



www.passivefiresafeindia.com india’s FiRsT magazine on passive FiRe... LaUnCHing ediTion... March-April 2023 Vol.1 No.1 Rs. 200/- Pages: 36
TRANSFORM YOUR ORDINARY DOORS TO HIGH-PERFORMANCE FIRE RESISTANT DOORS
Tested by: Building Fire Research Centre (BFRC) - Mysuru (Accredited by NABL & Recognized by BIS) As per IS 3614:1992 (Part-II)

CBRI - Roorkee
As per BS:476 (Part 20 & 22)-1987, IS 3614(Part-2)-1992
• Fire Resistant Doors (Metal)
• Acoustic Resistant Doors (Metal)
• Armored / Bullet Resistant Doors
• Water Tight Doors
• Strong Room Doors
• Clean Room Doors
• Rolling Shutters (Fire / Non Fire Resistant)
• Blast Resistant Doors

• Radiation Shielding Doors (Wood)
• Insulated Door
• Air Tight Doors
• Security Doors
• General Purpose / HMPS Doors
• Automated Entrance Gates
SWITCH TO RADIANT PASSIVE FIRE PROTECT SYSTEMS, TODAY !




Member of:
Contact Person: Mitesh Chokshi +91 98793 17938 | 93274 30813
Email: mdchokshi@yahoo.co.in | mit.safety@gmail.com
Stembridge Taylor +91 93740 66913
Email: perfectdoors@gmail.com
Address: Plot No. 17 Jagganath Industrial Park Nr. Naklank Mahadev, Dholka Road, Paldi-kankaj Gam, Ta. Daskroi, Dist. Ahmedabad. Gujarat
Contact Details:
Ph.: 9374066913 | 9327430813 | 8905166913
Email: marketing@radiantpassive.com | radiantpassive@gmail.com
Website: www.radiantpassive.com | www.perfectdoors.in | www.mitrasafety.com
Ou R MAN u FACT u RIN g ACTIVITIES W h IC h COMPRISE OF T h E FOLLOWIN g:

















| 3 March - April 2023 | www passivefiresafeindia.com 100% COMMITMENT TO QUALITY Works : Works - B -133, Mayapuri Industrial Area, Phase -1, New Delhi - 110064 : 9891139441 : www.sehgaldoor.com : sale@sehgaldoors.com Scientific Doors Decorative Residential Doors Fire Hose Cabinet Sliding Doors Fire Rated Doors Glazed Fire Doors Fire Resistant Glazing Partition Fire Curtain Fire and Water Retardant Hollow Metal Pressed Doors Pressed Steel Door Frames Acoustic Metal Doors Acoustic Dry Wall Panel Bullet Proof Doors Manufacturing of Fire Proof Doors, Sound Proof Doors, Pressed Steel Doors and Window Frames & Special Purpose Doors, Wrought Iron, Furniture & Iron Handicraf ts.







ARE YOu INTO PASSIvE buSINEES? www.passivefiresafeindia.com ¾ 30,000 Fire Industry professional reach... ¾ Inspiring stories for you... ¾ Improve your business with our news... ¾ Future technology and policy frame work ADVERTISE yO u R BRAND... 4 | March - April 2023 | www passivefiresafeindia.com
W E ARE CBRI T ESTED
Our Fire Doors are tested, evaluated or certified as per IS3614 part 2 and BS476 Part 20 & 22 in CBRI Roorkee.They are tested to withstand extreme conditions for longer duration to ensure complete safety of life and property during fire incidents.





Address:
Plot No. C/ 3 - B, Madhuram Industrial Estate, B/S. Vishala Estate, Near Kathwada G.I.D.C., S.P. RING ROAD, AHMEDABAD - 382 430, Gujarat, India.
Contact Details:
Ph.: +91 98989 26545 | +91 90337 27669

Email: info@shivshaktifabricators.in
bhaveshpanchal53@gmail.com
Website: www.shivshaktifabricators.in


 FIRE RATED DOOR EMERgENCy EXIT DOOR hOLLOW METAL PRESSED STEEL DOOR
CLEAN ROOM DOOR
FIRE RATED DOOR EMERgENCy EXIT DOOR hOLLOW METAL PRESSED STEEL DOOR
CLEAN ROOM DOOR
| 5 March - April 2023 | www passivefiresafeindia.com
Founder & Editor:
Yogita Nandkumar Mundhe (CEO) yogita@passivefiresafeindia.com
Printed, Publisher & Owned by Ms. Yogita Nandkumar Mundhe
VISION MEDIA HITECH PVT. LTD.
Neminath Square, 506, Chaitanya, Opp. Ram Mandir Signal, S. V. Road, Goregaon (West), Mumbal - 400 104
Mobile: +91 93244 82435 / 81699 67502
E-mail: editor@passivefiresafeindia.com passivefiresafeindia@gmail.com
Art & Layout designer@passivefiresafeindia.com
Web Online
VMH Web Solutions
Marketing Online sales@passivefiresafeindia.com

Accounts accounts@passivefiresafeindia.com
Circulation & Subscription admin@passivefiresafeindia.com
Passive Fire Safe India (Bi-Monthly Magazine) Owner, Printer and Publisher Ms. Yogita Nandkumar
Mundhe printed at Neminath Square, 506, Chaitanya, Opp. Ram Mandir Signal, S. V. Road, Goregaon (West), Mumbal - 400 104 (Maharashtra)
Editor: Yogita Mundhe
All rights reserved. Reproduction and Translation in any language in whole or in part by any means without permissions from Passive Fire Safe India is prohibited. Advertiser are responsible for there own advertisement content. The Publisher is not liable for any Legal, Patent, Image or Trade Mark disputes from advertisement or among advertisers. All disputes are subject to the exclusive jurisdiction of competent courts & forums in Mumbai, India.
07 Editor’s Note 09 understanding the Role of Fire-Rated Materials in Pasive Fire Protection by Mr. Tariq Kachwala 10 Investing in Fire Resistant Coating 12 uNIvERSAL ENTERPRISES Company Profile 14 Armacell’s New ArmaProtect Firestop Range with Fire Rating up to 240 Minutes Industry News 16 Pasive Fire Safety for Tall buildings by Mr. Hemant Khadse 18 A Guide to Passive Fire Protection Fundamentals and best Practice 21 Why is it Important to install Fire Doors as a Safety Practice? 22 Concerns Rise Over Malfunctioning Fire and Smoke Dampers in Hospitals 24 What You Need to Know About Your Passive Fire Protection System? 25 Why HvAC Maintenance is Important Year-Round? 27 Why is Fire Safety Such a big Deal in High Rise buildings? by Mr. P. Jothi Ramalingam 30 Role of Digital Technology in Passive Fire Protection Systems by Mr. Bill Mchugh 32 Passive Fire Protection Systems: A Rising Industry Concern
March-April 2023 Vol.1 No.1 CONTENTS March-April 2023 india’s 1st magazine on 6 | March - April 2023 | www passivefiresafeindia.com
Dear Readers,

Warm welcome to our first edition of Passive Firesafe India. Passive fire protection is an integral part of a buildings’ fire safety strategy and is important for saving lives and keeping buildings standing. Typically, when considering fire protection, one may imagine fire extinguishers and sprinklers, however, these active fire protection measures work in tandem with the more hidden passive measures to protect people and buildings. The actual prevention of fire spread and compartmenting of buildings can be key in protecting lives and giving emergency services time to react.
Passive fire protection is often overlooked and undervalued by most people. In an age where action movies demonstrate heroes fighting blazing fires with voluminous streams of water or all the sprinklers in a room discharging from an incipient or comedic fire, it is easy to overlook a fire wall that may protect half of the building or the fire-resistive stair enclosure that protects occupants exiting and firefighters staging. In the field of fire protection engineering, passive fire protection features can be equally beneficial as active suppression.
We are lacking far behind in the installation of passive fire systems, at schools, malls, hospitals, high rise buildings (Residential & Commercial), Sport academy, Training Institutions, Govt. offices and so on. Passive fire protection systems aim to protect occupants and/or a building through containment of fire and smoke. These systems are always present, and take no additional actions to activate in the event of a fire. Fire safety measure regulations for buildings whereby it is required buildings have measures in place to control the spread of flames. Such regulations exist for all kinds of buildings and demonstrates the importance of passive fire protection in terms of both legal compliance and great advantage to having effective measures in place. Low-quality and poorly installed fire protection can be ineffective in the event of a fire.
Please come forward and make an initiative to create more and more awareness in terms of Passive fire.
Hope you like our first edition of Passive Firesafe India. Comments or any suggestions you feel, you all are always welcome.

Kindly mail us at yogita@passivefiresafeindia.com
Yours Sincerely,
yogita Mundhe Editor & CEO

EDITOR’S NOTE | 7 March - April 2023 | www passivefiresafeindia.com

OF F IRE -R ATED M ATERIALS IN PASSI v E F IRE P ROTECTION
How is Passive Fire different from Active fire protection?
Fire protection in buildings is one of the most critical elements of design, whether for new or existing constructions. Broadly, fire protection can be categorized into two types: active fire protection and passive fire protection. Active Fire Protection requires motion or movement in response to fire to combat it, and these elements are clearly seen in new constructions such as water sprinkler systems, fire extinguishers, and water hoses. Apart from this, active fire protection also incorporates some intangible aspects such as fire drills and training of occupants in response to fire. Any kind of right department or department will undertake when a fire erupts.
In contrast, Passive Fire Protection does not require any motion or movement and is constructionbased. Fire-rated walls, smoke seals, and facade smoke barriers are some elements of passive fire protection. When it comes to fire-rated glass walls and partitions, glass is becoming an increasingly popular choice due to its remarkable property of transparency and durability that no other building material can provide. Advances in material technology have enabled the use of large-sized glass formats that not only look aesthetically pleasing and in sync with the overall architectural intent but can provide very high levels of fire protection, mostly on an average of two hours.
How do fire-rated materials provide passive fire protection, and why is this important in building design?
Fire-rated materials need to possess the important capability of having low coefficients of expansions so that the effect of temperature rise is kept to a minimum and the overall structural integrity of the base material is preserved. Within this space, glass offers a remarkable option to create fire-rated barriers and can protect against flames or gases as well as temperature rise. The biggest benefit of glass is its ability to offer transparency, and this becomes a critical element in the event of a fire where visibility becomes key and could be the difference between life and death. Apart from this, from an architectural perspective, glass as a material is very bespoke and
can be tailored to suit architectural needs as far as surface treatments and sizes go.

