
IsoClear® A XT
Product Code: FG00592


Product Code: FG00592
IsoClear® A XT is Astrea Bioseparations’ caustic-stable resin for the capture & removal of anti-A isoagglutinins.
Isoagglutinins are antibodies (IgM and IgG isotypes) which recognize and bind to type A or B blood group antigens. The presence of isoagglutinin antibodies in plasma-derived products (particularly plasma for transfusion and IVIG) can give rise to serious side effects, such as haemolysis, depending upon the type of isoagglutinin present (A or B) and the blood type of the recipient. Historically, individuals of AB blood type has been used as ‘Universal Plasma’ donors as their plasma does not contain isoagglutinin antibodies. However, AB is the rarest blood group possessed by a very low percentage of the population. As a result, AB plasma is in great demand and only available in limited quantities. In addition, regulatory authorities are demanding safer IVIG products with low levels of isoagglutinins, to minimize the risk of agglutination and haemolysis in patients receiving IVIG treatments.
Astrea Bioseparations Ltd and its affiliates have developed two affinity chromatography adsorbents (IsoClear® A XT & IsoClear® b XT) comprising of immobilized trisaccharide blood group antigens (A & B). These antigens are chemically synthesized and covalently attached to PuraBead® 6HF base matrix allowing for caustic stability. IsoClear® XT resins are highly selective for the removal of isoagglutinin antibodies, enabling cost-effective and efficient reduction of isoagglutinin titer for plasma and plasma-derived products.

LIGAND: Trisaccharide
FUNCTION: For the capture of anti-A isoagglutinins
RESIN APPEARENCE: White
MEAN PARTICLE SIZE (µm): 90 ± 10 µm
MATRIX:
® 6HF (Highly cross-linked 6% nearmonodisperse agarose)
RECOMMENDED PACKING CONDITIONS: 850 cm/h
RECOMMENDED PACKING SOLUTION: Equilibration buffer
RECOMMENDED OPERATIONAL FLOW RATES: Up to 600 cm/h
OPERATING PH: pH 3.0 to pH 14.0
CHEMICAL STABILITY: All commonly used aqueous buffers and co-solvents
CLEANING/SANITIZATION: 0.5 M NaOH
STERILIZATION:
Autoclavable in 0.1 M NaCl solution at 121°C for 30 minutes
STORAGE: 2–30°C, 20% ethanol

IsoClear® A XT resin is supplied in a preservative containing 20% ethanol. Before commencing the column pack, consult the relevant manufacturer’s instructions for the selected column hardware.
The method below describes the packing of Astrea Bioseparations’ IsoClear® A XT into axial 1 cm, diameter columns with a 1.6 cm bed height.
1. Allow all materials to equilibrate to the temperature at which the chromatography process is to be performed.
2. Determine the % slurry of the resin by agitating the resin in the bottle to form a complete slurry. Pour out ~ 15 mL into an appropriate measuring cylinder or 1 cm diameter column. Leave to settle for a minimum of 3 hours. Calculate the % slurry:
Slurry % calculation:
3. Calculate the volume of slurry you require, a compression factor (CF) of 1.19 (1.15–1.23) is recommended:
Column volume (CV) calculation:
Where ‘r’ is the radius of the column hardware in cm and ‘BH’ is the target bed height in cm.
Slurry volume (SV) calculation:
Where ‘CV’ is the column volume calculated above, ‘CF’ is the compression factor, and ‘slurry percentage’ is the slurry as calculated above.
4. Measure out the calculated volume of slurry required.

