Selective removal of glycoprotein impurities from yeast-expressed recombinant proteins using MiMode PuraBead® CBX1
Efficient removal of glycoprotein contaminants from recombinant proteins expressed in yeast is essential to meet regulatory and product quality requirements. This study demonstrates the use of boronate chromatography to selectively capture glycosylated impurities through reversible cis-diol binding under alkaline conditions. Elution under mild acidic pH enables separation of glycoproteins while preserving the integrity of the target recombinant product. MiMode PuraBead® CBX1 provides a robust and scalable solution for impurity clearance in downstream purification workflows of yeast-derived biologics.
Yeast expression systems are widely used for recombinant protein production due to their high yields and eukaryotic processing capabilities. However, endogenous yeast glycoproteins frequently co-purify with the target molecule, posing challenges for product purity and consistency. Removal of these glycosylated impurities often requires additional polishing steps to ensure compliance with stringent regulatory standards.
Aminophenylboronate chromatography exploits reversible covalent interactions with cis-diol groups of glycan moieties, enabling targeted capture of glycoproteins under alkaline conditions. The resulting flexibility allows the resin to function as either a capture or impurity removal tool in recombinant protein workflows.
This application note details a workflow for the selective removal of glycoprotein contaminants from a recombinant protein expressed in yeast using MiMode PuraBead® CBX1, demonstrating high selectivity and process compatibility.
To evaluate the resin’s performance for impurity removal, a clarified yeast-derived recombinant protein feedstock was prepared and adjusted to alkaline pH conditions optimal for boronate-diol complexation. The purification process was carried out using a pre-packed MiMode PuraBead® CBX1 column operated at controlled flow rates to ensure consistent interaction between the target impurities and the resin. Following equilibration, the feedstock was loaded onto the column, where the high pH of the equilibration and wash buffers promoted the formation of reversible complexes between the boronate ligand and glycoprotein contaminants. Non-glycosylated recombinant protein remained unbound and was collected in the flow-through fractions for further processing.
After loading and washing, the column was eluted using 20 mM sodium acetate at pH 4.0 to recover the bound glycoproteins selectively. Clean-in-place with 0.5 M sodium hydroxide ensured resin sanitization and reusability.
The chromatogram (Figure 1) demonstrates clear separation of flow-through and elution peaks. UV absorbance at 280 nm confirmed significant binding of contaminants eluted in a sharp, discrete peak during acidic elution.
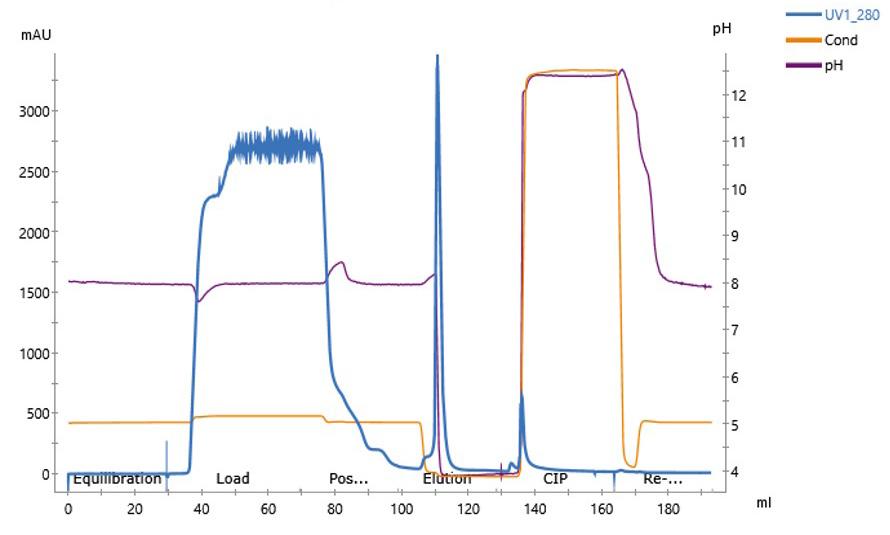
Figure 1: Chromatogram illustrating the capture and elution of glycoprotein impurities from yeast-expressed recombinant protein using MiMode PuraBead® CBX1. UV280 (blue), conductivity (orange), and pH (purple) profiles are shown.


Lane 1: Sample loaded onto MiMode PuraBead® CBX1
Lane 2: Flow-through pool
Lane 3: Sample loaded onto MiMode PuraBead® CBX1
Lane 4: Flow-through pool
Lane 5: Elution fraction
Figure 2: SDS-PAGE (left) and Western blot stained for glycoproteins (right). Lanes 1 and 3: Load samples; Lanes 2 and 4: Flow-through fractions showing reduced glycoprotein content; Lane 5: Eluted glycoproteins.
SDS-PAGE and glycoprotein-specific Western blot analysis of collected fractions (Figure 2) verified the effective removal of glycosylated impurities. The flow-through pool showed markedly reduced glycoprotein staining, while elution fractions were enriched in glycoprotein species.
The results demonstrate that MiMode PuraBead® CBX1 effectively captured glycoprotein impurities while allowing the non-glycosylated recombinant protein to pass through with minimal contamination, confirming its suitability as a selective polishing step.
Conclusion
This application note demonstrates the effective use of MiMode PuraBead® CBX1 for selective removal of glycoprotein impurities from recombinant proteins produced in yeast. The optimized workflow combines alkaline binding with mildly acidic elution to deliver high purity while preserving the integrity of non-glycosylated target molecules.
The performance and flexibility of this approach position MiMode PuraBead® CBX1 as a valuable tool for impurity clearance and process consistency in biomanufacturing of yeast-derived biologics.
For further information or assistance implementing MiMode PuraBead® CBX1 in your purification processes, please contact our technical support team or browse our resources.
Astrea Bioseparations is a world class provider of chromatography adsorbent and resin services. With over 30 years of chromatography manufacturing expertise, we deliver a unique and trusted service in close partnership with our clients. For more information, please don’t hesitate to reach out at sales@astrea-bio.com or visit astreabioseparations.com.
