
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Yashas K S
Software Engineer, Bangalore, KA, India
Abstract - Deeplearningisoneofthemostrapidlyevolving areas in research and development, with applications spanning a wide range of domains including healthcare, gamingandentertainment,andagriculture.Inthehealthcare sector, deep learning techniques have demonstrated significant potential in disease detection, enabling timely diagnosis andsupporting effective treatment planning.
Key Words: Deep Learning, Healthcare, Colon Cancer Detection, Computer Vision, Transfer Learning.
Coloncancer,alsoreferredtoascolorectalcancer,isamong the most prevalent and life-threatening forms of cancer worldwide.Earlydetectioniscriticalforimprovingsurvival rates and enhancing treatment outcomes. With the rapid advancement of medical imaging and computational technologies,thereisagrowingdemandfordiagnostictools thatareaccurate,automated,andnon-invasive.
Deeplearning,asubsetofmachinelearning,hasemergedas a powerful tool for analyzing complex medical data particularlyinimage-baseddiagnosis.ConvolutionalNeural Networks(CNNs)havedemonstratedremarkablesuccessin medical imaging due to their ability to learn spatial hierarchies and extract meaningful features from highdimensional image data. By leveraging such models, radiologistscanbesupportedinaccuratelyidentifyingcolon cancerfromCTscanimageswithincreasedconsistencyand efficiency.
Thisstudypresentsadeeplearning-basedapproachforthe detection of colon cancer in abdominal CT scan images. A custom CNN architecture is developed and trained on a publiclyavailabledatasettoclassifyimagesascancerousor non-cancerous.Theobjectiveistoevaluatetheeffectiveness ofdeeplearninginfacilitatingearlyandprecisediagnosisof coloncancer,therebypotentiallyalleviatingtheburdenon healthcaresystemsandenhancingpatientoutcomes.
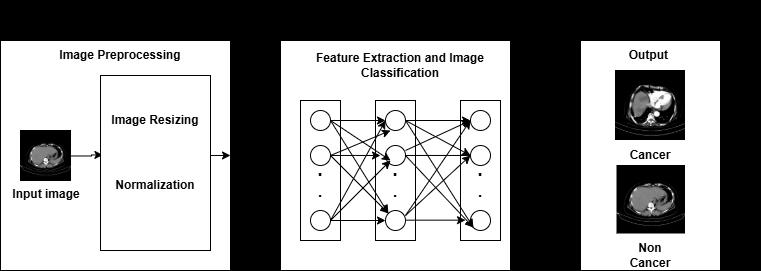
-1:Architecture
TheproposedCNNmodelconsistsofaninputlayer,aseries ofhiddenlayers,andanoutputlayerthatindicateswhether theimagebelongstothecancerclassorthenon-cancerclass. The input layer accepts abdominal CT scan images of size 512×512with3channels.Onceitgetstheinputimageit will perform the standard Image preprocessing tasks like ImageresizingandNormalizationtobringthepixelvalues between0to1.Thehiddenlayerscompriseasequenceof Conv2DlayersfollowedbyMaxPoolinglayers.
The output layer consists of two neurons, representing a binary classification, and determines whether the input imagebelongstothecancerornon-cancerclass.
The dataset consists of three folders: Train, Test, and Validation. The training dataset contains a total of 7,937 samples,ofwhich4,761belongtothenon-cancerclassand 3,176tothecancerclass.
The validation dataset consists of 1,701 samples, of which 1,020belongtothenon-cancerclassand681tothecancer class. The testing dataset consists of 1,702 samples, with 1,021belongingtothenon-cancerclassand681tothecancer class.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
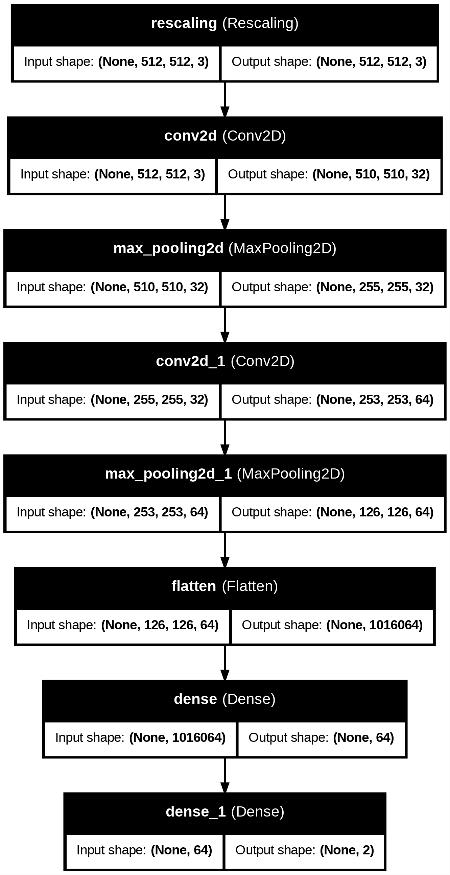
ThemodelwasimplementedinPythonusingtheTensorFlow framework and trained on a Tesla T4 GPU to leverage acceleratedcomputation.Thearchitectureoftheproposed CNNmodelisillustratedinthediagramabove.Trainingwas conductedover20epochs,duringwhichthemodelachieved 100%accuracyonthetrainingsetafterjustfourepochs.The Adam optimizer was employed to update the network weights,withbinarycross-entropyusedasthelossfunction. Accuracywasselectedastheprimaryevaluationmetricto assessthemodel’sperformance.
