


























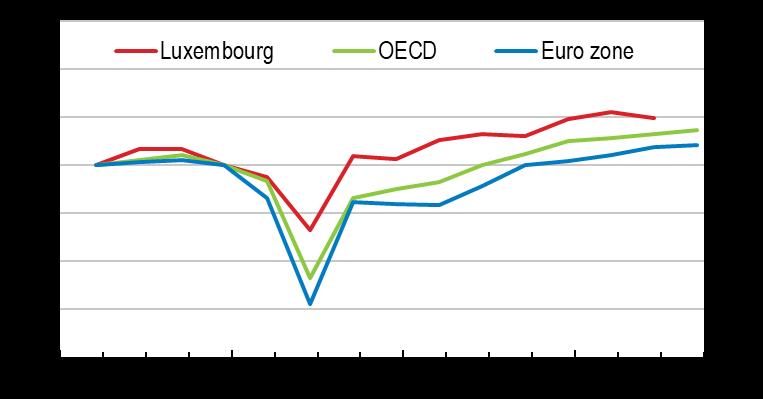
Real GDP Index 2019Q1 = 100

Economic Survey of Luxembourg 2022
Source: OECD Economic Outlook (database).

Economic Survey of Luxembourg 2022

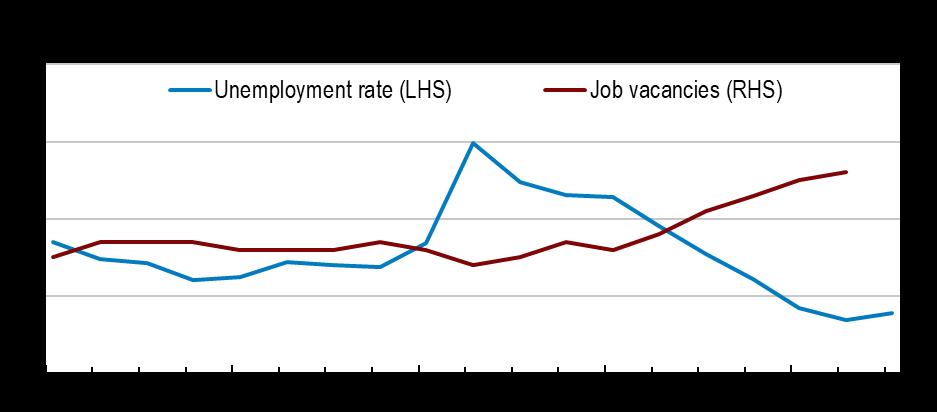
Note: Last observation: 2022Q (job vacancies); 2022Q3 (unemployment rate)
Source: OECD, and Eurostat.
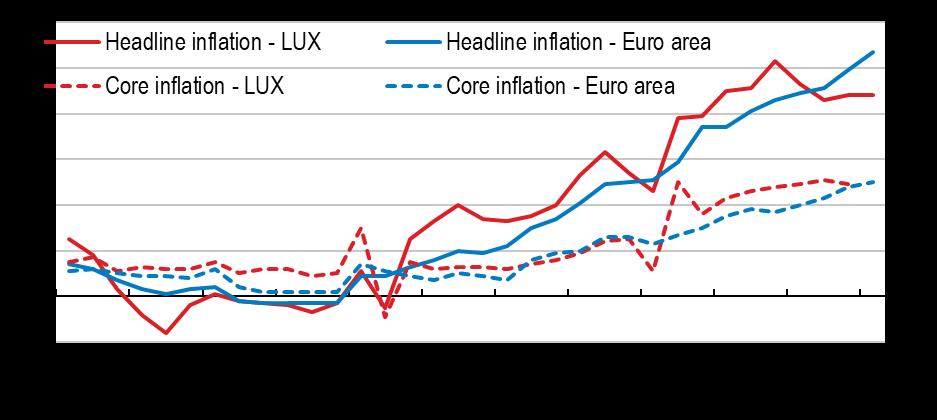

Economic Survey of Luxembourg 2022
Source: Eurostat, Harmonised Consumer Prices (database).

