SCIENCE
GRADE
ALIGNED WITH LATEST CBSE PATTERNS & GUIDELINES






































































SCIENCE – Code no. 086
CBSE ISSUED SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER
CLASS – X (2025-26)
Max. Marks: 80 Time Allowed: 3 hours
General Instructions:
(i) This question paper consists of 39 questions in 3 sections. Section A is Biology, Section B is Chemistry and Section C is Physics.
(ii) All questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice is provided in some questions. A student is expected to attempt only one of these questions.
Section – A
1 Select the group in which all organisms have the same mode of nutrition.
A. Cuscuta, yeast, legumes, leeches and tapeworm
B. Cactus, ticks, lice, leeches and cow
C. Cuscuta, ticks, lice, leeches and tapeworm
Marks
D. Cactus, grass, lice, lion and tapeworm 1
2 Which of the following options indicates the products formed after breakdown of the glucose in our muscle cells when there is lack of oxygen?
A. Ethanol + carbon dioxide + Energy
B. Lactic acid + Energy
C. Lactic acid + carbon monoxide + Energy
D. Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy 1
3 Which of the following is a correct combination of function and part of the brain?
A. Posture and balance: Cerebrum
B. Salivation: Medulla in midbrain
C. Hunger: Pons in hindbrain
D. Blood pressure: Medulla in hindbrain 1
4 The blood glucose level in a patient was very high. It may be due to inadequate secretion of:
A. growth hormone from pituitary gland
B. oestrogen from ovary
C. insulin from pituitary gland
D. insulin from pancreas 1
5 In a cross between black furred rabbit (B) and white furred rabbit (b), all offspring were found to have black fur. What can be inferred about the genetic makeup of the parent rabbits?
A. BB X bb
B. Bb X Bb
C. Bb X bb
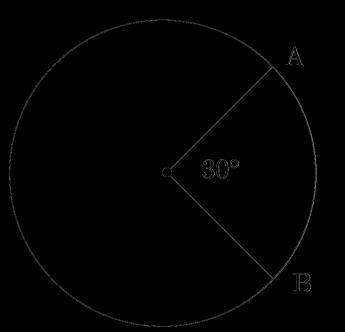
D. bb X bb
6 Which are the correct statements related to ozone?
(i) Ozone layer helps in increasing the UV radiations reaching earth.
(ii) Ozone is a deadly poison.
(iii) Ozone layer shields the earth from UV radiations.
(iv) Ozone layer prevents UV rays which cause skin cancer.
(v) Ozone is formed with the help of Chloroflurocarbons.
A. (i), (ii), (iii)
B. (ii), (iii), (iv)
C. (iii), (iv), (v)
D. (i), (iv), (v)
7 Which of the following human activities has resulted in an increase of nonbiodegradable substances?
A. Organic farming
B. Increase in tree plantation
C. Use of plastic as packaging material
D. Composting of kitchen waste 1
The following two questions consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true but R is false.
D. A is false but R is true
8 Assertion (A): Tallness of a pea plant is controlled by an enzyme. Reason (R): The gene for that enzyme makes proteins which help the plant to be tall. 1
9 Assertion (A): Vulture will always have the least amount of pesticides in a food chain.
Reason (R): Vulture occupies the last trophic level and it gets only 10% of energy of the previous trophic level. 1
10 Unlike animals, plants do not have any excretory products as they do not eat food. Comment upon the statement with justification. 2
11 Students to attempt either option A or B.
A. How many chambers are there in the heart of the following organisms? How is mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood prevented in their body?
(i) Fishes
(ii) Humans OR
B. Explain the mechanism by which the water is transported in plants? 2
12 About 100 acres of forest land was declared as Natural reserve park. The following organisms were predominant in the Natural reserve park: 2
rabbit, frog, grass, fish, fox, water insects, zebra, peacock, snake, trees, bird, owl, insects, tiger, vulture, duck.
Create a food web comprising two separate food chains with different producers by using the above data.
13 Draw and explain how the nerve cells help in transmission of impulses? 3
14 In a genetic experiment, plants with pure round green seeds (RRyy) were crossed with plants with wrinkled yellow seeds (rrYY).
(i) Show the gametes formed when F1 was self-pollinated.
(ii) A total of 144 seeds were produced which developed into saplings. Show the ratio in which these traits are independently inherited in these144 sapling. 3
15 Neha consumed boiled sweet potatoes and boiled eggs for breakfast. Help her to understand some steps in the process of digestion of the food taken by her by answering the questions given below.
Attempt either subpart A or B.
A. Which of these food items is rich in proteins? In which part of the alimentary canal is the digestion of this component initiated? Name the enzymes, conditions required and the glands associated with the digestion here.
OR
B. Which of these food items contains fats? How is it digested?
C. Which of these food items is rich in starch? How is its digestion initiated?
D. The figure given below represents parts of the human alimentary canal. Which of these parts will have the maximum amount of digested food as soon as the process of digestion is completed?
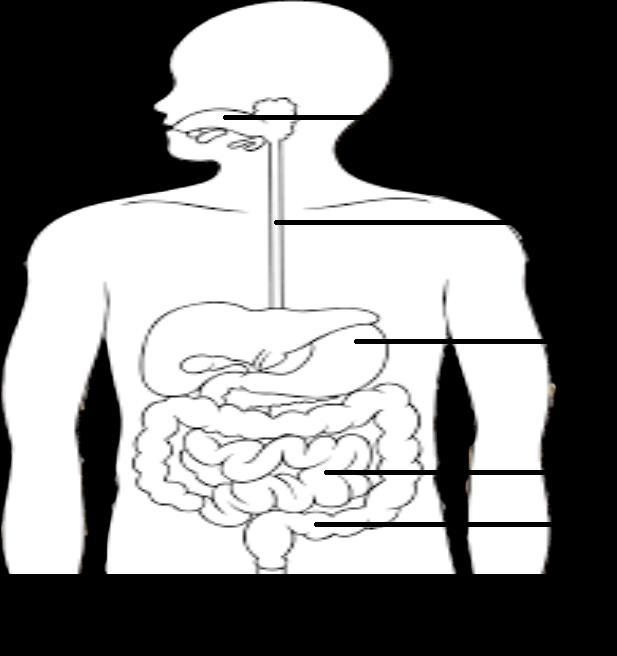
4
For visually impaired students
D. How will the digested food be taken up by the alimentary canal?
16 Attempt either option A or B.
A. Puneet wanted to grow banana plants.
(i) Based on your knowledge on plant reproduction should he opt for seeds or any alternate method of reproduction. Justify your answer.
(ii) Offsprings of a banana plant usually show very little variation. What causes variation and are variations good or bad? Justify. OR
B. Annie was conducting research on the number of fruits produced by watermelon under different conditions. She grew 25 watermelon plants each in both glass house A and B. She introduced pollinators in glass house A only.
(i) What difference will she observe in the number of fruits produced in the two glass houses? Explain with reason.
(ii) List 3 changes that will occur in a flower once it gets fertilized.
Section – B
17 Which of the following equations represent redox reactions and what are the values for ‘p’ and ‘q’ in these equations?
Equation 1: Fe2O3(s) + 2Al(s) Al2O3 (s) + p Fe(l) + heat
Equation 2: 2C4H10(g) + 13O2(g) △ 8CO2(g)+ q H2O(g)
A. Only equation 1 is a redox reaction, p =1 and q=3
B. Both equations 1 and 2 are redox reactions, p= 2 and q=4
C. Only equation 2 is a redox reaction, p= 2 and q= 10
D. Both equations 1 and 2 are redox reactions, p= 2 and q=10
18 Four statements about the reactions of oxides with dilute hydrochloric acid and aqueous sodium hydroxide are listed.
I. Aluminium oxide reacts with both dilute hydrochloric acid and aqueous sodium hydroxide.
II. Calcium oxide reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid and aqueous sodium hydroxide.
III. Zinc oxide reacts with both dilute hydrochloric acid and aqueous sodium hydroxide
IV. Sulphur dioxide does not react with either dilute hydrochloric acid or aqueous sodium hydroxide. Which statements are correct?
A. I and II
B. I and III
C. II and IV
D. III and IV 1
19 An iron nail is added to each of the two test tubes ‘P’ and ‘Q’ containing aqueous copper (II) sulphate, and aqueous silver nitrate respectively. Which of the following observation is correct?
A. In test tube ‘P’ iron nail is coated with a blue coating and in test tube ‘Q’ there is no reaction.
B. Iron nail is coated with a brown coating in test tube ‘P’ and silver coating in test tube ‘Q’.
C. There is no reaction in either of the test tubes ‘P’ or ‘Q’.
D. There is no reaction in test tube ‘P’ but a silver coating on iron nail is seen in test tube ‘Q’.
20 Methyl orange is added to dilute hydrochloric acid and to aqueous sodium hydroxide. What is the colour of the methyl orange in each solution?
21 Which of the following substances when dissolved in equal volume of water, will have the highest pH value?
A. Sulphuric acid
B. Acetic acid
C. Magnesium hydroxide
D. Sodium hydroxide
22 When excess of carbon dioxide is passed through lime water, the milkiness disappears because
A. water soluble calcium carbonate converts to water soluble calcium bicarbonate.
B. insoluble calcium carbonate converts to water soluble calcium bicarbonate.
C. water soluble calcium carbonate converts to insoluble calcium bicarbonate.
D. insoluble calcium carbonate converts to insoluble calcium bicarbonate.
23 In the reaction of aqueous solution of barium chloride with aqueous solution of sodium sulphate, the aqueous solution formed will be:
A. BaCl2
B. BaSO4
C. Na2SO4
D. NaCl
The following question consists of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true but R is false.
D. A is false but R is true
24 Assertion (A): C4H8, C4H6 and C4H10 are members of the same homologous series
Reason (R): C4H8, C4H6, C3H4, C3H6, C2H4, C2H2 are unsaturated hydrocarbons. 1
25 The following activity is set-up in the science lab by the teacher. He clamped an aluminium wire on a stand and fixed a pin to the free end of the wire using wax. Then he heated the wire with a burner from the end where the wire is clamped. Students observed the pin fall off.
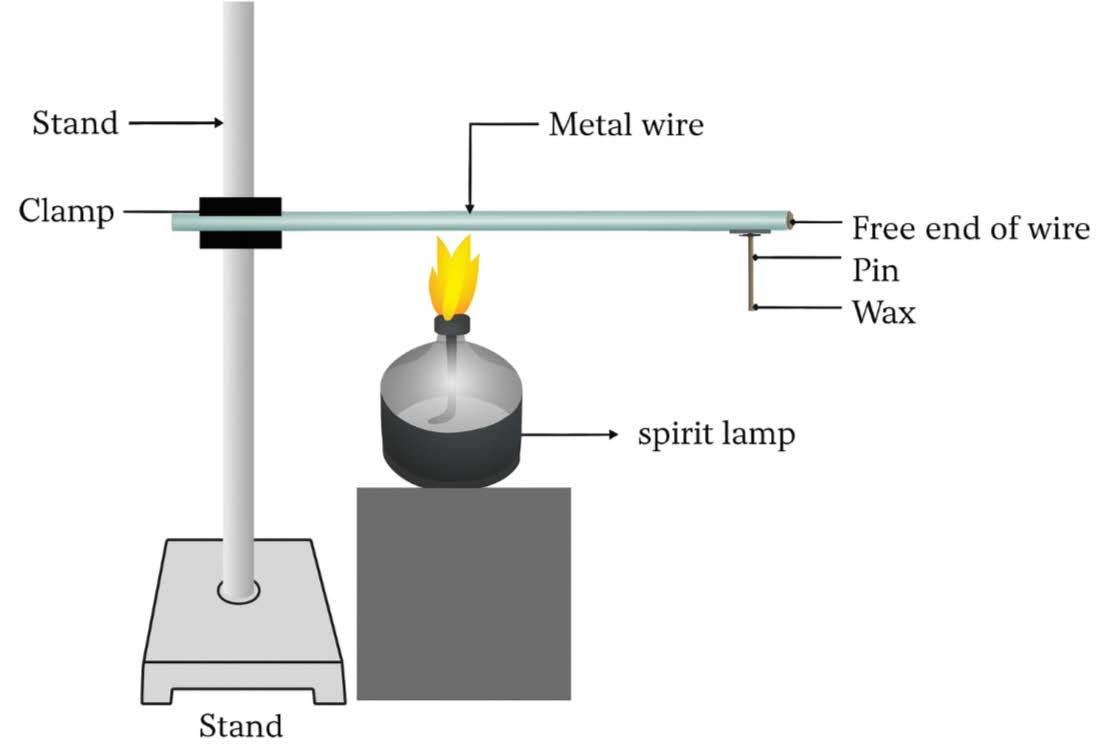
A. If the teacher replaces aluminium wire by silver wire, will the students’ observation change? Justify your answer.
B. Will the aluminium wire melt? Give reason for your answer. 2
26 Attempt either option A or B.
A. An element ‘X’ is stored in kerosene, and cannot be extracted from its ore using a reducing agent. ‘X’ forms an ionic compound on reaction with chlorine.
(i) Can we store ‘X’ in water? Give reason to support your answer.
(ii) Identify element ‘X’. Name the process used and write the equation for extraction of ‘X’ from its ore. OR
B. The domes of many building in Europe are made of copper. These domes now appear greenish in colour.
(i) Why do the domes appear greenish though copper is orange-red in colour?
(ii) In your opinion, should the copper domes be replaced by iron domes to overcome the problem of change of colour of copper domes?
(iii)Domes used to be made from thin sheets of metals. Why did the ancient architects use copper to make domes?
3
27 Amrita electrolysed distilled water using the set-up shown in figure 1. She was expecting two gases to be evolved at the anode and cathode respectively 3
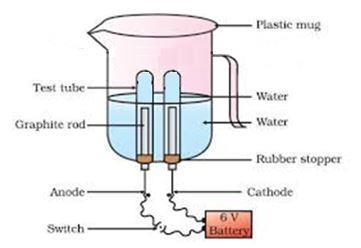
Fig.1
Suddenly, she realised that the bulb in the circuit did not glow when she used distilled water (figure 2)
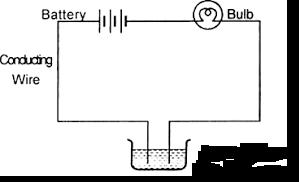
Fig. 2
After this realization, she added a substance to the distilled water for electrolysis to take place.
Answer the following questions based on the information given above:
A. Which gas was she expecting to be formed at the anode and which one at the cathode respectively?
B. Why did the bulb not glow when Amrita passed electricity through distilled water?
C. Which substance was added by Amrita to distilled water to get the expected result?
For visually impaired students
Identify the type of reaction:
A. ZnO + C Zn + CO
B. ZnCO3 heat ZnO + CO2
C. 2Mg + O2 2 MgO + heat
28 Sara took 2 mL of dilute NaOH solution in a test tube and added two drops of phenolphthalein solution to it. The solution turned pink in colour. She added dilute H2SO4 to the above solution drop by drop until the solution in the test tube became colourless. 40 drops of dilute H2SO4 were used for the change in 4
colour from pink to colourless. When Sara added a drop of NaOH to the solution, the colour changed to back to pink again.
Sara now tried the activity with different volumes of NaOH and recorded her observation in the table given below:
Answer the following questions based on the above information:
A. If Sara used concentrated H2SO4 in place of dilute H2SO4, how many drops will be required for the change in colour to be observed?
(a) 40
(b) < 40
(c) >40
Justify your answer.
B. Sara measured 20 drops of dil H2SO4 and found its volume to be 1 mL. If Sara observed a change in colour of NaoH solution by using 3 mL of H2SO4, how many mL of NaOH did she add to the test tube initially? OR
Sara takes 10 drops of dilute H2SO4 in the test tube and adds two drops of phenolphthalein solution to it. Then she adds NaOH dropwise. Sara observes a change in colour after adding 20 drops of NaOH. What change in colour would she observe and why?
C. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction taking place in the above experiment. Which of the following is true and why? The reaction is a
(a) neutralisation and double displacement reaction
(b) neutralisation and precipitation reaction
(c) precipitation and double displacement reaction
(d) neutralisation, double displacement as well as precipitation reaction.
29 Attempt either option A or B.
A. A hydrocarbon with the formula CxHy undergoes complete combustion as shown in the following equation:
2CxHy + 9O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O.
(a) What are the values of ‘x’ and ‘y’?
(b) Give the chemical (IUPAC) name of the hydrocarbon.
(c) Draw its electron dot structure.
(d) Name the alcohol which on heating with conc. H2SO4 will produce the above hydrocarbon CxHy. 5
(e) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction of CxHy with hydrogen gas in presence of Nickel.
B. The electronic structures of atoms P and Q are shown below
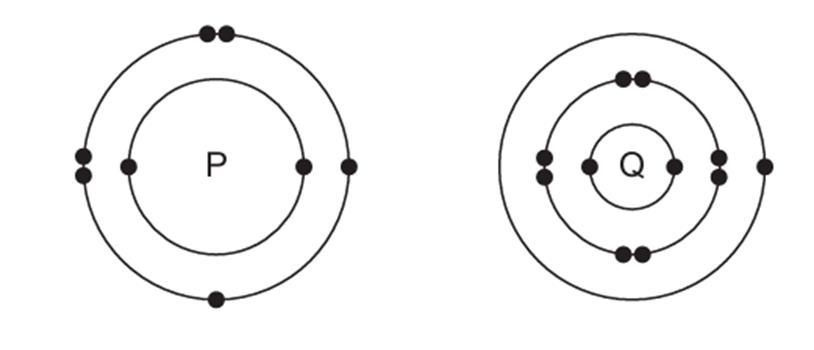
Based on the information given above, answer the following questions:
(a) If P and Q combine to form a compound, what type of bond is formed between them?
(b) Give the chemical formula of the compound formed.
(c) The compound so formed is dissolved in water. Is the resultant solution acidic or basic in nature? Justify your answer.
(d) Write the chemical equation for the reaction between ‘Q’ and ethanol.
(e) What will be the formula of the compound formed when ‘P’ undergoes bonding with carbon?
For visually impaired students
A. A hydrocarbon with the formula CxHy undergoes complete combustion as shown in the following equation:
2CxHy + 9O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O.
(a) What are the values of ‘x’ and ‘y’?
(b) Give the chemical (IUPAC) name of the hydrocarbon
(c) Is CxHy a saturated or an unsaturated hydrocarbon?
(d) Name the alcohol which on heating with conc. H2SO4 will produce the above hydrocarbon CxHy
(e) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction of CxHy with hydrogen gas in presence of Nickel.
B. Oxygen can combine with both metals and non-metals. It combines with Calcium to form CaO and with carbon to form CO2
(a) What type of bond is formed between carbon and oxygen?
(b) Identify the type of bond formed between Calcium and oxygen.
(c) Which of the above compounds will be a good conductor of electricity in molten state and why?
(d) Comment on the physical state (solid, liquid or gas) of CaO and CO2.
(e) What is the valency of carbon in CO2?
30 Arnav was making notes and he wrote down the following statements from his understanding of reflection from curved surfaces.
I. Concave mirrors can produce both real and virtual images depending on the position of the object.
II. Convex mirrors always produce real, inverted images regardless of the object’s position.
III. In both concave and convex mirrors, the image location can be determined using the mirror formula 1 �� = 1 �� + 1 �� where f is the focal length, v is the image distance, and u is the object distance. Choose from the following the correct option that lists the correct statements about reflection from curved surfaces.
A. I and II
B. I, II and III
C. II and III
D. I and III 1
31 Choose the correct option from the below which explains the reason for us to perceive the day sky as blue.
A. As sunlight passes through the atmosphere, shorter wavelengths, such as blue are scattered more than other colors.
B. The sky appears blue because all colors are scattered equally, but blue light is stronger and more visible to the human eye.
C. The blue color of the sky is due to longer wavelengths like red and orange scattering more than shorter wavelengths, making blue stand out more.
D. The atmosphere contains blue-colored particles that give the sky its blue appearance. 1
The following question consists of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true but R is false.
D. A is false but R is true
32 Assertion (A): A point object is placed at a distance of 26 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 26 cm. The image will not form at infinity.
Reason (R): For above given system the equation 1 �� = 1 �� + 1 �� gives v = ∞ 1
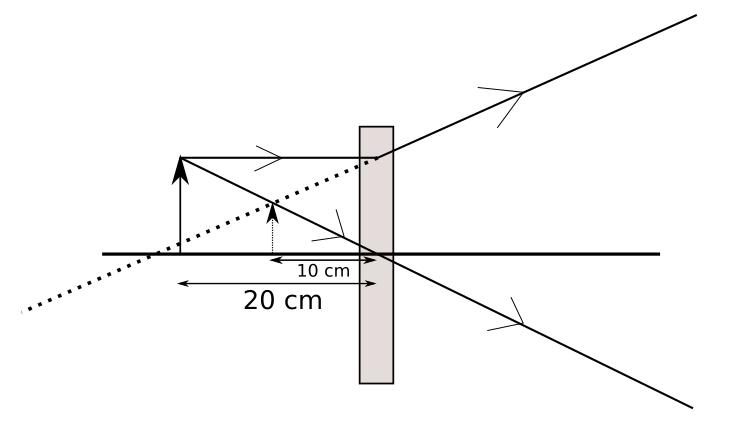
The above image shows the formation of an image with an optical instrument.
A. Identify the optical instrument (shown schematically as a rectangle) in the image.
B. What type of image is formed in this case?
C. Based on the measurements given in the image, calculate the focal length of the instrument.
For visually impaired students
A. Under what conditions can a convex lens form a virtual image?
B. Why does a piece of paper catch fire if we allow sunlight to pass through a convex lens onto the paper?
34 Attempt either option A or B.
A.
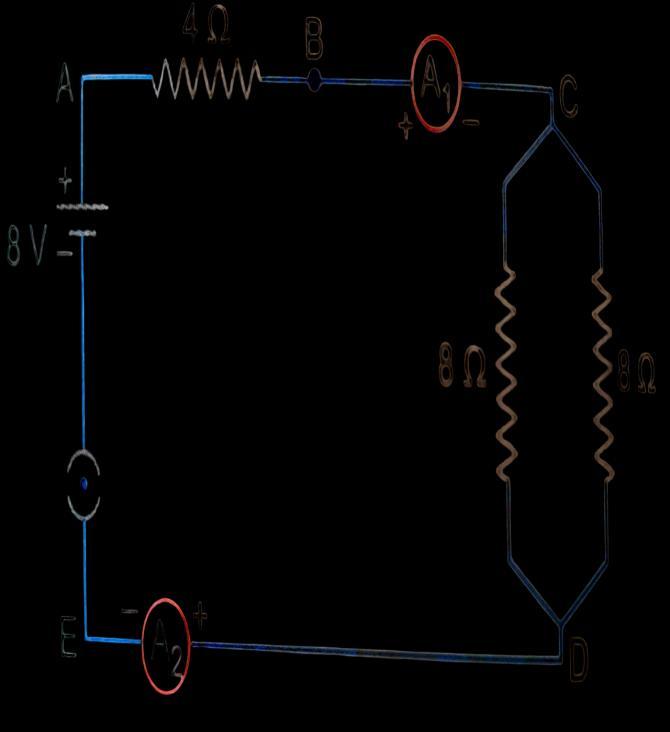
Find out the following in the electric circuit given in the figure(i) Effective resistance of two 8 ohm resistors in the combination. (ii) Current flowing through the 4-ohm resistor
B.
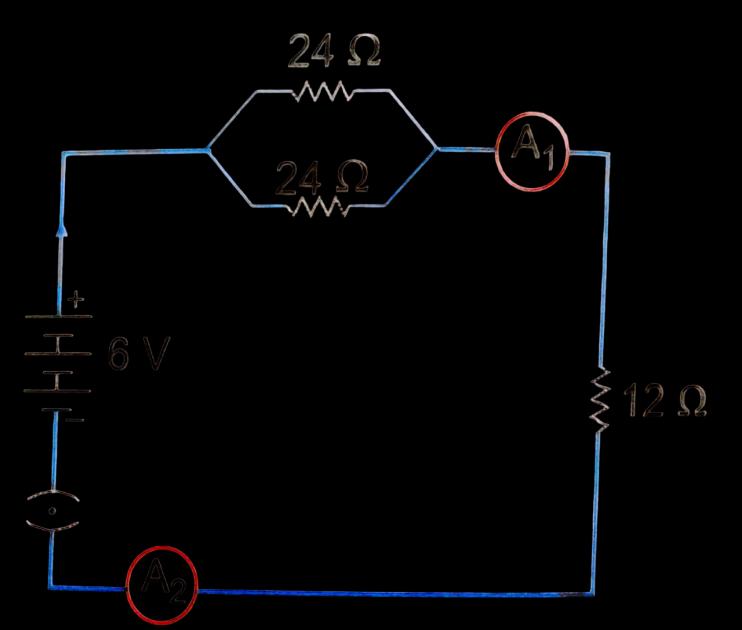
Study the circuit and find out-
(i) Current in 12 ohm resistor
(ii) Difference in the readings of ammeter A1 and A2 if any
For visually impaired students
A. You are given four resistors each having resistance of R ohm. Find the maximum and minimum resistance that can be made with these four resistors.
OR
B. A copper wire has a length L=2 m, a cross-sectional area A=0.5 mm2, and resistivity ρ=1.7×10 8 Ω-m. Calculate the resistance of another wire made of the same material whose length is twice the length of the wire but has the same cross-sectional area. 35
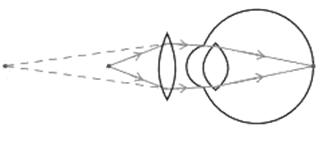
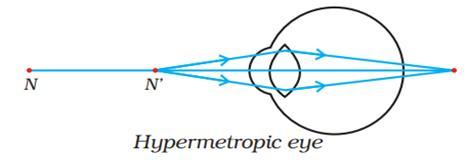
The above image shows a corrective measure for a particular defect of vision.
(i) Identify the defect of vision and state what kind of lens is used to correct this deficiency.
(ii) Draw and label a ray diagram that shows the defect of vision in the above case before correction.
For visually impaired students
(i) What is dispersion of light?
(ii) Explain the condition under which dispersion happens?
(iii) Give one reason that causes presbyopia.
36 A student needs to make a 0.12 Ω resistor. She has some copper wire of 0.80 mm diameter. Resistivity of copper is 1.8 × 10–8 Ωm
(i) Determine the cross-sectional area of the wire.
(ii) Calculate the length of wire required for the 0.12 Ω resistor. 3
37 Magnetic field lines are shown in the given diagram. A student makes a statement that the magnetic field at X is stronger than at Y.
(i) Explain with reason if the student’s claim is correct.
(ii) Also redraw the diagram and mark the direction of magnetic field lines.


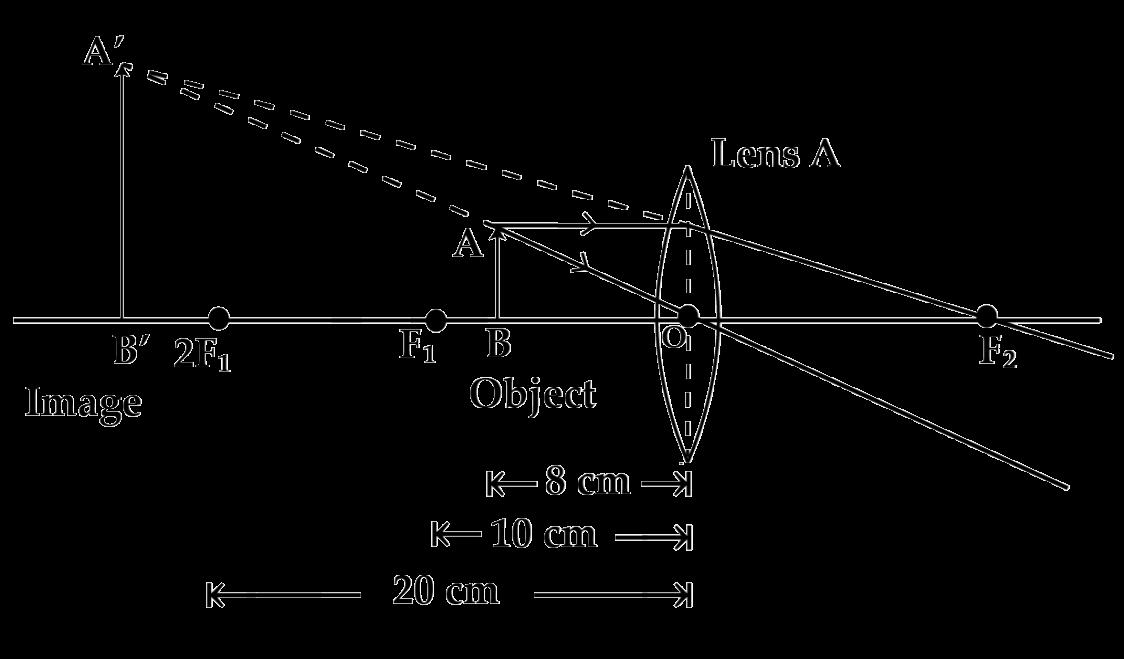
The above image is that of a Digital Single Lense Reflector (DSLR) Camera which are used to take high resolution photographs by professional photographers. The second image of the above two is a schematic diagram of how an image is formed on the sensor of the camera. Based on your understanding of the lenses, answer the following questions.
A. What type of lens is used in the DSLR camera shown in the image?
B. What type of image is formed on the sensor?
Attempt either subpart C or D.
C. A photographer is using a DSLR camera with a lens of focal length f=50 mm to take a close-up photograph of a small object. The lens projects an image onto the camera sensor that is located 60 mm behind the lens. Calculate the object distance (i.e., the distance between the object and the lens). 4
D. A photographer is using a DSLR camera to take a picture of a flower. The flower is positioned 150 mm away from the camera lens. The actual height of the flower is 80 mm, and the image height formed on the camera’s sensor is measured to be 20 mm. Calculate the focal length of the camera lens.
For visually impaired students
Zarina worked as an apprentice in a factory where flashlights and solar cookers are made. She learnt to make the circuits, the design of the light-box and light concentrators of the solar cookers as well. She learnt the uses of lenses in making all those tools. Based on your understanding of lenses, answer the following questions.
A. What kind of lenses are used in the flashlight and light concentrator of the solar-cooker?
B. Give reasons for your choices in your answer for part A. Attempt either subpart C or D.
C. An object is placed 40 cm away from a lens which is normally used in a solar-cooker. The image formed is twice the size of the object. Calculate the focal length of the lens. OR
D. An object is placed 20 cm in front of a lens which is used in a flashlight, and the image is formed 10 cm away from the lens on the same side as the object. Calculate the focal length of the lens.
39 Attempt either option A or B. A.
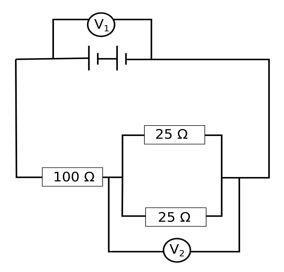
The arrangement of resistors shown in the above figure is connected to a battery.; The power dissipation in the 100 Ω resistor is 81 W. Calculate
(i) the current in the circuit
(ii) the reading in the voltmeter V2
(iii) the reading in the voltmeter V1
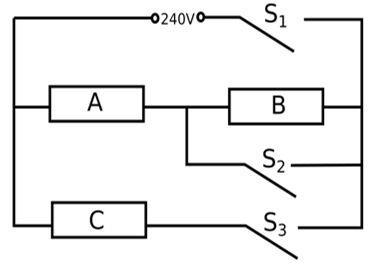
An electric heater consists of three similar heating elements A, B and C, connected as shown in the figure above. Each heating element is rated as 1.2 kW, 240 V and has constant resistance. S1, S2 and S3 are respective switches.
The circuit is connected to a 240 V supply.
(i) Calculate the resistance of one heating element.
(ii) Calculate the current in each resistor when only S1 and S3 are closed.
(iii) Calculate the power dissipated across A when S1, S2 and S3 are closed.
For visually impaired students
A.
(i) Explain why in household circuits only the fuse is connected in series with all the rest of the appliances but all appliances are connected in parallel to each other.
(ii) In a household circuit, an electric heater of power 1500 Wand a fan of power 500 W are connected in parallel to a 220 V supply. A fuse rated for 10 A is connected to the circuit to protect it from excessive current.
(a) Calculate the total current drawn by the heater and the fan.
(b) Determine whether the 10 A fuse is appropriate for this circuit or if it will blow.
OR
B. Two resistors, R1=6 Ω and R2=12 Ω, are connected in parallel to a 24V battery. The circuit operates for 5 minutes.
(i) Calculate the total heat generated in both resistors.
(ii) If each resistor has a power rating of 100 W, determine whether it is safe to use these resistors in the circuit.
It is completely wrong to say that plants do not produce any excretory products.
However, plants use completely different strategies for excretion than those of the animals.They get rid of these wastes in different manner (any two):
i. Oxygen, a photosynthetic waste, is removed through stomata.
ii. Excess water is removed by transpiration through stomata.
iii. Other metabolic wastes are either stored in dead cells, resins and gums or are removed through falling of old leaves. iv.
(i) There are two chambers in the heart of fish. The blood is pumped to the gills, is oxygenated there and passes directly to the rest of the body.
(ii) There are four chambers in the heart of a human being. Separation of the right side and the left side of the heart by septum prevents mixing of oxygenated and de-oxygenated bloods
B. Xylem moves water and minerals obtained from the soil through roots to all other parts of the plant in a unidirectional manner// Transpiration takes place from leaf which causes a transpirational pull in the tracheids and vessels of xylem facilitating upward movement of water// roots
actively uptake ions from the soil, leading to difference in concentration gradient, thereby water moves into the roots to eliminate this difference/ creating a steady movement of water into root xylem.
12 Tree food chain- tree, zebra, tiger /Any other food chain
Grassland food chain- grass, zebra, tiger / Any other food chain
Food web- Join the two food chains at a common point (zebra)
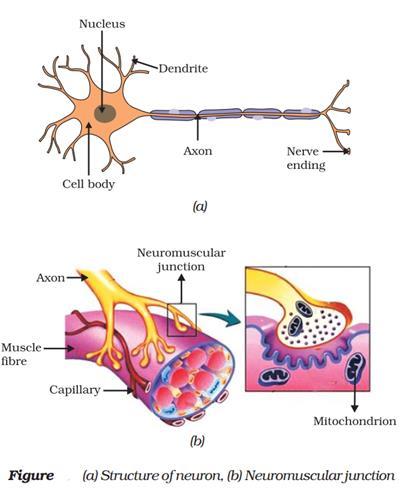
All information from our environment is detected by the specialised tips of some nerve cells. The information acquired at the end of the dendritic tip of a nerve cell (Fig. a), sets off a chemical reaction that creates an electrical impulse.
This impulse travels from the dendrite to the cell body, and then along the axon to its end.At the end of the axon, the electrical impulse sets off the release of some chemicals.
These chemicals cross the gap, or synapse, and start a similar electrical impulse in a dendrite of the next neuron. This is how nervous impulses travel in the body. (Fig b).
RY, Ry, rY, ry
The traits which are independently inherited are as follows
Short round: 27
Short wrinkled: 9
:- 9 : 3 : 3 : 1)
15 Students to attempt either subpart A or B.
A. Eggs are rich in proteins. The digestion of proteins is initiated in the stomach. Gastric glands present in the wall of the stomach release
hydrochloric acid, a protein digesting enzyme called pepsin and mucus. The hydrochloric acid creates an acidic medium which facilitates the action of enzyme pepsin.
OR
B. Eggs contain fats. Bile juice from the liver breaks down large fat globules into smaller ones for increasing the efficiency of the enzymes and making the medium alkaline. Emulsified fats are digested by lipase secreted by pancreas.
C. Sweet potatoes are rich in starch. The saliva secreted by salivary glands present in buccal cavity contain an enzyme called salivary amylase that breaks down starch which is a complex molecule to give sugar.
D. Small Intestine will have a maximum amount of digested food as the process of digestion is completed in the small intestine.
For Visually impaired students
D.The digested food is taken up by the inner lining of the intestine with the help of finger-like projections or villi which increase the surface area for the absorption.
16 Student to attempt either option A or B.
(i) Puneet should not choose seeds as banana plants have lost the capacity to produce seeds. He should go for vegetative propagation of banana (by stem cutting)
(ii) Errors and variations in DNA copying cause variation. Variation is good as it can help a population tide over unfavourable conditions by survival of some variants. It is bad as parents’ desirable characters are lost/ sometimes variants are not able to survive in the new conditions/ the variant is not able to use the cellular apparatus efficiently. OR
(i) Watermelon has unisexual flowers, the male and female flowers are separate.
The presence of pollinators will facilitate cross pollination between the flowers increasing the chance of fertilization and number of fruits being produced. Without pollinators the probability of pollen falling on stigma reduces in a unisexual flower, especially if they are far apart thus the number of fruits produced will be less.
(ii) The three changes observed are:
● Ovule develops a tough coat and becomes seed.
● Ovary grows and ripens to form fruit.
● Petals, sepals, stamen, style and stigma may shrivel and fall off. 5
Section – B
17 D.Both equations 1 and 2 are redox reactions, p=
25
26
27
A. The pin will drop but will take less time to drop because silver is a better conductor of heat than aluminium.
B. No, aluminium wire will not melt because metals have high melting points.
Attempt either option A or B.
A.
(i) No, ‘X’ is highly reactive and will catch fire.
(ii) Sodium.
It is extracted from molten sodium chloride by electrolytic reduction
Cathode: Na+ + e - Na
Anode: 2Cl- Cl2 + 2e(Potassium is also a correct option)
B.
(i) Copper gets oxidised/corroded to basic copper carbonate which is greenish in colour.
(ii) No, iron will rust and the reddish layer of rust will come off exposing iron to air, the dome will not be stable. Copper on the other hand on corrosion forms a protective layer which does not allow further corrosion.
(iii) Copper is a highly malleable metal, its thin sheets can be used to give different shapes of roofs, like the shape of a dome. 3
A. She was expecting Oxygen gas to be formed at the anode and hydrogen at the cathode.
B. Distilled water is a poor conductor of electricity.
C. Adding few drops of H2SO4 or some NaCl (or any other strong electrolyte).
For visually impaired students
A. Redox reaction 3
B. Decomposition reaction and endothermic reaction
C. Combination reaction and exothermic reaction
28 A. (b) < 40, because concentrated H2SO4 gives more H+ ions than dilute acid.
B. 3 mL of H2SO4 will be 60 drops, which will neutralise 6 mL of NaOH
S.No.
(2 mL)
3 mL = 60 drops
OR
Colour will change from colourless to pink. Phenolphthalein in colourless in acids and turns pink in basic solution.
C. 2NaOH + H2SO4 Na2SO4 + 2H2O
(a)neutralisation and double displacement reaction. Base NaOH is getting neutralised and forming salt + water. It is double displacement as Na+ ions are being replaced by H+ and OHby SO42-. It is not precipitation reaction because Na2SO4 is soluble in water.
29 Student to attempt either option A or B. A.
(a) x = 3, y = 6
(b) Propene
(c)
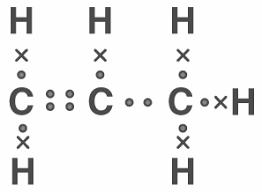
(d) Propanol

(e) C3H6 + H2 Ni C3H8 CH2=CH-CH3 + H2 CH3-CH2-CH3 OR
B.
