SCIENCE WORKBOOK





This book is intended for educational purposes only. The information contained herein is provided on an “as-is” and “as-available” basis without any representations or warranties, express or implied. The authors (including any affiliated organizations) and publishers make no representations or warranties in relation to the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of the information contained in this book for any purpose.
The authors (including any affiliated organizations) and publishers of the book have made reasonable efforts to ensure the accuracy and completeness of the content and information contained in this book. However, the authors (including any affiliated organizations) and publishers make no warranties or representations regarding the accuracy, completeness, or suitability for any purpose of the information contained in this book, including without limitation, any implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose, and non-infringement. The authors (including any affiliated organizations) and publishers disclaim any liability or responsibility for any errors, omissions, or inaccuracies in the content or information provided in this book.
This book does not constitute legal, professional, or academic advice, and readers are encouraged to seek appropriate professional and academic advice before making any decisions based on the information contained in this book. The authors (including any affiliated organizations) and publishers disclaim any liability or responsibility for any decisions made based on the information provided in this book.
The authors (including any affiliated organizations) and publishers disclaim any and all liability, loss, or risk incurred as a consequence, directly or indirectly, of the use and/or application of any of the contents or information contained in this book. The inclusion of any references or links to external sources does not imply endorsement or validation by the authors (including any affiliated organizations) and publishers of the same.
All trademarks, service marks, trade names, and product names mentioned in this book are the property of their respective owners and are used for identification purposes only.
No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored, or transmitted in any form or by any means, including without limitation, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written permission of the authors (including any affiliated organizations) and publishers.
The authors (including any affiliated organizations) and publishers shall make commercially reasonable efforts to rectify any errors or omissions in the future editions of the book that may be brought to their notice from time to time.
Subject to Hyderabad jurisdiction only.
Copyright © 2024 Rankguru Technology Solutions Private Limited. All rights reserved.
ISBN 978-81-967708-0-8
First Edition
1. Tick ( ) the correct habitat for the following plants.
Name of Plant Image of Plant Terrestrial Aquatic





2. Fill in the blanks.
a. The place where organisms like plants and animals grow is called its ______. (home/habitat)
b. _______ plants are the ones that grow on land. (Terrestrial/Aquatic)
c. Deserts are typically hot and dry with _____ terrain. (rocky/sandy)
d. _______ have a moderate climate that is neither too cold nor too hot. (Hills/ Plains)
e. Rubber and coconut grow in places which are closer to the ____. (hills/ocean)
3. Mark (T) for the true and (F) for the false statements.
a. Aquatic plants are the ones that grow in water.
b. Deserts are areas that receive very high rainfall.
c. Marshes are wet places with clayey soil.
d. Hilly areas usually have hot weather.
e. Underwater plants stay entirely beneath the water.
4. Circle the odd one out.
a. Desert, Pond, Plain, Hills
b. Cactus, Date palm, Cedar, Acacia
c. Maple, Coconut, Rubber, Pepper
d. Duckweed, Teak, Water hyacinth, Water Lilly
e. Hydrilla, Lotus, Oak, Tape grass
1. Complete the following flowchart.
Adaptation in Plants
plants
a. What do you mean by habitat? What are the different types of habitats?
b. How do floating plants move on the water surface without sinking? Give two examples of floating plants.
a. Define the following.
i. Terrestrial plants: ii. Aquatic plants: iii. Evergreen trees:
b. What are breathing roots?
c. Write any three characteristics of trees in hilly areas.
d. What do you mean by plains? What kind of trees are found in plains?
e. Why are the conditions in the coastal regions not good for plants? Give two examples of plants that are found here.
1. Why have cacti, found in deserts, adapted to store water in their stems? How does this adaptation help them survive in their habitat?
2. Compare some of the characteristics of terrestrial plants and aquatic plants that help them to live in their respective habitats.
3. If a plant were to move from a marshy habitat to a desert habitat, what adjustments would it need to make to survive in the desert habitat?
4. Why do you think grasslands are good for certain types of farming activities?
5. In aquatic plants, how do fixed plants and underwater plants differ in their characteristics?
1. Draw a diagram of a leaf and label these four parts: leaf apex, leaf blade, midrib and side veins.
2. Fill in the blanks.
a. The pointy end of a leaf is called ____________ (apex/root).
b. Plants make their food through a process called ____________ (photosynthesis/transpiration).
c. The green pigment in leaves that helps in photosynthesis is called ____________ (chlorophyll/ stomata).
d. The tiny openings on the surface of leaves that allow gases to enter and exit are called ____________ (stomata/veins).
3. Identify and name the parts of the plants that we eat.