5. Assemble the column and remove air from the dead spaces by flushing the end piece and adaptor with storage solution then close the column outlet.
6. Carefully pour the resin slurry into the column in a single continuous step. Pouring the slurry down the side of the column helps to prevent air becoming trapped within the resin bed. Use a packing reservoir if required
7. Allow the resin to settle, leaving a dead volume of packing solution above the resin bed. Top column up with packing solution (equilibration buffer)
8. Attach the top adaptor to the workstation and flush with packing solution. Fill the column with packing solution (equilibration buffer). Loosen the attachment of the top adaptor to the workstation to allow liquid to flow out and carefully add the top adaptor to the top of the column. Avoiding the introduction of air bubbles, adjust the adaptor to the top of the bed (note bed will drop as you insert the adaptor), tighten the connection to the workstation and tighten the adaptor into place.
9. Open the column outlet and apply a flow rate of 850 cm/h To avoid bed compression on operation, ensure that the packing pressure is higher than the operational pressure at the process step with the highest pre-column pressure Aim for an operational flow rate/pressure of up to 75% of the column packing flow rate/pressure.
10. After ≥8 CV, stop the flow and close the column outlet.
11. Mark a bed height of 1.6 cm on the column. Lower the top adaptor by loosening the top adaptor seal (the top adaptor must allow free flow from the workstation either by loosening the top adaptor connection or, if present, switching the top valve to waste) and drop the adaptor to the 1.6 cm bed height line.
Note: Once the flow is paused, the bed may relax and rise.
12. Re-tighten the top adaptor (if loosened) and attach back to the workstation (or switch valve back in-line). Open the bottom outlet and apply the packing flow to the column again for at least 8 CV. If a space is formed between the top of the bed and the adaptor mark where the bed compressed to, repeat the steps above dropping the adaptor to the marked position. If no space forms, the column is packed and ready to use.

1. Attach the column packed according to the ‘Column Packing’ section above to a workstation primed with a mobile phase solution of equilibration buffer.
2. Commence flow of mobile phase at 100 cm/h for at least 1 CV, ensuring that the column is equilibrated and a baseline obtained.
3. Inject 2% CV of a 1 M NaCl solution.
4. Continue flow until a conductivity peak is observed, and the trace has returned to baseline (≥1.5 CV).
Determine the asymmetry (As) factor as follows:
Where ‘BC’ is the peak tail width at 10% peak height and ‘CA’ is the peak front width at 10% peak height.
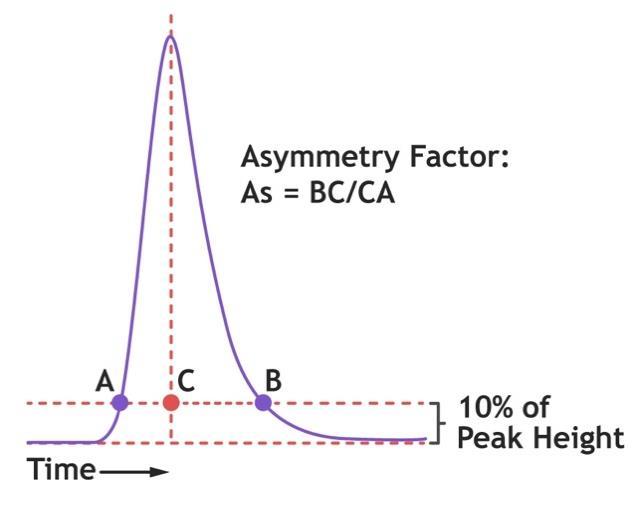
A typical acceptable range for asymmetry factor for packed cation exchange adsorbents is between 0.8 to 1.8, but the required range should be qualified to each process/application.
As >1.8 (tailing) indicates that the column is underpacked For asymmetry values significantly above 1.8, aim for a higher compression factor.
As <0.8 (fronting) indicates that the column is overpacked. For asymmetry values significantly below 0.8, target a lower compression factor

Determine the HETP and N values as follows:
Theoretical plates (N) value is a measure of the peak broadening and can be used to determine the column efficiency. The higher the plates value, the less dispersion and the more efficient peaks and separation. The plates (N) value is calculated by:
Where ‘VR’ is the retention volume and ‘Wh ’ is the peak width at half of the peak height.
HETP (H) is used to determine the column efficiency and corresponds to the distance between each plate. HETP is calculated by:
Where ‘L’ is the length of the column (bed height) and ‘N’ is the number of theoretical plates (as calculated above).
Plate count range required for the column should be verified for each process/application. The typical theoretical plates per meter count for an acceptable pack is ≥2000 N/m.
HETP trouble shooting
If the calculated plates/meter value is significantly below 2000 N/m, repack the column and repeat column efficiency testing.
The lower the HETP value (the higher the plate number), the more efficient the column is. When measured over time, the HETP can be used to monitor the column performance. If the HETP value increases, this indicates a reduction in the column performance and the column should be repacked