(a) Ionic bond
(b) Q2P
(c) Basic, metallic oxides are basic in nature.
(d) 2C2H5OH +2Q 2C2H5OQ + H2
(e) CP2
For visually impaired students
A.
(a) x = 3, y = 6
4
5
B.
(b) Propene
(c) Unsaturated hydrocarbon
(d) Propanol
(e) C3H6 + H2 Ni C3H8 OR

(a) Covalent bond
(b) Ionic bond
(c) CaO, due to presence of free ions in molten state.
(d) CaO is solid while CO2 is a gas.
(e) 4
Section – C
30 D.I and III 1
31
A.As sunlight passes through the atmosphere, Rayleigh scattering causes shorter wavelengths, such as blue and violet, to scatter more than other colors, but our eyes are more sensitive to blue than violet. 1
32 C.A is true but R is false 1
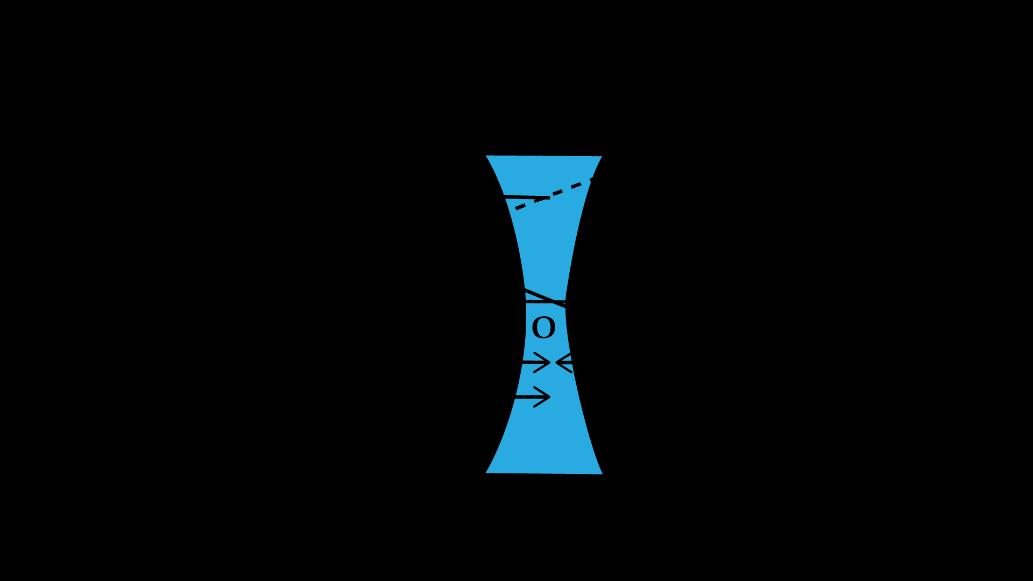
33 A. The optical instrument shown in the figure is a concave lens.
B. The image formed is a virtual image.
C. To find the focal length for of a concave lens, we can use the lens formula:
where:
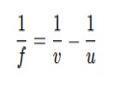
��= - 20 cm (object distance, taken as negative for concave lenses),
��= - 10 cm (image distance, also taken as negative since the image formed by a concave lens is virtual).
Solution:
1. Substitute the values into the lens formula:
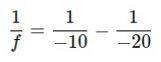
2. Simplify the terms:
3. Find a common denominator: 4. Solve for ��: ��= - 20 cm 2
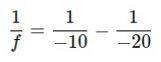
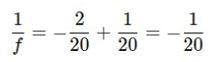
For visually impaired students
A. A convex lens can form a virtual image when the object is placed between the lens and its focal point.
B. A convex lens can focus parallel rays of sunlight to a single point, known as the focal point. Sunlight contains energy, and when this light is concentrated at a small point, the energy density increases significantly. This focused light energy raises the temperature at the focal point, which can become high enough to ignite a piece of paper placed at that point.
34 Student to attempt either A or B.
(ii) Same readings of A1 and A2
For visually impaired students A.
(i) Maximum Resistance:
To get the maximum resistance, connect all four resistors in series.
The total resistance Rmax in series is the sum of the individual resistance:
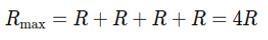
(ii) Minimum Resistance:
To get the minimum resistance, connect all four resistors in parallel. 2
The total resistance Rmin in parallel is given by:
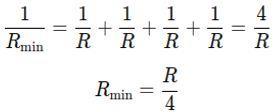

Step 1: Calculate the initial resistance R1 and �� = 2 m
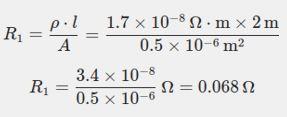
Step 2: Calculate the new resistance R2 and �� = 4 m (double length)
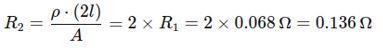
The resistance of the wire when the length is double is 0.136 Ω
(i) Hypermetropia is the deficiency in vision and the lens is convex lens. (ii)
For visually impaired students
(i) Dispersion of light is the phenomenon in which white light separates into its component colors (spectrum) when it passes through a medium, such as a prism. Different colours of light lend through different angles with respect to incident light, thus becoming district.
(ii) Dispersion occurs when light passes from one medium to another where the speed of light is different for each wavelength. For example, in a prism, each color of light has a different refractive index due to varying wavelengths, causing each color to bend at different angles as they exit the prism. Dispersion only happens if the medium has a variable refractive index across different wavelengths, like glass or water.
(iii)Presbyopia is caused by the gradual loss of flexibility in the lens of the eye, which occurs with aging. This reduced flexibility prevents the lens from changing shape effectively to focus on close objects, making it difficult to see them clearly.
36 (i) Show that the cross-sectional area of the wire is about 5 x 10-7 m2
The cross-sectional are A of a wire with diameter d is given by:
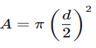
Substitute, d = 0.80 x 10-3 m:
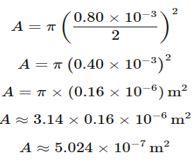
Thus, the cross-sectional are A is approximately 5 x 10-7 m2 (ii) To find the length �� of the wire, we can use the formula of resistance:
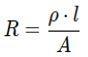
Rearrange to solve for �� :
Substitute the values:
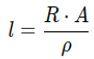
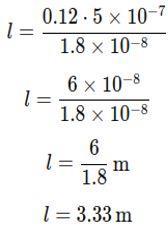
The student needs a length of approximately 3.33 m of given copper wire to make a 0.12 Ω resistor.
3
37
Closeness of magnetic field lines is directly related to strength of magnetic field.
Strength of magnetic field at point X (pole) is more than point Y.
If the student redraws the diagram he/she should mark arrows correctly from North to South.

38 A. Convex Lens
B. Real and Inverted
Student to attempt either subpart C or D.
C. To find the object distance (u) for the lens, we can use the lens formula:
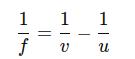
where:
● f = 50 mm (focal length),
● v = 60 mm (image distance),
● u is the object distance, which we need to calculate. Rearranging the formula to solve for u:
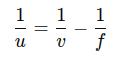
Substitute the values:
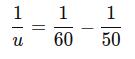
Calculate each term:
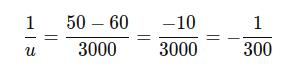
Thus, the negative sign indicates that the object is located 300 mm in front of the lens (on the opposite side from the image). So, the object distance is: u= 300 mm
D. image height = - 20 mm object height = 80 mm
The magnification (m) of the lens is given by:
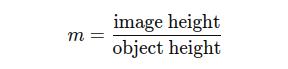
Substituting the
Thus, the magnification m = 0.25 mm.
Magnification is also given by:
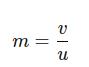
where:
● v is the image distance
● u = 150 mm
Rearrange to solve for v:
v = m × u = 0.25 × 150 mm = 37.5 mm
So, the image distance v = 37.5 mm.
The lens formula is:
Substituting the values of v and u:
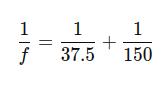
Converting to a common denominator:
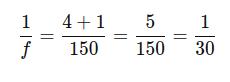
Thus, f = 30 mm
Answer: The focal length of the camera lens is 30 mm.
For visually impaired students
A. Concave Lens for Flashlight and Convex Lens for solar cooker.
B. Concave lens diverges the light rays which is needed for a wider reach of the flashlight. Convex lens converges the rays which helps to raise the temperature of the place where rays converge.
Student to attempt either subpart C or D
C. To find the focal length (��) of the lens, we can use the information about the object distance (��) and the magnification (��).
Given:
Object distance, �� = 40 cm
The image is twice the size of the object, so the magnification, �� = 2
Since the magnification �� = �� �� , we can rearrange this to find the image distance ��: �� =����
Substitute the values for �� and ��:
The lens formula is :
Substitute �� =80���� and �� = 40����:
Convert to a common denominator:
Thus, �� = 80 3 =26.67 cm (approximately)
Answer : The focal length of the lens is approximately 26.67 cm.
OR D.
Object distance, �� = - 20 cm
Image distance �� = - 10 cm (since the image is on the same side as the object)
We can use the lens formula to calculate the focal length (��) :
Substitute the values of �� and �� :
Finding a common denominator:
Thus, �� = 20 cm
Answer: The focal length of the lens is - 20 cm, indicating it is a diverging lens (concave lens).
39 Students to attempt either option A or B. A.
(i) Power across the 100 Ω resistance = 81 W
(ii) Voltage across the 25 Ω resistors = V2 = IReqv for the 25 Ω resistors
(ii) For S1 and S3 closed – Current in C
– Current in A and B
(iii)Power across
For visually impaired students
(i) In household circuits, the fuse is connected in series with all appliances to ensure that it can cut off the entire circuit in case of excessive current, preventing hazards like fires or damage. This way, any overload or short circuit causes the fuse to blow, protecting all appliances.
Appliances are connected in parallel to ensure each receives the same voltage from the mains and can operate independently. This setup allows appliances to work simultaneously and efficiently, with each drawing only the current it needs, without affecting others.
Give Data:
Power of heater, Pheater = 1500 W
Power of Fan, Pfan = 500 W
Supply Voltage, V = 220 V
Fuse rating = 10 A
Step 1: Calculate the Current Drawn by Each Appliance
Using the formula =
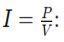
1. Current drawn by the heater:
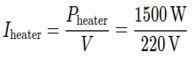
Iheater = 6.82 A (rounded to two decimal places)
2. Current drawn by the fan:
Ifan = 2.27 A (rounded to two decimal places)
Step 2 : Calculate the total curent in the circuit
Since the heater and fan are connected in parallel, the total curent Itotal is the sum of the currents through each appliance:
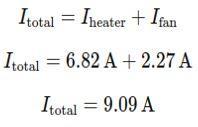
Step 3: Compare with the Fuse Rating
The fuse is rated for 10 A, and the total current drawn by the heater and fan together is 9.09 A.
Since 9.09 A < 10 A, the fuse will not blow and is appropriate for this circuit, as the total current is within the fuse’s capacity. OR
B. Given data:
Resistor R1 = 6 Ω
Resistor R2 = 12 Ω
Voltage V = 24 V
Time t = 5 Minutes = 5 x 60 = 300 seconds
Step 1: Calculate the Current through each Resistor
Since the resistors are connected in parallel, the voltage across each resistor is the same as the battery voltage, V = 24 V.
Using Ohm’s Law,
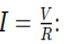
Current through R1
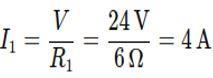
Current through R2:
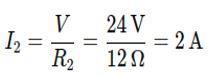
Step 2: Calculate the Heat Generated in Each Resistor Using Joule’s Law of Heating, H = I2Rt:
Heat generate in R1:
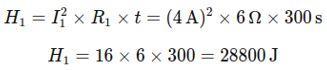
Heat generate in R2:
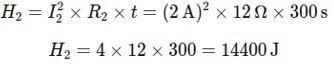
Total Heat Generated H:
So, the total heat generated in both resistor is 43200 J.
Step 3 : Determine if each Resistor is safe
The power dissipated by each resistor can be calculated using P = V xI
Power dissipated by R1 :
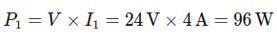
Power dissipated by R2:
Given that the power rating of each resistor is 100 W:
R1 is operating at 96 W, which is within the 100 W limit. Hence, it is safe.
R2 is operating at 48 W, which is also within the 100 W limit. Hence, it is safe.
SCIENCE
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER - 1
CLASS X (2025-26)
Max. Marks: 80 Time allowed: 3 hours
General Instructions:
1. This question paper consists of 39 questions in 3 sections. SectionAis Biology, Section B is Chemistry, and Section C is Physics.
2. All questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice is provided in some questions.Astudent is expected to attempt only one of these questions.
SectionA (Biology)
Which part of the human digestive system is the main site of nutrient absorption?
A. Stomach
B. Small intestine
C. Large intestine
D. Liver
Which gas is responsible for the greenhouse effect and global warming?
A. Oxygen
B. Nitrogen
C. Carbon dioxide D. Helium
Which organ in humans produces insulin? A. Liver B. Pancreas
C. Kidney D. Stomach
The maleness of a child is determined by
A. the X chromosome in the zygote
B. the Y chromosome in zygote
5.
C. the cytoplasm of germ cell which determines the sex
D. sex is determined by chance
Which part of the human brain is responsible for maintaining posture and balance of the body?
A. Cerebrum
B. Cerebellum
C. Medulla
D. Pons
Which plant hormone is responsible for cell division?
A.Auxin
B Cytokinin
C. Gibberellin
D.Abscisic acid
Which of the following is NOT an involuntary action?
A. Beating of heart
7.
B Walking
C. Peristalsis D Reflex action
Question No. 24 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true but R is false.
D. A is false but R is true
Assertion (A): Chlorophyll is essential for the process of photosynthesis in plants.
8.
Reason (R): Chlorophyll absorbs sunlight, which is necessary for the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis.
Assertion (A): In human males, the testes are extra-abdominal and lie in the scrotal sac.
Reason (R): The scrotum provides a temperature that is slightly higher than the body's core temperature, which is essential for spermatogenesis.
10. What is the function of the heart in the circulatory system?
To trace the inheritance of traits Mendel crossed pea plants having one contrasting character or a pair of contrasting characters. When he crossed pea plants having round and yellow seeds with pea plants having wrinkled and green seeds, h observed that no plants with wrinkled and green seeds were obtained in the generation. When the generation pea plants were cross-bred by self-pollination, the generation had seeds with different combinations of shape and colour also.
(i) Write any two pairs of contrasting characteristics of pea plant used by Mendel other than those mentioned above.
(ii) Differentiate between dominant and recessive traits.
(iii) State the ratio of the combinations observed in the seeds of generation (in the above case). What do you interpret from this result?
(iii) Given below is a cross between a pure violet flowered pea plant (V) and a pure white flowered pea plant (v). Diagrammatically explain what type of progeny is obtained in generation and generation:
violet flowering plant × Pure white flowered plant. (VV) (vv)
Describe in brief the role of (i)testis (ii) seminal vesicle, (iii) vas deferens, (iv) ureter and (v) prostate gland in the human male reproductive system.
Explain the meaning of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). Give two examples of STDs each, caused due to
17.
(i) bacterial infection and (ii) viral infection. State in brief how the spread of such diseases may be prevented.
Section B (Chemistry)
An alkali metal salt is often used to remove the permanent hardness of the water. Identify the salt.Also, mention its chemical formula.
A. Sodium carbonate, Na2CO3
B. Sodium carbonate dehydrate, Na2CO3.10H2O
C. Potassium chloride, KCl
D. Potassium carbonate, K2CO3
How do members of a homologous series differ in terms of-
A. Chemical property
18.
B. General formula
C. Functional group
D. Molecular mass
How many covalent bonds are present in molecules of butane C4H10?
A. 15
19.
B. 13
C. 11
D. 14
Which of the following compounds has chemical characteristics similar to butane?
A. Butyne
20.
B. Propene
C. Propyne
D. Pentane
If the first member of the homologous series is methane find the molecular formula of the 2���� and the 3���� members of the series.
A. C7H16, C3H6
21.
B. C2H6, C3H8
C. C2H4, C3H6
D. C2H2, C3H4
An alkane has C/H ratio (by mass) of 5.1428. Its molecular formula is:
A.C5H12
B. C6H14
C. C8H18
D.C7H16
Question No. 24 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true but R is false.
D. A is false but R is true
Explain and identify the decomposition reactions which are endothermic in nature from the following: (i)Respiration (ii)Heating of lead
Two acids ‘X’and ‘Y’were kept in beakers. Acid ‘X’undergoes partial dissociation in water, whereas acid ‘Y’undergoes complete dissociation in water.
(i)Of the two acids ‘X’and ‘Y’. Which is weak acid, and which is strong acid?
(ii)Give one example for weak acid and strong acid.
(OR)
Read the passage carefully and answer the following:
Decomposition reactions are chemical reactions in which a single compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances. These reactions may occur on heating, by electricity, or by light.
Now,answer the following:
a)Define a decomposition reaction.
b)Write two examples of thermal decomposition reactions.
c)Give one example of electrolytic decomposition.
d)Give one example of photochemical decomposition.
Given below are a few solutions and pH values. Match the solutions to the correct pH values.
a.Milk of magnesia
b.Gastric juices
c.Brine
d.Aqueous Sodium Hydroxide
Why is baking soda used in baking cake? Explain with the help of a balanced chemical equation. List down any other two uses of baking soda. OR
Read the passage carefully and answer the following:
Acid-base indicators are substances that change colour in acidic or basic solutions. Some indicators are natural, such as litmus, turmeric, and red cabbage juice, while others are synthetic, such as methyl orange and phenolphthalein. Indicators are widely used in titrations and in testing the acidity or alkalinity of substances in daily life.
Now, answer the following:
a)Define an acid-base indicator.
30.
b)Give two examples of natural indicators and two examples of synthetic indicators.
c)State the colour change of litmus and phenolphthalein in acidic and basic solutions.
d)Astudent tested a solution with methyl orange and phenolphthalein. Methyl orange turned red and phenolphthalein remained colourless. What is the nature of the solution? Justify your answer.
e)Give one real-life application of indicators in daily life.
Section C (Physics)
The ratio of the height of an image to the height of an object known as
A. Magnification
B. Refractive index
C. Lateral displacement
D. None of the above 1
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
A. Alonger wire has more resistance
31.
B. Athicker wire has more resistance
C. Resistance depends on temperature
D. Copper has lower resistivity than rubber 1
Question No. 32 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true but R is false.
D. A is false but R is true
32.
33.
Assertion (A):As light travels from one medium to another, the frequency of light does not change.
Reason (R): Frequency is the characteristic of source
Define electric power. Write an expression relating electric power, potential difference and resistance.
What is thevalueof farpoint andnearpoint for ayoungadult andhealthyhumanbeing?
(i) What is a solenoid?
What is the use of a solenoid?
Astudent complains that he is unable to see distant objects clearly, though nearby objects are distinct.
(i) Name the defect of vision he is suffering from. Give reason for your answer.
(ii)State two causes of this defect.
(iii)How can this defect be corrected? Explain with the help of a ray diagram.
State the laws of refraction of light. Explain the term ‘absolute refraction index of a medium’and write an expression to relate it with the speed of light in vacuum.
An insulated copper wire wound on a cylindrical carboard tube such that its length is greater than its diameter is called a solenoid. When an electric current is passed through the solenoid, it produces a magnetic field around it. The magnetic field produced by a current-carrying solenoid is similar to the magnetic field produced by a bar magnet. The field lines inside the solenoid are in the form of parallel straight lines. The strong magnetic field produced inside a current-carrying solenoid can be used to magnetize a piece of a magnetic material like soft iron when placed inside the solenoid.
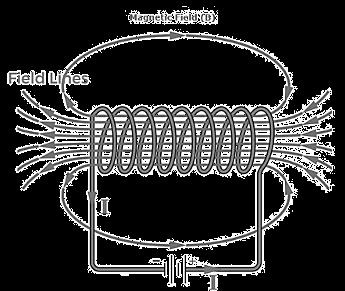
(i)What would be the strength of the magnetic field inside a long current-carrying straight solenoid?
(ii) Which end is north and which end is south pole when current flows through a solenoid?
(iii) How can a solenoid be used to magnetize a piece of iron?
(iii) A soft iron bar is placed inside a current-carrying solenoid. Explain how the bar becomes magnetized and what type of magnet it becomes.
An object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a concave lens of focal length 30 cm.
(i) Use lens formula to determine the distance of the image from the lens.
(ii) List four characteristics of the image (nature position, size, erect/inverted) in this case.
(iii) Draw a labelled diagram to justify your answer of part (ii)
(i) What is meant by power of a lens? Define its SI unit.
(ii) You have two lenses A and B of focal lengths +10 cm and - 10 cm, respectively. State the nature and power of each lens. Which of the two lenses will from a virtual and magnified image of an object placed 8 cm from the lens? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer.
Marking Scheme
SectionA(Biology)
8. A.BothAand R are true and R is the correct explanation of
The heart pumps blood throughout the body, providing oxygen and nutrients to tissues while removing waste products.
Xylem: Transports water and minerals from roots to other parts of the plant.
Phloem: Transports food (mainly sugars) from leaves to other parts of the plant.
Binary fission and multiple fission are two distinct forms of asexual reproduction.
Feature Binary Fission Multiple Fission
Multiple Fission
Occurrence
Asingle cell divides into two identical daughter cells. Asingle cell divides into multiple daughter cells simultaneously.
Commonly observed in bacteria. Observed in some protozoa, such as Plasmodium (malaria parasite).
A nephron is the functional unit of the kidney, responsible for filtering blood and forming urine. Each nephron consists of:
(a) Bowman's capsule: Encases the glomerulus and initiates filtration.
(b) Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT): Reabsorbs nutrients, ions, and water.
(c) Loop of Henle: Concentrates urine by reabsorbing water and salts.
(d) Distal convoluted tubule (DCT): Further adjusts ion concentrations.
(e) Collecting duct: Transports urine to the renal pelvis.
Nephrons filter waste products from the blood, regulate water and electrolyte balance, and maintain blood pressure.
14.
15.
The transmission of nerve impulses is considered an electrochemical process because it involves both electrical and chemical signals. Electrical impulses travel along the neuron due to ion exchange across the membrane, creating an action potential.At synapses, neurotransmitters are released, converting the electrical signal into a chemical one for communication 3
(i)Two pairs of contrasting characteristics of pea plants used by Mendel (other than seed shape and seed color):
Flower color: Violet vs. White.
Pod shape: Inflated vs. Constricted.
(ii)Difference between dominant and recessive traits:
Dominant traits
Expressed when only one allele is present (e.g., Tt or TT)
Recessive traits
Expressed only when two recessive alleles are present (e.g., tt)
Can mask the expression of recessive traits Must be inherited from both parents to be expressed
(iii)Mendel observed a 9:3:3:1 ratio for the different combinations of seed shape and color in the offspring when crossed by self-pollination. The F2 generation exhibited four combinations of seed shape and color.
9 round and yellow seeds (RRYY, RRYy, RrYY, RrYy)
3 round and green seeds (RRyy, Rryy)
3 wrinkled and yellow seeds (rrYY, rrYy)
1 wrinkled and green seeds (rryy)
This result follows Mendel's Law of IndependentAssortment, which states that alleles for different traits are inherited independently of one another. Therefore, the traits for seed shape and color are inherited independently, leading to a variety of combinations in the offspring. OR
(iii)Cross between a pure violet-flowered pea plant (VV) and a pure white-flowered pea plant (vv):
F₁ Generation:
All plants will have violet flowers (Vv) because violet (V) is dominant over white (v).
16.
F₂ Generation:
When F₁ plants (Vv) are self-pollinated, the progeny will have the following genotypes: VV, Vv, and vv.
The phenotypic ratio in the F₂ generation will be 3 violet-flowered plants (VV and Vv) to 1 white-flowered plant (vv).
Diagrammatically, it can be represented as:

Parent Generation: VV(violet) × vv (white)
F1 generation: Vv (all violet)
F2 generation: VV, Vv, Vv, vv
Phenotype Ratio: 3 violet: 1 white
Function in the male reproductive system of humans:
(i)Testis
The testis is the primary reproductive organ in males, responsible for the production of sperm (male gametes) and testosterone (a male sex hormone). The sperm is produced in the seminiferous tubules within the testis, while testosterone plays a key role in the development of male secondary sexual characteristics and the regulation of sperm production.
(ii)Seminal vesicle
Between the rectum and the bladder are two male reproductive glands called seminal vesicles. It secretes seminal fluid, an alkaline substance that stimulates sperm and balances the acidity of
urine.
(iii)Vas deferens
The long tube known as the vas deferens, or sperm duct, connects the testes to the urethra, which emerges from the bladder. The vas deferens transports the sperm produced in the testis to the urethra.
(iv)Ureter
These are two long, tubular, narrow, and thin-walled structures that begin in the kidney's hilum, run downward, and open up in the bladder. These convey the urine from the kidneys to urinary bladder.
(v)Prostate gland in human male reproductive system.
The prostate gland is located below the bladder and surrounds the urethra. It secretes a milky, alkaline fluid that helps in the activation of sperm, protecting it from the acidic environment of the female reproductive tract.
OR
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are infections that are mainly spread through sexual contact. These diseases can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or other microorganisms.
(i) Examples of STDs caused by bacterial infections:
(a) Chlamydia: Caused by the bacterium Chlamydia, it can lead to serious health problems if not treated.
(b) Gonorrhea: Caused by the bacterium Neisseria, it can infect the genital tract, rectum, and throat.
(ii) Examples of STDs caused by viral infections:
(a) HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus): This virus attacks the immune system and can lead toAIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome).
(b) Genital Herpes: Caused bytheHerpes SimplexVirus (HSV),it results in sores andblisters in the genital area.
Prevention of STDs:
(a) Consistently using condoms during sexual activity can reduce the risk of transmission.
(b) Vaccines are available for some STDs, such as HPV (Human Papillomavirus) and Hepatitis B.
(c) Getting tested regularly for STDs helps in early detection and treatment.
(d) Having a sexual relationship with one uninfected partner who does not have any other partners.
(e) Openly discussing sexual health and testing with partners.
Section B (Chemistry)
24. C.Ais true, but R is false.
Acids that get completely dissociated in an aqueous solution and produce more hydronium ions in an aqueous solution are said to be strong acids. For example, Sulphuric acid (��2����4), Hydrochloric acid (������), and nitric acid, etc.
25.
26.
Acids that don’t dissociate completely in an aqueous solution and produce less concentration of hydronium ions in an aqueous solution are said to be weak acids. For example,Acetic acid (����3��������), formic acid (����������), citric acid, phosphoric acid, etc.
Ahomologous series is a series of hydrocarbons that have similar chemical properties and share the same general formula. They are organic compounds having similar structures and functional groups. The constituents of the homologous series show a gradation in physical properties.
(i)They contain the same functional group throughout the series. Like a homologous series of alcohols will contain only ���� groups.
(ii)All the members of a homologous series can be represented by the same general formula, like the homologous series of alkanes, which can be represented by the same formula ����+2������2��+2, where n is an integer starting from 1.
���������� is methanoic acid as it has one carbon atom, and the carboxylic acid functional group is present over here (��������). So, its next homologue would be ethanoic acid ����3��������.
Both respiration and decomposition of organic matter are exothermic reactions.
27.
(i.) Respiration involves the breakdown of glucose in the presence of oxygen to produce energy. It is an exothermic reaction because it releases energy in the form ofATP.
The heating of lead nitrate and the Electrolysis of acidified water is an endothermic reaction where decomposition also happens.
28.
A single reactant decomposes in a decomposition reaction to produce a variety of products. A chemical reaction thatresults inthebreakdownofonereactantintotwoormoreproducts is known as a decomposition reaction.
Adecomposition reaction is generally represented as:
AB →A+ B, Where
AB = Reactant;A and B = Product molecules
(ii.) Heating of lead nitrate can be represented by the chemical equation given below:
2��������3 → 2������ + 4����2 + ��2
We can infer from the reaction that lead nitrate breaks down into lead oxide, nitrogen dioxide, and oxygen when heated. Lead oxide, nitrogen dioxide, and oxygen are produced as lead nitrate decomposes.
(iii.) Decomposition of organic matter is also an exothermic process as it releases energy during the breakdown of complex organic substances into simpler compounds.
(iv.)Electrolysis ofacidified wateris also anexampleofanendothermicdecomposition reaction.
When acidified water is subjected to an electric current, it breaks down into hydrogen and oxygen gas.As a result, there are twice as many hydrogen molecules produced as oxygen molecules.
Hence, heating of lead nitrate and Electrolysis of acidified water are the decomposition reactions which are endothermic in nature.
(i)Acid 'X' is a weak acid, and acid 'Y' is a strong acid.
Explanation:
Weak acids undergo partial dissociation in water, releasing only a small fraction of their hydrogen ions (H+). Strong acids, on the other hand, completely dissociate in water, releasing a high concentration of hydrogen ions.
(ii)Example of weak acid and strong acid are:
Weak acid:Acetic acid (CH₃COOH)
Strong acid: Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
Explanation:
Acetic acid undergoes partial dissociation in water, and hydrochloric acid completely dissociates, illustrating the characteristic behaviour of weak and strong acids, respectively. OR a)Definition: 2 1 1
A decomposition reaction is a chemical reaction in which a single compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances.
b)Thermal decomposition reactions:
Calcium carbonate on heating:
3 → heat
2
Mercury(II) oxide decomposes on heating to produce mercury and oxygen gas 2HgO → heat
c)Electrolytic decomposition:
Electrolysis of water: Water decomposes into hydrogen gas and oxygen gas when an electric current is passed through it.
d)Photochemical decomposition:
Decomposition of silver chloride in sunlight:
Silver chloride decomposes into silver and chlorine when exposed to light.
Solutions and their pH values are:
a. Milk of magnesia: 10
b. Gastric juices: 1
c. Brine: 7
d. Aqueous Sodium hydroxide: 13
During the thermal decomposition of baking soda Na2CO3, CO2, and H2O are formed. The production of CO2 gives the cake its fluffy and soft texture.
The balanced reaction is as follows:
Uses of baking soda are as follows:
• It is used in fire extinguishers.
• To neutralize the excess acid in the stomach, it acts as an antacid.
To neutralize the acidic effect of an insect sting. OR
a)Definition:
An acid-base indicator is a substance that changes colour depending on the pH of the solution, indicating whether it is acidic or basic.
b)Examples:
Natural indicators: Litmus, turmeric, red cabbage juice.
Synthetic indicators: Methyl orange, phenolphthalein.
c)Colour changes:
Litmus turns red in acidic solutions and blue in basic solutions.
Phenolphthalein is colourless in acidic solutions and turns pink in basic solutions.
d)Nature of the solution:
Methyl orange turned red → solution is acidic.
Phenolphthalein remained colourless → confirms acidic nature.
Therefore, the solution is acidic.
e)Real-life application:
Testing the pH of soil in agriculture.
Checking the acidity of food items.
Using in titrations in laboratories.
A. Far Point and Near Point for a Young, Healthy Human
• Far Point: Infinity.
• Near Point: 25 cm from the eye.
B.(i) A solenoid is a helical coil of wire that produces a magnetic field when current flows through it.
(ii) It is used in devices like electromagnets, relays, and electric motors to generate a magnetic field.
35.
(i) The defect of vision is Myopia (short-sightedness).
Reason: The student can see nearby objects clearly but is unable to see distant objects distinctly. This happens because the image of a distant object is formed in front of the retina instead of on it.
(ii) Two causes of this defect are:
1. The eyeball is too long from front to back.
2. The eye lens becomes too convex (too much converging power).
(iii) Myopia is corrected using a concave lens (diverging lens) in spectacles.
• The concave lens diverges the rays coming from a distant object, making them appear to come from a nearer point.
• The eye lens then focuses these rays exactly on the retina, forming a clear image.

Resistance per Unit Length:
Let the total length of the wire (circumference) be denoted as �� The resistance per unit length is:
Resistance per unit length = Total resistance Total
= 36٠��
Arc Lengths:
36.
• Let the arc length between pointsAand B be denoted as ��1.
Since the arc ���� subtends an angle of 30∘ at the center,
• The remaining arc (completing the circle) between points B andAis denoted as ��2.
37.
Resistance of theArcs:
• The resistance of arc AB(��1) is:
1 =(36Ω �� )×(112×��)=3Ω
• The resistance of the remaining arc (BA)(��2) is:
2
Effective Resistance (betweenA and B):
Since arcs AB and BAare connected in parallel, the effective resistance ��effective is:
38.
Thus, the effective resistance between pointsAand B is 2.75Ω.
First Law of Refraction:
The incident ray, the refracted ray, and the normal to the interface at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
Second Law of Refraction (Snell's Law):
For a given pair of media, the sine of the angle of incidence (i) bears a constant ratio to the sine of the angle of refraction (r):
The absolute refractive index (n) of a medium is defined as the ratio of the speed of light in air or vacuum (c) to the speed of light in the medium (v):
Here, c = 3×108 m/s (speed of light in vacuum) 3
(i) Magnetic field inside the infinite solenoid is uniform. Hence it is the same at all points. 1
(ii) The end of a current-carrying solenoid where the current flows in an anticlockwise direction behaves like a north pole. Conversely, the end where the current flows in a clockwise direction behaves like a south pole. This behavior can be understood using the right-hand rule.
(iii) When current flows through a solenoid, it creates a strong magnetic field inside. If a piece of iron is placed within this field, the iron becomes magnetized due to the influence of the magnetic field.
OR
(iii) When current flows through the solenoid, it produces a strong magnetic field inside the coil. The soft iron bar placed within this field gets magnetized due to the influence of the solenoid’s magnetic field. The bar behaves like a temporary magnet (electromagnet) it has a north and south pole, and it loses its magnetism when the current is switched off.
(i)Use Lens Formula to Determine the Image Distance
The lens formula is:
Where:
• �� is the focal length of the lens
• �� is the image distance
• �� is the object distance
Given:
• Object distance, �� = 30cm (since the object is on the same side as the incoming light for a concave lens, it's negative)
• Focal length, �� = 30cm (concave lens has a negative focal length)
Using the lens formula:
Thus, �� = 15cm .
The image is formed at a distance of 15 cm on the same side as the object.
(ii)Characteristics of the Image
For a concave lens with the object placed at 30 cm:
1. Nature: Virtual (since the image distance is negative).
2. Position: The image is on the same side as the object.
3. Size: The image is diminished (smaller than the object).
4. Orientation: Erect (since the image formed by a concave lens is always upright).
(iii)
(i)Power of a Lens
The power of a lens is defined as the ability of the lens to converge (or diverge) light rays. It is the reciprocal of the focal length of the lens (in meters).
The power (��) of a lens is given by:
Where �� is the focal length in meters. The unit of power is diopters (D).
(ii)Nature and Power of Lenses
• LensA(Convex lens): Focal length ���� =+10cm=0.1m.
Nature: Convex lens (positive focal length).
• Lens B (Concave lens):
Focal length ���� = 10cm= 0.1m.
Power ���� = 1 ���� = 1 01 = 10D
Nature: Concave lens (negative focal length).
LensA(i.e. convex lens) will form a virtual and magnified image of an object placed 8 cm from it, as shown.
SCIENCE
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER - 2
CLASS X (2025-26)
Max. Marks: 80 Time allowed: 3 hours
General Instructions:
1. This question paper consists of 39 questions in 3 sections. SectionAis Biology, Section B is Chemistry, and Section C is Physics.
2. All questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice is provided in some questions.Astudent is expected to attempt only one of these questions.
SectionA (Biology)
Which of the following statements regarding photosynthesis are correct?
(i) Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells.
(ii) Oxygen is a by-product of photosynthesis.
(iii) Photosynthesis requires chlorophyll, sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide.
(iv) Photosynthesis produces energy in the form ofATP as its final product.
1.
2.
The correct statements are:
A. and (ii)
B. (i), (ii), and (iii)
C. (ii), (iii), and (iv)
D. (i), (ii), (iii), and (iv) 1
Hormones:
(i) are chemical messengers secreted by glands.
(ii) are transported through the bloodstream to target organs.
(iii) always act on the organ that secretes them.
(iv) control only growth and reproduction in the body.
The correct statements are:
A. (i) and (ii)
B. (ii) and (iii)
C. (iii) and (iv)
D. (i) and (iv)
The part of the brain responsible for regulating involuntary functions such as breathing, heart rate, and digestion is known as:
A. Cerebrum
B. Cerebellum
C. Medulla oblongata
D. Thalamus
The process of cellular respiration:
(i) occurs in the mitochondria of cells.
(ii) produces glucose as a by-product.
(iii)requires oxygen to produce energy.
(iv)releases carbon dioxide and water as by-products.
The correct reason(s) in this process is/are:
A. (i) and (iii)
B. (ii) and (iv)
C. (i) and (iv)
D. (iii) and (iv)
Which of the following statements is true about the circulatory system in humans?
A. Oxygenated blood flows from the right ventricle to the lungs.
B. The left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to the lungs.
C. The right atrium receives oxygenated blood from the body.
D. The left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs.
Which of the following is an example of an excretory product in humans that is removed through the kidneys?
A. Oxygen B. Urea
Carbon dioxide
What is the primary purpose of vegetative propagation in plants?
A. To enhance genetic variation
B. To produce new plants quickly
C. To prevent fertilisation
D. To increase seed production
Question No. 8 to 9 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true but R is false.
D. A is false but R is true 8.
Assertion (A): Fertilization in flowering plants occurs inside the ovary.
Reason (R): The ovary contains ovules, where the male gamete fuses with the female gamete to form a zygote.
Assertion (A): The process of photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplasts of plant cells.
Reason (R): Photosynthesis occurs in the mitochondria of plant cells, where sunlight is absorbed to make glucose.
Name the part of the digestive system responsible for:
A. Protein digestion
B. Absorption of nutrients
C. Storing undigested waste
D. Emulsification of fats
(a) How is the folding of leaves in a Mimosa plant different from the movement of plant stems towards sunlight? Mention the type of movement and its cause.
(b) Which hormone is responsible for the fight-or-flight response in humans? Name the gland that secretes it and describe its effects on the body during stress.
What type of reproduction occurs in yeast? Describe the process of reproduction in yeast with the help of a labelled diagram.
(a) In an aquatic food chain: Phytoplankton → Zooplankton → Small Fish → Big Fish, what will happen if the population of zooplankton decreases? How will this impact other trophic levels?
(b) There is a gas in the atmosphere that plays a role in protecting living organisms by shielding them from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation. However, this gas is being depleted due to human activities.
14.
(i) Name the gas and explain how it protects living organisms.
(ii) What roles do Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) play in the depletion of this gas? Suggest one alternative to CFCs that can help reduce this depletion.
(a) Why is the surface area important for gas exchange in organisms? OR
(b) Give reasons for the following:
1. The diaphragm plays a crucial role in breathing.
2. Blood pressure is higher in arteries than in veins.
3. The heart beats faster during exercise.
4. The process of digestion is necessary for nutrient absorption.
(a) In a monohybrid cross between a pure tall plant (TT) and a pure short plant (tt):
(i) What will be the phenotype and genotype of the F₁ generation?
(ii) What is the phenotypic ratio and genotypic ratio observed in the F₂ generation?
15.
16.
(iii) How does this experiment validate Mendel’s Law of Segregation? OR
(b) Justify the statement: Adominant allele may not always express the dominant trait in an organism.
(a) Describe the process of menstruation in females. What happens if fertilization does not take place?