How is the fire resistance of materials tested, and what standards or codes are used to regulate fire safety in buildings?
As with any product, glass also has to be tested as per certain standards that determine the rate of temperature rise as well as the pressure. Internationally, the European and American standards are perhaps the most popular and cater to most building types as well as applications. Closer to home, we now have Indian standards, the IS3614, IS16945 and IS16947, that are designed to test as well as specify the properties of fire-rated glass and other elements.
The huge sport you would search for in the usage of fire-rated glazed doors and partitions, as well as facades, means that several tests are now getting conducted in national and international laboratories to test various systems, application spaces, and material types. It is extremely important for the client, at the time of finalizing the contract, to understand the finer nuances of this testing and ensure that whatever material is being used adheres strictly to these test protocols as well as performs as per the test requirements.

What are some challenges associated with using fire-rated materials in building design, and how can these be addressed?
Since fire-heated glass and glazing is a relatively new building material that has been in existence for just over a decade, awareness of this product in the general market is not very high. In such cases, the client needs to be properly educated in an unbiased way on the usage of fire-rated glass partitions and doors, as well as the type of materials that are used to create these.
There are several specifications that are now available in the market, designed to suit particular manufacturers, and this is not in the larger interest of the construction industry. Care has to be taken by specifiers, as well as designers and architects, to create specifications that provide a fair and equal platform for participants to bid so that the latest technologies and materials can be used.
uNDERSTANDING THE R OLE
| 9 March - April 2023 | www passivefiresafeindia.com
Mr. Tariq Kachwala Director, FG Glass
I N v ESTING IN F IRE R ESISTANT C OATING
Investing in fire resistant coating is a smart choice for fire safety. Fire resistant coating refers to a protective layer applied to a building’s structural elements, such as steel and concrete, to slow down or prevent the spread of fire.
This type of coating is especially important for buildings that are at high risk of fire, such as those in urban areas or those with a large occupancy.
Protection
When it comes to protecting a building from fire, it’s important to remember that it’s not just the flames that cause damage, but also the heat and smoke.
Fire resistant coating acts as a barrier, slowing down the spread of heat and smoke and giving occupants more time to evacuate the building.
This can also help reduce the amount of damage caused by a fire, potentially saving thousands of dollars in repairs.
Another key benefit of a fire resistant coating is that it can help improve the overall fire safety of a building.
A SMART CHOICE FOR FIRE SAFETY
By slowing down the spread of fire, it can give firefighters more time to respond and contain the blaze. This can ultimately save lives and reduce the amount of damage caused by a fire.
Financial & Regulations
It’s also worth noting that investing in a fire resistant coating can also be a smart financial choice. Not only can it potentially save money on repairs, but it can also increase the value of a building.
This is because potential buyers and tenants will see the building as being safer and more secure, making it more attractive to them.
In some countries, fire resistant coatings are an important consideration when it comes to building safety. Building codes and regulations require that certain buildings have a fire resistance rating (FRR) to ensure the safety of the building and its occupants.
By investing in fire resistant coating, building owners can ensure that their building meets these regulations and is as safe as possible.
Passive Fire Installations understands the importance of Passive Fire Protection Systems and we are able to guide you with expert advice, project management, and high-quality workmanship to help create a safe environment for you. Let us apply a fire resistant coating to your building’s structural elements.

10 | March - April 2023 | www passivefiresafeindia.com
(AN ISO 9001-2015 COMPANy)











| 11 March - April 2023 | www passivefiresafeindia.com
COMPANY PROFILE

u NI v ERSAL ENTERPRISES
(AN ISO 9001-2015 COMPANy)
“DousedFire” - Home grown brand from M/s Universal Enterprises, in reckoning in the field of passive fire prevention has been founded under ”Make In India” vision of our Hon PM Shri. Narendra Modi, Mr Ashit with his humble beginning into field of electrical and electronics dealerships started, ”DousedFire” in the year 2018. With over 25 years of industrial experience Mr Ashit has championed the art of understanding the pain points of his customers. In pursuit of his goal of making Indian Assets Fire resistant and to give golden moments to escape in case of any eventuality “DousedFire” Products have formulated. With 100% home-grown formulation “DousedFire” products meet and exceed all national and international standards for passive fire prevention, to the extend of being certified as an ISO 9001-2015 Company,
What is Passive Fire Prevention?
Passive fire prevention refers to the measures that are taken to slow down the spread of fire, and to protect people and property from its effects. Passive fire protection measures do not require any active intervention or operation to work, they are designed to provide protection automatically when a fire occurs. Examples of passive fire protection include fire-resistant walls and ceilings, fire doors, fireproofing materials, fire-rated glass, and smoke seals. These systems are typically installed during the construction of a building and are tested to ensure that they meet required fire safety standards. The goal of passive fire prevention is to create a safe environment for building occupants and to give firefighters more time to respond to a fire, to minimize damage and potential loss of life.
The use of passive fire prevention measures dates back to ancient times when fire was one of the biggest threats to life and property. Over the centuries, various cultures and civilizations developed various methods of fireproofing buildings and materials to protect against fire. Some examples include the use of clay and mud for fireproofing in ancient Greece and Rome, and the use of fire-resistant materials, such as stone and brick, in medieval Europe.
In the 20th century, advances in building materials and fire science led to the development of modern passive fire protection systems. The use of fireproofing materials, such as intumescent coatings, fireproof cable and conduit, and fireproof enclosures, became more widespread, and fire safety regulations and codes were established to ensure the proper use and installation of these systems.
Today, passive fire protection is an integral part of building design and construction, and is an essential component of fire safety. The development of new materials, products, and technologies continues to improve the effectiveness of passive fire protection systems, helping to protect people and property from the dangers of fire.
There are several types of passive fire coatings used in building construction to provide fire protection: Intumescent coatings: These coatings expand when exposed to heat, forming a protective layer over the underlying material to slow down the spread of fire.
Ceramic coatings: These coatings are made of fire-resistant materials and are used to provide insulation and fireproofing on structural steel.
Cementations coatings: These are fireproofing materials made from a mixture of cement, aggregate, and fire-resistant additives.
Vermiculite and Perlite-based coatings: These are fireproofing materials made from naturally occurring minerals that expand when exposed to heat.
Fireproof paint: This type of coating is used to provide a fire-resistant finish on walls and ceilings, helping to slow down the spread of fire.
Intumescent paint: This type of paint expands when exposed to heat, forming a protective layer over the surface it is applied to.
Mr. Ashit Prajapati Proprietor
12 | March - April 2023 | www passivefiresafeindia.com
Each of these passive fire coatings has specific properties and applications, and the best option for a particular project will depend on the specific requirements and building codes.
Passive fire prevention codes refer to the regulations and standards that govern the design, installation, and maintenance of passive fire protection systems in buildings. These codes aim to ensure that buildings are constructed in a way that provides adequate protection against fire and promotes the safety of occupants and first responders. Some common examples of passive fire prevention codes include:
International Building Code (IBC) National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) codes
American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) standards
Underwriters Laboratories (UL) standards Each country, state, or region may have its own specific fire codes, which are based on local fire safety requirements and building codes. Building designers, contractors, and fire protection professionals must be aware of these codes and standards to ensure that their projects meet the necessary fire safety requirements. Regular inspections and tests are also conducted to ensure that passive fire protection systems continue to function properly and provide adequate protection over time.
Passive Fire Prevention for Electrical Systems: Passive fire protection for electrical systems refers to the measures taken to protect electrical equipment and wiring from fire damage. The goal of passive fire protection for electrical systems is to prevent the spread of fire, to minimize damage to the electrical system, and to ensure that the electrical system continues to function during and after a fire. Some common examples of passive fire protection for electrical systems include:
Fireproof Enclosures: Fireproof enclosures are used to protect electrical equipment, such as switchgear, transformers, and panels, from fire damage.
Fireproof Conduit: This type of conduit is made of fire-resistant materials and is used to protect electrical wiring from fire damage.
Fireproof Cable: This type of cable is made of fire-
resistant materials and is used to protect electrical wiring from fire damage.
Fireproof Barriers: Fireproof barriers, such as fire-resistant walls and ceilings, are used to create fire-resistant compartments to prevent the spread of fire within a building.
Fireproof Cable Trays: These trays are made of fire-resistant materials and are used to support electrical wiring, helping to prevent the spread of fire.
In addition to these passive fire protection measures, electrical systems in buildings must also comply with local building codes and fire safety regulations, which may include fire resistance ratings, smoke detection and fire alarm systems, and emergency lighting systems.
Passive fire Protection Systems for Industries: Passive fire protection systems in industries refer to the measures taken to prevent or slow down the spread of fire. These systems are designed to maintain the structural integrity of a building and create a safe escape route for occupants in case of a fire. Some common examples of passive fire protection systems include fire-resistant walls, fire doors, fire-rated glass, fireproofing sprays, and fireproofing materials for structural steel. These systems are typically installed during the construction of a building and are tested to ensure that they meet required fire safety standards.
We at M/s Universal Enterprises (AN ISO 90012015 COMPANY), which is dedicated to providing absolute quality products & services in the field of Passive Fire Retardant Coatings, under the brand name of “DOUSEDFIRE”, some of our product ranges are,
9 “DousedFire” – 2 Hour rated Fire Retardant Paint for Structural Steel Metals etc.
9 “DousedFire” – FRLS PVC Additive Powder.
9 “DousedFire” – Intumescent Cable Coating.
9 “DousedFire”- Fire Retardant Transparent Coating for Fabric.
9 “DousedFire”- Fire Retardant Transparent Coating for Raw & Laminated Wooden Surfaces.
9 And Many More Products.
All these are backed by Government recognized Laboratory Test Certificates.
| 13 March - April 2023 | www passivefiresafeindia.com
A RMA c E ll’ S NE w A RMA P ROTE c T
FIRESTOP RAN g E w IT h FIRE RATIN g UP TO 240 MINUTES
NEW FIRESTOP SELECTOR WITH FIRE RATING uP TO 240 MINuTES
Regulated by building codes in many countries, buildings are subdivided into ”fire compartments” and in some cases also smoke compartments. In the event of a fire emergency in a building, the strategy is to keep the fire and smoke contained within a limited area of the building (the fire compartment) for a given amount of time (referred to as the fire rating). Fire ratings are country dependent and typically ranges between 30 and 120 minutes (partly even up to 240 minutes).
• Properly designed and installed, PFP systems complement fire compartments to provide multiple levels of fire safety, such as providing building users sufficient time to safely make their way to a means of egress and escape from the building.
• Keeping escape routes free from smoke and other toxic gasses, and allow in emergency responders to safely rescue building users from the fire scene and attempt to extinguish the fire.
Fire and flames cause severe harm but a key concern for humans is the inhalation of smoke and other toxic gasses.
For example, if there is a hole as small as 10 mm (0.4“) in diameter penetrating a fire rated floor or ceiling between the two rooms and a fire is to occur in a room, it would take less than 3 minutes for the adjacent room to be filled
with smoke.
In this situation, you would not be able to see your own hand even if placed just 45 cm (18“) in front of you. Incapacitation and physical impairment due to smoke inhalation occurs even faster.
Apart from being a safety issue for humans, smoke can also cause severe damage to assets and equipment, for example in hospitals and data centres.
The New ArmaProtect Firestop range keeps fire and smoke contained in a limited area for up to 240 minutes. ArmaProtect Firestop products reliably seal off penetrations in walls, floors or service shafts and keep escape routes free of smoke and toxic gases. This gives occupants valuable time to leave the building and rescue teams unhindered access for evacuation.
• Easy to install and highly reliable Globally tested.
• Certified in numerous combinations and configurations, making the ArmaProtect Firestop range a one-stop-shop solution.
• Easy to inspect and to maintain.
With new ArmaProtect Firestop Selector you will easily find the right passive fire protection solution, protect your assets and safe lives in case of fire.
ArmaProtect Firestop systems. Install it. Ensure safety.
FSAI Jou RNA l | JANUARY-FEBRUARY 2023 | 14
IND u STRY NEWS 14 | March - April 2023 | www passivefiresafeindia.com
ABOUT ARMACELL
As the inventors of flexible foam for equipment insulation and a leading provider of engineered foams, Armacell develops innovative and safe thermal, acoustic and mechanical solutions that create sustainable value for its customers. Armacell’s products significantly contribute to global energy efficiency making a difference around the world every day. With more than 3,200 employees and 27 production plants in 19 countries, the company operates two main businesses, Advanced Insulation and Engineered Foams. Armacell focuses on insulation materials for technical equipment, high-performance foams for hightech and lightweight applications and next generation aerogel blanket technology.

