Aging Care in Taiwan: Challenge and Opportunity

Ching-Min Chen, RN, DNS, FAAN, FFNMRCSI



Distinguished Professor National Cheng Kung University
Department of Nursing/Institute of Gerontology
chingmin@mail.ncku.edu.tw
1
Significant needs for aging care
The demands of the elderly and related policies and Services

Aged and Long term care services
Roles of nurses in escalating the health, well-being & overall quality of life older adults with disability
Outline
•
•
of the Presentation
•
•
2
Rapidly Aging Population
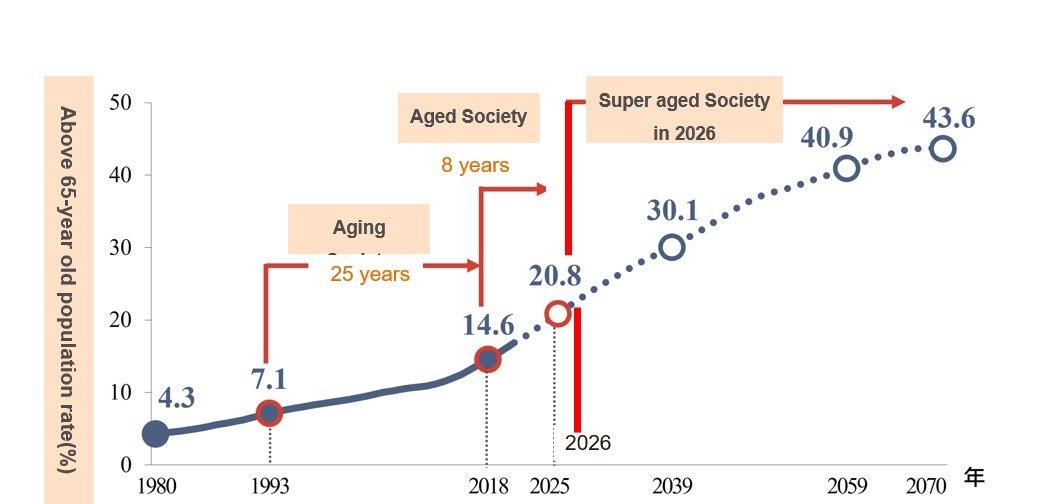
Taiwan has become an aged society in 2018

3
Rapid growth of aging population

Expected trend in aging in the major regions of Asia in 2000-2050, compared to the experience of Europe and North America in 1950-2000
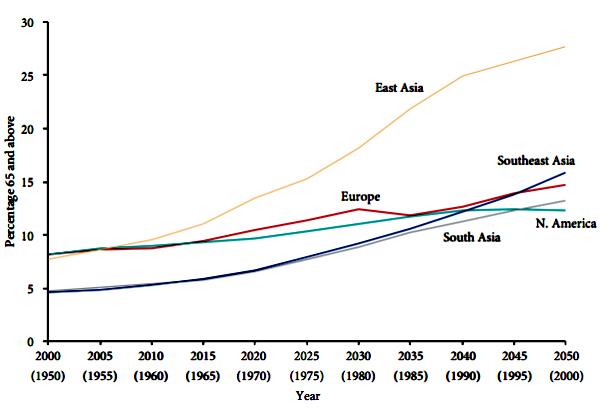
Percentage 65 and above
4
for the Development of Aged and Long term Care in Taiwan

• The expansion of the average life
• Changes of Family and Community structure
→ Decreasing number per household, Increasing numbers of women in job market
• The elderly population ↑
→ Proportion of chronic diseases & disabilities populations ↑
→ Needs for medical services and long-term care ↑
→ Urbanization of community, decreasing in community supports
• The social movement of 「 Aging in Place
• Paradigm of Aged Care has shifted
Significance
expectancy — 1961: 62.3 y/o, : 66.8 y/o — 2021: 77.67 y/o, : 84.25 y/o
」
5
Considerations for Future Aged Care
Next generation more educated
Better planning
More quality of life, healthy living
Prevention focused
Longevity

Early retirement
No prolong life, advanced directive
Less prolong institutionalization, assisted death
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
6
Aging in Place has become the Mainstream for Aged care
Elderly people, including those in need of care and support, should, wherever possible, be enable to continue living in their own homes, and that, where this is not possible, they should be enable to live in a sheltered and supportive environment that is as close to their community as possible, in both the social and geographical senses. (OECD, 1994)

7
Vision
Building a Healthy, Happy, Vital, and Friendly Aging Society.
• Extend health life expectancy.
• Improve the quality of life.
• Propose life without obstacles.
• Diminish discrimination
Strengthen support network