(b)Explain the process of regeneration in organisms such as Planaria. How does this mode of reproduction work? Illustrate with a labelled diagram.
Section B (Chemistry)
Which one has maximum number of atoms?
A. 24g of C
17.
B. 56g of Fe
C. 27g ofAl
D. 28g of Si
18.
Distinguish between metals and non-metals with respect to the nature of their oxide.
A. Oxides of metals are basic and oxides of non-metals are acidic
B. Oxides of metals are acidic and oxides of non-metals are basic
C. Oxides of both metals and non-metals are acidic
D. Oxides of both metals and non-metals are basic
Astudent tested the acidity of two solutions �� and �� with the help of a universal indicators. Solution �� turns orange, �� turns red. Which of the solutions is a more acidic?
A. Solution X
B. Solution Y
C. Neither solution X nor Y
D. Both solution X and Y
Which of the following has the smallest mass?
A. 6023 ×1023 atoms of He
B. 1 mole atoms of He
C. 4 g of He
D. 1 atom of He
Which of the following contains an alcoholic functional group?
A. CH2=CH-CH2OH
B. CH3-CH2-CH2-COOH
C. CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH=O
D. CH3-CH2-CH2-O-CH3
Select the incorrect statement.
A. Nitric acid is used in fertilizers.
B. Hydrochloric acid is used as a cleansing agent.
C. Carbonic acid is used in car batteries.
D. Tartaric acid is a constituent of baking powder.
Which of the following is an example of a neutralization reaction?
A. Using baking soda to soothe a bee sting
B. Using toothpaste to prevent tooth decay
C. Taking an antacid to ease heartburn
D. All answers are correct
24.
Question No. 24 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true but R is false.
D. A is false but R is true
Assertion (A): Two to three days after whitewashing walls become shining.
Reason (B): Calcium hydrogen carbonate is formed when calcium hydroxide reacts with carbon dioxide.
25.
Fresh milk has a pH of 6 When it changes into curd (yoghurt), will there be an increase or decrease in pH value? Why?
Arotten egg smell is obtained when an ore is treated with dil. HCl. Identify the ore and explain the process of extraction of metal from this ore.
A Abaker used baking soda instead of baking powder for baking the cake. Will this affect the taste of the cake? If yes how?
27.
28.
B. Explain the conversion of baking soda into the baking powder.
C. What causes the cake to be spongy and soft?
Ais a reddish-brown metal, which combines with O2 at < 1370 K giving B, a blackcoloured compound. At a temperature > 1370 K,Agives C which is red in colour. Find A, B, and C with chemical reaction equations.
Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow:
Iron and aluminium are two widely used metals. Iron is extracted from its ore haematite (Fe₂O₃) by reduction using carbon in a blast furnace, whereas aluminium is extracted from bauxite (Al₂O₃) using electrolysis of molten alumina. The methods of extraction depend on the reactivity of the metal.
Answer the following:
a. Why is carbon used to extract iron from haematite, but not for aluminium?
b. Write the chemical equation for the extraction of iron from haematite using carbon.
c. Name the process used to extract aluminium from bauxite.
d. Give one reason why electrolysis is necessary for extracting aluminium.
31.
What is methane? Draw its electron dot structure. Name the type of bonds formed in this compound. Why are such compounds:
(i)poor conductors of electricity?And
(ii)have low melting and boiling points? What happens when this compound burns in oxygen?
OR
Read the passage carefully and answer the following:
Aldehydes and ketones are organic compounds containing the carbonyl functional group (C=O). Aldehydes have the carbonyl group at the end of the carbon chain, while ketones have it within the carbon chain. Both can undergo characteristic reactions such as Tollens’test, Fehling’s test, and oxidation reactions.
Answer the following:
a)Define aldehyde and ketone with general formulas.
b)Draw the structural formula of ethanal and propanone.
c)Name the functional group present in aldehydes and ketones.
d)Write a chemical reaction to show the oxidation of ethanal.
e)Mention one distinctive chemical test to distinguish aldehydes from ketones and explain the observation.
For a mirror, linear magnification 'm' comes out to be +2. The conclusion that can be drawn from this is
A. Mirror is concave
B. Mirror can be convex or concave
C. Object lies between pole and infinity
D. Object lies beyond focus
When a 4 V battery is connected across an unknown resistor, there is a current of 100 mA in the circuit. The value of the resistance of the resistor is:
32.
Question No. 32 consists of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true but R is false.
D. A is false but R is true
Assertion (A): Aconcave mirror is used as a shaving mirror
Reason (R): When an object is placed between the pole and the focus of a concave mirror, a virtual, erect, and magnified image is formed.
33.
34.
Define the term power of accommodation. Write the modification in the curvature of the eye lens that enables us to see the nearby objects clearly?
Attempt either optionAor B.
A. Astudent has two resistors - 2 Ω and 3 Ω. She has to put one of them in place of R2 as shown in the circuit. The current that she needs in the entire circuit is exactly 9
A.Show by calculation which of the two resistors she should choose. OR
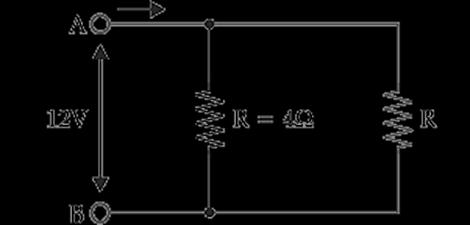
B. How many 132 Ω resistors in parallel are required to carry 5Aon a 220 V line?
A. Water has a refractive index of 1.33, and alcohol has a refractive index of 1.36. Which of the two media is optically denser? Give reasons for your answer.
35.
36.
B. Draw a ray diagram to show the path of a ray of light passing obliquely from water to alcohol.
C. State the relationship between the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction in the above case. 3
Calculate the total cost of running the following electrical devices in the month of September, if the rate of 1 unit of electricity is Rs 6.00.
(i)Electric heater of 1000 W for 5 hours daily.
37.
38.
(ii)Electric refrigerator of 400 W for 10 hours daily.
Can a freely suspended current-carrying solenoid stay in any direction? Justify your answer.Whatwillhappenwhenthedirectionofcurrentinthesolenoidisreversed?Explain
Read the passage on human eye and answer any four questions from Ato D
Eye is a natural optical device by which human could see objects around him. It forms an inverted, real image on a light sensitive surface. It works on the phenomenon of refraction of light through a natural convex lens. However, Meena was unable to see clearly the words written on the black board placed at a distance of approximately 3 m from her. Her mother discussed the same with the doctor. Doctor explained her about this defect of vision and its correction.
A.What kind of defect Meena is suffering from?
(i)Myopia
(ii)Hypermetropia
(iii)Astigmatism
(iv)Malnutrition
B.The possible cause this defect is
(i)eyeball is of same size
(ii)eyeball becomes long
(iii)eyeball becomes small
(iv)None of the above
C.The closest distance up to which a person can see without any strain in the eyes
(i)35 cm
(ii)15 cm
(iii)5 cm
(iv)25 cm
D.The defective eye of a person has near point 0.5 m and far point as 3 m. The power of both lens required for reading purpose and seeing far off objects is
(i)0.75 D and +4 D
(ii)+2D and – 1/3 D
(iii) – 2.5D and + 1/8D
(iv)0.85 D and – 2 D
39.
Attempt either optionAor B.
A. An electric lamp of resistance 20 Ω and a conductor of resistance 4 Ω are connected to a 6 V battery as shown in the circuit. Calculate:
(i)the total resistance of the circuit.
(ii)the current through the circuit.
(iii)the potential difference across the (i) electric lamp and (ii) conductor, and (iv)power of the lamp.
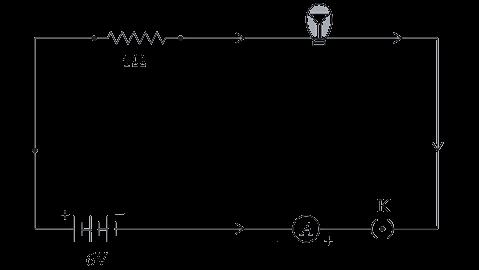
OR
B. (i) Three resistors R1, R2 and R3 are connected in parallel and the combination is connected to a battery, ammeter, voltmeter and key. Draw suitable circuit diagram and obtain an expression for the equivalent resistance of the combination of the resistors.
(ii)Calculate the equivalent resistance of the following network:
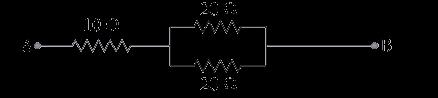
Marking Scheme
SectionA(Biology) 1.
5. D. The left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs.
8. A.BothAand R are true, and R is the correct explanation ofA.
9. C.Ais true, but R is false.
(i)Protein digestion: Stomach
The stomach secretes pepsin (an enzyme) and hydrochloric acid, which help in the digestion of proteins into smaller peptides.
(ii)Absorption of nutrients: Small intestine
10.
11.
The small intestine, especially the jejunum and ileum, has villi and microvilli that increase the surface area for efficient absorption of nutrients into the bloodstream.
(iii)Storing undigested waste: Large intestine
The large intestine stores undigested and unabsorbed material temporarily before excretion.
(iv)Emulsification of fats: Liver (via bile)
The liver produces bile, which is stored in the gallbladder and released into the small intestine. Bile salts help break down large fat globules into smaller droplets, aiding fat digestion.
a.The folding of leaves in a Mimosa plant is a nastic movement caused by changes in turgor pressure in response to touch, and it is independent of the direction of the stimulus. The movement of plant stems towards sunlight is a tropic movement (phototropism) caused by uneven distribution of auxin, and it occurs in the direction of the light source.
b. The hormone responsible for the fight-or-flight response is adrenaline (epinephrine), which is secretedbytheadrenalgland(specifically,theadrenalmedulla). Duringstress,adrenalinecauses several changes in the body: it increases heart rate, raises blood pressure, dilates the airways to improve oxygen intake, redirects blood flow to muscles, and stimulates the breakdown of glycogen into glucose for quick energy. These changes prepare the body for immediate action in stressful or emergency situations
12. Reproduction in Yeast: 1
Yeast reproduces asexually through budding. Process:
(a)Asmall bulge, called a bud, forms on the parent yeast cell.
(b)The nucleus of the parent cell divides, and one of the nuclei moves into the bud.
(c)The bud grows in size while remaining attached to the parent cell.
(d)Once fully developed, the bud detaches, forming a new yeast cell.
a.If the population of zooplankton decreases, the phytoplankton population (first trophic level) will increase due to reduced grazing pressure, which may lead to algal blooms and disrupt the aquatic ecosystem. Small fish (third trophic level), which rely on zooplankton as a primary food source, will face food scarcity, causing a decline in their population. This, in turn, will affect big fish (fourth trophic level), as the reduction in small fish will limit their food supply, leading to a decrease in their population as well Thus, the decline in zooplankton disrupts the balance of the entire food chain, impacting both the lower and higher trophic levels.
b.
(i) The gas ‘X’is ozone (O₃). It forms the ozone layer in the stratosphere, which absorbs harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun. This protection prevents UV rays from causing skin cancer, cataracts, and genetic damage in living organisms.
(ii) CFCs (Chlorofluorocarbons) are synthetic chemicals used in refrigeration, air conditioning, and aerosol sprays. When released into the atmosphere, CFCs rise to the stratosphere, where they break down under UV light, releasing chlorine atoms. These chlorine atoms react with ozone molecules, leading to the depletion of the ozone layer.
(iii) One alternative to CFCs is hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), which do not contain chlorine and, therefore, do not contribute to ozone depletion.
15.
a. The surface area is important for gas exchange because a larger surface area allows more oxygen to be absorbed and more carbon dioxide to be released, increasing the efficiency of gas exchange in organisms.
b. (i) The diaphragm is a muscle that helps us breathe. When it contracts, it moves down, creating more space in the chest for the lungs to expand and take in air. When it relaxes, it moves up, helping push air out of the lungs.
(ii) Arteries carry blood away from the heart, which pumps it with high pressure. Veins carry blood back to the heart at lower pressure because they don't have to push the blood as forcefully.
(iii)During exercise,yourmuscles need moreoxygen.Theheartbeats fasterto pump moreblood, supplying the muscles with the oxygen and nutrients they need.
(iv)Digestion breaks down food into smaller parts, like sugars, amino acids, and fats, so the body can absorb and use them for energy and growth. Without digestion, our bodies couldn’t absorb nutrients properly.
a Monohybrid cross
(i)In the F₁ generation, the genotype of all the plants will be Tt (heterozygous tall). Since tallness (T) is dominant over shortness (t), the phenotype of all the plants will be tall.
(ii)In the F₂ generation, the following outcomes are observed:
• Genotypic ratio: 1 : 2 : 1 ( TT : Tt : tt)
• Phenotypic ratio: 3 : 1 (Tall : Short)
This occurs because the F₁ plants (Tt) produce two types of gametes (T and t), which combine randomly to form the offspring.
(iii) This experiment validates Mendel's Law of Segregation, which states that the two alleles of a gene segregate or separate during gamete formation, and each gamete receives only one allele.
In the F₂ generation, the segregation of alleles (T and t) results in the reappearance of the recessive trait (short plants) in a 3:1 phenotypic ratio, which demonstrates the independent inheritance of alleles.
b Adominant allele can be inherited but may not always express the dominant trait due to factors like incomplete dominance or co-dominance. In incomplete dominance, the dominant allele does not fully express its trait when paired with a recessive allele, leading to an intermediate phenotype, like in some flower colors.
In co-dominance, both alleles contribute equally to the phenotype, such as in blood types, where bothAand B alleles are expressed together.Additionally, the presence of other genes or
16.
environmental factors can influence the expression of the dominant allele. Therefore, even though the dominant allele is inherited, it might not always fully express its associated trait.
a.(i) Menstruation is the process in which the thickened uterine lining, along with blood and mucus, is shed through the vagina. The uterine lining, also known as the endometrium, plays a crucial role during the menstrual cycle. It thickens and becomes enriched with blood vessels under the influence of hormones to prepare for the implantation of a fertilised egg. This thickened lining provides nourishment and support for the developing embryo if fertilization occurs.
If fertilization fails to occur, the hormone levels drop.As a result, the thickened uterine lining is no longer needed and is shed from the body in the form of blood and mucus during menstruation. This marks the beginning of a new menstrual cycle. This usually lasts 3-7 days, helping the body prepare for the next possible pregnancy.
b.Regeneration is a process in which certain organisms can regrow lost or cut body parts into a complete organism. In Planaria, if the body is cut into two or more parts, each part grows into a new, complete organism.
Steps of Regeneration in Planaria:
• The body of Planaria is cut into pieces.
• Special cells in the body, called neoblasts, divide and form new cells.
• These cells regenerate the missing body parts like the head or tail.
• Each piece grows into a fully functional new organism.
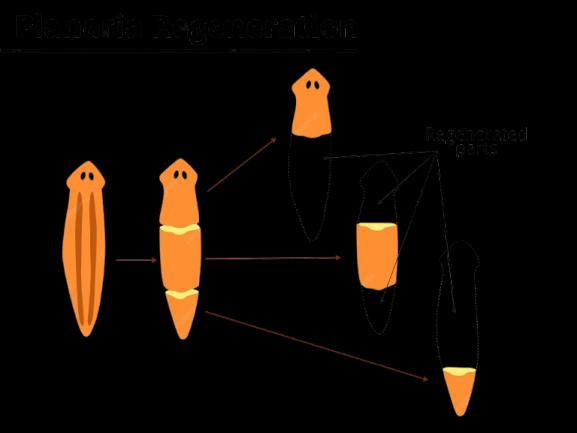
Section B (Chemistry)
25.
26.
When milk changes into curd, the pH value will change. The pH value of milk is 6 since it is acidic. However, when the milk is converted into curd due to the action of bacteria, lactic acid is formed, which is more acidic. Therefore, the pH value of the milk is reduced as it turns to curd.
The smell of rotten eggs is usually produced by sulphur. So, it must be sulphide ore. Let us assume that the one is a zinc blend (ZnS).
The concentration of ore:
First of all, the ore is concentrated by the method of froth flotation process. Then it is converted into its metal oxide via roasting in the supply of air. The chemical reaction is as follows:
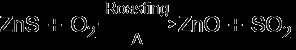
After that, it is converted into metal form by using a reducing agent like carbon,

It is further refined to get it in a pure form.
A If the baker uses baking soda instead of baking powder, the taste will be bitter as baking soda is bitter. This happens because of the formation of sodium carbonate. 2
27.
B. We can convert baking soda into baking powder by adding some tartaric acid. Baking soda is much stronger than baking powder. The ����2 evolving baking powder tries to escape out of the dough. This ����2 is responsible for making the cake spongy and soft. When baking powder mixes with water, sodium hydrogen carbonate reacts with tartaric acid to evolve ����2 gas. ����������3(����) + ��2 + (����) → ���� + (����) + ����2(��) + ��2��(��)
C. The ����2 gas produced gets trapped in the wet dough and bubbles out slowly, causing the cake (or bread) to rise and become soft and spongy.
The metalAis described as reddish-brown that combines with oxygen (O2) at a temperature less than 1370 K to form a black-colored compound B and at a temperature greater than 1370 K to form a red-colored compound C is likely to be copper. Let's go through the reactions:
Formation of Black Compound (B):
2Cu + O2 → 2CuO
At temperatures below 1370 K, copper (A) reacts with oxygen to form black copper (II) oxide (CuO).
Formation of Red Compound (C):
2Cu + O2 → 2Cu2O
At temperatures above 1370 K, copper (A) reacts with oxygen to form red copper(I) oxide (Cu2O).
28.
29.
So, in summary:
MetalA: Copper (Cu)
Compound B: Black Copper(II) oxide (CuO)
Compound C: Red Copper(I) oxide (Cu2O). OR
a) Iron is less reactive than carbon, so it can be reduced using carbon. Aluminium is more reactive than carbon, so carbon cannot reduce its oxide.
b) Fe2O3 +3C→2Fe+3CO
Carbon reduces iron oxide to iron
c)Aluminium is extracted by electrolysis of molten alumina (Al₂O₃).
d) Electrolysis is necessary because aluminium is highly reactive, and cannot be reduced by carbon. Electric current helps breakAl₂O₃ into aluminium and oxygen.
CH4 is the molecular formula of methane. Methane is a saturated hydrocarbon. It is a colourless and odourless gas. Electron dot structure of methane is
Type of bond: The single carbon atom in the molecule's centre and the four hydrogen atoms are connected by covalent bonds.
Structure of methane:
(i)Conductivity of methane-
Methane is a poor electrical conductor.All of the bonds in methane are covalent. Hence the molecule has no free electrons that may aid in electrical conductivity.
(ii)Melting and boiling point of methane:
Covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points due to the molecules' low intermolecular forces of attraction. Methane has a relatively low melting and boiling point since it is also a covalent compound.
Burning of methane in oxygen:
Methane produces carbon dioxide, CO2 and water as byproducts of burning when exposed to oxygen. The reaction is as follows:
4 + O2 → CO2 + H2O
a) Definition:
Aldehyde: Organic compounds with the carbonyl group (–CHO) at the end of the carbon chain.
General formula: R–CHO.
Ketone: Organic compounds with the carbonyl group (C=O) within the carbon chain. General formula: R–CO–R’
b)Structural formulas:
Ethanal (CH₃CHO)
Propanone (CH₃COCH₃):
c)Functional group:
Both aldehydes and ketones contain the carbonyl group (C=O).
In aldehydes, the carbonyl is at the end of the carbon chain, while in ketones, it is within the chain
d)Oxidation of ethanal:
Ethanal oxidizes to ethanoic acid in the presence of an oxidizing agent like acidified potassium dichromate (K₂Cr₂O₇/H₂SO₄).
CH3CHO+[O]→CH3COOH
Ketones, like propanone (CH₃COCH₃), generally do not oxidize easily under similar conditions.
e)Test to distinguish aldehyde from ketone: Tollens’test:
Aldehyde reacts with Tollens’reagent to form a silver mirror on the inner walls of the test tube.
Ketone shows no change.
This test confirms the presence of –CHO group in aldehydes.
32. A BothAand R are true; R is the correct explanation ofA
Theabilityoftheeyelens to adjust itsfocal lengthto clearlyfocus onobjects at varyingdistances is called the power of accommodation.
To see nearby objects clearly, the ciliary muscles contract, increasing the curvature of the eye lens, making it thicker. This decreases the focal length of the lens, enabling the eye to focus the image of the nearby object on the retina.
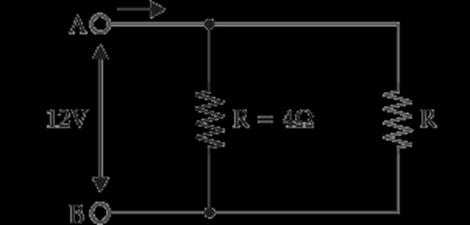
The overall current needed = 9A
Voltage = 12 V
By Ohm’s law, V = IR
The resistance for the entire circuit, R = V I = 12 9
Hence, R = 4 3 Ω
Here, R1 and R2 are in parallel,
Hence, R= R1R2 R1+R2
Or 4 3 = 4R2 4+R2
Therefore, R2 = 2 Ω
B. Given, V = 220 V, I = 5A By Ohm’s law, V = IR
In parallel combination, let the no. of resistors =��
The number of resistors =3
A. The refractive index of a medium indicates how much the speed of light decreases in that medium compared to vacuum. A higher refractive index means the medium is optically denser.
Since alcohol has a refractive index of 1.36, which is greater than water's refractive index of 1.33, alcohol is optically denser.
B. When a ray of light enters from water to alcohol, the ray bends towards the normal.
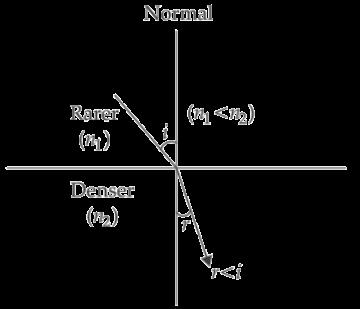
C. Relationship between the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction is given by Snell's Law: n1sini=n2 sinr
Since, n2 >n1, the angle of refraction (r) will be smaller than the angle of incidence (i)
Given, Rate of electricity: Rs 6.00 per unit
(a)Electric heater:
= 1 kW
Energy consumed in the month of September = 30 × 5kWh = 150kWh
Total cost = 150 × 6 = Rs900
(b)Electric refrigerator:
Power, P = 400W = 0.4kW
Time = 10 hours daily
Energy consumed per day = 0.4kW × 10h = 4kWh
Energy consumed in the month of September = 30 × 4kWh = 120kWh
Total cost = 120 × 6 = Rs720
Total cost = Cost of heater + Cost of refrigerator = Rs 1620
37. A current-carrying solenoid behaves like a bar magnet because it produces a magnetic field. When freely suspended, it aligns itself in the Earth's north-south direction due to its magnetic properties.
A freely suspended current-carrying solenoid does not stay in any direction. The solenoid's magnetic field interacts with Earth's magnetic field, causing it to align in a specific direction. Reversing the current in the solenoid reverses its magnetic poles. The end that was the north pole becomes the south pole, and vice versa, changing the alignment.
A. (i) Myopia
Explanation: Meena was not able to read the words written on the blackboard but she could see the nearby objects clearly. Thus, she was suffering from Myopia. Myopia, or nearsightedness, is a condition where a person can see nearby objects clearly but struggles to see distant objects.
B. (ii) eyeball becomes long
Explanation: In myopia, the eyeball elongates, causing light rays to focus in front of the retina instead of on it.
38.
C. (iv) 25 cm
Explanation: Anormal eye is not able to see distinctly the objects placed closer than 25 cm, without putting any strain on the eye. This is because the ciliary muscles of eyes are unable to contract beyond a certain limit. If the objects are placed at a distance less than 25 cm from the eye, then the objects appear blurred because light rays coming from the object meet beyond the retina.
D. (ii) +2D and – 1/3 D
Explanation: Let the object distance = u, image distance = v For reading purpose: u = -25 cm, v = -0.5 cm = -50 cm
For far away objects: u = - ∞, v = -3 m
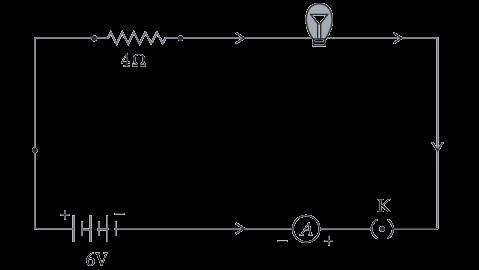
Given,
Voltage of the battery = 6 V
Resistance of the electric lamp, R1 = 20 Ω
Resistance of the conductor, R2 = 4 Ω
(i)Total resistance of the circuit, R = R1 + R2
Hence, total resistance = 20 Ω+4Ω=24Ω
(ii) Current through the circuit, I = V R (Using Ohm’s law)
I = 6 24 = 0.25A
(iii)Potential difference across the lamp, V1 = IR1
Hence,V1 = 20 × 0.25 = 5V
Potential difference across the conductor, V2 = IR2
Hence, V2 = 4 × 0.25 = 1V
(iv)Power of the lamp, P = I2R
P = (0.25)2 × 20
P = 1.25 W OR
B.(i) We know, Total current, I = I1+I2+I3
Let RP be the equivalent resistance of the resistors R1, R2 andR3
Total current in the circuit, I = V RP
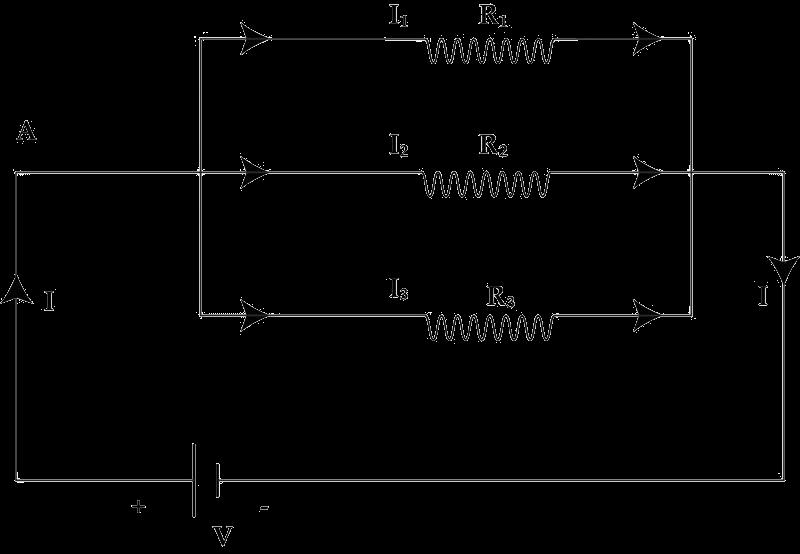
Now, I1 = V R1 , I2 = V R2 , I3 = V R3
Since, I = I1+I2+I3 Or I = V( 1 R1 + 1 R2 + 1 R3 ) = V RP Therefore, 1 R
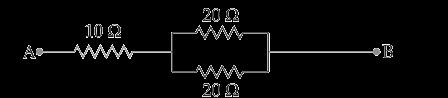
Here, both the 20 Ω resistances are in parallel combination
Hence, the equivalent resistance of the parallel connection, RP = R1R2 R1+R2
Or RP = 20×20 20+20 = 10 Ω
Now, RP is in series with 10 Ω
Therefore, the total resistance of the circuit, R = 10 Ω + 10 Ω = 20 Ω
SCIENCE
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER - 3
CLASS X (2025-26)
Max. Marks: 80 Time allowed: 3 hours
General Instructions:
1. This question paper consists of 39 questions in 3 sections. SectionAis Biology, Section B is Chemistry, and Section C is Physics.
2. All questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice is provided in some questions.Astudent is expected to attempt only one of these questions.
SectionA (Biology)
Which part of the human brain is responsible for maintaining posture and balance?
A. Cerebrum
1.
B.
C
2.
3.
The characteristic that is expressed in an organism when two different alleles are present is called:
A.Recessive trait
B.Dominant trait
C.Mutant trait
D Lethal trait
Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding the flow of energy in an ecosystem?
A.Energy flows in a unidirectional manner.
B.Energy is lost as heat at each trophic level.
C.Energy is recycled in an ecosystem.
D.Energy enters an ecosystem through producers.
What will be the consequence if the kidneys fail to function properly?
A. Increased oxygen transport
B.Accumulation of toxic waste in the body
C Increased food absorption
D. Enhanced cellular respiration
Which of the following is NOT an involuntary action?
A. Beating of heart B Walking C Peristalsis
D. Reflex action
Apure tall pea plant is crossed with a pure dwarf pea plant. What will be the phenotype of the F1 generation?
A.All dwarfs
B.All tall
C.50% tall, 50% dwarf
D.25% tall, 75% dwarf
During aerobic respiration, the complete oxidation of one molecule of glucose yields: A. 2ATP
36
38ATP
Question No. 8 to 9 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true but R is false.
D. A is false but R is true 8.
Assertion (A): Respiration is essential for survival of living organisms.
Reason (R): It provides energy by breaking down food molecules in the presence or absence of oxygen.
Assertion (A): The thyroid gland controls blood sugar level in humans.
Reason (R): The hormone thyroxine regulates carbohydrate, protein, and fat metabolism. 1
20.
21.
The most reactive metal among the following is:
A Zinc
B. Iron
C Sodium
D. Copper
Tooth decay begins at the pH of:
A 5.1
B. 5.8
C. 6.5
D 8
The IUPAC name of CH₃–CH₂–CHO is:
A. Propanone
22.
B. Propanal
C. Propanol
D. Propanoic acid
When you add a few drops of acetic acid to a test-tube containing sodium bicarbonate powder, which one of the following is your observation?
A No reaction takes place
23.
24.
B.Acolourless gas with pungent smell is released with brisk effervescence
C Abrown coloured gas is released with brisk effervescence
D. Formation of bubbles of a colourless and odourless gas 1
Question No.24 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true but R is false.
D. A is false but R is true
Assertion (A):Acids turn blue litmus paper red.
Reason (R):Acids release H+ions in aqueous solution.
Give one example each of:
25.
26.
28.
2)Anon-metal which is a good conductor of electricity.
Write a balanced chemical equation for the following and mention the type of reaction:
a)Potassium bromide + Barium iodide → Potassium iodide + Barium bromide
b)Zinc carbonate → Zinc oxide + Carbon dioxide
c)Magnesium + Hydrochloric acid → Magnesium chloride + Hydrogen
Write the molecular formula and IUPAC name of the following:
a)CH₃–CH₂–CH₃
b)CH₃–CH₂–OH
c)CH₃–COOH
Read the following text carefully and answer the questions that follow.
Aluminium is a very reactive metal, but it is widely used in making utensils and as a wrapping material for food. It also finds use in extraction of more reactive metals like chromium and manganese by thermite process. When exposed to moist air, aluminium does not corrode further like iron does.
1.Why does aluminium not corrode easily?
2. Write the thermite reaction of aluminium with Fe₂O₃.
3. Why is aluminium preferred for making food containers?
4. Name one property of aluminium that makes it useful in wrapping food items.
What is the metal reactivity series? Explain with examples how the position of a metal in the reactivity series decides the method of its extraction.
Teacher demonstrates the electrolysis of water, and two gases are collected at different electrodes.
a)Name the gases collected at the cathode and anode.
b)Why is the volume of gas collected at one electrode double the other?
c)Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction
Define a chemical reaction. Write a balanced chemical equation for the following reactions and state the type of each reaction.
a)Hydrogen burns in oxygen to form water.
b)Zinc reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce zinc chloride and hydrogen gas.
30.
c)Barium chloride reacts with sodium sulphate to give barium sulphate and sodium chloride.
d)Decomposition of water into hydrogen and oxygen.
Section C (Physics)
Aray of light passes from mediumAto medium B. The angle of incidence inAis greater than the angle of refraction in B. Which of the following is true?
A. MediumAis denser than B
B Medium B is denser thanA
C. BothAand B have the same optical density
D. The light will undergo total internal reflection
Which of the following phenomena is responsible for the reddish appearance of the sun at sunrise and sunset?
A. Dispersion
31.
B Internal reflection
C Scattering of light
D.Atmospheric refraction
Question No. 32 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true but R is false.
D. A is false but R is true 32.
Assertion (A): Two bar magnets attract when they are brought near to each other with the same pole.
Reason (R): Unlike poles will attract each other.
Why is a concave mirror used in a torch? Explain its working and determine the nature of the image formed.
34. Explain why the sky appears blue during the day but turns reddish-orange during sunset. 2
An object is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a concave mirror with a focal length of 15 cm. Determine the position, nature, and magnification of the image formed
Explain why a pencil appears bent when dipped in water. Support your answer with a ray diagram and mathematical explanation.
1)Acurrent through a horizontal power line flows in the east to west direction.What is the direction of the magnetic field at a point directly below it and at a point directly above it?
2) List two methods of producing magnetic fields.
Explain the function of the following parts:
Rahul was getting ready for a school play and needed to adjust his costume. He stood in front of a makeup mirror and noticed that when he moved closer, his face appeared larger, but when hesteppedback, theimagechanged. Curiousabout this, hestartedexperimenting with different distances.
1)Why does Rahul see a magnified image when he is close to the mirror?
2)How does the nature of the image change as he moves farther from the mirror?
3)Where should Rahul
1) Define Ohm’s Law along with a labelled circuit diagram.
2) Draw a circuit diagram showing the series combination of three resistors and derive an expression for the total resistance
1) Explain why resistance increases with an increase in temperature for metallic conductors.
2)A100W, 220V bulb is used for 5 hours daily. Calculate the energy consumed in a month (30
Marking Scheme
SectionA(Biology)
8. A BothAand R are true, and R is the correct explanation of
9. D Ais false, but R is true.
10.
Abscisic acid (ABA) is a plant hormone that inhibits growth and plays a crucial role in stress responses. It promotes leaf wilting, which minimizes transpiration and conserves water during drought conditions. 2
11. It facilitates the exchange of nutrients, oxygen, and waste between the mother and foetus. It secretes hormones like progesterone to maintain pregnancy.
12.
13.
The sex of a child is genetically determined by sex chromosomes. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, including one pair of sex chromosomes (XX in females and XY in males). During fertilization, the mother contributes an X chromosome, while the father can provide either an X or a Y chromosome. If the sperm carrying an X chromosome fertilizes the egg, the child will be female (XX). If the sperm carries a Y chromosome, the child will be male (XY). Thus, the father determines the sex of the child.
Veins have valves to prevent the backflow of blood and ensure its unidirectional flow toward the heart. Since veins carry deoxygenated blood at low pressure, valves help counteract gravity, especially in the legs. In contrast, arteries transport oxygenated blood under high pressure from the heart, so their thick, elastic walls and strong blood flow eliminate the need for valves.
The transmission of nerve impulses is considered an electrochemical process because it involves both electrical and chemical signals.
14.
Electrical impulses travel along the neuron due to ion exchange across the membrane, creating an action potential.
At synapses, neurotransmitters are released, converting the electrical signal into a chemical one for communication.
15.
Plants respond to stimuli using immediate responses or growth-related movements. Since they lack a nervous system, they use electrical-chemical signals to transmit information, and movement occurs by changing water pressure in cells.
Immediate Response to Stimulus (Nastic movements):
• These are quick movements not dependent on the direction of the stimulus.
• For example, in Mimosa pudica (touch-me-not), touch causes water loss from specific cells, making leaves fold.
Growth-Related Movements (Tropic movements):
These are slow and directional.
• Phototropism: Shoots bend towards light, while roots grow away.
• Geotropism: Roots grow downward (positive geotropism), while shoots grow upward (negative geotropism).
• Thigmotropism: Tendrils of climbers wrap around supports.
• Chemotropism: Pollen tubes grow towards ovules due to chemical signals. These adaptations help plants grow efficiently, ensuring survival and reproduction in changing environments.
Nutrition in humans involves ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation, and egestion.
• Food enters the mouth, where salivary amylase breaks down starch into maltose.
• The bolus moves through the oesophagus into the stomach, where gastric glands secrete pepsin, which digests proteins into peptides. Hydrochloric acid creates an acidic medium for enzyme action.
16.
• In the small intestine, bile from the liver emulsifies fats, while pancreatic enzymes act on food. Pancreatic amylase converts starch to maltose, trypsin breaks proteins into peptides, and lipase digests fats into glycerol and fatty acids. Intestinal enzymes like maltase, sucrase, and lactase further break down carbohydrates into simple sugars. Peptidases convert peptides into amino acids. Nutrients are absorbed through villi into the bloodstream, transported to cells for energy and growth.
• Undigested food moves to the large intestine, where water is absorbed. The waste then moves to the rectum and is then egested through the anus in the form of faeces
This ensures efficient nutrient utilization in the body.
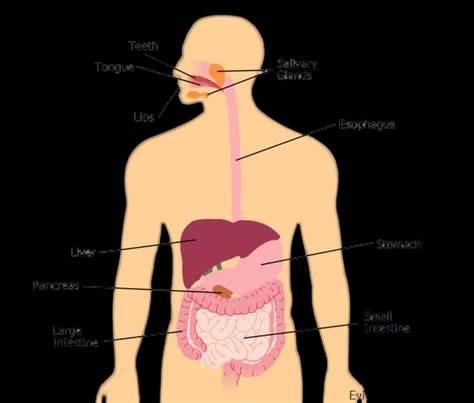
OR
Plants transport water and food through specialized vascular tissues: xylem and phloem.
1.Role of Xylem: Xylem transports water and minerals from the roots to the leaves through a process called transpiration pull. Water moves upward due to capillary action, root pressure, and cohesion-tension forces. The continuous loss of water from leaves (transpiration) creates a suction force, pulling water upward.
2. Role of Phloem: Phloem transports food, primarily sucrose, from leaves to other parts of the plant through translocation. This process occurs via pressure flow mechanism, where sugar from photosynthesis is actively loaded into the phloem, creating high pressure. Water follows by osmosis, pushing the food towards storage organs and growing tissues. Thus, the xylem ensures a steady supply of water for photosynthesis, while phloem distributes food for growth, storage, and energy needs, maintaining overall plant health.
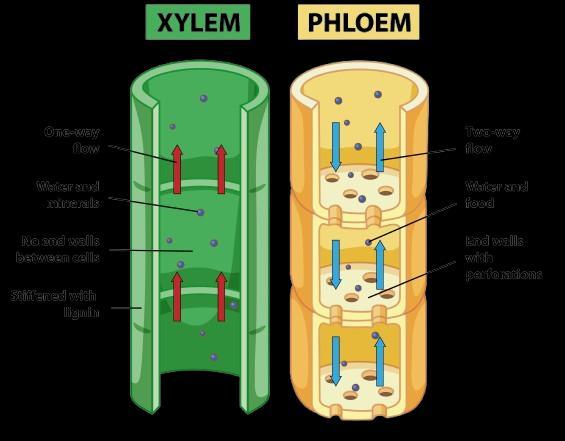
Section B (Chemistry)
17.
18.
19. A. Ethane + Cl₂ (in presence of sunlight)
20. C. Sodium
21. A. 5.1
22. B. Propanal
23. D Formation of bubbles of a colourless and odourless gas
24. A BothAand R are true, and R is the correct explanation ofA.
25.
26.
1) Sodium (or potassium) is stored in kerosene to prevent reaction with air
2) Graphite is a good conductor of electricity due to free electrons in its layers.
Balanced chemical equation are given for the following with the type of reaction:
a)KBr + BaI₂ → KI + BaBr₂ (Double displacement reaction)
b)ZnCO₃ → ZnO + CO₂ (Decomposition reaction)
c)Mg + 2HCl → MgCl₂ + H₂ (Displacement reaction)
a)Molecular formula: C₃H₈, IUPAC name: Propane
b)Molecular formula: C₂H₆O, IUPAC name: Ethanol
27.
