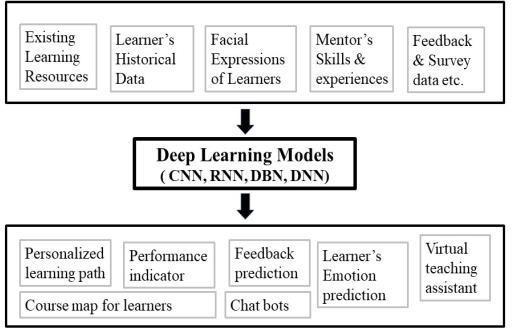
Fig 3:DeepLearningFrameworkforeLearning environment
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
The framework (see Fig. 3) illustrates how deep learning modelsmayhelpwitheLearningcreationbyincorporating:
Existinglearningmaterialstocreateacustomizedlearning pathandcategorizeinformationdependingonthelearner's interests. Learner’s historical data to predict their performance and associate course map for individual learners. Facial expressions of learners to predict their emotions in eLearning environment. Mentor’s skills and experience to support peer to peer interactions with the learners. For example, information may be available in a video, an infographic, a text file including the video transcript,andachat basedquizthatprovidesfeedback.
The researchers employed observation, participant observation, and a case study model as part of their approach. Furthermore, document analysis was used. In addition,asurveyofstudents(past,present,andfuture)was undertaken.Thiswasdonetoacquireanoverallideaofhow much AI and machine learning knowledge the student populationhas,aswellastobetterappreciatethepotential and difficulties that AI and machine learning provide in higher education. The survey was carried out using the model described in the article "AI in Higher Education:
Promises, Perils, and Perspective". Because we are all university professors active in learning processes and everyday interactions with students, we employed observation and observation with engagement. Literature analysisordocumentanalysisisalsoappropriateforsocial sciences and secondary research to compare and complementourresultswithrelevantviews.Asurveyisa usefultechniqueforgatheringdatathatcanbeutilizedfor quantitativeanalysisandhypothesistesting.Itisregardedas alow costtoolinitsdigital(online)version,aswellasuseful foridentifyingpersonswhoeffectivelyutilizetechnicaltools.
With qualitative data analysis, we were able to retain neutralityandeliminatebiasbyhavingmanypersonscode thedata.Thisenabledparticipantstoexamineourfindings. We utilized several statistical studies to ensure that the findings were accurate. A thorough literature analysis enabledustoconfirmourresultsusingotherdatasources andlookforalternativeexplanations.
Table1summarizestherecentapplicationsdeeplearningin eLearning,technicaladvantagesandlimitationsofeachdeep learningmodels
CNN
Predictthelatentfactorsofthe learningresources[36] Using facialexpressiontodetectthe emotionsofstudents[37].
RNN
DBN
StudentFeedbackPredictionusing Kinect[20]
Naturallanguageunderstanding [33],Large vocabularyspeech recognition[18],[25]
Visualrepresentationaltrans formationsindistancelearning [29]
DNN
Tools & Platforms
Provideverygoodperformancefor2D data.Modellearningisfast
Learnsequentialeventsandmodeltime dependencies.Providegoodaccuracyin speech&characterrecognitionandNLP relatedtasks
Supportsbothsupervisedand unsupervisedlearningmodel
Widelyusedwithgreataccuracy
Needlotsoflabeleddatafor classification
Needbigdatasets.Hasmanyissuesdue togradientvanishing
Initializationprocessmakesthetraining processcomputationallexpensive
Trainingprocessisnottrivialasthe errorpropagatedbacktotheprevious layersandbecomesverysmallLearning processisalsotoomuchslow
Features
AIaaS(AIaxaService)[4] CloudbasedAItoolsandalgorithmsfortheeLearningdevelopment
MicrosoftAzure[27] CloudbasedAIapplications,suchasimagerecognitionorbot basedapps
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
IBM’sWatson[21] Cloud basedAIservicestousewithWatsonplatform
AmazonWebServices[5] Amazon’scloud basedAIservices
Google’sTensorflow[38] Anopen sourceartificialintelligencelibrary,usingdataflowgraphstobuildmodelsandallowsdevelopers tocreatelarge scaleneuralnetworkswithmanylayers
Caffe[8] Across platformsupportC++,MATLAB,andPythonprogramminginterfaces
MXNet[28]
An open source of ware library for numerical computation using data flow graphs and supports DL architecturesCNNandRNN
Theano ProvidescapabilitieslikesymbolicAPIsupportsloopingcontrol(scan),whichmakesimplementingRNNs easyandefficient
Keras Theanobaseddeeplearninglibrary
ConvNet[13] MATLABbasedconvolutionalneuralnetworktoolbox
Deeplearning[15] Anopen source,Apache2.0 licenseddistributedneuralnetlibraryinJavaandScala
ApacheSinga[6] Open sourcelibraryfordeeplearning
Table2liststhedeeplearningtechnologiesandplatforms available in eLearning applications. The availability of commercial DL tools and components enables eLearning creators to buy or license algorithms rather than building theirown,savingtimeandmoney.
