
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 07 | Jul 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 07 | Jul 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Chandana T R1 , H P Mohan Kumar2
1Master of Computer Application PES College of Engineering, Mandya, Karnataka, India
2Computer Science and Engineering, PES College of Engineering, Mandya, Karnataka, India
Abstract - The sophisticated non-invasive diagnostic technique known as magnetic resonance imaging, or MRI, makesitpossibletoseeinsidebodypartswithremarkable precision.Magneticresonanceimaging(MRI)makesiteasier tocreatecomprehensivepicturesoforgans,softtissues,and the musculoskeletal system by fusing radio frequency radiation,strongmagneticfields,andcomputerprocessing. MRIisasaferalternativetodiagnosticprocedureslikeCT scansandX-rayssinceitdoesn'texposepatientstoionizing radiation,especiallywhenitcomestosofttissueevaluation. Clinicians frequently rely on MRI to identify, assess, and track various medical conditions, as it provides highresolutionimagesthatclearlydifferentiatebetweenhealthy andabnormaltissues.
Key Words: Medical imaging, MRI Image, Deep Learning
1.INTRODUCTION
MRI plays an essential role in contemporary medical diagnosticsbyofferinghigh-resolutionvisualizationsofthe body’sinternalanatomy.Despiteitseffectiveness,analyzing MRIscansmanuallycanbebothtime-intensiveandproneto inconsistenciesbydifferentradiologists.Theemergenceof deep learning particularly CNNs has introduced promising methods for automating with considerable precision. In order to organize the categorization of MRI data,thisstudylooksintoCNNstructures,withtheobjective of enhancing the diagnostic workflow and delivering consistent, data-driven insights to support clinicians. The primary aim is to develop a robust, accurate, and timeefficient system that can help professionals in the interpretation of MRI scans, thereby contributing to more timely and accurate diagnoses. Employing deep learning strategiesforMRIimageclassificationsignifiesamajorstep forwardinmedicalimagingtechnologies.ByleveragingCNN models, the project aspires to minimize the diagnostic burdenonhealthcareproviders,increasereliabilityinimage assessment, and ultimately foster improved outcomes in patientcare.
[1]IdentifyingfracturedregionsinMRIimagesbeginswith accurateimageclassification,whichservesasacrucialinitial step. This paper introduces an effective approach for classifying MRI scans to assist medical professionals and radiologists in making well-informed diagnostic decisions. The proposed methodology involves a systematic process
beginningwithimagepre-processingusingaGaussianfilter toeliminatenoise.Thisisfollowedbyimagesegmentation through the Fuzzy C-Means (FCM) algorithm and the extractionofstatisticalfeaturessuchaskurtosis,mean,and median.TheclassificationisthenperformedonMRIscansof variousbodypartsincludingtheface,head,skull,foot,and chest,usingthreemachinelearningtechniques:Probabilistic Neural Network (PNN), (SVM), and k-Nearest Neighbor (KNN) algorithm. The dataset consists of 300 MRI images sourced from Apollo Hospitals, Hyderabad. Among the methodsevaluated,SVMdemonstratedsuperiorperformance withanoverall93.1%,outperformingtheotherapproaches
[2] Deeplearningandmachinelearninghavesignificantly improvedcomputer-aideddetectionsystemsbyenhancing diagnostic accuracy in medical imaging. These techniques enable efficient analysis of large imaging datasets, particularly aiding in early detection of conditions like cancerandtumors
[3]ThearchitecturecombinesfeaturesfrompairedDCNNs andfeedsthemintoasynergicnetworktodetermineimage categorysimilarity.Synergicerrorsignals,generatedwhen onenetworkmisclassifies,helprefinethelearningprocess. Trainedend-to-end,theSDLapproachachievesstate-of-theartresultsondatasetslikeImageCLEFandISIC
[4 In addition, the review examines critical aspects of the classification workflow, such as dataset curation, feature extraction,andperformanceevaluation.Emphasisisplaced ontheroleoflarge,annotateddatasets,aswellastechniques like transfer learning and data augmentation, which contribute significantly to model accuracy and generalizabilityinmedicalimagingtasks.