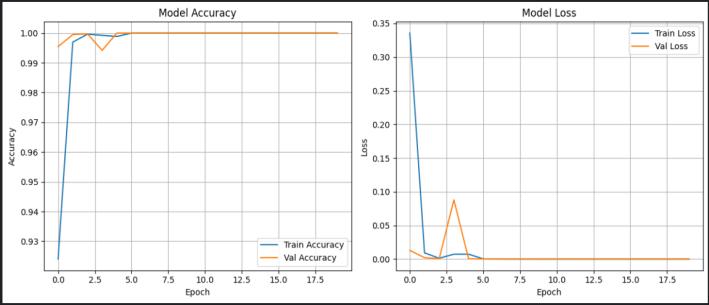
Theproposedmodelachieved100%trainingaccuracyafter justfourepochs.Thegraphontheleftillustratesthetraining andvalidationaccuracyoverthecourseoftraining,whilethe graph on the right depicts the corresponding training and validationloss.Accuracywasusedastheprimaryevaluation metricthroughoutthetrainingprocess.
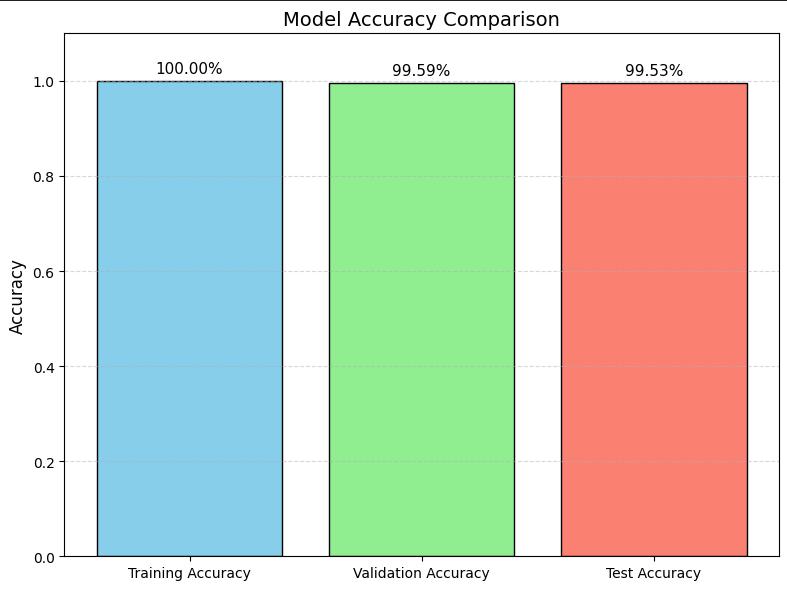
BelowbarchartshowsthemodelperformanceonTraining dataset,validationdatasetandthetestdatasetaftertraining for20epochs.
This study demonstrates the potential of deep learning modelsinaccuratelydetectingcoloncancerfromabdominal CTscanimages.TheproposedCNN-basedmodelachieved highaccuracy,showingpromiseforuseasadiagnosticaidin clinicalsettings.UsingtheColonCancerCT-2025dataset,the model achieved strong performance, indicating that deep learning can play a critical role in improving cancer diagnosis workflows. By leveraging convolutional neural networks, we were able to classify cancerous and noncancerous images with high precision. Colon Cancer DetectioninCTscanusingDeepLearninghelpstodiagnoize the illness early and cure it in time. The model is giving descentaccuracyonbothtrainingandtestingphase.
The model has been trained on the Convolutional Neural Network(CNN)andasafutureworkwecantrainthesame datasetontheStateofArtmodelslikeVGG16orResNet-50 etc.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Thebelowfigureshowsthepossibleenhancementsaspart ofthefuturescope.Thedatasetcanbepreprocessedusing DataAugmentationtechniqueslikerotation,Zoomin,Zoom out,normalizationetctoincreasethemodelaccuracy.Then thepreprocessedimageswillbesenttotheState-of-the-art modelslikeResNet,VGG16,DenseNetorEfficientNet.This mightincreasethemodelaccuracyastheState-Of-The-Art (SOTA)modelsaretrainedonthelargeamountofdata.
