






Automated Flexible Conveyor has introduced a conveyor discharge adapter as an option on its AFC SPIRALFEEDER flexible screw conveyors. The new discharge adapter features a proprietary design with a tri-clover sanitary fitting that maintains the position and stability of the tube enclosing the rotating screw conveyor while eliminating a traditional lip seal with its potential to capture and accumulate material. The conveyor discharge head is suitable for food, nutrition, pharmaceutical, and other sanitary processes.
Automated Flexible Conveyor
www.AFCSpiralFeeder.com

The SENTRY io Controller is a safety monitoring system for MSA Safety gas and flame detectors designed to reduce costs and provide access to data analytics that help to protect workers and facilities. The wall-mounted device acts as a centralized input and output hub that aggregates the signals it receives from gas and flame detectors and other field safety devices. By comparing signals, the controller triggers alerts and alarms and can activate important notification and hazard mitigation equipment that’s required to notify workers and safeguard a facility, according to the company. Historical data can be downloaded from the controller system to help us-ers monitor for developing threats and the controller features diagnostic tools to enable predictive maintenance.
MSA Safety
www.msasafety.com

EXAIR’s new PEEK 1/2 NPT Super Air Nozzle has been engineered to produce powerful blowoff without damage to expensive equipment. It is designed to provide non-marring protection to production items and excellent resistance to damage from harsh chemicals and temperatures up to 320°F (160°C). The PEEK Super Air Nozzle is designed for blowoff, cooling, and drying applications located in general industrial or corrosive environments.
EXAIR
www.exair.com

The TVGM Series family of miniature, high-definition handheld industrial-grade videoscopes is designed to support a variety of non-destructive testing and remote visual inspection tasks. Offered in four unique models with a choice of either a 3.9-mm or 6-mm camera, and either a 1.5-m or 3-m videoscope probe length, the TVGM Series features dual-key operation, a fully modular and ergonomic design, ease of portability, one-handed operation, and end-user capability to swap out probe lengths for increased application adapta-bility. The intuitive end-user interface of the TVGM Series also offers fully end-user selectable operation in up to 10 unique languages. Each TVGM Series videoscope features a powerful onboard controller delivering high-definition imaging, reliability, and stability.










Starting at $10.50 (PAM-AP-1A)
AchieVe PAE/PAM/PAK series inductive proximity sensors feature a rugged metal housing, three- or four-wire hookups, axial cable or quick-disconnect connections, and a great price.
• 8, 12, and 18 mm diameters
(flush and non-flush)
• 1.5 to 8 mm sensing distances
• Complete overload protection






• 304 stainless steel and nickel-plated brass housings
• IP67 protection rating
ADM/ADP Series IEC Limit Switches

Starting at $17.00 (ADM2F11Z11)

AchieVe ADM/ADP series heavy-duty IEC limit switches feature durable 50mm zinc alloy or reinforced thermoplastic housings with multiple conduit openings.

• Adjustable levers/head
• Various head actuator options
Also Available
Encoders




• 1 N.O. and 1 N.C. contacts
• IP65/IP66 protection rating


Starting at $191.00 (DD51E-SST-IP65F12)
Elesa position indicators monitor a rotating shaft and provide a precise reading of its position. They offer a large display with a wide viewing angle and a rugged polyamide housing suitable for applications requiring frequent washing.
• Values display in mm, inches, or degrees
• Absolute or incremental display mode
• 8 or 12 mm LCD heights
• 5- or 6-digit LCD
• IP65 or IP67 protection rating





Starting at $92.00 (BC-500TR)
Balluff BCS series are rugged capacitive proximity object detection sensors ideal for harsh industrial environments.
• Pigtail or M8 connectors (M12 for tubular version)
• Stainless steel or thermoplastic housings


Photoelectric Sensors





Process Sensors




• Liquid crystal polyme active face






• Up to IP66 protection rating

















Our shipping policies make it easier than ever to order direct
Fast free standard shipping* is available for most orders over $49 U.S., and that includes the brokerage fees (when using an AutomationDirect nominated broker). Using our choice of carrier, we can reach most Canadian destinations within 2 to 3 days.
*Free shipping does not apply to items requiring LTL transport, but those shipments can take advantage of our negotiated super-low at rates (based on weight) that include brokerage fees.
See Web site for details and restrictions at: www.automationdirect.com/canada


Motor brakes designed to eliminate downtime and costs for maintenance and adjustment

Force Control Industries’ MagnaShear motor brakes are mainte-nance-free, and require no adjustment, so they virtually eliminate motor brake downtime and maintenance costs, according to the company. MagnaShear motor brakes employ oil shear technology, which allows significantly longer service life in demanding applications like those with frequent start/stop cycles or where the motor is reversed each cycle. This lengthy life eliminates the need to stock spare brakes, friction discs, and other repair components, freeing up maintenance budgets and shelf space, according to the company. The totally enclosed MagnaShear brakes are impervious to moisture, dirt and dust that is common in many manufacturing environments. The motor brakes are available to accommodate a wide range of applications. Spring set torque ratings from 3 to 1,250 foot-pounds are available. MagnaShear motor brakes are available in multiple torques for the same motor frame. Force Control Industries www.forcecontrol.com
improved airflow, assisting in lowering the internal pump temperature. This extends service life of the lip seal and prevents any risks of oil leaks, according to the company. Edwards Vacuum www.edwardsvacuum.com
AMADA WELD TECH, Inc., recently announced that it is processing samples and providing product and process training in three technical centres across the U.S. The technical centres are located in Monrovia, Calif.; Wixom,
We understand how you need to reduce complexities at your plant.
Mich.; and High Point, N.C. All of the facilities can process samples using AMADA WELD TECH’s range of technologies, including resistance and laser welding; laser marking; hot bar bonding; and micro TIG welding. Laser cutting and micromachining currently only available at Monrovia location.

AMADA WELD TECH www.amadaweldtech.com
You strengthen your plant’s safety, productivity and availability with innovations and resources.

The nEDC300 from Edwards Vacuum is the company’s latest iteration of mono claw vacuum pumps, which boasts a range of inventive attributes to boost performance but also minimize noise levels, improve reliability, and facilitate on-site maintenance. It can be used in a wide range of applications, such as water and wastewater treatment, thermoforming, vacuum conveying, food processing or in medical systems. The claw pump features stainless steel rotors, as well as a durable stator coating, safeguarding its process wetted parts which ensures robustness in effective contaminant handling, according to the company. The nEDC300 offers improved serviceability through the modular design of the Edwards dry claw pumps. A separate, insulated pump element makes the inside of the pump easily accessible to users for maintenance, repairs and cleaning. The silencer has undergone a redesign for reduced noise levels, while preserving optimal vacuum performance. The new silencer also helps with




• Best in class flow measurement in custody transfer applications in mass or volume units due to unmatched accuracy for density determination, up to DN 250 (10”)
• Ideal for hydrocarbons with entrained gas thanks to the patented Multi Frequency Technology (MFT)
• Patented Heartbeat Technology for device verification during operation and permanent self-diagnostics
Over the past 12 years, no matter what industry I’ve been writing about, there seems to be one universal truth: few things are as costly to operations as unplanned downtime and unsafe operations. This is especially true in the world of processing, be it metals and mining processing, aggregates, food processing, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, plastics, oil and gas, or wastewater. For this reason, Canadian Process Equipment and Control News has dedicated this issue to maintenance and safety. Hopefully you will find the feature articles and latest technologies de- Andrew Snook, Editor
signed for enhancing safety and maintenance efficiencies helpful for your operations. Did you recently invest in a new technology that is enhancing your company’s safety or maintenance operations that you would like to showcase in an upcoming issue of CPECN? Drop me a line at my email or phone number, I’d love to hear all about it. And if there’s an opportunity to see it up close, even better! Hope to speak to you soon.

• RELIABLE QUALITY PRODUCTS



Since 2001, Valve Accessories & Controls has built a reputation as a company comitted to quality products, and a commitment to service, second to none.

• Pneumatic, Analog, and Digital Positioners
• Wide selection of Mounting Kits
• No Phone Mazes to Navigate
• Experienced Staff
• Service and Technical Support
Canadian Master Distributor: Belletek Controls Inc.
2535 Stallion, St. Lazare, Qc, Canada J7T 2E4
J.C. Labelle: (514) 916-5895
Fax: (514) 500-5802
Email: jc@belletek.com
the Positioner Industry for Over 20


READER SERVICE
Print and digital subscription inquiries or changes, please contact Angelita Potal Customer Service
Tel: 416-510-5113
Fax: (416) 510-6875
Email: apotal@annexbusinessmedia.com
Mail: 111 Gordon Baker Rd., Suite 400, Toronto, ON M2H 3R1
AUDIENCE MANAGER, Anita Madden 416.510.5183 amadden@annexbusinessmedia.com
BRAND SALES MANAGER, Pat Lorusso 416.518.5509 plorusso@annexbusinessmedia.com
EDITOR, Andrew Snook 416.510.6801 editor@cpecn.com
ACCOUNT COORDINATOR, Barb Vowles 416.510.5103 bvowles@annexbusinessmedia.com
GROUP PUBLISHER/VP SALES, Martin McAnulty mmcanulty@annexbusinessmedia.com
PRESIDENT/COO, Scott Jamieson sjamieson@annexbusinessmedia.com
CPE&CN is published bi-monthly by: Annex
111 Gordon Baker Rd, Suite 400, Toronto, ON M2H 3R1 T: 416-442-5600 F: 416-442-2230
© All materials in this publication are copyright protected and the property of Annex Business Media., the publishers of Canadian Process Equipment & Control News magazine.
For permission on reprinting or reproducing any materials, e-mail your requests to cpe@cpecn.com
Canadian Postmaster send address corrections to: 111 Gordon Baker Rd., Suite 400, Toronto, ON M2H 3R1
Canadian Process Equipment & Control News assumes no responsibility for the validity of claims in items reported.
Annex Privacy Officer privacy@annexbusinessmedia.com Tel: 800-668-2384
PUBLICATION MAIL AGREEMENT #40065710
Printed in Canada ISSN 0318-0859