Promote generations harmony.
Aged society
Healthy Happy Vital Friendly
• Encourage diverse social participation
• Enhance self-esteem
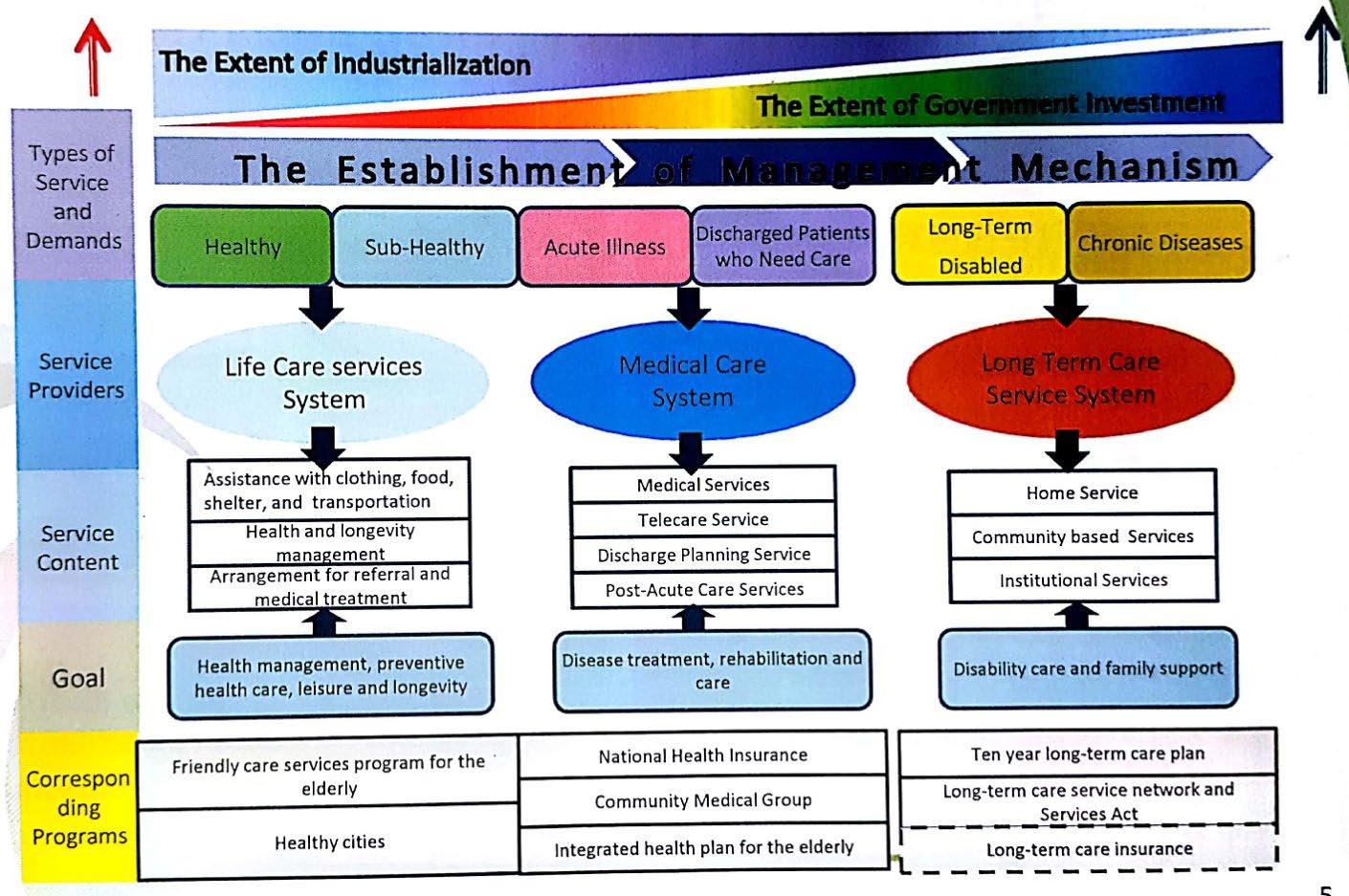
The demands of the Elderly and related policies and Services

The Establishment of management Mechanism
Active and Healthy Ageing
-Four Key Components
Healthcare Redesign
–
Disease management and preventive services.
–
Age-friendly health services.
Healthier Community
–

Community health promotion for older persons.
– Towards an age-friendly society.
•
•


11 2015
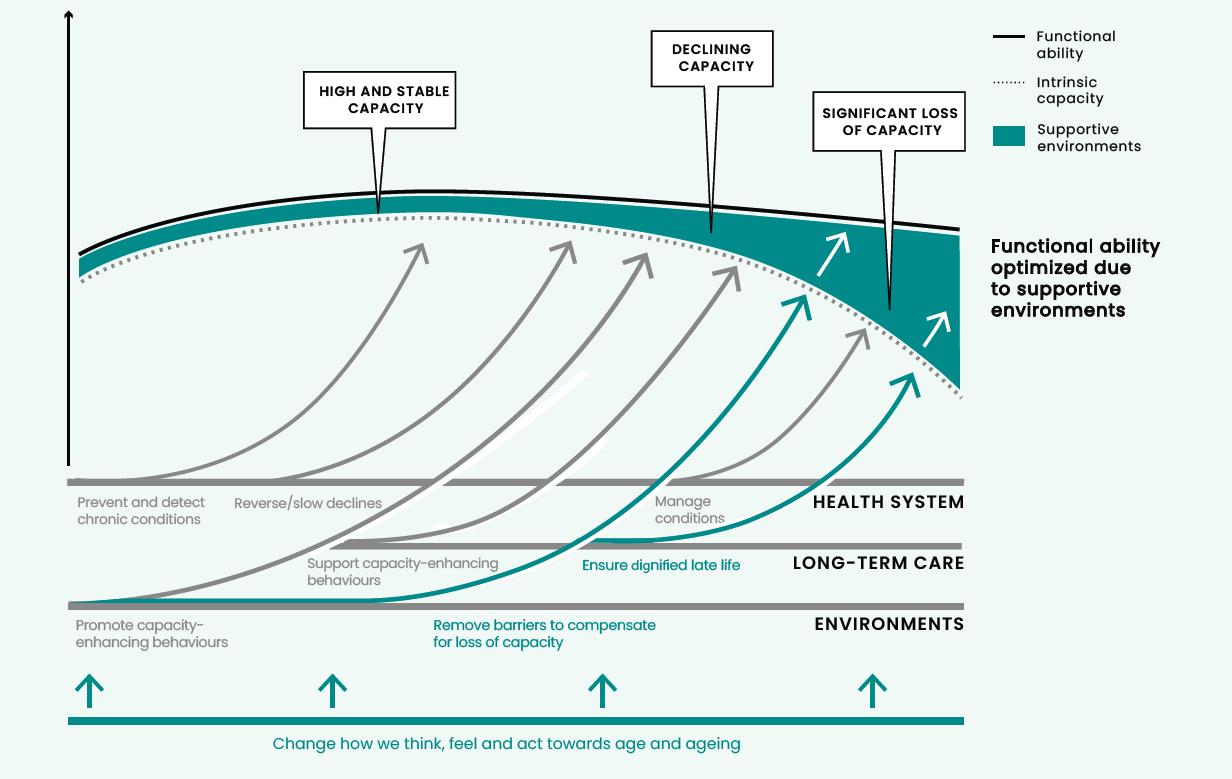
A public-health framework for Healthy Ageing
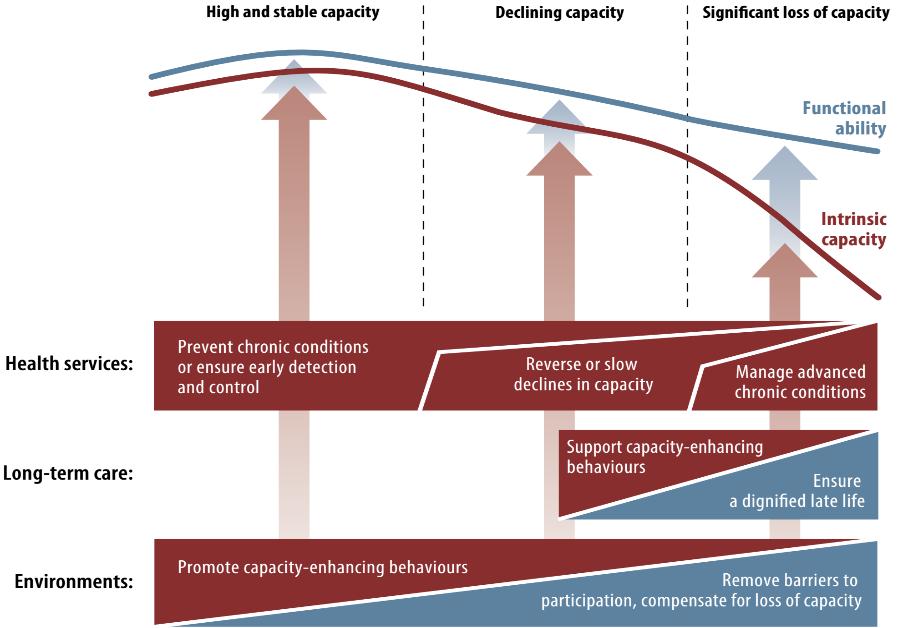