[5]Thepaper"Deeplearning-basedimageclassificationof MRIbrainimage"presentsaconvolutionalneuralnetwork (CNN)approachforclassifyingbrainMRIscansintonormal andabnormalcategories.Itemphasizesautomatedfeature extractionandhighaccuracy,reducingrelianceonmanual interpretation.Themodeldemonstratesstrongperformance in early detection of brain disorders, supporting clinical decision-making
[6] The paper "MRI Brain Images Classification Using ConvolutionalNeuralNetworks"explorestheuseofCNNs foraccuratelyclassifyingbrainMRIimagesintohealthyand diseased categories. It highlights the strength of deep learning in automatic feature extraction and improved

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 07 | Jul 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
diagnostic precision. The study confirms that CNN-based models outperform traditional methods in medical image classificationtasks.
[7]Thenetworkistrainedunderamultitaskframeworkfor tumordetection,classification,andlocalization,integrating advanced feature extraction and data augmentation techniquestoimproveaccuracy
[8] The study introduces a tailored convolutional neural networkdesignedspecificallyforbraintumordetectionfrom MRI scans, addressing the transparency issues typical of standarddeeplearningmodels.
[9]ThemodelintegratestheLIMEexplainabilitytechnique, whichhighlightsimageregionsinfluencingtheclassification decisions,boostingtransparencyandclinicianconfidence
[10]Thestudypresentsa fullyautomatedmultiscaleCNN thatprocessesMRIslicesatthreespatialresolutions(large, medium, small) via parallel pathways, mimicking human visualperceptionforimprovedfeatureextraction
[11]Thestudyhighlightstheutilityoftransferlearningfor efficient model training and robust performance in brain tumor classification, while noting persistent challenges in improving recall for certain tumor types and the need for enhancedmodelinterpretability
[12]ThestudyconcludesthattheproposedCNNstrikesan optimal balance between accuracy, speed, and simplicity, makingitasuitablechoiceforintegrationinclinicalsystems forearlybraintumor
[13]Adeepneuralnetworkwithattentionmodulesextracts multiscale features from segmented regions of interest (ROIs), feeding into an ensemble classifier to distinguish tumortypesaccurately.
[14] Their approach integrates segmentation, feature extraction,andensemblefusion leveragingcomplementary strengths of each network to achieve highly accurate tumordetection.
[15] It highlights that, across multiple disorders and MRI modalities, CNN-based methods consistently outperform otherarchitecturessuchasRNNs,autoencoders,andDNNs
Manual interpretation and classification of MRI scans present several challenges, such as being time-intensive, subject to variability among radiologists, and prone to human error. These issues can compromise diagnostic accuracyandpotentiallydelayormisleadclinicaldecisions, thereby affecting the overall quality of patient care. This project suggests using convolutional neural networks (CNNs), which can increase diagnostic consistency, speed, andreliabilitythroughsophisticatedpatternrecognitionand
data-drivenlearning,toimproveanautomatedMRIimage classificationsystemtodiscoursetheseissues.
ConvolutionalNeuralNetworks(CNNs)arehighlyeffective in classifying MRI pictures because of their capacity to automatically learn and extract layered properties from complexpicturedata.ParticularlyinMRIanalysis,medical imaging, CNNs are capable of examining pixel intensity distributions and spatial arrangements to uncover subtle indicatorsofvarioustissuetypesorpathologicalconditions. Whentrainedonextensive,annotatedMRIdatasets,CNNs canaccuratelydifferentiatebetweenhealthyanddiseased tissues,identifyspecificabnormalities,andsupportclinical decision-making. This automated approach minimizes the dependence on manual interpretation, thereby reducing inter-observer variability and expediting the diagnostic process. CNNs therefore play a major role in enhancing medicalimageanalysis'sprecisionandeffectiveness.
1. CNNsremovethetime-consuminganderror-prone human feature extraction by automatically extractingrelevantcharacteristicsfromMRIimages.