SUBSCRIPTION





The Model CT, manufactured by Conveyor Components Company, is comprised of a control unit and tilt probe, which senses the presence or absence of material. The intrinsically safe cULus Listed Control Unit is enclosed in a rugged cast aluminum housing with external red and green LED status indicator lights and surface mount printed circuit boards. Weatherproof, dust-ignition proof and explosion proof models are available. Optional black epoxy powder coating is available for corrosive environments. The tilt level controllers (CT-105, CT-106 or CT-107) have an intrinsically safe output to the tilt probe and are cULus listed as intrinsically safe when used with the cULus listed tilt probes. The Model CT is commonly used when other controls won’t work due to bin vibration, or actual bin walls aren’t available for mounting other controls. Typical applications include level detection in hoppers, silos, stackers, crushers and conveyor transfer points. The CT tilt probes are available as a standard 9” tilt probe or a compact 6” tilt probe and have 25 feet of electrical cable. Stainless steel probe housings are available as an option. Float ball and paddle accessories are also available for fine-grain materials. Conveyor Components Company www.conveyorcomponents.com

HEMCO Corporation’s Air Flow Monitor continuously monitors face velocity air flow of fume hood. Select and calibrate at desired FPM velocity set point. If the hood face velocity falls below set point, an audible alarm sounds and a visual red indicator light appears. Air flow alarm is factory installed or can be field installed, 115/60Hz AC. HEMCO Corporation www.hemcocorp.com/airflowmon.html
INDCO Incorporated’s TL-series direct drive cap-mounted IBC tote mixers are ideal for mixing or suspending solids in intermedi ate bulk containers. Available with air or electric operation, from 3/4 to 4 HP, models are configured for vigorous agitation in low viscosities or medium agitation for heavier bodied liquids. Units include shaft, three-bladed machined square pitch style impeller, and 6-inch screw cap for ease of installation. Air models are lightweight and vari-

able speed with speed control valve. Electric models feature handles to easily install mixer into tote. INDCO’s TL-series mixers are available with very short lead times ranging from same-day shipment to two business days. These mixers are ideal for a wide range of chemical mixing applications, including solvents and sanitizing solutions as well as paint processing or suspension of settled solids for bulk paint formulations in storage.
INDCO Incorporated www.INDCO.com






By Dan Vickers and Randy Piggott
The industrial chipper is key in the wood handling process. From providing the correct chipping geometry to optimizing log control, the chipper and its components are essential for maximizing production of high-quality chips. But not all maintenance plans are created equal. Predictive maintenance can help optimize your chipper throughout its life cycle so you can focus on your core business.
From knives and wear plates to slivers hardware and brake pads, a chipper is built with numerous components that require regular monitoring and maintenance. Furthermore, out of all the components within a chipper, its rotating components — like bearings — are closely tied to an operation’s viability, making proper maintenance essential.
Typically, wood chipper maintenance has relied on visual inspection of components prone to wear. In some components, features can provide visual indication. For example, in wear plates a hole tells the operator that it’s already worn through half its thickness, indicating that it’s time for replacement. Sound is sometimes used, too. An experienced operator may notice the equipment making a sound that suggests the

knives are getting dull.
Operators also rely on chipper equipment manuals to guide them as they determine when to replace components. In addition, mills use preventive maintenance schedules that are based on the equipment’s specific history.
While traditional maintenance methods — combined with skilled

operators — will likely always play a core role in mill operations, predictive maintenance is a technique that can further detect problems before they cause downtime. For example, a mill using only monthly visual inspections might note a bearing is fine during an inspection, only to have it fail by midmonth.
Rather than rely solely on periodic inspections by mill personnel or a maintenance schedule to detect problems, predictive mainte-
nance monitors specific conditions in real time and provides condition alerts when a reading falls outside of defined parameters.
This proactive approach can reduce unplanned downtime, extend the chipper’s life span and lower the cost of ownership over time. Predictive maintenance also helps ensure the equipment produces high-quality chips — safely and efficiently. Pulp makers can expect sustainability benefits, too, as predictive maintenance optimizes


raw material use.
Predictive maintenance is particularly suited for ensuring that crucial rotating components stay in operation. They can fail if they do not get proper lubrication or if they become worn to the point of excessive vibration. Failure in the component can cause catastrophic failure in the machine, taking a chipper out of commission for a week or more and risking workers’ safety. Damage to the disc can also reduce its life cycle, requiring a mill to replace it after 10 or 15 years instead of 20.
For example, resistance temperature detectors (RTDs) indicate when a temperature is too high, suggesting that a component, like a bearing, is too hot. By using the RTD to get a baseline when the bearing is new, production operators can then monitor the bearing via RTD during operation and compare it to the baseline. This comparison will indicate operational health and quality of life, providing an opportunity to schedule maintenance and avoid unplanned downtime before failure.
Likewise, vibration sensors — such as accelerometers — can also help predict when a bearing should be replaced, allowing crews to ensure the chipper has a good bearing with proper oil lubrication so the machine stays in operation as planned.
Currently, some mills use thermal infrared to provide visual indication of hot zones as well as digital quantification of bearing assemblies’ maximum external temperatures. For example, at one mill, the images below allowed operators to discover a pinched seal soon after start-up.
It’s important to note that these tools are most effective when integrated as part of systematic, real-time monitoring protocol. Checking temperature or vibration only occasionally, as part of a monthly maintenance list, can miss signs of failure that might have been detected with active monitoring.
Chip makers can have sensors and ports installed on bearing housing when they order new chippers, or they can be retrofitted to existing machines. To avoid

Sensors, like this wired accelerometer vibration sensor for chipper bearing assemblies, can help predict when a bearing should be replaced.
additional downtime, the best time to retrofit is typically when the chipper disc and shaft are in the shop for repair or regular maintenance. Once the sensors are installed, the mill’s electrical technicians can wire them into their programmable logic controller (PLC) or other computer systems for real-time monitoring of bearing conditions.
Mobile applications can also support predictive maintenance programs. For example, Valmet has developed an app to facilitate maintenance needs and planning in real-time. This app integrates with system application and product system, allowing maintenance technicians and production operators to report failures, record observations and collaborate on tasks.
Although predictive maintenance can yield previously unseen benefits by providing early failure warnings for end-of-life components, its implementation is not without minor challenges. For example, applying this technology may require mills to wire sensors to the PLC, program the PLC to integrate the sensors into an existing logic system, and then test each sensor to ensure it is integrated correctly. An experienced partner can help mills meet these challenges with, for example, wireless sensors that help alleviate the pains of running long sensor wires back to the PLC.
Pulp and chip makers should consider enhancing the power of predictive maintenance with
field service agreements. These collaborative partnerships allow expert technicians to periodically inspect chippers and provide maintenance services to maximize reliability and performance. Experienced partners may also be able to provide ongoing support by reviewing a mill’s predictive maintenance data and offering relevant recommendations.
Additional tools can also support a more holistic approach to maintenance programs. For example, systems that make it easier to change brake pads or swap out
knives and knife hardware support better maintenance that leads to improved chip quality and less downtime.
Choosing the right maintenance partner is another key part of building an effective maintenance program. It is important to work with a partner able to offer the expertise and resources to help develop modern maintenance processes. The most impactful maintenance partners offer a collaborative mindset and dedication to supporting safe and sustainable maintenance operations.
From upgrading a legacy chipper to developing a greenfield mill, predictive maintenance for chippers is an important part of any holistic maintenance plan that helps optimize wood handling operations.
Dan Vickers is a technology manager and Randy Piggott is a field service engineer for Valmet’s North America Wood and Pulp Handling Business Unit. Valmet www.valmet.com
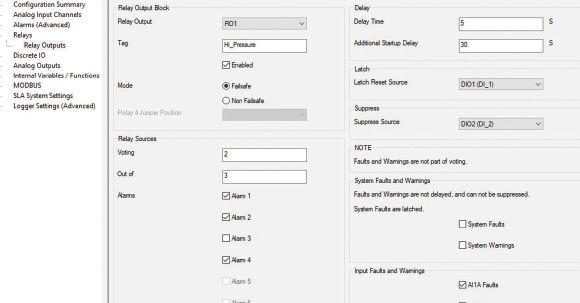
The exida approved SLA Multiloop Safety Logic Solver and Alarm simplifies complex safety loops with simple programming and I/O versatility to reduce the intricacy and cost of your safety instrumented systems.



By Del Williams
In industry, one-time-use rupture disks have long provided pressure relief on hydraulic and pneumatic equipment, serving as an effective passive safety mechanism to protect against potentially damaging overpressure or vacuum conditions. Each disk is typically designed to burst, rapidly changing from a leak-tight seal to a full diameter flow opening when a predetermined over or under pressure event occurs. At that point, the rupture disk needs to be replaced.
Rupture disks are a proven solution, particularly for the protection of certified pressure vessels whose protection is driven by the European Pressure Equipment Directive (PED) threshold of 0.5 bar and above and American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) threshold of 15 psig and above.
Demand for this type of sealed, fluid-containing safety equipment is increasing for aseptic products in the health care, liquid food, and cosmetics industries; and other applications where service pressures and even atmospheric pressure are much lower. Rupture disks are a critical component to seal fluid within the container under normal operating conditions and protect against overpressure caused by such events as external fire or an unexpected chemical reaction. Even noncombustible fluids can lead to overpressure conditions as they reach and exceed their boiling point.
With atmospheric storage equipment that is sealed, a particular challenge is that significant internal pressure fluctuations can also occur because of ambient temperature swings, particularly for vessels located out-

doors or otherwise exposed to daily temperature excursions. Consider that at common equipment application temperatures (–40° F to +175° F / –40° C to +80° C), the shift in pressure in a sealed container can range from -3 to +3 psi / -200 to +200 millibar.
“Although many fluids are stable under atmospheric pressure, when placed in a closed container, even normal fluctuations in ambient temperature or equipment operation can generate overpressure (as temperature rises) or vacuum (as temperature falls),” says Geof Brazier, managing director of BS&B Safety Systems Custom Engineered Products Division. “Over time, this can compromise simple metallic and non-metallic container integrity due to flex and fatigue, leading to potential quality and maintenance issues and ultimately uncontrolled rupture of the container.”
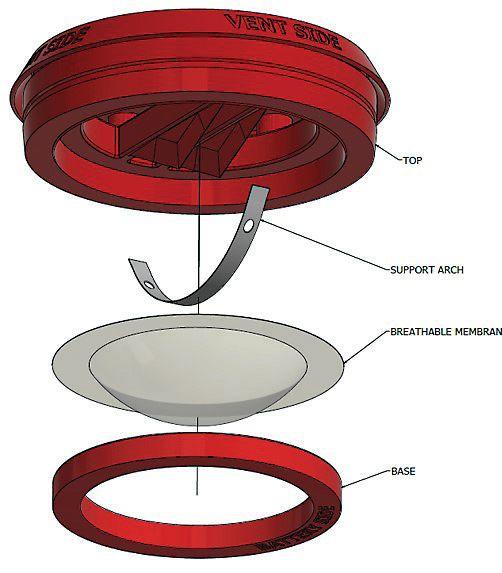
In response, an innovative new “breathable” rupture disk technology has been developed that provides overpressure and vacuum relief by allowing air to pass through a unique membrane to relieve minor variations in pressure.
“Rupture disks are traditionally installed for their excellent leak-tight performance under normal plant operating conditions. However, to improve reliability and longevity, the new requirement is for a rupture disk that will allow air flow in and out of a sealed container when a small pressure differential arises due to temperature change without the disk bursting,” explains Brazier.
To meet the development challenge, BS&B’s