4. Mark the following statements as true or false.
a. Leaves have chlorophyll, which converts sunlight into energy for plants. (True/False)
b. Stomata are tiny openings in leaves that facilitate gas exchange. (True/False)
c. Plants do not produce any storage form of food. (True/False)
d. Insectivorous plants do not eat insects for their survival. (True/False)
e. Animals are dependent on plants. (True/False)

1. Rewrite the sentences correctly.
a. A leaf has a flat part known as the leaf apex.
b. Stomata in plants capture sunlight.
c. Plants make their food, which is a kind of sugar called starch.
d. Energy flows from the sun to animals and then to plants and human beings.
2. Complete the following image by filling the blanks with factors of photosynthesis given below.
3. Answer the following questions.
a. How do leaves make food for the plants?
b. How do plants use the food produced by their leaves, and what happens to any extra food?
c. List the different parts of food that we eat.
d. What are the three main functions of leaves?
e. What are insectivorous plants? Give some examples.
1. Answer the following questions.
a. How are plants, animals, and humans dependent on each other?
b. Why are leaves called the food factory of plants?
c. What will happen if there are no plants? How would it affect humans and animals?
d. Which type of leaves does cacti have, and how does it help them?
1. Fill in the blanks.
a. Animals that eat dead animals are called __________.
b. A porcupine has a sharp __________ on its body.
c. Animals that are at higher risk or becoming extinct are called ____________ animals.
2. Mark (T) for the true and (F) for the false statements.
a. The lightweight and hollow bones of the birds allow them to fly in the air.
b. Webbed feet are an adaptation that helps animals swim and move easily in water.
c. Animals that eat both plants and animals are called carnivores.
3. Name the following.
a. Animals who live on land.
b. Animals who live both on land and water.
c. Animals that live mostly on trees.
d. Animals that live in water.
e. Animals that can fly.
4. Match the following.
Eat a lot and store as fat in their bodies.
Can breathe with skin in water and lungs on land.
Store fat in their humps.
Huddle together to keep warm in the cold.
Have hard shells to hide inside.
1. Define the following in one line and give two examples for each.
a. Aestivation
b. Parasites
c. Omnivores
d. Carnivores
e. Herbivores
2. How do the following animals protect themselves from enemies? Write in 1-2 lines.
a.
3. Answer the following questions briefly.
a. How do camels adapt to live in deserts?
b. What is migration? Give an example of one animal that migrates.
c. Write the differences between aquatic and amphibian animals.
1. Think about a bird and a monkey. How are they different in the way they live and find food? How do their bodies help them survive?
2. Explain why some animals sleep a lot during winter. What do they do before sleep, and why is it helpful for them?
3. If polar bears in the Arctic region did not have their white fur, how would it affect their survival and behaviour?
4. Imagine that you are participating in a wildlife conservation campaign. What do you think can be done to protect the endangered species.
1. Fill in the blanks.
a. In mammals, the baby is fed with ___________ from its mother.
b. Reptiles, like snakes and turtles, usually lay ___________.
c. The protective covering of an egg is called the ___________.
d. The process of change from a young tadpole to an adult frog is called____________.
e. Kangaroos and koalas are examples of ___________, a type of mammal that carries its babies in a pouch.
2. Write T for true and F for false statements.
a. All animals that lay eggs are birds. _________________
b. Marsupials, like kangaroos, give birth to fully developed young ones.
c. Insects like grasshoppers undergo metamorphosis with four distinct stages.
d. Bats and whales are mammals. __________
e. All birds build nests to lay their eggs. __________
3. Match the adult animals with their babies.




