Switching from Thoracoscopic to Robotic Platform for Lobectomy: Report of Learning Curve and Outcome Eric C Lee1 and Paul C Lee1, 2, MD, MPH 1Donald
and Barbara Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell, 2Long Island Jewish Medical Center Department of Thoracic Surgery
Results
Introduction
Methods We performed a retrospective chart review on prospectively collected data on patients over the age of 18 with resectable primary NSCLC by VATS or RATS. 175 patients were examined from 2016 – 2018. Of the 175 patients, 8 underwent operative conversion from a VATS or RATS and were excluded from lymph node analysis.
A robotic approach offered improved lymph node clearance compared to VATS, even for an experienced VATS surgeon in treatment of patients with NSCLC. There was improved lymph node dissection as more robotic lobectomies were performed. Lymph node clearance was greater in the RATS group compared to the VATS group but no significant difference in upstaging rates were found.
Table 1. Morbidity, Mortality, and Postoperative Recovery
Future Directions Further studies are necessary to elucidate the potential benefits of robotic lobectomy regarding pathological upstaging and the cost involved in adoption of robotic lobectomy.
Table 2. Pathologic Nodal Sampling and Upstaging Rates
Total # of Lymph Nodes Sampled
Lung cancer leads as the highest rate of cancer deaths within the United States (1). Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) and robotic-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (RATS) have been shown to improve peri- and post-operative outcomes compared to traditional thoracotomy approaches for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) removal (2). We hypothesize that RATS procedures allow for increased lymph node removal and higher upstaging rates due to improved visualization and dexterity offered over VATS. Here, we report perioperative, operative, and pathological outcomes for a single surgeon switching from VATS to RATS to better understand differences between the two procedures.
Conclusions
60 50 40 30 20 10 0
References
0
50
100
150
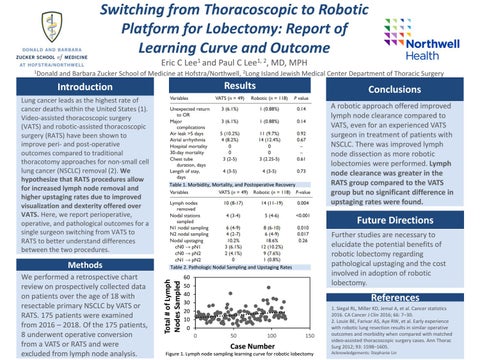
Case Number Figure 1. Lymph node sampling learning curve for robotic lobectomy
1. Siegal RL, Miller KD, Jemal A, et al. Cancer statistics 2016. CA Cancer J Clin 2016; 66: 7–30. 2. Louie BE, Farivar AS, Aye RW, et al. Early experience with robotic lung resection results in similar operative outcomes and morbidity when compared with matched video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery cases. Ann Thorac Surg 2012; 93: 1598–1605. Acknowledgements: Stephanie Lin