Understanding Sleep Apnea: How Pulmonologist Diagnose and Treat It
What is Sleep Apnea?
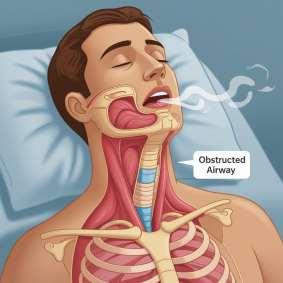
• A common sleep disorder characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep.
• These interruptions, called apneas or hypopneas, can last for seconds to minutes and occur many times an hour.
• Leads to reduced oxygen levels and fragmented, poor-quality sleep.
Types of Sleep Apnea
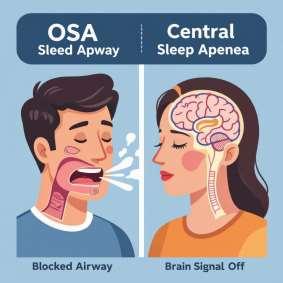
• Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): The most common form, caused by a physical blockage of the airway, usually when the throat muscles relax.
• Central Sleep Apnea (CSA): Occurs when the brain fails to send proper signals to the muscles that control breathing.
• Complex Sleep Apnea (or Treatment-Emergent Central Sleep Apnea): A combination of OSA and CSA.
Recognizing the Symptoms
• Loud, chronic snoring
• Episodes of breathing cessation during sleep, witnessed by others
• Abrupt awakenings accompanied by choking or gasping
• Excessive daytime sleepiness (hypersomnia)
• Morning headaches
• Difficulty concentrating and memory problems
Diagnosis: The Pulmonologist's Role
• Pulmonologists are specialists in respiratory and sleep disorders.
• They begin with a thorough medical history and physical examination.
• Discussion of symptoms, sleep patterns, and lifestyle factors.
• Assessment of risk factors like obesity, age, and certain medical conditions.
• Referral for diagnostic sleep studies.
The Gold Standard: Sleep Studies
• Polysomnography (PSG) is the most comprehensive sleep study.
• Monitors brain waves, eye movements, muscle activity, heart rate, blood oxygen levels, and breathing patterns.
• Can be performed in a sleep lab or, in some cases, at home (home sleep apnea test - HSAT).
• Results help determine the severity and type of sleep apnea (e.g., Apnea-Hypopnea Index - AHI).
Treatment: Lifestyle Modifications
• Weight loss: Losing even a small amount of weight can significantly improve OSA symptoms.
• Positional therapy: Avoiding sleeping on your back can help keep the airway open.
• Avoiding alcohol and sedatives: These can relax throat muscles and worsen apnea.
• Smoking cessation: Smoking can increase inflammation and fluid in the upper airway.
Treatment: Medical Interventions
• CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure): The most common and effective treatment. A machine delivers pressurized air through a mask to keep the airway open.
• APAP (Auto-adjusting Positive Airway Pressure): Adjusts pressure levels automatically based on breathing.
• BiPAP (Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure): Delivers different pressures for inhalation and exhalation, often for more severe cases or those who can't tolerate CPAP.
• Oral Appliances: Custom-fitted mouthguards that reposition the jaw and tongue to keep the airway open. Consult Best Pulmonology Treatment Hospital in Hisar.
Partner with Experts for Better Sleep
• Don't let sleep apnea impact your health, relationships, or daily life.
• Sarvesh Health city provides comprehensive diagnosis and personalized treatment plans for sleep disorders.
• We are dedicated to helping you achieve restful sleep and a healthier life.
• Your Best Pulmonology Treatment Hospital in Hisar.