AUFSATZ
Sebastian Latz, Frank Scholzen, Andreas Thewes, Stefan Maas
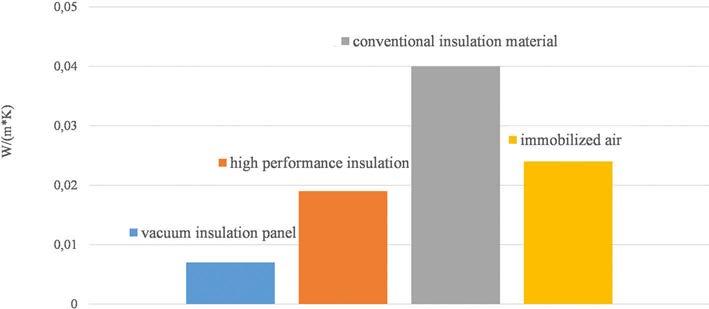
Comparison of high-performance and conventional internal insulation materials based on hygrothermal analysis using in situ measurements and simulation Following the European directive to reduce CO2 emissions of existing buildings by improving energy efficiency, internal insulation systems play a central role in the renovation of historically valuable buildings which cannot be insulated from the outside for reasons of monumental protection, or in cases where no additional exterior space is available. However, besides the thermal property of insulation systems, there are other relevant properties to be considered before choosing an internal insulation system, such as the hygrothermal behavior which plays a particularly important role in diffusion-open interior insulation systems. As the internal insulation layer reduces the temperature of the existing wall during the heating season, its drying potential after rain events is considerably reduced. In addition to the effects of moisture from the outside (mainly wind driven rain), the entry of humidity from the inside through diffusion plays an important role. In the presented study, high performance insulation materials with nanostructure based on silicon dioxide and polyurethane are compared to conventional material based on wood fiber from a hygrothermal point of view by analyzing in situ measurements and simulations.
Vergleich von Hochleistungsdämmstoffen mit einem konventionellen Innendämmstoff auf der Grundlage einer hygrothermischen Analyse mit In-situ-Messungen und Simulation Im Zuge der europäischen Richtlinien zur Senkung der CO2Emissionen bestehender Gebäude durch Verbesserung der Energieeffizienz spielen Innendämmsysteme eine zentrale Rolle bei der Sanierung historisch wertvoller Gebäude, die aus Gründen des Denkmalschutzes nicht von außen gedämmt werden können, oder in Fällen, in denen keine zusätzlichen Außen flächen zur Verfügung stehen. Neben der wärmetechnischen Eigenschaft von Dämmsystemen gibt es jedoch noch weitere relevante Eigenschaften, die bei der Auswahl eines Innendämmsystems zu berücksichtigen sind, wie z. B. das hygrothermische Verhalten, das insbesondere bei diffusionsoffenen Innendämmsystemen eine wichtige Rolle spielt. Da die Innendämmschicht die Temperatur der bestehenden Wand während der Heizperiode absenkt, wird ihr Trocknungspotenzial nach Regenereignissen erheblich reduziert. Neben den Feuchteeinflüssen von außen (vor allem durch Schlagregen) spielt auch der Feuchteeintrag von innen durch Diffusion eine wichtige Rolle. In der vorgestellten Untersuchung wurden Hochleistungsdämmstoffe mit Nanostruktur auf Basis von Siliziumdioxid und Polyurethan mit einem konventionellen Dämmmaterial auf Basis von Holzfasern aus hygrothermischer Sicht verglichen, indem In-situ-Messungen und Simulationen analysiert wurden.
Keywords internal insulation; hygrothermal in situ measurements; hygrothermal simulation; high performance insulation
Stichworte Innendämmung; hygrothermische In-situ-Messungen, hygrothermische Simulation; Hochleistungsdämmstoffe
1
potential of the insulation materials technically and to find a well-suited product for the renovation of Luxembourg’s historic public buildings. Since it is not always possible or desired to insulate the façade from outside, interior insulation plays an important role.
Introduction
In the context of climate change, society is looking for ways to reduce its CO2 emissions. Although very strict EU energy efficiency directives for new buildings have been put in place for about two decades, the building sector is still responsible for a major part of around 40 % of the total energy consumption [1]. In Luxembourg, more than 80 % of final energy consumption per dwelling was used for space heating in 2016 [2]. Nevertheless, the energy consumption of existing buildings can be considerably reduced by retrofitting, e.g., with insulation systems. In order to achieve the EU’s 2050 emission reduction targets in the building sector, it is urgently necessary to renovate existing buildings to make them more energy efficient. For this reason, the Luxembourg Public Buildings Administration in cooperation with the University of Luxembourg launched a field test. The aim is to evaluate the
AUFSATZ ARTICLE
DOI: 10.1002/bapi.202100039
In addition to the thermal property of internal insulation systems, there are other relevant properties to be considered before choosing an internal insulation system, such as the hygrothermal behaviour. Because internal insulation of the external walls increases moisture performance challenges with risk of condensation on the cold side [3], frost damage, interstitial condensation and others [4]. The temperature drop in the insulation causes the masonry to cool down considerably during the heating period, resulting in a diffusion flow from the humid indoor air into the masonry. There are two approaches to control this problem: a diffusion-open insulation versus a diffusion-tight
© 2022 Ernst & Sohn Verlag für Architektur und technische Wissenschaften GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin. Bauphysik 44 (2022), Heft 1 9
00_BAPI_0122_Buch.indb 9
19.01.22 09:32