12
Healthy Aging is an important Public Health Issue

*Source: WHO (2021). Framework for countries to achieve an integrated continuum of long-term care.
13
Towards an age-friendly society: Policy guidance & system design – WHO's action
Active Ageing- a policy framework, 2002.


Global Agefriendly City: A Guide, 2007.


14
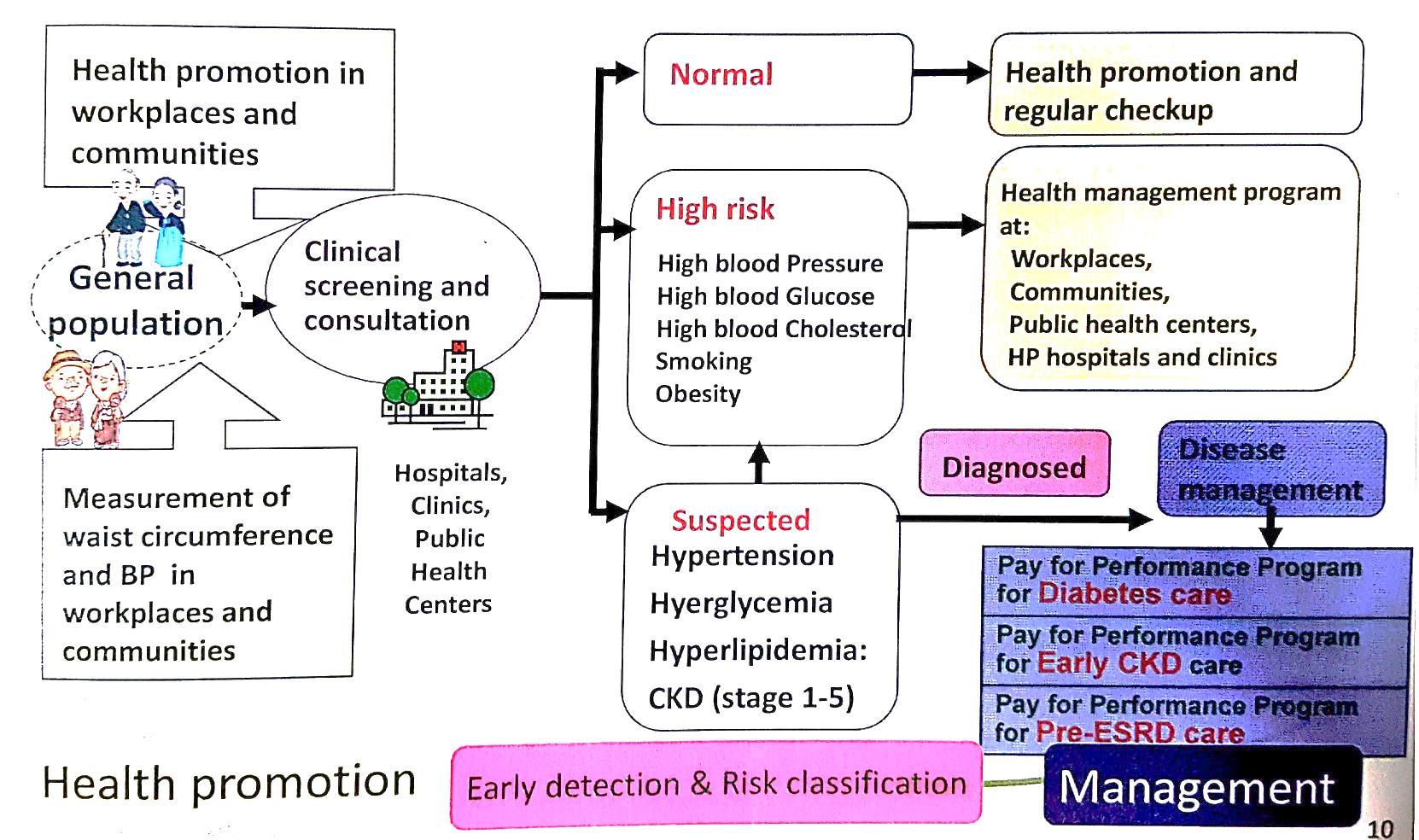
Coordinated Care for Chronic Conditions
Harmonizing Health promotion, Early detection, Risk management and Disease management.