| 15 March - April 2023 | www passivefiresafeindia.com
PASSIvE FIRE SAFETY FOR TALL buILDINGS
 by Hemant Khadse
by Hemant Khadse
Fire safety of high-rise buildings has attracted extensive attention in recent past. There are many serious high-rise building fire accidents In metros like Mumbai , Delhi and Bangalore resulting in catastrophic loss of human lives and properties occurred frequently in recent years. Compared to normal compartment fires, the fire behaviour in high-rise buildings has some inherent challenges, that includes:
(1) the extensive use of external facade insulation materials;
(2) fire and smoke transfer due to complex building structures;
(3) Building materials that adds fire hazard;
(4) human evacuation.
Fire also brings threats to the structures of high-rise buildings. The fire can emerge from the unprotected openings, shafts, doors and window and will not be easily controlled.
As tall buildings become more complex with dramatic changes in building envelope and materials, it is vital to consider passive fire safety implications of new buildings or other construction or refurbishment projects at the concept design stage. The following factors need
to be considered for designing passive fire:
• Regulations compliance
• Fire modelling, and risk assessments


• Heat transfer to the structure
• Materials fire rating
• Vertical and Horizontal openings in the building
• Smoke movement
• Fire and smoke barriers/ Compartmentation
• Exit signages and
• Emergency escape lighting
The main objective of passive fire safety design is to save lives and to prevent smoke spread within building. The primary objective is to reduce the potential for death or injury to the occupants of a building and others who may become involved, such as the fire and rescue services. It is also crucial to during fire emergencies within buildings, ensure that, visibility and tenability for fire fighters is maintained.
compartmentation and evocation route, as well as other factors such as means of warning, should be guaranteed in the design.
Architectural details in design of tall buildings plays a significant role in the fire safety of the building. The case of Grenfell Tower in 2017 became a disaster largely because of wrong material selection and detailing on the façade cladding. The panels were preferred aluminium instead of zinc panels, which had more resistant insulation core in honeycomb shape, only because of economic benefits.
WITH A FIRE RESISTANT BARRIER SLAB
WITHOUT A FIRE RESISTANT BARRIER SLAB
16 | March - April 2023 | www passivefiresafeindia.com
The most important thing to remember about compartmentation is that it does not work if the wall, floor, or ceiling has an unprotected opening in it through which fire and smoke can spread. Penetrations through fire-rated barriers must be kept to a minimum. If a penetration is necessary, the penetration must be protected according to code to maintain the fire rating of the barrier.
The fire can spread either through the exterior of the facade or the interior gaps. To avoid the first route of spread, the material
used in the facade should have sufficient fire resistance. The main design strategies for High rise fire safety are;

• Prevention: controlling fire ignition.
• Warning: ensuring that the occupants are informed in the event of fire.
• Containment: fire should be contained to the smallest possible area.
• Evacuation: ensuring that the occupants of buildings and surrounding areas are able to move to places of safety; ensuring also that adequate means of

- Hemant Khadse, CEO East Corp Group



- For more info visit www.eastcorpgroup.com
- Contact +91 9819893536
- Reach hemant@eastcorpgroup.com
escape and protection of escape routes are provided.

