
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume:12Issue:07|Jul2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume:12Issue:07|Jul2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
1Ajay Vijaykumar Khake and
2
Dr. S.A.Naveed
1CSMSS Chh.Shahu College of Engineering, Chh.Sambhajinagar-MH-431011 India
2Professor and Head Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College, MGM University, Chh.Sambhajinagar-MH-431003 India
Abstract:-Every day, as the population grows, so do the number of cars on the road and the number of highways; air pollution, wasted fuel, travel time, and other issues related to transportation are also rising. Thus, keeping a close eye on traffic is the biggest task facing traffic administration authorities. Related research has demonstrated how artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things can be combined to provide methods for improved urban and decision-making. In order to gather, process, and store traffic data in real time using the Internet of Things, a system model is developed in this document. By instantly updating roadside communications and uncommon occurrences, the goal is to guarantee seamless transportation. Pre-alerting messages, in particular, help to avoid or postpone traffic jams during rush hours. The administrative sensor database's traffic updates are also sent by the system. The suggested technique assesses the model's features and displaystheanticipatedpreciseoutcomesforcardetection as well as the lowest possible error in the occupancy predictions.
Keywords: Traffic Control, Traffic Monitoring, InternetofThings.
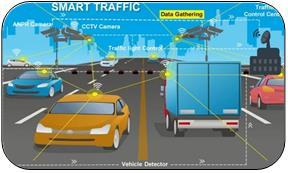
I. Introduction:- Theamountofcarsontheroadtoday makes for extremely difficult, albeit safe, heavy traffic. Ordinary people have a far worse and more uncomfortable experience with this issue, especially in large cities. To help with traffic flow at crossings, an intelligent traffic management system based on video processing is offered. This method makes it possible to gatherdataonsignificanttrafficissues,whichaidsinthe development of better transportation regulations. The automatic implementation of a road and road control system is the project's goal. There are several uses for theInternetofThings(IoT).
Furthermore, the idea of smart cities has been developing. Within an intelligent urban environment, the city's physical infrastructure is outfitted with intelligent devices that reliably generate multidimensional data from several domains and utilize it to obtain infrastructure intelligence. Global positioning systems,sensors,testvehicles,andcarsaresomeof the tools for connecting infrastructure that are used to
collect road data in real time. The most widely used, powerful, and cost-effective sensors for vehicle monitoring are acoustic and magnetic sensors [5]. Data about traffic from several sources can be utilized to predict and control traffic congestion. Most existing technologies provide real-time data on traffic on metropolitan roads, especially when utilizing smart mobiledevices.
Through roadside sensors, the sensing layers gather vehicle data from the Wi-Fi-based microcontroller in real time and transmit it to the service layer. There are several open-source cloud IoT solutions available for managing, storing, and analyzing linked devices. In this survey, Thinger IO serves as a service layer for the integration of data fusion systems. End users can get dashboards and roadside traffic updates. Physical equipment like sensors and displays are placed at specific road crossings. At the main intersectionsoftheroutearecommunicationunitsbuilt, rather than more intelligent technology and drivers for actual traffic. To assist in handling the situation, authorities may also report unexpected road events in addition to expected clearance timeframes or other recommended routes. By reducing driver travel times, thesuggestedsystem with EarlyWarning Messageswill benefit the public. In a nutshell, the suggested system hasthefollowingattributes:
i.i)Appropriateforcalculatingtrafficcongestionbyroute
i.ii)Enhance individuals with real-time display messagingonthesideoftheroad
i.iii) Keep an eye on the mobility and density of smart campuses,especiallyduringrushhours.
i.iv)Aidagenciessubmitnoteworthyincidentmessages.
i.v)Provideadashboardwithreal-timetrafficupdates.
II. Proposed System: Astrongresearchmethodology isnecessarytomeettheobjectivesofthestudy.Thefive primaryphasesofthedesignscienceprocessareusedto conduct research. The five stages are displayed in the figures below. Analyzing the research background, defining the objective, designing and developing,

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume:12Issue:07|Jul2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
demonstrating,andevaluatingtheworkarethefirstfive steps.