1. Define.
a. Incubation:
b. Hatching:
c. Moulting:
2. Look at the life cycle of a frog and explain its stages.
3. Give two examples of each.
a. Animals that lay eggs:_____________ _____________
b. Animals that give birth to young ones:_____________ _____________
c. Animals that lay eggs in shallow pits near rivers: _____________ _____________
4. Answer the following questions.
a. What are the ways animals can reproduce?
b. How do birds take care of their eggs during incubation?
c. Name the stages of the life cycle of a butterfly.
d. Draw the diagram of a hen’s egg and label its parts. Write the function of each of its parts.
1. Read the statements and mark the correct answer in the word search.
a. Animal that teaches their babies to find food.
b. Animals that give birth to their young ones.
c. Insect eggs that hatch into larvae.
d. The butterfly’s eggs hatch into caterpillars.
e. Cockroaches eggs hatch and become young insects.
2. Answer the following questions.
a. Why do you think birds build nests to lay their eggs? What is the usefulness of nest in the process of reproduction?
b. Why do you think some animals, like fish, lay so many eggs? What is the benefit of this?
c. Human activities like throwing trash in the water affect animals that lay eggs there. What can we do to help them survive better?
LEVEL 1
1. Tick the food items that belong to the nutrient group, which is our main energy source.







2. Fill in the blanks.
a. __________ keeps our body warm.
b. __________ gives good vision.
c. __________ helps the body to fight diseases.
d. __________ helps to keep our bones and teeth strong.
e. __________ removes waste in the form of sweat.
f. __________ helps to remove undigested food from the body.
3. Mark (T) for true and (F) for false statements.
a. Fats give us less energy than carbohydrates.
b. Vitamins and minerals are protective nutrients.
c. We must eat a balanced diet to stay healthy.
d. Roughage can be digested by the body.
e. Regular exercise makes our muscles strong.
f. We should eat more cheese and less vegetables.
4. Match the following.
a. Orange, Lemon, Tomato
b. Salt, Oil, Vinegar
c. Dried Fruits, Red Chilli
d. Whole grains, Nuts, Olives
i. Preservatives
ii. Vitamin E
iii. Vitamin C
iv. Dehydration

1. Circle the odd one out and explain your reason in one line.
a. Wheat, Cheese, Potato, Rice
b. Calcium, Vitamin A, Potassium, Iron
c. Fish, Meat, Fruits, Eggs
d. Boiling, Canning, Cooking, Freezing
2. Give reasons for the following.
a. Milk is considered to be a complete food.
b. Proteins are called body-building nutrients.
c. Leftover food goes bad over a period of time.
3. Answer the following.
a. Name the five types of nutrients.
b. What is a balanced diet, and why is it important?
c. Name two benefits of exercise.
d. Mention three good cooking habits.
e. How does freezing help to preserve food?
f. Mention why the following are important in our diet.
Vitamins: _____________________________________________________________
Water: ________________________________________________________________
Fats: __________________________________________________________________
1. Answer the following.
a. Shikha loves to eat junk food. She always forgets to wash her hands before eating anything. One day, she fell ill and got tremendously weak. The doctor asked her to eat green vegetables. What do you think is the reason behind Shikha’s illness?
b. Look at the food pyramid below and answer the following questions.
i. Why do you think carbohydrates are at the base of the pyramid?
ii. Why are fats at the top of the pyramid?
iii. Imagine you are planning a meal. How would you use the food pyramid to decide the proportions of carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals, proteins, and fats in your meal?
c. Look at the given pictures and describe the food preservation method.