28.
c)Molecular formula: C₂H₄O₂, IUPAC name: Ethanoic acid
1) Aluminium does not corrode easily because when it is exposed to air, it quickly reacts with oxygen to form a thin, compact, and strongly adherent layer of aluminium oxide (Al₂O₃). This oxide coating acts as a protective barrier that prevents further contact of aluminium with air and moisture, thereby stopping any further corrosion.
2) The thermite reaction involves the displacement of iron from iron(III) oxide by aluminium, as aluminium is more reactive than iron. The balanced chemical equation is:
In this reaction, aluminium reduces ferric oxide to molten iron while itself getting oxidised to aluminium oxide.
3) Aluminium is preferred for making food containers because it is a light metal, has high strength, and does not corrode due to its protective oxide layer. Moreover, aluminium does not react with food substances under normal conditions, keeping the food safe and uncontaminated. Its durability and resistance to rust make it a reliable choice for household and industrial uses. 1 1 1
4) One important property of aluminium is that it is highly malleable, meaning it can be beaten or rolled into very thin sheets without breaking. This property allows aluminium to be easily converted into foils, which are extensively used for wrapping food items to preserve freshness and prevent contamination.
OR
Definition: The reactivity series is the arrangement of metals in the decreasing order of their chemical reactivity. Metals like potassium, sodium, and calcium are highly reactive, while metals like silver and gold are least reactive.
Highly reactive metals (K, Na, Ca,Al, Mg):
These cannot be reduced by carbon because they are more reactive than carbon. They are extracted by electrolysis of their molten chlorides or oxides.
Example: Sodium is extracted from molten NaCl by electrolysis.
Moderately reactive metals (Zn, Fe, Pb, Cu):
These metals are less reactive than carbon. Their oxides can be reduced using carbon or carbon monoxide.
Example: ZnO + C → Zn + CO
Least reactive metals (Ag,Au, Pt):
These occur in the native state (in free form) because they do not react easily with air, water, or acids. Hence, they can be extracted simply by physical methods or by heating.
Example: Gold is extracted by washing and separation.
Conclusion: Thus, the method of extraction of metals depends on their position in the reactivity series. Higher the reactivity, more energy-intensive is the method of extraction.
a)The gases collected at the cathode and anode are:
Cathode: Hydrogen gas,
Anode: Oxygen gas
b)The volume of gas collected at one electrode double the other because water (H₂O) has twice as many hydrogen atoms as oxygen, so twice the volume of hydrogen is collected.
c)The balanced chemical equation for the reaction is: 2H₂O → 2H₂ + O₂.
This reaction follows the decomposition process, where water breaks down into hydrogen and oxygen due to electricity.
OR
Definition:Achemical reaction is a process in which one or more substances (reactants) are transformed into new substances (products) with different chemical properties.
a) Combination reaction: Hydrogen and oxygen combine to form water.
2+O2⟶2H2O
b) Displacement reaction: Zinc displaces hydrogen from hydrochloric acid. Zn+2HCl⟶ZnCl2 +H2 ↑
c) Double displacement reaction: Insoluble barium sulphate precipitate is formed. BaCl2 +Na2SO4 ⟶BaSO4 ↓+2NaCl
e) Decomposition reaction (Electrolysis): Water decomposes into hydrogen and oxygen on passing electric current.
30. B Medium B is denser thanA
Section C (Physics)
31. C Scattering of light 1
32. D. A is false, but R is true 1
Aconcave mirror is used in torches to produce a strong, focused beam of light.
Working Principle:
• Apoint source of light is placed at the focus of the concave mirror.
33.
34.
• After reflection, the rays emerge as a parallel beam in front of the mirror. This helps in projecting light to a large distance.
Nature of the Image:
• The image formed is real, highly magnified, and inverted at infinity.
• The parallel beam ensures maximum efficiency of the torchlight.
The sky appears blue during the day because short-wavelength blue light scatters more than other colours when sunlight interacts with air molecules (Rayleigh scattering).
During sunset, sunlight passes through a thicker layer of the atmosphere, scattering shorter wavelengths (blue and violet) out of view, allowing longer wavelengths (red and orange) to dominate the sky's colour.
35. We use the mirror formula:
Given:
Focal length, f= 15cm (concave mirror)
Object distance, u= 20cm
Substituting values:
36.
So, the image is formed at 60 cm in front of the mirror. Now, magnification is given by: m= v u = ( 60) 20 = 3
Since the magnification is negative, the image is real, inverted, and magnified. Thus, the image is real, inverted, and three times the size of the object, formed beyond the centre of curvature.
OR
When a pencil is partially submerged in water, light rays from the part of the pencil underwater refract at the air-water interface.As light travels from water (denser) to air (rarer), it bends away from the normal, making the submerged part appear displaced. This is called refraction of light.
According to Snell's Law: ��1 �������� = ��2 �������� where ��1 (water) = 1.33, ��2 (air) = 1, and i is the angle of incidence, r is the angle of refraction. Since ��1 > ��2, the light bends away from the normal, shifting the image.

1) By applying the Right-Hand Thumb Rule, if the thumb points along the current (east to west), the curled fingers give the direction of the magnetic field around the wire.
• At a point directly below the wire, the magnetic field is directed towards the south.
• At a point directly above the wire, the magnetic field is directed towards the north. 2) Magnetic fields can be generated in the following ways: 3
37.
• By using a permanent magnet, which naturally possesses magnetism. The field around it can be made visible by spreading iron filings on a sheet of paper placed above the magnet, where the filings align along the magnetic field lines.
• By passing an electric current through a conductor such as a straight wire, a circular coil, or a solenoid. The flow of current produces a magnetic field around the conductor, and its direction can be determined with the help of the right-hand thumb rule.
a) Retina
The retina is the light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye that contains photoreceptor cells (rods and cones). It captures the image formed by the lens and converts it into electrical signals, which are sent to the brain via the optic nerve.
b)
Cornea
The cornea is the transparent, curved outermost layer of the eye that allows light to enter. It focuses most of the light entering the eye by bending (refracting) it toward the lens.
c) Optic Nerve
The optic nerve transmits electrical signals from the retina to the brain, where they are interpreted as visual images
1)Aconcave mirror forms a magnified, upright, and virtual image when the object is placed between the focus (F) and the mirror. Since Rahul is standing close to the mirror, within the focal length, the image appears larger.
2)As Rahul moves farther:
• Beyond F but within C → The image becomes real, inverted, and magnified.
38.
39.
• At C (Center of Curvature) → The image is real, inverted, and of the same
• size.
• Beyond C → The image becomes real, inverted, and diminished.
3)Rahul should stand beyond the focal point (F) because a concave mirror forms an inverted image when the object is placed beyond the focus.
1) Ohm’s law states that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across its ends, provided the temperature and other physical conditions remain constant. V∝I
where R is the resistance of the conductor.
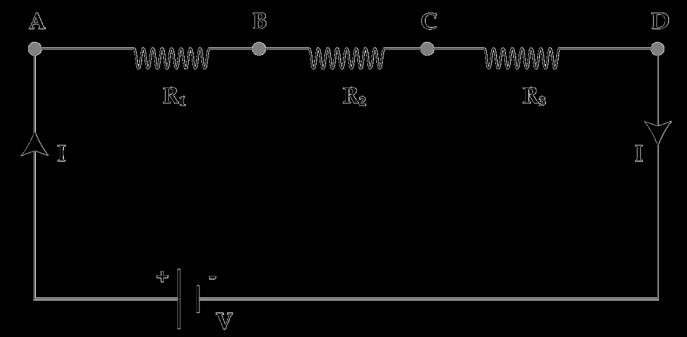
Let us consider 3 resistors R1,R2 and R3 are connected in series In a series circuit, the same current (I) flows through all resistors: V=V1 +V2 +V3
Using Ohm's Law (��=IR) for each resistor:
Cancelling I from both sides:
1) When temperature increases, the metal atoms vibrate more intensely, leading to increased collisions with free electrons. Due to frequent collisions, the movement of free electrons is obstructed, increasing the resistance.
2) We know, Energy = Power × Time
Power =100W, time =5h
On substituting the values:
Energy per day =100W×5h=500Wh=0.5kWh
Energy for 30 days =0.5×30=15kWh
The energy consumed in a month is 15 kWh
Max. Marks: 80
General Instructions:
SCIENCE
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER - 4
CLASS X (2025-26)
Time allowed: 3 hours
1. This question paper consists of 39 questions in 3 sections. SectionAis Biology, Section B is Chemistry, and Section C is Physics.
2. All questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice is provided in some questions.Astudent is expected to attempt only one of these questions.
SectionA (Biology)
Within the neural system, which of the following types of neurons is responsible for transmitting information from sensory receptors to the central nervous system (CNS)?
A.Motor neurons
1.
2.
B.Interneurons
C.Efferent neurons
D.Sensory neurons
In which part of the human female reproductive system does fertilisation occur?
A.Ovary
B.Uterus
C.Fallopian tube
Which of the following determines the sex of a child in humans?
A.Mother's genetic contribution
3.
B.Father's genetic contribution
C.Both parents equally
D.Environmental factors
What is the term for the movement of a stem towards sunlight?
4.
5.
C.Positive phototropic movement
D.Positive geotropic movement
During glycolysis, one molecule of glucose is converted into:
A.Two molecules of pyruvate
B.One molecule of acetyl-CoA
C.Three molecules of carbon dioxide
D.Four molecules ofATP 1
Which of the following is true about blood pressure in the pulmonary artery?
A.Same as that in aorta
6.
B.More than that in the carotid
C.More than that in the pulmonary vein
D.Less than that in the vena cavae 1
What prevents the stomach from digesting itself despite the production of highly corrosive hydrochloric acid?
A.The presence of an alkaline mucus layer
7.
B.The production of trypsin inhibitors
C.Constant cell turnover in the stomach lining
D.Inhibition of enzyme activity during fasting 1
Questions No. 8 to 9 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true, but R is false.
D. A is false, but R is true
8. Assertion (A):Asexual reproduction results in genetically identical offspring.
Reason (R): In asexual reproduction, gametes from two parents fuse to form a zygote. 1
Assertion (A): Sweat glands are also called excretory organs.
9.
Reason (R): Sweat glands help in the removal of excess salts and other materials from the body. 1
10. Compare the processes of binary fission inAmoeba and multiple fission in Plasmodium. 2
What is the function of receptors in our body? Think of situations where receptors do not work properly. What
Describe the double circulation of blood in human beings in detail.
Describe in detail the process of urine formation in human beings, including the three main steps.
Aman with blood groupAmarries a woman with blood group B. Their child has blood group O. The couple is confused and consults a geneticist.
a)What are the possible genotypes of the parents?
b)Explain how the child inherited blood group O from the parents. c)What
20.
C.NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H₂O
D.2Mg + O₂ → 2MgO
Soap forms scum in hard water due to presence of:
A. Sodium ions
B. Calcium and magnesium ions
C. Chloride ions
D. Sulphate ions
Which of the following is a noble metal?
A. Gold
21.
B. Zinc
C. Lead
D. Nickel
Vinegar is the common name for:
A. Ethanol
22.
B.Acetic acid
C. Methanoic acid
D. Propanoic acid
When CO₂ gas is passed through lime water, it turns milky due to:
A. Formation of CaO
23.
B. Formation of CaCO₃
C. Formation of Ca(OH)₂
D. Liberation of hydrogen gas
Question No.24 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true but R is false.
D. A is false but R is true
Assertion (A): Neutralisation of an acid with a base is an endothermic process.
24.
Reason (R): Heat is released during formation of salt and water.
25. Why are ionic compounds usually hard and have high melting points?
When sodium hydroxide solution is added to aluminium chloride solution, a white precipitate forms.
Answer the following:
1. Name the precipitate formed.
2. Write the balanced chemical equation.
3. Why does the precipitate dissolve in excess NaOH?
4. Classify the reaction.
Ashining brown coloured element 'X' on heating in air becomes black in colour.
1. Name the element 'X' and the black coloured compound formed.
2. Write the chemical equation for the reaction.
3. Classify the type of reaction.
4. How can the black colour be reversed to the original shining brown colour? Explain with a balanced chemical equation.
Read the following text carefully and answer the questions that follow:
Ahydrocarbon (P) has the molecular formula C10H22.Ahydrocarbon (Q) has two carbon atoms less than (P) and belongs to the same homologous series.Ahydrocarbon (R) has two carbon atoms more than (P) and belongs to the same homologous series.
i.What is the molecular formula of (Q)?Also write its IUPAC name.
ii.To which homologous series do the compound (P), (Q) and (R) belong?
iii.State two characteristics of a homologous series? (2)
An alcohol has the molecular formula C3H8O. It belongs to a homologous series whose members are used as fuels and solvents.
i.Write the molecular formula of the next two members of this homologous series.
30.
ii.How does the molecular mass change between consecutive members of this series?
iii.State the functional group of this homologous series and draw the structure of the given alcohol.
Section C (Physics)
Aconcave mirror forms an image that is real, inverted, and of the same size as the object. The position of the object must be:
A At the focus
B At infinity
C.At the centre of curvature
D. Beyond the centre of curvature 1
The splitting of white light into its constituent colours when it passes through a prism is called:
A. Refraction
31.
32.
B. Dispersion
C Scattering
D. Diffraction 1
Question No. 32 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true but R is false.
D. A is false but R is true
Assertion (A): The V–I graph for a metallic conductor at constant temperature is a straight line passing through the origin.
Reason (R): The resistance of a metallic conductor remains constant if temperature is kept unchanged. 1
33.
Why are convex mirrors preferred as rearview mirrors in vehicles? Explain the nature of the image formed by a convex mirror and how it helps in driving 2
Explain the process of accommodation in the human eye. Why do older people require reading glasses?
A magician is performing a trick using a concave mirror of radius of curvature 40 cm. He places a small toy of height 5 cm at a distance of 20 cm from the mirror. Find the 1)The position of the image 2)The nature of the image
Meera was decorating her room with colourful lights. She placed a candle in front of a concave mirror kept on her table. She noticed that sometimes the candle’s image appeared larger, sometimes smaller, and at certain positions it even appeared on the wall behind the mirror. Curious, she discussed this with her elder brother.
1)Why does Meera see a real inverted image of the candle on the wall at some positions?
kind of image will she see if the candle is placed between the pole and focus of the
Ahousehold electrical system operates at 220V and includes a 1000W heater, a 200W fan, and a 100W light bulb.
1)Calculate the total current drawn from the supply if all appliances operate simultaneously.
2)If a fuse of 5Ais used in the circuit, explain whether it will blow or not. Justify your answer.
3)Suggest
Astudent wants to connect three resistors in a circuit.
1)If the resistors are connected in series, how does the current change across each resistor?
2)If the resistors are connected in parallel, how does the voltage across each resistor change?
3)Write down the differences between the series and parallel combination of circuits
Scheme
Process Parent cell splits into two daughter cells Parent cell divides into multiple daughter cells simultaneously
unfavourable conditions
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants synthesize glucose using carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight. The reaction is: 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Light Energy ⟶ C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ The process takes place in chloroplasts, specifically in the grana and stroma.
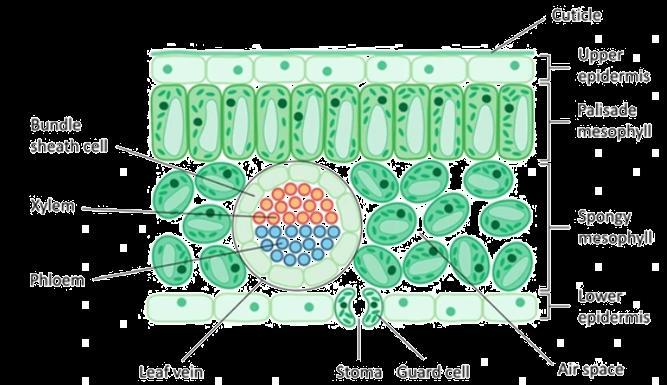
Bio-magnification is theprogressiveincreasein theconcentrationofharmful, non-biodegradable substances (like DDT, pesticides, mercury) in organisms at each higher trophic level of a food
13.
chain. Small organisms absorb these chemicals, and when they are eaten, the toxins get transferred and accumulated.
At higher trophic levels, the concentration becomes very high because predators eat many contaminated organisms. Thus, top consumers (like birds of prey, large fishes, or humans) are the most affected, showing harmful effects such as reproductive failure, hormonal imbalance, and nervous system damage.
Differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration:
Aerobic respiration
Anaerobic respiration
It occurs in the presence of oxygen. It occurs in the absence of oxygen. Glucose is completely broken down into CO₂ and water with the release of energy.
Glucose is broken down into alcohol, CO₂, and energy.
It occurs in all organisms, like mammals. It usually occurs in lower organisms like yeasts. It occurs in higher organisms during activities.
Organisms that use the anaerobic mode of respiration are as follows:
• Yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae): Yeast is a single-celled fungus used in baking and brewing that undergoes anaerobic respiration, producing ethanol and carbon dioxide as byproducts.
• Clostridium botulinum: This bacterium can perform anaerobic respiration and is responsible for causing botulism, a severe and potentially fatal form of food poisoning.
• LacticAcid Bacteria (e.g., Lactobacillus species): Certain bacteria, like Lactobacillus, can carry out anaerobic respiration, producing lactic acid as a byproduct. These bacteria are used in the fermentation of foods like yogurt and cheese.
14.
Receptors are specialized proteins or cells that detect and respond to internal and external stimuli, converting them into electrical or chemical signals for the nervous system.
Functions:
They regulate cell binding, signal transduction, ion channel control, immune responses, and metabolism. Proper receptor function ensures sensation, vision, hearing, taste, smell, hormonal balance, and temperature regulation.
Malfunctioning receptors:
If receptors fail, it can cause loss of sensation, vision or hearing impairment, taste and smell disorders, hormonal imbalance, neurological conditions likeAlzheimer’s, or poor temperature control. Thus, receptors are vital for communication between body and environment, enabling survival and maintaining internal homeostasis.
Double circulation refers to the two separate pathways blood takes through the heart in one complete cycle: pulmonary and systemic circulation.
Pulmonary Circulation:
• Blood low in oxygen (deoxygenated) returns from the body to the right atrium of the heart via the venae cavae.
• This deoxygenated blood is pumped from the right atrium to the right ventricle.
• The right ventricle pumps the deoxygenated blood to the lungs via the pulmonary arteries.
• In the lungs, carbon dioxide is exchanged for oxygen, and the blood becomes oxygenated.
Systemic Circulation:
15.
• Oxygenated blood returns from the lungs to the heart's left atrium via the pulmonary veins.
• This oxygenated blood is then pumped from the left atrium to the left ventricle.
• The left ventricle pumps the oxygenated blood out to the rest of the body through the aorta.
• Oxygen and nutrients are delivered to tissues and organs, and carbon dioxide and other waste products are collected from the tissues into the blood. Diagram
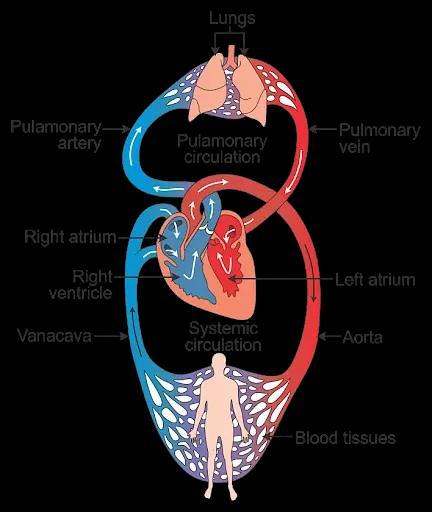
OR
Urine formation in humans occurs in the nephrons of the kidneys and involves three main steps:
Filtration (Glomerular Filtration): Blood enters the glomerulus, where high pressure forces small molecules like water, glucose, salts, and urea into the Bowman's capsule, forming a filtrate. Larger molecules like proteins and blood cells remain in the blood.
Reabsorption: Essential nutrients (glucose, amino acids, water, and salts) are selectively reabsorbed into the blood as the filtrate passes through the nephron's tubules.
Secretion (Tubular Secretion): Waste products like hydrogen ions and toxins are actively secreted into the nephron to maintain the body's acid-base balance. Finally, urine is collected in the collecting duct, moves to the renal pelvis, and is stored in the urinary bladder before excretion through the urethra. Diagram
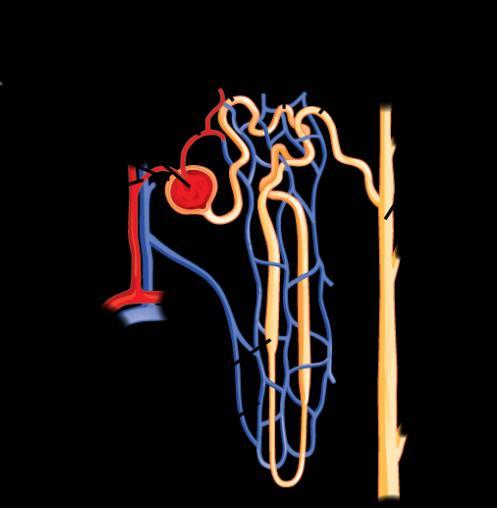
16.
a)Blood groups are determined by theABO system, which follows multiple allele inheritance (IA, IB, and i).
• Blood groupAcan have the genotype IAIAor IAi.
• Blood group B can have the genotype IBIB or IBi.
Since their child has blood group O (ii), both parents must carry the recessive ‘i’allele. Therefore, the possible genotypes of the parents are:
Father (A): IAi Mother (B): IBi
b)The child’s blood group is ‘O(ii)’, which means they must inherit one ‘i’allele from each parent.
Since both parents are heterozygous (IAi and IBi), they can pass either the dominant (IAor IB) or recessive (i) allele.
c) If both parents contribute the ‘i’allele, the child’s genotype becomes ii, resulting in blood group O.
Punnett Square:
25. Ionic compounds are made up of oppositely charged ions held together by strong electrostatic forces of attraction.
amount of energy is
to overcome these strong forces, which makes them hard and gives them high
Displacement: Zn + CuSO₄ → ZnSO₄ + Cu
27. Baking soda, or sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3), is a versatile chemical compound used in various applications due to its ability to release carbon dioxide and its basic nature.
1) Baking Powder
Baking soda is mixed with a mild edible acid to create baking powder. When baking powder is added to dough, it reacts with water to release carbon dioxide gas. This gas gets trapped in the dough, causing it to rise and become light and fluffy.
2)Antacids
As a mild alkali, baking soda can neutralize excess stomach acid (HCl) that causes indigestion. The reaction produces harmless salt, water, and carbon dioxide, providing quick relief from a burning sensation.
3)Fire Extinguishers
In some fire extinguishers, baking soda is stored with an acid. When activated, they mix and react to produce a large amount of carbon dioxide gas. This gas is heavier than air, so it forms a blanket over the fire, cutting off the oxygen supply needed for combustion and extinguishing the flame.
28. 1.Aluminium hydroxide,Al(OH)₃
2.AlCl₃ + 3NaOH →Al(OH)₃ ↓ + 3NaCl
3.Al(OH)₃ is amphoteric and reacts with excess NaOH to form soluble Na[Al(OH)₄]
4. Precipitation reaction / double displacement reaction OR
1. 'X' is Copper (Cu). The black coloured compound is Copper(II) Oxide (CuO).
2. 2Cu(s)+O2(g) → heat 2CuO(s)
3. Combination reaction or Oxidation reaction. (1 mark)
4. The black colour can be reversed by passing hydrogen gas over the heated copper oxide. This is a redox reaction.
The equation is: CuO(s)+H2(g) → heat Cu(s)+H2O(g)
29. i. Since (Q) has two carbon atoms less than (P) (C_10H_22), its molecular formula is C8H18. Its IUPAC name is octane
ii. The given formula C10H22 fits the general formula CnH2n+2, which corresponds to the alkane homologous series. Therefore, P, Q, and R all belong to the alkane homologous series.
iii. Two characteristics of a homologous series are:
*All members have the same general formula.
*Consecutive members differ by a CH2 unit in their molecular formula and by 14 u in molecular mass.
OR
i. Next two members are C4H10O and C5H12O.
(These are the 4-carbon and 5-carbon alcohols butanol and pentanol respectively.)
ii. The molecular mass increases by 14 u between consecutive members (the mass of a –CH₂–unit: 12 + 2×1 = 14 u).
iii. Functional group is the hydroxyl group (–OH).
Structure of the given alcohol (one common isomer, propan-1-ol / 1-propanol):
Condensed formula: CH₃–CH₂–CH₂–OH
C (Physics)
30. C At the centre of curvature
31. B. Dispersion
32. A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A. 1
33. Aconvex mirror is used as a rearview mirror in vehicles because it provides a wider field of view, allowing drivers to see more of the road behind them. The image formed is always virtual, erect, and diminished, ensuring a clear and broad view of the surroundings.
34. Here, V =220 volts; R=440Ω; t = 30 s
(i) We know,
(ii) The heat produced, H =
36.
When a ray of light travels from water (refractive index, n=1.33) to glass (refractive index, n=15), the following changes occur:
Change in Speed:
The speed of light in a medium is given by the equation:
Since the refractive index of glass is greater than that of water, the speed of light decreases when it enters the glass.
Change in Direction:
According to Snell's Law,
Since nglass >nwater , the angle of refraction r is smaller than the angle of incidence i.
This means the light ray bends towards the normal when entering glass. 3
Accommodation is the ability of the eye lens to change its shape to focus on near and distant objects by adjusting its focal length.
The ciliary muscles control the curvature of the eye lens.
For near objects: The muscles contract, making the lens thicker and increasing its power. For distant objects: The muscles relax, making the lens thinner and decreasing its power. With age, the flexibility of the eye lens decreases. The ciliary muscles weaken, making it difficult to focus on close objects.
Reading glasses with convex lenses are used to compensate for the reduced accommodation ability.
OR
At noon, the Sun is almost overhead, so sunlight passes through a shorter thickness of the atmosphere. Hence, very little scattering of light takes place. All the wavelengths, including blue and red, reach our eyes almost equally, so the Sun appears bright white.
During sunrise and sunset, sunlight has to travel a much longer path through the atmosphere. The shorter wavelengths (blue and violet) get scattered away in different directions, while the longer wavelengths (red and orange) are least scattered and reach our eyes, making the Sun look reddish.
37.
An electromagnet works on the principle that when an electric current passes through a coil of wire wound around a soft iron core, it produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field magnetizes the soft iron core, making it behave like a magnet. The magnetism remains only as long as the 3
38.
current is flowing; when the current is switched off, the magnetism disappears. This makes electromagnets temporary magnets
Two applications of electromagnets are –
1.Electric bells – Used to produce a magnetic force that moves a hammer to strike the bell.
2.Magnetic cranes – Used in industries to lift heavy iron and steel objects, such as scrap meta
Given:
Radius of curvature R= 40cm, so the focal length f= R 2 = 40 2 = 20cm.
Object distance �� = 20cm (object is placed in front of the mirror)
1) Calculating the Position of the Image
The mirror formula is:
Substituting the values:
39.
Thus, the image is formed at infinity
2) Nature of the Image
When the object is placed at the focal length of a concave mirror, the image is real, inverted, highly magnified and formed at infinity.
1)Areal inverted image is formed when the object is placed beyond the focus (F) of a concave mirror. In this case, the light rays actually meet in front of the mirror after reflection and the image can be caught on a screen or wall.
2)When the candle is placed between the pole (P) and the focus (F), the concave mirror forms a virtual, erect, and magnified image. This image cannot be obtained on a screen.
1) Total power:
Using the formula:
Total current drawn is 5.91A
2)Since the current drawn (5.91A) exceeds the fuse rating (5A), the fuse will blow to prevent overheating and potential fire hazards.
3)Asuitable fuse rating should be slightly higher than 5.91A, such as 10A, to allow normal operation while protecting against excessive current.
Fuses prevent short circuits and electrical fires by breaking the circuit when current exceeds a safe limit.
OR
1)In a series circuit, the same current flows through all the resistors regardless of their resistance.
2) In a parallel circuit, the voltage across each resistor remains the same as the supply voltage.
3) The differences between series and parallel circuits are:
Series Circuit
Components are connected end to end so that the same current flows through each of them.
Parallel Circuit
Components are connected across the same two points so that the potential difference across each is the same.
The same current flows through all the components. The current divides among the different branches.
The total voltage of the source is shared among the components.
Total resistance is the sum of individual resistances: R = R1 + R2 + R3 +⋯
If one component fails, the whole circuit is broken and current stops.
Used where current has to be the same (e.g., fairy lights, some old electrical circuits).
The voltage across each component is equal to the source voltage.
Reciprocal of total resistance is the sum of reciprocals: 1 �� = 1 R1 + 1 R2 + 1 R3 +
If one component fails, the other branches continue to work normally.
Used in household wiring, so that each appliance works independently.
SCIENCE
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER - 5
CLASS X (2025-26)
Max. Marks: 80 Time allowed: 3 hours
General Instructions:
1. This question paper consists of 39 questions in 3 sections. SectionAis Biology, Section B is Chemistry, and Section C is Physics.
2. All questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice is provided in some questions.Astudent is expected to attempt only one of these questions.
SectionA (Biology)
Which gas is primarily responsible for ozone layer depletion?
1.
A.Carbon dioxide B.Chlorofluorocarbons
Which among the following is an advantage of sexual reproduction?
A.Produces genetically identical offspring B.Ensures faster reproduction C.Leads to genetic variation
D.Requires only one parent
Which of the following is a correct sequence of blood circulation in the human body?
A.Heart ⟶ Lungs ⟶ Body ⟶ Heart
B.Heart ⟶ Body ⟶ Lungs ⟶ Heart
C.Lungs ⟶ Heart ⟶ Body ⟶ Lungs
Which of the following plant hormones is known as the "stress hormone"?
Why is it essential to segregate biodegradable and non-biodegradable waste?
A. To reduce the risk of infectious diseases
B To recycle non-biodegradable materials and compost biodegradable waste
C To reduce pollution and environmental hazards
D.All of the above
Which of the following STDs is caused by a virus?
A.Gonorrhoea
B.Syphilis
C.HIV/AIDS D.Chlamydia
Which hormone is responsible for increasing water reabsorption by the kidneys? A.Oxytocin
Question No. 8 to 9 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true but R is false.
D. A is false but R is true
Assertion (A): Arteries have thick and elastic walls.
Assertion (A): Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimulates ovulation in females.
Reason(R):LHsurgetriggerstheruptureoftheGraafianfollicleand releaseoftheovum.
Explain the structure and function of a neuron with a well-labelled diagram.
Explain the endocrine function of pancreas with a neat labelled diagram of the Islets of Langerhans.
a. What is the primary function of dialysis? b. Name one component that is removed from the blood during dialysis.
20.
C. Double displacement reaction
D. Displacement reaction
Match the hydrocarbons with their type:
ColumnA(Compound)
CH4
C2H2
C2H4
C6H6
A. 1–b, 2–c, 3–a, 4–d
B. 1–c, 2–a, 3–d, 4–b
C. 1–a, 2–b, 3–c, 4–d
Column B (Type of Hydrocarbon)
a)Alkene
b)Alkane
c)Alkyne
d)Aromatic hydrocarbon
D. 1–d, 2–b, 3–a, 4–c 1
Which of the following metals will not react with cold water but reacts with steam?
A. Sodium
21.
B. Calcium
C. Magnesium
D. Potassium 1
Which of the following compounds will decolourise bromine water?
A. Ethane
22.
B. Benzene
C. Ethene
D. Methane 1
Which of the following is not a use of acids?
A. Cleaning metals
23.
B. Manufacturing fertilizers
C. Neutralizing bases
D. Making soap 1
Question No. 24 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true but R is false.
24.
27.
A is false but R is true
Assertion (A): Baking soda is used in antacids.
Reason (R): Baking soda neutralises excess acid in the stomach.
Ametal 'X' is more reactive than iron but less reactive than magnesium. When 'X' is added to an aqueous solution of iron(II) sulfate, a reaction occurs.
1)What would you observe in this reaction?
2)Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction.
Explain why dry HCl gas does not change the colour of dry litmus paper, but HCl solution does.
Explain why alloys are generally preferred over pure metals. Give two reasons and provide an example of an alloy with its use
Passing CO₂ into lime water first causes milkiness, then it clears upon excess CO₂.
Answer the following:
1. Name the precipitate responsible for milkiness.
2. Write equations for both reactions.
3. Explain why the solution clears on excess CO₂.
4. Give one practical application of this reaction.
OR
Astudent is performing an experiment in a chemistry lab. They have four colourless solutions in beakers labelledA, B, C, and D. They know that these solutions are dilute hydrochloric acid, sodium hydroxide, vinegar, and pure water, but they don't know which is which. To identify them, they use a universal indicator and observe the following colour changes:
SolutionA: The indicator turns a dark red colour.
Solution B: The indicator turns a light orange colour.
Solution C: The indicator turns a bluish-green colour.
Solution D: The indicator turns a deep violet colour.
i.Based on the colour changes, identify the substance in each beaker. Justify your answer using pH values.
ii.If the student mixes an equal volume of solution B with a few drops of solution D, what would be the colour of the resulting mixture? Explain the change in pH.
iii.Name the type of reaction that occurs when solution B is mixed with solution D. 1
Read the following text carefully and answer the questions that follow.
Carbon is a unique element that can exist in various forms, called allotropes. These allotropes have different physical properties but the same chemical properties. Two of the most common allotropes are diamond and graphite. Diamond is an exceptionally hard, transparent solid, while graphite is a soft, black, and slippery solid.Athird allotrope, buckminsterfullerene, has a spherical shape. The unique properties of these allotropes are due to the different ways carbon atoms are bonded together.
Answer the following
1.Why is diamond used in cutting tools and graphite used as a lubricant?
2.Draw the structure of a carbon atom. How is the bonding in diamond different from that in graphite?
3.What is the common name for buckminsterfullerene, and what type of bond holds the carbon atoms together in all allotropes?
Differentiate between soap and synthetic detergent. Why are detergents preferred in hard water?
The focal length of a convex lens is 15 cm. Where should an object be placed to obtain an image at infinity?
A.At 15 cm
B.At 30 cm
C At 45 cm
D.At infinity
The near point of a normal human eye is approximately:
A 10 cm
B. 25 cm
C 50 cm
D. Infinity
Question No. 32 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true but R is false.
D. A is false but R is true
Assertion (A): A freely suspended current-carrying solenoid comes to rest in East-West directions.
Reason (R):Acurrent-carrying solenoid behaves like a bar magnet.
Aperson suffering from hypermetropia can read distant signs clearly but struggles with reading books. Explain why and suggest a corrective measure.
Aconvex lens is used to form an image of an object placed 30 cm from it. If the image formed is real and inverted at a distance of 60 cm, calculate the focal length of the lens
Describe the phenomenon of atmospheric refraction. Explain why stars appear to twinkle and planets do not.
Read the text carefully and answer the questions:
An insulated copper wire wound on a cylindrical cardboard tube such that its length is greater than its diameter is called a solenoid. When an electric current is passed through the solenoid, it produces a magnetic field around it. The magnetic field produced by a current-carrying solenoid is similar to the magnetic field produced by a bar magnet. The field lines inside the solenoid are in the form of parallel straight lines. The strong magnetic field produced inside a current-carrying solenoid can be used to magnetize a piece of a
the solenoid.
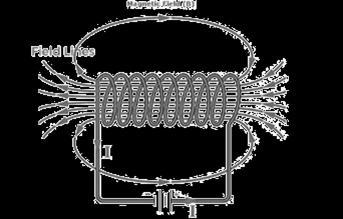
1)What would be the strength of the magnetic field inside a long current-carrying straight solenoid?
2)Which end is north and which end is south pole when current flows through a solenoid?
3)How can a solenoid be used to magnetize a piece of iron? OR
Rahul and Meera were conducting an experiment in their school laboratory using a current-carrying coil and a bar magnet. Rahul placed the bar magnet near the coil and observed that it got attracted. Meera then increased the number of turns in the coil and noticed a stronger attraction.
1)Why did the bar magnet get attracted to the coil? Explain the underlying principle.
2)How did increasing the number of turns in the coil affect the strength of attraction?
Justify your answer.
3)If Rahul wants to further increase the strength of the magnetic field, what changes should he make in the setup?
During a science class experiment, Ananya passes a beam of white light through a glass prism. She observes that the light splits into a band of seven colours on the screen. She becomes curious and asks her teacher a few questions.
1) What is this phenomenon called and why does it occur?
2) Which color deviates the most and which the least? Give reason.
3) Name the band of seven colors obtained.
OR
Riya is reading her book late at night under dim light. She notices that her eyes take some time to adjust when she suddenly switches on a bright lamp. She also remembers that her grandfather uses a convex lens in his spectacles to read the newspaper.
1)Which part of Riya’s eye controls the amount of light entering, and how does it adjust in dim and bright light?
2)Why does Riya’s grandfather need a convex lens for reading? Name the defect of vision.
3)What is meant by the power of accommodation of the eye?
8.
9.
Marking Scheme
SectionA(Biology)
11.
Atrophic level represents the position of an organism in the food chain, indicating its role in the transfer of energy.
Trophic Levels in a Food Chain:
• Producers (First Trophic Level) – Plants that prepare food via photosynthesis. (e.g., grass, algae, etc.)
• Primary Consumers (Second Trophic Level) – Herbivores that feed on producers. (e.g., deer, cow, etc.)
• Secondary Consumers (Third Trophic Level) – Carnivores that eat herbivores. (e.g., frogs, snakes, etc.)
• Tertiary Consumers (Fourth Trophic Level) – Top carnivores that eat other carnivores. (e.g., lion, eagle, etc.)
Significance of Trophic Levels:
It helps in understanding energy flow in an ecosystem. It explains the 10% Law, which states that only 10% of energy is transferred from one level to the next. It maintains a balance in ecosystems.
DNAcopying in reproduction
DNA carries the genetic information of an organism. During reproduction, DNA is copied and passed on to the offspring. Ensures that the basic body design, functions, and characteristics of the species are transmitted from one generation to the next. Provides similarity between parent and offspring, maintaining the identity of a species. At the same time, small variations may occur during copying, which become the basis for evolution and adaptation.
12.
ByfaithfulDNAcopying,organisms ensurethatlifecontinuesgenerationaftergenerationwithout breaking. Variations introduced help populations survive changing environmental conditions, ensuring long-term survival of life on Earth.
Abscisic acid (ABA) is a plant hormone that inhibits growth and plays a crucial role in stress responses. It promotes leaf wilting, which minimizes transpiration and conserves water during drought conditions. 2
Gregor Mendel performed monohybrid crosses to study the inheritance of a single trait. His experiments with pea plants helped establish the Law of Segregation, which states that each individual has two alleles for a trait, and these alleles separate (segregate) during gamete formation, with each gamete receiving only one allele.
Example: Monohybrid Cross for Plant Height Cross:
-P Generation (Parental Cross):Tall (TT) × Dwarf (tt)
-F₁ Generation (First Filial Generation):All plants were Tt (Tall)(Heterozygous, showing dominant phenotype).
-F₂ Generation (Self-crossing Tt × Tt):
13.
14.
