

GOODBYE OUTDATED.
INTRODUCING THE
FOREVER WET AUTO SPRAYER
for use with Ruhof’s Prepzyme® Forever Wet Enzymatic Pre-Cleaner
The cleaning process begins at the point of use. When soils dry, they become harder to remove and increase the risk of corrosion, biofilm formation, and HAI’s. The Forever Wet Auto Sprayer delivers a consistent application of Prepzyme® Forever Wet in less than half the time—keeping instruments moist for up to 72 hours.













Decontamination— No Dilution, No Delay. Ready-to-use, non-enzymatic foam spray safe for ophthalmic instruments.
Initiates pretreatment at the point of use in the OR or ED, giving SPD teams a head start.
Broad-spectrum formula emulsifies and lifts all soil types, making bioburden easier to remove.

hmark.com
800.521.6224

Helps prevent biofilm and corrosion, protecting instruments from the start. Now is the perfect time to try XEN Xcelerate. For a limited time, purchase one case and get one free—making it easier than ever to stock up and clean without compromise. Don’t miss this opportunity to enhance your pretreatment process while doubling your value.
Scan here to see how XEN aligns with your department’s pre-cleaning protocol



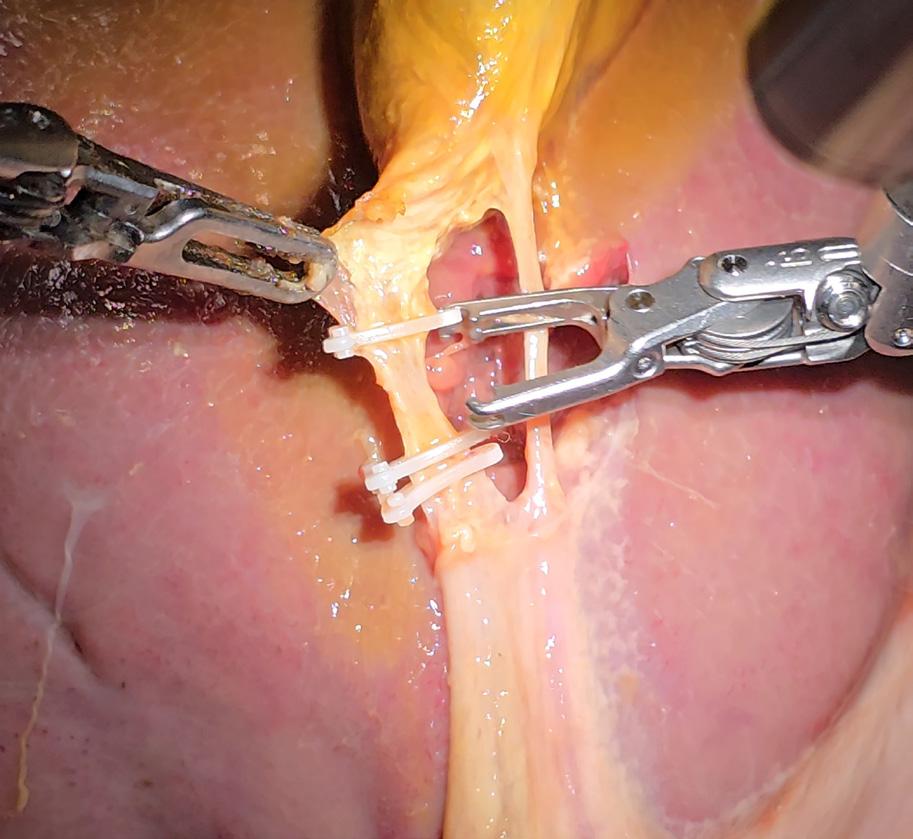
Robot Performs Realistic Surgery Without Human Help
A robot trained on videos of surgeries performed a lengthy phase of a gallbladder removal without human help. The robot operated for the first time on a lifelike patient, and during the operation, responded to and learned from voice commands from the team – like a novice surgeon working with a mentor.
The robot performed unflappably across trials and with the expertise of a skilled human surgeon, even during unexpected scenarios typical in real life medical emergencies.
The federally funded work, led by Johns Hopkins University researchers, is a transformative advancement in surgical robotics, where robots can perform with both mechanical precision and human-like adaptability and understanding.
“This advancement moves us from robots that can execute specific surgical tasks to robots that truly understand surgical procedures,” said medical roboticist Axel Krieger. “This is a critical distinction that brings us significantly closer to clinically viable autonomous surgical systems that can work in the messy, unpredictable reality of actual patient care.”
The findings are published in Science Robotics.
In 2022, Krieger’s Smart Tissue Autonomous Robot, STAR, performed the first autonomous robotic surgery on a live animal – a laparoscopic surgery on a pig. But that robot required specially marked tissue, operated in a highly controlled environment, and followed a rigid, predetermined surgical plan. Krieger said it was like teaching a robot to drive along a carefully mapped route.
But his new system, he says, “is like teaching a robot to navigate any road, in any condition, responding intelligently to whatever it encounters.”
Surgical Robot Transformer-Hierarchy, SRT-H, truly performs surgery, adapting to individual anatomical features in real-time, making decisions on the fly, and self-correcting when things don't go as expected.
Built with the same machine learning architecture that powers ChatGPT, SRT-H is also interactive, able respond to spoken commands (“grab the gallbladder head”) and corrections (“move the left arm a bit to the left”). The robot learns from this feedback.
“This work represents a major leap from prior efforts because it tackles some of the fundamental barriers to deploying autonomous surgical robots in the real world,” said lead author Ji Woong "Brian" Kim, a former postdoctoral researcher at Johns Hopkins who’s now with Stanford University. “Our work shows that AI models can be made reliable enough for surgical autonomy – something that once felt far-off but is now demonstrably viable.”
Next the team would like to train and test the system on more types of surgeries and expand its capabilities to perform a complete autonomous surgery.
Authors include Johns Hopkins PhD student Juo-Tung Chen; Johns Hopkins visiting graduate student Pascal Hansen; Stanford University PhD student Lucy X. Shi; Johns Hopkins undergraduate Antony Goldenberg; Johns Hopkins PhD student Samuel Schmidgall; former Johns Hopkins postdoctoral fellow Paul Maria Scheikl; Johns Hopkins research engineer Anton Deguet; surgical fellow Brandon M. White, Stanford University assistant professor Chelsea Finn; and De Ru Tsai and Richard Cha of Optosurgical.
The work was supported by Advanced Research Projects Agency for Health (ARPA-H) 75N91023C00048; National Science Foundation/ Foundational Research in Robotics 2144348; National Institutes of Health R56EB033807; and National Science Foundation Division of Graduate Education 2139757.
Getinge, Zimmer Biomet Announce ASC Partnership
Global MedTech companies Getinge and Zimmer Biomet Holdings Inc., have announced a strategic partnership where Zimmer Biomet will distribute Getinge’s Operating Room (OR) capital products to its ambulatory surgery center (ASC) customers. This partnership creates a turnkey solution for ASC customers, who can now access Getinge’s infection control and surgical portfolio and Zimmer Biomet’s broad menu of best-in-class implants and surgical robotics from a single source.
ASCs are modern healthcare facilities focused on providing same-day surgical care, without the need for patients to stay overnight. A growing part of the U.S. healthcare landscape, more than 22.5 million procedures are performed in ASCs annually.1 The global market is projected to grow steadily, driven by cost efficiency, convenience and advances in MedTech. For more than four decades, ASCs have demonstrated an exceptional ability to improve quality and customer service while simultaneously reducing costs.2
As part of Zimmer Biomet’s ZBX ASC Solutions offering, customers will be able to access Getinge’s infection control and surgical portfolio – surgical equipment, OR integration and lighting – with Zimmer Biomet’s industry-leading joint replacement implants and technology.
“For us, this partnership represents a significant
advancement in our efforts to innovate and expand the boundaries of healthcare. We are thrilled to collaborate with Zimmer Biomet to deliver value to healthcare professionals and patients within the orthopedic ASC sector. This collaboration shows our commitment to making life-saving technology accessible to more people,” said Patricia Fitch, President of North America at Getinge.
“Together with Getinge, we’re expanding our ability to deliver a comprehensive, turnkey solution for our ASC customers – faster and more seamlessly – from a company they know and trust,” said Jehanzeb Noor, Senior Vice President, Chief Strategy, Innovation and Business Development Officer, Zimmer Biomet. “As orthopedic surgeries increasingly migrate from traditional hospital settings to ASCs, the imperative to drive efficiency, enhance patient safety, and improve clinical outcomes has never been greater. By aligning with Getinge, we’re accelerating our ability to support surgeons in advancing these priorities, while shaping the future of orthopedic care.”
The partnership will be implemented in phases, starting in the U.S., with the ambition to eventually offer the combined portfolio of ASC solutions in additional regions around the world.
Jackson Healthcare’s Workplace Culture Among Most Inspiring
Jackson Healthcare, a provider of healthcare workforce services, has been named in the 2025 Top 100 Inspiring Workplaces North America awards. Compiled by an independent panel of judges, the recently published list highlights people-first companies going above and beyond to create outstanding environments and experiences for their employees.
This annual awards program is presented by Inspiring Workplaces Group, a global organization championing positive change around the world both inside and outside the office. The Top 100 Inspiring Workplaces list recognizes companies of all sizes and industries, including start-ups, nonprofits and government entities. Honorees are evaluated based on how effectively they create cultures that inspire, engage and empower their workforces to thrive.
“At Jackson Healthcare, we believe that when you create an environment where people feel valued, supported and connected to a greater purpose, incredible things happen,” said Shane Jackson, president, Jackson Healthcare.
“This honor is a reflection of the culture our associates help cultivate every day and a shared commitment to our mission of improving the delivery of patient care and the lives of everyone we touch. I’m proud of how our associates show up each day to make a meaningful difference in the lives of millions nationwide and appreciate Inspiring Workplaces Group for its recognition of our collective efforts.”
In addition to being named to the Top 100 list, Jackson Healthcare received “best-in-class” distinctions in the leadership category for fostering a workplace where leaders inspire growth and success; and in the culture and purpose category for embedding its mission into decision-making at every level of the organization.
Jackson Healthcare has been recognized on the North America list every year since its inception in 2023 and has earned two consecutive appearances on the Global Top 100 Inspiring Workplaces list.
INDUSTRY INSIGHTS
news & notes
Chamberlain University, SSM Health Address Nursing Shortage
Chamberlain University, the nation’s largest School of Nursing and part of Adtalem Global Education Inc, and SSM Health, a leading Catholic health system, have announced the launch of the Aspiring Nurse Program – a large-scale partnership designed to fund nursing education, enhance clinical readiness and create a pathway to employment across SSM Health’s care sites in Missouri, Oklahoma, Illinois and Wisconsin.
The ambitious partnership is the first of its kind in the nation – offering a direct, employment-focused pathway for aspiring nurses by combining tuition support with immersive clinical experience, and the opportunity for job placement within SSM Health facilities after graduation. In return, students commit to joining SSM Health’s workforce, creating a sustainable talent pipeline that is projected to produce more than 400 new nurses annually.