1. Fill in the blanks.
a. The _______ keeps the tooth in place. (crown/root)
b. Small food pieces in the mouth that make a sticky layer on the teeth is called ______. (plaque/flux)
c. Any food that isn’t digested goes to the ______ intestine. (small/large)
d. Protozoa are tiny, ____ -celled organisms. (one/multi)
e. We need a special tool called a ____ to see microbes. (telescope/microscope)
2. Mark (T) for the true and (F) for the false statements.
a. By the time we are 3 years old, we have a full set of 10 baby teeth.
b. We have 32 permanent teeth in total, 14 in the upper jaw and 18 in the lower jaw.
c. Next to the incisors on each side, we have canines.
d. From the stomach, the food goes into the large intestine.
e. Some bacteria are helpful, and some are harmful for our body.
3. Look at the given image of a tooth structure. Label the picture with the words from the box.
4. Choose the correct answer for the following questions from the options given.
a. What do we call the part of the teeth that we can see?
i. Gum ii. Root iii. Crown iv. Neck
b. What is the toughest substance in our body?
i. Pulp ii. Enamel iii. Dentine iv. Gum
c. Where do special juices mix with the food so that food can be absorbed by the body?
i. Small intestine ii. Stomach iii. Food pipe iv. Rectum
d. Undigested food from small intestine goes to which part of the digestive system?
i. Food pipe ii. Rectum iii. Stomach iv. Large intestine
e. Which of the following are the types of microbes?
i. Bacteria ii. Virus iii. Protozoa iv. All of them
1. Answer the following questions.
a. Why do baby teeth are known as temporary teeth?
b. Compare the four types of teeth on the basis of:
i. Number of each type of teeth
ii. Functions Incisors Canines Premolars Molars
c. What are the three layers of a tooth? Write down its function in one line.
i.
ii. iii.
d. What happens to the food in the following organs:
i. Mouth:
ii. Stomach:
iii. Small intestine:
iv. Large intestine:
e.. Write any four healthy eating habits.
i.
ii.
iii.
iv.
f. What are microbes? Write briefly about any two types of microbes.
g. Some microbes can be useful. Justify this statement.

1. Draw a neat and clean diagram of our digestive system and label its parts.
2. Imagine you are a dentist. How would you advise someone to take care of their teeth to prevent cavities? What tips would you give?
3. You saw your friend is eating food too fast without properly chewing it. What would you explain to him so that he starts chewing his food properly?
4. How can you make sure that you have a balanced and healthy diet?
1. Tick ( ) for the good habit and ( ) for bad habit. S. No. Image of the Habit Good Habit Bad Habit






2. Fill in the blanks.
a. ______ rules are essential rules that should be followed to prevent accidents and ensure your well-being. (Safety/Dance)
b. We should keep kitchen floors to prevent slipping. (wet/dry)
c. We should wear clothes when handling firecrackers. (synthetic/cotton)
d. We should use the _____ crossing while crossing the road. (zebra/horse)
e. The solution of baking soda acts as first aid in case of minor ____. (bites/burns)
3. Mark (T) for the true and (F) for the false statements.
a. We should not alert an adult if we detect the smell of gas in the kitchen.
b. We should not leave soap bars on bathroom floors to prevent slipping accidents.
c. We should not seek our parents’ permission before taking any medication.
d. We should throw objects around in the classroom to keep the campus clean.
e. If the dog looks scared or growls, we should move away slowly.
4. Fill in the blanks with the correct answer from the options given below.
a. The immediate help given to an injured person is called
i. First aid
iii. Third aid
b. Always walk on the .
i. Footpath
iii. Road divider
ii. Second aid
iv. Fourth aid
ii. Road
iv. Middle Road
c. Most of the accidents occur due to our .
i. Carelessness
iii. Awareness
d. To treat an insect bite, we use ________.
i. Calamine lotion
iii. Anti-tetanus
ii. Activeness
iv. Cleanliness
ii. Burnol
iv. Toothpaste
e. When a person faints, we should sprinkle .
i. Hot water
ii. Cold water
iii. Shampoo iv. Oil
1. Answer the following questions
a. What do you mean by safety rules? Write two kitchen safety rules.
b. Write any three general safety rules to be followed at home.
c. Write four safety rules that we should follow at school.
d. What are three specific rules you should always remember to stay safe?
e. What are some important safety rules that you should follow when you are in a public place, like a park?
f. List three important safety rules that you should follow when you are at the beach.
g. Write some safety rules we should follow when playing with a pet.
h. What is first aid? What points should we keep in mind while giving first aid?
i. Define first aid kit.
j. How should we provide first aid help for minor cuts and wounds?
k. What is the procedure for giving first aid for minor burns?
l. What are the first aid tips for insect bites?
1. Answer the following questions.
a. Compare the safety rules in the school and the safety rules on the road. What similarities and differences do you notice?
b. What is the importance of wearing a helmet while riding a bicycle?