2. Whentrainedonsuitablybigandvarieddatasets, CNNshaveshowngreataccuracyinmedicalpicture classificationtasks.
3. Oncetrained,CNNscanprocessMRIscansquickly, potentiallyreducingturnaroundtimes
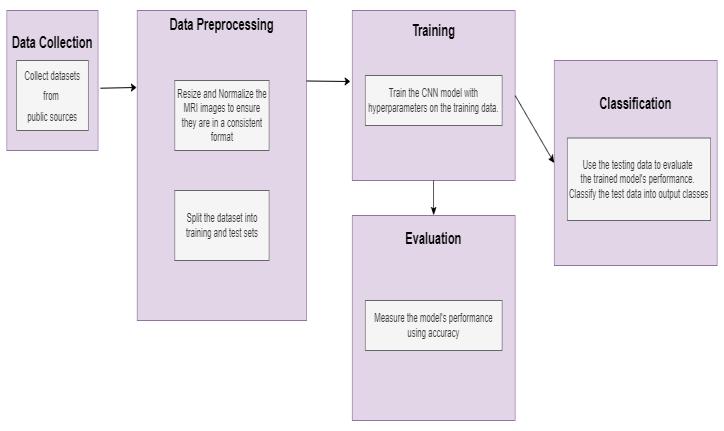
It refers to the conceptual framework that outlines the structure,functionality,andoperationalaspectsofasystem. It acts a foundational model that captures how various componentsoftheapplication,function,andareorganized. An architectural description provides a structured and formalrepresentationofthismodel,enablingclearanalysis and reasoning about the system's design, behavior, and inter-componentrelationships.
The provided system architecture shows how a algorithm CNNisusedinanMRIimagecategorizationsystem.Thefirst step of the procedure is data collecting, which comprises acquiringMRIpicturesfrom publicallyaccessiblesources.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 07 | Jul 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
After that, these photos go through preprocessing, which involves reducing and normalizing them to preserve consistencyandenhancemodel performance.Tofacilitate learningandassessment,trainingandtestingdatasetsare furtherdivide.
With the trained dataset model is trained using cnn, with specifichyperparameterslikelearningrateandbatchsize. After training, the model is evaluated to measure its accuracyandeffectiveness.Finally,inthecatalogingstage, the trained model is tested on unseen data to classify the MRI images into their respective output classes. This structuredpipelineensuresaccurate,efficient,andscalable imageclassificationformedicalapplication.
TheusageofCNN algorithm for MRIimagecategorization followsastructuredmethod.Theapproachbeginswiththe gathering and processing of MRI datasets, which involves normalizingpixelintensitiesandscalingpicturestomaintain uniformitythroughoutthedataset.TheCNNarchitectureis then constructed to contain crucial components such as, recognizing edges and textures, pooling layers for dimensionality reduction while maintaining essential information, and fully connected layers for final classification.
The intricacy of the classification problem and the processingresourcesathanddeterminewhichCNNdesignis best. Data augmentationtechniqueslike rotation,flipping, and zooming are used to artificially increase the training dataset and introduce variability in order to enhance the model'scapacityforgeneralization.
After constructing the model architecture, training is performedontheaugmenteddataset,duringwhichtheCNN learns to alter its parameters via back propagation. Followingtraining,Performancemetricslikeaccuracyand lossareusedtoassessthemodelonadifferenttestset.This analysis sheds light on the model's ability to accurately identify MRI images and its potential to support medical diagnosis.
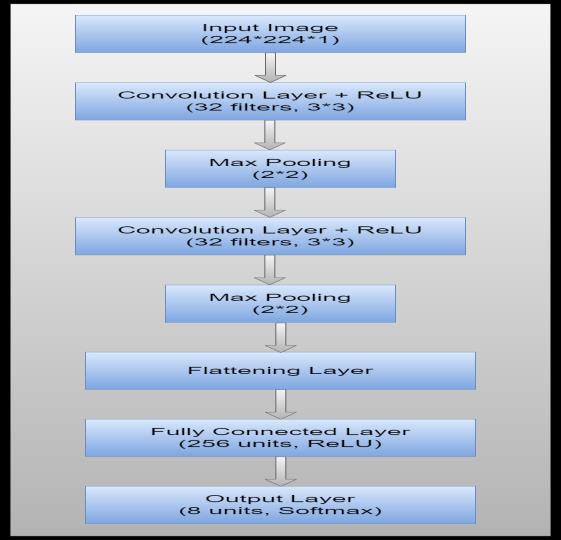
Input Layer: SinceMRIimagescanvaryintheiroriginal dimensions, they are typically resized to a standardized resolution, such as 224×224 pixels, to ensure uniformity acrossthedataset.Thisresolutiondefinesthespatialsizeof eachinputimage.