Students will train directly within SSM Health facilities –where they may eventually work – gaining firsthand experience with the health system's work culture, care practices and technology systems before starting their professional careers.
“The nursing shortage demands bold, scalable solutions,” said Laura S. Kaiser, FACHE, president & CEO of SSM Health. “The Aspiring Nurse Program is a strategic long-term investment in our people and our mission. It’s designed to meet today’s workforce challenges while building a stronger, more resilient future for nursing.”
This partnership also represents a leap forward in Adtalem’s strategy to become the clinical workforce partner of choice for providers nationwide.
“This partnership with SSM Health demonstrates the transformative power of large-scale collaboration between education and healthcare,” said Steve Beard, chairman and chief executive officer, Adtalem Global Education. “When forward-thinking health systems invest in comprehensive workforce partnerships – combining funding, hands-on facility training and a direct line to employment – we create sustainable pipelines that scale with provider needs. We’re building the foundation for long-term workforce stability while ensuring graduates are day-one ready. This is the future of strategic healthcare workforce development.”
The Aspiring Nurse Program launches in Oklahoma this fall through Chamberlain’s online Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) program, with additional cohorts to follow in St. Louis and Jefferson City, Missouri, as well as in Illinois and Wisconsin.
“This program is more than a solution to the nursing shortage – it’s a bold reimagining of how we grow and support the next generation of nurses,” said Amy Wilson, DNP, chief nurse executive for SSM Health. “By investing in education and clinical experience from day one, we’re not only preparing students for success– we’re strengthening the future of patient care across our communities.”
Founded as Deaconess College of Nursing, Chamberlain’s legacy is rooted in a mission to serve communities through care and education. This alignment fosters a values-driven learning environment that not only prepares students clinically, but also instills a deep commitment to service, empathy and holistic care – qualities essential to delivering exceptional patient outcomes within SSM Health.
"We are excited to partner with SSM Health to place future nurses where they're needed most across multiple states," said Karen Cox, Ph.D., RN, FACHE, FAAN, president of Chamberlain University. "Nurses are essential to community health, and expanding the workforce supports both patients and current caregivers. As the nation's largest School of Nursing, we're eager to create innovative and immediate opportunities for our graduates in communities where they'll make a real impact."
Stryker Receives FDA Clearance for Incompass Total Ankle System

Stryker has received U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) 510(k) clearance for the Incompass Total Ankle System, an implant intended for patients with ankle joints damaged by severe rheumatoid, post-traumatic or degenerative arthritis. This new platform integrates the innovative technologies of Stryker’s Inbone and Infinity systems into a single, comprehensive solution for total ankle replacement.
“Incompass reflects our commitment to redefining what’s possible in total ankle replacement,” said Adam Jacobs, vice president and general manager of Stryker’s foot and ankle business. “By building on decades of clinical experience and leveraging extensive data insights, we’re setting a new standard – one that empowers surgeons to deliver more personalized care with greater efficiency and confidence.”
Incompass incorporates Adaptis Boney Ingrowth Technology and redesigned instrumentation to support long-term fixation, surgical flexibility and streamlined workflow. Developed to address key challenges in total ankle replacement, including intraoperative adaptability and procedural efficiency, the system is informed by data from more than 85,000 CT scans and 100,000 clinical cases. It also offers a broad range of implant and instrumentation options to support patient-specific care.
Built using the Stryker Orthopaedic Modeling & Analytics (SOMA) platform in combination with arthritic ankle scans from the company’s Prophecy Surgical Planning System, Incompass provides a continuum of implant and instrument options designed to accommodate surgeon preference and patient anatomy. System enhancements include a redesigned alignment system for greater control across multiple planes, updated implant holders and trial tools for improved handling, and instrumentation refinements designed to reduce surgical steps and set up time.
KEEP YOUR OR STAFF COOL
The lightweight CoolOR® Circulating Water System is a proven solution for keeping surgeons and staff cool and comfortable.
CONVENIENT, EASY-TO-USE AND PORTABLE DESIGN
VEST STYLE CHOICES
Adjustable and fitted cooling vests cool by circulating cold water through a series of tubes sewn into the vest.
WATER-TIGHT COOLING RESERVOIR
Neoprene gasket seal with secure stainless steel compression latches.
NO ELECTRICAL CORDS

Optional lithium-ion battery offers increased mobility with more than six hours per charge.

