Health Care Education in Indonesia in Digital Era
Henik Tri Rahayu, Ph.D., RN
Faculty of Health Science, University of Muhammadiyah Malang (UMM)
Indonesia





Henik Tri Rahayu, Ph.D., RN
Faculty of Health Science, University of Muhammadiyah Malang (UMM)
Indonesia







 Indonesian MOH, 2019
Indonesian MOH, 2019
A part of them are elderly

In 2021: there were around 371 thousand hospital beds in Indonesia. In that same year, the country had around 2,522 functioning hospitals. there were about 10.3 thousand functioning community health centers in Indonesia and its steadily increasing during the period measured.
In the period between 2017 and 2021, the number of hospitals in the country increased by 9,6 percent.

• The great forces in human and technology development that affect the future in all areas of human activity
• Health care innovation have led to “Open Health” or peer-to-peer health that enables sharing of knowledge with innovation as critical shift.
• A digital revolution in health care is speeding up → Telemedicine, predictive diagnostics, wearable sensors and a host of new applications will transform how people manage their health
Health education for adults and elders


• The digital age holds out the promise of innovative technology and business models
• Internet and smartphone penetration is growing, and the technology infrastructure is moving to cloud-based services.
• Health care providers need to address the major changes that are driving patient behavior and adopt a customer service mindset.
Health care practitioners should keep in mind that medicine must always be patient-centric treatment, and technology is merely a tool to improve the patient’s health outcome
• to describe the use of information technology system in health care industry to provide an easier access between health care providers and patients, especially from remote area.
→ technology for patient’s health care self-management
• Telemedicine is defined by the WHO as “the use of information and communications technology (ICT) to deliver health care particularly in settings where access to medical services is insufficient”.
The broadest term : Telehealth incorporates not only technologies that fall under “telemedicine,” but also direct, electronic patient-toprovider interactions and the use of medical devices (e.g., smartphone applications (“apps”), activity trackers, automated reminders, blood glucose monitors, etc.) to collect and transmit health information, often with the intent to monitor or manage chronic conditions → helps with developing and improving health-related education, health administration, and improving general public health.
The term eHealth → an even broader scope of digital information tools, ranging from electronic health records (EHRs), which facilitate the exchange of patient data between health care professionals. The concept of eHealth is not limited only to provide long-distance health care, but also to increase health care efficiency as a whole
• synchronous (live video)
A live and two ways interaction between a person that could act as a patient, caregiver, or provider and a provider using audiovisual telecommunications technology
• asynchronous (store-and-forward)
A type of transmission of recorded health history, the examples are pre-recorded videos and digital images (X-rays and photos) through a secure electronic communications system to a specialist practitioner
• Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
Personal health and medical data gathering from an individual in a certain location through electronic communication technologies
• mobile health (m-Health)
When mobile communication devices such as cell phones, tablet computers and PDAs support health care and public health practice and education
• Suffice to say, COVID-19 has accelerated and catalysed several aspects of digital health care across Indonesia
• Indonesia’s Internet penetration rate was 74% as of January 2022, with some 205 million Internet users
• A boom for digital start-ups response to COVID-19 Pandemic
• Hospitals enter the fray → On the back of the rapid uptake of telemedicine services and patients’ reluctance to visit hospitals amidst the pandemic
• (survey: >80% respondents afraid to visit hospitals)

• Strong economic growth is leading Indonesia towards middle-income country status.
• The growth is unfortunately does not reflect in the government’s budget allocation’s for national health budget, which is relatively low → leading to insufficient facilities and workforce needed for public services, and encouraging the growth of private health facilities
Lack of sophisticated health infrastructure in Indonesia has also been causing Indonesian’s wealthy people to go abroad in seeking better medical treatments, as neighboring countries’ health care providers are perceived as adequate to provide affordable high quality care and services.




Telehealth is going to be very beneficial for both the developer and consumer when it is successfully implemented in Indonesia.
"Over the next few years, the hospital network intends to collaborate with digital health care companies to extend its telemedicine services to new market, including Indonesian cities where it does not yet have a presence."
Nurhadi Yudiyantho, Managing Director of BMHS (Bundamedik Healthcare System)"The digital system enhances patient safety and lowers the chance of human error by connecting the data from the various departments of the hospital."
Aditya Wijaya, Head of Investor Relations, Mitra Keluarga Hospita
24-hours-homecare service and telemedicine services by its homecare service, health care force will come to patient’s house, therefore increase the accessibility to health care professionals in the underserved areas.
 Public Sector
Public Sector
2. JKN Mobile
3. BPJS Digital Claim Verification (Verifikasi Digital Klaim/ Vedika)
• Badan Penyelenggara Jaminan
Sosial (BPJS) Kesehatan, the provider of the National Health
Insurance – Healthy Indonesia
(JKN –KIS) program, is harnessing technology to create a better national health system to serve all Indonesians