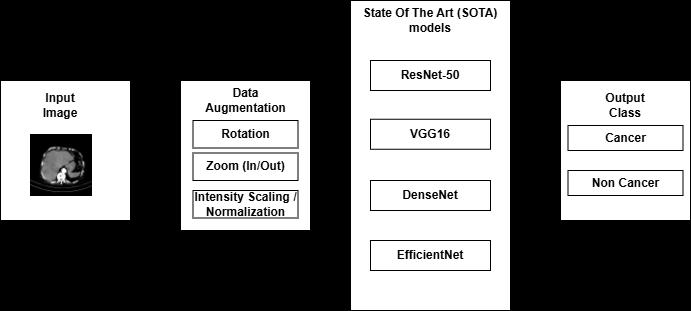
Fig -5:Adiagramillustratingthepotentialfuture enhancements.
Transfer learning facilitates efficientfeature extraction by leveragingmodelspre-trainedonlarge-scaledatasets.Image augmentation techniques helps the model to learn from diverseperspectivesandvariationsofthedata,potentially improvingitsgeneralizationandperformance.
Futureworkcanfocusonevaluatingthemodelacrossmulticenterdatasetstoassessitsgeneralizabilityandrobustness. Additionally, integrating explainability techniques such as Grad-CAM can enhance the interpretability of the model’s predictions.Improvingmodelexplainabilityisacrucialarea offutureresearch,asitprovidesinsightsintothefeatures influencingtheclassificationofimagesascancerousornoncancerous.
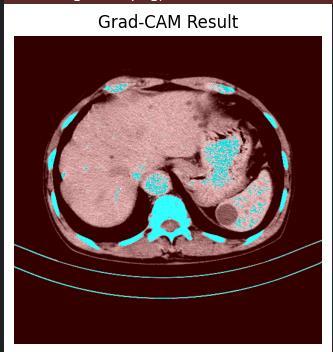
TheimageaboveillustratesasampleGrad-CAM(GradientweightedClassActivationMapping)visualizationappliedto themodel.TechniqueslikeGrad-CAMcanbeusedtoidentify
the regions of the image that the model focuses on when makingitsclassificationdecisions.
[1] Farhana Sultana, Abu Sufian, Paramartha Dutta, “Advancements in Image Classification using ConvolutionalNeuralNetwork”,IEEE2018.
[2] OliviaNocentini,JaeseokKim,MuhammadZainBashir, Filippo Cavallo, “Image Classification Using Multiple ConvolutionalNeuralNetworksontheFashion-MNIST Dataset”.
[3] Alex Krizhevsky, Ilya Sutskever, Geoffrey E. Hinton, “ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional NeuralNetworks”.
[4] Srinija Srimamilla, “Image Classification Using ConvolutionalNeuralNetworks”,IJRASET.
[5] Leiyu Chen, Shaobo Li, Qiang Bai, Jing Yang, Sanlong Jiang, Yanming Miao, “Review of Image Classification AlgorithmsBasedonConvolutionalNeuralNetworks”.
[6] Vega-Rodríguez, M.A. Review: Feature Extraction and ImageProcessing.Comput.J.2004.
[7] D, Z.; Liu, B.; Sun, C.; Wang, X. Learning the Classifier CombinationforImageClassification.J.Comput.2011.
[8] Zeiler, M.D.; Fergus, R. Visualizing and Understanding ConvolutionalNetworks.arXiv2013,arXiv:1311.2901.
[9] Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv 2014,arXiv:1409.1556.
[10] Rawat, W.; Wang, Z. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Image Classification: A Comprehensive Review.NeuralComput.2017,29,2352–2449.
[11] Y. Lecun, Y. Bengio, and G. Hinton, “Deep learning,” Nature,vol.521,no.7553,pp.436–444,52015
[12] I.Goodfellow,Y.Bengio,andA.Courville,DeepLearning. MITPress,2016,http://www.deeplearningbook.org
[13] R.Hecht-Nielsen,“Theoryofthebackpropagationneural network,” in International 1989 Joint Conference on NeuralNetworks,1989,pp.593–605vol.1.
[14] G.E.Hinton,N.Srivastava,A.Krizhevsky,I.Sutskever, and R. Salakhutdinov, “Improving neural networks by preventingcoadaptationoffeaturedetectors,”CoRR,vol. abs/1207.0580, 2012. [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1207.0580

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[15] I. Jolliffe, Principal Component Analysis. Berlin, Heidelberg:SpringerBerlinHeidelberg,2011,pp.1094–1096.[Online].Available:https://doi.org/10.1007/9783-642-04898-2455
© 2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page626