Framework of Ageing-friendly Hospitals and Health services
Taiwan’s framework of age-friendly hospitals and health services

– Developed based on:
• WHO age-friendly principles

• WHO standards of health promoting hospitals
– World’s first government-driven, nationwide Age-Friendly Hospitals and Health Services recognition – Year 2023: 888 healthcare organizations got recognition
•
Health promotion strategies for the elderly
-The examples of community care center
• {Health Bureaus, health centers}+{Hospitals, clinics}
+{Community resources}+{Social welfare network] cooperation
Priority topics in health issues

Health service Medical service Community Social welfare
activity 5.Smoking cessation
prevention 6.Mental health promotion
participation
health
1.Physical
2.Falls
3.Nutrition 7.Social
4.Oral
8.Screening
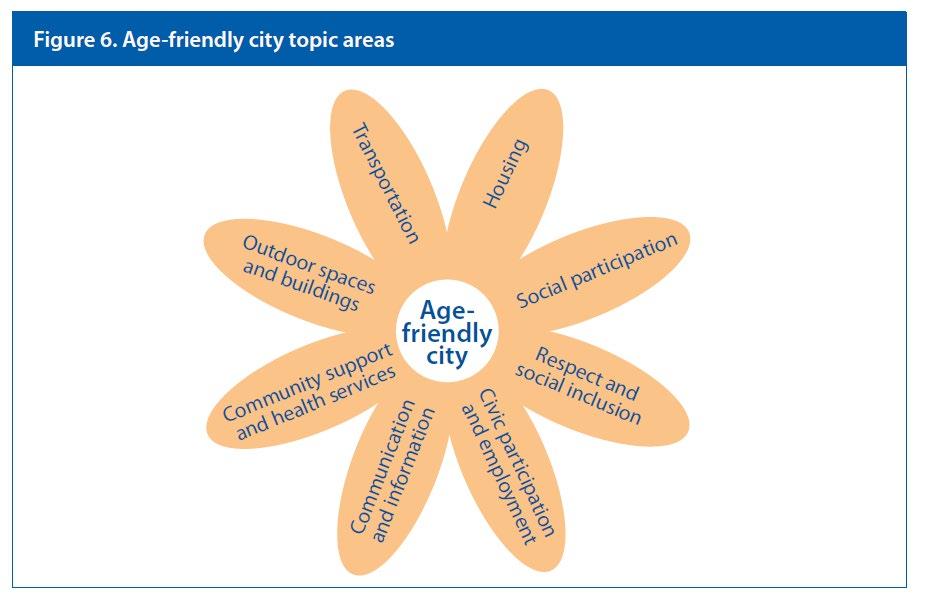
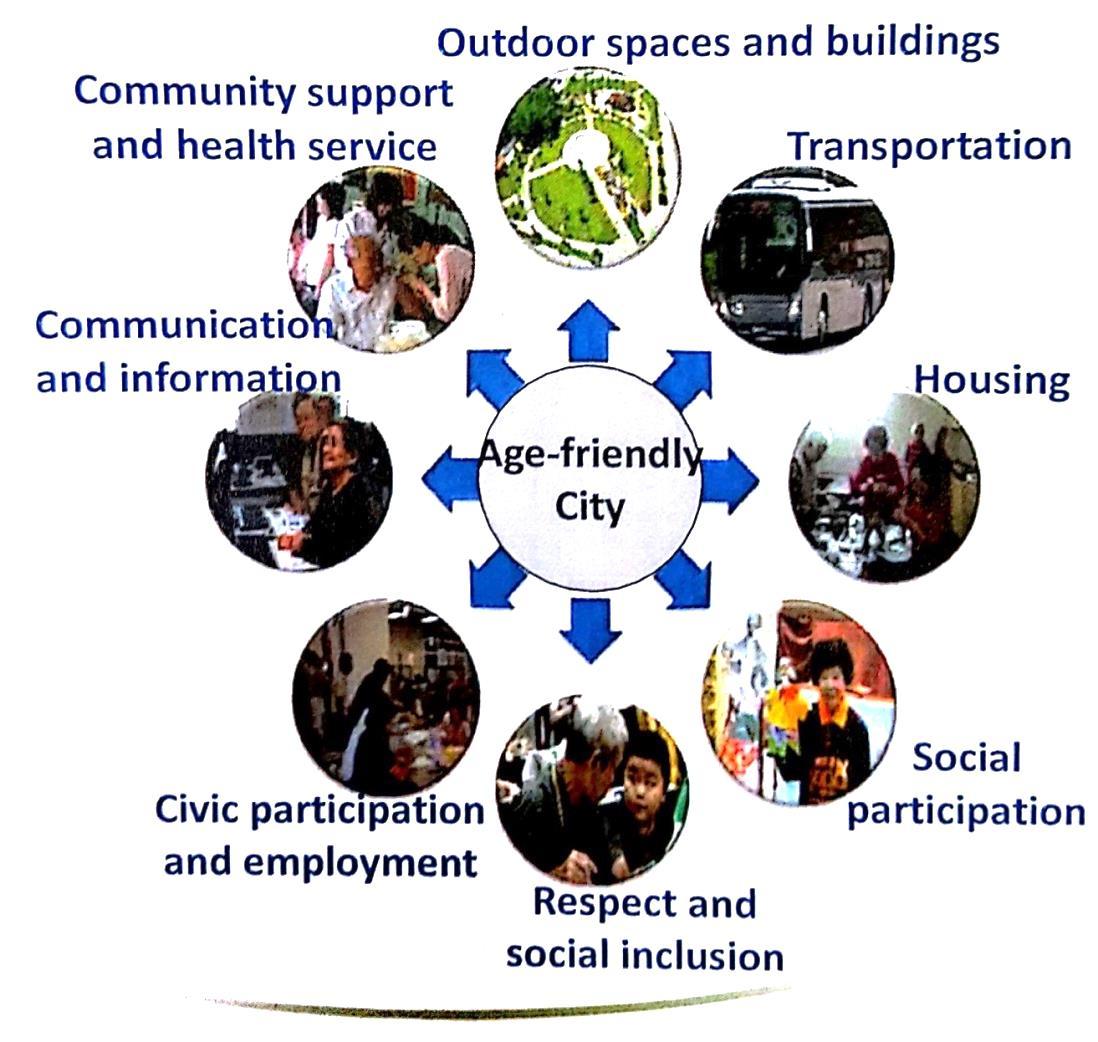
WHO-Age Friendly Cities( 8 dimensions)
An age-friendly city(AFC)

– An inclusive and accessible urban environment that promotes active Ageing.(WHO, 2007)
– Collaboration, coalition & partnership between central and local government and across sectors.
•
Age-friendly Cities Project

In 2010: 1 pilot city
In 2013: – All 22 counties/cities in Taiwan joined Age-Friendly Cities & Signed the WHO Age-friendly Cities ”Dublin
Declaration” – First around the world.