Abackgroundstudyonresearchisconductedinorderto provide an objective definition. In transportation projects,wirelesssensorgridshaveshowntobepopular and are useful for both identifying and lessening traffic congestion. Various kinds of sensors are employed in real-time traffic tracking. Sensors can be chosen based on factors like energy consumption, cost, sensitivity, dependability, etc. Specialized sensors are available for vehicle identification and classification in the related field, in addition to conventional traffic monitoring sensors including magnetic, infrared, and ultrasonic sensors.
It is accurate to measure occupancy on roads and roadways. Longitudinal occupancy measures are included sincecollectorhighways are primarily used by smallcars.Whendeterminingtheamountofroadspace, the vehicle length, buffer length, and safety distance betweencarsarealltakenintoconsideration.Safely,two meters separate the two cars. The length of a vehicle is increased when it enters a street zone and lowered when it exits. Based on a review of the literature, this studychosetoemploymagneticsensors alsoknownas magneticsensor-basedPCBs forthecollectingoftraffic data because of their great precision in detecting vehicles. You can learn how to create, demonstrate, and assessthesysteminthepartsthatfollow.
III. Development and Design of System:-The suggested system model, necessary software components, and implementation methodologies are all covered in this section. A central server located in the cloud and roadside components together offer a suggested approach for system communication. There are message panels and sensors by the side of the road. The sensors and panels are connected to the road stretch at two intersections. The primary servers are interfaces, cloud services, and data storage. WiFi is availableforaccessingthecomponents.
IV. Development of System: The fundamental componentsofthearchitectureofanIoT systemarethe network layer and the application layer. The equipment transmitsdatatotheservicelayerviathenetworklayer, which then gathers and analyzes data from the application layers and the sensing layer. The service layer also keeps an eye on the equipment. System developmentinvolvesfourprimaryoperations:
(i)Locatingandevaluatingatruck,
(ii)Expandingtheline,and
(iv)Updating traffic displays. Includes databases, electronicdisplayunits
Sensors,IoTplatforms,andgeographicmapI.
Followingaresomeofthecomponents:-
V. Components of Software and Hardware: Various technology and system components have been the subject of a literary analysis. The hardware and software parts that went into creating the system are listedbelow.
v.i) Map of Open Street: One of the useful map data initiatives for OpenStreetMap is Open Street Map. Data for the OSM map (wiki.openstreetmap.org) is freely accessible. The OSM is developed by individual users, whose geographic information input is vital to the OSM. OSMhastheabilitytoedit, export,anduploaddata.The export function can generate photos or row map data. Therawdatacanbeprocessedbyothersystemsthatuse geographicdata.TheJavainterfaceoftheOSMissimilar tothatofclassicgeographicdataupdatesandmaps,such asJavaOpenStreetMap(JOSM).
v.ii) Mongo Database: It provides documentation for JSON data at sever website. MongoDB allows objects to be used as values and provides flexible access to data. MongoDB includes versions for the enterprise and the community. This study makes use of MongoDB's

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume:12Issue:07|Jul2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
community edition. In MongoDB, a record's field and value pairs are essentially documents. Similar to tables, MongoDB documents are gathered and kept. The OpenStreetMaphasbeendownloadedinGeojsonformat andstoredintheMongoDBforfurtherinvestigation.We chose MongoDB because of its effectiveness and extensive query language. The magnet sensor has three advantages: (i) itissimpletoputonthesideoftheroad; (ii) it lowers detection error; and (iii) it is not affected bytheweather.
v.iii) Magnetometers: Due of its great sensitivity and economical nature, The three- axis magnetic Honeywell HMC5883L sensor is used in a number of traffic monitoring surveys. Automotive data collected with the HMC5883Lmagneticsensorservedasthefoundationfor this study. There are many PCBs with the necessary vehicle detection and classification components, as the literature study notes. It is significant to remember that these boards have firmware and physical sensors. The cost-effectiveness of using these pre-made nodes makes theconcepttoadvancethemworthwhileaswell.
v.iv) Thinger IO: Thinger.io is an open-source platform for managing, collecting, analyzing, and displaying sensordatafortheInternetofThings.Cloud,IoT,andBig DataIntegrationapplicationsareprovidedbyThinger.io (www.thinger.io)fordatafusion.Anysensorcanbeused to provide remote sensing, control, and connectivity devices. Thinger.io is distinct due to its transmission efficiency-optimized Protoson encoding algorithm. Thinger.iooffersreal-time,two-waycommunicationand is incredibly interoperable. Data pads, also known as Io, are used to store documents on MongoDB and other systems. The Thinger storage control mechanism. An interfaceforcreatingdata bucketsanddevicemodelling toolsisofferedbytheThinger.ioplatform.