engineering team focused on the unique properties of sintered PTFE film, which is produced in sizes, quantities and thicknesses suited to the construction of low-pressure rupture disks. The PTFE film can produce rupture disks in sizes from under 1” burst diameter to over 6” burst diameter (DN25 to DN150) using plastic film down to 0.1 mm in thickness. The unique film is processed to achieve a specific level of porosity that allows air to pass through at a pressure differential of a few inches of water column/millibar, but prevents passage for fluids like water until much higher differential pressures of around 0.5 bar are reached.
Constructing a rupture disk from only breathable PTFE film solves the low-pressure fluctuation challenge due to temperature. However, adding a second level of safety by having such a rupture disk burst due to a greater over or under pressure condition is a further challenge since the mechanical properties of the film are too strong to meet the low burst pressure requirements of atmospherically stored equipment; typically below 7.5 psi / 0.5 bar. According to Brazier, variations in ambient temperature can also lead to unacceptably large tolerances in burst pressure from a plastic film acting alone as the pressure relief member. A simple, flat PTFE membrane does not make a good rupture disk due to wide burst pressure spread, sensitivity to temperature, and potential fatigue. However, the fact that the porous material could allow air flow in either direction – without allowing liquid through – remained a desirable characteristic.
The BS&B engineering team resolved the second level of safety issue by combining the structural and thermal stability of a traditional metal domed rupture disk with the PTFE film. Under normal operating conditions, the metal support arch holds the PTFE dome, and air is free to pass in either direction. In the event of an overpressure event, the metal support arch collapses and the dome is cut by a blade on the downstream side to relieve the pressure. Brazier notes that this is possible with burst pressure capability as low as 2” water column/5 millibar.
“By combining the proven reliability and accuracy of metallic rupture disk components with the calibrated air/gas transmission performance of the PTFE film, a dual function rupture disk device can be constructed. Normally, this permits air flow to maintain atmospheric pressure due to daily temperature changes. For safety, the disk activates at a predetermined set pressure in one or two directions [positive pressure or vacuum relief],” says Brazier.
The patent-pending, dual function, pressure equalization and relief device is ideal for use on low-pressure vessels that are often below the design limits of PED and ASME Standards.
To accommodate the size and weight

The new requirement is for a rupture disk that will allow air flow in and out of a sealed container when a small pressure differential arises without the disk bursting.
limitations of many light duty atmospheric storage containers, the rupture disk is designed in an integral assembly that includes the rupture disk as well as housing. The integrated assembly is certified to perform at the desired set pressure and allows for easier installation and quick removal, if the rupture disk is activated. The device is designed for installation between sanitary/ aseptic fittings or traditional pipe flanges, or a custom installation configuration can be accommodated.
While process industry operators and OEMs have long relied on rupture disks in their hydraulic and pneumatic equipment, low-pressure environments susceptible to ambient temperature changes have been a challenge.
Fortunately, with the availability of rupture disks that can “breathe” to provide pressure relief while still bursting open when a true overpressure condition arises, users can significantly enhance equipment safety, reliability, and product quality, while reducing maintenance expense.
Del Williams is a technical writer based in Torrance, California. BS&B Safety Systems www.bsbsystems.com
23_011329_CPECN_FEB_CN Mod: January 10, 2024 8:34 AM Print: 01/10/24 page 1 v2.5






By Lucas Faulkner
Filter fans protect electrical enclosures from external environmental damage. From heat control to mitigating the ingress of liquid and solid objects, filter fans provide another layer of protection for the electrical equipment housed within enclosures. Filter fans protect critical equipment by reducing thermal load and filtering out airborne particles larger than 5 microns. The dual fan and filter composition keeps electrical equipment running at optimal temperatures while mitigating the amount of dust and other particulate matter from causing buildup and damage.
When selecting a filter fan for an enclosure, it’s important to consider the application’s heat load, optimal temperature, and environmental conditions in which it will be operating. Environmental considerations are particularly important for outdoor enclosures, as rain, snow, ice, and sunlight all pose risks to electrical equipment.
Filter fans are necessary for a wide range of outdoor electrical equipment. Some applications, however, require intentionality and extra consideration when choosing the appropriate filter fan. These include irrigation pump panels, water and wastewater, lighting control boxes for traffic signals or fields and stadiums, outdoor communication and information technology structures, energy storage and charging systems (such as in electric vehicles), and transportation systems, including bridges, toll stations, and electrical rail equipment.
When properly designed and integrated, outdoor filter fans can provide an energy efficient solution for heat load maintenance while also protecting enclosures from dust, ice, water, and sunlight. However, many filter fans on the market do not effectively protect critical electrical equipment. When improperly designed, filter fans can be subject to ice and dust buildup or damage from UV radiation and rainwater. These conditions can cause short circuiting within the enclosure. While there are workarounds for water infiltration, such as adding a rain hood, these additional steps increase space requirements and initial investment costs.
Given these challenges, there are some tips to keep in mind when selecting a filter fan for an outdoor electrical enclosure.
Selecting an outdoor filter fan begins with de-

termining the application’s heatload and airflow requirements while considering environmental exposure. Electrical enclosures in dry, hot weather require different filter fan needs than those used in areas with snow, ice, and highly variable temperatures. For applications where environmental conditions cannot be determined ahead of time, a filter fan that can accommodate each of these possibilities is best.
While determining application needs, it is beneficial to consult with an expert to help determine specific risk factors. An expert can help with considerations around which airborne particulates are present and if they are corrosive, as well as what ambient temperatures can be expected and how direct or indirect sunlight can affect operating temperatures.
The Pfannenberg Outdoor Rated Filterfan (NEMA 3R rated) is designed for outdoor weather where direct sunlight and extreme weather, like rain and ice formation, are important factors. This filter fan utilizes UV-resistant plastics to prevent premature degradation from direct sunlight. Additionally, the filter fan’s design protects against the ingress of falling dirt, rain, sleet, snow, and even external ice formation.
Filter fans generally require little maintenance outside of regular filter replacement. However, it is crucial to change the filter as specified by the manufacturer as filter clogs reduce airflow, causing extra strain on the fan and increasing the potential for overheating.
Well-designed filter inserts, including the filter for Pfannenberg’s Outdoor Rated Filterfan described above, provide longer service life. Pfannenberg’s fluted filter-mat enables longer mean time between maintenance. It accom-

plishes this with its increased dust holding capacity. As a result, the need for service is reduced, saving maintenance time, costs, and stress, which is especially helpful for electrical enclosures located in remote areas.
Filter fans for outdoor applications require a design that balances airflow optimization with low initial investment. A filter design that minimizes maintenance needs should also ensure unrestricted airflow throughout the fan’s service life. However, it must do so without compromising on water and dust protection capabilities. Combining a filter that fits these needs with a filter fan housing design that does not require metal rain hoods, achieves an excellent balance of protection, airflow management, and minimizing upfront costs.
Filter fans are critical for protecting electrical equipment from overheating, water, and airborne debris so the equipment can run safely and efficiently. In outdoor environments, this task is particularly challenging. Finding a filter fan suitable for outdoor environments without significant drawbacks requires careful research. By considering heatload, environmental conditions, and maintenance needs before selecting a filter fan, it is possible to keep costs low. In applications ranging from pump panels and lighting control boxes to communication technology and energy storage systems, well-designed filter fans keep outdoor electrical equipment functional and safe.
Lucas Faulkner is a solutions engineer with Pfannenberg USA. Pfannenberg USA www.pfannenbergusa.com
By Alex McCans
A100-year-old wheat mill that once was a backdrop for a Hollywood movie has won a fight against blowouts in its pneumatic pipeline elbows. Lehi Mills in Lehi, Utah, processes roughly 49.6 tonnes (45 tons) of flour per day for bread flour, baking flour, whole wheat flour, and its own line of pre-blended mixes for desserts, waffles and pancakes. Founded in 1906 as a family-run enterprise, the mill still occupies its original building. A dilute phase pneumatic conveying system was specified to move dry and tempered wheat throughout the process within the historic plant’s height restrictions, but the mill staff soon noticed signs of erosion in the system’s sweep elbows.
“Abrasive, fast-moving grain was causing frequent blowouts, requiring the mill to shut down every few months,” explains Todd Berry, mill superintendent and director of quality control.
Incoming dry wheat is pneumatically conveyed through separators, sifters, aspirators and washers that filter out foreign material and remove impurities. The dry


wheat line runs 7.6 m (25 ft.) horizontally, 16.8 m (55 ft.) vertically, and includes two 90-degree bends. Berry noted that erosion in the dry wheat line’s two sweep elbows began almost immediately, and that it worsened as the wheat grain, travelling at high speeds through the circuit, generated heat and friction due to impacting the elbows’ outside radius.
“The wheat ate through the sweep elbows and eventually just shot out the side,” he said. “We tried a heavier elbow, but within weeks the wheat ate through that one, too.”
Circuitous routing on the pneumatic line conveying tempered

wheat included a high number of sweep elbows. This compounded the problem by creating more opportunities for blowouts to occur.
The superintendent says the tempered wheat line initially employed six sweep elbows at various angles to convey the tempered wheat to a holding bin which allows time for the moisture to soak into the wheat before milling. Over time, however, the abrasive wheat wore through the sweep elbows, even after steel backing plates were welded onto them.
To reduce shutdowns due to el-
bow failure, the mill re-configured the tempered wheat line, reducing the number of bends, and installed Smart Elbow deflection elbows in lieu of conventional sweep elbows in both lines.
Unlike sweep elbows, in which material impacts the outside radius at high speed to change direction, the Smart Elbow design incorporates a spherical vortex chamber that extends partially beyond the flow path around the bend. Within this chamber, the airflow creates a ball of material that rotates in the same direction as the airstream, acting as a buffer to gently deflect and redirect the incoming wheat around the bend without impacting the elbow wall.
The mill reports that no blowouts have occurred to date, since two deflection elbows were installed on each of the dry and the tempered wheat circuits.
“Before the HammerTek elbows, the abrasive wheat would just eat through the elbows regardless of what we did,” Berry said. “I’m glad that we found the deflection elbows. They’ve made my life easier.”
Alex McCans is the national sales manager for HammerTek Corporation. HAMMERTEK CORPORATION www.hammertek.com