Note: The following recommendations are not prescriptive A thorough investigation of these parameters at small-scale should be conducted to reveal the level of flexibility that can be tolerated with the chromatography resin, buffer, and protein combination selected.
IsoClear® A XT column kits are also available for screening experiments.
The following method is recommended (as a starting point) using a 1–2 mL column volume in a 0.5 or 1 cm diameter column. An initial flow rate to give a 1-minute residence time for the column chromatography steps should be used. Subsequent increases/decreases in the flow rate can be investigated to improve binding capacity or decrease processing times. Aim for an operational flow rate of up to 75% of the column packing flow rate.
Filter all buffers and feedstock through an appropriate filter, prior to running the column.
Equilibrate the column with up to 10 CV of equilibration buffer. The equilibration buffer should match the pH and conductivity of the feedstock or Sodium acetate pH 4.5-5.5 with the feedstock adjusted to match the buffer.
Note: NaCl may interfere with binding of isoagglutinins, so its presence should be fully investigated. In the first instance, if NaCl is required, a maximum of 150 mM NaCl is recommended. If low binding of isoagglutinins is observed, NaCl concentration should be reduced further.
Apply the clarified/filtered protein feedstock onto the equilibrated column. Recommended residence time is 1 minute.
Remove any non-bound material from the column with up to 10 CV of 50–100 mM NaCl, or until the UV trace returns to baseline.
It is recommended to strip the column prior to cleaning the column. This can be done with 1 M acetic acid.
If the isoagglutinins need to be eluted under milder conditions, 50 mM glycine pH 3 or equilibration buffer with 1 M NaCl can be used.
After each use, the resin should be regenerated with at least 2 CV of a high-salt buffer (1.0 M NaCl).

A clean-in-place (CIP) step is recommended to avoid buildup of process impurities over multiple cycles. This maintains column efficiency, capacity, and separation performance.
If a CIP is required, use ≥5 CV of 0.5 NaOH. Flow rate should be 100 cm/h and a contact time of >30 minutes should be used. No less than 5 column volumes are recommended.
When a more intensive cleaning cycle is required, the following are recommended:
• If lipid fouling is a major issue, use 30%–40% isopropanol in combination with NaOH
• If iron and calcium fouling is an issue, use 50% citric acid.
• If aggregated/precipitated proteins are an issue, or a crude lysate feedstock has been loaded onto the column, wash the resin with either 8 M urea or 6 M Guanidine-HCl.
• Acid base cycling, 1 M NaOH, 1 M Acetic acid, 1 M NaOH, 1 M Acetic acid.
Re-equilibrate column with up to 10 CV of equilibration buffer (to remove sodium hydroxide or neutralize the resin), and check that the pH and conductivity of the column eluate is equal to that of the buffer entering the column before storage or re-use.
If the column is to be stored for future use, place the column into the storage solution (20% ethanol is recommended) and store at 2–30°C.
Optimization may be required to gain the required performance. Conductivity of the equilibration buffer, load and post-load wash solution to reduce the binding of IgG can be investigated, as can the pH of the equilibration buffer and load. If a crude feedstock is used, it is likely that a more stringent strip and CIP regime will be required A more stringent CIP can be to increase the contact time of the 0.5 M NaOH, or to add in an additional step as mentioned above. A recommended starting point would be with 8 M urea or 6 M GuanidineHCl. The required level of cleaning should be qualified against the processes feedstock to ensure that it is fully cleaned after each cycle.

FG00592 -00100 IsoClear® A XT
FG00592 -00500 IsoClear® A XT
FG00592 -01000 IsoClear® A XT
Astrea Bioseparations also supplies larger volumes of bulk resins for cGMP development and manufacturing-scale processes.
Astrea Bioseparations can also provide column packing services. For more information on this, or any other matters please do not hesitate to contact us at sales@astrea-bio.com