VI. Activities of System Development:
Geographical Data Processing Map: Highways, crossroads, and trains are depicted on the geographical map. Information is loaded and extracted from the bulletin board into the database using the maps. Using theuser-generated map, youmaydecide where to put a message board [23]. The junctions where there are numerous road sections are the ideal locations for alert displays.Theboard'splacementsareselecteddepending ontheirexpositiontomaximizemessagevisibility.Since maximizing message visibility is the goal, choosing the message board should be viewed as a maximization problem.
vi.i) Vehicle detection and physical length estimation: Real-time data collected by magnetic sensorsforthevehicle isusedtodetectandestimateits length. One of the parameters used to calculate the vehicle length is the projected speed of the vehicle.
Magnetic sensors monitor the vehicle's magnetic length in the Earth's magnet field and pick up on distortions causedbymovingautos.Magnetlongitude(MLV)isused to assess the length of the vehicle. The experiments demonstrate that a single magnetic sensor can detect vehicleswith99percentaccuracy.
vi.ii) Road occupancy and lengthening lines: A number of factors, including speed, confidence, maintenance, space, and duration, are important in determining the degree of traffic congestion. Using the roads to gauge the increasing street line is one such procedure. The sensors calculate the VPL. When a vehicletravelsthroughsensornodes,thephysicallength of the occupancy measurement is lengthened; when the vehicle exits points, the length is deleted. When a car is detectedbytheC-sensor,sensorDmeasuresitsduration and transmits the information to the B sensor. The consumption measurement is continuously maintained bytheSensor-BMicrocontroller.
vi.iii)Displaywarningmessages:Real-timeupdateson traffic density and authority communications on noteworthytrafficoccurrencesarethetwocategoriesof trafficwarningmessages.Theseupdatesareavailableto driversinavarietyofways,includingthroughTV,radio, and clever mobile apps. Another approach is to place message panels at strategic crossroads. These units try tocontactasmanypeopleastheycanandassistthemin choosingdifferentpaths.
Threeprimarypurposesofthesystemare:(i)managing maps;(ii)gathering trafficstatistics;and(iii)displaying and storing information. It takes data on the path and eliminates the message unit positions from the opensource Wiki map. For the purpose of detecting and measuring vehicle length and road use, magnetic sensorsareusedintheinformationgatheringprocess.A prototype demonstrates the system's viability. Accurate findingsareobtainedfromtheuniqueevaluationofeach module. A wireless communication magnetic sensor by the microcontroller and along the road is part of the systemarchitecture.Theprimarygoalofthiseffortisto evaluate how long the car will be on the road. The test demonstrates 100% vehicle detection accuracy. The tests also demonstrated that the high length and speed rates are 97% high and that the projected road usage errorrateisverylow.However,becausetheyaretypical at these colleges, estimations have been calculated for vehicles with lengths between 1.5 and 5.48 M. Between 200 and 500 meters are used to evaluate the route portions. The converse is true, according to test results, for the distance to the error rate. Consequently, the suggested system model will function effectively in actualdrivingsituations.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume:12Issue:07|Jul2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
VIII. Evaluation:-The graduation process validates three important features: (i) the positioning and processing of maps; (ii) the gathering and processing of vehicleinformation;and(iii)thedashboard.
viii.i) Selection of message board location: The OpenStreetMap website allows users to select the location of the message board on a campus map. It is possible toloadandconvert OSMfilestoMongoDB. The exact map script treatment is measured and recalled with precision. The effectiveness of the data collection process is evaluated using these metrics. (Collected junction amount/Junction quantity) = 100% is the precision percent. Keep in mind that percent (there are several junctions on this map)= 100% = 100%. On the message board, the script locates the number of threshold pathways. The OSM map is analogous to a manualMapcartatool.