Festo’s HPPF diminutive flat parallel gripper delivers great force in tight spaces. The HPPF ranges from 19 mm to 41 mm among its four sizes: 8, 12, 16, and 20. The stroke ranges from a narrow 8 mm to a wide 80 mm, with gripping forces from 60 N to 377 N. These specs make the new HPPF ideal for space-constrained applications in small parts and electronics assembly. That includes battery manufacturing, since each HPPF contains less than 1-per-cent copper/ zinc/nickel. Twin piston rack and pinion motion and ball bearing guides give these units high accuracy – ≤ 0.03 mm to ≤ 0.06 mm – and maintenance-free long-service life. Twin pistons provide these compact units with a high grip force. Units are symmetrical for flexibility in mounting. Both sides feature a C-slot for sensors. Machine builders can adjust the stroke and there is an elastic cushioning option. Weight is exceptionally low – ideal for today’s smaller footprint, more sustainable machines – 68 g for the smallest unit and up to 1,326 g for the largest.
Festo
www.festo.ca

performed in 30-per-cent less time than other pycnometers, making the AccuPyc the fastest gas pycnometer available, the company stated. An analysis temperature range of 4°C to 60°C empowers users to measure density at their process temperature, whether replicating refrigerated biopharmaceutical storage or elevated-temperature manufacturing. A new hinged, self-aligning lid provides frustration-free operation and constant chamber volume, ensuring reproducibility. The new Breeze touchscreen interface provides intuitive instrument control and results review for users with any level of experience. The integrated MIC Net centralizes density data across the lab, including forward compatibility with existing AccuPyc systems. A wide analysis volume range from 100 cm3 to 0.1 cm3 permits large volumes that eliminate sampling error in heterogenous materials through low volumes that conserve scarce materials.
Micromeritics Instrument Corp. www.micromeritics.com/accupyc

Emerson has introduced the Fisher 63EGLP-16 Pilot Operated Relief Valve for installation on pressurized bullet tanks used to store liquid propane and anhydrous ammonia. The new valve is certified under UL132 and American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) Section VIII. With a pre-installed national pipe tapered (NPT) thread standard 2-inch male hex nipple, this new product serves the need for a solution with a 2-inch connection that provides the same benefit as traditional multi-ported valves, but with simplified installation and maintenance. For this application, the PRV must be connected directly to the tank, with no isolation valve between the tank and the PRV. This National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) 58 code requirement presents challenges when testing the PRV while the tank is pressurized and in operation. Operation is implemented with a dual pilot array, providing redundancy, and allowing for removal of one pilot for testing while the other is operational. Because this is a critical safety-related application, reliable operation over a long lifecycle is needed. This requirement is met by the 2-inch PRV because it is similar in design to the Fisher 63EGLP 4-inch CL300 model, which has been proven in use over the past 10 years, the company stated.
Emerson
Micromeritics Instrument Corp. has released the new AccuPyc gas pycnometer. Every AccuPyc features new AccuTemp thermoelectric temperature control. Temperature stability within ±0.025°C enhances measurement repeatability and reduces analysis time. Analyses can be
Plast-O-Matic’s adapters convert female NPT connections to female BSPT. Simply thread into any FNPT valve or fitting and it will accept male BSPT threaded pipe or fittings. Fittings are MNPT x FBSPT. They are available in 1/2” to 4” in PVC, CPVC, Natural Polypro, Kynar PVDF. The adapters are designed to eliminate leaks, cross-threading, and other installation problems. They are precision machined in the U.S. and are designed to meet ASTM D2467, F1970, D4101, D3222. Adapters are used for all Plast-O-Matic products that are not offered with standard BSP connections. They are also available separately to provide a convenient and reliable method for connecting any FNPT product to a BSPT installation.
Plast-O-Matic Valves, Inc. www.plastomatic.com


Torrey Pines Scientific’s WaferPlate Programmable Bake Plate offers uniform heating across the surface of better than 1% over a heating range from room temperature to 350°C. It is ideal for precisely heating 12” (304.8mm) and smaller silicon wafers, electronic chips, displays, adhesives, and for doing photo-resists and more. The WaferPlate Model HP90 has a large circular 13.875” (352.4mm) milled-flat plate aluminum surface with temperature uniformity better than 1% across the centre 12” (304mm), making it ideal for working with 12” or smaller silicon wafers. The unit is controllable remotely from a PC or industrial controller via the RS232 I/O port using the command set provided. Also provided is a bench top controller, which is fully programmable holding five routines of 10 steps each in memory for instant and repeatable recall and use. Each program can be made to repeat itself automatically from 1 to 98 times or infinitely. The plate surface can be set from room temperature to 350°C and can be set and controlled directly to 1°C. Accuracy is better than 1% of the heater setting over the entire range.

Temperature sensing is by platinum RTD built into the heater plate. The HP90 has temperature ramping from 1°C/hour to 450°C/hour, countdown timer with alarm, and user settable Auto-Off and RS232 I/O port. The units are supplied with temperature calibration certificates traceable to NIST. The WaferPlate Model HP90 is available in 100, 115, and 230 VAC, 1500 watts, 50/60 Hz models. ETL, CSA, and CE certification is pending.
Torrey Pines Scientific www.torreypinesscientific.com
Z-Range safety switch system components

AutomationDirect has added modular Z-Range safety switch system components to their existing portfolio of safety products. The Z-Range safety switch system offers simplicity and modularity, allowing up to 30 Z-Range safety devices to be connected to one safety relay while maintaining PLe performance rating. These devices are an excellent choice for modular machines and are rated for SIL3 as well as PLe and feature built-in local diagnostics. Available devices include non-contact safety switches, solenoid locking RFID tongue interlock safety switches, tongue interlock safety switches, hinge interlock safety switches, cable-pull safety switches, emergency stop control stations, and Z-Range safety switch system accessories. Wiring is simplified with premade wires, T-cables, and junction blocks.
AutomationDirect
www.automationdirect.com

The R5 RA from Busch now comes in an improved version with a completely redesigned interior. The new vacuum pump is 25-per-cent more energy efficient than its predecessor, thanks to the optimized compression ratio, pump stage dimensions, and oil discharge path. It is also available with ECOTORQUE, the Busch variable speed drive (VSD), that enables the pumping speed to be adapted to the exact requirements of any process. As a result, additional energy savings of up to 50 per cent and a 20-per-cent increase in pumping speed can be achieved. The accessory extends the supply voltage range supported by the vacuum pump, making it suitable for use in almost all countries around the world. This compact and cost-effective solution is also available as a retrofit. Compared to the previous generation, the R5 RA 0520 A has a 20-per-cent smaller footprint, is 25-per-cent lower in height, and the absence of external piping improves leak tightness. The compact and hygienic design features surfaces that repel water and dirt. The total number of spare parts has been reduced by 40 per cent with all service-related parts located on one side. Heat emissions have also been decreased through an improved cooling system that combines optimal pump operating temperature with compact construction. The new vacuum pump is made for continuous operation in the rough vacuum range with vacuum levels down to 0.1 hPa (mbar).
Busch Vacuum Solutions
www.buschvacuum.com
Bonomi’s new LOCPOWER control valve is a finalist in the 2024 AHR Expo Innovation Awards. The LOCPOWER is a patented energy harvesting control valve for water from the Bonomi Group. LOCPOWER converts energy dis sipation from processes such as flow, pressure, tempera ture, and level control into mechanical power and then into clean electricity.
Unlike traditional control valves where the pres sure drop is achieved through a single- or multi-stage trim, LOCPOWER regulates the flow by splitting the pres sure drop through a single- or multi-stage trim-turbine, designed to fit perfectly into the valve’s body and to max imize energy recovery. LOCPOWER’s design allows smart utilities and industries to control pipeline flow and pressure, offering energy harvesting features without sacrificing safety. With LOCPOWER, flow regulation and control and power generation, are parts of an integrated system. Using advanced active front-end inverters, LOCPOWER generators can exchange energy with the domestic grid, local supply, or energy storage systems. This gives users electricity to power operations, provide back-up power for emergencies or to sell to electric utilities. LOCPOWER turns pipelines into valuable, renewable energy resources. LOCPOWER’s state of the art synchronous electric generators, ranging from 5kW to 300kW, will harvest even the smallest portion of energy from pipeline flow. LOCPOWER is available in sizes from 3 inches through 24 inches.
Bonomi North America www.bonominorthamerica.com










When high purity & absolute retention are prerequisites for your filtration process, MicroVantage cartridges deliver. Membrane Cartridges Melt-Blown Depth Cartridges Pleated Filter Cartridges








Endress+Hauser has announced that Dr. Peter Selders has taken over as CEO of the Swiss-based global specialist for measurement technology and automation solutions. The 54-year-old Selders holds a doctorate in physics, has been with the company since 2004 and was previously managing director of the competence centre for level and pressure measurement technology based in Maulburg, Germany. He is only the fourth CEO in the family-owned company’s 70-year history. His predecessor, Matthias Altendorf (56), is moving to the Supervisory Board after 10 years at the helm. In 2014, he became the first non-family CEO, succeeding Dr. Klaus Endress. He is now replacing the 75-year-old Endress as president of the Supervisory Board. Peter Selders has been succeeded at Endress+Hauser Level+Pressure by Dr Dirk Mörmann (50), who was previously head of technology and a member of the management board. Endress+Hauser www.endress.com
ABB has announced that it has agreed to acquire Canadian company Real Tech, a leading supplier of innovative optical sensor technology that enables real-time water monitoring and testing. Through the acquisition, ABB will expand its presence in the water segment and complement its product portfolio with optical technology critical for smart water management. Financial terms of the transaction that is expected to close in Q1 2024 were not disclosed. Unlike traditional water quality measurement, which can be a time-consuming process, Real Tech’s product portfolio provides critical measurements in real-time. This enables better process control and continuous water quality assurance. Real Tech’s patented solutions cover the entire digital water value chain for water quality monitoring with a focus on data creation and analytics. Real Tech’s portfolio includes optical sensors, controllers and a suite of optional accessories that allow each system to be configured according to customer needs. Leveraging the power of light, the sensors measure water composition. They use spectrophotometry and fluorescence measuring techniques to move testing from the lab to the process environment for real-time use. Liquid AI, a proprietary AI software platform, completes the service offering, providing an easy and accurate way to analyze data from Real Tech sensors. The company has approximately 40 employees and is based in Whitby, Ont.
ABB
www.abb.com
Metro has competed the acquisition of Tedd Engineering, a privately owned company specialized in automation, control systems and electrical solutions for mobile equipment and aftermarket primarily for the aggregates business. The acquisition was initially announced on October 2, 2023.
Metso
www.metso.com
Process Sensing Technologies (PST) a leading provider of measurement instrumentation and monitoring systems for process-critical applications, recently finalized its acquisition of Fluid Components International (FCI), a specialist manufacturer of thermal mass flow meters and switches. FCI’s unique technology has positioned the company as a market leader, with products delivering superior measurement accuracy and application reliability across a broad range of demanding industries, including chemicals, water and wastewater, oil and gas, power, aerospace, nuclear power, and many others, PST stated in a recent press release. The purchase will allow PST to expand its product range and measurement capabilities, leveraging FCI’s reputation for performance, quality, and excellent customer service, the company stated. The acquisition marks PST’s first-ever entry into the flow meters sector, which it stated is “highly complementary to PST’s existing capabilities.” The San Marcos, Calif.-based business has a team of over 200 employees, led by president Randy Brown, along with its current leadership team. In connection with the transaction, Objective Capital Partners served as FCI’s exclusive financial advisor and Sheppard Mullin served as FCI’s legal advisor.
Process Sensing Technologies www.processsensing.com

