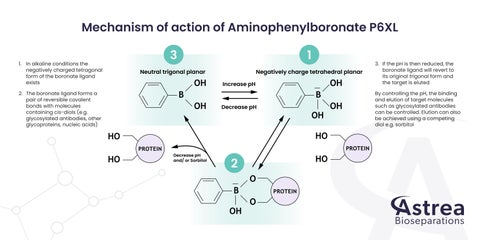
Mechanism of action of Aminophenylboronate P6XL 1. In alkaline conditions the negatively charged tetragonal form of the boronate ligand exists
3
1
Neutral trigonal planar
Negatively charge tetrahedral planar
OH B
2. The boronate ligand forms a pair of reversible covalent bonds with molecules containing cis-diols (e.g. glycosylated antibodies, other glycoproteins, nucleic acids)
OH
OH
Increase pH
B
Decrease pH
OH
PROTEIN
HO
By controlling the pH, the binding and elution of target molecules such as glycosylated antibodies can be controlled. Elution can also be achieved using a competing diol e.g. sorbitol
OH
HO
HO
PROTEIN Decrease pH and/ or Sorbitol
2
HO O
B OH
PROTEIN
O
3. If the pH is then reduced, the boronate ligand will revert to its original trigonal form and the target is eluted