MRIscansaregenerallygrayscale,meaningtheyconsistofa singlechannel.Asaresult,theinputshapefortheseimages is typically defined as 224×224×1, where "1" denotes the number of color channels. Standardizing the input dimensionsisacrucialpreprocessingstep,asitenablesthe
modeltoprocessthedataconsistentlyandeffectivelyduring trainingandinference.
Convolutional Layers: Thefirstconvolutionallayerinthe CNN applies 32 filters, each of size 3×3, to the input MRI images. This convolutional operation is essential for detecting low-level features, such as edges, corners, and textures, which are critical for the initial stages of image analysis.Thesefeaturesserveasthefoundationalelements thatdeeperlayerscanbuildupontorecognizemorecomplex patterns.
Followingtheconvolution,theReLU(RectifiedLinearUnit) activation function is employed. ReLU introduces nonlinearityintothemodel bytransformingall negativepixel valuestozerowhileretainingpositivevalues.Thisactivation functionenablesthenetworktolearncomplexpatternsand improves the model's ability to approximate non-linear relationshipswithintheimagedata.
Pooling Layers: FirstMaxPoolingLayer:Theoutputofthe first convolutional layer is passed through a max-pooling layer with a 2x2 filter. This layer reduces the spatial dimensionsofthefeaturemapsbyselectingthemaximum value in each 2x2 window, which helps in reducing the complexityofthemodelandpreventingoverfitting.
Further Convolution and Pooling: Second Convolutional Layer:Similartothefirst,thislayerapplies another set of 32 convolutional filters of size 3x3 to the pooledfeaturemaps,learningmorecomplexfeaturesfrom theMRIimages.
Second Max Pooling Layer: Another max-pooling layer follows, further reducing the spatial dimensions of the featuremaps.
Flattening Layer: Thislayerflattensthe2Dfeaturemaps intoa1Dvector.Thisflattenedvectorservesastheinputfor thefullyconnectedlayers.
Fully Connected Layers: The network can learn highlevel representations of the characteristics by passing the flattenedvectortothefirstfullyconnectedlayer,whichhas 256neurons.
Output Layer: If there are 8 possible risk classes, the outputlayerwillhave8neuronswithaSoftmaxactivation function, providing a probability distribution over the classes.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 07 | Jul 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Dataset: ThecollectioncontainsgrayscaleMRIpictures, methodicallycategorizedintofouruniquecategories:Brain, Chest, Lower Body (Kidney Pelvis), and Lumbar. Each picturedepictsadistinctanatomicallocation,obtainedusing MRI images, and shows diverse tissue architectures and internalcompositionsvitalformedicalstudy.
Thismodelistrainedandvalidatedusingthisheterogeneous dataset with the goal of automatically categorizing the photosintotheappropriateclasses.Themodel'scapacityto learn discriminative characteristics across various body parts is improved by the addition of diverse anatomical areas,whicheventuallyimprovesthemodel'sgeneralization and diagnostic capabilities. The model may help medical personnel recognize and interpret MRI scans more accurately and efficiently if it can successfully understand thesevariances.
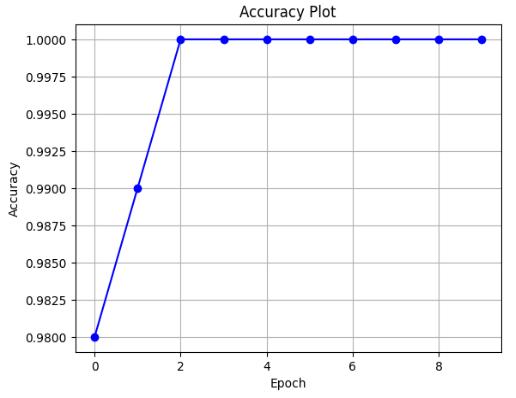
Chart -1: Accuracy of Dataset
TheproposedMRIimageclassificationmodeldemonstrates superior accuracy when compared to existing approaches discussed in related research[1]. Through optimized preprocessing,featureextraction,andtheuseofaneffective machinelearningalgorithm(CNN),themodelachievedan accuracyof93.1%.