2022-23, % of 2022 GDP2

Economic Survey of Luxembourg 2022
1. Targeted measures are directed at households or firms, based on criteria such as income or energy consumption levels. 2. 2022 GDP is based on an OECD forecast. Source: Ministry of Finance, Draft Budget Plan 2023, OECD estimates.
Nominal house prices Index 2017=100, s.a.
Economic Survey of Luxembourg 2022

Source: OECD Analytical House Price Indicators.

Economic Survey of Luxembourg 2022

Economic Survey of Luxembourg 2022

Source: European Commission, The Ageing Report 2021.
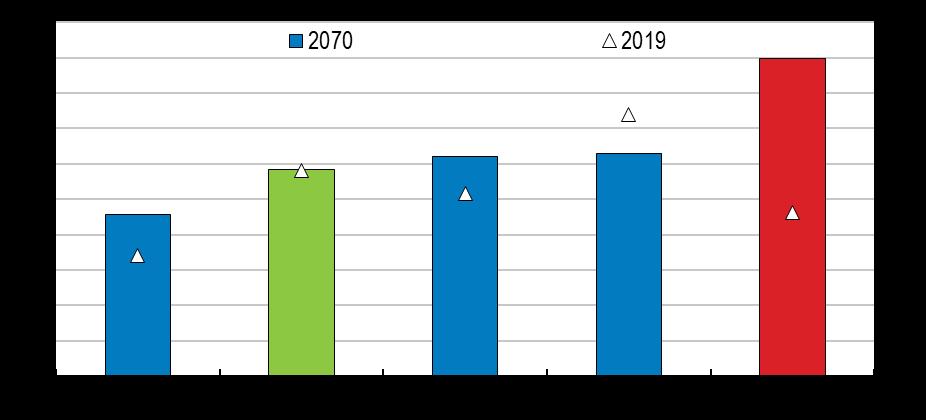
Labour force participation rate
%, 55 64 year olds, 2020
Economic Survey of Luxembourg 2022

Source: OECD, Labour force participation rate (database).
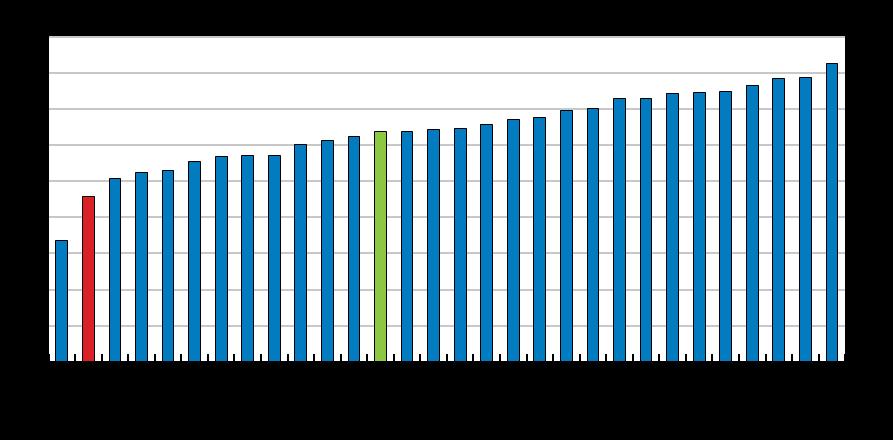
Economic Survey of Luxembourg 2022

Source: OECD, Labour Force Statistics (database).


