Infertile eggs, bangers, late mortalities, and living embryos You can establish which eggs contain dead embryos up to day 7 with lamp candling. After that time, the embryo will have grown and light is no longer able to shine through as well. This depends on the candling machine settings. With the heartbeat method, you can determine which eggs contain dead or live embryos at the time of transfer. Combining different candling techniques gives you an accurate impression of various groups of eggs that you want to exclude from transfer. You can then handle them differently.
The display on the candling unit shows which eggs are infertile (blue), and which have mortalities (red). The remaining eggs contain a living embryo.
d
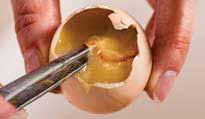
Infertile or an early mortality?
py
rig
ht
pr ot
ec
te
How can you recognise truly infertile eggs when candling on day 10 or 18? How can you detect unhatched eggs (embryos that died after day 18 or live chicks that failed to hatch)?
co
It is easy to recognise a truly infertile egg on day 18. The yolk and albumen have aged; the egg has been stored at a higher temperature in the incubator for 18 days. The yolk is still dark yellow but it has a thinner membrane, which causes the yolk to form a flat disc or break when opening the egg. The albumen has become watery, and the thick (chalaziferous) albumen has disappeared. You can still recognise a small white dot on the yolk.
Method
Light
If the embryo died before the blood ring stage, there will be clearly recognisable colour changes in the yolk. Formation of sub-embryonic fluid causes the water content of the albumen to pass through the embryo and into the yolk, this changes its colour to light-yellow. The yolk always breaks after 18 days of incubation: in this case, the yolk membrane has become very fragile. Sometimes you can still see extra-embryonic membranes in the broken yolk: a sign that the embryo was there but not really viable.
Heartbeat
Infrared
This is how it looks
How does it work?
116
Strong light does not penetrate through the embryo, and it produces a certain image. A dead embryo produces a different illuminated image.
This method detects the embryo’s blood circulation and the oxygen content of the blood. A dead embryo has no circulation of oxygen-rich blood.
The embryo’s heat production is detected. A dead embryo does not produce any heat.
Ha tc he ry S i gnal s