•
•
Needs for medical services and long-term care

Year >65Y/O 65-74 Y/O >75Y/O Needs for LTC 1/14 75-84(1/5),>85(1/2) N (thousand) % N (thousand) % N (thousand) % 2008 2,397 10.4 1,365 57.0 1,032 43.1 2018 3,480 14.7 2,028 58.3 1,452 41.7 2028 5,361 22.5 3,147 58.7 2,215 41.3 2056 7,616 37.5 3,069 40.3 4,547 59.7 資料來源:行政院經建會,中華民國台灣97至145年人口推計,97年9月。 註:本表內數據為中推計
20
The














Family Burden of Supporting the Elderly in the Super-aged
Increased Social Support Burden
The burden on young people will increase from 1:5 in 2018 to 1:2 in 2040 (i.e. an average of 1 elderly person for every 2 young people).
Changed Living Patterns
Increased potential of living in residential institutions
Decreased three generation families, and increased stem families
Decreased intention of living with children and increased intention of living with the spouse alone
Nearly 30% of elderly population is living alone or cohabiting only with spouses。

資料來源:衛生福利部
107年老人狀況調查報告
21
What is Long Term Care?
• Long-term care (LTC) is a variety of services which help meet both the medical and non-medical needs of people with a chronic illness or disability who cannot care for themselves for long periods of time.
• Long-term care can be provided at home, in the community, in assisted living facilities or in nursing homes. Long-term care may be needed by people of any age, although it is a more common need for senior citizens

22
Evolution of Long-term Care
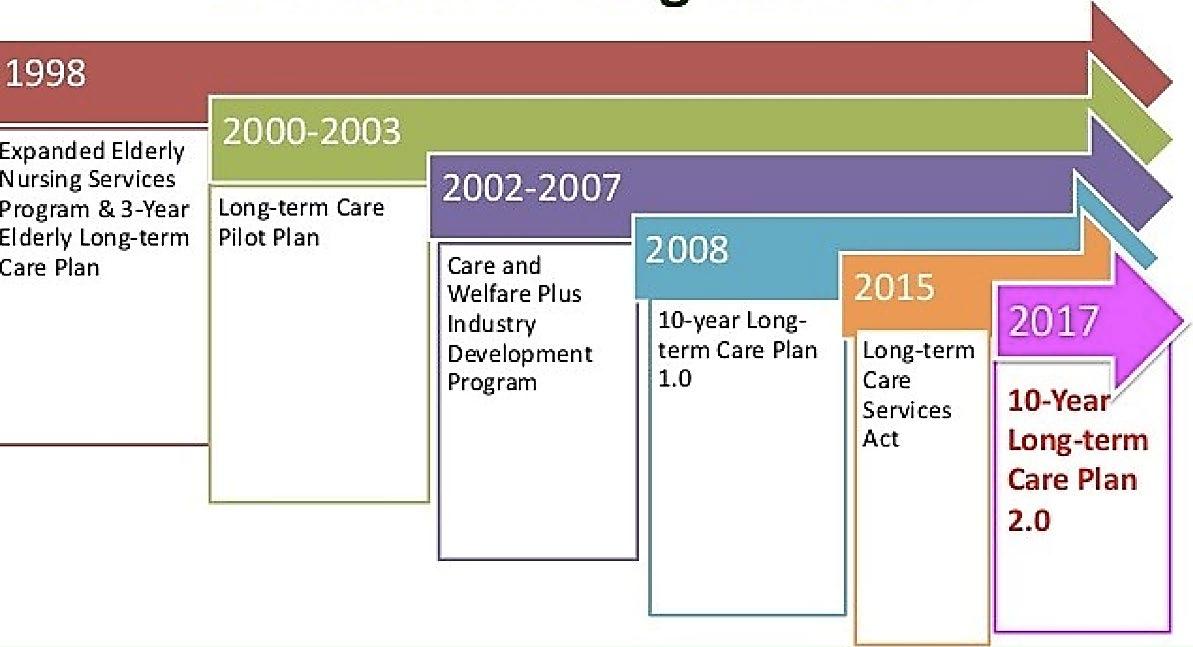

23
Long-term Disabled












Assessment
Care
Management
Long-term care plan – single entrance Consulting
Referral
Management LTC
Center
24
Long-term care plan- a tax funded system
• Senior age above 65
• The indigenous aged above 55
Care services
Subjects Service
Home services
Day care
Family foster care
Assistive devices and home accessibility
Nutrition catering services for the elderly
Transportation services
Long-term care institution services
Rehabilitation
Home nursing
Respite care service
• The physically and mentally disabled aged above
• Seniors living alone.
LTC Management Center
Care manager
Base on
Assessment of disability
Multidimensional evaluation
Care plan and resources

integration
































Tracking and quality control
Establish co-payment mechanism
25
Goals of LTC 2.0
Building a 3A Community-based Model for Aged Society
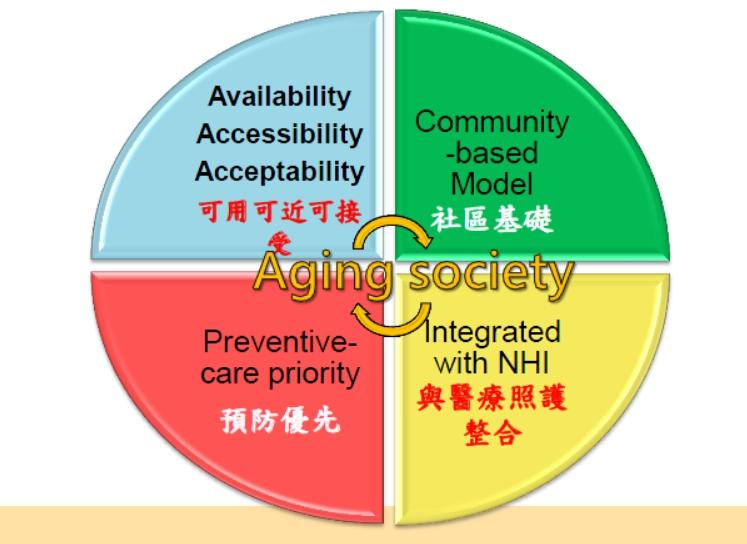
Preventive oriented
Integrated with health care