• Extinguishment: ensuring that fire can be extinguished quickly and with minimal consequential damage.
It is time we need to learn from accidents and build passive fire strategy while design planning. It is the mix of Processes, People and Products that can transform to safe building design. It is said, ‘Fire is good servant but bad master’. If we learn to manage and contain fire, we can save lives and protect from tall building fires.
 Hemant Khadse is CEO of East Corp, fire and life safety consultant. He is engineering graduate with work experience of 30 years in fire and security; He has travelled and worked internationally. He is also fire safety trainer and conducted many FLS audits and risk assessments.
Hemant Khadse is CEO of East Corp, fire and life safety consultant. He is engineering graduate with work experience of 30 years in fire and security; He has travelled and worked internationally. He is also fire safety trainer and conducted many FLS audits and risk assessments.
| 17 March - April 2023 | www passivefiresafeindia.com
A GuIDE TO PASSIvE FIRE PROTECTION: FuNDAMENTALS AND bEST PRACTICE
What is Passive Fire Protection (PFP)?
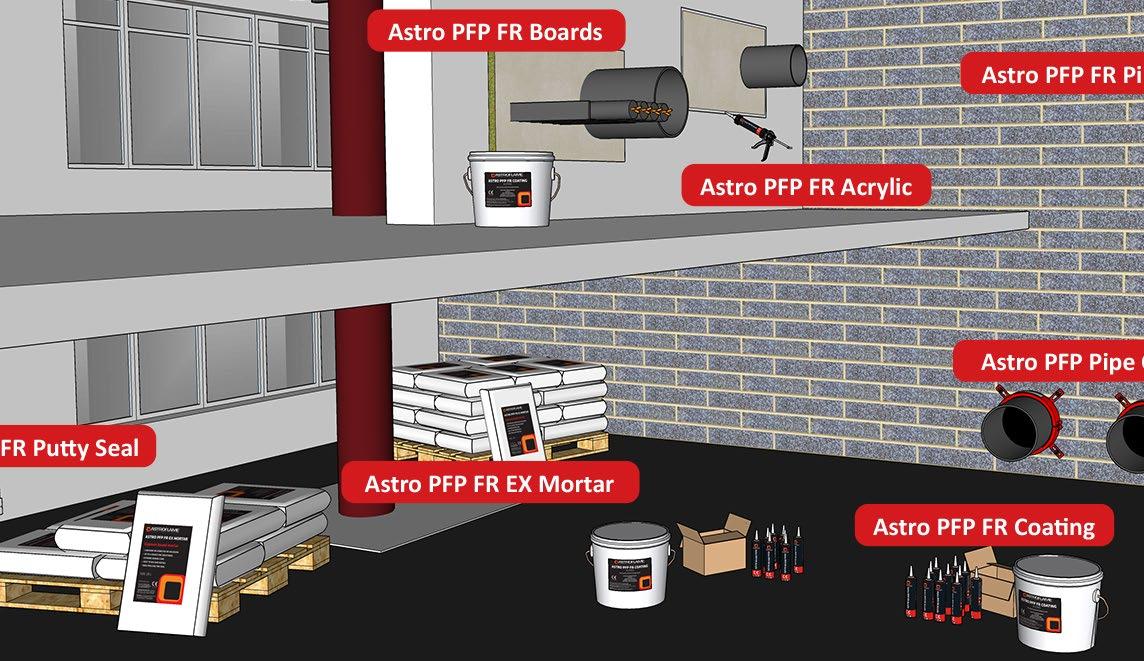
Like a vaccine, passive fire protection helps stop the spread of fire and reduces its severity. The term can include a wide range of products and practices, but it generally refers to materials built into structures that make them more fire-resistant.
The goal of employing PFP is twofold: to make a building safer for evacuation and, what’s even more significant, to prevent a fire from ever turning into a threat to life.
Fire tends to spread from item to item and then from room to room. Certain products address the former, while intumescent materials address the latter. Regardless of what method is used, the fundamental goal of PFP is to delay or stop the spread of fire.
What’s the difference between Active and Passive Fire Protection?
Active fire protection refers to equipment installed in buildings that start working when the equipment itself (or a person) detects a fire: a fire alarm, a sprinkler system, or a fire extinguisher, for example.
While all this equipment is essential, prevention is the best cure. It’s far better for a fire not to spread because a combination of passive measures has already stopped it.
But, of course, you don’t have to choose which method to use. A comprehensive fire protection plan will include both active and passive measures. Exactly which actions you choose depends on
factors including the design, size, and purpose of the building and other considerations such as water availability in the area and the time established for evacuation.
Active fire protection is the first line of defence. And a plan to both defend and attack means people inside the building are as safe as possible.
Why use a Passive Fire Strategy?
Every building, no matter how large or small, should have an emergency fire strategy. A PFP is an integral component of that strategy as it is designed for three key reasons:
1. To limit the financial damage caused by the fire
2. To increase the time Fire and Rescue Services (FRS) have to evacuate a building
3. To save lives
And, it does this in three principal ways:
1. By safeguarding the structure of the building
2. By curbing the spread of fire and smoke
3. By protecting escape routes
How does Passive Fire Protection work?
The pillar of passive fire protection lies in compartmentation. Walls, floors, and rooms are separated using different techniques (which we will discuss below) to divide the building into areas or compartmentalised. This leads to improved safety for people inside buildings and gives them longer to evacuate.
18 | March - April 2023 | www passivefiresafeindia.com
The principles of Passive Fire Protection
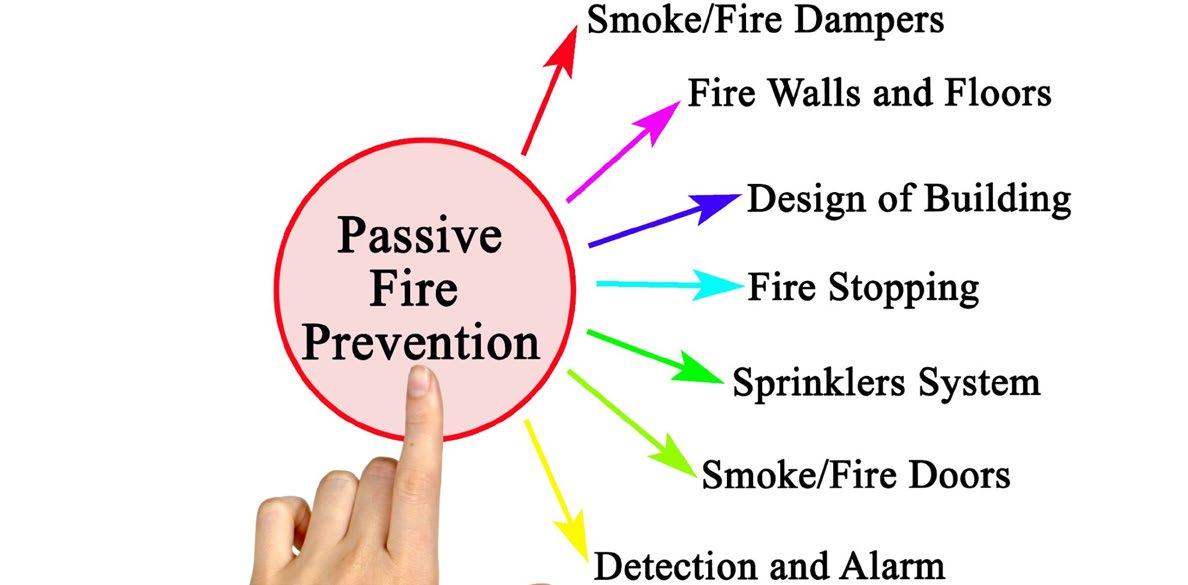
• Protecting escape routes by keeping safe waypoints
• Protecting building integrity
• Resisting heat conduction (insulation)
• Limiting the spread of fire, hot gases and smoke by containing it within a single zone or compartment
Load-bearing beams, walls, and floors have to be able to support their load under fire conditions. Doors, walls, glazed screens, and suspended ceilings have to stop fire ingress (flames and heat). Building services ducts need to be fire-stopped to ensure the ducting does not provide an easy route for fire. All fire resistance measures must be correctly designed, specified, installed, and maintained.
What are examples of Passive Fire Protection Products?
Fire doors
A fire door is fire-resistant or has a fire-protection rating. It reduces the spread of fire or smoke between rooms and acts as a protective barrier for people inside the building.
Fire dampers
Fire and smoke dampers are used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning ducts to prevent the spread of fire inside the ductwork. They can sense if there is a temperature rise and automatically close.
Firewalls
Firewalls are fire-resistant structures usually made of concrete, concrete blocks, or reinforced concrete designed to restrict fire spread through compartmentalisation. The key defining feature of firewalls is their structural independence.
Coatings
Today, spray-applied epoxy intumescent and subliming are the most commonly used coatings. Other available types of coatings include phenolic foam, glass fibre, and elastomer rubber.
Additional Products and Systems
PFP products and systems can be installed in a building or be part of the fabric of a building. They should be installed by certified, competent parties and correctly maintained. Other examples include:
• Fire-resisting walls, floors, ceilings, and ducts
• Firestopping and fire protection for structural members
• Fire-resistant epoxy coatings that can be spray applied
• PFP sheets
• Fire-protective boxes or wardrobes
• Fire shutters
• Fire-resisting glazing
• Suspended ceilings
• Fire fighting shafts and stairwells
• Fire-resisting walls and partitions
• Fire-resisting ductwork
• Industrial fire shutters and curtains
• Linear gap seals
• Penetration seals for pipes, cables, and other services
• Cavity barriers
• Fire-resisting air transfer grilles (mechanical or intumescent)
What are Fire Protection best practices?
Firestopping is the sealing of any openings to prevent fire, smoke, and heat from passing through to different areas of buildings either laterally or vertically. The building is made safer by creating fire resisting compartments.
Best practice should always be followed when a building is first designed and before its construction. If the building is extended or refurbished, firestops should also be included in the design.
The national standard for electrical installations, and it requires any wiring systems to be correctly sealed to provide an efficient firestop.
Fire Protection Surveys
The first step is to carry out a Fire Risk Assessment. You can either do this yourself or contract a professional fire safety consultant. Your Fire Protection Survey will use the findings to identify a plan of action to carry out in the building. It could include the following:
• Identifying equipment needed
• Making the escape routes clear
• Removing any potential hazards
Make sure to pay special attention to the type of people using the building children, the elderly, or people with special needs, for example?
| 19 March - April 2023 | www passivefiresafeindia.com
Whose responsibility is Passive Fire Protection?
The onus is on building owners, managers, occupiers, and designers to undertake regular fire risk assessments. These should include an evaluation of the PFP in the building and adhere to regulations, which state people must be able to safely exit a structure that will not collapse when on fire.
Regardless of whether the building is domestic or non-domestic, PFP provision is required in all buildings. If a fire separating element is to be effective, every joint or imperfection of fit, or opening to allow services to pass through the element, should be adequately protected by sealing or fire stopping so that the fire resistance of the element is not impaired.
Compartmentation
Key concept: Stop the fire from spreading throughout the building.
It is easier for the FRS to fight a fire if it is contained within one area of a building. People are also more likely to be able to evacuate safely. Ensuring walls, ceilings, and floors can withstand the heat and installing some of the fire stopping products listed above will help the fire from spreading wildly throughout the whole building.
Smoke Extraction and Ventilation Ducts
Key concept: Remove smoke and slow down the fire from spreading
Toxic smoke inhalation kills more people than the fire itself. It reduces visibility, causing confusion and can lead to suffocation. Smoke also helps a fire to spread. For these reasons, a correct duct system to extract smoke is a crucial part of any passive fire protection plan.