c. Think what might happen if someone does not follow safety rules while playing with pets. How can it become a problem?

d. Based on what you know about safety rules at the beach, why is it important not to swim in some areas without lifeguards?
e. If you were in a park with your friends, and one of them suddenly faints, what immediate actions would you take to ensure their safety?

1. Match the following. Column
2. Tick the correct answer.
a. We all need clothes to ___________________.
Eat
Sleep
Wear
Drink
b. Woollen clothes keep our body ___________________.
i. Warm
ii. Dry
iii. Cool
iv. Airy
c. Children go to school in ___________________.
i. Formals
ii. Casuals
iii. Raincoat
iv. Uniform
d. There are _________ types of fibres.
i. One
ii. Two
iii. Three
iv. Four
e. Synthetic fibres are produced in ___________________.
i. Plants
ii. Animals
iii. Factories
iv. Insects
3. Label the clothing for each season.
Seasons: Summer, Winter, Monsoon/ Rainy


1. Unscramble the letters to find the name of a natural fibre.
a. E J T U______________________________________________________
b. E N N I L______________________________________________________
c. N T O O T C___________________________________________________
d. O L W O______________________________________________________
2. Answer in one word.
a. What do lawyers wear?
b. What is another word for human-made fibres?
c. What do factory workers wear?
d. What is the term for fibres obtained from natural sources?
3. State whether the following statement is True or False.
a. The clothes which are worn at home are called formal clothes.
b. Woollen and silk clothes are sturdy and cannot be easily damaged.
c. We should not iron and fold the clothes after they dry.
d. Nylon is made in factories.
4. Answer the following.
a. Write two ways to take care of your clothes.
b. List two examples each of synthetic and natural fibres.
c. Which type of clothes need gentle cleaning? How are these clothes cleaned?
1. Answer the following questions.
a. Why do we need clothes?
b. What is the difference between synthetic and natural fibres? Synthetic fibre
fibre
c. How do we decide what clothes to wear in different seasons?
d. Why do factory workers wear snug clothes?
2. Draw and colour different types of clothing on the basis of different seasons.
1 Tick ( ) the correct option.
a. Which of these is a natural satellite?
i. Sun
iii. Saturn
ii. Moon
iv. Earth
b. An imaginary line that runs through the centre of the Earth is:
i. Pole
iii. Equator
c. It causes a change in seasons on the Earth.
i. Rotation
iii. Hemisphere
d. Venus in the western sky is called _____.
i. Evening star
iii. Morning star
ii. Axis
iv. Orbit
ii. Spinning
iv. Revolution
ii. Red planet
iv. Gas planet
2. Mark (T) for true and (F) for false statements.
a. Orion is the name of a constellation.
b. Earth orbits in an elliptical path around the moon.
c. The sun is a white dwarf star.
d. Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars are called rocky or terrestrial planets.
e. All the planets except Venus in the solar system rotate in east to west direction.
3. Fill in the blanks with the correct answer.
a. Jupiter has a total of ____________ moons.
b. Earth completes one _____________ around the sun in 365¼ days.
c. Lithosphere, also known as ________, is the outermost layer of Earth.
d. The moon completes one revolution around the Earth in _____ days.
4. Give one word for the following.
a. A group of stars that together form a pattern: _________________
b. Celestial bodies that revolve around planets and have no light: _________________
c. The spinning of an object on its axis: _________________
d. The innermost part of the Earth that contains dense iron and nickel. _________________
e. Huge amounts of energy released by the Sun at times. _________________
5. Match the planets in column A with their characteristic in column B.
Column A Column B
a. Mars i. Evening star
b. Earth
c. Venus
d. Jupiter
e. Neptune
ii. Red planet
iii. Blue planet
iv. Farthest planet
v. Largest planet
6. Name the type of Earth’s movement shown in figures a and b.