INDUSTRY INSIGHTS AAMI
How Superheated Steam Damages Sterile Barriers
M ore than a decade ago, Dr. William Leiva, senior program manager of sterile reprocessing at Medtronic, observed something troubling. He noticed that some sterile barrier systems (SBS), like peel patches, looked “brittle” or “toasted” after sterilization.
This observation led Leiva to investigate the nuances of the steam sterilization cycle and the impact of superheated steam on sterile barrier systems. With support from the AAMI Foundation in the form of a KILMER grant, he focused on the effects of superheated steam on sterile barrier systems (SBS), such as peel pouches.
Leiva’s research is undergirded by basic differences in steam quality and performance. Wet saturated steam has a “tremendous amount of energy” in the form of latent heat. The moisture
allows the steam to transfer energy to medical devices during sterilization. But dry saturated steam has lower enthalpy, or ability to transfer heat. Further, superheated steam has no enthalpy.
While steam sterilization cycles tend to follow the same pattern, and the sterilization plateau is constant despite some regional differences, real-world circumstances can lead to variance.
Leiva also pointed out that larger steam sterilizers typically have an inner chamber that, if over-pressurized, can create superheated steam.
The impact of steam of inadequate quality, such as superheated steam, can be substantial. Leiva also noted that there is major variance between hospital and industrial settings. Hospitals usually have “different loads every single day,” which can lead to different steam diffusion characteristics. Latent heat is “significantly reduced” in the event of reduced saturation.
Wet loads remain the primary cause for load reprocessing, and increasing jacket pressure enables dryer loads. The rise of new kinds of polymers and load configurations also creates complexities. Leiva also stated that steam sterilizers calculate temperature based on pressure, meaning that if superheated steam is present, the actual temperature within the chamber is likely higher than indicated.
Levia joined AAMI Foundation leader Ralph Basile in the AAMI Studio to chat more about this important research.
Study Aims and Structure
Faced with these issues, Levia adopted three research goals:
• First, validate a reproducible method to generate superheated steam in a test laboratory vessel.
• Second, expose samples to control and experimental superheated steam conditions.
• Third, conduct performance testing of sterile barrier after exposure conditions for both control and superheated steam.
The goal? Determine “if the sterile barrier is compromised” or if it maintains sterility.
After subjecting the SBS systems to test sterilization cycle of 15 minutes exposure, 10 minutes of drying, and a two-minute vacuum time at both 121 degrees Celsius and 132 degrees Celsius, Leiva conducted three tests on the SBS systems exposed to superheated steam.
1. A visual inspection, finding that some SBS systems were damaged at both 121 degrees Celsius.
2. A peel test, finding that superheated steam made the packaging weaker, and that the packages used in the experiment had a lower peel force.
3. A bubble test in accordance with
ASTM F2096, finding significant correlation of experimental conditions and failure of the bubble test.
The SBS systems showed signs of damage at both 121 and 132 degrees Celsius.
Study Conclusions
Leiva concluded that the damage suggests that superheated steam does pose risks to sterile barrier systems. The proposed method was validated and delivered statistically significant results on cycle performance for both control and experimental sample groups. Levia also found a strong positive relationship between experimental conditions and decreased performance of sterile barriers. The visually damaged sterile barrier systems are comparable to both paper
production vessels.
Leiva noted that relying solely on built-in physical parameters may lead to approval of cycles with inadequate exposure conditions, saying, “We may be missing some information.”
What’s Next?
Leiva concluded by suggesting several concrete steps for future research that could provide a better understanding of issues surrounding SBS and superheated steam. First, he proposed including an assessment of cycle parameters, including cycle temperature, cycle drying time, and drying pressure. Second, assessing different sterile barrier systems to determine reliability for short storage could be useful. Check out AAMI’s YouTube channel for an interview with




Reluctant Staying
By James X. Stobinski, Ph.D, RN, CNOR, CSSM(E), CNAMB(E)

This article starts with data provided by the American Association of Colleges of Nursing (AACN) in their Nursing Workforce Fact Sheet.1 The AACN updates this fact sheet periodically and there is much good news in the current, concise bullet points. In example, the outlook for nursing employment remains solid with projections of over 200,000 new RN positions to be created each year to the year 2031. The average salary for American RNs is nearly $78,000. We are also told that, as of 2022, 71.7% of the RN workforce holds a baccalaureate or higher degree as their highest level of education.1
The AACN Fact Sheet is a wealth of information on the American nursing workforce and dovetails nicely with the World Health Organizations report on the state of the world’s nursing workforce which was the focus of a previous column.2 As I reviewed the AACN data it also struck me that there is additional context underlying nursing workforce data and that there is connection to a concept that I spoke to in that previous column. With all the good news in the AACN Fact Sheet, we must also be aware that there are some countervailing forces impacting American nursing.
We have record employment
in nursing, projections for strong future growth and also reports that enrollment in Bachelor of Science nursing programs have again increased in 2024 as have enrollments in RN – BSN programs.³ All of this good news is counterbalanced with widespread reports that a high percentage of nurses plan to soon leave their current position or leave the nursing profession entirely. While it is a net positive that more new nurses are entering the profession we must acknowledge that this may not alleviate current shortages. It is possible that those leaving the profession and the increased demand for nurses in American healthcare may still leave us with a net shortage. Last month, I mentioned the term “reluctant staying” relative to American nursing. This term refers to nurses who remain employed despite experiencing dissatisfaction or burnout. Nurses continue in the profession because of financial necessity, lack of alternative job opportunities, or personal commitment and altruism. We all have known nurses who reluctantly, and perhaps unenthusiastically, remain in the profession. While these nurses do maintain vital staffing they frequently are not the best of our teams and may not be fully engaged in their every day work. These nurses count in the record total of working nurses, but these numbers can be deceiving. Other, less publicized factors also impact nursing.
We are experiencing a large-scale shift in the settings where healthcare is delivered to include far more ambulatory and home-based care. In perioperative nursing the proportion of ambulatory surgery is rapidly increasing; this requires new skill sets and precipitates workforce shifts. Perioperative nurses have a unique skill set that does not easily transfer to other nursing roles. This limits the mobility of these nurses and may narrow their employment choices. The closure of hospitals, especially in rural settings, continues at a steady pace. This may leave nurses in these settings with few options. Some of these nurses, if unable to make the transition to the ambulatory setting or move to a new location, may also leave the profession. There are opportunities for nurses who have the ability to adapt and perhaps move to a new specialty or work setting. Nurses lacking this capacity may become a
reluctant staying nurse or perhaps leave the profession. These choices cloud the overall picture, and we are left with incomplete data on the total nursing workforce.
— James X. Stobinski, Ph.D., RN, CNOR, CSSM(E), CNAMB(E), is the director of hospital and ASC relationships with National Institute of First Assisting (NIFA). He is also a member of the Central Michigan University faculty.
References

1. American Association of Colleges of Nursing. Nursing Workforce fact sheet. (April 2024). https://www. aacnnursing.org/news-data/fact-sheets/ nursing-workforce-fact-sheet?utm_
content=%F0%9F%92%8C%20 discover%20the%20number%20of%20 rns%20licensed%20in%20the%20u%20 s&utm_campaign=7%2f2%2f2025&utm_ source=activecampaign&utm_ medium=email
2. World Health Organization. (2025). State of the world’s nursing 2025: Investing in education, jobs, leadership and service delivery. https://iris.who.int/bitstream/ha ndle/10665/381329/9789240110236eng.pdf?sequence=1
3. Taylor, M. (2025, June 27). Nursing school enrollment on the rise: 7 notes. Becker’s Hospital Review | Healthcare News & Analysis. https://www. beckershospitalreview.com/quality/ nursing/nursing-school-enrollment-onthe-rise-7-notes/?origin=BHRE&utm_ source=BHRE&utm_ medium=email&utm_ content=newsletter&oly_enc_ id=0705J2387567B1E



INDUSTRY INSIGHTS ACHC

Elevating Standards in Surgery through Accreditation
By Deanna Scatena, RN
I n surgical environments, ensuring patient safety isn’t just a goal, it’s a baseline expectation that depends on systems designed to support consistency, accountability and excellence.
This is where accreditation plays a pivotal role. As a program leader with the Accreditation Commission for Health Care (ACHC), I can attest that achieving and sustaining the standards associated with accreditation is more than meeting regulatory requirements. We provide hospitals and surgical centers with a trusted partner to support the creation of a sustainable culture of safety, quality and accountability.
ACHC Standards are organized in chapters and while it may be tempting to limit your review to those specific to surgical care (e.g., anesthesia services, surgical services), successful surgical outcomes depend on a process that begins well before the patient arrives in the OR. Whether the period from pre-admission assessments to discharge occurs in under 24 hours in an outpatient setting, or over a longer period in an inpatient setting, it is essential to align each step with evidence-based protocols.
Accreditation serves this need as an organization-wide commitment. Beginning with your leadership and administrative structure, recognizing your physical plant as your biggest piece of “medical equipment,” and continuing to specific, departmentand function-level requirements, the standards as a whole reflect an integrated, facility-wide commitment to patient care quality. Within the OR, each regulation is designed to reduce risk, improve outcomes, and support clinical best practices across all roles in the operating room. Accreditation standards for the floor plan, utility and equipment set-up, use of sterile technique, infection prevention and other risk reduction strategies such as surgical site verification and defined team roles work together to foster an efficient, predictable, well-managed environment. This serves your surgical teams just as much as it does your patients. When every member of the team knows and follows the same procedures, collaboration improves, and the risk of complications decreases. Any deviation that occurs will be immediately noted and responded to. Data consistently demonstrate that accredited organizations adhering to best practice guidelines are associated
with reduced complication rates and decreased average lengths of stay compared to facilities lacking accreditation.
I am biased based on my role, but I have seen accreditation from the provider side as well as from the perspective of several accrediting organizations. In my view, ACHC Accreditation is a shared promise, a pledge from every member of my team and of the surgical teams we serve to uphold the highest standards of care. Accreditation isn’t a box to be checked. It’s not a periodic hassle to be avoided. It’s not about compliance for the sake of compliance. At its core, accreditation is about delivering the kind of care we want for ourselves and our families – intentional, consistent and collaborative.
– Deanna Scatena is the associate program director for acute care and critical access hospital accreditation at ACHC. She has worked in accreditation since 2017, guiding product development for specialty care certification and providing standards interpretation before moving into her current leadership role.






ENVIRON-MATE® DM6000 SERIES

















INDUSTRY INSIGHTS
Ensure Proper Use of Chemical Indicators
BY Tony Thurmond, CRCST, CIS, CHL, FCS
During initial training, sterile processing (SP) technicians become aware of chemical indicators (CIs). They may see them in a package to be sterilized or one that has already undergone sterilization. It is crucial that CIs are understood, used and interpreted correctly (there is more to it than just seeing a color change).
There are six types of CIs, and each is categorized accordingly (Type 1 through Type 6). The three variables that determine each type of indicator are temperature, exposure time, and steam quality. An indicator using one or more variables is designed to indicate what happened during the sterilization process. Note: The color change of any CI indicates that the product has been exposed to a process, but it is not an indicator that the contents are sterile.
• Type 1 – A Type 1 CI is considered a process indicator, showing that a package or container has been exposed to a steam sterilization process. This type is usually an external indicator, meaning it can be seen outside the package or container. A Type 1 indicator can come in different forms, including indicator tape, indicator label, container indicator card, or a tamper-resistant device such as a lock. Most peel packs
have a Type 1 indicator on the peel pouch that will change color when the temperature is increased.
• Type 2 – This type is used for specific test procedures, such as the BowieDick, which checks for evidence of an air leak, leaky seals, or steam supply or steam trap issues. This test should be completed after a warmup cycle at the beginning of the day. Type 2 indicators are typically packaged in a specially designed pack to simulate a thick barrier of steam penetration. The test indicates how well the sterilizer pulls air from the chamber to ensure effective steam sterilization.
• Type 3 – A Type 3 CI is designed to monitor exposure of a single critical variable, such as temperature or time. Unlike the Type 1 indicator, this type is intended to be placed inside the package to be sterilized. The CI reacts to the variable and undergoes a color change when the required level of exposure to that variable has been reached; however, it does not indicate time or steam quality or provide complete cycle verification.
• Type 4 – A Type 4 CI is an internal indicator designed to react to two or more critical process variables. These are often used for sterilization in clinic settings.
• Type 5 – This type of CI, an integrating indicator, reacts to all critical process variables for various
sterilization cycles. This is the most common CI for pack monitoring. Note: This indicator is found in most process challenge devices (PCDs); it is combined with a biological indicator (BI). With a passing BI, a steam load can be released for nonimplant and implant-related items.
• Type 6 – This type is also known as an emulating indicator. It is designed to react to all critical process variables for a specified sterilization cycle. These indicators are time-specific and should be used only with that cycle time in mind. For example, a 10-minute Type 6 CI can only be used on 10-minute cycles. What follows are general guidelines for proper CI use. Regardless of the CI type, proper use requires diligent adherence to the indicator manufacturer’s instructions for use (IFU). Even CIs that appear similar may have different processes or steps in the IFU. Before the products’ use, technicians must read and understand the IFU and recognize what the CI looks like before and after its use. If any questions or confusion about a CI or its IFU arise, the manufacturer should be contacted to provide clarification.
• External CIs – This indicator only indicates that the wrapped package, container, or peel pack has been exposed to a steam sterilization process and does not guarantee sterility. External indicators should
not be covered (i.e., do not place a label on top of sterilization tape).
• Internal CIs – Type 5 or Type 6 CIs provide more information about the critical parameters for sterilization; however, it is essential to remember that Type 5 indicators react to all critical parameters across a range of sterilization cycles, and Type 6 indicators react to all critical parameters for only specified cycles. Using a Type 6 for an incorrect cycle would be ineffective. For example, if using a Type 6 CI designed for a 10-minute cycle on a cycle that is only four minutes, the indicator will consider the cycle a failure because the 10-minute cycle requirement would not have been met. CIs should be placed in an area considered the least accessible to steam
REGISTRATION
penetration to help verify that steam has sufficient contact with items being sterilized. CIs should be placed in a location that allows the user to locate and see the results easily when the tray is opened. Always follow the CI’s IFU to ensure its correct and proper placement and never use tape or other adhesives to secure internal CIs to the inside of a package or tray. Multi-layer trays should have at least one indicator per layer. CIs in different layers might read differently. For example, the indicator on the top layer might have a color change all the way to the end, while another indicator two levels down may have just barely passed the “accept” line.
CONCLUSION
CIs are essential tools for monitoring
sterilization parameters and are integral to the tray-building process. Technicians must be knowledgeable about the different types of CIs and what they monitor. They must always follow the products’ IFU to ensure the indicators are placed correctly and their results are interpreted properly. This knowledge can be shared with end users who open the packages at the point of use.
– Tony Thurmond, CRCST, CIS, CHL, FCS, is a sterile processing manager at Dayton Children’s Hospital.
Source: Much of this information was summarized from ANSI/AAMI ST79: 2017/(R)2022 Comprehensive guide to steam sterilization and sterility assurance in health care facilities.
Join perioperative professionals throughout the Southeast for CE-accredited education, exhibits with leading vendors, and great networking events.

INDUSTRY INSIGHTS ACSA
Advocating for Better Patient Care
BY Bill Prentice
W ith the rising demand for outpatient procedures and the need for high-quality, costeffective care, ASCA’s advocacy efforts are critical in shaping policies, influencing regulations and ensuring that ASCs continue to thrive and provide essential services to millions of patients each year. We advocate to ensure surgery centers have the policy support, legislative protection and financial resources they need to operate effectively. We work with federal, state and local officials to protect the interests of surgery centers and their patients. Our primary advocacy focus areas are Medicare reimbursement and payment policies, Medicaid and private insurance, regulatory issues and oversight.
One of our key advocacy initiatives is the expansion of ASC services through changes in healthcare policy. ASCA works with lawmakers to expand the procedures that can be safely and effectively performed in an ASC setting, freeing up hospitals to focus on non-elective procedures and emergency cases. This includes advocating for the addition of more specialty surgical procedures to the ASC Covered Procedures List (ASC-CPL) and
expanding insurance coverage for outpatient surgeries.
As part of our advocacy efforts, we invite our members to lobby their members of congress through initiatives such as National Advocacy Day, facility tours and National Advocacy Month.
Fair Pay for Patients
ASCA advocates for policies that place patients’ needs first. Recently, we supported the introduction of the Medicare Beneficiary Co-Pay Fairness Act of 2025 (H.R. 3006/S.1776).
Representatives Mike Kelly (R-PA), Robert Menendez Jr. (D-NJ), Troy Balderson (R-OH) and John Larson (DCT) introduced the bill in the House in April, and Senators Richard Blumenthal (D-CT) and Bill Cassidy, MD (R-LA), introduced a Senate companion bill three weeks later in May. When passed, the legislation will reduce beneficiary costs by capping the maximum Medicare copayment for procedures performed in ASCs at the inpatient deductible.
In introducing the bill, Senator Cassidy said, “If your grandmother depended on Medicare for life-saving treatment, you would not want to hear that Medicare was cutting corners. This bill makes costs fairer for patients while keeping the quality of care high.”
In June, ASCA led a coalition of 48 leading healthcare organizations to send
a letter to congressional committees urging support for this bill. The letter was addressed to the relevant congressional committees of jurisdiction – the House Committees on Energy and Commerce and Ways & Means, and the Senate Committees on Finance and Health, Education, Labor & Pensions (HELP). The coalition includes organizations such as the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, the American Society of Anesthesiologists and the Medical Device Manufacturers Association. The support of these organizations shows the widespread appreciation for surgery centers and the services they provide. The absence of a limit on beneficiary coinsurance creates greater patient expense without justification, limiting their access to the high-quality, low-cost care that ASCs provide.
Medicare beneficiaries who receive treatment in either an ASC or hospital outpatient department (HOPD) are typically responsible for 20 percent of their cost of care. In HOPDs, this 20 percent copay is capped at the hospital inpatient deductible amount, which is $1,676 for 2025. In ASCs, however, there is no copay cap. As a result, Medicare patients treated in an ASC face higher copays for approximately 183 procedures.
Moreover, when the copay cap is applied in an HOPD, the hospital is

made whole, meaning that Medicare pays the hospital the difference between what 20 percent of the procedure would have yielded and the capped amount of $1,676. Since Medicare reimburses HOPDs significantly more than ASCs for virtually every procedure, current policy incentivizes beneficiaries to choose the higher-cost site of care, adding unnecessary costs to the Medicare program.
Surgery centers are the high-quality and cost-effective site of service for an ever-growing number of outpatient procedures. The current absence of a limit on Medicare beneficiary out-ofpocket costs in ASCs unintentionally drives patients to higher-cost care settings. The copay fairness act will allow beneficiaries to receive care in the ASC setting without paying more for the procedure.
Better Care for Seniors
A second piece of legislation that we backed recently is the Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act of 2025 (H.R.3514/S.1816), a bipartisan bill that will streamline the prior authorization process for Medicare Advantage (MA) beneficiaries. We joined a coalition of more than 235 organizations, 52 senators and 120 representatives to ensure the passage of this bill.
The prior authorization process
places a significant administrative burden on healthcare workers, forcing them to spend hours submitting requests in the form of detailed paperwork or electronic forms, following up if the initial request is denied or needs additional information, and appealing denials. In addition, audits by the Office of Inspector General at the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) have revealed that a significant percentage of initially denied requests are ultimately approved, and that MA plans have incorrectly denied access to services.
If passed, this legislation will establish an electronic prior authorization process for MA plans and, consequently, reduce paperwork burden on healthcare providers and give millions of seniors improved access to essential services. It also will increase transparency, clarify HHS’ authority to set time frames for e-prior authorization requests, expand beneficiary protections, and require HHS and other agencies to report to Congress on program integrity efforts. Best of all, this bill is projected to cost nothing to taxpayers.
Senators Roger Marshall, MD (R-KS), and Mark Warner (D-VA) reintroduced the legislation in May. Senator Marshall emphasized that “prior authorization is the number one administrative burden facing physicians today across all specialties.” Senator
Warner said that “our seniors deserve high-quality care delivered in a timely fashion.”
Representatives Mike Kelly (R-PA), Suzan DelBene (D-WA), John Joyce, MD (R-PA), and Ami Bera, MD (DCA), introduced a companion bill in the House also in May.
We believe that by reducing administrative burdens, this act will allow surgery centers to continue to provide high-quality, cost-effective surgical care and better advocate for their patients. In addition, it will ensure that the more than 32.8 million Americans enrolled in MA plans receive timely and appropriate care. This will result in a more efficient and accountable healthcare system.
More than 6,300 Medicare-certified ASCs currently operate in the U.S., performing a wide variety of outpatient procedures. Surgery centers represent a significant source of savings potential for both patients and payers because they can perform procedures with greater efficiency and at a lower cost than hospitals. According to an analysis from KNG Health Consulting, surgery centers are projected to reduce Medicare program costs by $73.4 billion from 2019 to 2028.
ASCA will continue to advocate for policies that place patients’ needs first while promoting innovation, transparency and efficiency throughout the healthcare continuum.
IN THE OR market analysis
UVC Market Could Triple in 10 Years
The UVC disinfection products market is projected to expand from $12.66 billion in 2025 to $39.64 billion by 2035, according to a report from Future Market Insights (an ESOMAR certified market research organization and a member of Greater New York Chamber of Commerce).
This growth is driven by heightened demand for effective pathogen control across healthcare, retail, and public sectors. North America leads the market, while South Asia & Pacific are expected to witness the fastest growth.
This substantial growth is driven by increasing global awareness of hygiene and infection control across healthcare, commercial, and residential sectors, bolstered by mounting concerns over airborne and surface pathogens intensified by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Regulatory endorsement plays a critical role in market confidence and adoption. The USA Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) have formally recognized UVC technology as an effective disinfection method, reinforcing safety and efficacy standards.
As reported in the 2024 International Ultraviolet Association (IUVA) report, adoption rates for UVC disinfection systems in hospitals and public transportation increased by over 30% between 2022 and 2024.
Asia Pacific market is projected to lead growth owing to rapid industrialization, expanding healthcare infrastructure, and stringent regulatory frameworks aimed at combating infectious diseases. For
example, China’s “Healthy China 2030” initiative includes targeted investments in advanced disinfection technologies, which have driven a 35% increase in UVC product adoption in hospitals between 2021 and 2024 (China National Health Commission, 2024).
North America and Europe continue steady growth, supported by heightened awareness of hospital-acquired infections (HAIs). The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported a 12% decline in HAIs in USA hospitals employing UVC disinfection protocols between 2020 and 2023, reinforcing adoption in healthcare facilities.
Technological innovations such as mercury-free and far-UVC lamps are enhancing safety and expanding application areas. A 2023 study published in Environmental Science & Technology demonstrated that far-UVC light effectively inactivates airborne viruses while being safe for human exposure, enabling use in occupied spaces such as schools and airports. Additionally, collaborations like the 2024 partnership between Philips and the Mayo Clinic have accelerated development of tailored UVC systems for critical care units, addressing specific microbial challenges.
The market for UVC disinfection robots alone is expected to reach a CAGR 14.6%. The rapid rise in these robot operators is following a growing increase in infection control measures at hospitals, airports, and public spaces. Top manufacturers, including Xenex, UVD Robots, and Tru-D SmartUVC, are optimizing their worldwide presence while hospitals in America and Europe have adopted the UVC robot to cut hospital-acquired infections (HAIs) by as
much as 30%.
UVC robotic solutions have also received significant government investment. China has deployed 5,000 in the medical field, and Los Angeles International Airport (LAX) and Singapore’s Changi Airport have added UVC disinfection robots to their settings to promote safer travel.
Hospitals & Medical Centers segment holds a dominating market share of UVC disinfection product market of 28.4% in 2025. This dominance is driven by the need to combat healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) that impact more than 1.7 million patients each year in the United States alone. With 99,000 deaths in the United States due to HAIs each year, UVC-based disinfection systems are being implemented to enhance infection control within the hospital.
Government initiatives and strict hygiene regulations are driving adoption. In addition to antibiotic-resistant bacteria responding positively to this method, both the CDC and EPA recommend UVC disinfection, leading top-tier hospitals like Mayo Clinic and Johns Hopkins Hospital to embrace UVC robots in their advanced ICUs and operating rooms.
Germany’s Robert Koch Institute supports UVC deployment in hospitals in Europe, and healthcare budgets have been directed in France and the UK to integrate UVC sanitization. China’s National Health Commission has implemented over 5,000 UVC robots across their medical institutions, while pilot programs in India with the support of the country’s Ministry of Health place UVC robots in over 300 hospitals to test their effectiveness in high-risk regions..
Surfacide
Helios+ UV-C System
Experience rapid and thorough microbial reduction with Surfacide’s latest UV-C technology, Helios+ UV-C System. Helios+ is an FDA Class II medical device for whole room microbial reduction using continuous 254 nm germicidal UV light and 3 emitters in a single cycle. Direct UV-C light eliminates harmful microorganisms while 3 UV-C emitters work together to minimize shadows and assure microbial reduction on vertical and horizontal surfaces. This patented multiple emitter approach requires no repositioning in patient or operating rooms, delivering speed, efficacy, and adaptability to healthcare facilities worldwide.
XENEX
LightStrike+

LightStrike+ is the first FDA authorized "whole room microbial reduction" UV medical device. Successful surgical procedures start with a clean operating room, and the LightStrike+ robot, powered by broad spectrum UV light, is proven to reduce the risk of pathogen transmission from contaminated OR surfaces to patients. It’s simple to use and provides fast cycle times (as short as 2 minutes for bacteria). Whether it’s the last step of terminal cleaning, after a dirty case, or between every case, LightStrike+ can help quickly reduce the number of pathogens on OR surfaces (including non-critical medical device surfaces) as part of a comprehensive disinfection strategy.

Akara UV Robot
The Akara UV Robot is a patented disinfection system developed from over a decade of research at one of Europe’s leading research universities. It is specifically designed to overcome three key limitations of conventional UV disinfection systems, making it uniquely suited for use in operating rooms and other safety critical healthcare settings. Second, Akara’s robot uses AI and digital twin technology to plan and verify disinfection. It simulates UV coverage in 3D, reduces missed areas due to shadowing, and confirms that all target surfaces receive sufficient dose, overcoming key limitations of existing systems. And finally, where existing systems must

be manually moved and closely managed by staff, Akara’s robot operates autonomously, disinfecting without supervision. This reduces dependence on human cleaning teams, shortens downtime between cases, and enables extended disinfection cycles after hours.



Hospitals don’t have time to wait for results. That’s why Surgical Solutions guarantees measurable OR improvements within 90 days. We’re not just advising from the sidelines. We’re in your OR, making it happen.
















The Newest OR TECHNOLOGY
By Don Sadler
COVER STORY
Technology is making major inroads in practically every industry today, including healthcare. Technological advances in operating rooms and ambulatory surgery centers are especially exciting.
Robotic surgical systems, hybrid operating rooms with real-time imaging, intraoperative image guidance, augmented reality (AR), the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT), OR Black Box recording, smart OR analytics and, of course, artificial intelligence (AI) are transforming ORs and ASCs into high-tech environments rivaling the most technologically advanced industries on the planet.
From Theoretical to Practical
According to orthopedic surgeon Evan D. Collins, MD, MBA, the innovator-inresidency for the Houston Methodist Center for Innovation, OR technology is moving from theoretical possibilities to practical probabilities.
“New technologies offer the potential to fundamentally change how patient care is delivered,” he says.
Collins lists artificial intelligence and ambient intelligence (AmI) as technologies that are being implemented across specialties to enhance the overall patient and provider experience.
“For example, we’re using AI to improve recognition of structures and tasks during an operation, which augments surgeon training,” he says.
“Other technology innovations are being deployed to improve OR efficiency and leverage better data processing technology to increase efficiencies and decrease waiting times for surgeries,” adds Collins.
By using AI, AmI and advanced systems to create more efficient, accurate and patient-centered processes, these technologies are addressing the growing demand for healthcare services while maintaining high quality patient care.
“However, we are steadfast in our view that AI and AmI function as a support system rather than a displacer,” says Collins. “For example, AI is excellent at processing large amounts of data and
recognizing patterns, but the nuanced understanding of a patient’s individual needs can only come from a human clinician.”
Smart Hospital Optimizes AI
Houston Methodist Cypress Hospital opened in March as a “smart hospital” designed with some of the most advanced perioperative technologies available. It was built to optimize AI and human workforces to deliver more efficient patient care and improved outcomes.
“Houston Methodist is a hospital system rooted in innovation,” says Collins.
The hospital’s smart ORs feature ambient intelligence cameras that capture information about how cases are progressing and notify post-op team members about progress. These automatic alerts mean PACU doesn’t have to call the OR to find out when patients are headed their way. Family members are also updated on the patient’s status.
“Since we first launched ambient intelligence cameras in our ORs, we’ve been able to identify bottlenecks, gain real time insights and establish a culture of continuous improvement,” says Collins. “In addition, the technology has helped physicians optimize their time across multiple patients. Its success stems from consistent, transparent use and its ability to provide accurate, objective data that can drive process improvements.”
OR turnover time has improved by 16% since the hospital started using the ambient cameras, which has led to more than 1,500 additional cases. The efficiency gains allowed one surgeon to add a third case.
Houston Methodist Cypress Hospital is piloting the ambient camera technology with Apella.
“The technology helps predict and optimize surgical turnaround times, gain real-time insights and improve efficiency and accountability,” says Collins.
In addition, the hospital has implemented two-way cameras in patient rooms and deployed remote patient monitoring such as the BioButton, which offers continuous surveillance and early detection of changes in patient conditions.
“The ‘smart hospital’ concept isn’t always about having the most technology,” says Collins. “Rather, it’s about creating an adaptable infrastructure that can evolve with technological advancements.”
AI is a Game Changer
Tammy Hanks, DNP, APRN, PCNS-BC, NEA-BC, EBP-C, CNOR, Perioperative Practice Specialist with the Association of periOperative Registered Nurses (AORN), believes it’s hard to pinpoint the most impactful new technologies because it depends on what is needed for a specific patient population or specialty and whether the organization has the required infrastructure to support the new technology.
“As we all know, AI is a game-changer for perioperative nursing and has the potential to improve workflows and efficiency when leveraged appropriately,” says Hanks. “I believe almost all organizations can implement AI in some way that is meaningful for their staff and patient population.”
Hanks believes it’s also exciting to see how organizations and leaders are using smart OR analytics for scheduling, staffing and block utilization. “The OR Black Box Recording is another new technology with great potential to impact patient safety,” she says.
The biggest benefit of new OR technologies is their ability to improve patient safety and outcomes. “This should really be the driving force and common goal behind any new technology,” says Hanks.
There’s also the obvious competitive advantage for hospitals that comes with having the latest and greatest technology.
“Patients have many options when choosing where to have surgery,” says Hanks. “It does make a difference when organizations can tout not only new technology, but also its impact on patient outcomes and satisfaction.”
For perioperative teams, new OR technologies can play a big role in improving workflow, documentation and communication of critical intraoperative information while providing data and platforms for team training, education and



clinical support.
“If organizations aren’t investing in new technology, they’re missing the opportunity to collect and leverage valuable data that can benefit the entire organization,” says Hanks.
Overcoming Staff Hesitation
Overcoming initial staff hesitation is a common challenge of implementing new OR technology.
“Hesitation may be due to fear of the unknown or a lack of confidence in their ability to master a new technology,” says Hanks. “Healthcare organizations and leaders are responsible for creating work environments where perioperative staff feel safe and trust that they are being heard and their concerns are being addressed.”
This includes listening to staff concerns and learning what hesitancies they have and why they are hesitant, which Hanks says is foundational to understanding how to promote change and the adoption of new technology.
“We need leaders who are committed to providing staff with comprehensive training and education on new technologies, verifying competency and identifying early adopters,” says Hanks. “We also need champions who can provide support to other staff members during the critical technology adoption time and clearly articulate how the new technology will positively impact staff and patients.”
Hanks believes that perioperative nurses
should be included on the interdisciplinary team that evaluates and decides what new technology the organization should invest in.
“Their expertise and experience are vital to ensuring successful implementation of new technology,” she says. “Not only are they able to speak to the impact new technology will have on patients and workflow, but they will be crucial to ensuring staff buy-in during implementation.”
Collins believes that staff hesitation to adopt new technology is actually helpful in the long run.
“It’s not a problem to overcome, but rather a healthy part of the process,” he says. “Skepticism forces innovators to validate and prove new technologies, which ultimately benefits both patients and providers.”
With some new OR technologies, such as robotic surgery and hybrid ORs, the most important factor isn’t necessarily the technology itself but rather the surgeon’s level of expertise. “Innovative technology and techniques aren’t automatically better – you have to factor in the surgeon’s skill and experience,” says Collins.
Integrated AR-assisted Surgery
Vangie Dennis, MSN, RN, CNOR, CMLSO, FAORN, Partner, Perioperative Consulting LLC, believes that one of the most impactful new technologies introduced to the OR recently is ARassisted surgery integrated with robotic platforms (e.g., da Vinci, Medtronic Hugo)
and AI-based navigation systems (e.g., Medivis, Stryker’s AR systems).
“AR integrates with patient-specific 3D anatomy from CT/MRI scans and is directed to allow the surgeon’s view in real time,” Dennis explains.

This improves localization of tumors, nerves and vasculature; decreases the risk of damaging critical structures; and allows for more precision cuts, resections and implant placements.
This technology also improves anatomical accuracy by overlaying 3D reconstructions of the patient’s anatomy directly onto their body during surgery.
“Surgeons can see tumors, vessels, nerves or bones in real time without making large incisions,” says Dennis. “This reduces the risk of damaging critical structures and improves surgical accuracy.”
In spine surgery, for example, AR guidance has been shown to reduce pedicle screw misplacement rates compared to traditional methods.
AR is also a minimally invasive approach that allows surgeons to use smaller, targeted incisions.
“This lowers the risk of infections, blood loss, post-op pain and complications like hernias and adhesions,” says Dennis. “Patients also typically recover faster with fewer complications.”
There are also fewer imaging requirements since AR platforms can minimize intraoperative radiation exposure by reducing reliance on fluoroscopy (real-time X-rays).
“For example, in orthopedic and spine
Evan D. Collins Houston Methodist Center
Tammy Hanks AORN
Vangie Dennis Perioperative Consulting LLC
COVER STORY
“
The ‘smart hospital’ concept isn’t always about having the most technology — it’s about creating an adaptable infrastructure that can evolve with technological advancements.
— Evan D. Collins, MD, MBA

surgeries, preoperative CTs are fused with AR systems, which limits the need for repeated scans,” says Dennis.
AR-assisted surgery also reduces human error and allows faster and more confident decision-making. “Real-time data and AIenhanced AR help surgeons quickly assess margins, angles or anomalies,” says Dennis.
The technology also enables immersive training for residents via simulation with real patient data, as well as remote assistance with specialists guiding surgeons in real-time via shared AR views. “This helps standardize care and improve outcomes in under-resourced settings,” says Dennis.
Using Robotics for TJRs
Last January, DISC Surgery Center in Newport Beach, California, introduced the use of a robotic arm to assist with total joint replacement (TJR) surgeries.
“Using robotic technology for total joint replacements has been going on for nearly a decade,” says OR Manager Justin Julian, who worked with OR nurse Christian Crothers to set up the technology. “We currently have two robots to assist with these procedures.”
According to Julian, using a robotic arm to assist with TJR surgery allows for improved accuracy of bone cuts and implant placement compared to traditional methods. “This is accomplished by taking a CT scan pre-operatively which
is then used in surgery to create a 3D model of the patient’s joint,” he explains.
“During surgery, the robotic arm provides real-time feedback to surgeons, guiding them within the pre-defined boundaries of the surgical plan,” says Julian.
Through June, DISC Surgery Center had performed 131 robotic-assisted total joint replacement surgeries in 2025. This was nearly as many TJR surgeries (140) as were performed in all of 2024.
Technology to Prevent Hypodermic Needlestick Injuries
When Karen D. Orr, PA-C/CEO suffered a needlestick injury a few years ago and the patient had known Hepatitis C, she wondered why there wasn’t a product on the market to keep healthcare workers safe when using hypodermic needles.
“The good Lord gave me an idea for a new product that became HypoHolder,” says Orr.
After about three years of development, HypoHolder came to market in April.
“At first I sat on the idea because I didn’t know anything about entrepreneurship,” says Orr. “But no one was doing anything to keep us safe from needlestick injuries, so I asked a couple of friends to help me develop the idea into a product.”
HypoHolder is a safety engineered medical device that secures a hypodermic needle, allowing healthcare workers
to uncap, recap and dispose of the hypodermic unit with just one hand.
“At least 70 percent of hypodermic needlestick injuries occur during these three tasks,” says Orr.
Product evaluations with hospitals and ASCs started in July.
“The reactions have been amazing!” says Orr. “There’s an audible gasp or exclamation during demos as soon as I uncap a hypodermic needle with just one hand.” A few common reactions she hears: ‘That’s amazing!’ ‘Shut up!’ ‘Are you kidding me?’
Orr says she and her team are on a mission to stop hypodermic needlestick and other sharps injuries, which are up 16% from a decade ago, according to AORN.
“Healthcare is hard right now, so we want healthcare workers to know there are people who care about and appreciate them and the care they provide,” she says.
Embracing Technological Innovation
In his role as the innovator-in-residency at Houston Methodist’s Center for Innovation, Collins says it has been exciting to embrace technological innovation while maintaining a laser focus on patient outcomes and high-quality patient care.
“I’m optimistic about the future of healthcare technology, especially in the OR setting,” he says.
OUT OF THE OR health

At Risk of High Cholesterol? Taking Fish Oil May Help
Athens, Ga. | Fish oil supplements are a multibillion dollar industry in the U.S. and abroad, with about two out of every 25 people popping the popular omega-3 pills.
And a new study from the University of Georgia might encourage a new population to start looking into the supplements as well: people with a genetic predisposition to high cholesterol.
Using genetic data from more than 441,000 participants, the researchers calculated a score to predict the genetic likelihood of high levels of total cholesterol, high LDL cholesterol (which is often referred to as “bad” cholesterol), triglycerides and HDL cholesterol (or “good” cholesterol).
“Recent advances in genetic studies have allowed us to predict someone’s genetic risk of high cholesterol,” said Yitang Sun, a recent doctoral graduate from UGA’s Department of Genetics. “But the current prediction has room for improvement because it does
not consider individual differences in lifestyles, such as taking fish oil supplements.”
The researchers found that participants who reported taking fish oil supplements have lower blood lipid levels than predicted, especially for total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol and triglycerides.
“Our study shows that considering lifestyles will improve genetic prediction,” said Kaixiong Ye, corresponding author of the study and an assistant professor of genetics in UGA’s Franklin College of Arts and Sciences. “Our findings also support that fish oil supplements may counteract the genetic predisposition to high cholesterol.”
It’s no secret that high cholesterol is bad for the body. Arteries start to harden, and the risk of heart attack or stroke increases.
While a healthy diet and exercise can help prevent it, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that more than 86 million American adults – or about one in four – have high
cholesterol.
Millions more are at risk of developing high cholesterol due to a variety of factors including one they can’t control: genetics.
For people whose families have a history of high cholesterol, the study’s findings offer another possibility to help safeguard their health.
“Taking fish oil is associated with a shift toward a healthy lipid profile,” Ye said.
The researchers also analyzed the effects of fish oil on HDL cholesterol and found the supplements are beneficial in raising the so-called “good” cholesterol.
– Published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, the study was led by Yitang Sun, a doctoral student in UGA’s Department of Genetics. Additional coauthors include Tryggvi McDonald, Abigail Baur, Huifang Xu and Naveen Brahman Bateman, of UGA’s Franklin College; Ye Shen of UGA’s College of Public Health; and Changwei Li, of Tulane University.

OUT OF THE OR fitness

Work Legs to Build Muscle
By Miguel J. Ortiz
L eg work or training is a big component in building muscle – even though its commonly neglected. Now, of course, we all have different goals. Let’s concentrate on general strength training. If your goal is to increase muscle, then you should increase your training regimen.
From a functional standpoint, training legs is ideal for many reasons. It assists in proper posture, picking up heavy household items and developing stronger core muscles. Let’s look at three ways to incorporate more leg exercises into your routine. This will make certain to keep body feeling good and fully functional.
First, doing cardio and calling that strength training legs won’t cut it. You need to incorporate strength routines. It doesn’t need to be a heavy weight, but there should a leg segment to every athlete’s program. So, please at least follow this one tip. Being able to perform the leg exercise movement without any weight is crucial for
keeping good form and preventing injury. It will also assist in providing better muscle memory which will be necessary if you decide to challenge yourself in the future. Having a good range of motion and understanding how exercises like squats, deadlifts, lunges and single leg step-ups impact the joints will help prevent pain and build lean muscle. Remember, form always comes first.
Second, build your strength endurance before trying to pack on weight with max strength. Doing exercises weighted (or not) up to 12-20 reps, or combining them with other leg exercises, will increase the muscle’s time under tension. The additional muscular utilization will help build lean muscle mass. And, since the legs are a large muscle group, you should never skip leg day. I work legs, in some fashion, at least twice per week in addition to cardio work. So, spread your routine out leaving at least 1-2 days between leg days. Maybe try working posterior one day and anterior the other, there are plenty of variations.
Third, make time for recovery.
This is huge and should not be taken lightly. Your recovery is extremely critical as tight muscles and joints will lead to muscular imbalances. It can lead to poor posture as well as more pain. And, if we’re getting a workout, we want a reward.
We want to look and feel better. Feeling worse isn’t in the plan, but it’s a part of the fitness journey. If you struggle with stretching, try massage, stretching classes, cryo therapy, yoga or Pilates. These are all great ways to balance out the body and keep pushing forward to crush goals. Recovery is necessary, so don’t leave it out of the playbook.
Have fun adding more leg routines into your weekly workouts and never skip leg day!
- Miguel J. Ortiz is a personal trainer in Atlanta, Georgia. He is a member of the National Personal Trainer Institute and a Certified Nutritional Consultant with more than a decade of professional experience. He can be found on Instagram at @migueljortiz.

OUT OF THE OR
EQ Factor

Hidden Roadblocks to Resolving Conflict
By Daniel Bobinski, Th.D.
Perhaps you’ve seen workplace conflicts continue unresolved. People stop talking, tension abounds and productivity plummets. In many cases, the real barrier to resolution isn’t the topic of the dispute, but something deeper. It's fear.
Don’t misunderstand. We need fear in our lives. It keeps us from stepping into traffic or swimming in dangerous waters. But the same emotion that protects us can also sabotage our efforts at resolving conflict. When people are afraid, they can dig in their heels, resisting even reasonable solutions.
To be better at resolving conflict,
it helps to minimize people’s fears. Therefore, it helps to know that five universal fears affect everyone. Let’s look at these common fears so we can work to minimize them.
The Five Universal Fears
Fear of criticism tops the list. Nobody likes being criticized, even if it's constructive. We know we need feedback to improve, but receiving suggestions for improvement can still sting.
Fear of failure runs equally deep. People do not want to look incompetent, so they'll often resist any discussion that shows how they were doing something wrong.
Fear of rejection taps into our
fundamental need to belong. Human beings are wired for connection, and the prospect of being cast out or losing relationships can be terrifying.
Fear of not getting what you want can even prevent people from engaging in conflict resolution. If someone believes the outcome won't meet their expectations, they might avoid participating in the process.
Fear of losing what you have keeps people protective and territorial. When people worry that resolving a conflict might cost them something valuable, they become resistant to participate.
These fears exist in everyone to varying degrees. In conflict resolution, the mistake most
people make is focusing solely on solving the problem while ignoring the emotional landscape. That can be like trying to perform abdominal surgery while a patient is still conscious. Patients aren’t eager to try it.
Making Fear Your Ally
The goal is not to eliminate these fears. The objective is to minimize fears to the point people feel safe enough to engage in honest problem-solving.
This is where emotional intelligence is crucial. Then, when you can help people feel heard and understood, their fear levels drop significantly. Instead of seeing conflict resolution as a threat, they can see it as an opportunity to improve their situation.
Bottom line, if we are involved in working to resolve a conflict, we should acknowledge that the conflict is probably uncomfortable for everyone involved. We need to allow people to express their concerns without judgment, because without people feeling heard, finding a solution will be difficult.
In other words, when we acknowledge that fears exist and work to minimize them, we often discover the actual problem is much easier to solve. I’ve found those who are most effective at conflict resolution aren't the ones who can argue the best case, they're the ones who can help people feel safe enough to let their guard down enough to work toward a solution.
SINGLE USE SOLUTIONS
Single-use, nonwoven garments and bedding are redefining protection, comfort, and efficiency across the continuum of care.
One Solution. Every Setting. Total Confidence.
• Superior infection control & comfort for high-stakes surgical environments

• Comprehensive protection for staff, patients, and bedding



— Daniel Bobinski, Th.D., is a best-selling author and a popular speaker at conferences and retreats. For more than 30 years he’s been working with teams and individuals (1:1 coaching) to help them achieve excellence. He was also teaching Emotional Intelligence since before it was a thing. Reach him by email at DanielBobinski@protonmail. com or 208-649-6400.






Unlock the Power of Foods That Help Prevent Disease
By Grace O
I n today’s fast-paced world, where health concerns like cancer, arthritis, and diabetes are on the rise, the adage "you are what you eat" has never been more relevant. “Diseasepreventing" foods – those that not only reduce the risk factors for chronic conditions but also help navigate existing health challenges – are important to put on your plate. There’s a wealth of research indicating that the foods you eat can make a significant difference in disease management.
Your diet isn’t just about fueling your body – it’s about protecting it. Here are some steps you can take to fight or prevent disease:
• Adopt a Healthy Dietary Pattern: The first step towards disease prevention is minimizing highly processed foods. Instead, focus on a sustainable, balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods. Remember, good health isn’t reliant on any one food but on a diverse range of foods with different beneficial properties.
• Create a Healthy Plate: Today’s healthy plate has evolved beyond
the USDA food pyramid. It consists of half fruits and vegetables, modest portions of high-fiber whole grains, lean proteins, and smaller quantities of healthy fats. This balanced approach supports overall wellbeing.
• Embrace a Plant-Based Diet: Journalist and author Michael Pollan offers simple advice: “Eat food. Not too much. Mostly plants.” A plantbased diet, which limits or excludes animal products, is proven to reduce inflammation in the body and lower the risk of chronic diseases.
• Explore the Mediterranean Diet: For those who prefer not to “diet,”
the Mediterranean approach offers a flavorful, adaptable option. Heavy on fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, this diet has been linked to a decreased incidence of chronic diseases.
• Consider the DASH Diet: Specifically designed for those with high blood pressure, the Dietary Approach to Stop Hypertension (DASH) focuses on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and low-fat dairy while reducing salt intake. This plan is effective in reducing blood pressure and promoting heart health.
TOP DISEASE-FIGHTING FOODS
No matter which dietary plan you choose, incorporating these diseasefighting foods can help minimize your risk of chronic diseases:
• Black Tea: Enhances circulation,
may lower triglycerides and bad cholesterol, and could even inhibit the rapid multiplication of cancer cells.
• Brown, Red or Black Rice: These high-fiber rice varieties contain cholesterol-lowering compounds and unique antioxidants that support digestive health and reduce chronic inflammation.
• Legumes: Beans, peas, and lentils are rich in plant-based, high-fiber protein, which can improve blood sugar levels and decrease the risk of diabetes, cardiovascular disease and some cancers.
• Leafy Greens: Collard greens, kale and Swiss chard are packed with fiber and antioxidants, reducing inflammation and supporting eye health.
• Olives and Extra Virgin Olive Oil: A great source of vitamin E and
Quesadillas can be high in fat and calories, but you can lighten them up by adding high-fiber protein and antioxidant-rich vegetables. Inspired by Loma Linda, California’s Blue Zone, this version uses spinach and beans for a hearty base, with spicy salsa for flavor. I top mine with Aztec Chipotle Salsa and Guacamole with Pomegranate Seeds.
Ingredients
• Olive oil spray to coat
• 4 (6-inch) corn tortillas
• 1 cup shredded cheese (Mexican blend or Jack), divided
• 1 cup vegetarian refried beans, divided
• 1 cup roughly chopped fresh spinach, divided
Procedure
1. Coat a skillet lightly with the spray and warm over medium heat. Place 1 tortilla in the pan.
2. Top with ¼ cup cheese, ½ cup refried beans, and ½ cup spinach.
3. Top the mixture with ¼ cup of additional cheese and another tortilla.
4. Press the top tortilla down lightly, then cook for 2–3 minutes on each side or until the quesadilla is golden brown and the cheese has melted.
5. Move the quesadilla to a cutting board and cut into quarters.
6. Repeat to make the remaining quesadilla. Serve hot with your choice of salsa and guacamole.
antioxidants, these foods protect against cancer-causing free radicals.
• Salmon: This fatty fish is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which support cognitive function and reduce inflammation, promoting heart health.
• Walnuts: High in phytonutrients, walnuts are anti-inflammatory and may help prevent chronic diseases like cardiovascular disease and certain cancers.
– Grace O is the creator of FoodTrients, a unique program for optimizing wellness and longevity. She is the author of three award-winning cookbooks. Her latest cookbook is Anti-Aging Dishes from Around the World. You can find more age-defying recipes at Foodtrients.com/recipes. Recipes and photos reprinted with permission of FoodTrients.com and Anti-Aging Dishes from Around the World by Grace O.

Blue Zone
Vegetable Quesadillas
Yields 2 quesadillas

Calling all Perioperative Nurses, Sterile Processing Professionals, and Surgical Technologists
JOIN
US
FOR education, networking, product demonstrations, and more!
OCTOBER 11-12, 2025
Omni New Haven at Yale
EARN OVER 6.5+ CEs!

NEW AGENDA!
SATURDAY, OCTOBER 11
7 am
8-11:45 am
12-1:30 pm 2-3 pm 3-6 pm
Registration Opens
Education
Lunch & Learn
Education
Exhibit Hall Grand Opening
SUNDAY, OCTOBER 12
6:45 am 6:45 am 7:45-8:45 am 9-10 am 10 am-12 pm 12:30 pm
Registration Opens
Continental Breakfast
Education
Closing Keynote
Exhibit Hall (Brunch w/vendors)
Closing Remarks

2025 Periop Connect is approved for over 6.5 CE credits from the California Board of Registered Nursing.
The 2025 Periop Connect conference has been approved for 6.5 CE by the Healthcare Sterile Processing Association (HSPA).
The 2025 Periop Connect conference has been approved for 9.75 Contact Hours by the Certification Board for Sterile Processing and Distribution (CBSPD).

Periop Connect is approved for 6.5 CE credits by the Association of Surgical Technologists, Inc. for continuing education for the Certified Surgical Technologist, Certified Surgical First Assistant, and Associate members of AST. This recognition does not imply that AST approves or endorses any product or products that are included in presentations.

