
When to Visit a Specialist for Jaundice Management
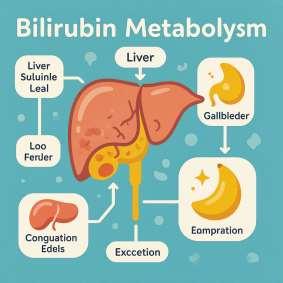
Jaundice Basics
• Jaundice is yellowing of skin and eyes from elevated bilirubin.
• It reflects an imbalance in bilirubin production, processing, or excretion.
• Common in newborns; in older children/adults it often signals an underlying condition.

Red Flags: Seek Urgent Care

• Sudden or rapidly worsening yellowing with fever or severe abdominal pain.
• Confusion, excessive sleepiness, or severe weakness.
• Dark urine with pale/white stools or persistent vomiting.
• Newborn jaundice in the first 24 hours of life.

Infants & Children: When to See a Specialist

• Jaundice in first 24 hours, or lasting beyond 2 weeks (breastfed) or 1 week (formula-fed).
• Poor feeding, lethargy, high-pitched cry, arching, or dehydration.
• Prematurity, G6PD deficiency risk, blood group incompatibility, or rapid bilirubin rise.
• For timely care in Hisar, consult Sarvesh Health City — Best Pediatric Hospital in Hisar.

Adults: When to See a Specialist

• Painless jaundice, weight loss, itching, or pale stools (possible bile duct obstruction).
• Jaundice with fever or right-upper-quadrant pain (possible infection).
• Recent new medications, herbal supplements, or significant alcohol use.
• Recent travel, hepatitis exposure, or known liver disease.
Key Diagnostic Tests
• Serum bilirubin (total/direct), liver function tests (ALT, AST, ALP, GGT), and albumin.
• CBC, reticulocyte count, Coombs test (hemolysis workup).
• Viral hepatitis panel; consider autoimmune markers when indicated.
• Ultrasound first-line imaging; MRCP/HIDA/CT as needed; newborn transcutaneous bilirubin.


Who Manages Jaundice?
• Pediatrician/Neonatologist: newborn and child jaundice evaluation and treatment.
• Gastroenterologist/Hepatologist: adult and complex liver/biliary disorders.
• Hematologist: hemolysis or red cell disorders causing jaundice.
• Your primary physician coordinates referrals to the right specialist.

Treatment Pathways
• Newborns: feeding support, phototherapy; IVIG/exchange transfusion for severe hemolysis.
• Obstructive causes: ERCP or surgery to relieve bile duct blockage.
• Infectious/autoimmune: antivirals/antibiotics or immunosuppression as indicated.
• Medication-induced: stop offending drug; supportive liver care and monitoring. Expert pediatric and neonatal jaundice management — Best Pediatric Hospital in Hisar.

Care at Sarvesh Health City
• 24/7 labs, ultrasound, and phototherapy; multidisciplinary liver and GI care.
• Family-centered counseling, follow-up plans, and prevention guidance.
• Contact Sarvesh Health City to schedule an evaluation or second opinion.