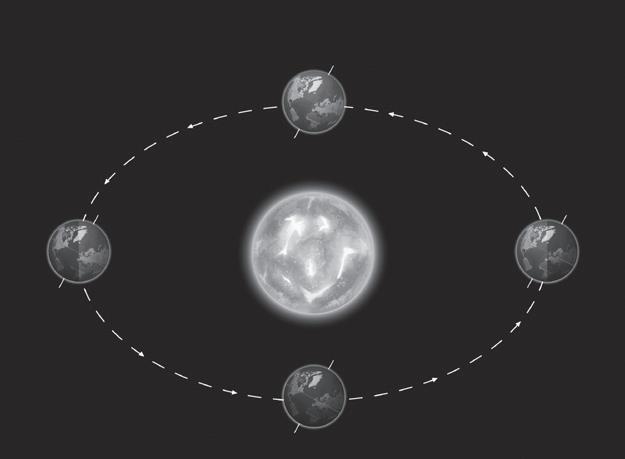
1. Look at the images below and answer the questions.

a. What is a constellation?
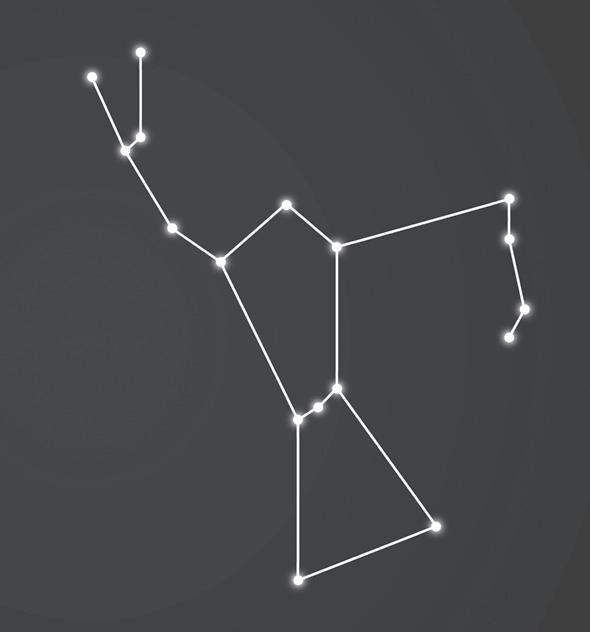
b. Identify the constellations shown in Figure a and b. i. ii.
c. How were constellations useful for sailors a long time back?
2. Answer the following questions.
a. What causes day and night?
b. What is the Equator? How has it divided the Earth?
c. How many layers is Earth made up of?
3. Give two examples for each of the following.
a. Rocky planets: _____________________________________________________
b. Gas planets:
c. Planets that have natural satellite:

I. Answer the following questions.
a. Describe what you would see and experience during one complete revolution of the moon around the Earth.

b. Why do the oceans on the Earth’s surface experience tides?
c. How is the tilt of the Earth’s axis responsible for the change in seasons?
d. How do you think the Earth’s rotation makes the Sun appear to move across the sky during the day? Draw a simple picture to illustrate this concept.

1. Match the following.
Column A
a. Land pollution
b. Water pollution
c. Air pollution
d. Soil erosion
e. Sources of water
Column B
i Respiratory and heart conditions
ii. Loss of fertile top layer of soil
iii. Rainfall and rivers
iv. Marine dumping
v. Fertilizers and pesticides
2. Fill in the blanks.
a. World Environment Day is observed on ____________ every year.
b. Our food, like fruits, vegetables, milk, eggs, and meat, comes from plants and ___________.
c. Combustion of fossil fuels cause _________ pollution.
d. Things that make air, land, or water unfit for us are called____________.
e. _________ can lead to the discolouration of historical monuments like the Taj Mahal.
f. Afforestation helps prevent _______ pollution.
3. Mark (T) for true and (F) for false statements.
a. Polluted water is fit for drinking.
b. Deforestation has a positive impact on water quality.
c. Growing trees helps in reducing air pollution.
d. The use of chemical fertilisers causes land pollution.
e. Plants do not help in cleaning the air.
f. We need clean air to stay healthy.
4. Look at the pictures and identify the causes of pollution.