• In 2013, Indonesia’s Ministry of Health, together with Indonesia AIDS Coalition (IAC)

▪ are the two telemedicine pilot projects initiated by the Ministry of Health in 2012, with the concept of teleimaging and telediagnostic, specifically in referring the results of electrocardiography (ECG) and X-Ray.
▪ In 2013, there are 12 primary care facilities and 2 referral center hospitals (dr. Cipto Mangunkusumo National Central General Hospital (Rumah Sakit Umum Pusat Nasional
• aim to support AIDS prevention programs.
• AIDS Digital contains information on services comprised of HIV testing, AntiRetroviral (ARV) therapy, PL-HIV support groups, vertical prevention, sterile needle syringe methadoneservices,services and STI services.
(RSUPN) Dr. Cipto Mangunkusumo/ RSCM) & Harapan Kita Hospital).
• a mobile application platform that focuses on giving high quality medical information that is easily understood by Indonesian-speaking users.
• Contents from diseases, drugs and daily difficulties that based on research are what AloDokter provides in their website and mobile app.
GO-MED is a mobile based application created by GO-JEK and Halodoc.

It is one of the features that integrated within the GOJEK application. GO-MED provide services which enables users to order their need of medicine via online application. Users can easily choose or input the product needed and the driver will directly buy the medicine and send it to the user.







 Developed by: Sugiharto, MAN, Ph.D.
Developed by: Sugiharto, MAN, Ph.D.
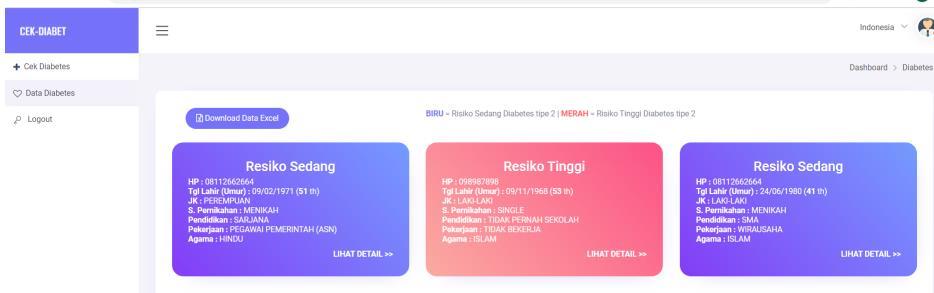
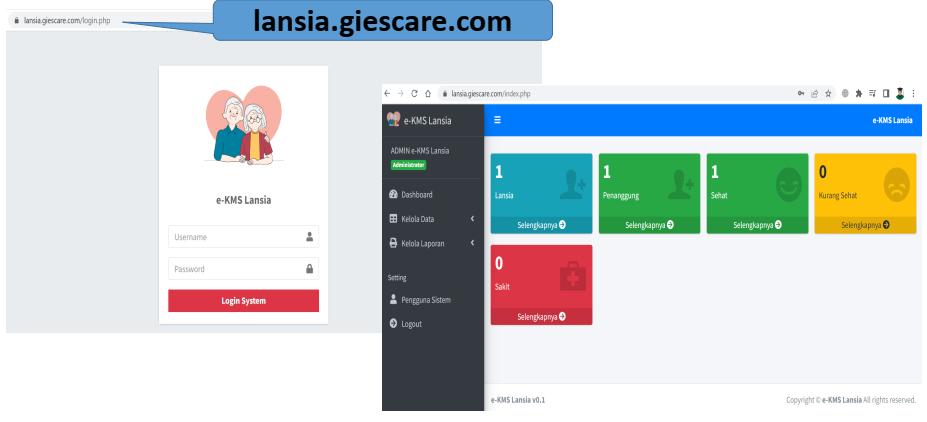
• Despite the benefit, the obstacle in implementing and developing a comprehensive eHealth environment in Indonesia can be perceived as massive, since Indonesia is still in the midst of their infrastructure development.
• Other than that, community acceptance, competence of the users, interoperability, and slow growth adaptation from the policy makers are other reasons that slow down the process even more
Infrastructure Limitation/Problems
➢ Power Source / Connectivity
➢ Communication Network
Community Acceptance