Turboden S.p.A. (Turboden), a Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Group company, has been selected by Strathcona Resources Ltd. (Strathcona) to design and produce North America’s largest single-shaft turbine Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) system with a gross nameplate capacity of up to 19 megawatts. The ORC system, which is planned to be implemented at Strathcona’s Orion thermal oil facility located near

Cold Lake, Alta., will use waste heat recovery to generate carbon free electricity, offsetting approximately 80 per cent of the facility’s existing grid-power consumption.
Implementing ORC technology at steam assisted gravity drainage (SAGD) operations, like Orion, will allow Strathcona to capture previously lost low-grade thermal heat at approximately 150°C and convert it to emissions free electricity that can be used to help self-power operations and reduce need to draw from the local power grid. Lowgrade thermal heat from the Orion facility was previously released through aerial coolers.
“We see tremendous value in implementing Turboden’s ORC system at our Orion facility,” shares Rob Morgan, president and CEO of Strathcona Resources. “The technology will convert a waste energy stream from our SAGD operation into usable electricity, lowering power supply costs and reducing the carbon footprint of our operation − demonstrating once again how technology can be applied to improve both the economic and environmental performance of our industry.”
Strathcona’s ORC implementation is slated for completion in the first half of 2025. The project will be constructed within the facility’s existing operational footprint and is estimated to result in approximately 740,000 tonnes of GHG emissions reductions over the project lifetime, the equivalent of taking approximately 226,000 cars off the road.
Turboden www.turboden.com

Flow instrumentation manufacturer AW-Lake, a TASI Group company, announced that Micah Feinberg has been hired as the company’s new controller. Tammie Steiner has moved into a sustainability role at TASI Test and Automation. Feinberg will be overseeing the forecasting, strategizing, and budgeting of company financial programs as well as support EXACT Dispensing Systems with financial planning and goals. He is responsible for both accounting departments, including payroll, accounts payable, tax, audit, budget, general ledger, consolidated financial reporting, cash management and staffing functions. Feinberg comes to the company with more than 20 years of experience in accounting and finance, with demonstrated skills in financial modeling, cost reduction, change management, and ERP implementation. He previously held controller positions for several industrial manufacturers where he streamlined and automated various AP, AR and closing activities and upgraded legacy ERP/accounting systems.
AW-Lake
www.aw-lake.com
Yokogawa has announced PSS Group as its new representative for the company’s industrial automation products portfolio consisting of field, control, and analytical instrumentation in Eastern Canada. Geographical coverage includes the provinces of New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, Ontario, Prince Edward Island, and Quebec. PSS Group serves the process automation market and consists of Process & Steam Specialties, Summit Instrument Specialties, Moffatt Supply & Specialties, and Conval Quebec. PSS Group is known for excellent
customer service and support network along with complete turnkey capabilities, Yokogawa says. The PSS Distribution Group is headquartered in Oakville, Ont., and operates with a network of over 200 employees throughout Canada, across multiple sales office locations. Yokogawa www.yokogawa.com
ABB recently announced that Mathias Gaertner has been named General Counsel, Company Secretary and a member of the company’s executive committee. Gaertner will join ABB in 2024 succeeding Natalia Shehadeh, who has held the position of General Counsel and Company Secretary ad interim since June 1, 2023. Shehadeh will continue in her role as chief integrity officer of ABB. Mathias comes to ABB with a strong track record of managing international M&A transactions, litigations, IP and compliance. He is currently Head Legal & Compliance of global construction materials company Holcim and has been a member of its group executive committee since 2021. Prior to that role, he spent 10 years at Honeywell Building Technologies, most recently as General Counsel. Mathias has also worked for law firms Skadden, Arps, Slate, Meagher & Flom LLP and Affiliates and Baker & McKenzie. Mathias studied at the University of Münster, Germany, where he obtained his PhD, and is admitted to the German bar. ABB
www.abb.com



Dow recently announced that its Board of Directors has approved the go-ahead for the company’s Path2Zero Project, which involves the construction of the world’s first net-zero Scope 1 and 2 emissions integrated ethylene cracker and derivatives facility at a brownfield site in Fort Saskatchewan, Alta.
The project, which includes a US$8.5 billion (CAD$11.5 billion) investment from Dow and partner companies (not including government subsidies and incentives) is expected to decarbonize 20 per cent of Dow’s global ethylene capacity while growing the company’s ability to meet growing customer demand in high-value markets such as packaging, infrastructure and hygiene, the company stated.
“The project serves as a leading example that industrial decarbonization is both possible and profitable,” said Jim Fitterling, Dow Chair and CEO. “The opportunity to decarbonize our assets while driving growth is central to Dow’s business strategy. All our stakeholders benefit from this investment – creating value for our customers and shareholders, new opportunities for our employees, economic growth for the community, and fewer greenhouse gas emissions for the environment.”
Construction is expected to begin in 2024. Capacity additions are expected to come online in phases, with the first phase starting up in 2027, adding approximately 1,285 KTAiv of ethylene and polyethylene capacity, and the second phase starting up in 2029, adding an additional approximately 600 KTA of capacity, the company stated.
“This investment paves the way for growth of our entire Packaging and Specialty Plastics portfolio. It gives us the opportunity to become the industry’s first provider of zero-emissions products and solutions,” said Karen Carter, Dow president, Packaging & Specialty Plastics. “Our commitment to innovation and designing products for circularity allows us to meet the evolving needs of our customers across growing sectors such as packaging, infrastructure, and hygiene, among others.
“Plastics have long been recognized for their environmental advantages, with a greenhouse gas footprint that is typically less than half of alternative materials. With this strategic investment and our commitment to transform plastic waste to create circular and renewable solutions, we are poised to achieve even greater reductions in emissions, empowering our customers to make significant strides in their sustainability efforts.”
Dow stated that the decision to select the Fort Saskatchewan site stemmed from Western Canada offering “highly cost-competitive natural gas relative to other regions, as well as cost-advantaged ethane, a key feedstock for ethylene production.”
The Government of Alberta stated that the project would create about 6,000 jobs during construction, while the Government of Canada estimated upwards of 8,000 construction jobs at peak time. Both governments stated that the new facility would create 400 to 500 fulltime jobs once it is operational.
“This investment by Dow is further evidence of the opportunity that exists in Alberta,” stated Premier of Alberta Danielle Smith. “We are proud that Dow has chosen to build and launch their project here. This project does not just mean net-zero emissions, it means more jobs and a stronger economy. I look forward to the next steps, including construction starting next year.”
The project will receive significant federal and provincial funding including approximately $1.8 billion from the Energy and Minerals’ Alberta Petrochemicals Incentive Program (APIP).
“APIP has been doing exactly what it was designed to do, attract investment. And because it’s working, Alberta can look forward to thousands of construction jobs and hundreds of permanent positions through Dow’s investment,” Smith stated. “It is another step forward in expanding Alberta’s diversified energy economy as we do more with our resources and add value to them. And it’s further proof of our province’s determination to reach carbon-neutral status by 2050.”
The Dow project will be the first to access Canada’s new Investment Tax Credit (ITC) program. The Government of Canada stated that Dow will be supported by upwards of $400 million from Canada’s ITC program for the implementation of new clean technologies at the Fort Saskatchewan facility, including its carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) technology; and enhancements in its operations to produce clean hydrogen, which will be used as a clean fuel supply for the site’s furnaces.
“When we announced our major investment tax credits – a pillar of our government’s economic plan – we said that they would attract new investment and create great careers for Canadians. With hundreds of new Canadian jobs on the way, today’s investment by Dow in Fort Saskatchewan is proof that our economic plan is delivering for Canadians,” stated Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of Finance Chrystia Freeland.
The Government of Canada and Dow stated the combined technologies will reduce emissions by approximately 1 million metric tonnes of CO2e per year by converting hydrogen from cracker off-gas as a clean fuel as well as CO2 capture and storage.
Dow stated that its investment leverages approximately $2 billion of investment from third-party companies for circular hydrogen, CO2 capture, and other infrastructure assets critical to the project execution.
Multiple suppliers have already been selected for the massive project. Linde has been selected as Dow’s industrial gas partner for the supply of clean hydrogen and nitrogen for the site, and Fluor was selected for front-end engineering and design. Dow stated that it is also partnering with Wolf Midstream to provide CO2 transportation along the Alberta trunk line, and with Ravago, which will provide third-party logistics for finished products from the site.
“This project will have a profound positive impact on our employees and the community, creating jobs and economic opportunity while positioning the region to be a leader in low emissions manufacturing,” stated Diego Ordonez, Dow Canada President. “Our collaboration with government officials, the community of Fort Saskatchewan, our Indigenous neighbors, and the host of partner companies involved has been key to enabling this investment to move forward.”
Dow www.dow.com

with industry thought leaders whose shared goal is to promote gender equity, diversity and inclusion in Canadian manufacturing.
MARCH 6, 2024
https://www.automationmag.com/virtual-events/women-in-manufacturing-2024/





AutomationDirect has added the new AchieVe series of inductive proximity sensors which offers great value for general industrial applications. These tubular inductive proximity sensors made from stainless steel are offered in 8-mm, 12-mm, and 18-mm barrel sizes. Flush and non-flush mount styles offer a range of sensing distances up to 8mm. Both PNP and NPN logic models are available, and all have an N.O. output. Connection options include an M12 Q/D connector for 12-mm and 18-mm models; an M8 Q/D connector for 8-mm models; and a 2-metre pigtail cable style available for select PNP logic models. AutomationDirect
system without electromagnetic interference or noise interrupting the signal and operation of associated equipment.