1 Give reasons for the following statements.
a. We should care for our environment.
b. Human activities cause air pollution.
c. We should plant more trees.
2. Unscramble the words.
a. ITELRTGNI: __________________________
b. NOPLTUTLA: __________________________
c. LIOS ISOERON: __________________________
3. Answer the following questions.
a. What does the environment provide us?
b. Write any two causes and two effects of land pollution.
Causes:
Effects:
c. How does water pollution affect humans, animals and plants?
d. What is global warming, and how is it connected to air pollution?
e. What is the purpose of World Environment Day?
f. How can using public transportation help reduce air pollution?
1. Identify the types of pollution in the following image and write a few sentences on the ways to prevent them.













2. Choose any one kind of pollution and write about its effect on the environment and the people.
3. In your neighbourhood, you have noticed that a lot of plastic trash near and inside the river. People do not know it harms the river and the animals that live there.
a. What can you do to help with the plastic trash near the river?
b. Think about how you can tell people why it is important not to throw plastic in the river.
c. Suggest easy ways for everyone to throw away their trash.
4. In your school, the road nearby is busy, and the cars and buses make a lot of noise and smoke. Some friends are coughing more because of it. What can you and your friends do to improve the air near your school?
1. What difference in the weather conditions can you see in both pictures? Write in one sentence below.
2. Fill in the blanks.
a. ________ is the term for the specific combination of wind, rain, sunshine, and clouds at a particular place and time. (Weather/Sunlight)
b. The conditions of weather can change ________ and ________. (Monthly and yearly/Daily and hourly)
c. The sun is directly overhead at ________, making afternoons the hottest. (Noon/Evening)
d. About______of the Earth’s surface is covered with water. (Three-fourth/ Onefourth)
e. Rain cools down the earth, providing relief from ________. (Summer heat/ Winter)
f. Moving air is called ________. (Wind/Storm)
3. State whether ‘True’ or ‘False’.
a. Nights are the warmest when the sun is directly overhead.
b. Cooling of water vapours leads to the formation of clouds.
c. Air is a mixture of oxygen, iron, and carbon dioxide.. _______
d. The majority of water is found in rivers..
e. Storms can cause damage to trees and buildings.
4. Underline the odd one out.
a. Thunder, lightning, rain, snow.
b. Hot, cold, boiling, windy.
c. Evaporation, condensation, precipitation, photosynthesis.
d. Hail , dew, frost, foam.
e. Filtration, sedimentation, decantation, freezing.

1. Differentiate between land breeze and sea breeze in the table given below.
2. Complete the chart given below and briefly describe the process of the water cycle. Water Cycle
3. Define the following.
a. Weather:
b. Atmosphere:
4. Answer the following questions.
a. How are the following precipitations formed?
i. Dew:
ii. Hail:
iii. Frost:
iv. Snow:
b. List four ways to conserve water.
i.
ii. __________________________________________________________
iii. ___________________________________________________________
iv.
c. Name a chemical that is commonly used to treat water and remove germs.
d. Explain any one method of removing insoluble impurities.