F₂ Phenotypic Ratio (3:1)
-Tall (TT, Tt, Tt) – 3 parts
-Dwarf (tt) – 1 part
F₂ Genotypic Ratio (1:2:1)
-TT (Homozygous Tall) – 1 part
- Tt (Heterozygous Tall) – 2 parts
-tt (Homozygous Dwarf) – 1 part
Mendel’s monohybrid cross demonstrated that traits are inherited in a predictable manner, with dominant traits masking recessive ones in F₁ but reappearing in F₂ in a 3:1 ratio.
Hormones play a crucial role in maintaining control and coordination in animals by acting as chemical messengers. They are secreted by endocrine glands and travel through the bloodstream to target organs, influencing growth, metabolism, reproduction, and response to stimuli.
Afew examples of hormones and their functions are:
15.
• Adrenaline prepares the body for emergency situations by increasing heart rate and breathing rate.
• Thyroxine regulates metabolism.
• Growth hormone controls development
• Insulin regulates blood sugar levels.
Hormone secretion is tightly regulated by a feedback mechanism to maintain balance. For instance, when blood sugar rises, the pancreas releases more insulin to lower it. Once the sugar level decreases, insulin production is reduced. Similarly, the hypothalamus regulates the release of hormones like growth hormone by signalling the pituitary gland. This system ensures that hormones are produced in the right amounts, preventing disorders like diabetes, goitre, and growth abnormalities
Aneuron is the basic structural and functional unit of the nervous system. It is specialized in transmitting nerve impulses.
Aneuron consists of three main parts:
1.Cell Body (Soma): Contains the nucleus and cytoplasm, responsible for maintaining cell functions.
2.Dendrites: Short, branched structures that receive signals from other neurons and conduct them towards the cell body.
3.Axon: Along, single fibre that carries impulses away from the cell body. It is covered by a myelin sheath (in some neurons) that speeds up impulse transmission.At the end of the axon, axon terminals release neurotransmitters that pass the signal to the next neuron across a synapse.
Functions:
Neurons play a crucial role in processing and transmitting information in the nervous system. They receive, process, and transmit electrical and chemical signals, enabling reflex actions, sensory perception, and muscle control.
Here is a well-labelled diagram of a neuron
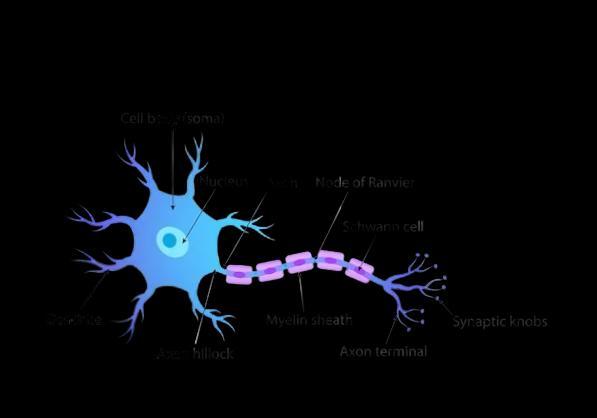
OR
The pancreas serves a dual role in the body, functioning both as an exocrine and an endocrine gland.As an endocrine gland, it produces and releases hormones directly into the bloodstream. The endocrine part of the pancreas contains a large group of cells called Islets of Langerhans.
The islets of Langerhans have three types of cells:
1.Alpha cells which constitute 10-20%
2.Beta cells which constitute 70-80%
3.Delta cells constitute 5%.
Alpha cells secrete the glucagon hormone and the beta cells secrete insulin, which regulates blood sugar levels. Insulin lowers blood sugar by facilitating the uptake of glucose into cells, while glucagon raises blood sugar levels by stimulating the liver to release stored glucose.
Through these hormones, the pancreas plays a vital role in maintaining glucose homeostasis, ensuring cells receive a steady supply of energy for proper functioning.
Here is a well-labelled diagram of a islets of Langerhans.
a. Dialysis functions as an artificial kidney by filtering waste products, excess salts, and excess water from the blood when the kidneys fail to do so. It helps maintain the body's electrolyte and fluid balance.
b. One component removed during dialysis is urea, a waste product formed from protein metabolism.
c. Dialysis mimics nephron function but lacks hormonal regulation.
Feature Normal Kidney Dialysis Machine
Filtration Filters blood naturally through nephrons Filters blood externally using a dialyzer
Waste Removal Removes urea, excess salts, and water Removes similar waste products
Selectivity
Working Process
17. B. Salt and water
18. D. Propane
Regulates ions and water balance precisely
Natural and continuous process
Section B (Chemistry)
Less precise, requires controlled settings
External and intermittent processes (a few times a week)
19. B. Decomposition reaction
20. A. 1–b, 2–c, 3–a, 4–d 1
21. C. Magnesium
22. C. Ethene
23. D.Making soap
24. A. BothAand R are true, and R is the correct explanation ofA. 1
25.
26.
1)Since metal X is more reactive than iron, it will displace iron from its salt solution. The solution of iron(II) sulfate, which is pale green, will gradually become colorless as the concentration of iron(II) ions decreases and zinc sulfate, a colorless salt, is formed.Adark gray or black solid (iron) will be deposited on the surface of the metal X.
2)The metal 'X' is zinc (Zn) as it is positioned between magnesium and iron in the reactivity series. The balanced chemical equation is: Zn(s)+FeSO4(aq)→ZnSO4(aq)+Fe(s)
• Dry HCl gas does not dissociate to produce H⁺ ions.
• Litmus requires H⁺ ions to show acidic property.
• In aqueous HCl solution, HCl dissociates: HCl → H⁺ + Cl⁻, which turns blue litmus red.
Alloys are preferred over pure metals because:
Increased strength and hardness:Alloys are usually stronger and harder than the pure metals they contain, making them more suitable for construction and tools.
27.
28.
Resistance to corrosion and wear:Alloys are less likely to rust or get worn out, so they last longer in practical applications.
Example:
Steel (an alloy of iron and carbon) is used in making bridges, machines, and vehicles because it is strong and durable.
1. Calcium carbonate (CaCO₃)
2. Step1: Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 ↓ + H2O.
Step2: CaCO₃ + CO₂ + H₂O → Ca(HCO₃)₂
3. CaCO₃ dissolves to form soluble Ca(HCO₃)₂
4. Whitewashing of the wall
OR
i SolutionA: This is dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl). The dark red colour indicates a very low pH (around 1-2), which is characteristic of a strong acid.
Solution B: This is vinegar (acetic acid). The light orange colour indicates a weak acid with a pH of around 3-4.
Solution C: This is pure water. The bluish-green colour suggests a near-neutral pH (around 7).
Solution D: This is sodium hydroxide (NaOH). The deep violet colour indicates a very high pH (around 13-14), which is characteristic of a strong base.
ii. When a few drops of a strong base are added to a larger volume of a weak acid, a neutralization reaction occurs. The pH of the mixture increases from its initial acidic value. The universal indicator will turn green or bluish green, indicating the solution is now closer to neutral.
iii. The reaction that occurs when an acid (vinegar) is mixed with a base (sodium hydroxide) is a neutralization reaction.
1.Diamond is used in cutting tools because it is the hardest natural substance. Each carbon atom forms four strong covalent bonds in a rigid 3D tetrahedral structure, making it extremely hard and durable. In contrast, graphite is soft and slippery, as its carbon atoms form layers that can easily slide over one another, making it useful as a lubricant.
2.
Acarbon atom has 6 protons and 6 electrons (2 in the inner shell, 4 valence electrons). It forms 4 covalent bonds. In diamond, each atom bonds to 4 others in a tetrahedral 3D network, while in graphite, each bonds to 3 others, forming layers.
3. The common name for buckminsterfullerene is buckyball. The carbon atoms in all allotropes are held together by covalent bonds.
• Soaps: Sodium/potassium salts of higher fatty acids, work well in soft water but form scum in hard water.
• Detergents: Sodium salts of long-chain benzene sulfonic acids or alkyl hydrogen sulphates, can work in hard water.
• Inhardwater,detergentsdonotforminsolubleprecipitateswithCa²⁺andMg²⁺ions,unlike soap.
• Example of detergent molecule is sodium alkylbenzene sulfonate.
• Therefore, detergents are preferred over soaps in industrial and domestic cleaning where hard water is used.
30. A At 15 cm
31. B. 25 cm
32. D. A is false, but R is true
Formula for parallel resistance:
Section C (Physics)
33.
34.
Here, R1 =3Ω,R2 =6Ω
Substituting values:
The equivalent resistance of the combination is 2Ω
Hypermetropia occurs when the eyeball is too short or the eye lens is too flat, causing light rays from nearby objects to converge behind the retina. This makes it difficult to focus on close objects.
Corrective convex lenses are used to converge the incoming light rays so that they focus directly on the retina, improving near vision. 2
35. Given:
• Object distance u= 30cm (since the object is on the left side of the lens, it's negative),
• Image distance v=60cm (since the image is real, it's positive).
The lens formula is:
36.
Substituting the values:
37.
Thus, the focal length of the lens is 20 cm.
Atmospheric refraction is the bending of light as it passes through layers of the Earth's atmosphere with varying densities. This occurs because the refractive index of air changes with altitude due to variations in temperature and pressure. It is responsible for phenomena such as the apparent shift in the position of stars, the twinkling of stars, and the apparent flattening of the Sun at sunrise and sunset
Stars are far away and appear as point sources of light.As their light passes through different layers of the Earth's atmosphere, it gets refracted in different directions due to varying air densities. This causes the star's brightness and position to appear to change slightly, creating the twinkling effect.
Planets are closer to Earth and appear as small discs rather than point sources of light. The light coming from different parts of a planet’s disc undergoes multiple refractions, which cancel out the variations, making planets appear steady rather than twinkling.
Myopia, also called short-sightedness, is a defect of vision in which a person can see nearby objects clearly, but distant objects appear blurred. This happens because the image of a distant object is formed in front of the retina instead of on it. The defect arises either when the eyeball becomes too long or when the eye lens has excessive converging power.As a result, the light rays from a distant object meet before reaching the retina. This defect is corrected by using a concave (diverging) lens. The concave lens diverges the parallel rays of light coming from a distant object in such a way that after refraction by the eye lens, the rays appear to come from a nearer point and get focused exactly on the retina. Thus, the person can see distant objects clearly. 3
38.
We know that:
Substituting values:
Current flowing through the coil
We know that:
Substituting values:
Thus, the resistance of the heater coil is 48.4Ω, and the current flowing through it is 4.55A.
1)The magnetic field inside a long current-carrying solenoid is uniform and strong, meaning it has the same strength at all points within the solenoid. The field lines inside are parallel and closely spaced, indicating that the field is consistent throughout the length of the solenoid.
2)The end of the solenoid where the current flows in an anticlockwise direction behaves like a north pole. The end where the current flows in a clockwise direction behaves like a south pole.
This can be determined using the Right-Hand Rule: If you curl the fingers of your right hand around the solenoid in the direction of current flow, your thumb will point towards the north pole of the solenoid.
3)When a solenoid carries current, it generates a strong magnetic field inside. If a piece of soft iron or another magnetic material is placed within the solenoid, the iron becomes magnetized due to the influence of this strong magnetic field. This process is used to create electromagnets, which are widely used in various applications like electric bells and cranes. OR
1)The bar magnet was attracted to the coil because the current-carrying coil acts as an electromagnet. When electric current flows through it, a magnetic field is produced, similar to a
bar magnet. The attraction occurs due to the interaction of opposite poles of the coil and the bar magnet.
2)Increasing the number of turns strengthens the magnetic field because the field from each turn adds up. The strength of a solenoid’s field is directly proportional to the number of turns, making the attraction stronger.
3)In order to increase the strength of the magnetic field, Rahul can:
• Increase the current flowing through the coil.
• Use a soft iron core to concentrate the magnetic field.
• Increase the number of turns in the coil for a stronger effect.
1)The phenomenon is called dispersion of light. It occurs because different colors of white light have different wavelengths and hence different refractive indices in glass. Each color bends by a different amount, splitting white light into its constituent colors.
2)Violet light deviates the most and red light deviates the least. This is because violet has the shortest wavelength, so it is refracted more, while red has the longest wavelength, so it is refracted the least.
3)The seven colors are Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange, Red (VIBGYOR).
OR
1)The iris controls the amount of light entering the eye by adjusting the size of the pupil.
• In dim light, the pupil enlarges to allow more light.
• In bright light, the pupil contracts to reduce light entry.
2) Riya’s grandfather has hypermetropia (farsightedness). In this defect, nearby objects appear blurred because the image is formed behind the retina. It is corrected using a convex lens, which converges the rays before they enter the eye.
3)The power of accommodation of the eye is its ability to adjust the focal length of the lens so that objects at different distances can be seen clearly.
SCIENCE
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER - 6
CLASS X (2025-26)
Max. Marks: 80 Time allowed: 3 hours
General Instructions:
1. This question paper consists of 39 questions in 3 sections. SectionAis Biology, Section B is Chemistry, and Section C is Physics.
2. All questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice is provided in some questions.Astudent is expected to attempt only one of these questions.
SectionA (Biology)
Which of the following is not a product of anaerobic respiration in yeast?
A.Ethanol
1.
2.
In the human digestive system, bile juice is secreted by: A.Stomach B.Liver C.Pancreas
D.Gall bladder
Which of the following hormones regulates the amount of sugar in the blood? A.Insulin
In plants, the movement of auxin is responsible for: A.Hydrotropism
Which of the following statements about sexual reproduction is correct?
A.Offspring are genetically identical to parents
B.Two parents are always required
C.Gametes fuse to form a zygote
D.It occurs only in higher animals
Which of the following is an example of a recessive trait in human beings?
A.Curly hair
B.Free ear lobes
C.Colour blindness
D.Rolling of tongue
Which of the following is a biodegradable waste?
A.Aluminium foil
B.Glass bottle
C.Plastic bag
D.Vegetable peels
Questions No. 8 to 9 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true, but R is false.
D. A is false, but R is true
(A): The pancreas acts as both an endocrine and an exocrine gland.
(A): Variations are important for the survival of species.
(R): Variations always give rise to harmful traits.
16.
Why is vegetative propagation by stem cuttings commonly used in horticultural practices? Give two reasons.
(a) Give an account of the human excretory system along with a neat, labelled diagram. OR
(b)Explain Mendel’s monohybrid cross with a suitable diagram.
Read the passage and answer the following:
Ravi observed that the plants near a window bend towards the sunlight. He also noticed that weeds in his garden grow faster than his ornamental plants. His biology teacher explained that growth hormones are involved in such processes.
(a)Which plant hormone is responsible for the bending of plants towards light?
(b)Name two other functions of this hormone.
(c)Why do weeds grow faster than ornamental plants?
(d)Suggest one eco-friendly way to control weeds.
Section B (Chemistry)
When dilute HCl reacts with Na₂CO₃, which gases are released?
A. H₂ only
17.
B. CO₂ only
C. H₂ and CO₂ D. Cl₂ and H₂
Which of the following represents the correct IUPAC name?
A. CH₃–CH₂–CH₃ → Ethane
18.
B. CH₃–CH₂–CH₂–CH₃ → Butane
C. CH₃–CH₂–OH → Methanol
D. CH₄ → Ethane
When silver nitrate solution is kept in sunlight, it decomposes to form:
A.Ag + NO₂ + O₂
B.Ag + NO + O₂
C.Ag₂O + NO₂ D.Ag₂O + O₂
20.
An organic compound, 'X', on heating with concentrated sulfuric acid at 443 K gives an unsaturated compound, 'Y'. Compound 'Y' decolorizes bromine water. What are 'X' and 'Y'?
21.
A. X is ethene and Y is ethane.
B. X is ethanoic acid and Y is ethyl ethanoate.
C. X is ethanol and Y is ethene.
D. X is ethanol and Y is ethane.
An element reacts with oxygen to give a compound with a high melting point. This compound is also soluble in water. The element is likely to be:
A. Calcium
B. Carbon
C Silicon
D. Iron 1
The property which enables carbon to form a large number of compounds is:
A. Combustibility
22.
B. Catenation
C. Isomerism
D.Allotropy 1
Very often, the farmers add lime to the soil before ploughing because
A. High concentration of lime aids the plant growth
23.
B Lime takes up the extra moisture of the soil
C The soil becomes soft, and it becomes easy to plough
D. Lime decreases the acidity of the soil. 1
Question No.24 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true but R is false.
D. A is false but R is true
Assertion (A): Sodium hydroxide is a strong base.
24.
Reason (R): It completely dissociates in water to produce hydroxide ions. 1
25. What is galvanization? How it is useful? 2 26.
2 mL of sodium hydroxide solution is added to granulated zinc in a test tube and warmed.A gas evolves which is tested with soap solution.
i. Write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction 3
28.
ii. Name the gas evolved
iii. Write the reaction of zinc with a dilute acid showing the same gas is released
Why do silver articles become black after some time while copper articles develop a greenish layer?
Astrip of copper metal is immersed in a solution of silver nitrate.After some time, the solution turns blue, and a shiny gray deposit is formed on the copper strip.
i. Why does the solution turn blue?
ii. What is the chemical name of the shiny gray deposit?
iii. Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction
iv. What is the type of chemical reaction?
OR
Apiece of limestone (CaCO3) is heated in a kiln.Agas 'A' is produced, which is passed through a solution of calcium hydroxide. This results in the formation of a white precipitate 'B'.
i. Name the type of reaction that takes place when limestone is heated.
ii. Identify the gas 'A' and the precipitate 'B'.
iii. Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction between gas 'A' and calcium hydroxide.
Describe the process of esterification. What are the reactants and products of this reaction?
Explain why this reaction is called a reversible reaction. Give an example of an esterification reaction with a balanced chemical equation.
OR
i. Give a chemical test to distinguish between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons.
ii. Name the products formed when ethane burns in air. Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction showing the types of energies liberated.
iii. Why is the reaction between methane and chlorine in the presence of sunlight considered a substitution reaction?
Section C (Physics)
On reducing the focal length of a lens, its power
A. Increases
30.
B. Decreases
C. does not change
32.
D. first increases then decreases
In the following diagram showing dispersion of white light by a glass prism, the colours P and Q respectively are-
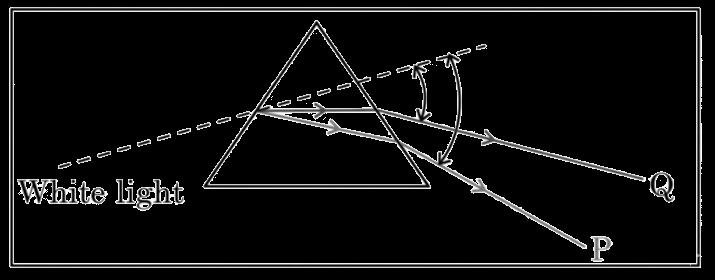
A. Violet and Red
B. Orange and Green
C Red and Blue
D. Red and Violet 1
Question No. 32 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true but R is false.
D. A is false but R is true
Assertion (A): When a magnet is immersed in iron filings, more iron filings are attracted at centre of the bar magnet
Reason (R): Magnet has maximum pole strength at its poles. 1
How does a lens of the human eye focus on objects at different distances? OR
33.
34.
35.
Explain how the dispersion of light by a prism demonstrates that white light is composed of different colours. 2
One-half of a convex lens is covered with black paper. Will the lens produce a complete image of an object? Explain your answer and suggest how this can be verified experimentally. 2
Aconcave mirror has a radius of curvature of 24 cm.At what distance from the mirror should an object be placed so that the mirror forms a virtual image which is three times larger than the object? 3 36.
Calculate the effective resistance between P and Q
37.
38.
39.
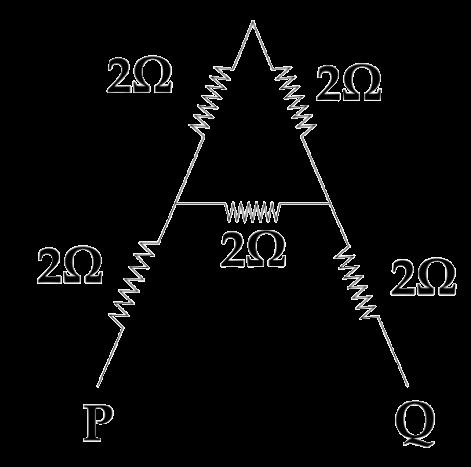
Adomestic electric circuit consists of a live wire, neutral wire, and earth wire. Explain their significance. Why is earthing important in an electric circuit? 3
Read the following text carefully and answer the questions that follow:
Astudent fixes a sheet of white paper on a drawing board and places a bar magnet at the centre. She sprinkles iron filings uniformly around the magnet and gently taps the board. The iron filings arrange themselves in a particular pattern.
1) What causes the iron filings to arrange themselves in a definite pattern?
2) How is the direction of the magnetic field at a point determined using magnetic field lines?
3) Why do two magnetic field lines never cross each other?
How can a small compass be used to trace the magnetic field lines of a bar magnet?
Anarrow beam of white light is allowed to pass through a glass prism, and the emergent beam is observed on a screen.
1) What happens to the white light after it emerges from the prism? Name this phenomenon and state its cause.
2) Mention one natural occurrence where this phenomenon can be observed.
3) Based on this observation, what conclusion can be drawn about the composition of white light? OR
Mr. Sharma is a 55-year-old man who enjoys reading newspapers and doing small craft work at home. Recently, he has noticed that he struggles to read the newspaper clearly and finds it difficult to do close work, such as threading a needle or reading small text, even though he can see distant objects clearly without any problem. Concerned about this change in his vision, he visits an eye specialist.
1)Name the defect of vision that Mr. Sharma is suffering from.
2)Explain the reason for this defect in terms of the structure and functioning of the human eye.
3)Suggest a suitable corrective lens and explain how it helps him see nearby objects clearly.
8.
9. C.Ais true but R is false
10.
11.
Marking Scheme
SectionA(Biology)
12.
Arteries carry blood from the heart at very high pressure. Their thick, muscular, and elastic walls prevent bursting and allow them to expand and contract, maintaining continuous and regulated blood flow.
(a)The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain, controlling intelligence, reasoning, memory, emotions, and voluntary activities like writing or walking.
(b)The cerebellum controls balance, posture, and coordination of smooth muscular movements.
Self-pollination: Transfer of pollen from anther to stigma of the same flower or another flower on the same plant; leads to less variation.
Cross-pollination: Transfer between flowers of different plants of the same species; increases genetic diversity.
13. The placenta is a temporary disc-like organ that connects the foetus with the uterine wall.
Role of placenta:
It supplies oxygen and nutrients (like glucose, amino acids, vitamins) from the mother’s blood to the foetus. It also removes carbon dioxide and nitrogenous waste from foetal blood. It produces hormones such as progesterone and hCG to maintain pregnancy.
Importantly, it prevents the mixing of maternal and foetal blood.
Vegetative propagation by stem cuttings is preferred because:
14.
(1) Plants produced are genetically identical to the parent, ensuring true-to-type qualities like taste, colour, and yield.
(2) It is a quick and economical method, saving time compared to seed germination.
(3) It allows mass production of desirable plants, even those that do not produce viable seeds. 3
The human excretory system removes nitrogenous wastes like urea, regulates water balance, and maintains ionic concentration. Its major parts include:
• Kidneys: Bean-shaped organs that filter waste from blood through nephrons.
• Ureters: Thin tubes carrying urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
• Urinary bladder: Muscular sac storing urine temporarily.
• Urethra: Tube for elimination of urine from body.
This system ensures osmoregulation, acid-base balance, and toxin removal.
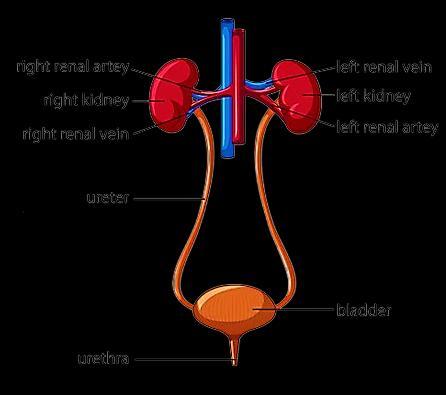
OR
Mendel’s monohybrid cross
Mendel crossed pure tall pea plants (TT) with pure dwarf pea plants (tt).All F1 offspring were tall (Tt), showing dominance of tall trait.
On self-pollination of F1 plants, the F2 generation showed tall and dwarf plants in a 3:1 ratio.
This proved Mendel’s Law of Segregation, stating that two alleles separate during gamete formation and unite randomly at fertilization.
16.
This experiment explained how traits are inherited across generations and laid the foundation for genetics.
(a) The hormone responsible is Auxin
(b) Functions:
(i)Promotes cell elongation
(ii)Delays the falling of leaves and fruits
(c) Weeds grow faster than ornamental plants due to their high adaptability, better nutrient utilization, faster germination, and efficient reproduction. They compete strongly with crops and garden plants, reducing yield and growth.
(d) Eco-friendly way: Use of bio-herbicides, mulching, crop rotation, or manual uprooting instead of chemical herbicides to avoid environmental damage.
Section B (Chemistry)
27.
Galvanization is the process of coating iron or steel objects with a thin layer of zinc to protect them from rusting.
The zinc layer prevents direct contact of the metal with air and moisture, and even if scratched, zinc provides sacrificial protection by corroding in place of iron.
i. Reaction with NaOH: Zn+2NaOH → heat Na2ZnO2 +H2 ↑
Sodium zincate is formed and hydrogen gas evolved.
ii. Gas evolved:
The gas is hydrogen (H₂), which can be tested by bringing a burning splinter near it.It burns with a ‘pop’sound.
iii. Reaction with dilute acid (e.g. HCl): Zn+2HCl→ZnCl2 +H2 ↑
• Silver articles react with hydrogen sulphide (H₂S) present in the atmosphere to form a thin black coating of silver sulphide (Ag₂S) on the surface.
28.
• Copper articles, on the other hand, react slowly with carbon dioxide, oxygen, and moisture in the air to form a green layer of basic copper carbonate [CuCO₃·Cu(OH)₂].
• These surface layers (black on silver, green on copper) spoil the metallic shine and appearance of the articles, though they sometimes protect the underlying metal from further corrosion.
i. The solution turns blue because copper displaces silver from the silver nitrate solution to form copper nitrate [Cu(NO3)2], which is a blue-coloured salt.
ii. The shiny grey deposit is silver (Ag).
iii. Cu(��)+2AgNO3(����)→Cu(NO3)2(����)+2Ag(��)
iv. It is a displacement reaction.
OR
i. The reaction is a thermal decomposition reaction.
ii. Gas 'A' is carbon dioxide (CO2), and precipitate 'B' is calcium carbonate (CaCO3).
iii. The equation for the reaction is Ca(OH)2(aq)+CO2(g)→CaCO3(s)+H2O(��)
i. Esterification is the chemical reaction in which a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol in the presence of a few drops of concentrated sulphuric acid (H₂SO₄) as a catalyst to form an ester and water.
ii. Reactants: Carboxylic acid (–COOH group) andAlcohol (–OH group)
iii. Products: Ester (–COOR group) and Water (H₂O)
iv. Why reversible? The ester formed can hydrolyse back into the carboxylic acid and alcohol in the presence of an acid or base. Thus, esterification is a reversible reaction.
v. General equation: R COOH+R′ OH → H2SO4 R COOR′ +H2O
vi. Example: Ethanoic acid reacts with ethanol in the presence of concentrated H₂SO₄ to form ethyl ethanoate and water: CH3COOH+C2H5OH → conc. H2SO4 CH3COOC2H5 + H2O
vii. Here, ethyl ethanoate is the ester formed, which has a fruity smell.
OR
i. Test to distinguish hydrocarbons:
Add bromine water (orange in colour) to the hydrocarbon.
Unsaturated hydrocarbons (with double or triple bonds) decolourise bromine water due to addition reaction. Saturated hydrocarbons do not decolourise bromine water.
ii. Combustion of ethane: When ethane burns in the presence of oxygen, it produces carbon dioxide and water with the release of heat and light energy.
Balanced equation: 2C2H6 +7O2 →4CO2 +6H2O+ Heat + Light
iii. Substitution reaction of methane with chlorine: In the presence of sunlight, chlorine atoms replace hydrogen atoms of methane one by one, forming chloromethane and hydrogen chloride. CH4 +Cl2 → Sunlight CH3Cl+HCl
This is called a substitution reaction because one atom (H) is substituted by another atom (Cl).
30. A. Increases
31. A. Violet and Red
32. D. A is false, but R is true
33.
The human eye focuses on objects at different distances through a process called accommodation. The ciliary muscles in the eye contract or relax to change the curvature of the eye lens, which in turn alters its focal length. When the object is nearby, the ciliary muscles contract, making the lens thicker and more convex to focus the light on the retina. For distant objects, the muscles relax, making the lens thinner and less curved, so that the light rays are brought to focus on the retina. This adjustment ensures that a clear image is always formed on the retina regardless of the object’s distance. OR
When a beam of white light passes through a glass prism, it bends or refracts at the two surfaces of the prism. Because each colour in white light has a different wavelength, each one bends by a different amount while passing through the prism. This causes the light to spread out into its constituent colours, forming a spectrum. This phenomenon is called dispersion of light. 2
34.
The appearance of all the individual colours from violet to red clearly shows that white light is not a single colour but is made up of many different colours.
Yes, the lens will still produce a complete image of the object, but it will be less bright. Covering part of the lens reduces the amount of light passing through, but does not change the path of the rays from the uncovered part, so the full image is still formed.
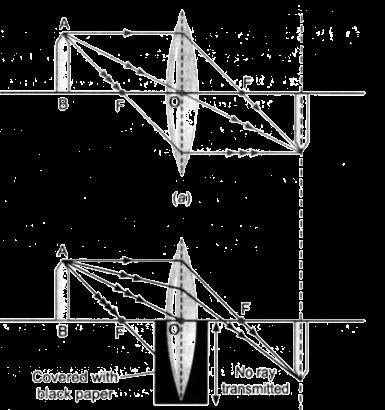
Experimental verification: Place an object in front of the convex lens and cover its lower half with black paper. Observe the image on a screen. You will notice that the entire image is visible, but it is dimmer compared to when the full lens is uncovered. The dimming occurs because many rays incident on the covered part of the lens are blocked.
The upper part of the lens still refracts the rays emerging from the candle and brings them to focus on the screen. This demonstrates that even a partially covered lens can form a complete image, though with reduced brightness.
Given, R= 24cm,f= 12cm
Here, hl =3×h0
We know, m=
35.
From the mirror formula,
⇒u= 8
The object distance is 8 cm. The negative sign indicates that the object is placed towards the left side of the pole of the spherical mirror.
In the given figure, the two resistors on the top are in series, Hence, R1 = 2Ω+2Ω=4Ω
Now, R1 =4Ω,R2 =2Ω are in parallel connection
36.
37.
Now, 2Ω, 2ΩandRP are in series connection
Hence, Effective resistance between P & Q is -
38.
Adomestic electric circuit consists of three main wires:
1.Live wire (Phase wire) – It carries high voltage (220 V in India) from the power source to the appliances. It is usually red or brown in colour.
2. Neutral wire – It completes the circuit by providing a return path for the current. It is at zero potential and is usually black or blue in colour.
3. Earth wire – It is a safety wire that provides a direct path for excess current to flow into the ground, preventing electric shocks. It is usually green or yellow green in colour.
Earthing is essential for safety in an electric circuit. It prevents electric shocks by diverting leakage current safely into the ground. If a fault occurs, the earthing wire carries excess current away, preventing electric shocks and protecting appliances from damage 3
1) The iron filings arrange themselves in a definite pattern because each filing becomes a tiny magnet due to induced magnetism when placed in the magnetic field of the bar magnet. These tiny magnets experience forces along the magnetic field lines and align themselves accordingly, forming a pattern that represents the shape of the magnetic field around the magnet.
2) The direction of the magnetic field at any point is given by the tangent to the magnetic field line at that point. By observing the alignment of the iron filings or the orientation of a small 1 1 2
39.
compass needle placed at that point, one can determine the direction in which the north pole of a test compass would point.
3) Two magnetic field lines never cross each other because the magnetic field at a particular point can have only one direction. If two lines were to intersect, it would indicate that the magnetic field at the intersection point has two different directions simultaneously, which is impossible.
OR
Asmall compass needle can be used to trace the magnetic field lines of a bar magnet. When placed near the magnet, the north pole of the compass aligns along the magnetic field. By moving the compass gradually around the magnet and marking the direction at different points, a series of points is obtained. Connecting these points carefully forms continuous magnetic field lines, which emerge from the north pole and enter the south pole of the bar magnet, showing the complete path of the magnetic field.
1) When a narrow beam of white light passes through a glass prism, it bends (refracts) at the two surfaces of the prism. Because different colors in white light have different wavelengths, each color bends by a different amount. This causes the light to spread out into a spectrum of colors ranging from violet to red. This phenomenon is called dispersion of light, and it occurs due to the different degrees of refraction for different colors of light.
2) This phenomenon can be observed in nature as a rainbow, which appears in the sky when sunlight is dispersed by water droplets in the atmosphere after rain.
3) From this observation, it can be concluded that white light is not a single colour, but is actually made up of many colors of different wavelengths. Each constituent colour bends differently when passing through a medium like a prism, revealing the composite nature of white light.
OR
1)Mr. Sharma is suffering from Presbyopia, which is a common defect of vision that occurs with advancing age, making it difficult to see nearby objects clearly while distant vision remains normal.
2)With age, the ciliary muscles of the eye become weaker and the lens loses its elasticity. The lens can no longer become sufficiently convex to focus light from close objects onto the retina. As a result, images of nearby objects, such as newspaper print or small craft items, are formed behind the retina, causing them to appear blurred. This gradual loss of the eye’s ability to accommodate for near vision is the main reason for presbyopia.
3) Presbyopia can be corrected using convex (converging) lenses. These lenses converge the light rays from nearby objects before they enter the eye, effectively reducing the demand on the weakened lens to bend the rays. This allows the light to focus correctly on the retina, enabling Mr. Sharma to read newspapers and see close objects clearly again.
Max. Marks: 80
General Instructions:
SCIENCE
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER - 7
CLASS X (2025-26)
Time allowed: 3 hours
1. This question paper consists of 39 questions in 3 sections. SectionAis Biology, Section B is Chemistry, and Section C is Physics.
2. All questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice is provided in some questions.Astudent is expected to attempt only one of these questions.
SectionA(Biology)
In which part of the alimentary canal is the complete digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats achieved?
A.Stomach
1.
2.
B.Small intestine
C.Large intestine
D.Oesophagus
Which of the following statements about transpiration is correct?
A.It occurs only at night
B.It helps in upward conduction of water
C.It decreases the rate of water absorption
D.It occurs only in roots
In a synapse, neurotransmitters are released from:
A.Axon terminal of presynaptic neuron
3.
B.Dendrite of postsynaptic neuron
C.Node of Ranvier
D.Myelin sheath
4.
Which part of the human brain controls voluntary actions like walking and writing? A.Cerebellum
5.
B.Cerebrum
C.Medulla oblongata
D.Pons
Which of the following methods of reproduction involves binary fission? A.Hydra
6.
man with blood group ‘A’marries a woman with blood group ‘O’. What possible blood groups can their children have?
A.OnlyA
B.Only O
C.Aand O
D.A, B,AB, O
Which of the following is a non-biodegradable pollutant?
A.Cotton cloth
7.
D.Vegetable peel
Questions No. 8 to 9 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true, but R is false.
D. A is false, but R is true
8. Assertion (A): Stomata regulate the process of transpiration.
Reason (R): Guard cells control the opening and closing of stomata.
9. Assertion (A): The sex of a child in humans is determined by the mother.
Reason (R): The ovum may carry either an X or Y chromosome. 1
10. Why is the small intestine in herbivores longer than in carnivores?
11. State the role of (a) adrenaline and (b) insulin in the human body.
(a) Explain the female reproductive system in humans.
(b)Explain the process of double fertilization in flowering plants
Read the passage and answer the questions:
Akshat read that the ozone layer in the stratosphere protects life on Earth. However, he also learned that ozone is being depleted due to the release of certain harmful chemicals. His teacher explained that this depletion can lead to harmful effects on human health and the environment.
(a)What is the function of the ozone layer?
(b)Name one chemical responsible for ozone depletion.
(c)Mention two harmful effects of ozone layer depletion.
(d)Suggest one measure to reduce ozone
Section B (Chemistry)
Find the incorrect statement:
A.Sodium hydroxide is prepared by the electrolysis of brine
B.Gypsum is added to cement to increase its setting time
C.Washing soda is Na₂CO₃·10H₂O D.Plaster of Paris is CaSO₄·10H₂O
The IUPAC name of CH₃–CH₂–COOH is:
acid
acid
acid
acid
Which statement about metals and non-metals is incorrect?
A.Metals are generally electropositive in nature.
B.Non-metals generally form acidic oxides.
C.Metals form cations by gaining electrons.
20.
D.Non-metals are poor conductors of electricity.
Match the processes with the correct description:
ColumnA(Process)
(a)Roasting
(b)Calcination
(c)Thermite reaction
(d)Electrolysis
A.a–iii, b–i, c–iv, d–ii
B.a–i, b–iii, c–ii, d–iv
C.a–iv, b–ii, c–i, d–iii
21.
22.
23.
Column B (Description)
(i)Heating ore in absence of air
(ii)Electrolytic reduction of bauxite
(iii)Heating sulphide ore in air
(iv)Welding broken railway tracks
D.a–iii, b–ii, c–i, d–iv 1
Which of the following non-metals is lustrous?
A.Sulphur
B.Phosphorus
C.Iodine
D.Carbon (coal) 1
CH3CH2OH → KMnO4 alkaline CH3COOH
Here alkaline KMnO4 acts as
A.Oxidising agent
B.Reducing agent
C. Dehydrating agent
D.Catalyst 1
During the dilution of a concentrated acid, a large amount of heat is produced. What is the safest way to carry out this process?
A. Slowly add the acid into water while stirring continuously.
B. Pour water into acid with constant stirring.
C. First add water to acid, then add a base.
D. Mix base into acid with constant stirring. 1
Question No.24 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
24.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true, but R is false.
D. A is false, but R is true
Assertion (A): Sodium oxide (Na2O) and potassium oxide (K2O) dissolve in water to form strong alkalis.
Reason (R): Metal oxides of highly reactive metals form soluble hydroxides in water, whereas most non-metal oxides form acidic solutions.
25.
Name two metals that are good conductors of heat and two metals that are poor conductors of heat.
The PH of three solutions are given in the table.
Answer the Questions that follows
28.
(1)Identify which solution is acidic, basic, and neutral.
(2)Arrange the solutions in the order of increasing hydroxide ion concentration.
(3)Which
Given three metals: Magnesium,Aluminium, and Copper. How would you experimentally arrange them in decreasing order of reactivity?
The atomic number of an element is 12.
(a)Write its electronic configuration.
(b)State whether the element is a metal or non-metal.
(c)Write the valency of the element and the name and formula of the compound it forms with chlorine.
(a)Thermal decomposition of lead nitrate is carried out in a test tube. State the observations and write the balanced chemical equation.
(b)Identify the type of reaction and state the nature (acidic/basic/neutral) of the oxide formed.
29.
Astudent takes two solutions in separate test tubes: lead nitrate (Pb(NO3)2) and potassium iodide (KI). She mixes them and observes the formation of a bright yellow precipitate.
(a)Name the type of reaction taking place. Write the balanced chemical equation.
(b)Explain why the precipitate forms.
(c)If copper metal is added to silver nitrate solution, a reaction occurs. Explain why copper reacts but silver does not react with copper sulphate solution.