NewTek offers heavy duty, industrial shielded cable with resistance to noise, vibration, moisture and spills. Available in custom lengths up to 100 feet, cables that carry a 4-20 mA signal are less vulnerable to outside movement and noisy environments typical of packaging and assembly lines. Users can also use their own cable assemblies in lengths up to 1,000 feet or more. The sensor can be placed on the manufacturing floor with cable running to the control room to provide output. Factory-made for a connector to plug directly into the LVDT, cable assemblies can be quickly connected and disconnected for installation, maintenance, or refurbishment. One end of the cable assembly is the mating plug with a rugged shell. The cable terminates with flying leads that are easily connected to a PLC, signal processing equipment, or an LVDT signal conditioner.

KROHNE, Inc. recently launched its OPTIMASS 6000, OPTIMASS 7000, OPTIMASS 1000, and OPTIMASS 2000 Coriolis mass flow sensors with the latest version of the compact or field-mounted MFC 400 converters. OPTIMASS flowmeters are designed to provide highly accurate mass, volume flow, and temperature measurement of liquids and gases, as well as density, and concentration measurement for liquids. The sensor design results in a lower pressure drop, which translates into energy savings and possible reduced meter sizes. These flowmeters maintain operation over a wide range of gas volume fractions, even up to 100 per cent with Entrained Gas Management (EGM), as a unique standard feature in each and every OPTIMASS. This permits the meter to operate in the presence of complex multiphase flowing conditions. The OPTIMASS’ EGM capabilities maintains accurate and reliable measurement by withstanding the dynamic process conditions that might cause unexpected, entrained gas or liquids to come up in an otherwise homogeneous flow stream. The OPTIMASS sensors also feature crosstalk and vibration immunity that allows for their installation in extremely tight spaces with no impact on measurement, which is ideal for skid mounted systems. OPTIMASS Coriolis mass flowmeters allow secure wireless access via Bluetooth or remotely via HART in safety-related applications allowing for parameter changes or meter verification from a distance.
KROHNE, Inc.
https://cmp.krohne.com/coriolis/
NewTek Sensor Solutions offers its Hermetically Sealed 4-20mA sensors accept long cables for process control and factory automation applications when standard lengths cannot reach distant control rooms, signal conditioners, PLCs and/or data loggers. The robust analog 4-20mA current loop output enables the use of longer cables from a sensor to a control
NewTek Sensor Solutions www.newteksensors.com

ABB’s Sensi+ GLA533-NG model is a single, compact gas analyzer that detects simultaneously multiple gas contaminants in real time in complex and time-varying natural gas streams. It provides continuous measurements of hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), carbon dioxide (CO₂), and water (H₂O), which represent both a safety and a pipeline integrity risk. This natural gas contaminants analyzer uses a unique tunable diode laser (TDL) technology called Off-Axis Integrated Cavity Output Spectroscopy (OA-ICOS). This natural gas technical analysis provides accurate measurement and facilitates fast response time for quick actions to process upsets. Sensi+ is an essential tool for natural gas measurement for custody transfer, tariff compliance, and process monitoring. Moreover, it also protects natural gas pipelines, storage facilities, and other mission-critical assets.
ABB
https://new.abb.com/ca

For decades, the food and beverage industry’s been looking for a food safe, in-line pH sensor that withstands cleaning processes. The InPro X1 provides exactly this while meeting all major regulations for food contact applications. The risk of glass contaminating products has meant that food and beverage companies have not been able to use in-line, glass pH sensors in critical processes, despite the huge benefits that real-time monitoring brings. The InPro X1 with its unique X-Chip technology has solved this problem. The X-Chip is a solid pH sensing element with very high mechanical resistance. It uses the same potentiometric measurement princi-

ple as the pH-sensitive glass used in pH sensors, but unlike traditional sensors, the X-Chip is extremely robust and cannot shatter. Additionally, the InPro X1 HLS offers fast response times, tolerates CIP without sacrificing accuracy or sensor lifetime and the ISM technology in the sensor predicts when maintenance and replacement should be performed.
www.mt.com

In a tank gauging system, a tank’s content volume is measured with multiple temperature sensors mounted throughout the tank, in often hard-to-reach locations and may require very low temperature calibration. Distributors use these measurements to determine the value of their product (often petrochemical) and establish a pricing structure. Precise measurements are critical to maintain an accurate record of inventory, and protect a company’s bottom line. The portable RTC-157 temperature calibrator is easy to transport and can cool down to -45°C. The RTC Series provide precision temperature calibration of sensors through an innovative active dual-zone heating technology. Then, to bring active dual-zone technology to an even higher level, JOFRA has developed the patented DLC system, making it possible to perform top calibration specifications without being affected by the actual load: for example, many or very big sensors. Cameron Instruments www.cameroninstruments.com

Hygienic design is a set of principles and standards that reduce the risk of food safety issues. The most important factor is that the equipment is easily cleaned. Rechner sensors traces the contact materials used in each sensor from raw to the final sensor serial number. The company’s PEEK material is a food contact safe, FDA-approved material (FDA 21 CFR 177.2415). During production, special gloves are used to handle all sensors that are to be used in hygienic applications. A product contact surface roughness smoother than 0.8 Ra is required for all hygienic designs, EHEDG Certification, and EHEDG Conformance. The mounting connection is important. A hygienic process connection will seal on the sensor and leave no crevice for bacteria to collect and grow. The sensor creates an aseptic seal where the beveled edge of the sensor meets the metal edge of the mounting adaptor. Rechner Automation has 13 sensor models to choose from.
Rechner Automation Inc. www.rechner.com

Endress+Hauser has endowed a new generation of Micropilot 80 GHz radar sensors with a range of capabilities and features that make each instrument easy to locate, install, commission and monitor so as to adapt to each customer’s unique operating conditions. This new generation – comprising the Micropilot FMR60B, FMR62B, FMR63B, FMR66B and FMR67B – is designed to meet challenges such as measuring points that are difficult to access or dusty environments. Thanks to the new Micropilot’s compact design, it can be used in confined installation situations. Suitable versions are available for challenging process conditions such as aggressive media or extreme process temperatures. The measurement performance of the Micropilot’s new radar chip combined with the smart Heartbeat Technology monitoring function helps to increase productivity and avoid unscheduled downtime. The new Micropilot meets all safety requirements. It has been developed in accordance with IEC 61508 using Endress+Hauser’s 20 years of SIL expertise and can therefore be used in SIL2 or SIL3 applications, for example, with homogeneous redundancy. Endress + Hauser www.ca.endress.com


Moore Industries-International, Inc. is your one-stop shop for temperature solutions with ready-to-install temperature assemblies. They include temperature transmitters; the unique “WORM” flexible and straight RTD and thermocouple sensors; general, hazardous area and explosion-proof/flameproof connection heads and enclosures; thermowells, flanges and fittings. The WORM Flexible RTD and Thermocouple Sensors are the standard for the company’s temperature assemblies. Unlike conventional sensors, such as straight sensors, the WORM’s flexible design allows it to slide right through the connection head port easily, and into the assembly, without removing any assembly components. The WORM Flexible Sensor Kits are field-cuttable and work in new and retrofit applications, replacing restrictive straight sensor probes allowing you to stock one sensor for multiple thermowell lengths and configurations. The WORM flexible sensors also boast faster response times and less susceptibility to in-process vibration damage due to its lower overall mass. See The WORM whitepaper at www.miinet.com/WORM-WP. Moore Industries-International www.miinet.com

By Bob Myles
Safety procedures, methods and designs are not novel concepts for the industrial manufacturing sector. In fact, layers of protection were put in place to protect personnel in manufacturing facilities dating back to the industrial revolution.
Today, industrial process and manufacturing companies have predominately adopted and settled on a common safety standard: IEC 61511 Functional Safety - Safety Instrumented Systems for the Process Industry Sector. This lifecycle guidance provides details on the analysis, design, operation and even decommissioning of the
safety system by the organization. And of course, implementation of IEC 61511 cannot be accomplished without referencing the parent standard IEC 61508: Functional Safety of Electrical/Electronic/Programmable Electronic Safety-related Systems.
At the heart of the IEC 61511 standard is the SIS or Safety Instrumented System, which is implemented to mitigate and prevent unacceptable risk by an organization to protect its personnel, facility and/or surrounding community and environment. Each SIS is made up of one or more SIFs, or Safety Instrumented Functions that bring a process or loop to a desired safe state. The basic elements of a SIF
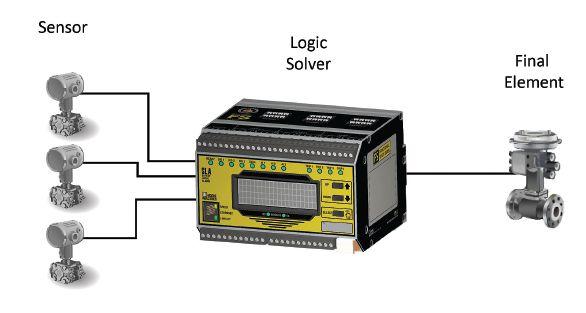
are the sensor, logic solver and final element. The sensor monitors the process and transmits that information to a logic solver where in turn that data is compared against predetermined settings to determine whether the final element should be adjusted, activated or engaged (Figure 1).
Of the three main components typically contained in the SIF, the logic solver is the most critical. The logic solver is responsible for determining whether dangerous conditions have been met and is responsible for the final element’s ultimate effect on the mitigation function or strategy.
Two types of products have become widely accepted tools in implementing the logic solver component in Functional Safety applications. They are the Programmable Logic Controller, or Safety PLC, and the Single Loop Logic Solver. The Safety PLC, which is the generic name given to larger point count logic solvers, offers much more flexibility but does so at a significantly higher price and with greater complexity, while the Single Loop Logic Solver is more