•
•
•
26
Comprehensive Community Care System for Long Term Care

Home Visits Phone Call Meal Services Health Improvement • Home service • Food service • Assistive tools services and Rent • Improve home care barrier-free environment • Home nursing care • Home rehabilitation care • Home respite care • Day care • Family support service • Transportation service • Community rehabilitation service • Institutional respite care • Long-term care institution • Care facility • Dementia care institution • Nursing home Home Care Community care Institutional Care Community care center Formal Care Resources Primary Prevention Long-term care Management Center 27
Holistic Community Care Model
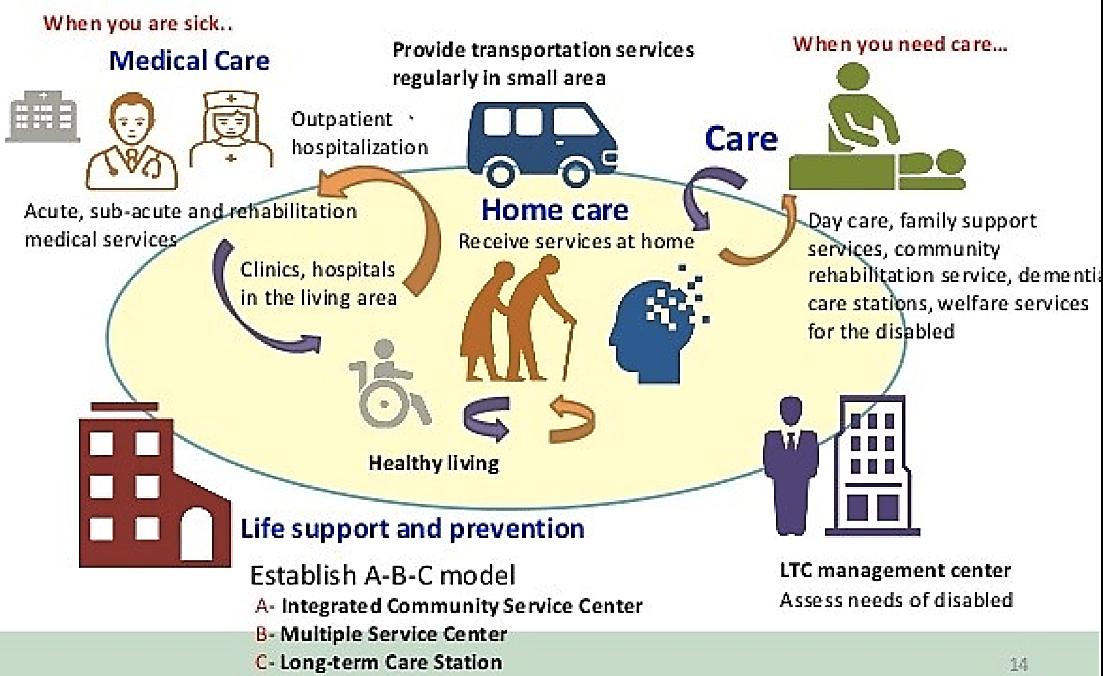

28
Integrate health care and long-term care service
1. Discharge program
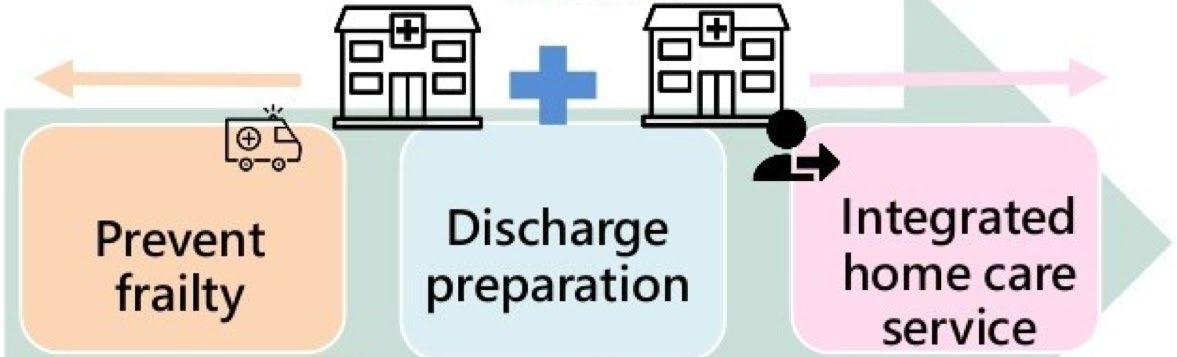

2. Evaluate case needs
1. Basic home care
2. Severe home care
3. At-home hospice
1. Muscle strengthening exercise
2. Life rehabilitation training
3. Social participation
4. Oral health
5. Nutrition and diet
6. Knowledge promotion
3. Assist in the referral of NHI family physician with integrated care program in the community
29
Strategy-Strengthen governance and accountability: Long-Term Care Services Act
LTC Services
Home-based, communitybased, residential institutionbased, family caregivers
LTC Systems

LTC network, subsidies, limitations for improper expansion
Announced in 2017
Comprehensive LTC network Integration & better quality
Personnel management Training, ContinuousCertification, Education Program
Institutional management
Dignity and rights of caregivers & care receivers
LTC payment
Regulations, registrations, audit & assessment
Accountability, support network, caregiver training
Provide Care & Professional services, Respite services, Auxiliary appliance service and home accessibility improvement services, Transportation services
30 30