Astudent is performing experiments with a few organic compounds. She is given propene(C3H6), ethanol (C2H5OH), acetic acid (CH3COOH) and propane (C3H8) She is asked to identify each compound based on their chemical reactions and classify them as alkene, alkane, alcohol, or carboxylic acid.
(a)Suggest a test to identify propene from the given compounds and write the chemical equation.
(b)Suggest a test to identify ethanol and write the reaction equation.
(c)Suggest a test to identify acetic acid and write the reaction equation.
(d)Explain why propane does not give any of the above tests.
(e)Classify all the compounds.
OR
i.It is observed that covalent compounds are bad conductors of electricity. Give reason.
ii.Carbon can neither form C4+cation nor C4- anion. Why?
iii. Identify hetero atom(s) in the following compounds:
Section C (Physics)
Amagnetic field can exert a force on a
A Stationary magnet
30.
B Moving magnet
31.
Two resistors of 4 Ω and 6 Ω are connected in series. The equivalent resistance is: A 10 Ω
Question No. 32 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true, but R is false.
D. A is false, but R is true 32.
Assertion (A): The space appears dark to an astronaut. Reason (R): There is no atmosphere in the space.
33. Define magnetic field lines. Mention any two properties of magnetic field lines.
In the experiment to study the dependence of current (I) on the potential difference (V) across a resistor, a student obtained a graph as shown.
1) What does the graph depict about the dependence of current on the potential difference?
2) Find the current that flows through the resistor when the potential difference across it is 2.5 V.
What are the common defects of vision that can be corrected by the use of suitable eyeglasses or spectacles?
Explain why the sun is visible to us about 2 minutes after actual sunset.
Can a freely suspended current carrying solenoid stay in any direction? Justify your answer. What will happen when the direction of current in the solenoid is reversed?
37.
1) Write the mathematical expression for Joule's law of heating.
2)An electric kettle connected to a 220 V supply draws a current of 4 A Calculate the heat produced in the kettle in 5 minutes.
Astraight cylindrical conductor is suspended with its axis perpendicular to the magnetic field of a horse-shoe magnet. When a current is passed through the conductor, it gets displaced towards the left.
What will happen to the displacement of the conductor if:
1) the current through it is increased?
38.
39.
2) the horse-shoe magnet is replaced by a stronger magnet?
3) the direction of current is reversed?
Name the rule used to determine the direction of force on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field and state it.
1) Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the refracted ray in each of the following cases:
Aray of light incident on a concave lens:
i) parallel to its principal axis, and
ii) is directed towards its principal focus.
2)Aconvex lens produces a real image of an object. When the object is placed at a distance of 18 cm from the lens, the image formed is twice the size of the object.
Determine the position of the object if a real image three times the size of the object is to be formed.
1) Define power of a lens and write its SI unit. Name the type of lens whose power is negative.
2) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of an image by a concave mirror when the object is placed:
i)at the centre of curvature (C), and
ii)between the pole (P) and the focus (F) of the mirror.
State the nature, size, and position of the image formed in each case.
Marking Scheme
Section
7.
8. A. BothAand R true, R correct explanation.
9. D.Ais false, but R is true.
10.
11.
Herbivores consume plant-based food, which contains cellulose that is hard to digest.Alonger small intestine provides more time and surface area for digestion and absorption. Carnivores have shorter intestines as animal proteins are easier to digest.
Adrenaline: Secreted by adrenal glands during stress; increases heartbeat, blood pressure, and glucose release for energy.
Insulin: Secreted by the pancreas; regulates blood sugar by promoting glucose uptake and storage as glycogen in liver and muscles.
Binary fission: Parent divides into two identical daughter cells (e.g., Amoeba).
12.
Multiple fission: Parent divides into many daughter cells simultaneously (e.g., Plasmodium). Binary is simple and faster; multiple ensures survival under adverse conditions.
13. Acquired traits: Characteristics developed during an individual’s lifetime due to environmental influence or habits; not passed to offspring. Example: learning to play guitar, muscle build due to exercise.
Inherited traits: Traits controlled by genes, transmitted from parents to offspring. Example: eye color, blood group.
Thus, inheritance ensures continuity of genetic information, while acquired traits end with the individual.
Soil degradation: Fertilizers reduce soil fertility over time by killing beneficial microbes.
Water pollution: Excess chemicals leach into rivers/lakes, causing eutrophication and fish death.
14.
Health hazards: Pesticide residues enter the food chain, leading to diseases like cancer, neurological disorders, and biomagnification.
Thus, overuse affects soil, water, environment, and human health severely.
The human female reproductive system produces ova (eggs), provides a site for fertilization, and supports foetal development.
Main parts:
• Ovaries:Almond-shaped organs producing eggs and hormones (oestrogen, progesterone).
• Oviducts (fallopian tubes): Carry ovum to uterus; fertilization usually occurs here.
• Uterus: Pear-shaped organ where zygote implants and develops into foetus.
• Vagina: Canal receiving sperm and serving as birth passage. This system ensures continuity of species through sexual reproduction.
OR
In flowering plants, fertilization involves two male gametes fusing with different cells in the embryo sac:
1. One male gamete fuses with the egg cell to form a diploid zygote (syngamy).
2. The second male gamete fuses with two polar nuclei to form a triploid endosperm nucleus (triple fusion).
This phenomenon is called double fertilization, unique to angiosperms.
• Zygote → develops into embryo.
• Endosperm → provides nutrition to developing embryo. This process ensures simultaneous formation of embryo and nutritive tissue, making reproduction efficient.
(a) The ozone layer absorbs harmful UV radiation, preventing skin cancer, cataracts, and DNA damage in organisms.
(b) Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs).
(c) Two harmful effects:
(1) Increased incidence of skin cancer, cataracts, and a weakened immune system in humans.
(2) Damage to phytoplankton, crops, and disruption of ecosystems.
(d) Measures: Use CFC-free refrigerators and air conditioners; adopt eco-friendly technologies like hydrofluorocarbons.
Section B (Chemistry)
19. C.Metals form cations by gaining electrons. 1
23. A.Slowly add the acid into water while stirring continuously. 1
24. A. BothAand R are true, and R is the correct explanation ofA. 1
25.
26.
Metals like copper and silver are very good conductors of heat because they allow heat to pass through them quickly. In contrast, lead and mercury are poor conductors of heat as they do not transfer heat efficiently. 2
(1)A(pH 3) is acidic, B (pH 9) is basic, and C (pH 7) is neutral.
(2)Order of increasing OH⁻ concentration:A< C < B.
(3)SolutionA(pH 3) will turn blue litmus red because acids change blue litmus to red.
Displacement reactions with salt solutions (principle):Amore reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal from its salt solution.
• Magnesium displacing copper from copper sulphate: Mg+CuSO4 ⟶MgSO4 +Cu
• Aluminium displacing copper from copper sulphate: 2Al+3CuSO4 ⟶Al2(SO4)3 +3Cu
• Magnesium displacing aluminium from aluminium sulphate (to show Mg is aboveAl): 3Mg+Al2(SO4)3 ⟶3MgSO4 +2Al
27.
28.
• No reaction when copper is placed in magnesium or aluminium salt solutions, Cu+MgSO4 (no reaction)
From the above, Mg displaces Al and Cu;Al displaces Cu but not Mg; Cu displaces neither hence the order of decreasing reactivity is: Magnesium >Aluminium > Copper.
(a) Electronic configuration: 1s22s2sp63s2
(b) Nature of element: Metal (magnesium is an alkaline earth metal).
(c) Valency and compound with chlorine:
1.Magnesium has 2 valence electrons, so its valency is 2.
2.It forms magnesium chloride, with the formula: MgCl2
(a)When lead nitrate crystals are heated strongly in a test tube, the following observations are made:
• The crystals melt and a yellow solid (lead oxide, PbO) is formed.
• Brown fumes of nitrogen dioxide (NO₂) gas are observed.
• Acolourless gas, oxygen (O₂), is also released.
• The balanced chemical equation is:
2Pb(NO3)2(s)→ Δ 2PbO(s)+4NO2(g)+O2(g)
(b)This reaction is a thermal decomposition reaction, where a single compound breaks down into simpler products on heating. The oxide formed, lead oxide (PbO), is basic in nature because it reacts with acids to form salts and water
PbO(s)+2HCl(aq)⟶PbCl2(s)+H2O(l) OR
(a)Reaction type: Double displacement (precipitation reaction)
Pb(NO3)2(aq)+2KI(aq)⟶PbI2(s)↓+2KNO3(aq)
Lead(II) iodide (PbI2) is insoluble in water, so it precipitates as a bright yellow solid.
(b)Copper and silver reaction: Copper is more reactive than silver (reactivity series). It can displace silver from silver nitrate solution:
Cu(s)+2AgNO3(aq)⟶Cu(NO3)2(aq)+2Ag(s)
Silver is less reactive than copper, so it cannot displace copper from copper sulphate solution.
(a)Identification of propene (C3H6) : Add bromine water to the compound. Bromine water decolorizes from reddish-brown to colourless.
CH3 CH=CH2 +Br2 ⟶CH3 CHBr CH2Br
Propene is an alkene (unsaturated), so it reacts with bromine via addition reaction.
(b)Identification of ethanol (C2H5OH):
Test:Acidified potassium dichromate (K₂Cr₂O₇ / H₂SO₄) test.
Observation: Colour changes from orange to green due to formation of Cr³⁺ ions.
3C2H5OH+2[O]⟶3CH3CHO+3H2O
Ethanol is an alcohol, which can be oxidised to an aldehyde.
(c)Identification of acetic acid (CH3COOH):
Test: React with sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO₃).
Observation: Effervescence due to CO₂ evolution.
CH3COOH+NaHCO3 ⟶CH3COONa+H2O+CO2 ↑
Acetic acid is a carboxylic acid and reacts with carbonates to release CO₂
(d)propane(C3H8) :
Propane is a saturated hydrocarbon. It does not decolorize bromine water and does not react with dichromate or carbonates under normal conditions.
e)Classification:
Compound
propene (C3H6)
Ethanol (C2H5OH)
Acetic acid (CH3COOH)
Propane(C3H8)
Type
Alkene (unsaturated hydrocarbon)
Alcohol
Carboxylic acid
Alkane (saturated hydrocarbon)
OR
(i)Covalent compounds are bad conductors of electricity
Reason: Covalent compounds consist of molecules held together by covalent bonds, where electrons are shared and not free to move.
Electrical conductivity requires mobile charged particles (ions or electrons). Since covalent compounds do not have free electrons or ions, they cannot conduct electricity in solid or molten state.
(ii)Carbon cannot form C4+ or C4-
Reason: Carbon has 4 valence electrons and needs 4 more electrons to complete its octet.
Formation of C4+ cation would require losing 4 electrons, which needs very high ionization energy, making it highly unstable.
Formation of C4- anion would require gaining 4 electrons, which is also highly unstable due to strong electron–electron repulsion.
Hence, carbon forms covalent bonds instead of ionic C4+ or C4-
(iii)Identification of hetero atoms:
a.CH3OH → Oxygen (O) is the hetero atom.
b.CH3NH2 → Nitrogen (N) is the hetero atom.
Section C (Physics)
32. A.Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A. 1
Magnetic field lines are imaginary lines that represent the direction and strength of a magnetic field. They indicate the path a north pole would follow in the field.
Properties of Magnetic Field Lines are –
33.
1.They never intersect – If they did, it would mean two different directions of the magnetic field at the same point, which is not possible.
2.They emerge from the north pole and enter the south pole externally, forming closed loops. 2
35.
1)The graph shows a straight line passing through the origin, which indicates that the current (I) is directly proportional to the potential difference (V) across the resistor. This confirms Ohm’s Law, which states that the current flowing through a resistor is directly proportional to the voltage applied across it, provided the temperature remains constant.
Mathematically, I ∝ V or V = IR, where R is the resistance of the resistor.
2) When a potential difference of 2.5 V is applied across the conductor, the current flowing through the circuit is 0.25A.
The common defects of vision are:
1. Myopia (short-sightedness): In this defect, nearby objects are seen clearly but distant objects appear blurred. It is corrected using concave lenses.
2. Hypermetropia (long-sightedness): In this defect, distant objects are seen clearly but nearby objects appear blurred. It is corrected using convex lenses.
3. Presbyopia: This age-related defect occurs due to weakening of ciliary muscles and loss of flexibility of the eye lens, making it difficult to see nearby objects. It is corrected using convex lenses or bifocal lenses.
OR
The sun remains visible for about 2 minutes after it has set below the horizon because of atmospheric refraction. The rays of the sun from below the horizon are refracted in the Earth’s atmosphere and bend towards the normal. This bending makes the sun’s apparent position higher than its actual position. Thus, even when the sun has already gone below the horizon, we continue to see it for a short while.
Acurrent-carrying solenoid behaves like a bar magnet because it generates a magnetic field similar to the one produced by a magnet. When a solenoid is freely suspended, it aligns itself in the Earth's magnetic field.
3
36.
37.
The solenoid’s magnetic field interacts with the Earth’s magnetic field, causing it to align in the north-south direction, with one end acting like the north pole and the other end acting like the south pole.
When the direction of the current in the solenoid is reversed, the magnetic poles of the solenoid are also reversed. The end that was previously the north pole becomes the south pole, and the end that was the south pole becomes the north pole, leading to a change in the alignment of the solenoid with respect to the Earth's magnetic field.
1)According to Joule’s law, the heat produced in a conductor due to the flow of current is directly proportional to:
1. The square of the current (I2),
3
3
38.
2. The resistance of the conductor (R), and
3. The time for which current flows (t).
Mathematically,
where H is the heat produced in joules.
2) Given data:
• Voltage, V=220V
• Current, I=4A
• Time, t=5min=5×60=300s
Now, the electrical power consumed:
Heat produced in time t :
H=I2Rt
P=V×I=220×4=880W
H=P×t=880×300=2,64,000J
The heat produced in the kettle in 5 minutes is 2.64×105 J(264kJ).
1)If the current is increased, the magnetic force on the conductor increases, so the displacement of the conductor will increase.
2) If the horse-shoe magnet is replaced by a stronger magnet, the magnetic field strength increases, which also increases the magnetic force, causing a larger displacement of the conductor.
3) If the direction of current is reversed, the direction of the magnetic force acting on the conductor also reverses, so the conductor will be displaced towards the right instead of the left. OR
The direction of the force on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field is determined using Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule
According to this rule, the thumb, forefinger, and middle finger of the left hand are stretched mutually perpendicular to each other. The forefinger points in the direction of the magnetic field (B), the middle finger points in the direction of the current (I), and the thumb shows the direction of the force (F) acting on the conductor.
This rule helps to find the direction of motion of a conductor placed in a magnetic field.
39. 1)
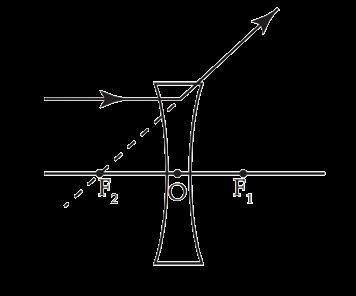
i.) When a ray of light is incident parallel to the principal axis of a concave lens, it refracts and diverges away from the lens. The refracted ray appears to come from the principal focus on the same side of the lens as the incident ray.
ii.) When a ray of light is directed towards the principal focus of a concave lens on the opposite side, after refraction it emerges parallel to the principal axis.
2) Case 1
Size of image =2× Size of object
So Size of image Size of object =2
Here, m= 2 (for inverted, real image)
And v is +ve, u is ve
18cm
2= v 18
From lens formula,
Focal length of the lens is 12 cm
Case 2
Size of image =3× Size of object
m= size of image size of object =3
m= v u = 3 (For real image)
v= 3u
From the lens formula,
The object distance is 16 cm The negative sign indicates that the object is placed to the left side of the optical centre of the lens.
OR
1) The power of a lens is defined as the reciprocal of its focal length in metres. It indicates the ability of the lens to converge or diverge a beam of light.
P = 100 f(incm) or P = 1 f(inm)
The SI unit of power of a lens is the dioptre (D).
Aconcave lens has negative power because it is a diverging lens and its focal length is taken as negative.
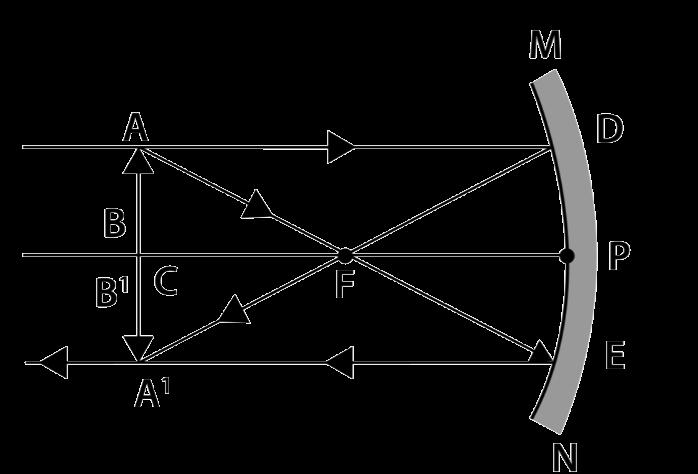
i) Object at the Centre of Curvature (C):
• The image is formed at C itself.
• It is real, inverted, and of the same size as the object.
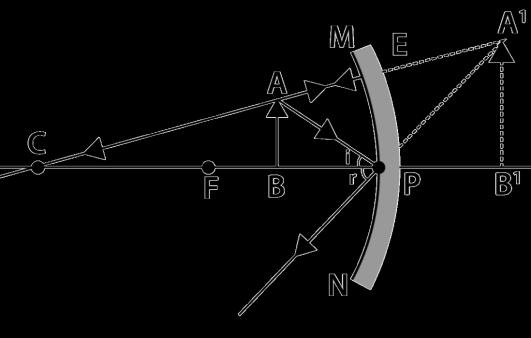
ii) Object between the Pole (P) and Focus (F):
• The image is formed behind the mirror.
• It is virtual, erect, and magnified.
SCIENCE
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER - 8
Class X (2025-26)
Max. Marks: 80 Time allowed: 3 hours
General Instructions:
1. This question paper consists of 39 questions in 3 sections. SectionAis Biology, Section B is Chemistry, and Section C is Physics.
2. All questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice is provided in some questions.Astudent is expected to attempt only one of these questions.
SectionA(Biology)
Which enzyme is secreted in the stomach that digests proteins?
A.Amylase
1.
3.
Which of the following transports water in plants? A.Phloem
Reflex actions are controlled by:
A.Brain
B.Cerebrum
C.Spinal cord
D.Cerebellum
Which reproductive method is followed by Planaria?
A.Binary fission
B.Fragmentation
C.Budding D.Multiple fission
Across between a tall pea plant (TT) and a dwarf pea plant (tt) will result in:
A.All tall plants
B.All dwarf plants
C.3 tall : 1 dwarf
D.1 tall : 1 dwarf
Which of the following contributes to acid rain?
A.Carbon monoxide and nitrogen gas
B.Sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides
C.Methane and ozone
D.Chlorofluorocarbon
Which of the following is the functional unit of the kidney?
A.Neuron
7.
Questions No. 8 to 9 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true, but R is false.
D. A is false, but R is true
(A):
Assertion (A): Phototropism in plants occurs due to unequal distribution of auxins. Reason (R): Auxin accumulates more on the illuminated side of the stem, causing more growth there.
14. Write three differences between food chains and food webs. Give one example of each. 3 15.
(a)Discuss in detail the human respiratory system and support your answer with a welllabelled diagram.
(b)Describe the mechanism of reflex action in humans with the help of a flow chart/diagram.
Read the passage and answer the following:
Priya’s grandmother, who lives in a village suffers from frequent respiratory infections. In the last few years, the trees around the village, has been cut down to expand the land area for the construction of roads and factories.
16.
17.
(a) What is large-scale cutting down of trees known as?
(b) List any two harmful effects this activity has on the environment.
(c)How does this activity contribute to global warming?
(d) Suggest one measure that can help reduce the harmful impacts of this activity.
Section B (Chemistry)
Which of the following reactions represents a double displacement reaction? A. Zn+H2SO4 →ZnSO4 +H2
Sodium carbonate reacts with dilute HCl. What is the gas evolved?
Hydrogen
Consumption of adulterated or improperly distilled alcohol can cause blindness and even death. Which of the following compounds is responsible for these toxic effects?
20.
C.Acetone (CH3COCH3)
D.Acetaldehyde (CH3CHO)
The reaction of aluminium with ferric oxide to produce aluminium oxide and iron is called:
A. Electrolysis
B. Thermite reaction
C. Displacement reaction
D. Oxidation reaction 1
Ammonium chloride when heated with slaked lime (Ca(OH)₂) produces:
A. CO₂
21.
B. NH₃
C. H₂
D. O₂ 1
Which of the following oxides is amphoteric?
A. Na₂O
22.
B.Al₂O₃
C. SO₂
D. CO₂ 1
Which of the following compounds contains a covalent bond?
A. NaCl
23.
B. CaO
C. CO₂
D. KBr 1
Question No.24 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true but R is false.
D. A is false but R is true
24.
25.
Assertion (A): Sodium hydroxide reacts with aluminium to form a soluble complex. Reason (R):Aluminium is a reactive metal and can react with acids and bases. 1
Which metals can be extracted in their pure form by simply heating their oxides in air? Give one example. 2
26.
27.
a)Why do chips packets appear puffed when purchased from the market?
(b)Why is paint applied on iron objects? Explain.
Azinc strip was immersed in a blue copper sulfate solution.After some time, the blue colour of the solution started fading, and the zinc strip developed small pits on its surface.
(a)Explain the reason for these observations.
(b)Write the chemical equation for the reaction that took place.
(c)Name the type of chemical reaction involved.
OR
i. Metals such as copper and aluminium are used in electrical transmission lines instead of iron, even though iron is stronger. Explain why.
ii. Why are metals generally lustrous and malleable?
iii. Name a metal that is light, strong, and resistant to corrosion, often used in aerospace applications.
Ravi took 5 mL of dilute HCl solution in a conical flask and added 3 drops of methyl orange indicator to it. The solution appeared red in colour. He added dilute NaOH solution drop by drop until the solution turned orange, indicating neutralisation. He recorded that it took 25 drops of NaOH for the colour change.
He repeated the experiment with different volumes of HCl and recorded his observations in the table below:
S.no
Volume of dilute HCl (mL) Drops of dilute NaOH used
Now answer the following
A. If Ravi used concentrated NaOH instead of dilute NaOH, how many drops will be required for the colour change?
(a)25
(b)<25
(c)>25
Justify your answer.
B. If 20 drops of dilute NaOH were measured to be 1 mL, how many mL of NaOH were required to neutralise 7 mL of HCl according to the table?
C. Explain why the colour changes from red to orange during the experiment.
OR
Sandeep was conducting an experiment to compare the conductivity of different solutions. He set up a circuit with a bulb as indicator and tested dilute hydrochloric acid, dilute sulphuric acid, glucose solution, and alcohol solution. He observed that only in acid solutions the bulb glowed brightly.
i. Why does the bulb glow when dilute acids are used but not with glucose or alcohol?
ii. What ions are responsible for the conduction in acid solutions?
iii. Write two real-life uses of this property of acids.
iv. Why do glucose and alcohol solutions fail to conduct electricity?
Ahydrocarbon with the molecular formula CxHy undergoes complete combustion as shown below: CxHy+5O2 →3CO2 +4H2O
(a)Determine the values of x and y.
(b)Write the IUPAC name of the hydrocarbon.
(c)Draw its electron dot structure of hydrocarbon.
(d)Name the alcohol which on heating with concentrated H₂SO₄ gives the above hydrocarbon.
(e)Write a balanced chemical equation for the hydrogenation of CxHy using hydrogen in the presence of Ni catalyst.
OR
Carbon is a versatile element that forms the backbone of many organic compounds due to its tetravalency and ability to bond with elements like hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and chlorine. Answer the following questions:
(a)Define hydrocarbons.
(b)List two properties of carbon that allow it to form a large variety of compounds.
(c) Write the functional group present in alcohols and amines.
(d)Write a chemical equation for the reaction between ethanol and ethanoic acid in the presence of concentrated H₂SO₄ as a catalyst.
30.
31.
32.
Section C (Physics)
Afull length image of the Taj Mahal can definitely be seen by using
A.Aplane mirror
B.Aconcave mirror
C.Aconvex mirror
D.All of these
1 volt is equal to
A. 1Js 1
B. 1JC 1
C. 1Nm 1
D. 1CJ 1
Question No. 32 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true but R is false.
D. A is false but R is true
Assertion (A): Sky appears blue in the daytime Reason (R): White light is composed of seven colors.
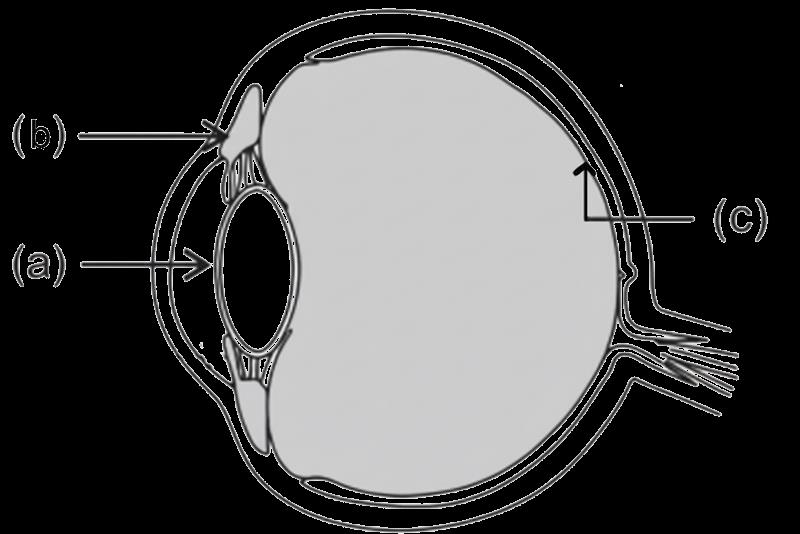
35.
A. In an experiment to study the dependence of current on potential difference across a resistor, a student obtained the graph as shown in the diagram.
From the graph find the value of resistance of the given resistor.
B. Apiece of wire of resistance 20 Ω is drawn out so that its length is increased to twice its original length. Calculate the resistance of the wire in the new situation.
Can a freely suspended current carrying solenoid stay in any direction? Justify your answer. What will happen when the direction of current in the solenoid is reversed?
3
36.
An object 4 cm in height, is placed at 15 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm . At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed to obtain a sharp image of the object. Calculate the height of the image.
Abeam of white light falling on a glass prism gets split up into seven colours marked 1 to 7 as shown in the diagram. A student makes the following statements about the spectrum observed on the screen.

(a)The colours at positions marked 3 and 5 are similar to the colour of the sky and the colour of gold metal respectively.
Is the above statement made by the student correct or incorrect? Justify.
3
38.
(b)Which two positions correspond closely to the colour of (i)a brinjal (ii)'danger' or stop signal lights?
(a)When two resistors of resistance R1 and R2 are connected in parallel, the net resistance is 3Ω. When connected in series its value is 16Ω. Calculate the value of R1 and R2.
(b)Calculate the ratio of current drawn in both the cases from the power supply of 24 V .
A.An object 4.0 cm in size, is placed 25.0 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm
(a)At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed in order to obtain a sharp image?
(b)Find the size of the image.
(c)Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image in this case. OR
B. Analyse the following observation table showing variation of image-distance (��) with object distance (��) in case of a convex lens and answer the questions that follow, without doing any calculations:
39.
(a)What is the focal length of the convex lens? Give reason to justify your answer.
(b)Write the serial number of the observation which is not correct. On what basis have you arrived at this conclusion?
(c)Select an appropriate scale and draw a ray diagram for the observation at S.No. 2.
Also find the approximate value of magnification.
Marking Scheme
The left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to the entire body through the aorta, requiring higher pressure. Hence, its wall is thicker than the right ventricle, which pumps blood only to the lungs.
The thyroid secretes thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3).
Role of thyroid hormones:
• These hormones regulate metabolism, growth, and development.
• They control protein, carbohydrate, and fat utilization and influence the rate of cellular respiration in the body.
12. Pollination:
• The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of a flower
• Example: via various agents such as wind, insects, water, etc Fertilization: The fusion of the male gamete (pollen nucleus) with the female gamete (egg cell) inside an ovule.
13. The advantages of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction are:
(1) Genetic variation: Offspring inherit genes from two parents, introducing variations.
(2) Adaptability: Variations increase the chances of survival under changing environmental conditions.
(3) Elimination of harmful traits: Sexual reproduction helps natural selection remove
Thus, sexual reproduction ensures evolution and long-term survival of the species, unlike asexual reproduction, which produces identical clones. 14.
Food chain:
The linear sequence of organisms showing the transfer of energy from producers → consumers → decomposers.
Example: Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Hawk.
Food web:
Anetwork of interconnected food chains showing the energy flow in an ecosystem.
Example: Grass eaten by grasshoppers, deer, and rabbits, all preyed upon by tigers.
Food webs maintain stability better than single food chains.
Diagram of a food web:
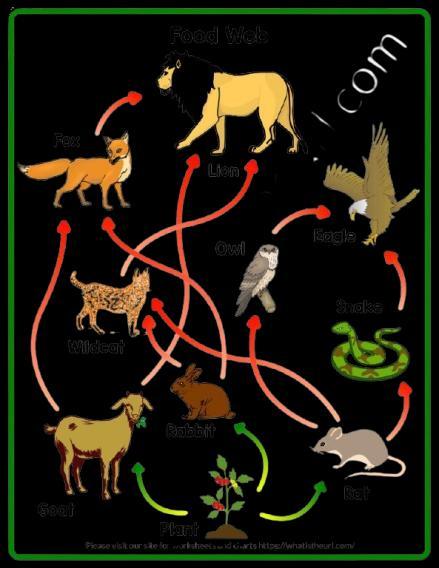
(a) Human respiratory system
It is responsible for gaseous exchange taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide.
Parts of the respiratory system:
• Nasal cavity: Filters, warms, and moistens air.
• Trachea (windpipe): Passage for air, lined with cilia and mucus to trap dust.
15.
• Bronchi: Two tubes branching from trachea into lungs.
• Bronchioles: The two bronchi further branch into thin bronchioles after they enter the lungs.
• Lungs: Primary organs of respiration
• Alveoli: at the end of each bronchiole is attached a small, thin-membraned, sac-like structure called the alveolus Here, the actual gaseous exchange takes place
• Diaphragm: Dome-shaped muscle aiding in breathing movements.
Mechanism:
• Inhalation: Diaphragm contracts and moves downward, chest cavity expands, air enters lungs.
• Exhalation: Diaphragm relaxes, chest cavity reduces, air is expelled. This system ensures efficient oxygen supply to body cells for respiration and removal of carbon dioxide.
Diagram of the human respiratory system:
(b) Reflex action in humans
Reflex action is an automatic, involuntary response to a stimulus, protecting the body from harm.
Pathway (ReflexArc):
• Stimulus (e.g., hot object touches skin).
• Receptor detects change.
• Sensory neuron carries impulse to spinal cord.
• Relay neuron passes signal to motor neuron.
• Motor neuron carries impulse to effector (muscle).
• Effector responds by withdrawing hand.
Significance: Reflex actions are quick, bypassing the brain’s conscious control to ensure immediate survival.
Diagram of reflex action:
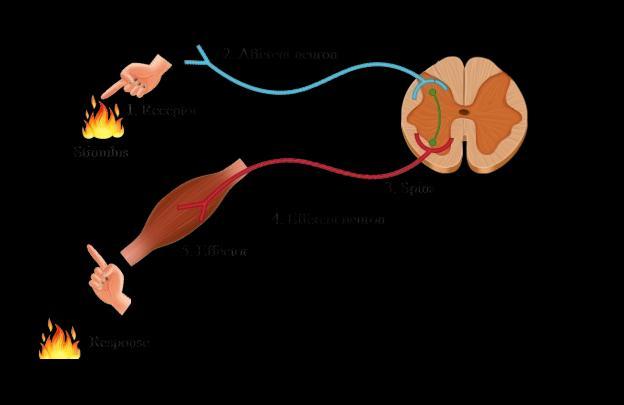
(a) Large-scale cutting down of trees is called deforestation
(b) Two harmful effects of deforestation on the environment are:
• Loss of biodiversity: Many plants and animals lose their natural habitat, leading to extinction or decline of species.
• Soil erosion: Tree roots bind soil; their removal results in loose soil being washed away by wind and water.
(c) Trees absorb carbon dioxide during photosynthesis. Cutting them reduces CO₂ absorption, causing excess CO₂ in the atmosphere, which traps heat and contributes to global warming
(d) One effective measure is afforestation/reforestation, i.e., planting new trees to replace lost forests, restoring ecological balance, and improving air quality.
Section B (Chemistry)
Metals obtained by heating their oxides in air are generally very reactive metals that can be reduced easily by heat alone.These are usually metals below carbon in the reactivity series, which do not require chemical reduction.
26.
Example: Mercury (Hg)can be obtained by heating mercury(II) oxide: 2HgO → heat 2Hg+O2
a)Chips packets are puffed
Chips packets are filled with nitrogen gas (N₂).
Reason:
Nitrogen is inert, so it prevents the chips from oxidation and spoilage. It cushions the chips, preventing them from breaking during transportation. This is why the packets appear puffed or inflated when we buy them.
(b)Paint is applied on iron articles
Reason:
Paint acts as a protective coating that prevents iron from coming in contact with air and moisture.
Iron reacts with oxygen and water to form rust (Fe₂O₃·xH₂O), which weakens the metal. By painting, the surface is protected from corrosion, increasing the durability of the iron objects.
(a)Reason for observations:
• Zinc is more reactive than copper.
• When a zinc strip is placed in copper sulfate solution, it displaces copper from the solution.
• The blue colour of CuSO₄ fades because Cu²⁺ ions are removed from the solution.
• Small pits appear on the zinc strip because zinc slowly dissolves as Zn²⁺ ions enter the solution.
(b)Chemical Equation: Zn(s)+CuSO4(aq)→ZnSO4(aq)+Cu(s)
• Zinc goes into the solution as Zn²⁺ ions.
27.
• Copper ions gain electrons and deposit as metallic copper.
(c)Type of Reaction:
This is a single displacement (or substitution) reaction, because a more reactive metal (zinc) displaces a less reactive metal (copper) from its salt solution. OR
a)Reason for choice in electrical lines:
Copper and aluminium have high electrical conductivity due to delocalised electrons, allowing efficient current flow.Iron has lower conductivity and is prone to corrosion, making it less suitable despite its strength.
28.
(b)Reason for lustre and malleability:
Metals are lustrous because free electrons reflect light efficiently.Metals are malleable because metallic bonds are non-directional; metal ions can slide over each other without breaking the bond.
(c)Example:
Titanium (Ti) – lightweight, strong, and highly resistant to corrosion; used in aircraft and spacecraft.
A.Answer: (b) < 25 drops
Reason: Concentrated NaOH has higher molarity, so fewer drops are needed to provide the same number of OH⁻ ions for neutralisation.
B. 20 drops = 1 mL → 1 drop = 0.05 mL
For 35 drops → Volume of NaOH = 35 × 0.05 = 1.75 mL
C. Methyl orange turns red in acidic solution and yellow in basic solution.
At neutral point, the colour appears orange, indicating neutralisation of HCl by NaOH. OR
i. The bulb glows in dilute acid solutions because acids ionise in water to produce ions, which carry electric current.
Glucose and alcohol do not ionise appreciably in water, so they do not conduct electricity.
ii. The ions responsible for conduction in acid solutions are:
H⁺ (hydrogen) ions from the acid
Anions from the acid (e.g., Cl⁻ from HCl, SO₄²⁻ from H₂SO₄)
iii. Two real-life uses of this property of acids:
Electroplating and electrorefining – acids conduct electricity to deposit metals.
Batteries and storage cells – acids act as electrolytes, conducting current.
iv. Glucose and alcohol are molecular compounds and do not dissociate into ions in water. Without ions, no conduction of electricity occurs, so the bulb does not glow.
29. (a)Finding x and y:
From the combustion equation: CxH�� +5O2 →3CO2 +4H2O
Number of carbon atoms: x = 3 (from 3 CO₂ molecules)
Number of hydrogen atoms: y = 8 (from 4 H₂O molecules → 8 H)
So, the hydrocarbon is C₃H₈
(b)IUPAC Name: Propane
(c)Electron Dot Structure:

(d)Alcohol that gives C₃H₈ on dehydration:
Propan-1-ol or Propan-2-ol
On heating with conc. H₂SO₄, water is removed to form propane.
(e)Hydrogenation reaction (addition of H₂):
(If the hydrocarbon were unsaturated, hydrogenation converts it to saturated propane.)
(a)Hydrocarbons:
Hydrocarbons are organic compounds made up of only carbon and hydrogen atoms.
b)Two properties of carbon:
Tetravalency – Carbon can form four covalent bonds, allowing the formation of a wide variety of compounds.
Catenation – Carbon atoms can link with each other to form long chains, rings, and branched structures, increasing the number of possible compounds.
(c)Functional groups
Alcohols: –OH
Amines: –NH₂
(d) Esterification reaction (ethanol + ethanoic acid):
Here, ethyl ethanoate is formed along with water.
Concentrated H₂SO₄ acts as a dehydrating agent and catalyst.
Section C (Physics)
30. C.Aconvex mirror
31. B. 1JC 1
32. B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
33. (a)Lens –
(b)Ciliary muscles – They change the curvature of the lens to adjust its focal length (helps in accommodation).
(c)Retina – It contains light-sensitive cells (rods and cones) that convert light into electrical impulses, which are carried to the brain by the optic nerve.
A. From Ohm's law: R= V I
From the graph, when V=4V, the current I=0.4A. R= V I = 4 04 =10Ω
The resistance of the given resistor is 10Ω.
B. We know:
34.
35.
Resistance of a wire �� =�� �� ��
• When the length is doubled ( ��′ =2�� ), the volume of the wire remains constant.
• So, if length becomes 2L, area becomes A′ = A 2 .
Given R=20Ω :
The new resistance of the wire =80Ω
No.Afreely suspended current-carrying solenoid does not stay in any direction; it aligns itself along the Earth’s N–S direction.
Reason/Justification:Acurrent-carrying solenoid behaves like a bar magnet (it develops a north and a south pole as given by the right-hand grip rule), so in Earth’s magnetic field it settles with its magnetic axis along north–south.
On reversing the current in the solenoid, the polarity of its ends reverses (the end that was North becomes South and vice versa). Hence, the suspended solenoid rotates through 180° to align again with the Earth’s field.
Given: ℎ�� =4cm,�� = 15cm,�� = 10cm (concave mirror, Cartesian convention)
Image distance:
36.
37.
So the screen should be placed 30 cm in front of the mirror (same side as the object).
Height of image:
2×4= 8cm
Screen at 30 cm; image height 8 cm (inverted, real, magnified 2× ).
(a)The statement is incorrect.
In a glass prism, colours appear from top → bottom as R O Y G B I V (red least deviated at top, violet most at bottom).
So, position 3 = Yellow (gold-like), position 5 = Blue (sky-like). The student swapped them.
(b)
(i)Colour of a brinjal ≈ violet/purple → position 7 (bottom).
(ii)‘Danger/stop’signal is red → position 1 (top).
(a)Finding ��1,��2
Given:
38.
Hence ��1 =12Ω,��2 =4Ω (order interchangeable).