Economic Survey of Luxembourg 2022

1. The combined contribution from increases in the employment rate and the working age population. Labor efficiency measures the contribution from combining labor and capital to potential growth.
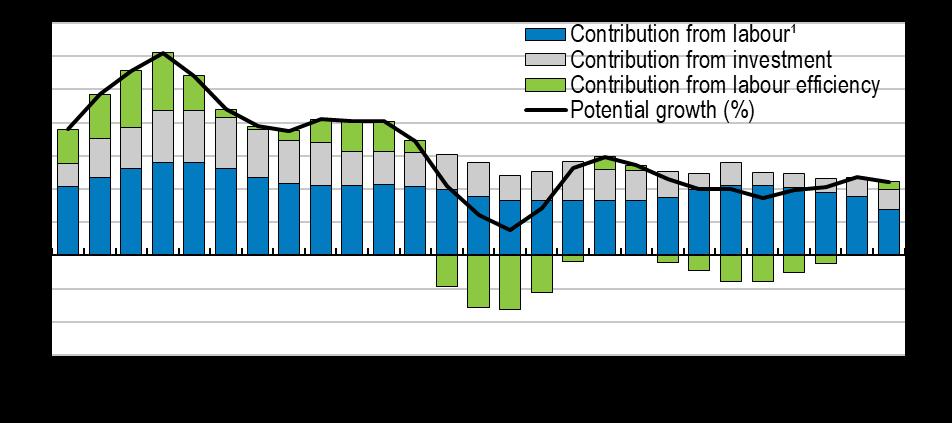
2. 2022 data are forecast.
Source: OECD Economic Outlook (database).
Economic Survey of Luxembourg 2022

Source: OECD Main Science and Technology Indicators.



Economic Survey of Luxembourg 2022
Source: OECD, ICT Access and Usage (database).

Index scale (0-6) from the most to the least competition friendly (6=most restrictive)

Economic Survey of Luxembourg 2022
Source: OECD 2018 PMR database.
Economic Survey of Luxembourg 2022

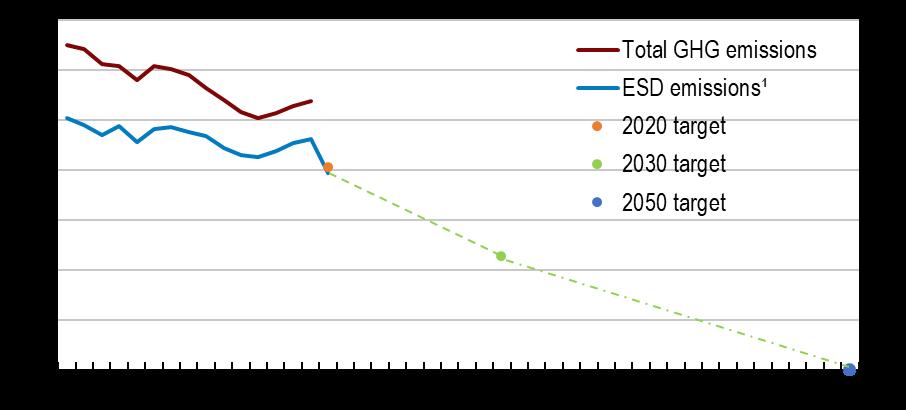
1 ESD = Effort Sharing Directive. These emissions are covered by the EU Effort Sharing Directive and are not part of the EU Emissions Trading Scheme.
Source: Eurostat, Effort Sharing Directive emissions and Air emissions accounts.