When considering using deep learning in the eLearning development,it’sadvisabletochooseaplatformcarefullyas eachplatformhasitsownstrengthsandweaknesses.Italso dependsontheneedsofthedevelopersandlearnersaswell asthetechnicalskillsofthedeveloperswhowillbebinding these toolsand servicestocreatedeep learning enhanced eLearningtools.
DeeplearningprovidesmoretailoredeLearningmaterialby predicting outcomes based on historical performance and individuallearningobjectives,allowingformorecustomised chevaliercontent.Formoreproficientonlinelearners,itmay skipmultiplee learningcoursesorfollowamorecomplete, linearapproachforindividualswhostillneedfundamental information.Inaddition,ifanonlinelearner'spastsuggests that they favour tangible eLearning activities, the system modifies the learner's course map to provide suggestions thatdevelopassociatedskillsandabilities.[31]Proposeda frameworkforautonomousonlinepersonalizationthrougha recommendationprocessbasedonartificialneuralnetwork methodsappliedtovariousdatasets.
Fig 4:ROCCurveLogisticRegression
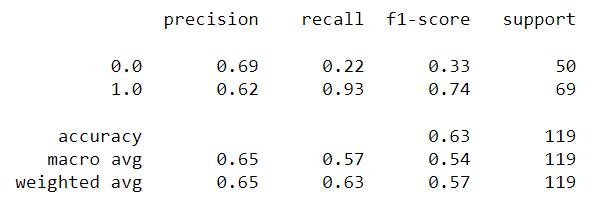
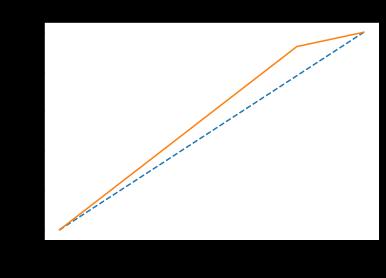
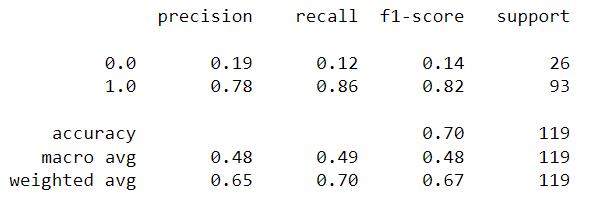
Fig 5:LogisticRegressionAccuracyResult
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
DeeplearningprovidesmoretailoredeLearningmaterialby predicting outcomes based on historical performance and individuallearningobjectives,allowingformorecustomized chevaliercontent.Formoreproficientonlinelearners,itmay skipmultipleeLearningcoursesorfollowamorecomplete, linearapproachforindividualswhostillneedfundamental information.Inaddition,ifanonlinelearner'spastsuggests that they favor tangible eLearning activities, the system modifies the learner's course map to provide suggestions thatdevelopassociatedskillsandabilities.[31]Proposeda frameworkforautonomousonlinepersonalizationthrougha recommendationprocessbasedonartificialneuralnetwork methodsappliedtovariousdatasets.
