2 minute read
Measurement of oil
Open the hood. Remove the coolant expansion tank. Slowly unscrewing the lid, reset the pressure in the system. Check the coolant. Top up the coolant to the COLD mark if necessary.
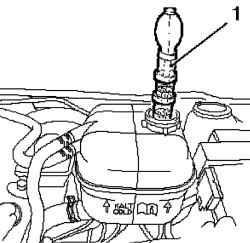
Fig. 2.66. Installing the tool on the
coolant expansion tank: 1 - tester
Set the tester at the coolant expansion tank (Figure 2.66). Start the engine. Check the engine for leakage.
NOTE Transparent cylinder tester contains a blue reactive liquid that turns yellow in the presence of air containing trace of carbon monoxide. If you pull fresh air in the test fluid, it is restored and regains blue.
The air is taken from the coolant expansion tank with a rubber bulb.
NOTICE Coolant should not fall into the tester.
If the blue liquid in the main chamber of the tester was yellow, the cylinder head gasket or cylinder head leaky.
Check tester
The fluid can be tested by a fence of gases from the exhaust pipe. In this case the test liquid should be yellow. Disconnect tester and carefully reset the pressure. Replace the cover expansion tank coolant. Close the hood.
Under the oil consumption of internal combustion engine means the amount of oil consumed in the process of combustion. Oil consumption should not be confused with the loss of oil due to leakages through seals oil pan and the lid of the cylinder head. Motor oil is designed to separate the friction surfaces of the oil film, ie, to prevent dry friction, and dissipation of heat produced by friction and remove products of combustion. All this leads to a gradual flow of oil during engine operation. In addition to the operating conditions on oil consumption affects driving style and manufacturing tolerances. Need to top up the oil, when its level falls below «MIN» on schupe to measure. It is also important to ensure that the oil level did not exceed the mark «MAX» to schupe to measure, because it can lead to increased consumption of oil. Since oil consumption is determined by technical factors, we can conclude that the motor does not consume oil, under certain operating conditions, which lead to the dilution of oil. Subject to frequent launches of a cold at the beginning of motion, until the engine operating temperature, oil falls back into the oil pan, carries with it a fuel. Fuel "dissolved" oil and its level rises. Such dissolved oil loses its lubricating ability and may cause engine damage, if not complied with the prescribed oil change intervals.