limited in its capability but can adequately reduce risks and meet safety system requirements with less expense and complexity.
Safety PLCs certainly fill key requirements within Functional Safety. Large point and loop counts. Safety PLCs are very capable but come with an extremely high price tag and often require sophisticated programming, maintenance and documentation.
Conversely, there is the fully capable but smaller Single Loop Logic Solver that handles one loop and just a few points. Like Safety PLCs these are often IEC 61508 certified but have a much smaller footprint and cost far less than Safety PLCs. Additionally, the programming is less complicated and does not require any software licensing.
This is where the logic solver gap lies– functionality, complexity, and cost between these two types of logic solver options are vast (Figure 2). While each certainly has its place, many Functional Safety applications require just two loops, or three loops with six inputs and six outputs and perhaps some simple 1oo2 or 2oo3 voting or math. The Safety PLC could certainly handle this, but is it overkill? Alternative-
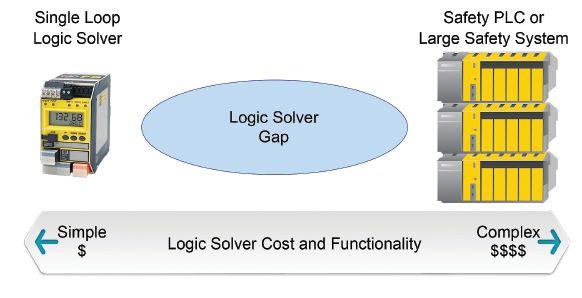
ly, Single Loop Logic solvers might be able to handle this with output relay wiring for voting, but point counts are limited and voting architectures can become convoluted with relay inter-wiring. What is needed to fill this gap is a less expensive, less complex, multipoint, voting capable and IEC 61508 certified logic solver that allows safety practitioners an option that meets the functionality below that of the Safety PLC but above the capabilities of the Single Loop Logic Solver. Recently the marketplace has borne a few multichannel and multiloop logic solvers that fall squarely into this gap. These midsize, certified logic solvers offer plenty of capability with smaller point counts and far less programming overhead.
Safety Instrumented Functions (SIF) are designed to achieve or maintain a safe state for a specific hazardous event within a process. Each SIF provides a defined level of risk reduction represented by its Safety Integrity Level (SIL), with SIL 4 having the highest level of safety integrity and SIL 1 the lowest. Any device used in the SIF for a specific SIL level requirement must be properly evaluated to ensure that it has the suitable proven in-use history or calculated safety data such as failures and rates, Safety Failure Fraction (SFF), Probability of Failure on Demand (PFDavg), Systematic Capability (SC), etc. associated with it, typically outlined in the equipment manufacturer’s Failure Modes Effects and Diagnostic Analysis (FMEDA) report or safety certificate.
The selection of a logic solver in an SIF most often falls into one
of three categories: device chosen due to proven in-use history (individual components or whole device itself), device comes with published failure data such as a FMEDA report from the manufacturer, or device was manufactured in full compliance with IEC 61508 and has third party approval, along with accompanying FMEDA report and certificate.
While proven in-use data is certainly an acceptable means of documenting a device’s capability and effectiveness to assist in a SIF, end users often find it extremely difficult or next to impossible to put their hands on such historical performance per device, especially for logic solvers. Utilizing failure data from the manufacturer’s report is certainly less burdensome, but for Type B devices which include most currently available logic solvers, this failure data does not cover the unknown systemic failures that can occur within software/firmware. Therefore, most safety practitioners have more confidence in and find it much more cost-effective to acquire products that were designed and manufactured in compliance with the IEC 61508 standard and have third-party approval. In addition, safety devices that are fully compliant with IEC 61508 further address and resolve systematic faults of the device through a full assessment of fault avoidance and fault control measures during hardware and software development.
As mentioned prior and illustrated in Figure 2, the pricing and capabilities for different types of logic solvers can vary widely. This not only pertains to the initial expense
of purchase, but also for the implementation of and life cycle costs in maintenance and programming. The most common determining factors in choosing which logic solver best fits a safety application are loop and point counts, communication requirements, and the complexity of logic required for safety mitigation.
When dealing with high-density point and loop counts in a centralized location where there is interdependency on various points and loops, a larger more complex logic solver such as a safety PLC may be the best choice. Larger systems like these more easily afford themselves to more complex control logic and voting schemes with high reliability across a multitude of loops with several points. If points are not centralized, many of these larger safety systems can be networked together for flexibility in cross-communication, as well as for future expansion. The tradeoff is that the initial costs of purchase, programming, and installation for a larger safety system or PLC can be very expensive— twenty-five thousand dollars or much more, not to mention the high lifecycle costs.
For scenarios where only one or a few points need to be monitored in a single SIF loop, a much less expensive and complex Single Loop Logic Solver can be a very effective choice. An example for this type of application would be simple on/off functionality for pump/valve control when filling, emptying, or preventing overflow in a container or tank. In fact, Single Loop Logic Solvers, also known as Alarm Trips, have made significant strides in their capabilities since they were first installed in SIS

applications. These advanced capabilities include programmable inputs, local configuration using on-board controls, safe password protection, process display and comprehensive internal, input and sensor diagnostics. Standalone Single Loop Logic Solvers are of course less expensive and easy to program but are quite limited in their ability to handle multiple loops, accept multiple inputs, perform logic or internal voting, or provide digital communication with a BPCS (Basic Process Control System) or host system.
In the wide space that exists for applications that require higher density loop/point counts with more advanced logic and loop monitoring of only a few points, a Multiloop Logic Solver may be a more effective and better-sized fit for many SIFs (Figure 3). Like the larger safety systems and PLCs, the standalone Multiloop Safety Logic Solver can accept multiple I/O points, handle one to three loops, performs logic and math equations, and offers significant flexibility for voting architectures at a fraction of the cost and complexity of larger safety systems and PLCs. Multiloop Logic Solvers typically harness the cost and configuration simplicity of Single Loop Logic Solvers, but also offer much of the advanced functionality of the larger safety systems and PLCs, albeit at smaller loop and point counts.
Another consideration when selecting a logic solver is whether you need to purchase custom or licensed software and how easily it can be programmed to meet your SIS requirements. Many safety PLCs and larger safety systems
offer their own proprietary software but often come with lofty initial price tags, annual licensing requirements or both. Alternatively, today’s marketplace includes very capable single and multiloop logic solvers with license-free and powerful programming software, including FDT (Field Device Technology) compliant interfaces.
The rigor of programming and long-term maintenance should always be a key consideration when choosing a suitable logic solver. To implement logic routines in these safety systems will require someone with significant knowledge of the programming language being used, whether it be ladder logic, function block diagram or structured text. This creates the need for programming expertise and adds additional time and expense to day-to-day operations and long-term maintenance of your safety solution.
Depending on the requirements of your safety system, single or multiloop logic solvers usually offer much more straightforward programming options with easy-to-understand dropdown menus, check boxes, radio buttons, pre-built common control functions and math equation generation utilizing Excel-like formulas. While these smaller logic solvers are not quite as elaborate and may be limited on their I/O count, you may be surprised to
find out how powerful but easy to program these logic solvers have become (Figure 5).
With the growing need for SIS logic solvers to communicate with a BPCS and higher-level monitoring systems, the ability to communicate via open and widely supported protocols is paramount. Proprietary communication protocols may offer tighter integration when equipment is designed and manufactured by the same supplier, but seldom are the SIS logic solver and basic process control systems available from the same company.
Just as HART has become the de-facto digital communication method for lower (or floor) level field devices, many major industrial instrumentation and automation equipment vendors offer MODBUS as their preferred protocol for communication with ancillary control and monitoring systems. Like HART, MODBUS is the most ubiquitous and open industrial communication protocol that can run over virtually all communication media including twisted pair wires, wireless, fiber optics, Ethernet, cellular and satellite networks.
MODBUS/TCP, MODBUS RTU and several other proprietary industrial communication protocols support read and write
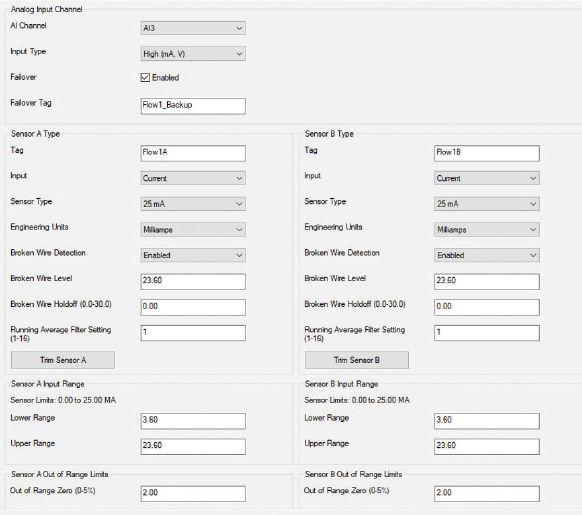
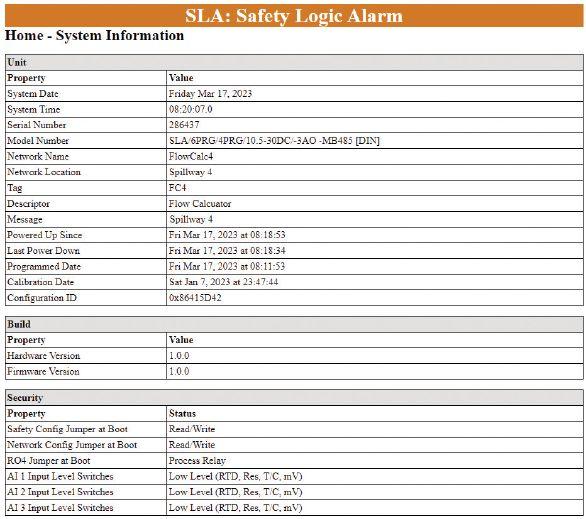
commands. However, since logic solvers are typically the last line of defense, safety practitioners should strongly review whether allowing write access to the logic solver from a remotely connected host, or potentially unauthorized device is warranted or safe. If remote communication is required, consider choosing a logic solver that allows just “read-only” access over the industrial protocol. This still allows access to the logic solver’s process data and internal variables but prevents unauthorized access to setpoints, outputs and other critical safety parameters.
Some newer logic solvers may provide access to variables and other key parameters via a simple web browser, which can be a convenient feature (Figure 7). However, when using a web browser to access a logic solver, it is extremely important that the logic solver’s embedded web server serves up read-only data. This eliminates unwarranted changes being made to the logic solver’s safety parameters and variables.
Today’s logic solvers come in many different shapes and sizes with a wide range of capabilities. The fundamental requirements of your Safety Instrumented System will ultimately determine what type of SIS logic solver best fits your needs. Large safety PLCs are not necessari-