availability:
1. digital health service applications
2. health information systems
3. helpdesk or customer management systems
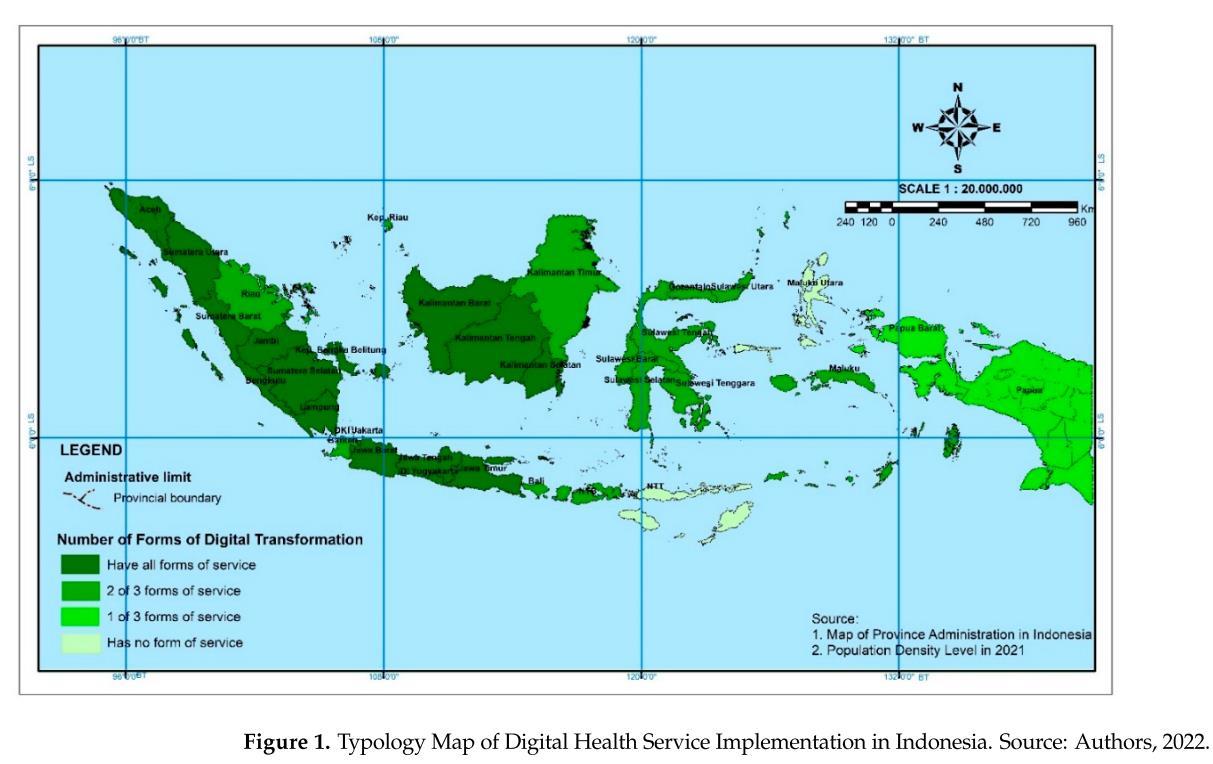




Strength
✓Implementation of digital health services as one of the strategies of the central government
✓The digital literacy of the Indonesian people is quite good
✓Demography bonus Save cost
✓Save time especially in waiting time for service Diagnosis and treatment can be performed faster
✓Easy to use digital healthcare platform Reducing the number of clinical visits
✓ Low and uneven distribution of health workers
✓ Geographical physical barriers in providing services Health care infrastructure is limited and unequal
✓ Poor technical quality
✓ Uneven condition of telecommunication network connectivity
✓ Patients are afraid and anxious to do
face-to-face consultations and visit the hospital
(Rohmah et al., 2023)
The development of ICT that encourages the growth of innovation in the field of health services
Optimizing the use of technology and regional innovation for the development of digital health services
Adopt technology to improve the quality of healthcare
Number of platforms for healthcare users
Increasing users of digital health services
Optimizing health service governance
The many types of healthcare platforms available
Outreach to unreached community groups to optimize digital health services
Provision of supporting infrastructure through government programs and cooperation schemes
The digital healthcare business opportunity in Indonesia is very high
Collaborating with various stakeholders in the development of a healthcare platform
✓ Personal data security ✓ Carry out personal data security test studies on digital healthcare platforms
Raising awareness of the importance of health services in Indonesia
✓ Limited funding ✓ Develop special regulations in the regulation of security and confidentiality of digital health service user data
Establishing a conducive climate for collaboration in the development of digital health service platforms
✓ Limited framework for private sector engagement
✓ Improving people’s digital literacy, especially in digital health services
Synergize and collaborate with various stakeholders in the development of digital health services in Indonesia
➢Lack of capability to access the internet and telemedicine → need highly role of family supports

➢Some of telemedicine/e-health non-elders friendly
Literacy
Payment
Unclear feedback/interpretation
Utility