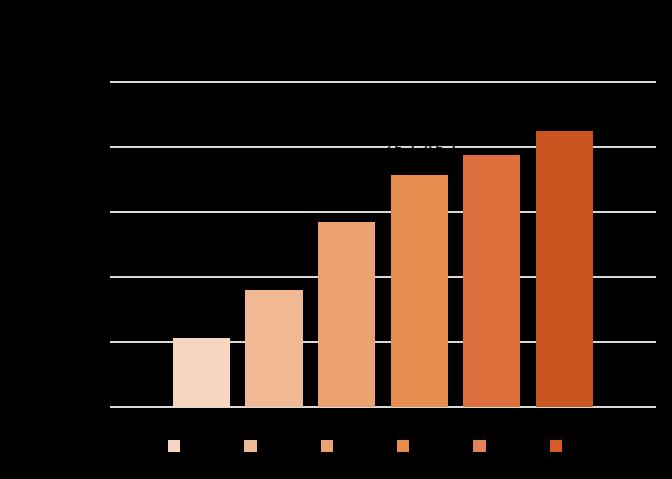


31 Strategy-Payments and benefits system & Utilization Service items Care & Professional services Transportation services Auxiliary appliance service and home accessibility improvement services Respite services *2021.10~2022.09: Coverage rate of LTC services is 68.34%. Utilization of the LTC services Unit: persons • Home service • Day care • Family care • Professional service
Strategy-Community-based integrated care service network
Community-based integrated care service network
1 School district 1 Daycare center
• Community life circles
• Daycare centers in every junior high school district
• ~2022.09: 668 school districts (target completion rate: 82.1%).
1 Township 1 Residential LTC institution
• Reduce disparities between urban and rural areas
• Affordable Residential LTC institutions

~Sep. 2022: 679A-7,240B-3,741C, 11660 in total
A (community integrated service centers): increases 8.5 times.
B (combined service centers) increases 36.4 times.
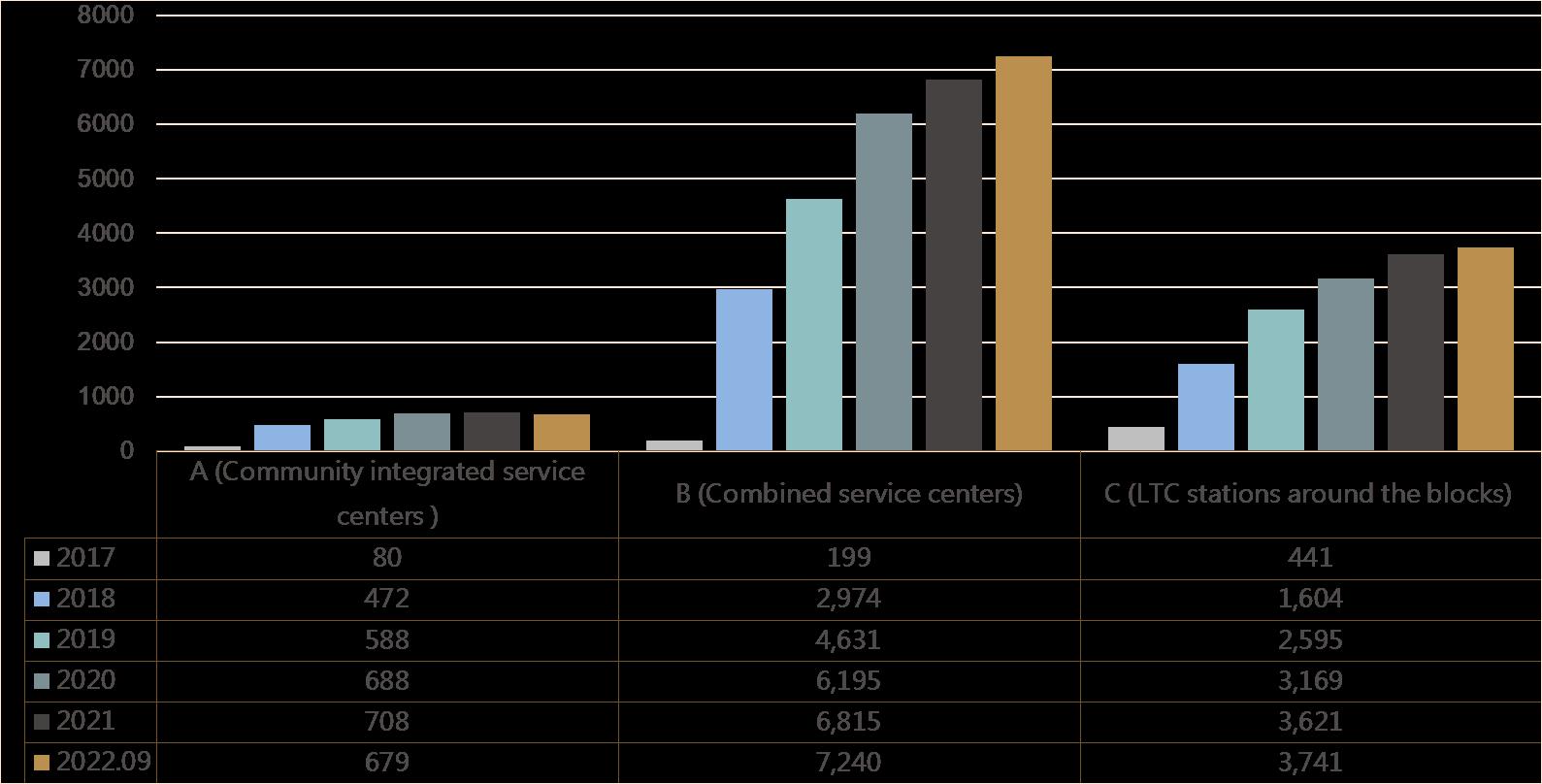
C (LTC stations around the blocks ) increases 8.5 times.
• ~2022.09: 296 townships(target completion rate: 80.4%).
32 32
Strategy-Family caregivers supportive & innovative plan
Purposes
•
To ease the family care burden, improve family care quality, and develop suitable services in different places.
Services
Individualized services High burden family caregiver case management, home-based care skills training, (psychological) counseling…
Group services
Innovative services
Supportive groups, long-term care courses & skill training, companions…
Organized by local governments, giving innovative ideas to support family caregivers.