[1] A.Fayyoumi,H.Mohammad,andH.Faris,"Mobilebased learning and examination: Students and instructors’ perceptions fromdifferent Arabcountries," Journal of SoftwareEngineeringandApplications,vol.6,2013,doi: https://doi.org/10.4236/jsea.2013.612079
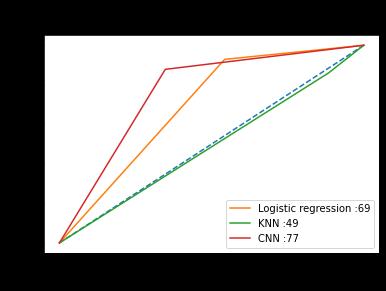
[2] A. Graves, R. Mohamed, and G. Hinton, "Speech Recognition with Deep Recurrent Neural Networks," Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, IEEE InternationalConference,vol.6,2013,pp.6645 6649, doi:https://doi.org/10.4236/jsea.2013.612079

[3] A.Krizhevsky,I.Sutskever,andG.E.Hinton,"Imagenet classificationwithdeepconvolutionalneuralnetworks," Advancesinneuralinformationprocessingsystems,vol. 6, pp. 1097 1105, 2012, doi: https://doi.org/10.1145/3065386
[4] AIaaS. https://www.bmc.com/blogs/ai as a service aiaas/
[5] Amazon Web Services. https://aws.amazon.com/machine learning/
[6] ApacheSinga.http://singa.apache.org/en/index.html
[7] Britain, S., and Liber, O., "A Framework for the Pedagogical Evaluation of Virtual Learning EnvironmentsReport41,JISCTechnologyApplications Programme,2004.
[8] Caffe.(2018).http://caffe.berkeleyvision.org/
[9] Chapman,B.(2010).HowLongDoesItTaketoCreate Learning? [Research Study]. Available from: www.chapmanalliance.com
[10] ColaceFrancesco,Santo,MassimoDeandGreco, Luca, “E LearningandPersonalizedLearningPath:AProposal Based on the Adaptive Educational Hypermedia
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
System,”InternationalJournalofEmergingTechnologies in Learning (iJET), vol. 9, pp. 9 16, 2014, doi: https://doi.org/10.3991/ijet.v9i2.3211
[11] Clark,R.C.,andMayer,R.E.(2003).E Learningandthe science of education: Established strategies for consumersanddesignersofmachinelearningsystems. SanFrancisco,CA:Jossey Bass/Pfeiffer.
[12] Collis, B. (1997). Tele learning in a digital world: The future of distance learning. London: International Thomson Computer Press. ConvNet, https://github.com/sdemyanov/ConvNet,lastaccessed2 019/05/15.
[13] Deep learning in Oncology. (2013) Available from: https://www.techemergence.com/deep learning in oncology/
[14] Deep learning https://deeplearning4j.org/,lastaccessed2019/05/15.
[15] Ebner, M. (2007). E Learning In Conf. on Availability, ReliabilityandSecurity.IEEEARES,1235 1239.
[16] Edelstein,H.A.(1999).IntroductiontoDataMiningand KnowledgeDiscovery. 3rd Edition, CrowsCorporation, Potomac.
[17] G.E.Dahl,D.Yu,L.Deng,andA.Acero,(2012).Context dependentpre traineddeepneuralnetworksforlarge vocabularyspeechrecognition.Int.Conf.IEEEAcoustics,
[18] Speech and Signal Process. Vol. 20, pp. 30 42. https://doi.org/10.1109/tasl.2011.2134090
[19] HassinaSeridi,ToufikSariandMokhtarSellami.(2006). AdaptiveInstructionalPlanningusingNeuralNetworks inIntelligentLearningSystems,TheInternationalArab JournalofInformationTechnology,vol.3,pp.183 192.
