Understanding
Angiography: How This Test Saves Lives
What is Angiography?
• A medical imaging technique used to visualize the inside of blood vessels.
• It helps detect blockages, narrowing, or abnormalities in arteries and veins.
• Crucial for diagnosing and planning treatment for cardiovascular diseases.

Why is Angiography Important?

• Enables early detection of life-threatening conditions like heart attacks and strokes.
• Provides detailed anatomical information about blood flow and vessel health.
• Essential for guiding interventional procedures and surgical planning.
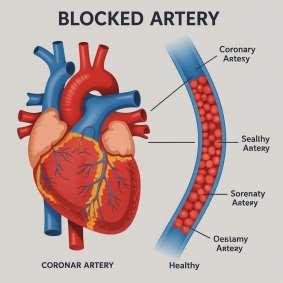
When is Angiography Recommended?

• Symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) such as chest pain (angina).
• Suspected heart attack or recent cardiac event.
• Congenital heart defects.
• Blood clots or blockages in arteries of limbs, brain, or kidneys.

The Angiography Procedure Explained

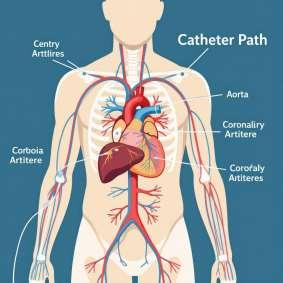
• A thin, flexible tube (catheter) is inserted into a blood vessel, usually in the groin or arm.
• The catheter is carefully guided to the area of interest (e.g., the heart's arteries).
• A special dye (contrast agent) is injected through the catheter.
• X-ray images are taken to visualize the blood vessels in detail.
Key Types of Angiography
• Coronary Angiography: Visualizes the arteries supplying blood to the heart muscle.
• Cerebral Angiography: Examines blood vessels in the brain for issues like aneurysms or blockages.
• Peripheral Angiography: Assesses blood flow in the arteries of the limbs, kidneys, and other body parts.