(b)Ratio of current drawn ( 24 V supply)
Series:
Current ratio (parallel : series) = 8
39. A. Given: ℎ�� =4.0cm,�� = 25.0cm,�� = 15cm (concave mirror; Cartesian sign convention)
(a)Image distance
Answer (a): Place the screen 37.5 cm in front of the mirror (real image forms on the same side as the object).
(b)Size (height) of image
Magnification �� = ℎ�� ℎ�� = �� ��
Answer (b): Image height =6.0cm, inverted (negative sign).
(c)The required ray diagram to show the formation of image is given below
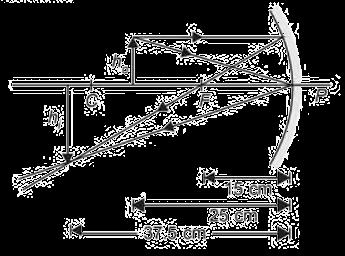
OR
B. (a) Focal length and reason (no calculation):
From S. No. 3, the observation is �� = 40cm,�� =+40cm.
For a convex lens, when object distance = image distance, the object is at 2�� and the image also forms at 2��. ⇒2�� =40cm⇒�� =20cm.
(b)Incorrect observation and why:
S.No. 6 is incorrect. Here �� = 15cm which is less than �� =20cm Aconvex lens with �� <�� forms a virtual, erect image on the same side as the object (so �� should be negative).
But the table shows �� =+120cm (real, on the other side), which contradicts the lens behaviour.
(c)Ray diagram for S. No. 2 and magnification:
Take S. No. 2: �� = 60cm,�� =+30cm.
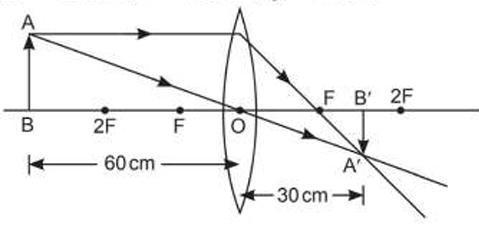
Approximate magnification (from geometry / table): �� = �� �� = 30 60 = 0.5 (negative sign indicates inverted)
So, the image is about half the size of the object, inverted.
SCIENCE
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER - 9
CLASS X (2025-26)
Max. Marks: 80 Time allowed: 3 hours
General Instructions:
1. This question paper consists of 39 questions in 3 sections. SectionAis Biology, Section B is Chemistry, and Section C is Physics.
2. All questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice is provided in some questions.Astudent is expected to attempt only one of these questions.
SectionA(Biology)
Which process in plants is responsible for release of oxygen into the atmosphere?
A.Respiration
B. Photosynthesis
C. Transpiration
D. Translocation
Which part of the human brain controls voluntary actions like writing and walking?
A. Cerebellum
B. Medulla
C. Cerebrum
D. Hypothalamus
Which of the following organisms reproduces by binary fission?
A. Hydra B.Amoeba C. Spirogyra D. Yeast
Which Mendelian principle is demonstrated by the 9:3:3:1 ratio in a dihybrid cross?
A.Law of Segregation
B. Law of Independent Assortment
C. Law of Dominance
D. Law of Purity of Gametes
Which of the following is a greenhouse gas that contributes to global warming?
humans, fertilization takes place in the:
(Fallopian tube)
Which of the following statements is true about tropism in plants?
A.Shoots show negative phototropism
B. Roots show positive geotropism
C.Shoots show negative hydrotropism
D. Roots show negative geotropism
Questions No. 8 to 9 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true, but R is false.
D. A is false, but R is true
15.
16.
(a) Why do sons always inherit X-linked traits from their mother and not from their father?
(b)Explain Darwin’s theory of natural selection with an example.
Read the passage and answer the following questions:
Ravi noticed that the roots of a plant growing in a pot were bending and growing sidewards towards a region of moist soil He also observed that when the pot was tilted, the roots still grew downwards. Curious, he concluded that roots respond to more than one type of stimulus in their environment.
(a)What is the response of roots towards moisture called?
(b)Which type of tropism is responsible for roots growing downward?
(c)If both stimuli (as discussed above) act on roots, which stimulus usually dominates?
(d) Which stimulus is more important for the survival of plants?
(e)How do plant responses to such stimuli differ from animal responses?
Section B (Chemistry)
Which of the following particles are present in dilute aqueous solution of hydrochloric acid?
A. H3O+ +Cl
17.
18.
B. H+ +OH
C. Cl2 +H2O
D. H2 +Cl
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic property of covalent compounds?
A. Low melting and boiling points
B. Poor electrical conductivity
C. Formation of ions in aqueous solution
D. Formation of molecules
19. Rancidity can be prevented by:
A. Storing food in open sunlight
B.Adding antioxidants to food
C. Exposing oils to more oxygen
D. Keeping food at high temperature
20. When soap is used in hard water, scum is formed. This is because:
21.
A. Soap reacts with magnesium and calcium salts to form insoluble compounds
B. Soap undergoes hydrolysis in hard water
C. Soap gets oxidised in hard water
D. Soap decomposes to form insoluble carbonates
During electrolytic refining of copper, the anode is:
A. Pure copper plate, which gains mass
B. Impure copper block, which loses mass
C. Graphite rod, which remains unchanged
D. Platinum electrode, which dissolves in the electrolyte 1
Which type of isomerism is shown by but-1-ene and but-2-ene?
A. Chain isomerism
22.
B. Functional group isomerism
C. Position isomerism
D. Metamerism
Match the following with correct response
Column -A
(i)Baking soda
(ii)Washing soda
(iii)Slaked lime
23.
1
24.
(iv)Plaster of Paris
A.(i) → c, (ii) → a, (iii) → b, (iv) → d
B.(i) → b, (ii) → d, (iii) → a, (iv) → c
C.(i) → d, (ii) → c, (iii) → b, (iv) → a
Column - B
(a)Sodium carbonate
(b)Calcium hydroxide
(c)Sodium bicarbonate
(d)Calcium sulphate hemihydrate
D.(i) → a, (ii) → b, (iii) → c, (iv) → d 1
Question No. 24 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true, but R is false.
D. A is false, but R is true
Assertion (A): Olfactory indicators are substances that show different odours in acidic and basic solutions
Reason (R): In acidic medium, onion loses its smell, while in basic medium it retains the smell.
25.
Rohit burnt a small amount of phosphorus in a spatula and collected the gas released in an inverted test tube. State the effect of this gas on:
26.
What is a redox reaction? Give a balanced chemical equation for a redox reaction involving zinc. Name another element which can show similar behaviour. Why can’t silver take part in the same kind of redox reaction?
OR
Identify the type of reaction:
a)CaCO₃ (s) → CaO (s) + CO₂ (g)
b)Fe (s) + CuSO₄ (aq) → FeSO₄ (aq) + Cu (s)
c)HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq) → NaCl (aq) + H₂O (l)
27.
28.
How can this oxide layer on an aluminium object be made thicker and more protective? What is the process called? Explain briefly. 3
Read the following text carefully and answer the questions that follow: Salts play a very important role in our daily life. Sodium chloride which is known as common salt is used almost in every kitchen. Baking soda is also a salt used in faster cooking as well as in baking industry. The family of salts is classified on the basis of cations and anions present in them.
a.Identify the acid and base from which Sodium chloride is formed.
b.Find the cation and the anion present in Calcium sulphate.
c."Sodium chloride and washing soda both belong to the same family of salts." Justify this statement.
OR
The pH of a substance indicates how acidic or basic it is. It plays an important role in many aspects of our daily life, from food preparation to maintaining health and cleaning. Proper knowledge of pH helps in agriculture, medicine, and household activities.
Now, answer the following:
a)Give two examples of acidic substances used in daily life and their typical pH values.
b)Give two examples of basic substances used in daily life and their typical pH values.
c)Explain why it is important to maintain the pH of soil in agriculture.
d)Why is the
The following organic compounds are given:
i)CH₃–CH₂–OH
ii)CH₃–COOH
iii)CH₃–CH₃
iv)CH₃–CHO
Answer the following:
a)Identify the type of functional group present in each carbon compound.
b)Write the IUPAC name of each compound.
c)State one physical property of alcohols and one chemical property of carboxylic acids.
OR
Read the diagram below carefully and answer the questions:
Adiagram shows three test tubes each containing an iron nail:
Test TubeA: Iron nail with air only (no water)
Test Tube B: Iron nail covered with boiled water and a layer of oil (no air)
Test Tube C: Iron nail exposed to both air and water. Only the nail in Test Tube C shows rust.
a)Based on the diagram, what are the necessary conditions for rusting of iron? Explain using observations from all three test tubes.
b)Write the chemical equation for the rusting of iron.
c)Name and explain a method to prevent rusting of iron in daily life.
d)State two harmful effects of rusting in real life situations.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
Section C (Physics)
Choose the incorrect statement regarding Ohm's law.
A. It is temperature independent
B. It is valid for constant temperature
C. It is valid for ohmic resistance
D. It defines the relationship between potential difference and current through the conductor. 1
If the radius of a current carrying circular loop is doubled keeping all other factors remain same, then the magnetic field at the centre of the loop becomes
A. Remains same
B. Twice the original
C. Half the original
D. Thrice the original 1
Question No. 32 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below:
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true, but R is false.
D. A is false, but R is true.
Assertion (A): Magnetic field lines do not intersect each other.
Reason (R): Magnetic field lines are imaginary lines, the tangent to which any point gives the direction of the field at that point.
Space is mostly vacuum, devoid of any medium.
(a)What colour does the sun appear to the astronauts on the International Space Station?
(b)Give reason for your answer to (a).
Attempt either optionAor B.
A. In what time is 400 joules of heat produced across a 16 Ω resistor at 80 V potential difference?
1
2
B. How much current will an electric bulb draw from 220 V source, if the resistance of the bulb is 1200 Ω? If in place of bulb, a heater of resistance 100 Ω is connected to the sources, calculate the current drawn by it. 35.
(i) Why is a fuse or a circuit breaker connected in series in a household circuit?
(ii) Why is the household wiring system arranged in parallel instead of in series?
(iii)How does an electric fuse prevent the electric circuit and the appliances from a possible damage due to short circuiting or overloading? 3 36.
(a)Find the absolute refractive index of a medium in which light travels with a speed of 14×108 m/s
(b)How do we distinguish a medium to be rarer or denser? Give two reasons. 3 37.
Study the diagram given below and answer the questions that follow it.
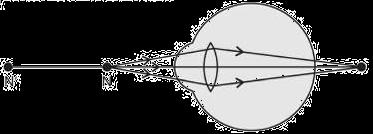
(a)Identify the defect of vision. Give reason for your answer.
(b)State two possible causes of this defect.
(c)How can we rectify this defect? Explain with a diagram. 3 38.
An object placed on a metre scale at 8 cm mark was focussed on a white screen placed at 92 cm mark, using a converging lens placed on the scale at 50 cm mark.
(a)Find the focal length of converging lens.
(b)Find the position of the image formed if the object is shifted towards the lens at a position of 29.0 cm
(c)State the nature of the image formed if the object is further shifted towards the lens. 4
A. (a) Define electric power. Express it in terms of potential difference �� and resistance ��.
(b)An electrical fuse is rated at 2A. What is meant by this statement?
(c)An electric iron of 1 kW is operated at 220 V. Find which of the following fuses that respectively rated at 1A,3A and 5Acan be used in it.
B. Study the following electric circuit in which the resistors are arranged in three arms ��,�� and ��

(a)Find the equivalent resistance of arm C.
(b)Calculate the equivalent resistance of the parallel combination of the arm B and C
(c)Determine the current that flows through the ammeter.
Marking Scheme
SectionA(Biology)
8. A.BothAand R are true, and R is the correct explanation ofA
9. C.Ais true, but R is false.
10. Peristalsis is the rhythmic, wave-like contraction and relaxation of muscles in the alimentary canal. It pushes food forward, mixes it with digestive juices, and aids in absorption of nutrients.
11. Reflex action
• It is an involuntary and immediate response
• It is controlled by the spinal cord. Walking
• It is a voluntary and learned action
• It is under the brain’s control. Thus, reflex is automatic, while walking is consciously controlled.
12. An ecosystem is a functional unit where living organisms interact with each other and their physical environment. Its two components are:
• Biotic - plants, animals, and microorganisms • Abiotic - air, water, soil, temperature, etc.
13. The pituitary gland, located at the base of the brain, secretes several important hormones. It regulates growth through growth hormone, controls metabolism and thyroid function via TSH, stimulates gonads with FSH and LH, and regulates water balance through ADH It is called the “master gland” because it controls the activity of other endocrine glands such as thyroid, adrenals, and gonads, thereby coordinating overall endocrine function.
14.
15.
Stem cutting:
• Apiece of stem with a node is planted to grow a new plant.
• Example: rose, hibiscus.
Grafting:
• Tissues of two plants are joined; the rootstock of one is fused with the scion of another.
• Example: mango, apple.
Stem cutting is simple and cheap; grafting combines desirable traits. 3
(a) Sons always inherit X-linked traits from their mother because of the way sex chromosomes are passed from parents to offspring.
Reason: Chromosomal Basis of Sex
• Males have XY chromosomes.
• Females have XX chromosomes.
Inheritance of Sex Chromosomes:
• Ason inherits the Y chromosome from his father (which determines male sex).
• He inherits the X chromosome from his mother since males must get their X from their mother (fathers do not pass an X chromosome to sons).
Implication for X-Linked Traits:
• Since X-linked traits (genes present on the X chromosome) are carried by the mother, any X-linked disorder or characteristic a male child inherits must come from her.
• The father's X chromosome is never passed to his son, so he cannot transmit X-linked traits to him.
OR
(b)Charles Darwin proposed natural selection as a mechanism of evolution.
• Within a species, variations occur naturally.
• Individuals with traits better adapted to the environment survive and reproduce.
• These favourable traits are inherited by the next generation.
• Over time, this leads to evolution of new species.
Example: Industrial melanism, peppered moths in England.
Dark-coloured moths survived industrial pollution by camouflaging on soot-darkened trees, while light-coloured ones were eaten. Post-pollution control, lighter moths again became common.
Thus, natural selection explains how advantageous traits spread and species adapt.
16. (a) The response of roots towards moisture is called positive hydrotropism 1
(b) Positive geotropism is responsible for roots growing downward.
(c) When both water and gravity influence roots, hydrotropism dominates over geotropism. This ensures roots grow towards water, even if it means bending away from the vertical path dictated by gravity.
(d) Hydrotropism is essential because it enables roots to locate water sources in the soil, ensuring absorption of water needed for photosynthesis, transport of minerals, and maintaining cell turgidity. Without it, plants may not survive in dry conditions.
(e) Plant responses are slow, directional, and regulated by plant hormones like auxins, without a nervous system. In contrast, animals show quick, nerve-based and hormonal responses, allowing immediate reaction to stimuli for survival.
Section B (Chemistry)
20. A.Soap
i)On dry litmus paper – No change is observed because the gas does not show acidic or basic properties in the absence of water.
ii)On moist litmus paper – The gas dissolves in water to form an acid, which turns blue litmus paper red.
(Gas
26. Redox Reaction :
Aredox reaction is a chemical reaction in which oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously.
Oxidation: Loss of electrons.
Reduction: Gain of electrons.
Equation involving Zinc
When zinc reacts with copper sulphate solution: Zn(s)+CuSO4(����)→ZnSO4(����)+Cu(s)
Zinc is oxidised: Zn → Zn²⁺ + 2e⁻
Copper is reduced: Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Cu
Iron (Fe) shows similar behaviour because it is also more reactive than copper and can displace it from its salt solution.
Fe(s)+CuSO4(����)→FeSO4(����)+Cu(s)
Silver cannot show this behaviour
Silver (Ag) is less reactive than copper and lies below copper in the reactivity series. Hence, it cannot displace copper from its salt solution and therefore does not take part in such redox reactions.
OR
a)CaCO₃ (s) → CaO (s) + CO₂ (g)
This is a decomposition reaction because a single compound, calcium carbonate, breaks down on heating into simpler products, calcium oxide and carbon dioxide.
b)Fe (s) + CuSO₄ (aq) → FeSO₄ (aq) + Cu (s)
This is a displacement reaction. Here, iron, being more reactive than copper, displaces copper from copper sulphate solution, forming iron sulphate and copper metal.
c)HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq) → NaCl (aq) + H₂O (l)
This is a neutralisation reaction, which is a type of double displacement reaction.An acid (HCl) reacts with a base (NaOH) to form salt (NaCl) and water, showing neutralisation of acidic and basic properties.
• The thin oxide layer on aluminium can be made thicker and more durable by passing an electric current through dilute sulphuric acid using the aluminium object as the anode. This process is known as anodisation.
28.
• During anodisation, oxygen gas is liberated at the anode, which combines with aluminium to form a thick, uniform, and strongly adherent layer ofAl₂O₃.
• This thicker oxide layer not only enhances the corrosion resistance of aluminium but also makes the surface suitable for dyeing and decorative purposes.
a. Sodium chloride (NaCl) is formed when hydrochloric acid (HCl) reacts with sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
HCl+NaOH→NaCl+H2O
b. Calcium sulphate (CaSO₄) contains the cation Ca²⁺ (Calcium ion) and the anion SO₄²⁻ (Sulphate ion).
c. Both sodium chloride (NaCl) and washing soda (Na₂CO₃·10H₂O) are salts of a strong base, sodium hydroxide (NaOH), combined with different acids.
NaCl is formed from NaOH and HCl.
Na₂CO₃ is formed from NaOH and H₂CO₃ (carbonic acid).
Thus, since they share the same cation (Na⁺), they belong to the same family of salts. OR
a)Acidic substances in daily life:
Lemon juice – pH ~2
Vinegar (acetic acid solution) – pH ~3
Acids are used in cooking, food preservation, and as cleaning agents.
b)Basic substances in daily life:
Soap solution – pH ~9–10
Baking soda (NaHCO₃) – pH ~8
Bases are used in cleaning, neutralising acids, and in baking.
c)Importance of pH in soil:
The pH of soil affects nutrient availability to plants.
Most crops grow well in slightly acidic to neutral soil (pH 6–7).If soil is too acidic or too basic, plants cannot absorb minerals efficiently, reducing crop yield.
d)pH of human blood:
Normal blood pH is slightly basic (~7.35–7.45).
This slightly basic pH is necessary for proper functioning of enzymes and metabolic processes.
a)Type of carbon compound:
i)CH₃–CH₂–OH →Alcohol
29.
ii)CH₃–COOH → Carboxylic acid
iii)CH₃–CH₃ →Alkane (Hydrocarbon)
iv)CH₃–CHO →Aldehyde
b)IUPAC Names:
i)CH₃–CH₂–OH → Ethanol
ii)CH₃–COOH → Ethanoic acid
iii)CH₃–CH₃ → Ethane
iv)CH₃–CHO → Ethanal
c)Physical and chemical properties:
• Alcohol (Ethanol): Miscible with water, has a characteristic sweet smell.
• Carboxylic acid (Ethanoic acid): Reacts with metals to produce hydrogen gas: 2CH3COOH+Zn→(CH3COO)2Zn+H2 ↑ OR
a)Necessary conditions for rusting of iron
From the diagram with three test tubes:
• Test tubeA(Iron + water + air): Iron gets rusted → Observation: reddish-brown layer of rust forms.
• Test tube B (Iron + water only / airtight): No rust forms → Observation: Iron remains shiny.
• Test tube C (Iron + air only / no water): No rust forms → Observation: Iron remains unchanged.
Conclusion: Rusting occurs only in the presence of both moisture (water) and oxygen (air).
b)Chemical equation for rusting of iron
The simplified reaction: 4Fe+3O2 +6H2O→4Fe(OH)3
On drying, Fe(OH)₃ dehydrates to form Fe₂O₃·xH₂O (rust).
c)Method to prevent rusting :
Painting / Oil coating / Galvanisation are common methods.
Example – Galvanisation: Iron is coated with a layer of zinc. Zinc acts as a sacrificial metal, protecting iron from rusting even if the coating is scratched.
d)Two harmful effects of rusting :
• Weakening of structures: Bridges, gates, and machinery lose strength due to rusting, increasing the risk of accidents.
• Economic loss: Rusted iron tools, pipes, and vehicles require frequent replacement, leading to higher maintenance costs.
Section C (Physics)
30. A. It is temperature independent 1
31. C. Half the original 1
32. A. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A. 1
(a)White.
33.
34.
(b)In space there’s no atmosphere, so there are no air molecules/dust to cause Rayleigh scattering. Sunlight reaches the eye unaltered across all wavelengths, so the combined light appears white (with a black sky as background).
A. Given: V=80V,R=16Ω,H=400J
Joule's law: H= V2 R t⇒t= HR V2
35.
So, time =1s.
B. Using Ohm's law I= V R :
• Bulb ( R=1200Ω ):
• Heater (R=100Ω) :
So, bulb draws ≈0.18A, heater draws 2.2A.
(i)Afuse or circuit breaker is always connected in series so that the entire current of the household circuit passes through it. In case of overloading or short-circuiting, the current exceeds the safe limit, the fuse wire melts (or the breaker trips), and the circuit is broken. This disconnects the supply at once, thereby protecting the entire wiring and appliances from damage.
(ii) In a parallel arrangement, each appliance gets the same voltage (220 V in India) as the main supply, which allows them to operate efficiently. If the wiring were in series, the voltage would be divided, and appliances would not function properly. Moreover, in parallel, each appliance can be switched on or off independently without affecting the operation of others. Thus, parallel wiring ensures both safety and convenience.
(iii)Afuse is a safety device made of a thin wire of low melting point, connected in series with the household circuit. When excessive current flows due to short-circuiting or overloading, the 1 1 1
36.
fuse wire gets heated up and melts because of Joule heating (I2R). This breaks the circuit, cutting off the supply, and prevents overheating, fire hazards, and damage to appliances.
(a)Absolute refractive index �� = �� �� = 30×108 14×108 ≈2.14 (unitless).
(b) Between two media, the one with the larger refractive index (or equivalently, the smaller speed of light) is called the optically denser medium, while the other is referred to as the optically rarer medium.
Distinguishing Features:
1. Speed of light: The speed of light is greater in a rarer medium than in a denser medium, i.e., ��rarer >��denser
2. Refraction of light: When a ray of light passes from a rarer medium into a denser medium, it bends towards the normal. Conversely, when light passes from a denser medium into a rarer medium, it bends away from the normal.
(a) The defect of vision is Hypermetropia (farsightedness).
Reason: In this defect, a person can see distant objects clearly but is unable to see nearby objects distinctly. This happens because the image of a nearby object is formed behind the retina instead of on it.
(b) State two possible causes of this defect.
1. The eyeball is too short from front to back, so light rays focus behind the retina.
2. The eye lens loses sufficient converging power (decreased curvature), reducing its ability to focus nearby objects.
1 2
1 1 1
37.
38.
(c) Hypermetropia is corrected by using a convex lens (converging lens) in spectacles.
• The convex lens causes the incoming light rays from a nearby object to converge before entering the eye, so that the eye lens can then focus the rays exactly on the retina, producing a clear image.

Object at 8 cm; lens at 50 cm; screen (real image) at 92 cm
(a)Focal length of the converging lens
Object distance (Cartesian): �� =8 50= 42cm
Image distance: �� =92 50=+42cm
Lens formula: 1 �� = 1 �� 1 ��
39.
(b)Image position when object is moved to 29 cm mark
New object distance: �� =29 50= 21cm= ��
With �� = ��, rays emerge parallel ⇒�� =∞
Image at infinity (no image on screen).
(c)If the object is shifted further towards the lens (i.e., |��|<�� )
The lens forms a virtual, erect, magnified image on the same side as the object, which cannot be obtained on a screen.
A. (a) Electric power is the rate at which electrical energy is consumed (or work is done) in a circuit. P=VI and I= V R⇒P=V(VR)=V2 R
(Also P=I2R, for reference.)
(b)Afuse rated at 2Ameans it allows current up to 2Asafely; if the current exceeds 2A, the fuse element melts and breaks the circuit to protect the appliance/wiring.
(c)For the electric iron: �� =1kW=1000W,�� =220V I= P V = 1000 220 ≈455A
Choose a fuse slightly higher than the operating current →5A is suitable.
1Aand 3Aare too low and would blow during normal use. OR
B. (a) Equivalent resistance of arm C
Arm C has resistors 10Ω,20Ω,30Ω in series
RC =10+20+30=60Ω
(b)Equivalent resistance of the parallel combination (B and C)
Arm B has 5Ω,10Ω,15Ω in series
RB =5+10+15=30Ω
Parallel of B and C:
RBC = RBRC RB +RC = 30×60 30+60 = 1800 90 =20Ω
(c)Current through the ammeter
ArmAhas 5Ω,15Ω,20Ω in series
RA =5+15+20=40Ω
Total circuit resistance:
Rtotal =RA +RBC =40+20=60Ω
With a 3 V source, I= V Rtotal = 3 60=0.05A(50mA)
So,
• RC =60Ω
• RBC =20Ω
• Ammeter reading =005A
MOST EXPECTED QUESTIONS
1. Gregor Mendel conducted experiments with pea plants to study the inheritance of traits. In one of his experiments, he cross-pollinated pure-bred tall (dominant) pea plants with pure-bred dwarf (recessive) pea plants to produce the F1 generation. He then selfpollinated the F1 generation to obtain the F2 generation.
(A)Describe the phenotype and genotype of the F1 generation.
(B)What phenotypic ratio did Mendel observe in the F2 generation? Attempt either subpart (C) or (D)
(C)How did Mendel ensure that his pea plants were true-breeding before starting his experiments?
OR
(D)In Mendel's pea plant experiments, how did he determine that traits are inherited independently?
2. How does the human digestive system process fat differently compared to proteins and carbohydrates?
3. Why is the process of photosynthesis crucial for life on Earth?
4. Discuss the role of hormones in human sexual reproduction.
5. Compare asexual and sexual reproduction.
6. Imagine a garden where different plants reproduce asexually. Describe the methods of asexual reproduction you would observe in this garden, and provide examples of how each method works.
7. Picture a scenario where a person experiences stress and an unexpected drop in blood sugar levels. Describe how the endocrine system responds to these situations and the role of key endocrine glands in managing these conditions.
8. Analyse the situations given below and list one consequence of each situation in an individual.
(i)During gametogenesis, the germ cells fail to undergo meiotic division.
(ii)A feeding mother has been diagnosed with HIV infection.
(iii)The pituitary gland is not secreting follicle stimulating hormone in a female.
(iv)The ovary of a women has been found to have numerous cyst-like structures.
(v)The fallopian tube of a women is blocked.
9. (i) Amit was chased by a dog. He developed fast heartbeat and goosebumps because of fear. Which hormone do you think is secreted in his body in response to his fear of dogs and name the organ responsible for secretion of this hormone.
(ii)Why does the growing shoot of a plant bend after being exposed to unidirectional light? Name the phytohormone that helps in breaking the dormancy of buds.
10. List the steps for the synthesis of glucose by the plants. What special feature is found in desert plants related to this process?
11. Explain the role of the following enzymes in the process of digestion of food in humans:
(i)Salivary amylase
(ii)Pepsin
(iii)Trypsin
(iv)Lipase
12. In a family, the characteristic of having attached earlobes is inherited in a recessive manner. Attached earlobes are a recessive trait, while free-hanging earlobes are dominant. Both parents in this family have free-hanging earlobes but are carriers of the gene for attached earlobes. They have two children, one of whom has attached earlobes.
Answer the following questions based on the above case study:
(A)What are the possible genotypes of the parents for the trait of earlobe attachment?
(B)What is the probability that the parents will have a child with attached earlobes?
Attempt either subpart (C) or (D)
(C)Create a Punnett square to illustrate the inheritance pattern for the earlobe trait. OR
(D)If one child has attached earlobes, what does this indicate about the child's genotype?
13. Describe the structure and function of the human heart, including double circulation.
14. Compare nervous and hormonal mechanism for control.
15. Draw a well labeled diagram of female reproductive system and mention its parts.
16. What are decomposers and what is the importance of them in the ecosystem?
17. Describe triples fusion in plants? Where does it occur? Draw a neat and clean well labeled diagram to support your answer.
18. Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary actions. Give one example of each.
19. When a solution of lead(II) nitrate (Pb(NO3)2) is mixed with a solution of potassium iodide (KI), a yellow precipitate is formed. Describe the chemical reaction taking place, including the balanced chemical equation. Identify the type of reaction and explain how you can confirm the formation of the precipitate.
20. (i) A student sets up an experiment to test the corrosion of iron nails in different environments. The nails are placed in three different conditions: (1) in air, (2) in air with a layer of oil, and (3) in a solution of saltwater. Describe the expected observations in each case and explain the underlying reasons for these observations.
(ii)Based on your observations, suggest a method to prevent the corrosion of iron nails in a high-humidity environment.
21. (i) A student performs electrolytic refining of copper metal. The setup includes a copper anode, a cathode, and an electrolyte solution of copper(II) sulphate (CuSO4). Describe the changes occurring at both the anode and cathode during the electrolytic refining process.
(ii)Explain how impurities in the copper anode affect the electrolytic refining process and the quality of the refined copper obtained at the cathode.
22. (i) Discuss the esterification reaction between ethanol and ethanoic acid.
(a)Write the balanced chemical equation for the esterification reaction.
(b)Name the ester formed and describe its smell.
(ii) (a) What catalyst is used in the esterification reaction, and why is it necessary?
(b)Write one use of esters.
23. (i) Explain why a solution of cane sugar does not conduct electricity, while a solution of common salt is a good conductor of electricity. Provide a detailed explanation based on the properties of the substances involved.
(ii)Show the formation of magnesium oxide (MgO) by the transfer of electrons, including the electron-dot diagrams.
24. An element ' �� ' with electronic configuration 2, 8, 7 combines separately with sulphate and carbonate anions.
(i)Identify the chemical formulae of the compounds formed.
(ii)Predict the nature of the bond formed by element ' Y ' and give a suitable reason.
(iii)Discuss the solubility and electrical conductivity of these compounds in water.
25. Explain the difference between balanced and unbalanced chemical equations with examples.
26. (i) Explain the concept of pH and its importance in everyday life.
(ii)How does the pH scale relate to the strength of acids and bases?
(iii)Why is it important to maintain a certain pH level in the soil for agriculture?
27. (i) Discuss the preparation of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) by the electrolysis of brine.
(ii)Write the balanced chemical equations for the reactions occurring at the anode and cathode.
(iii)Explain the industrial importance of the chlor-alkali process.
28. A metal X is observed to corrode rapidly when exposed to air and moisture, while another metal Y is highly resistant to corrosion under the same conditions.
(i)Based on this observation, which metal is likely to be more reactive?
(ii)Explain why metal Y is less prone to corrosion. Use the reactivity series to support your answer.
29. (i) Describe the process of electrolytic refining of copper. Include the role of the anode, cathode, and electrolyte in the refining process.
(ii)Write the chemical reactions occurring at both electrodes.
30. The given reaction shows one of the processes to extract metals like chromium and iron.
(A)Give a reason why the above reaction is known as a thermite reaction?
(B)Explain the thermite reaction with a balanced chemical equation. Mention one application of this reaction.
31. A greyish metal ' �� ', when exposed to moist air, forms a green compound ' �� '. When ' B ' is dissolved in hydrochloric acid, a colourless solution ' C ' and a gas ' �� ' are formed. ' �� ' is widely used in the galvanization process. Identify ' A ', ' B ', ' C ', and ' D '. Explain the process of galvanization with a well-labeled diagram.
32. An element ' X ' with electronic configuration 2,8,2 combines separately with nitrate and phosphate anions.
(i)Identify the chemical formulae of the compounds formed.
(ii)Predict the nature of the bond formed by element ' X ' and give a suitable reason.
(iii)Discuss the variation in electrical conductivity of these compounds in solid and molten states.
33. (i) In the given series of reactions, name the compounds X and Z.
(ii)Which type of reaction is X to Z?
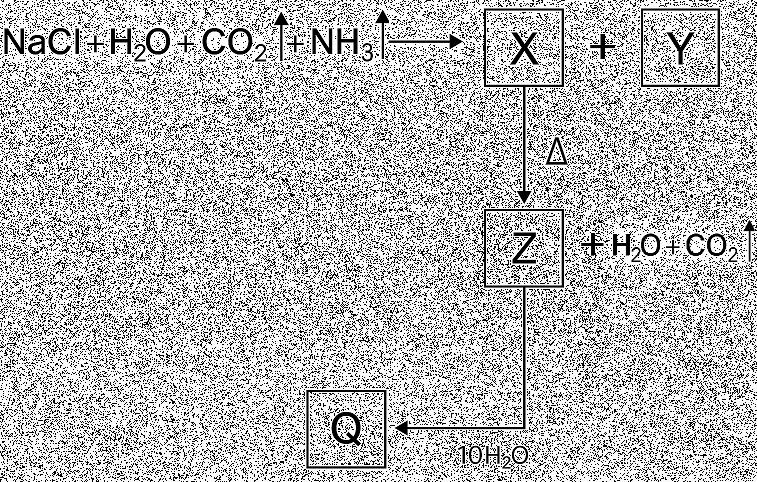
(iii)You are given 3 unknown solutions A,B, and C with pH values of 6,8 and 9.5 respectively. In which solution will the maximum number of hydronium ions be present?
(iv) Arrange the given samples in increasing order of H+ion concentration.
34. Two acids ‘X’ and ‘Y’ were kept in beakers. Acid ‘X’ undergoes partial dissociation in water, whereas acid ‘Y’ undergoes complete dissociation in water. (i) Of the two acids ‘X’ and ‘Y’. Which is weak acid, and which is strong acid? (ii) Give one example for weak acid and strong acid.
35. What would be the pH of an aqueous solution of sulphuric acid which is 5 × 10-5 mol litre-1 in concentration?
36. How does pH play an important role in everyday life? Explain.
37. (i) How is a voltmeter connected in the circuit to measure the potential difference between two points?
(ii)What is meant by the electric resistance of a conductor?
(iii)If a wire with length L and resistance R is stretched so that its length is doubled and its cross-sectional area is halved, how will its resistance change? Will its resistivity change?
38. (i) Two lamps, one rated at 100 watts and 220 volts and the other at 60 watts and 220 volts, are connected in parallel to an electrical main supply. What current is drawn from the line if the supply voltage is 220 volts?
(ii)Why is the tungsten used almost exclusively for the filament of electric lamps?
39. (i) What is electrical power and how is it calculated in an electric circuit?
(ii)What does it mean when we say the potential difference between points A and B in an electric field is 1 volt?
(iii)How much energy is given to each coulomb of charge passing through a 6 volt battery?
40. (i) Why doesn't the heater cord glow? What causes the heater element to glow but not the cord?
(ii)Determine the electrical current flowing through and the heat generated (in joules and calories) by an electric iron with a 500Ω resistance connected to a 250 V power supply over a 20 -second period.
41. A household uses the following electric appliances
(i)Refrigerator of rating 400 watt for 10 hours each day
(ii)Two electric fans of rating 80 watt each for 12 hours each day.
(iii)Six electric tubes of rating 18 watt each for 6 hours each day.
Calculate the electricity bill of the household for the month of June if the cost per unit of electric energy is Rs 3.00
42. How can three resistors with resistances of 2Ω,3Ω, and 6Ω be connected to achieve a total resistance of:
(a) 4Ω
(b) 1Ω ?
43. Name the defect of vision which a diverging lens can correct. Show by a ray diagram how the lens corrects the defect.
44. State what would happen to the direction of rotation of a motor if (i)the direction of electric current is reversed. (ii)the direction of the magnetic field is reversed. (iii)both the direction of electric current and magnetic field are reversed simultaneously.
45. (i) What is a solenoid?
(ii)Explain how the magnetic field inside a solenoid is utilised in making an electromagnet.
46.
The above figure shows the formation of an image by a lens shown by a thick line. Analyse the figure and answer the following questions.
(i)What is the type of lens used?
(ii)What is the nature of the image?
(iii)If the image is formed at a distance of 30 cm from the lens and the image is twice the size of the object, then where is the object placed?
47. Determine the following for the electrical circuit shown in the figure:
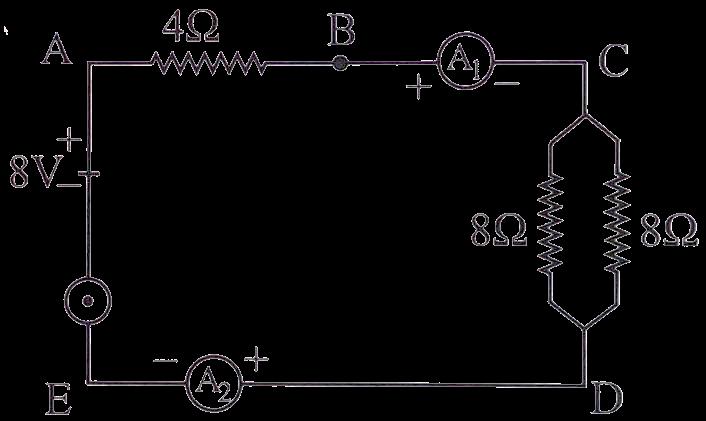
(i)The effective resistance of two 8 Ω combination of resistors
(ii)The current flowing through the 4Ω resistor.
(iii)The potential difference across the 4Ω resistor.
48. (i) State Snell’s law of refraction.
(ii)A ray of light enters from air into a glass slab (refractive index 1.5) such that the angle of incidence is 300. Find the angle of refraction in the glass slab.
49. (i) Why is the sky blue? Why does the Sun appear reddish at sunrise and sunset?
(ii)What is atmospheric refraction? State two phenomena in nature which occur due to atmospheric refraction
50. Two students connect identical resistors in two different ways: one makes a series circuit and the other makes a parallel circuit, both across the same battery.
(i)Which student’s circuit will have the higher total resistance?
(ii)In which case will the current drawn from the battery be larger? Why?
(iii)Which arrangement is preferred in household circuits and why?
SOLUTIONS
1. (A) Phenotype and Genotype of F1 Generation:
• Phenotype: All plants in the F1 generation were tall.
• Genotype: Each F1 plant had one allele for tallness (T) and one allele for dwarfness (t), making their genotype heterozygous (Tt ).
(B)Phenotypic Ratio in F2 Generation:
When Mendel self-pollinated the F1 generation, the F2 generation displayed a phenotypic ratio of approximately 3:1. This means three-fourths of the plants were tall and one-fourth were dwarf.
Student to attempt either option (C) or (D)
(C)Mendel ensured true-breeding by allowing the plants to self-pollinate for several generations, confirming that they consistently produced offspring with the same traits.
OR
(D)Mendel determined that traits are inherited independently by performing dihybrid crosses. He crossed plants with two different traits (e.g., round yellow seeds with wrinkled green seeds). The F2 generation showed a phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1, indicating that each trait segregated independently according to the law of independent assortment.
2. The primary difference is where and how digestion begins. Fat digestion starts with emulsification by bile in the small intestine and is broken down by lipases into fatty acids and monoglycerides, which are then reformed and enter the lymphatic system. Carbohydrate digestion begins in the mouth with salivary amylase and protein digestion begins in the stomach with proteases, both breaking down into smaller, directly absorbable units (monosaccharides and amino acids) that enter the blood.
Fat Digestion
Emulsification: Fats are large molecules and don't mix with water. Bile, produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder, breaks large fat globules into smaller droplets, a process called emulsification.
Enzymatic Action: Pancreatic lipases and other fat-digesting enzymes in the small intestine break down these smaller fat droplets into fatty acids and monoglycerides.
Absorption & Reassembly: These fatty acids and monoglycerides are absorbed by intestinal cells. Inside these cells, they are reassembled into triglycerides, then packaged into chylomicrons, a type of lipoprotein.