Structural Protection
Key concept: Prevent the building from collapsing
What should a Passive Fire Protection plan include?
A Fire Escape Route
Key concept: People should have enough time to react to a fire and evacuate safely.
People’s ability to safely evacuate a building must be guaranteed. Due to external factors and confusion, people are likely to need more time to evacuate than might be thought sufficient. Regardless of what is happening in the rest of the building, the escape route must be able to resist fire for long periods.
When subjected to fire, a building’s structure can collapse. However, if the building’s load-bearing structure is safeguarded, it will be more able to withstand high temperatures. Fitting a building out with structural protection may also save the building after a fire. In addition, an efficient structural protection system will mean the building is more likely to be repaired rather than demolished.
Conclusion
Protecting people inside burning buildings is not easy. It requires the right mix of products, procedures, and systems. Getting it right depends on every building, as each one has its unique requirements based on size, shape, purpose, and materials used in construction. However, taking both active and passive measures will guarantee that every person stands a better chance of being safely evacuated from a building on fire.
SubMIT YOuR ARTICLES/bLOGS/PRESS RELEASE/PRODuCT SHOWCASE TO editor@passivefiresafeindia.com 20 | March - April 2023 | www passivefiresafeindia.com
W HY IS IT IMPORTANT TO INSTALL FIRE DOORS AS A SAFETY PRACTICE ?
Simply put, fire doors save lives. The doors are tested against the elements and designed to withstand roaring fires for as long as possible. They allow buildings to compartmentalise, thereby delaying the spread of fire.
As the times are evolving, we can see a lot of evolution and innovations taking place in the manufacturing, construction and infrastructure industries. Fire doors are one such innovation that is considered a boon. It plays a very important role in ensuring the occupants’ well-being and safety in a particular premise or building.
Installing fire doors as a part of safety practice is extremely important as they help prevent dangerous accidents that can occur due to fire which can cause irreversible damages. Hotels, schools, residential and commercial buildings require high-quality fire doors to ensure people’s safety. Fire doors have a fire-resistant rating and are used as a part of a building’s passive fire protection system, an essential requirement for public buildings, offices, and factories. They prevent the fire or smoke from spreading across the build¬ing and keep the fire contained to a particular compartment or room.
In India, fire doors are certified for 30 minutes, 60 minutes, 90 minutes and 120 minutes’ fire rating, with different heights and thickness depending on its stability, in¬tegrity and insulation. They are fire-tested in approved and renowned laboratories. Fire doors are available in various types and with different fire ratings, made of different materials and finishes, which gives the buyers options to choose from. Materials of international standards are efficient, cost-effective and are used to make them.
Furthermore, in case of any fire emergency, the fire doors do not get heated, ensuring that the occupants get a longer time to escape and move to a safer area while also giving the firemen more time to rescue those trapped and put out the fire.
Fire doors need to comply with certain standards like they should be self-closing. For example, some companies have interior fire doors that typically remain open between departments during normal business hours, but they will automatically close in the event of an emergency. Moreover, using anything other than fire-rated, fail-safe hardware can lead to injury or even loss of life in an emergency that requires quick evacuation.
Over time, the fire resistance and rating of a fire door may deteriorate. These doors must be inspected yearly to ensure that the door is well maintained and still assures adequate protection. Therefore, to make sure they are in a good state, the recommended maintenance and repair schedules should be followed. The need for replacement depends on the wear and tear that it experiences.
Overall, fire doors play an extremely important part in the safety facilities that need to be implemented in a building. As people are getting more aware and conscious of their safety, there is a rise in the demand for fire doors among all the sectors, including residential spaces. Thus, installing fire doors will ensure the safety of the people who step into the premises of any area and also, the property would be less prone to destruction as the fire doors will prevent the fire from spreading to other parts of the building.

| 21 March - April 2023 | www passivefiresafeindia.com
MALFuNCTIONING FIRE AND SMOKE DAMPERS IN HOSPITALS
Every hospital has a complex HVAC system of ducts carrying conditioned air throughout the facility. This labyrinth of ductwork contains a series of fire and smoke dampers that are building and fire code mandated to stop the spread of fire and smoke along the fire and smoke rated barriers.
Given that this series of ductwork covers the entire facility’s footprint, moves air (think smoke) efficiently throughout the facility, and provides a direct pathway for fire and smoke to travel across fire and smoke compartments, the airtight closure of a damper in the presence of fire and smoke serves a crucial life-saving purpose. Were dampers not in place or unable to close, fire and smoke would spread rapidly throughout the facility.
Two National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) standards NFPA 80, NFPA 105 regulate the installation and maintenance of fire and smoke dampers. Compliance with these mandates is complicated because of the three different types and three different configurations of dampers in current use today. In many cases, these various damper types and configurations are installed throughout a single facility.
Quick Primer on Fire and Smoke Dampers

Three different fire and smoke dampers are in use today fire dampers, smoke dampers, and fire/smoke dampers. Within each of these damper types are three different configurations. The first (and oldest) is a curtain damper, which operates when a heatsensitive fusible link heats up and melts, causing the thin metal curtain holding up the damper to drop in place. These curtain style dampers are only used as fire dampers.
Newer pneumatic dampers, on the other hand, involve the use of air hoses to hold the damper in an open position. If the hose melts or air flow is cut off to the damper, the air pressure holding the damper
in the open position is released, resulting in the damper’s closure.
The most recent and increasingly prevalent type of damper is an electric damper, which is most often controlled by sensors within a facility’s fire alarm and/or fire sprinkler systems. When smoke or fire is detected, the electrical power maintaining the damper’s open position is shut off, resulting in its closure.
Most far-reaching of all these concerns is the failure rate of some dampers. “We’ve gone into hospitals and seen electric damper failure rates of 25 percent to 50 percent,” “Yet, fewer safety measures in a hospital are more important than damper reliability.”
All three damper configurations serve the ultimate purpose of halting the flow of fire and smoke through ductwork. But, each configuration has its plusses and minuses. Curtain dampers, for instance, are the least expensive of the three configurations to install. Their failure rate also is the lowest. Common causes of failure include damper misalignment due to incorrect installation and a physical impediment that restricts closure, such as a screw that comes loose through years of constant duct vibration. The primary drawback is that these dampers do not provide smoke control.
Electric and pneumatic dampers fail for similar reasons, but on a more frequent basis than curtain type dampers, with electric dampers failing the most. “Electric dampers utilize actuators to keep the damper open that unfortunately have a tendency to fail over time for a variety of reasons. Complicating damper inspection is the possibility that a hospital will have all three damper configurations in place. NFPA 80 mandates the actuation the closing and reopening of all dampers. This is not an easy process. With regard to curtain dampers, the fusible links
CONCERNS
RISE OvER
22 | March - April 2023 | www passivefiresafeindia.com
must be removed to ensure the curtain drops to a fully closed position. With electric and pneumatic dampers, power or airflow to the attached actuators needs to be curtailed to assess closure efficacy.
When you multiply this process by hundreds of dampers, the work can be extremely protracted, since contractors generally price their quotes on a per damper basis as opposed to a ‘time and materials’ basis, there is pressure to finish the work as quickly as possible to maintain profit margins.
This project buyout method can backfire disastrously if the hospital does not require proof of inspections, including the actuation of the damper. The best proof is a picture of the damper in both an open and closed state. Only then do you really know if it has been performed.There is a financial incentive for contractors on a fixed price method to work as fast as possible. The reality is an unscrupulous contractor may skip inspecting hard to reach dampers or those with blocked access.
Beyond Fire and Smoke Control
For pneumatic and electric dampers, the failed state is most often a closed damper. While this insures that fire and smoke will not cross these protected barriers, there could be other significant consequences such as:

• An increased frequency of hot/cold calls
• Conditioned air not replacing contaminated air
• Humid air not cycled out and replaced with conditioned air
• Air pressure inside and outside of rooms not being maintained as designed.
Patient satisfaction and infection control are two of the most important things to a hospital. Inoperable fire and smoke dampers can have a massive impact on this. Considering these dampers are on
a mandated 6years inspection and repair cycle, dampers are often broken for years before being addressed. Many hospitals are increasing their inspection frequency from 6 years to 2 or 3 years in critical health areas such as operating rooms, NICU, emergency rooms, etc.
Pathway to Compliance
In the past, many hospitals would simply put a HVAC technician in the role of CMS compliance for their fire and smoke dampers. However, with the increasing complexity and new standards this is often not feasible. Working knowledge of HVAC system is definitely a part of success; but now you need someone who also understands building and fire code, NFPA standards, blueprints and life safety plans, and can organize all of the paperwork. Ultimately, they need all of the right tools to capture and organize all of the data digitally. It has gone from fairly simple to significantly complex in a short period of time.
In light of the vital role that dampers play to preserve the health and safety of people, combined with the new standards and complexity of the issue, many hospitals have determined the optimal “sleep easy” solution is to outsource their maintenance and inspection.
“What we do is give the facilities director and national CMS accrediting organizations like The Joint Commission the confidence they need to know all the dampers are working as designed. And we prove it, taking a photograph of each damper in both its closed and open positions. That is what makes your accreditation inspections go well.
With concerns growing over hospital-acquired infectious diseases, and ongoing fire and smoke hazards, reliably functioning dampers are a must.
T
BSCRIBE NOW... | 23 March - April 2023 | www passivefiresafeindia.com
READ
h E LATEST u PDATES Su
Many people tend to think of fire protection as something that happens after a building is already built, and in some cases, especially for older buildings, that could be true. However, passive fire protection systems are actually components that are included right from the start of the building process and are often already planned out before the building even begins.
That means that there are elements used right from the structural outset that are intended to form part of your fire protection. Here at Passive Fire Installations Limited, we love to share more knowledge and insight so that you know exactly what to expect. Let’s take a look!
What Exactly is a Passive Fire Protection System?
A passive fire protection system is a structural system that slows down or impedes the spread of fire. It is a vital building component that enables the building to become more resilient to the passage of fire, as
well as heat transfer and smoke. While the name might suggest that this is a dormant or “passive” system – the truth is that this system of protection is always active or “always on”. That is because it is built-in protection from the structural level up and includes components such as fireproofed building materials, structural mechanics and joining systems, and even fire doors form part of this system.
Why does a Passive Fire Protection System Work?