[20] Hu, Shanfeng et al. (2018). A Dual Stream Recurrent NeuralNetworkforStudentFeed backPredictionusing Kinect. In: SKIMA, Cambodia. https://doi.org/10.1109/skima.2018.8631537
[21] IBM’sWatson.https://www.ibm.com/watson/
[22] Jenkins, M., Browne, T., and Armitage, S. (2001). Management and implementation of Virtual Learning Environments. Report. UCISA. Available from: https://www.ucisa.ac.uk/
[23] Khan B.H. (1998). Web based Instruction (WBI): An Introduction.EducationalMediaInternational,vol.35, pp.63 71.https://doi.org/10.1080/0952398980350202
[24] KhanB.H.(2000).Discussionofresourcesandattributes of the web for the creation of meaning full learning
environments.CyberPsychology&Behavior,vol.3,pp. 17 23.
[25] L.Deng,G.Hinton,andB.Kingsbury.(2013).Newtypes ofdeepneuralnetworklearningforspeechrecognition andrelatedapplications:Anoverview,inProc.Int.Conf. IEEEAcoustics,SpeechandSignalProcess.,Vancouver, BC, Canada, pp.8599 8603. https://doi.org/10.1109/icassp.2013.6639344
[26] Lecun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, et al. (1998). Gradient basedlearningappliedtodocumentrecognition.In:Proc IEEE Inst Electr Electron Eng 86: 2278 324.https://doi.org/10.1109/5.726791
[27] Microsoft Azure. https://azure.microsoft.com/en us/overview/ai platform/
[28] MXNet.http://mxnet.incubator.apache.org.
[29] Patrick McClure and Nikolaus K. (2016). Representational Distance Learning for Deep Neural Networks. Front Comput Neurosci, 10: 131. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncom.2016.00131
[30] Pahl,C.(2003).Managingevolutionandchangeinweb basedteachingandlearningenvironments.Computers in Education, 40. 99 114. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0360 1315(02)00100 8
[31] P. Ralph and J. Parsons. (2006). A Framework for Automatic Online Personalization, Proc. 39th Ann. HawaiiInt'l Conf. System Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1109/hicss.2006.10
[32] Rosenberg M.J. (2002). E Learning: Strategies for DeliveringKnowledgeintheDigitalAge,NewYork,NY, USA:McGraw Hill,Inc.
[33] Ruhi Sarikaya, Geoffrey E. Hinton, and Anoop Deoras. (2014). Application of DBN for natural language understanding. IEEE / ACM Trans. Audio, Speech and Lang. Proc. 22 (4): pp. 778 784. https://doi.org/10.1109/taslp.2014.2303296
[34] Sayan Guha (2018). AI Chatbots In eLearning: Trends Embracing across Digital Land scape. https://elearningindustry.com/ai chatbots in elearning trends digital
[35] Science Daily. (2016). Artificial intelligence course creates AI teaching assistant. Available from: https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2016/05/160 509101930.htm.
[36] Shen Xiaoxuan, et. al. (2016). Automatic RecommendationTechnologyforLearningRe sources withConvolutionalNeuralNetwork.30 34.
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal |

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 05 | May 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
[37] Sun,Ai.,Li,Ying Jian.,Huang,Yueh Min.,andLi,Qiong. (2017).UsingFacialExpressiontoDetectEmotioninE learning System: A Deep Learning Method. 10.1007/978 3 319 71084 6_52.
[38] Tensorflow.https://www.tensorflow.org
[39] Wang, M., Vogel, D., and Ran, W. (2011). Creating a performance orientede learningenvironment:Adesign scienceapproach.InformationandManagement,48(7): 260 269.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2011.06.003
[40] Y. Shen, X. He, J. Gao, L. Deng, and G. Mesnil. (2014). Learningsemanticrepresentationsusingconvolutional neural networks for web search, Proceedings of the companion publication of the 23rd international conference on World wide web companion, pp.373 374.https://doi.org/10.1145/2567948.2577348
[41] ZacharyCLipton,DavidC.Kale,CharlesElkan,Randall Wetzel. (2016). Learning to Diagnose with LSTM Recurrent Neural Networks. International Conference onLearningRepresentations(ICLR).
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal
