6 minute read
General
4.2. Wheels and tires
General
Alignment wheels
The design of cars is the most important development of safe systems, steering and suspension. Each component must be strong enough to withstand and absorb the load limiting steering control, and front and rear suspension should operate geometrically with the body of the car. Steering system and suspension requires that the front wheels were self-returning, and to grip the rotating wheel and the road surface guarantees low driving force with the least effort and the greatest comfort. Full check of installation angles of the wheels should include measurement of convergence and collapse of the rear wheels. Adjustable mounting angles of the four wheels ensures that all wheels will roll strictly in one direction. When adjusted adjusting the angles of the wheels, saving fuel consumption and resource path reaches its maximum value, improves handling.
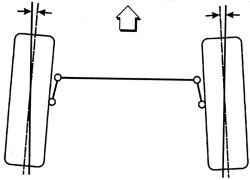
Convergence
Fig. 4.14. Scheme of convergence (wheels are installed inside forward)
Convergence is turning the wheels inside, opposite toe-wheels - wheels that turn outward from the center line. Convergence of the wheels provides parallel planes of rotation of the wheels.
Convergence is used to neutralize the small deviations of the wheel, taking place when the vehicle is moving forward. Installed the angle of convergence - the ability to install that angle at which the 0 ° between the planes of rotation of the front wheels and the center line of a moving car (no convergence). Incorrect toe or toe back wheel leads to premature tire wear and increase fuel consumption. Individual components of steering and suspension wear, depending on the mileage, an additional toe necessary to equalize wear. Always adjust the angle of convergence in the least.
The angle of inclination of the axis of kingpin
Angle of inclination of the axis of the hinge pivot is the highest point of the axis of the kingpin forward or backward from the vertical at the sight of the car on the side. Tilt back and forth is a positive - negative. The angle of inclination of the axis of kingpin affect the control of the direction of steering control, but does not affect tire wear. Weak (with a draft of) a spring or an overloaded vehicle affect the angle of inclination of the axis of kingpin. One wheel with a large positive slope of the axis of kingpin pulled to the center of the car. This causes a movement or tilt the vehicle towards the wheel with a smaller positive angle of inclination of the axis of kingpin. Angle is measured in degrees, but not regulated.
Collapse
The collapse of the wheels is the angle between the longitudinal axis of the wheels and the vertical to the plane of the road.
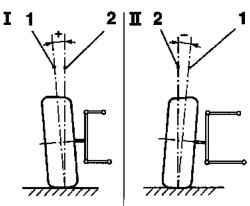
The collapse of the wheels - positive (I), if the center line wheel is tilted outward from the vertical line. The collapse of the wheels - a negative (II), if the center line wheel is tilted inward relative to the vertical line.
To achieve high lateral forces and, consequently, better handling when driving in turn, modern cars are usually designed with a negative camber.
Effect of irregular angles of the wheels
The collapse of the wheels, too big (negative value): - An improved lateral control when driving in the turn; - At high speed and high axle load, invalid shoulder heating zones tires; - Damage to the tire overheating; - Premature wear on the internal bus. The collapse of the wheels are too small (positive value): - Deterioration of transverse controllability of the motion in the rotation; - Increased wear on the outside of the tires (only if the simultaneous convergence of the improper adjustment of the wheels).
Angle of the longitudinal axis of rotation of the wheels
Fig. 4.16. Angle of the longitudinal
axis of rotation of the wheels: 1 the angle between the line passing through the axis of the kingpin, 2 direction of the axis of symmetry
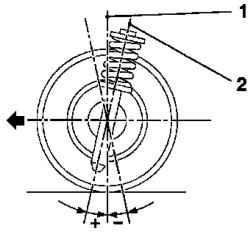
Angle to the longitudinal axis of rotation of the wheels is the angle between the line passing through the axis of the kingpin in the direction of the axis of symmetry, and the vertical to the road, passing through the center of the wheel.
Angle of the longitudinal axis of rotation of the wheels is negative if the point of intersection of this imaginary line to the plane of the road - the rear wheel contact point. Angle of the longitudinal axis of rotation of the wheels - yes, if - before the point of contact with the plane of the road wheels. A positive angle to the longitudinal axis of rotation of the wheels creates a force on the wheels, which helps to bring the wheels in position rectilinear motion after passing the bend.
Effect of irregular angles of the wheels
Angle of the longitudinal axis of rotation of the wheels are too negative: - Incomplete return of the steering in the initial position;
- Susceptibility to defects in the tires (taper, corner effect); - May cause distortion; - Beat wheel; - Sensitivity to lateral wind. Angle of the longitudinal axis of rotation of the wheels too positive: - Increased effort on the steering wheel and the effort to keep the car. Angle of inclination of the longitudinal axis of rotation of the wheels on the left differs from the angle of inclination of the longitudinal axis of rotation of the wheels on the right: - Susceptibility to distortion.
Caster
Caster is the angle between the center line of the kingpin and the vertical to the road crossing the axis of symmetry.
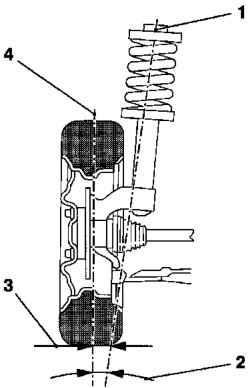
Fig. 4.17. Caster: 1 - center line of
the kingpin, 2 - angle; 3 - horizontal displacement, 4 - vertical road
Caster - positive (the normal situation), if the center line of the kingpin is directed inwards to the top of the vertical line.
Positive caster wheels provide a return to the position of the rectilinear motion after cornering and prevents "self-oscillation" wheels.
Effect of irregular angles of the wheels
Caster is too small: - Incomplete return of the steering in the initial position; - Susceptibility to defects in the tires (taper, corner effect); - May cause distortion. Too much caster: - Increased effort on the steering wheel and the effort to keep the car. Caster on the left differs from the caster on the right - Susceptibility to distortion.
Maximum angle of rotation from stop to stop (angle)
The maximum angle of the front wheels is the angle through which the wheels are turning (left and right) about the axis of symmetry. It defines the circle of rotation of the car.
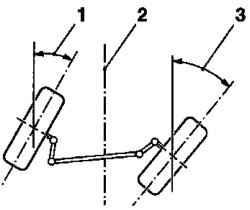
Fig. 4.18. Maximum angle of
rotation from stop to stop (the angle of rotation): 1, 3 - angle of the front wheels, 2 - axis of symmetry
Maximum angle of the front wheels is manifested as distinct angles of convergence on the left and right, and also gives information about the state of the steering linkage and steering mechanism.
Because the regulation of the maximum angle the front wheels are usually available only in vehicles off-road, it should be checked only on the cars of this type. Maximum angle of the front wheels is measured at full lock when turning the inner wheel. Depending on the steering linkage, external rotation with the wheel should have the same negative difference, within a specified tolerance.
Sample
Maximum angle of the front wheels on the right: 34 °. Angle lock, left: 32 ° ± 1 °. Difference: 2 °. Tolerance: ± 1 °.
Effect of irregular angles of the wheels
Difference of the circle of rotation of the vehicle (with the right and left turn).
Identification of the wheel and tire Wheels
Fig. 4.19. Identification marking
discs
Code may be present in full or in abbreviated form. For example: 6 J 16.