The goal of a passive fire protection system is to maintain the integrity of the building structure for as long as possible in the event of a fire. Why? Because the more time you have, the more time that is created through this system, and the more it helps people to exit and escape the building safely.
Additionally, these systems prevent the leakage of smoke during a fire event which is a major cause of fatalities. Passive fire protection systems save lives.
W HAT YO u N EED TO K NOW Ab O u T YO u R
24 | March - April 2023 | www passivefiresafeindia.com
PASSI v E F IRE P ROTECTION S YSTEM ?
W HY H vAC M AINTENANCE IS I MPORTANT Y EAR -R O u ND ?
HVAC maintenance is vital no matter the season, but your maintenance tasks will change depending on the time of year. Read our guide to spring, summer, fall and winter HVAC maintenance. Regular HVAC maintenance keeps your HVAC system performing efficiently and delivering conditioned air everywhere you need it. The nature of HVAC maintenance changes depending on the season, however. Here’s what you can expect throughout the year.
How to do HVAC Maintenance All Year?
Different parts of the system require different maintenance depending on the conditions they’re exposed to. Here are some of the maintenance tasks you’ll likely need to schedule on the different components of your HVAC system, though note that you should follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for how and how often to do maintenance on each part.
Coils

The coils and tubes in your HVAC equipment are responsible for heat transfer during both heating and cooling seasons. Heat is transferred out of your space during the summer and into your space during the winter via the fluid flowing through your coils. Dirty equipment won’t transfer heat and energy quite as well, so cleaning is the name of the game when it comes to annual coil maintenance.
Air-handling units should have their chilled water and hot water coils cleaned annually.
“Rooftop units and condensing units are a little different because these units are typically outdoors. “For rooftop units, you want to clean the evaporator coils. You’ll clean the condenser coils for both rooftop units and condensing units.”
For condensing units, this involves spraying the condenser coils (which are exposed to unfiltered outdoor air)
This condenser needs to be cleaned. Without regular maintenance, the condenser won’t transfer heat as efficiently, forcing the unit to work harder. The coils should be sprayed with an antimicrobial treatment to keep microorganisms from growing.
| 25 March - April 2023 | www passivefiresafeindia.com
with a microbial treatment that will prevent microorganisms from growing on the exposed coil.
You may need to clean more often than annually if your location demands it — for example, a building near a tree line that results in leaves getting trapped in the equipment.
Tubes
Tubes are very similar to coils in that they transfer heat. Pull out tubes annually to check for clogs and remove all of the debris — it can decrease your equipment’s capacity and efficiency. Plate and frame heat exchangers should also have their plates cleaned and the gasket replaced. Make sure nothing is clogging the space between the plates.
Cleaning tubes in the winter because chillers won’t be operating as much. Typically you might have one operating at partial load in the winter, so you can always service the other one while one is operating and vice versa.
Controls
Checking controls annually will ensure that your HVAC system is running properly.
Temperature sensor and thermostat calibration is one area you definitely want to focus on. Say the cooling setpoint of the space is 75 degrees F., but your thermostat is miscalibrated by 2 degrees. Therefore, in the summer, when your space is 77 degrees the thermostat is going to think you’re satisfied. You want to calibrate every year.
Control calibration tends to drift gradually, so periodic checkups are crucial to maintaining accurate operation. In addition to the main HVAC system checking the controls monitoring the temperature on heat tracing and other auxiliary equipment. The setpoints on heat tracing can drift just like the setpoints on any other controls.
Fans
Fans, as we all know, are chief components of many pieces of HVAC equipment. Many pieces of HVAC equipment incorporate fans, and they need to be maintained quarterly for maximum longevity. Concentrating maintenance in three key areas.
1. Wheels. The first item you want to look into for increasing the longevity of a fan is a dirty wheel. “That will put a lot of stress on the motor and reduce the airflow. It may also cause the fan to wobble, which puts a lot of stress on the bearings and causes noise issues.” He suggests vibration monitoring, which can reveal whether you have worn bearings that may be a symptom of something else.
2. Belts and belt tension. Belts that are too loose will slip, and belts that are too tight will stress the motor and bearings. Inspect the belts quarterly to make sure they’re not cracked or worn.
3. Bearings. Make sure your bearings are lubricated properly to reduce friction and corrosion.
Filters
Many pieces of your HVAC system also incorporate filters. Clogged filters increase the pressure drop in your HVAC system, making your fan work harder to maintain the same airflow (and ultimately reducing the airflow once your fan is working at maximum capacity). A quarterly cleaning for most filters, unless you’re in an area with higher-than-average particulates, such as high-pollen areas.
As we increase the total pressure as our filter gets clogged, our operating costs increase more and more. By adding an inch of static pressure, it’ll increase the operating costs of these units. If you have multiple units, that adds up.
Strainers
Strainers filter water in HVAC systems rather than air. Like air filters, a clogged strainer will increase the pressure drop in your HVAC system. For coil strainers, a blowdown process to flush debris out of the strainer so that you don’t have to isolate and drain that one piece of equipment.
26 | March - April 2023 | www passivefiresafeindia.com
W HY IS F IRE S AFETY S u CH A b IG DEAL IN H IGH RISE bu ILDINGS ?
-Mr. P.Jothi Ramalingam, Afiti Global
Architect Reena Mukherjee looked up in horror at the smoke billowing from the 27th floor of the building where her own swanky luxury apartment was located in Worli. Her newly built penthouse flat was located on the top floor of these 39 storied glasses clad high-rise. The fire was raging and as she watched some of the glass panels shattering and the flames leapfrogging towards the floor above. The high winds were fanning the fire burn even more vigorously and it looked like very soon the entire structure above the 27th floor will be fully gutted. Only divine intervention can help. She prayed fervently with all her heart. “OH God please do something. Please let the fire douse. Please save my family and all those people who are stuck in the building and fighting for their lives”. Will her prayers be answered?
This is a familiar scenario which plays out many times a year across India and any one of us could be in the place of Reena Mukherjee. Our colleagues, our family members or even we ourselves could be stuck in a similar situation. Unfortunately there is no one on earth who can give you a guarantee that the building which houses your office or home can be made absolutely fire proof . But if the architect, consultant, and developer of such superlative high-rise buildings decide to keep fire safety as a priority then they can definitely make the building extremely safe against fire accidents.
Fire Safety and Fire Engineering is a vast and highly technical subject which is yet to become popular in India despite its criticality. When we speak about Fire Safety, we need to understand that this entire subject can be categorized into active fire systems and Passive systems.
Active fire protection systems are the most visible and most popular part of fire protection systems in India. The NBC has extensively prescribed the different requirements of such systems and awareness for these are relatively high in India. Active Fire Systems include those equipment which get activated, either manually or automatically, as soon as a fire happens within a building and the prime focus of active fire systems is to bring the fire under control and eventually douse it.
While active fire systems play a very critical role during a fire accident in a building there is another equally important role played by some products silently in the building which effectively prevent the fire and smoke from spreading and compartmentalize the smoke and fire within a given zone for a specified period of time. These products which are built into the building during construction which play a very critical role in preventing the spread of smoke and fire are called Passive fire protection systems.
The effectiveness of these passive fire protection systems can only