Vehicle detection and road occupancy estimation: Vehicle detection was tested using a single roadside node. The experimental setup of the Renault Duster automobileandthemagneticfieldswingsat100cm.The intensity of magnet f as well as the x, y, and z components in the geomagnetic field when the sensor detectsit.
IX. Conclusion:-The technology uses magnetic sensor nodes to gather vehicle data in real time. Real-time processing and transmission of the data to an IoT platform is accomplished via Wi-Fi capable microcontrollers. In contrast, the suggested model of cars lacks any smart, feature-rich equipment like internet, GPS, or sensors. All intelligent urban projects, including the closed intelligent facilities and the intelligent university campus, should take the suggested system intoaccount.Resultsofprototypedemonstrationsreveal a high precision of vehicle detection and a relatively small error in estimates of road occupancies, indicating theviabilityofthesuggestedmethodology.Thesystem's goalistogivepassengersaccesstodynamicinformation and remove informational obstacles so they can make informed decisions about smart transportation in real time
[1] Atta A, Abbas S., Khan M. A., Ahmed G., and Farooq U.(2020), “An adaptive approach: Smart traffic congestion control system,” Journal of King Saud University,Inf.Sci.,vol.32,no.9,pp.1012–1019.
[2] Babu, P. R. K. S. M. R. (2016). Real-time smart traffic managementsystemforsmartcitiesbyusinginternetof things and big data. 2016 International Conference on EmergingTechnologicalTrends(ICETT).
[3]NareshK.S.,FrancisJkalliath,ShravanAruljothi,Arni Tharakaram Hariram, Harshith Shivakumar (2020), ‘Smart Traffic management system using IOT’, International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology (IJETT- Scopus Indexed) – Special IssuesICT2020,pp.122-129.
[4] Pable SN, Welekar A & Gaikwad-Patil T (2014), “Implementation on Priority Based Signal Management in Traffic System”, International Journal of Engineering ResearchTechnology(IJERT),Vol.3,No.5,pp.1679-1682.
[5]PratikPrakash,AadarshSingh,AayushParasrampuria and Gargi Sharma (2021), ‘An IOT based Smart Traffic Management System’, International Journal of Electrical, ElectronicsandComputers,Vol-6,Issue-5,pp.6-11.
[6]Pendurthy Bhavana, Pediredla Likhitha, Chiluvuri Manoj, Lakshmi Sutha Kumar (2023), ‘IoT based Dynamic Road Traffic Management System’, Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 4th National Conference on Communication Systems, pp. 1-9. doi:10.1088/17426596/2466/1/012025.
[7] Sonekar S.V. (2022), ‘A Revie on IOT Based Traffic Control Management’, International Journal of Creative ResearchThoughts,Vol-10,Isue-10,pp.972-977.
[8] Singh L, Tripathi S & Arora H. (2009), “Time optimization for traffic signal control using genetic algorithm”, International Journal of Recent Trends in Engineering,Vol.2,No.2,pp.4-6.
[9] Trivedi, Janak & Sarada Devi, Mandalapu & Dhara, Dave.(2017).ReviewPaperonIntelligentTrafficControl system using Computer Vision for Smart City. International Journal of Scientific and Engineering Research.8.14-17.
[10]TalukderM.Z.,TowqirS.S.,RemonA.R.,andZaman H. U., “An IoT based automated traffic control system withreal-timeupdatecapability,”in2017Conferenceon Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies(ICCCNT),2017,pp.1–6.
[11]VennilaC.,ChandraprabhaK.,VijayrajM.,KavithaS., Vimalnath S., and Kalaichelvi K. (2017), ‘Traffic Control andMonitoringusingIoT’,JournalofPhysicsConference Series,IOPPublication,pp.1-11.
[12]Wang,R.,Zhang,L.,Sun,R.,Gong,J.,&Cui,L.(2011). EasiTia: A pervasive traffic information acquisition system based on wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 12(2),615-621