What Are the Main International Large-Scale Student Assessments?
97
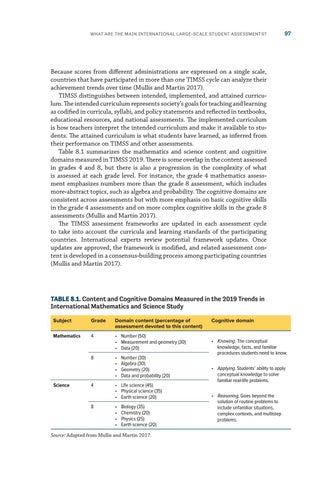
Because scores from different administrations are expressed on a single scale, countries that have participated in more than one TIMSS cycle can analyze their achievement trends over time (Mullis and Martin 2017). TIMSS distinguishes between intended, implemented, and attained curriculum. The intended curriculum represents society’s goals for teaching and learning as codified in curricula, syllabi, and policy statements and reflected in textbooks, educational resources, and national assessments. The implemented curriculum is how teachers interpret the intended curriculum and make it available to students. The attained curriculum is what students have learned, as inferred from their performance on TIMSS and other assessments. Table 8.1 summarizes the mathematics and science content and cognitive domains measured in TIMSS 2019. There is some overlap in the content assessed in grades 4 and 8, but there is also a progression in the complexity of what is assessed at each grade level. For instance, the grade 4 mathematics assessment emphasizes numbers more than the grade 8 assessment, which includes more-abstract topics, such as algebra and probability. The cognitive domains are consistent across assessments but with more emphasis on basic cognitive skills in the grade 4 assessments and on more complex cognitive skills in the grade 8 assessments (Mullis and Martin 2017). The TIMSS assessment frameworks are updated in each assessment cycle to take into account the curricula and learning standards of the participating countries. International experts review potential framework updates. Once updates are approved, the framework is modified, and related assessment content is developed in a consensus-building process among participating countries (Mullis and Martin 2017).
TABLE 8.1. Content and Cognitive Domains Measured in the 2019 Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study Subject
Grade
Domain content (percentage of assessment devoted to this content)
Mathematics
4
• Number (50) • Measurement and geometry (30) • Data (20)
8
• • • •
Science
4
8
Number (30) Algebra (30) Geometry (20) Data and probability (20)
• Life science (45) • Physical science (35) • Earth science (20) • • • •
Biology (35) Chemistry (20) Physics (25) Earth science (20)
Source: Adapted from Mullis and Martin 2017.
Cognitive domain
• Knowing. The conceptual knowledge, facts, and familiar procedures students need to know. • Applying. Students’ ability to apply conceptual knowledge to solve familiar real-life problems. • Reasoning. Goes beyond the solution of routine problems to include unfamiliar situations, complex contexts, and multistep problems.