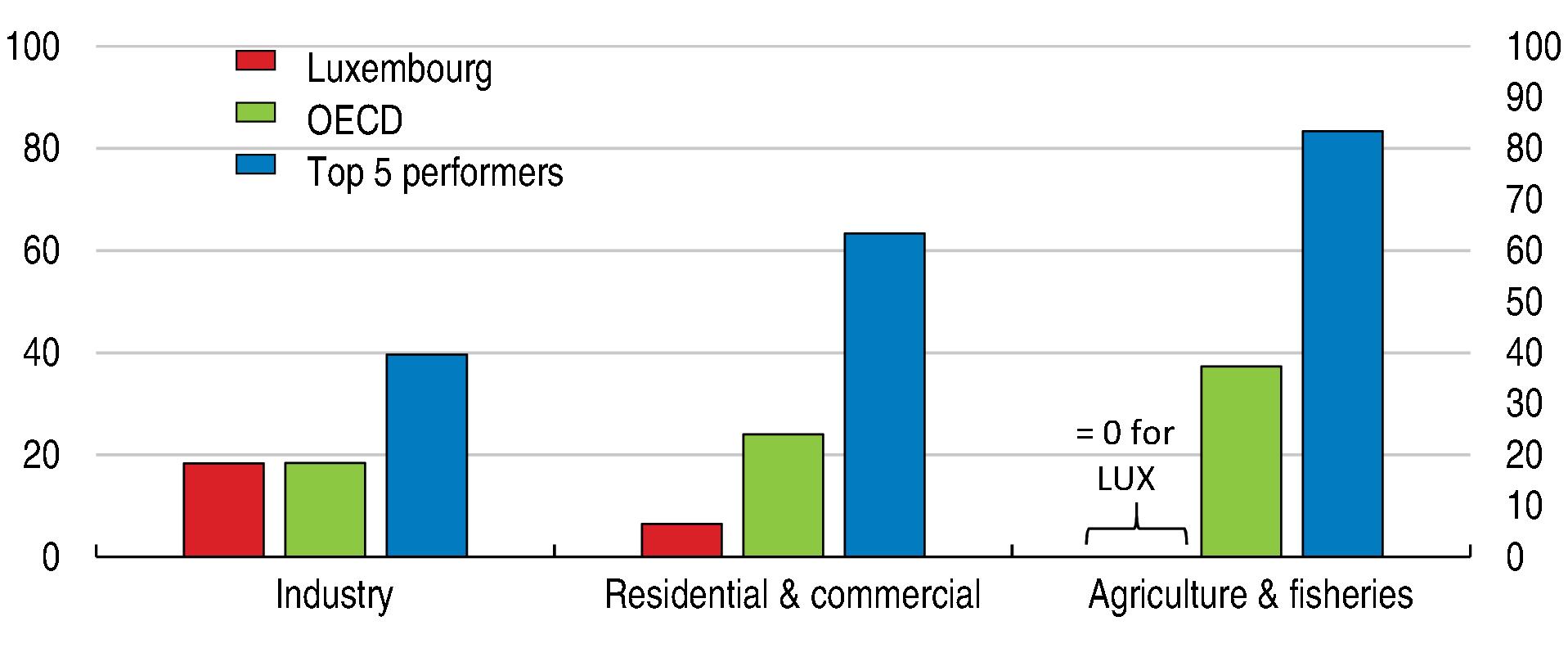

Economic Survey of Luxembourg 2022
Source: OECD Effective Carbon Tax Rates.


Source: European Environment Agency.
Summary• Support vulnerable households with targeted and temporary measures - to manage the impact of the energy crisis and maintain incentives for energy savings.

• Increase retirement ages through pensions reform and lifelong learning - to ensure fairness for younger workers in the future and to reduce the resource needs of the workforce
• Encourage higher R&D investments and faster take up of digital technology for small and medium sized business by matching public funding for private investment – to support living standards and the sustainable use of resources
• Strengthen signals for sustainable agriculture – to reduce emissions, fertilizer use and encourage greater biodiversity
• Introduce a medium- and long-term carbon-pricing path, together with adequate support for vulnerable firms and households – to encourage investments to reduce fossil fuels consumption
• Raise housing supply whilst densifying homes and gradually raising the cost of road use – to support plans to lower car use, raise homes’ energy efficiency and reduce the resources required by growth
Survey of Luxembourg 2022



The statistical data for Israel are supplied by and under the responsibility of the relevant Israeli authorities. The use of such data by the OECD is without prejudice to the status of the Golan Heights, East Jerusalem and Israeli settlements in the West Bank under the terms of international law
This document and any map included herein are without prejudice to the status of or sovereignty over any territory, to the delimitation of international frontiers and boundaries and to the name of any territory, city or area.
