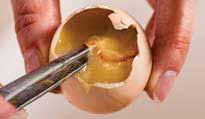
Hatching egg quality
Embryo The egg must contain a good quality embryo that is ring-shaped and 4-5 mm in diameter (doughnut shape).
The quality of the fertile hatching eggs largely determines the hatching results. A number of quality criteria determine what a good hatching egg is: shape, weight, shell, yolk, embryo and hygiene.
Eggshell The shell must not be cracked, ridged or dirty. These eggs lose too much weight and dry out or break during transfer. The shell must be sufficiently thick, perfectly shaped, clean, smooth and undamaged. Avoid scraping or sanding the eggshell surface to remove dirt. This will only make the problem worse.
ec
te
d
Yolk The yolk should have a uniform colour. In addition, the yolk should also contain sufficient nutrients, vitamins and antibodies (through vaccinations, immunity and parent stock health status). Air cell The air cell must be stable and located at the blunt end of the egg.
rig
ht
Shape A good hatching egg is round with a length-width ratio based on the Phi ratio (golden ratio) of 1:1.309 (shape index 100 * width/length = 0.76). A distinct point is especially important for correct placement in the setter trays. Wrong point setting leads to up to 30% lower hatchability and very weak chicks compared to those from correctly positioned eggs. The embryos do not survive in-ovo vaccination. The shape depends on breed, climate conditions and age of the parents (young parent stock around 74%, older parent stock often a bit rounder: 76%). Look at the information from the breeding organisation.
pr ot
Weight The optimal weight of a hatching egg is 50-70 grams, depending on the breed and parent stock age. Older hens lay heavier eggs which are more difficult to hatch.
Geometry of the egg
py
= 2Φ 2+√2 Φ = 1+√2
co
1
Φ
Φ3
Φ Φ
Double-yolk eggs will not hatch. Remove them. This is what an egg with a double yolk looks like under a candling lamp. Two dark spots are visible. These are the two yolks.
Example of type, parent stock age and hatchability Type of bird 1 +
1=
=Φ
2Φ 2+√2
2Φ
The shape index is the width divided by the length of an egg. 99% of eggs have a shape index between 0.69 and 0.85. A low shape index signifies an elongated egg, a high shape index is a rounder egg. In the picture the mathematical calculation is based on the golden ratio (Phi = Φ = (1+√5)/2 = 1.618). The shape index will then be 2Φ/Φ3.
4. E gg h a n d l i n g a n d q u al i ty
Parent stock age
Hatchability set eggs
Average egg weight
Broiler young
24 weeks
70%
51 g
Broiler peak
34 weeks
90%
61 g
Broiler old
60 weeks
70%
70 g
Laying hens young
24 weeks
90%
54 g
Laying hens peak
26-80 weeks
95%
62 g
60 weeks
93%
65 g
Laying hens old
Eggs from broiler parent stock have much greater variation in hatchability during production than those from laying hen parent stock.
49