33
Difficult to say goodbye 說再見 不容易



34



35
Patient Right to Autonomy Act




36
In the future : Age-friendly city + Dementia friendly city + Compassionate city







37
Significant needs for aging care
The demands of the Elderly and related policies and Services

Aged and Long term care services
Roles of nurses in escalating the health, well-being & overall quality of life older adults with disability
Outline
•
•
•
•
38
of the Presentation
Three components of the Elderly Care
Living care (Social Care)
Acute illness care (Acute Medical Care)
Disability care (Long-term Care)

39
–
The Care Model for the sick elderly
Bicycle Type

The sick elderly (such as: hypertension, diabetes), not only need for life care, also need support for National Health Insurance, such as out-patient and hospitalization in acute medical care settings.
–
The settings for care including: clinics, hospitals, intermediate care facilities and rehabilitation institutions.
Social Care Acute Care
Care 40
Long-Term
The Care Model for the disable elderly
Large chain-type
Elderly people suffering from serious chronic diseases, loss of function to a certain extent, they will need living care, acute medical and long-term care, all three are equally important and must be coordinated division of labor, so that the elderly can be provided with continuity, integrity of care, but also can prevent them from stranded in the acute medical settings.

─
41
Care Social Care Acute Care
Long-Term
The Care Model for the healthy elderly
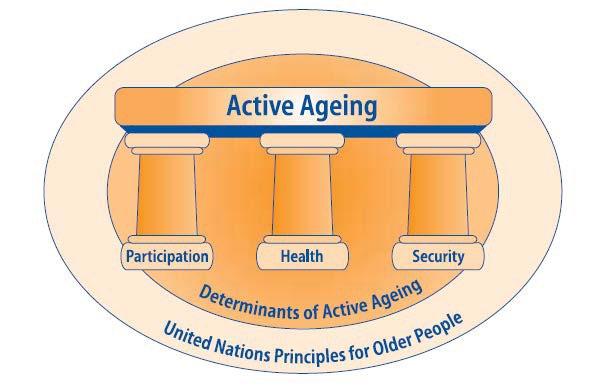
Mickey Mouse-type
Primary care for the active, elderly, and occasionally need emergency medical care and long term care services.
• The main focus of the National Pension Service, the elderly apartments, activities and cultural and recreational facilities for the elderly in-home services

•
42
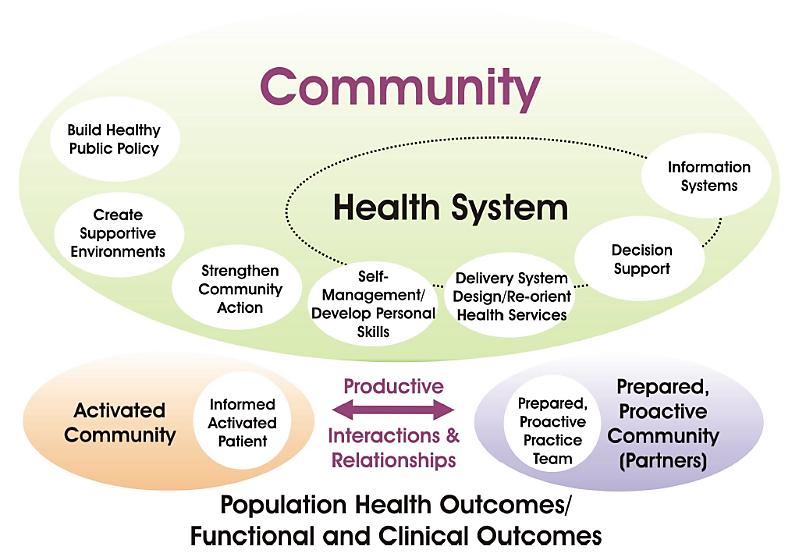
Chronic care model


43
1. Assessment





Function of Public Health
2. Policy development
3. Assurance
44
Assessment

Number of people with needs for care, health status of older adults with disabilities
Social and environmental factors influencing the health of older adults with disabilities
Responsiveness of health care systems to older adults with disabilities
Used of health care services by older adults with disabilities
Need, both met and unmet, for care
.
45
Policy Development

Assess existing policies, systems, and services, including an analysis of the needs, experiences, and views of older adults with disabilities, identify gaps and priorities to reduce health inequalities and plan improvements for access and inclusion.
Make required changes in policies, systems, and services to comply with the convention on the rights of persons with disabilities (CRPD).
Establish health care standards related to care of older adults with disabilities and frameworks and enforcement mechanisms to ensure standards are met.
Involve older adults with disabilities in audits and related development and implementation of policies and services.
46
Assurance

Ensure that older adults with disabilities benefit equally from public health care programmers'.
In countries where private health insurance dominates health care financing, ensure that older adults with disabilities are not denied insurance and consider measures to make the premiums affordable for people with disabilities.
Use financial incentives to encourage health-care providers to make services accessible and provide comprehensive assessments, evidence-based treatment, and follow-ups.
Consider targeted conditional cash transfer schemes linked to the use of health care to improve affordability and the use of services.
Consider providing support to meet the indirect costs associated with accessing health care, such as transport.
47
Conclusion
The elderly care needs with the increasing aging society is a global issue, Taiwan has no exception

The prolong of average life expectancy, improvement of public health and enhance of the living standard, and the surge of the elderly population, so that the burden of care has been increasing heavily
The need for services, education, research and policy for resource allocation has evolved The great opportunities for roles expansion
48
Value of Nursing Everywhere As Needed

Each stage of life need nursing services Business opportunities
6 y/o 20 y/o 45 y/o 65 y/o Acute medical care Follow -up care Long-term care Pregnancy Death Prenatal care Infant and child care School health Family health Occupational disease prevention Chronic disease prevention and control Middle-aged health care Elderly care Nursing homes care Terminal care 49
Thank you

50















































































































