CHAPTER 6:
ht
pr ot
ec
te
d
Egg transport and storage
rig
Hatching eggs are transported all over the world. During this process, hatching eggs are sometimes repacked several times. This causes undesirable movements and fluctuations in the climate conditions.
co
hatching eggs.
py
Temperature fluctuations, condensation, jolts and vibrations significantly reduce the quality of
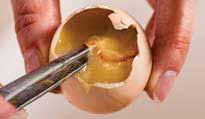
This chick has an extra leg. This may have been caused by jolts and vibrations (e.g. a faulty automatic turner). This is a particular risk during the embryonic cell differentiation stage: from the moment the fertilised egg is in the hen’s body until the first few days in the incubator.
76
When a hen lays a hatching egg, it already contains a tiny embryo, consisting of around 40,000 cells. The first stages of organ development have already taken place: the embryo is in a dormant state. During storage, the goal is to maintain the resting phase of the embryo. Avoid temperature fluctuations during storage. After storage, the embryo temperature is brought back above physiological zero to the incubation temperature. This is a temperature range in which the embryo is warmed up gradually in 6-24 hours. Completing this process any faster or slower is not advisable, as it causes too much disruption to embryonic development. Uniform temperature increases for all eggs is more important by that time.
Ha tc he ry S i gnal s