be ascertained when each of them are put through vigorous testing process as per established standards. There are two kinds of testing to check the performance of any passive fire products.
1. Resistance to fire which studies those properties of materials or their assemblies that prevents or retards the spread of excessive heat, hot gasses or the flames across different compartments in the building during a fire. The classification for Resistance to fire will be as follows
E30 to E120 where E denotes the ability of the product or system to have integrity to prevent the spread of flames and smoke/gasses and 30, 60, 90,120 denoting the number of minutes the product or system successfully stops this. (The NBC specifies E120 and EI 20 as the bare minimum requirement for doors and partitions used in the escape corridors and refuge areas.)
EW 30 to EW 120 where EW denotes the ability of the product to not just stop the spread of fire and smoke but also ensure that the radiation passing through the glass and frame of the system is always below 15KW per Sq mt per hour. This is the minimum radiant heat required to have spontaneous combustion happening on the non fire side during a fire. As such most specifications worldwide fall in this category.
| 27 March - April 2023 | www passivefiresafeindia.com
EI 30 to EI 120 where EI denotes the not just the fire resistant properties but also the insulation properties of the system thus ensuring that the maximum temperature on the non fire side never exceeds 185 degrees cent.
2. Reaction to classifies materials on the basis of how they behave during a fire to withstand fire exposure. This can be broadly classified for the following characteristics
Flammability from A1, A2 to F where A is non flammable and F is unfit to be tested since it is highly combustible.
Smoke Index from S0 to S3 where 0 means low smoke and 3 is heavy smoking if the product is on fire
Burning Droplets from d0 to d2 where 0 means no burning droplets are produced during fire and 3 being high number of burning droplets falling down which can create secondary fires.
Based on these characteristics there are two kinds of agencies who certify the products to be used in buildings.
1. ISO17025 accredited independent laboratories who can test the products for either resistance or reaction to fire and issue test certificates classifying them according to the relevant standards.
2. International Certifying bodies that use the data generated during the testing either in their own laboratories or in third party accredited laboratories and then classify the products either according to international standards or their own (UL). These certifying bodies will also audit the manufacturing process of the manufacturers and undertake to do random tests on samples to ensure that every product sold is as per the tested specification. There are several reputed such agencies worldwide and UL, INTERTEK, FM GLOBAL, EXOVA are a few
well known brands. A product which is certified by any of these entities gives a reassurance to the end user that the performance of products used by him will be consistent and will adhere to the relevant standards.
The most important aspect to be kept in mind is that when a system gets tested and certified the certification holds good only if all the components which were used in the original test are used while the system is manufactured in the factory. Even if one component is replaced they the validity of the test report will become void.
Once tested products and systems are used in the building the risk of fire incurring and spreading reduces drastically. The chart attached below gives the details of most commonly used passive products in buildings for fire safety and their relevant testing specifications
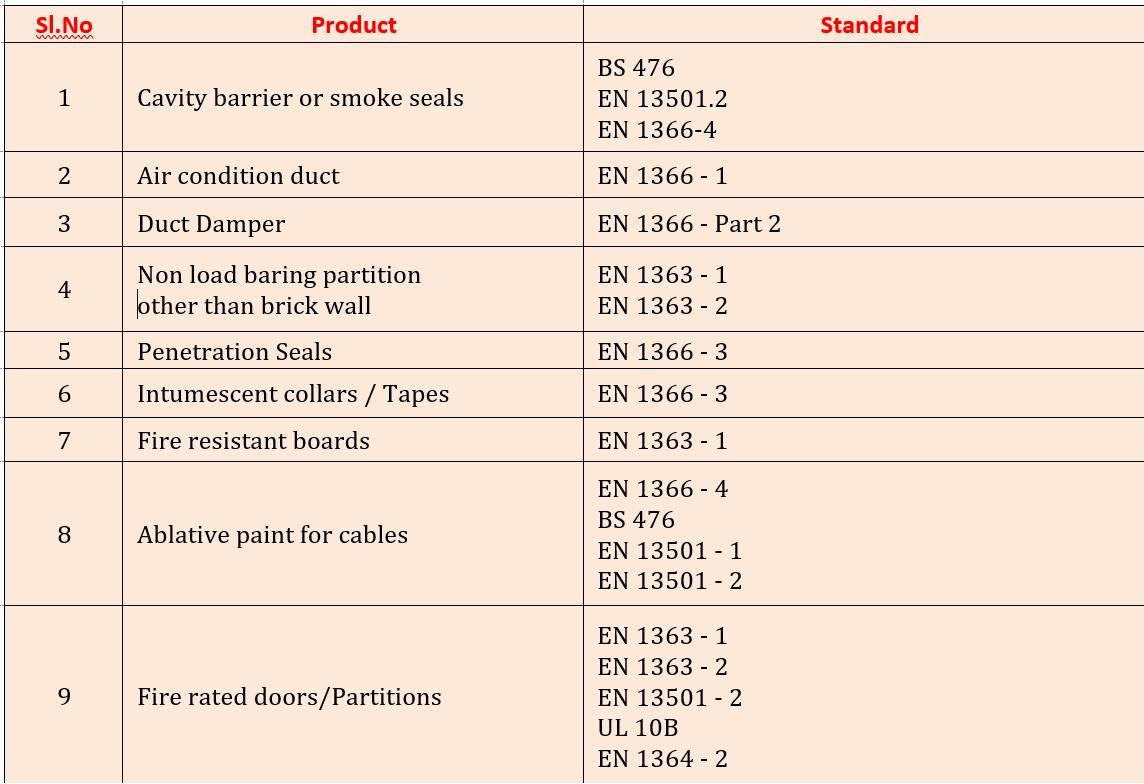
28 | March - April 2023 | www passivefiresafeindia.com
Fire Safety is a vast subject which has gained immense interest in India in the recent past .However in most advanced countries this is a very critical subject which is dealt by professionals with the utmost seriousness it deserves. The objective of the fire specialist would be to make the building as fire resistant as possible by ensuring that only tested and certified products are used in the project. No doubt such tested and certified products would be more expensive but then that is the price one needs to pay to keep human life safe in these buildings.
Fire happens in a building mostly as an accident and sometimes as a result of arson. Irrespective of the causes let us stick to how its impact on the people who occupy that building and the building itself can be minimized. The focus for the fire consultant would be to design the building in such a way that even if there is an outbreak of fire it is confined to a limited zone or compartment for as long as it’s necessary. This gives adequate time to the occupants to evacuate safely out of the building, without panicking, while the active systems get triggered and start working to douse the fire. At the same time this will also allow the fire rescue teams to access the hot zone without any hindrance.
When it comes to facades there are only two critical areas which need to be taken into consideration to make the facade resist the fire from spreading The hundreds of fire accidents which
continue to occur worldwide offer fire professionals enough clues about why the fires occur and what could have been done to prevent it and even if it was not preventable how to minimize the losses. It is important that every professional working on the design and execution of high rise project keep fire safety in mind while designing. Fire can be accident but the consequential damage from that fire need not be left to chance. With all the information on fire safety freely available on the net no one can take umbrage under the excuse that they did not have adequate inputs while designing the project
Even within the building care must be taken to minimize the use of inflammable products made of wood or polymers and make the building more resistant to fire. Certified passive products must be used wherever necessary in the HVAC ducts, cable trays and pipes as they travel through the building from one compartment or one floor to another. This applies to both residential as well as commercial buildings. Passive fire products get to work in the event of a fire and prevent the smoke and fire from spreading through the HVAC ducts and the space above the false ceiling. We all know smoke kills more people in the event of a fire than fire itself and therefore every fire safety system must also consider the risk of smoke spread along with fire.
All the doors facing the escape
corridors must be fire rated to keep these zones free of smoke and fire for at least 120 minutes. This will allow the occupants to reach safe zones without panicking. The fire rated doors and partitions must be tested and certified as a complete system and not assembled by the supplier with test certificates from individual component manufacturers. Such a product has no one agency giving the guarantee and in the event of a fire it will only lead to finger pointing going round to take the blame when the system fails.
Damage to life and property can avoided or at least minimized if a proper fire safety design is build into a high rise project. Then even in the event of a fire no one needs to panic as there is a built I system to ensure that the occupants reach a safe zone without any loss or injury.
Coming back to the Reema Mukerjee story, she remembered clearly the focus she and her team had put in while designing the fire safety systems, both active and passive for this project and she believed that these systems will ensure that this fire does not go out of control. Half hour later she got a call from her parents telling her that they along with all other family members are safe and the fire services have reached the spot and doused the fire. Under these circumstances the fire code book that she had referred was a life saver like any other holy book she had read.

| 29 March - April 2023 | www passivefiresafeindia.com
ROLE OF DIGITAL TECHNOLOGY IN PASSI v E FIRE PROTECTION SYSTEMS

The Passive Fire Protection Systems used in buildings provide both fire-resistance-rated structural and compartmentation for buildings –new and existing.
Structural fire-resistance can consist of steel frame buildings with Spray Fire-Resistive Materials, Intumescent Fire-Resistive Materials, Boards or Wraps applied to prevent steel from reaching its point where the steel loses the capability to support loads applied.
Effective fire-resistance-rated compartmentation features the ability contain fire to the room of origin – preventing fire-spread and protecting egress paths, forming havens of safety in buildings, separating spaces and occupancy types. Some compartmentation walls can also be structural in nature as well.
New Construction
During new construction, fire-resistance-rated
Mr. Bill Mchugh Firestop Contractors International Association & National Fireproofing Contractors Association

structural and compartmentation structural building elements and assemblies are chosen from the various testing laboratory directories either by the design professional or fire-resistance installation contractor. The structural fireresistance-rated building elements and assemblies are typically noted on plans by the design professional. The walls and horizontal assemblies are usually also noted on plans with design numbers referring to a listing directory online, while many of the fire-resistance compartmentation features listings are chosen by the installation contractor. Fire rated walls can be constructed of concrete, concrete block, gypsum panels and metal or wood studs, or fire-rated glazing, tested in accordance with ASTM E119 or UL263.
The fire-resistance-features include firestopping for breaches made for penetrating items, joints and voids, fire doors and frames, fire-dampers, fire-smoke dampers, or combination firesmoke dampers. Some are specified by design
30 | March - April 2023 | www passivefiresafeindia.com
professional, others are chosen by the firestop, fire-damper, fire-door installation contractor.
Fire-Resistance Listing Directories
Fire-resistance really revolves around a listing. The listings are the proof that the combination of materials or structural assemblies have passed a fire-test at an accredited fire-test laboratory. The listings can be found online.
UL Solutions – www.UL.com/PiQ
Intertek – www.Intertek.com
FM Approvals – www.ApprovalGuide.com
Thomas Bell Wright International Consultants, India Institute of Technology, Gandhinigar.
Some of the fire-test laboratory directories offer search capabilities and the ability to compile submittals. Many manufacturers of products used in fire-resistance-rated assemblies for both structural and compartmentation purposes, offer online listing selection systems and product information. Product information AND listings are critical to correct installation procedures. Why? Building codes state to install products in accordance with their listing and manufacturers installation instructions.
Several product manufacturers offer online submission systems where listings, manufacturers installation instructions, safety data sheets, and product data sheets can be assembled and downloaded for specific projects. Some specialist installation contractors use their own custom systems for this process.
New Construction Closeout
Design professionals have done well the past 25+ years building specifications for each fireresistance-rated building element or assembly. The specifications communicate requirements to the contractors construction requirements.
Additionally, leading architects and engineers are using MasterFormat Section 01-78-39, Project Record Documents, to direct General Contractors to gather the listings and manufacturers installation, inspection and maintenance instructions for the building owner.
These closeout documents are used to build an ongoing system that maintains fire-resistance protection for the building life cycle. These can also be assembled digitally as well.
Existing Buildings
Where the digital world is quite needed, is in maintaining protection existing buildings. The
building and fire-codes worldwide require that fireresistance in buildings be maintained and ready to protect against fire (or smoke, if specified) spread continuously. There is a countless amount of fireresistance-rated and or smoke resistive assemblies – both walls and floors – to keep maintained. The number of breaches through those assemblies is a large amount as well.
Breaches made in fire-resistance-rated and smoke resistive walls and floors then get protected with fire doors with hardware that has been tested and listed, penetration and joint firestop systems, firedampers, combination fire/smoke dampers, smoke dampers, and fire-rated glazing need to be visually inspected to assure compliance for the building life cycle.
The India National Building Code is quite amazing when it comes to maintaining protection in existing buildings. It’s unusual to have this is a building code, but India’s does direct many parties involved in construction and maintenance from new construction through operation in the National Building Code of India’s Chapter 9.
9 BUILDING MAINTENANCE – METHODS AND MANAGEMENT
9.1 General – “Any building (including its services) when built has certain objectives and during its total economic life, it has to be maintained in proper condition to meet those objectives. Maintenance is a continuous process requiring a close watch and taking immediate remedial action. It is interwoven with good quality of housekeeping. It is largely governed by the quality of original construction. The owners, engineers, constructors, occupants and the maintenance agency are all deeply involved in this process and share a responsibility….”.
Technology helps Management Work
Technology makes a lot of sense to manage India’s existing buildings, from the moment they are turned completed until they are demolished to make way for new construction. Software providers, passive fire protection manufacturers, passive fire protection contractors have programs that can help India’s building owners and managers handle this process efficiently.
Bill McHugh is Executive Director of the Firestop Contractors International Association and National Fireproofing Contractors Association. He travels internationally most recently in India for the launch of Fire Safe Build India. Bill can be reached at bill@ FCIA.org or bill@NFCA-Online.org.
| 31 March - April 2023 | www passivefiresafeindia.com
P ROTECTION S YSTEMS : A RISING IND u STRY CONCERN
The inherent risk of faulty systems has just got bigger.
In recent years there have been a number of new build and refurbishment projects that have been completed and occupied only to be decanted and occupants provided with alternative accommodation while the project is reconstructed due to inadequate passive fire protection.
Unfortunately, the correct installation of dry lining fire rated elements requires more specialist knowledge than that of a masonry or block-work construction. Also generally very skilled construction professionals do not have this level of specialist knowledge required to identify fire related defects before they are covered up. Many buildings with defective systems have been approved, inspected and issued completion certificates and warranties yet they may not satisfy the functional requirements of the Building Regulations when put to the test.
Passive Fire Protection is the primary measure integrated within the constructional fabric of a building to provide inherent resilience against flame, heat and smoke to maintain the fundamental requirements of building compartmentation, structural stability, fire separation and safe means of escape. Moreover, the fire safety design philosophy of the building may rely entirely on its adequacy of passive fire protection system.