1. Answer the following questions.
a. One day Aayu’s father noticed that the water coming from the tap was not clean. He collected the water in a vessel and started boiling it. Why do you think he did that? What are the other things he could have done to clean the water?
b. Which type of breeze, sea breeze or land breeze, would you prefer to fly your kite? Explain your choice.
c. How does the sun play a role in the water cycle?
d. Imagine you are walking to school early in the morning on a cold day. You cannot see anything clearly due to something that looks like white smoke. What is this white smoke-like thing actually is, and how is it formed?
1. Fill in the boxes with the correct states of matter.
2. Choose the correct options to fill in the blanks.
a. Matter exists in three forms: liquid, gas and ___________.
i. Water
ii. Solid
iii. Boiling
iv. Vapours
b. The process of conversion of vapours into liquid is called ________.
i. Evaporation
ii. Condensation
iii. Melting
iv. Freezing
c. Matter exists in _______ forms.
i. Three
ii. Two
iii. Four
iv. Five
d. The process of conversion of liquid into solid is called ___________.
i. Boiling
ii. Melting
iii. Freezing
iv. Burning
e. __________ has a definite shape.
i. Liquid
ii. Solid
iii. Gas
iv. Water
3. Colour the liquids blue.

4. State whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F).
a. The molecules join to form an atom.
b. Liquids do not have a fixed shape, but they have a fixed volume.
c. The molecules of solids are loosely packed.
d. The process of a liquid changing into vapours is called melting.
e. Solubility is the ability of a substance to dissolve in a liquid.
LEVEL 2
1. Arrange the following in increasing order of the space between their molecules.
a. Water, Sugar, Oxygen __________ __________ __________
b. Milk, Air, Table __________ __________ __________
c. Smoke, Paper, Oil __________ __________ __________
2. Look at the image given below and write the correct terms in the given space.
3. Fill in the blanks using the words given in the box.
Solubility, Matter, Molecules, Solids, Gas
a. _____________ has no definite shape and volume.
b. The molecules in _____________ are packed tightly.
c. The ability of any substance to dissolve in water is called _________.
d. Anything that occupies space and has mass is called _____________.
e. If we heat a liquid, the _____________ start to move around rapidly.
4. Write the changing states of matter.
1. Answer the following questions.
a. What is a solution? Explain solute and solvent.
b. Write two properties each of solid, liquid and gas.
c. Define the following terms.
i. Evaporation
ii. Condensation
iii. Sublimation
2. Write two examples each of melting and freezing.
LEVEL 1
1. Identify and write the forces involved in the following situations.
Gravitational Force
Mechanical Force
Muscular Force
Frictional Force
2. Tick the correct answer.
a. How many main types of simple machines exist?
i. 4
ii. 6
iii. 8
iv. 10
b. The ability to do work is called ___________________.
i. work
ii. force
iii. machines
iv. energy
c. Bottle opener is an example of a ___________________.
i. wheel and axle
ii. pulley
iii. lever
iv. wedge
d. The tools that help us do our work more easily and quickly are called ___________________.
i. machines
ii. force
iii. energy
iv. work
e. The Sun is a source of ___________________.
i. electrical energy
ii. solar energy
iii. magnetic energy
iv. heat energy
f. If a ball is thrown up, _____________ pulls it down.
i. friction
ii. force
iii. gravity
iv. energy
3. Match the following.
Column A
Lifting an object
Rubbing hands
Steering wheels
Knife
Falling objects
Hammers
Column B
Wheel and axle
Levers
Gravitational force
Muscular force
Wedge
Frictional force
1. Answer in one word.
a. Which energy is generated from moving water?
b. What type of force is applied to an unstretched rubber band?
c. What is the energy stored in electrical appliances called?
d. What is another name for ‘moving air’?
e. Write the type of energy stored in magnets.
2. State whether the following statements are true or false.
a. The energy which is caused by vibrations in or through an object is called heat energy.
b. Force changes the direction of moving objects.
c. A pulley is used to hold objects together securely.
d. Frictional force tries to stop things from moving.
e. A wedge is used to split things apart.
1. Answer the following questions.
a. What do you understand by machines?
b. What is an axle? Give two examples.
c. Name the main types of simple machines.
d. What is energy? Write different forms of energy.
e. What do you understand by work? Write two examples of work done in our daily life.
f. What is light energy? Name two sources of light energy.
g. Write two effects of force.
2. Draw the following.
a. Hammer
b. Screw
c. Knife
d. Bottle Opener