Lymphatic Transport: Unlike simple sugars and amino acids, chylomicrons are too large to enter the blood capillaries directly. Instead, they enter lacteals (lymphatic capillaries) in the small intestine and are transported through the lymphatic system before entering the bloodstream.
Protein Digestion
Initiation in the Stomach: Protein digestion begins in the stomach with pepsin (a protease) and hydrochloric acid, which begins to break down complex proteins.
Completion in the Small Intestine: In the small intestine, pancreatic proteases further break down proteins into smaller peptides and then into individual amino acids.
Direct Absorption into Blood: Amino acids are water-soluble and are directly absorbed into the bloodstream and transported to tissues.
Carbohydrate Digestion
Initiation in the Mouth: Carbohydrate digestion starts in the mouth with salivary amylase, which begins to break down complex carbohydrates.
Continuation in the Small Intestine: The process continues in the small intestine with pancreatic amylase.
Absorption into Blood: Carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars called monosaccharides. These are then directly absorbed into the bloodstream.
3. Photosynthesis produces glucose for energy and oxygen for respiration; it is the base of food chains and removes CO₂ from the atmosphere.
Overall equation:
6 CO₂ + 6 H₂O (light, chlorophyll)→ C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6 O₂
Main steps:
• Light-dependent reactions (thylakoid membranes): chlorophyll absorbs light → photolysis of H₂O → O₂ released + ATP & NADPH produced.
• Calvin cycle (light-independent) (stroma): ATP & NADPH used to fix CO₂ into carbohydrates (glucose).
• Desert plant special feature: CAM pathway stomata open at night to take CO₂ (stored as organic acids), stomata close in day to reduce water loss; CO₂ is released for Calvin cycle during day.
4. Hormones are crucial in regulating human sexual reproduction.
• In females, hormones such as estrogen and progesterone manage the menstrual cycle, ovulation, and preparation of the uterine lining for pregnancy.
• Estrogen aids in the development of secondary sexual characteristics like breasts, while progesterone stabilizes the endometrium to support a fertilized egg.
• In males, testosterone controls sperm production and the development of secondary sexual characteristics such as a deeper voice and facial hair.
• During pregnancy, hormones like human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and progesterone play critical roles. hCG maintains the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone to support the embryo and maintain the uterine environment.
• Proper hormonal balance is essential for reproductive health, ensuring that all processes from gamete production to pregnancy occur smoothly and effectively.
5. Asexual reproduction is the mode of reproduction in which a single parent produces offspring without gamete fusion. Offspring are genetically identical to the parent.
Sexual reproduction involves two parents and the fusion of male and female gametes to form a zygote. Offspring show variation.
Feature Asexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction
Number of parents Involves one parent Involves two parents
Gametes No gamete formation or fusion Fusion of male and female gametes
Cell division Only mitosis
Meiosis forms gametes, fertilisation restores diploid state
Genetic variation Offspring are genetically identical (clones) Offspring show variations
Examples Amoeba (binary fission), Hydra (budding), potato (vegetative propagation) Humans, animals, flowering plants
6. In this garden, you might observe several asexual reproduction methods:
• Vegetative Propagation: For instance, if you see a strawberry plant producing runners, these are horizontal stems that grow new plants at their tips, allowing the garden to expand quickly.
• Budding: Consider a hydra placed in a small pond nearby; it reproduces by forming small buds on its body. These buds eventually detach and grow into independent hydras.
• Binary Fission: In a pond near the garden, you might find bacteria dividing by binary fission. Here, a single bacterial cell splits into two identical cells, each becoming a new organism.
• Fragmentation: If you have a starfish in a small aquarium, you could see it regenerating from a lost arm, as new starfish can grow from the detached arm. These methods enable rapid and efficient reproduction in varying conditions.
7. In response to stress, the body's endocrine system activates to manage the situation:
• Adrenal Glands: They release adrenaline, which increases heart rate and energy availability, helping the person cope with immediate stress.
• Pancreas: If there's a drop in blood sugar levels, the pancreas releases glucagon, which signals the liver to release stored glucose into the bloodstream, restoring normal sugar levels.
• Additionally, the pituitary gland might release stress-related hormones, influencing other glands to support the body's response. These coordinated actions help stabilize
the body's internal environment and manage the effects of stress and blood sugar imbalances effectively.
8. (i) Germ cells failing to undergo meiotic division:
If germ cells do not complete meiosis, haploid gametes are not formed. This can lead to infertility since normal fertilisation requires haploid sperm and eggs. In rare cases, diploid gametes may be produced and take part in fertilisation, but the resulting zygote would often be polyploid, which usually causes early embryonic loss or severe developmental defects.
(ii)Feeding by an HIV-positive mother:
Breastfeeding carries the risk of transmitting HIV from mother to child through breast milk. This is why counselling and careful medical management are essential. With antiretroviral therapy (ART), the risk of transmission is greatly reduced, and doctors provide guidance on whether exclusive breastfeeding or alternatives are safer for both mother and child.
(iii)Pituitary gland not secreting FSH in a female:
FSH is necessary for the growth and maturation of ovarian follicles. Without it, follicle development does not occur, ovulation fails, and menstruation becomes irregular or may stop completely. Infertility results, and low estrogen levels due to lack of follicle activity can also cause additional symptoms such as hot flashes, mood changes, or bone density loss over time.
(iv)Ovary with numerous cyst-like structures:
This condition is often linked to Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), a hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It is characterised by irregular periods, lack of ovulation, and excess androgen levels. PCOS commonly leads to infertility and may also increase the risk of metabolic issues such as obesity and insulin resistance. Diagnosis and treatment require proper medical evaluation.
(v)Blocked fallopian tube:
If one or both fallopian tubes are blocked, the egg and sperm cannot meet, preventing natural conception. In some cases where the blockage is partial, fertilisation may occur
but the embryo could implant in the tube itself, leading to an ectopic pregnancy, which is a medical emergency.
9. (i) The hormone secreted in Amit's body is Adrenaline, which is responsible for the regulation of blood pressure. The hormone is secreted by the adrenal gland, located above the kidneys.
(ii)The movement of plants towards light is called phototropism, which is caused by the action of auxin hormone, synthesized in the meristematic tissue at the tip of the stem.
When sunlight is unidirectional, auxin gets accumulated towards the shady region of the shoot. This causes the cells to elongate and stem to bend towards light. The plant hormone that helps in breaking the dormancy of buds is ethylene.
10. Steps of synthesis of glucose in plants:
• Light absorption & water photolysis (thylakoid): light energy absorbed by chlorophyll splits H₂O → O₂ + electrons; ATP and NADPH produced.
• Conversion of light energy to chemical energy and splitting of water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen.
• Reduction of carbon dioxide into carbohydrates.
• Desert plants take up carbon dioxide at night and prepare an intermediate which is acted upon by the energy absorbed by the chlorophyll during the day.
11.
• Salivary amylase - breaks down starch which is a complex molecule to sugar.
• Pepsin - Helps to digest proteins in stomach.
• Trypsin - It helps in digesting proteins to amino acids.
• Lipase - Breaking down of emulsified fats to fatty acids and glycerol.
12. (A) Since attached earlobes are recessive (denote the gene for attached earlobes as e and for free-hanging earlobes as E), and the parents have free-hanging earlobes but are
carriers, their genotype must be Ee.
(B)To determine the probability, use the Punnett square. Each parent with the genotype 'Ee' can pass on either 'E' or 'e'.
Student to attempt either option (C) or (D)
(C)Here is the Punnett square:
• EE: Free-hanging earlobes (homozygous dominant)
• Ee: Free-hanging earlobes (heterozygous dominant)
• ee: Attached earlobes (homozygous recessive)
According to the Punnett square, the potential genotypes of the offspring are:
• 1/4EE1/4EE (free-hanging)
• 2/4Ee2/4Ee (free-hanging)
• 1/4 ee (attached)
Therefore, the probability of the offspring having attached earlobes is 25%.
OR
(D)The child with attached earlobes must have the genotype 'ee', inheriting the recessive allele from both parents.
13. The human heart is a strong, muscular organ with four chambers: two atria on the top and two ventricles at the bottom. Valves make sure blood flows in one direction only. It ensures oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood never mix.
• The right side of the heart carries blood low in oxygen to the lungs.
• The left side carries oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body.
• This system is called double circulation because blood passes through the heart twice in one complete round –
• Pulmonary circulation – right ventricle → lungs → left atrium.
• Systemic circulation – left ventricle → body → right atrium.
14. The nervous system provides rapid, short-term control using electrical impulses through neurons for quick actions like reflexes, while the hormonal system offers slower, prolonged control using chemical hormones transported via the bloodstream to regulate slower, long-term processes like metabolism and growth.
Feature Nervous control
Hormonal control
Nature Fast, uses electrical impulses Slow, uses chemical messengers (hormones)
Speed of action
Very rapid (milliseconds) Slow, long-lasting
Pathway Carried by neurons (nerves) Transported via blood
Effect Immediate but short-lived Delayed but prolonged
Examples
Reflex action, muscle contraction
Insulin regulating blood sugar, thyroxine controlling metabolism
15. It has ovaries, oviducts (fallopian tubes), uterus, cervix and vagina.
Ovaries make eggs and hormones.
Fallopian tubes are the place where egg and sperm meet (fertilisation).
Uterus is where the baby develops.
Cervix + vagina help in childbirth and entry of sperm.
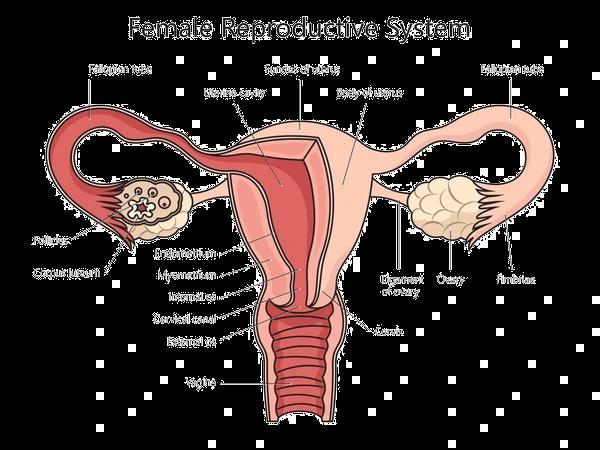
16. Decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi, are organisms that break down dead or decaying organic matter, like plants and animals, into simpler inorganic substances. They are crucial for ecosystems because they recycle essential nutrients back into the environment, providing them for producers (plants and algae) to use, and they act as Earth's "cleanup crew" by removing dead materials
Importance of Decomposers:
Nutrient Recycling: They are vital for the cycling of matter in an ecosystem, releasing the nutrients locked in dead organisms back into the soil and water.
Support for Producers: These recycled nutrients are then available for plants and algae (the producers) to absorb and use for their growth, enabling further primary production in the ecosystem.
Environmental Cleanup: Decomposers perform the essential function of breaking down dead organisms and waste, preventing them from piling up and keeping the environment clean.
Maintain Ecosystem Health: Without decomposers, essential nutrients would be locked away in dead matter, and the ecosystem would eventually run out of the resources needed to support new life, making them indispensable for ecological stability.
17. Triple fusion in plants is the process in which a male gamete nucleus fuses with two polar nuclei to form a primary endosperm nucleus (PEN), which is triploid (3n). This crucial event happens within the embryo sac, the female gametophyte of an angiosperm (flowering plant). The resulting endosperm provides essential nourishment and stored food for the developing embryo. In flowering plants, when pollen reaches the ovule:
• One male gamete fuses with the egg → forms a zygote (baby plant).
• The other male gamete fuses with two polar nuclei in the central cell → forms a triploid nucleus, which grows into endosperm (food for the baby plant).
• This process is called triple fusion, and it happens inside the embryo sac of the ovule.
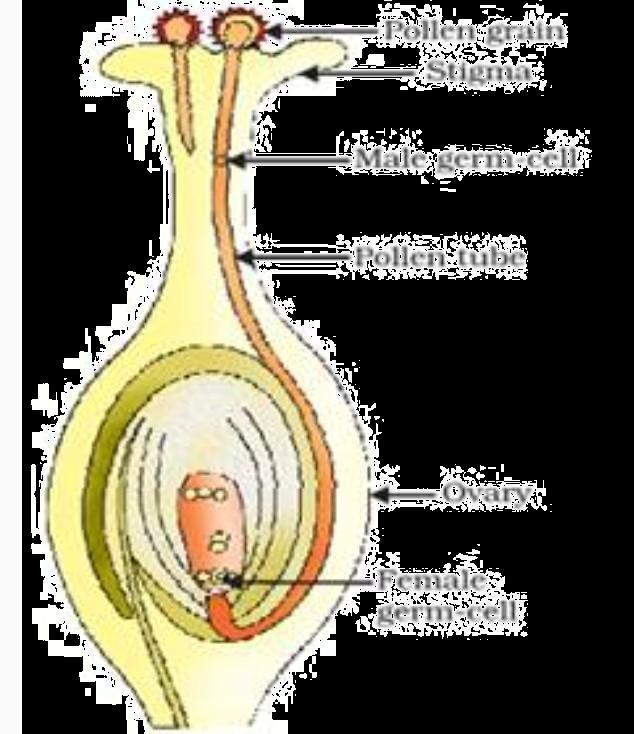
18. Voluntary actions are the movements that we carry out by our own choice. They are regulated by the somatic nervous system, a part of the peripheral nervous system. This system passes sensory and motor signals between the brain/spinal cord and the body.
Voluntary actions make use of skeletal muscles, which move only when we consciously command them. Examples: walking, speaking, writing, eating.
• Involuntary actions, on the other hand, are processes that happen without conscious control. They are governed by the autonomic nervous system, which manages the working of internal organs like the heart, lungs, stomach, and intestines. This system has two divisions:
• Sympathetic nervous system activates the body during stress or danger (“fight or flight” response).
• Parasympathetic nervous system calms the body after stress and manages routine functions (“rest and digest”).
• Examples of involuntary actions include heartbeat, breathing, digestion, and pupil contraction in bright light.
19. Chemical Reaction: When lead(II) nitrate reacts with potassium iodide, the following double displacement reaction occurs:
Pb(NO3)2(aq)+2KI(aq)→PbI2(s)+2KNO3(aq)
In this reaction, lead(II) iodide (PbI2) is formed as a yellow precipitate, and potassium nitrate ( KNO3 ) remains in solution.
Type of Reaction: This is a double displacement reaction, also known as a double replacement reaction, where two ionic compounds react in aqueous solution and exchange their ions to form a precipitate.
Confirmation of Precipitate: The formation of a yellow precipitate can be confirmed by filtering the mixture and observing the yellow solid collected on the filter paper.
20. (i) Iron Nail in Air: The iron nail exposed to air will undergo corrosion, resulting in the formation of rust (iron oxide). This occurs because iron reacts with oxygen and moisture in the air to form rust: 4Fe+3O2 +6H2O→4Fe(OH)3
Rust will appear as a reddish-brown coating on the nail.
• Iron Nail in Air with a Layer of Oil: The iron nail covered with a layer of oil will experience minimal or no corrosion. The oil acts as a protective layer, preventing moisture and oxygen from reaching the surface of the nail. This prevents the oxidation reaction necessary for rusting.
• Iron Nail in Saltwater: The iron nail placed in a saltwater solution will corrode more rapidly compared to the nail exposed to air. Saltwater accelerates corrosion because the salt (sodium chloride) increases the conductivity of the solution, facilitating the flow of electrons and enhancing the rate of the redox reaction involved in corrosion:
This results in faster formation of rust.
(ii)
• To prevent the corrosion of iron nails in a high-humidity environment, a practical method is to apply a protective coating such as paint or a layer of oil.
• This coating creates a barrier between the iron and the surrounding moisture, thus preventing contact with oxygen and water.
• Another effective method is galvanization, which involves coating the iron with a layer of zinc.
• Zinc acts as a sacrificial metal, corroding preferentially over the iron and thus protecting it from rusting.
21. (i) Anode Reaction: At the anode, copper metal undergoes oxidation. Copper atoms lose electrons to form copper ions, which dissolve into the electrolyte solution:
Cu(s)→Cu2+ +2e
This process gradually dissolves the copper anode.
Cathode Reaction: At the cathode, copper ions from the electrolyte are reduced and gain electrons to deposit as pure copper metal:
Cu2+ +2e →Cu(s)
The copper metal is deposited on the cathode, increasing its mass and purity.
(ii)Impurities in the copper anode affect the electrolytic refining process as follows:
• Formation of Sludge: Impurities, such as silver, gold, and other metals, do not dissolve into the electrolyte solution like copper. Instead, they are left behind as anode sludge. This sludge contains valuable metals that can be recovered later.
Quality of Refined Copper: The refined copper deposited at the cathode is generally of high purity because only copper ions are reduced and deposited. Impurities are excluded from the deposit and remain in the electrolyte or anode sludge. However, if impurities dissolve and are present in significant amounts, they might cause slight contamination in the refined copper. The high purity of the copper cathode is a key advantage of this refining process.
22. (i) (a) Esterification is a chemical reaction in which an alcohol reacts with a carboxylic acid to form an ester and water. When ethanol (an alcohol) reacts with ethanoic acid (a carboxylic acid).
• The following reaction occurs:
(b)The ester formed in this reaction is called ethyl ethanoate (commonly known as ethyl acetate). Ethyl ethanoate has a sweet, fruity smell, often reminiscent of pear drops or certain fruits. This pleasant aroma makes it a popular choice in perfumes and flavourings.
(ii)
(a)The catalyst used in the esterification reaction is concentrated sulphuric acid (H2SO4). The presence of concentrated sulphuric acid is necessary for several reasons:
Dehydrating agent: Sulphuric acid acts as a dehydrating agent, removing water formed during the reaction and thus shifting the equilibrium towards the formation of more ester.
Catalytic role: Sulphuric acid donates protons ( H+ions) which help to protonate the carbonyl oxygen of the carboxylic acid. This increases the electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon, facilitating the nucleophilic attack by the alcohol (ethanol), leading to the formation of the ester.
(b)Esters are widely used in the manufacture of fragrances and flavourings due to their pleasant smells. They are key ingredients in perfumes, cosmetics, and food flavourings.
23. (i) A solution of cane sugar (sucrose) does not conduct electricity because cane sugar is a covalent compound. When dissolved in water, cane sugar molecules disperse but do not break into ions. Since the presence of free-moving ions is essential for electrical conductivity, the absence of ions in a sugar solution means it cannot conduct electricity.
• On the other hand, common salt (sodium chloride) is an ionic compound. When dissolved in water, it dissociates into its constituent ions, sodium (Na+)and chloride ( Cl2 ). These ions are free to move within the solution, allowing it to conduct electricity. The presence of these free-moving charged particles (ions) is what enables a solution of common salt to be a good conductor of electricity.
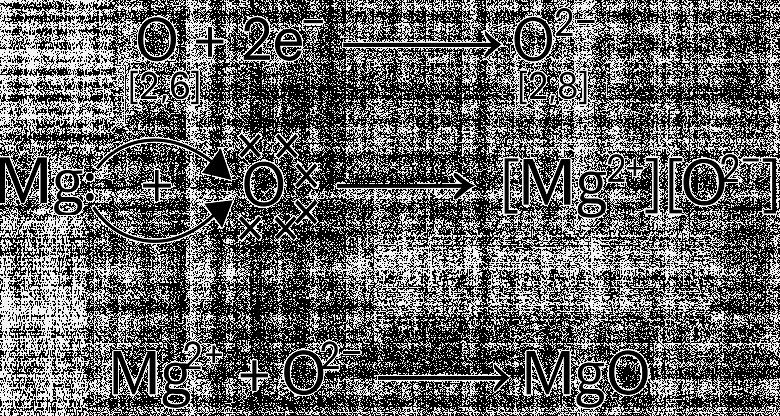
24. (i) Sulphate Anion ( ������ �� ): Element ' Y ' has an electronic configuration of 2,8,7, indicating it needs to gain one electron to achieve a stable configuration. Thus, it forms a Y ion. To balance the charge with sulphate ( SO4 2 ), two Y ions are needed. The chemical formula for the compound formed is Y2SO4
Carbonate Anion (CO3 2 ) : Similarly, for carbonate (CO3 2 ), two Y ions are needed to balance the charge. The chemical formula for the compound formed is Y2CO3.
(ii)The bonds formed by element ' Y ' with sulphate and carbonate anions are ionic. This is because element ' �� ' (with 7 valence electrons) tends to gain one electron to achieve a stable
octet configuration, forming a Y ion. When it combines with sulphate (SO4 2 ) and carbonate (CO3 2 ) anions, the electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions results in the formation of ionic compounds.
(iii)Solubility in Water: Ionic compounds generally dissolve in water because the polar water molecules can surround and stabilize the individual ions. Thus, Y2SO4 and Y2CO3 are expected to be soluble in water.
Electrical Conductivity:
• In Solid State: In the solid state, the ions in Y2SO4 and Y2CO3 are fixed in place and cannot move freely. Therefore, these compounds do not conduct electricity when solid.
• In Aqueous Solution: When dissolved in water, the ions in Y2CO4 and Y2CO3 are free to move within the solution, allowing them to conduct electricity. Thus, these compounds are good conductors of electricity in their aqueous states.
25. Difference Between Balanced and Unbalanced Chemical Equations:
• Balanced Chemical Equation: A balanced chemical equation has the same number of atoms of each element on both the reactant and product sides. This reflects the law of conservation of mass, which states that matter cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction.
Example: The balanced equation for the combustion of methane is:
CH4 +2O2 →CO2 +2H2O
Here, there are 1 carbon, 4 hydrogen, and 4 oxygen atoms on both sides of the equation.
• Unbalanced Chemical Equation: An unbalanced chemical equation does not have the same number of atoms of each element on both sides of the reaction. This means the law of conservation of mass is not reflected, and the equation needs to be balanced.
Example: An unbalanced equation for the combustion of methane is:
CH4 +O2 →CO2 +H2O
In this equation, there are 1 carbon and 4 hydrogen atoms on the reactant side, but the oxygen atoms are not balanced ( 2 on the left and 3 on the right).
To balance the unbalanced equation, you need to adjust the coefficients to ensure the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides.
26. (i) - The pH scale measures the acidity or alkalinity of a solution, ranging from 0 to 14. A pH of 7 is neutral, values less than 7 are acidic, and values greater than 7 are basic.
• The importance of pH in everyday life includes maintaining the correct pH levels in the body for proper enzyme function, determining the suitability of water for drinking, and ensuring the health of aquatic life.
(ii)The pH scale is logarithmic, meaning each whole number on the scale represents a tenfold difference in acidity or alkalinity. Strong acids have a pH close to 0 , while strong bases have a pH close to 14 . Weak acids and bases have pH values closer to 7 but are still below or above 7, respectively.
(iii)
• Maintaining the correct pH level in soil is crucial for agriculture because it affects the availability of nutrients to plants.
• Most plants thrive in soil with a pH between 6 and 7.5. If the soil is too acidic or too alkaline, it can lead to nutrient deficiencies or toxicities, adversely affecting plant growth and crop yield.
27. (i)
• Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is prepared by the electrolysis of brine (concentrated sodium chloride solution).
• The process, known as the chlor-alkali process, involves passing an electric current through the brine, resulting in the formation of NaOH , chlorine gas (Cl2), and hydrogen gas (H2)
(ii)The balanced chemical equations for the reactions at the electrodes are:
• At the anode (oxidation): 2Cl (aq)→Cl2(g)+2e
• At the cathode (reduction): 2H2O(��)+2e →H2(g)+2OH (aq)
Overall reaction: 2NaCl(aq)+2H2O(l)→H2(g)+Cl2(g)+2NaOH(aq)
(iii)The chlor-alkali process is industrially important because it produces three (1) essential chemicals: chlorine, hydrogen, and sodium hydroxide.
Chlorine is used in water purification, the production of PVC, and disinfectants. Hydrogen is used as a fuel and in the production of ammonia for fertilizers. Sodium hydroxide is widely used in the manufacture of paper, soaps, and detergents.
28. (i) Metal X (More Reactive): If Metal X is observed to corrode rapidly, it is likely positioned higher in the reactivity series. For instance, metals like magnesium, aluminum, and iron are higher in the reactivity series and prone to rusting or corrosion.
Metal Y (Less Reactive): Metal Y is likely positioned lower in the reactivity series. Metals like copper, silver, and platinum are lower in the reactivity series and show greater corrosion resistance.
Metal X is more reactive and corrodes quickly because it readily reacts with oxygen and moisture. Metal Y, being less reactive, does not corrode easily because it is lower in the reactivity series and forms a protective layer or does not react significantly with environmental elements.
(ii)Corrosion Resistance: Metal Y is highly resistant to corrosion because it is less reactive. According to the reactivity series, metals that are lower in the series do not easily lose electrons or oxidize. Therefore, metal Y forms a protective layer or oxide layer that prevents further corrosion.
Reactivity Series: For example, metals like gold and platinum are very low in the reactivity series and do not react easily with oxygen or moisture, which makes them highly resistant to corrosion. On the other hand, metals like sodium and potassium are very high in the reactivity series and corrode rapidly.
29. Electrolytic Refining of Copper:
The electrolytic refining of copper involves using an electrolytic cell to purify copper. The cell contains an anode made of impure copper, a cathode made of pure copper, and an electrolyte solution, typically copper sulphate (CuSO4) with sulfuric acid (H2SO4).
Role of Components:
Anode: The impure copper is placed as the anode. During electrolysis, copper from the anode dissolves into the electrolyte solution.
Cathode: The pure copper is deposited onto the cathode. The copper ions from the electrolyte are reduced and deposited as pure copper on the cathode.
Electrolyte: The electrolyte solution, which is usually copper sulphate, allows the movement of copper ions between the anode and cathode and facilitates electrochemical reactions.
Chemical Reactions: At the anode (oxidation reaction):
Cu(s)→Cu2+(aq)+2e
At the cathode (reduction reaction):
Cu2+(aq)+2e →Cu(s)
30. (A) The above reaction is known as a thermite reaction because it involves the reaction of a metal oxide (Chromium(III) oxide) with a more reactive metal (Aluminum) to produce molten metal (Chromium) and a large amount of heat. This reaction is highly exothermic and is used to weld metals and extract metals from their ores.
(B)The thermite reaction involves a metal oxide reacting with aluminum to produce molten metal and aluminum oxide, releasing a large amount of heat. The balanced chemical equation for the reaction of iron(III) oxide with aluminum is:
Fe2O3(s)+2Al(s)→2Fe(��)+Al2O3(s)+ Heat
This reaction is highly exothermic and is used in welding and metal extraction processes. One significant application is in railway track welding, where the intense heat generated by the reaction melts the metal, allowing for the seamless joining of railway tracks.
31. (A) ' A ' is zinc ( Zn ), ' B ' is zinc carbonate ( ZnCO3 ), ' C ' is zinc chloride ( ZnCl2 ), and ' D ' (0.5) is carbon dioxide (CO2). When zinc (A) is exposed to moist air, it reacts with carbon dioxide and water to form zinc carbonate (B):
Zn+H2O+CO2 →ZnCO3
• When zinc carbonate is dissolved in hydrochloric acid, zinc chloride (C) and carbon dioxide (D) are produced:
ZnCO3 +2HCl→ZnCl2 +CO2 +H2O
• Galvanisation is the process of coating iron or steel with a layer of zinc to prevent corrosion. This is done by dipping the metal in molten zinc. The zinc layer acts as a protective barrier and, even if scratched, it provides sacrificial protection by corroding itself instead of the underlying metal.
Galvanisation process
32. (B) Element ' X ' with an electronic configuration of 2,8,2 is likely to be magnesium (Mg) as it has two electrons in its outermost shell and tends to lose these electrons to achieve a stable noble gas configuration.
When magnesium combines with NO3
Mg2+ +2NO3 →Mg(NO3)2
Chemical formula: Mg(NO3)2
When magnesium combines with PO4 3
3Mg2+ +2PO4 3 →Mg3(PO4)2
Chemical formula: Mg3(PO4)2
The bond formed between magnesium and the anions (NO3and PO4 3 ) is ionic. Mg2+ ion has positive charge while nitrate (NO3)and phosphate (PO4 3 ) ions have negative charge, so
they form ionic bonds.
These ionic compounds exhibit different electrical conductivity in solid and molten states. In solid form, they do not conduct electricity due to the fixed positions of the ions. However, when molten or dissolved in water, these ions are free to move, allowing the compound to conduct electricity.
33. (i) X=NaHCO3;Z=Na2CO3
(ii)Decomposition reaction
(iii)Solution A
(iv)Increasing order or H+ions C<B<A
34. (i) Acid 'X' is a weak acid, and acid 'Y' is a strong acid.
Explanation: Weak acids undergo partial dissociation in water, releasing only a small fraction of their hydrogen ions (H+). Strong acids, on the other hand, completely dissociate in water, releasing a high concentration of hydrogen ions.
(ii)Example of weak acid and strong acid are:
Weak acid: Acetic acid (CH₃COOH)
Strong acid: Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
Explanation: Acetic acid undergoes partial dissociation in water, and hydrochloric acid completely dissociates, illustrating the characteristic behavior of weak and strong acids, respectively.
35. Sulfuric acid (H2 SO4) is a strong diprotic acid that ionizes completely in water, producing two moles of hydrogen ions (H+) per mole of sulfuric acid. The dissociation of sulfuric acid can be represented as:
H2 SO4 → 2H+ + (SO4)
Given that the concentration of sulfuric acid (H2SO4 ) is 5 ×10-5 mol/L, the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) will be twice this value, as two moles of hydrogen ions are produced per mole of sulfuric acid.[H+] = 2 × 5 × 10-5 =10-4 mol/L
The pH of a solution is calculated using the formula: pH= −log10 [H+]
Substitute the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) into the formula: pH = −log10 (10-4) = 4
Therefore, the pH of the aqueous solution of sulfuric acid with a concentration of 5×10-5 mol/L is 4.
36. pH plays an important role in everyday life-
Our body works within the pH range of 7.0 to 7.8. Living organisms can survive only in a narrow range of pH changes. Different body fluids have different pH values.
Eg: the pH of blood is ranging from 7.35 to 7.45. Any increase or decrease in this value leads to diseases. The ideal pH for blood is 7.4.
pH in our digestive system: It is interesting to note that our stomach produces hydrochloric acid. It helps with the digestion of food without harming the stomach. During indigestion, the stomach produces too much acid, and this causes pain and irritation. The pH of stomach fluid is approximately 2.0.
pH changes as the cause of tooth decay: pH of the saliva normally ranges between 6.5 to 7.5. The white enamel coating of our teeth is calcium phosphate, the hardest substance in our body. When the pH of the mouth saliva falls below 5.5, the enamel gets weathered. Toothpaste, which is basic, is used to clean the teeth that can neutralize the excess acid and prevent tooth decay.
The pH of soil: In agriculture, it is important. Citrus fruits require slightly alkaline soil, while rice requires acidic soil and sugarcane requires neutral soil.
The pH of rainwater: The pH is about 7, which means it is neutral and represents its high purity.
If the atmospheric air is polluted with oxide gases of sulphur and nitrogen, they get dissolved in the rainwater and make its pH less than 7. Thus, if the pH of rainwater is less than 7, then it is called acid rain. When acid rain flows into the rivers, it lowers the pH of the water. The survival of aquatic life in such rivers becomes difficult.
37. (i) A voltmeter is connected in parallel across the points in an electric circuit, where potential difference is to be measured.
(ii)Electric resistance (R) of a conductor is defined as the ratio of potential difference (or voltage) across the conductor to the current passing through the conductor i.e. R=V/I
(iii)We know R= ρL A - (i)
When new length =2L and A′ ( new area of cross section) =A/2
Dividing eqn. (ii) in eqn. (i), we get R′
=4
Thus, the resistance of a wire becomes 4 times its original resistance.
As the resistivity of a wire does not depend on its length and area of cross section show the sensitivity of the wire remains the same.
38. (i) Power of two lamp in parallel =100+60=160W
Supply voltage, V =220V
Current drawn, I = P V =160/220=0.727A
(ii)The tungsten is used almost exclusively for filament of an incandescent lamp because of the following reasons:
• It has a very high melting point (about 3642 K), so it can be heated to very high temperatures without melting. This allows it to glow and emit bright incandescent light.
• Tungsten can be drawn into very thin wires, which increases its resistance and makes it suitable for producing heat and light.
• It has sufficient mechanical strength even at high temperature, so the filament does not break or sag when glowing.
39. (i) Electrical power is the rate at which electrical energy is consumed or produced in a circuit.
It is calculated using the formula, P=VI, where V is voltage and I is the electric current.
(ii)Potential difference : Potential difference between two points A and B in an electric field is said to be 1 volt if one joule of work is done in moving a charge of 1 coulomb from point A to point B.
(iii)Given,
Amount of charge needs to be moved, (Q)=1C
Potential at the given point (V)=6V
Work done or energy given (W)= ?
Using relation, V=W/Q, and substituting the values, we have
40. (i) The heater cord does not glow because it has very low resistance compared to the heating element. Since the heat produced H∝I2R, with the same current, the cord (low R)produces negligible heat, while the heating element (high R) produces enough heat to reach a high temperature and glow.
(ii)Calculation of current
Potential difference (V)=250V
Current (I)= ?
Resistance (R)=500Ω
Applying Ohm's law, we have I= V R
Substituting the respective values in this formula, we have
I= 250V
500Ω = 1 2 =0.5 ampere
Current flowing in the circuit is 0.5 A .
Calculation of heat energy:
The heat energy in joule can be calculated using the formula
H=I2 ×R×t
I=0.5A,R=500Ω and t=20s
Substituting these values in the above formula, we have H=(05)2 ×500×20=2500J
We know, 1 calorie = 4.2 J
Heat energy in calories = 2500 42 =595.2 calories
41. Here, energy consumed by refrigerator in 30 days
=400×10×30=120000Wh=120kWh
Energy consumed by two electric fans in 30 days
=2×80×12×30=57600Wh=576kWh
Energy consumed by 6 electric tubes in 30 days
=6×18×6×30=19440Wh=19.44kWh
Total energy consumed in the month of June
=120+576+1944=19704kWh
Cost of
consumed =197.04× Rs. 3= Rs. 591.12
42. (i) First, both 3Ω and 6Ω resistances are joined in parallel and then the combination is joined in series with 2Ω resistance to get effective resistance of 4Ω.
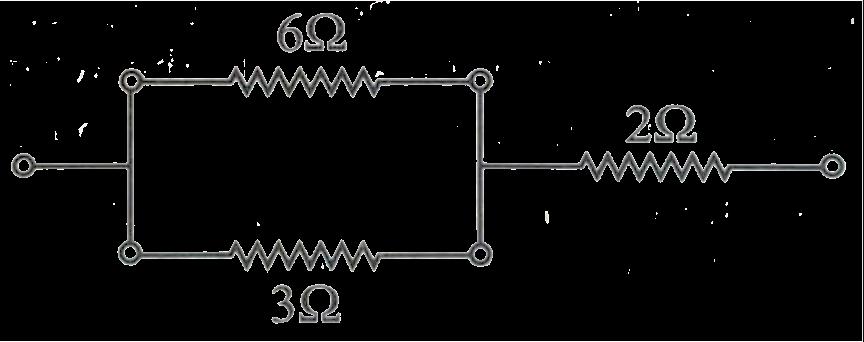
Rp = 3×6 3+6 = 18 9 =2Ω
Rp is connected in series with 2Ω resistance, so effective resistances is 2+2=4Ω (ii)To get an effective resistance of 1Ω, all the three resistors of 2Ω,3Ω and 6Ω are connected in parallel. As
1
Rp = 1 2 + 1 3 + 1 6 = 6 6 =1
⇒Rp=1Ω
43. The defect of vision which can be corrected by a diverging lens is myopia. A ray diagram for it is as shown.
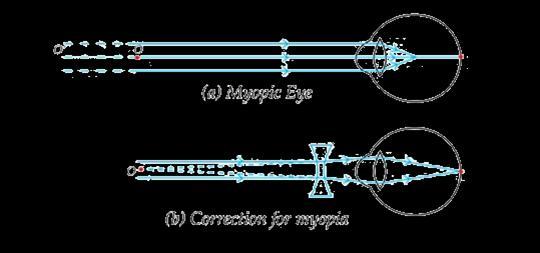
44. The direction of the force on the coil of the motor depends on the direction of the electric current in the coil and the direction of the magnetic field it is placed. Thus,
(i)When the direction of the electric current is reversed keeping the direction of the magnetic field constant, the direction of rotation of the motor would also be reversed.
(ii) When the direction of the magnetic field is reversed keeping the direction of the electric current constant, the rotation of the motor would also reverse.
(iii) When both the directions of the electric current and magnetic field are reversed simultaneously, the rotation of the motor remains the same or unchanged.
45. (i) A solenoid is a cylindrical coil of insulated wire wound closely in the form of a helix such that its length is greater than its diameter. When an electric current passes through the solenoid, it produces a magnetic field similar to that of a bar magnet.
(ii) The magnetic field inside a solenoid is strong and nearly uniform. If a soft iron rod is placed inside the solenoid and current is passed through it, the iron rod becomes strongly magnetised. This combination of the solenoid and the soft iron core forms an electromagnet, which is a temporary strong magnet used in devices like electric bells, cranes for lifting iron scrap, and electric relays.
46. (i) The lens is a convex lens.
(ii)The image is virtual.
(iii)Magnification for lens, m = v u = hi h0 =2
Hence �� = 15cm
The object distance u = −15 cm (negative sign indicates that the object is placed on the lefthand side of the lens, as per sign convention).
47. (i) As two resistors of 8Ω each are in parallel, so their effective resistance is given by 1/Rp=1/8+1/8=1/4 or Rp=4Ω
(ii)Net resistance of the circuit, R=4Ω+4Ω=8Ω
Current in the circuit, I=V/R=8/8=1A
Hence, current flowing through 4Ω resistor =1A
(iii)Potential difference across 4Ω resistor, V=IR =1×4=4V
48. (i) Snell's law states that the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant for a given pair of media.
sin i sin r =μ21
where i= angle of incidence, r= angle of refraction, and μ21 = refractive index of medium 2 with respect to medium 1.
(ii) μ= sin i sin r
1.5= sin 30∘
sin r 1.5= 0.5
sin r
sin r= 0.5 15 =0.333… r=sin 1 (0.333)≈19.5∘
So, the angle of refraction =19.5∘ (approx.)
49. (i) The scattering of light by air molecules and fine particles in the atmosphere is called Rayleigh scattering. Since shorter wavelengths (blue) are scattered more than longer wavelengths (red), the sky appears blue during the day. At sunrise and sunset, sunlight travels a longer path through the atmosphere, so most of the blue and violet light is scattered away and the Sun looks reddish.
(ii) The refraction of light by the Earth’s atmosphere due to variation in air density is called atmospheric refraction.
Two natural phenomena due to atmospheric refraction are:
1. Apparent early sunrise and delayed sunset: The Sun appears about 2 minutes early at sunrise and 2 minutes late at sunset due to atmospheric refraction.
2. Twinkling of stars: Light from stars undergoes continuous refraction in the atmosphere of varying density, making them appear to twinkle.
50. (i) The student who connects the resistors in series will have a higher total resistance, since resistances add up in series.
(ii)The parallel arrangement will draw a larger current from the battery because its equivalent resistance is smaller than that of the series arrangement.
(iii)The parallel arrangement is preferred in household circuits because each appliance gets the same voltage, and if one device fails, the others continue to work.