Many building with defective systems have been approved, inspected and issued completion certificates. Those responsible for installing such systems and checking the works on site are in some instances unaware of this fact. Evacuation strategies adopted for residential flats/apartments are a typical example. The ‘Stay put’ evacuation strategy, which has been common place since post war building studies, is one such strategy that places a reliance on fire being contained to the compartment of fire origin.
Passive Fire Protection measures achieve their intended purpose by raising the fire resistance of the structure, protecting the structure against the effects of fire, reducing fire spread through secondary ignition, limiting the movement of flame and smoke, and minimizing the danger of fire-induced collapse or structural distortion. Unfortunately, in some instances there are clear breaches in compartmentation, which may consist of large holes in compartment elements or inadequate fire stopping leaving gaps where services pass through an element which would provide an easy route for fire to migrate. This sort of issue should be relatively easy to spot by both builder and enforcer. There is also a subtler issue in the correct installation of modern fire resistant wall and ceiling construction, which relies on the designer, installer and reviewer to have specialist knowledge.
In order to guarantee their performance in the event of fire the fire resisting elements must be installed as per the manufacturers recommendations taking heed of the manner in which they were tested. The potential issues are wide ranging and include; allowing for the heat related expansion in the design; the use of correct fixing spacing; and the use of the correct materials/fixings. It is all too common on construction sites to find evidence of ‘pic n mix’ dry-lining systems whereby various components from
PASSI v E F IRE
32 | March - April 2023 | www passivefiresafeindia.com
differing manufacturers have been utilized because that was the material available from the contractor’s yard. Whilst it is commendable to minimize construction waste and utilize material which was surplus to requirements it must also be acknowledged that passive fire protection systems are intended to perform in a particular way.

It may be that the incorrectly installed element may provide the required nominal required time rating of 30, 60, or 120 minutes when exposed to the ‘Standard Cellulosic Time-Temperature Curve’ under test conditions. Conversely a relatively small alteration to the recommended installation might result in the element achieving far less of a rating that originally specified.
The issue is that unless it is installed in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions, the rating of the element is unknown. Therefore, there is no guarantee that the system will prevent fire spread from one dwelling to another and with a single flat evacuation, occupants of other adjacent dwellings may be at serious risk. Healthcare environments which adopt a progressive horizontal evacuation strategy are another example of a use class of building which relies heavily on the performance of passive fire protection systems. Within a healthcare environment evacuation of the buildings occupants is undesirable and an absolute last resort which may result in fatalities not directly linked to the fire emergency. Passive fire protection has a vital role to play in this environment in order to avoid simultaneous evacuation of patients.
Passive fire protection design, incorporating passive fire protection materials, systems and assemblies, serves by fire containment to protect life, safeguard the building structure, protect assets, maintain building serviceability after fire, minimize rebuild costs, and facilitate quick business recovery and continuity. Third party certification of contractors has been instrumental in improving standards of installation of fire protection products/systems to the benefit of the construction industry and the clients it serves. However more needs to be done to raise awareness among contractors and Architects, designers, Project managers, Clerk of works, Building Control Surveyors, Warranty providers who design and inspect works on site.
It is an advantage to all the above parties to get this right first during the installation. However, the potential for those defective systems that remain hidden and unidentified for many years until tested by fire occurrence presents a far more worrying prospect.

| 33 March - April 2023 | www passivefiresafeindia.com

34 | March - April 2023 | www passivefiresafeindia.com
Bank Details:
You can also do the NEFT/RTGS DETAILS:

Soft Copy PDF (Version) 500/-*


Yearly
*5% GST Extra Applicable
5% GST Applicable*
Advertisement Sizes (All Size in Centimeters (cm)
Full Page (Non Bleed)
21cm width x 28cm height
Full Page (Bleed)
21cm width x 29.7cm height (Extra Bleed Mark)
Half Page (Horizontal)
19cm width x 13cm height
Half Page (Vertical)
8.5cm width x 28cm height
Gate Fold / Double Spread (Non Bleed)
38cm width x 28cm height
Gate Fold / Double Spread (Bleed)







24cm width x 29.7cm height (Extra Bleed Mark)
Quarter Page (Horizontal)
9.5cm width x 6.5cm height
Company Name: Address: __________________ Mobile No: __Office No:__________________
Address: Vision Media Hitech Pvt. Ltd., Neminath Square, Chaitanya, 506, 5th floor, Opp. Ram Mandir Signal, S. V. Road, Goregaon (W), Mumbai - 400104, Maharashtra, India. ����+91 8169967502 ���� passivefiresafeindia@gmail.com







Our Other Publication s

www.safesecuremagazine.com www.securecitiesreview.com www.vmhwebsolutions.comm 2023 - 2025 2023 - 2025 passivefiresafeindia@gmail.com www.passivefiresafeindia.com Advertisement Tariff Bi-Monthly Subscription Offers POSITION PRICE ₹ | $ G a t e fold 65 ,000 1000 Double Spread 1, 1 0,000 1692 Cover Page 1,00,000 1538 Front Inner Page 80 ,000 1230 Back Inner Page 80 ,000 1230 Full Page 3 0,000 461 Half Page 2 0,000 307 Quarter Page 15 ,000 230
Branch:
Branch Current A/C Name: VISION
Bank Name: HDFC Bank Ltd.
Goregaon (W)
MEDIA HITECH PVT. LTD. Current A/C No: 50200005022206
Swift
GST
Form: Advertisement Option: Half Page Full Page Quarter Page Premium: Cover Page Get Fold Cover Inner Back Inner Back Page Tag Page Payment: Cheque / DD: Cheque No._____ Date__/_ / Online (NEFT/RTGS) Digital (UPI Wallet) Cheque Should be in favor of “Vision Media Hitech Pvt. Ltd ” Name: ________________________Designation:____________
NEFT/RTGS IIFSC: HDFC0000322
Code: HDFCINBB
No : 27AAECV7628Q1ZG Please tick the option in the Order
Signature
Date
Published By
Email:_________________ Website: _______________________________________ Seal of Company:
:__________
:______________
TERM ISSUE COURIER SERVICE (INR) 1 Year 6 Issues ₹ 1,200/-* 3 Years 18 Issues ₹ 2,500/-* 5 Years 30 Issues ₹ 4,500/-* 7 Years 42 Issues ₹ 6,500/-* Life Time Magazine Subscription ₹ 50,000/-*
Life Time Magazine Subscription











































 FIRE RATED DOOR EMERgENCy EXIT DOOR hOLLOW METAL PRESSED STEEL DOOR
CLEAN ROOM DOOR
FIRE RATED DOOR EMERgENCy EXIT DOOR hOLLOW METAL PRESSED STEEL DOOR
CLEAN ROOM DOOR






















 by Hemant Khadse
by Hemant Khadse







 Hemant Khadse is CEO of East Corp, fire and life safety consultant. He is engineering graduate with work experience of 30 years in fire and security; He has travelled and worked internationally. He is also fire safety trainer and conducted many FLS audits and risk assessments.
Hemant Khadse is CEO of East Corp, fire and life safety consultant. He is engineering graduate with work experience of 30 years in fire and security; He has travelled and worked internationally. He is also fire safety trainer and conducted many FLS audits and risk assessments.








