For classifying MRI images a CNN Algorithm offers a compellingapproachtoaddressingthelimitationsofmanual image analysis. This research aims to create a highly accurate and effective automated classification model by utilizing a vast and varied dataset in conjunction with cutting-edgedeeplearningtechniques.
The successful deployment of such a system holds the potential to enhance diagnostic precision, alleviate the workloadofmedicalprofessionals,andultimatelycontribute toimprovedpatientoutcomes.Moreover,thetechniquesand resultspresentedinthisstudyhighlightthegrowingroleof CNN-based solutions in medical imaging, signaling a promising direction for future innovations in automated diagnosticsystemsandintelligenthealthcaretechnologies.
Itisourgreatpleasuretopresentthepaperforourproject titled "Deep Learning for MRI Image Classification using CNN".
IwouldliketoexpressprofoundgratitudetomyguideDr.H PMohanKumar,Professor&HOD,DepartmentofCS,PES CollegeofEngineering,Mandyaforhiscontinuesguidance andsupporttopublishmyresearchpapersuccessfully.
[1]Cmak Zeelan Basha;A Likhitha;P Alekhya;V Aparna, “ComputerisedClassificationofMRIImagesusingMachine LearningAlgorithms”,IEEE,04August2020.
[2]MeghaviRana&MeghaBhushan,“Machinelearningand deep learning approach for medical image analysis: diagnosistodetection”,SpringerNatureLink,Volume82,24 December2022.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 07 | Jul 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[3]JianpengZhang,YutongXie,QiWu,YongXia,“Medical imageclassificationusingsynergicdeeplearning”,Science Direct,Volume54,May2019.
[4] Destiny Agboro, “Medical Image Classification with Machine Learning Classifier”, Predictive Analytics with KNIME2023.
[5] X. Xie, Deep learning-based image classification of MRI brain image, ResearchGate (College of Medicine and Biological Information Engineering, Northeastern University),2021.
[6]A. Elbachariet al, MRIBrainImagesClassification Using Convolutional Neural Networks, published via Springer in AI2SD(partofLectureNotesinArtificialIntelligence),2020.
[7]P. Maheshet al., Enhancing brain tumor classification in MRIscanswithamulti-layerCNN,FrontiersinComputational Neuroscience,2024
[8] CustomizedCNN withSHAP,LIME,Grad-CAMauthors, Utilizing customized CNN for brain tumor prediction with explainableAI,ScienceDirect(Journal),2024.
[9]CNN-TumorNetteam, Leveraging explainability in deep learning for precise brain tumor classification (CNN-TumorNet),FrontiersinOncology,2025
[10]FranciscoJavierDíaz-Pernas,MarioMartínez-Zarzuela, Míriam Antón-Rodríguez, David González-Ortega, A Deep Learning Approach for Brain Tumor Classification and Segmentation Using a Multiscale Convolutional Neural Network,arXiv(alsocross-postedforpeerreview),2024
[11]TeamatMDPI(advancedclassification), AdvancedBrain Tumor Classification in MR Images Using Transfer Learning (Xception, DenseNet201, EfficientNetB5), MDPI (Cancers journal),2024–2025.
[12]StudyinBMCMedicalInformaticsandDecisionMaking, MRI-based brain tumor detection using convolutional deep learning,BMCMedInformDecisMak,2023.
[13] Authors of automated deep learning framework, An automated deep learning framework for brain tumor classification,ScientificReports(NaturePublishing),2025.
[14] Authors of Ensemble technique, Ensemble Deep LearningTechniqueforDetectingMRIBrainTumor,Wiley/ Hindawi,2024.
[15]ApplicationofDeepLearninginDetectingNeurological Disorders from MRI (2020, Brain Informatics review) Surveys CNN-based architectures (VGG16, InceptionV4, ResNet)forAlzheimer’sdetectionandotherneurodisorders


Chandana T R, received her Bachelor’s degree from Mandya University Mandya, and she currently pursuing MCA in PES CollegeofEngineeringMandya,
Dr. H P Mohan Kumar, obtained MCA, MSc Tech and PhD from University od Mysore, India in 1998,2009and2015respectively. He is working as a Professor in department of CS, PES College of Engineering, Mandya, Karnataka, India, His area of interest are ComputerVision,andDataMining.