ly a requirement, or they could be only a part of the total SIS solution. Your final implementation may be a hybrid of a full-blown safety PLC and standalone multiloop capable logic solvers strategically dispersed to best meet the requirements for your safety applications, as well as fit your budget. Paramount for all types of logic solvers are key performance attributes such as ambient operating temperature, isolation protection, operating power and noise immunity which should always be carefully reviewed. Whatever you decide, choosing a logic solver that has full third-party approval to the IEC 61508:2010 standard can save you significant time and money and will also give you the confidence that you’ll meet the SIL requirements for your SIFs that are part of your SIS.
Bob Myles is director of engineering for Moore Industries International. He is an exida-certified Functional Safety Practitioner (FSP) with nearly 40 years of experience in development of safetycritical systems for commercial aerospace (DO-178C/ DO-254/ ARP4761/ARP4754), military (DO-160), and process monitoring industries (IEC-61508). Moore IndustriesInternational www.miinet.com
By Del Williams
To provide food processors with insight into the industry’s current challenges and opportunities, Cablevey Conveyors, a global specialty conveyor manufacturer, and Automated Handling Solutions, a service-focused subsidiary of Cablevey, have released results from an annual proprietary survey conducted among food processing companies.
The report, The Food and Beverage Industry 2023 State of Conveying, highlights the latest market trends as well as top concerns and objectives related to conveying systems. The findings reveal the predominant obstacles now facing the industry, along with the promise of innovative conveyor automation and product testing options that can help to optimize both production and future purchases.
In modern food processing plants, the art of conveying foods has evolved into a finely tuned process that prioritizes efficiency, hygiene, and safety. For processors, the report now provides trend analysis and new findings not only about the industry but also about how organizations are specifically conveying food products in their facilities.
“As food processing continually embraces innovation, industry professionals are committed to making the best decisions possible for their specific conveying needs. To make those decisions, the industry needs data. This report builds on the data and findings from 2022 to provide food processors with the new and updated data they need to make the best decisions moving forward,” says Brad Sterner, Cablevey CEO.
Cablevey contracted with independent outside research firm Ascend2 to reach more than 320 professionals at food processing firms, including production managers, engineers, and executive managers. These individuals work in the food manufacturing and processing industry in the U.S., U.K., Mexico, and Brazil. The responses were collected in July 2023.
The most prevalent product categories conveyed in the processing facilities surveyed included frozen food (49%), snack foods (39%), blends and mixes (37%), breakfast cereal (30%), coffee (26%), and nuts (23%), as well as rice, powders, pet foods, specialty seeds and beans, specialty and brewery grains, hemp, and other products.
The good news is that the food processing industry is rapidly growing. Almost two-thirds of respondents’ companies grew at least 10% in

the past year, and almost one-quarter grew at least 20%. This mirrors the growth from 2022 and indicates a long-term trend for the industry.
However, the cleaning and maintenance of food process conveyor systems is still a major concern for the industry. Over half (54%) of survey respondents cited cleaning and maintenance as the primary challenge related to conveyors.
In fact, more than two-thirds (69%) of those surveyed clean their conveying systems three or more times per week, and 38% clean their systems four or more times per week. For 31% of those surveyed, this process takes more than 2 hours, and for another 60% the process takes 1 – 2 hours. Related to cleaning and maintenance, downtime was the next greatest challenge at 33% (up from 28% last year).
Nearly all (97%) of those surveyed agree that they would benefit from finding a more efficient way to clean their conveying systems. Most (79%) move multiple products through their system that make cleaning necessary.
For those requiring greater efficiency, innovative solutions can now automate the conveyor wet cleaning process, eliminating most manual labor while reducing downtime and the risk of improper cleaning. Due to their need, many respondents (61%) have shopped for or purchased a new conveyor system in the last year. 82% plan to update or replace parts of their conveying systems in the next two years. Of those surveyed, virtually all (98%) agree that testing products on a new conveying system is a critical step to take before purchase, with 67% strongly agreeing.
Research firm Ascend2 also used the survey data to rank seven types of conveyors (roundlink chain conveyors, cable conveyors, pneumatic conveyors, bucket elevators, vacuum conveyors, aero mechanical conveyors, screw augers) based on maintaining product integrity, energy

and efficiency, maintenance and downtime, and accommodating facility requirements.
Cable conveyors ranked top in each category, followed by pneumatic conveyors, bucket elevators, and round-link chain conveyors in that order. Tubular drag cable conveyors gently move product through a sealed tube using a coated, flexible stainless-steel drag cable pulled through on a loop. Solid circular discs (flights) are attached to the cable, which push the product through the tube without the use of air. These conveyors excel in transporting delicate, precise blends for a wide variety of food types in versatile layouts and configurations.
To help industry professionals make more informed purchasing decisions, the survey provides free conveyor evaluation tools. The study contains links to an ROI Calculator that estimates food processors’ savings based on minimizing their conveyor cleaning and maintenance. A link is also included in the report to a collection of white papers and guides that cover issues designed to improve conveyor reliability, performance, efficiency, and safety.
Food processors that keep abreast of the latest market trends, industry concerns, and objectives will make more effective strategic decisions. The report by Cablevey Conveyors and Automated Handling Solutions offers food processors key insights into important industry trends along with timely guidance about the benefits offered by innovative conveying systems. With this data, food processors can make informed decisions about their investments in production technology.
To access the full survey results, check out The Food and Beverage Industry 2023 State of Conveying at: https://cablevey.com/white-papers-and-guides/2023-state-of-conveying/.
Del Williams is a technical writer based in Torrance, Calif.
By Sinja Stentoft, Busch Vacuum Solutions
Production downtime is one of the biggest risks in the manufacturing industry. From equipment failures to shortages of raw materials, any production downtime can result in major losses in revenue and market share. There are two types of downtime: planned and unplanned.
Planned downtime is a scheduled shutdown of manufacturing equipment or processes to perform maintenance, inspections, repairs, upgrades or manufacturing setups. It is essential to plan downtime for maintenance to keep your equipment in its optimum condition and to avoid unplanned downtime. Although planned downtime interrupts your manufacturing process, you are still in control of productivity processes.
Unplanned downtime occurs when there is an unexpected shutdown or failure of your manufacturing equipment or process. It causes foodstuffs to spoil if they are not packaged, as well as expensive delays in production and delivery schedules. Additionally, when operations are unstable, it is more difficult to adhere to environmental regulations and comply with sustainability measures. This could result in an increase of environmental incidents.
Thus, preventing production downtime is key to ensuring productivity. Follow our seven tips to reduce machine downtime in your production line.
1. Develop a system for quickly identifying and resolving production issues

The system should gather and analyze data that gives insight into the equipment’s total maintenance requirements. Interpretation of the data can help your teams resolve production issues by carrying out preventive maintenance. The implementation of such a system allows factories cut down on time lost due to production issues and prevent costly unplanned downtime by alerting employees of possible upcoming equipment failures.
2. Use predictive analytics to identify potential problems before they occur
Predictive analytics detect patterns in real-time machine data that could lead to the onset of a
problem. Data analytics can inform you weeks in advance about which parts of a machine are likely to fail. This allows you to plan your maintenance schedules and order spare parts in advance, effectively reducing downtime and lessening the likelihood of issues reoccurring.
3. Implement a preventive maintenance program
Preventive maintenance programs are one of the most effective ways to minimize unplanned machine downtime. You can routinely collect valuable information about your equipment for a systematic maintenance approach. With the right targeted maintenance, you can react to predicted equipment failures or accidents before they occur. By reducing the possibility of unexpected downtime, your staff can focus on more profitable tasks.
4. Create a system for dealing with glitches and problems as they arise

Having a system that tracks and monitors glitches as they arise allows you to identify the root cause of an issue in your production line. This will enable you to understand how production failures occur and how to prevent them from happening again. This reduces unplanned machine downtime while increasing manufacturing efficiency.
5. Automate as many processes as possible to reduce human error Reduce downtime and make your production


process more efficient by automating repetitive and tedious tasks that are prone to human error. This will give your staff more time to focus on profitable tasks and develop their skill sets, which will translate into higher profits for your company and show your workforce that they are your most valuable resource.
6. Train operators on how to properly operate equipment

Training operators to properly use equipment can significantly reduce downtime in your manufacturing process. If operators know how to use equipment correctly, they are less likely to halt production and can respond faster in emergency situations. Proper training also prevents unplanned downtime caused by human error and decreases the risk of workplace accidents.

six tips too many? Then use tip 7 for an allin-one solution! Intelligent IoT solutions help reduce downtime by providing you with a system that quickly identifies and resolves production issues (tip 1). It tracks and monitors your equipment and process with predictive analytics, enabling you to create a maintenance schedule and order the necessary spare parts ahead of time (tip 2). Sensors and data analytics enable IoT to continuously track and monitor performance and process optimization data from your equipment. This gives you the opportunity to implement preventive maintenance (tip 3) and predict potential issues as they arise (tip 4), effectively lessening the frequency of planned or unplanned downtime. IoT also enables the automation of tasks, shortening the time it takes to complete them and ultimately boosting productivity and reducing human errors (tip 5). Thanks to its user-friendly tools, it is easy to learn how to operate IoT. Your workforce will be able to use it properly in no time (tip 6).
Busch Vacuum Systems
www.buschvacuum.com

Russelectric, A Siemens Business, manufactures UL-listed cogeneration systems for combined heat and power (CHP) applications in which the generator sets are run to serve the connected load and heat is also recovered for other uses. Designed and built for mission critical facilities such as healthcare, research and development and campus facilities, Russelectric cogeneration systems are designed to provide maximum protection for operators and maintenance personnel and to minimize the danger of operator error. All Russelectric cogeneration systems are UL listed, offer programmable logic controller (PLC) system controls, and are supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) capable. They feature utility/generator and other power assets paralleling control, and provide active synchronization and soft loading. Systems use a utility-approved interconnecting protective relay system. Russelectric cogeneration power control switchgear may have additional controls and monitoring to optimize heat recovery. The systems can be designed to operate in parallel with the utility to optimize power and heat balance. Russelectric www.siemens.com
conductivity. The induced voltage is picked up by two sensing electrodes which are in contact with the measuring agent and sent to the measuring amplifier. The flow rate is calculated based on the cross-sectional area of the pipe. The measurement does not depend on the process liquid and its properties such as density, viscosity and temperature. The two outputs can be independently set to switch, or provide an analog or frequency output. A batching function can also be selected, where output 1 is set to switch as NPN/PNP/PP and output 2 is set as the control input.
KOBOLD www.koboldusa.com


Emerson has announced the release of its Fisher FIELDVUE L2t Liquid Level Controller, designed primarily for use in the separators found at most oil and gas well sites. Compared to alternatives using electric on-off valves, the new Fisher controller makes it possible to save significant energy and maintenance costs by minimizing valve movement, and by simplifying the level measurement and control processes. Level control is critical for achieving the best performance in separators, which remove gas and water from incoming crude oil feeds. Traditional solutions typically use a level gauge and control valve in one control loop, with an oil/water interface level instrument and control valve in a second loop, and with each loop executed by a separate controller. This complex mix of multiple instruments and valves is typically powered by natural gas pressure, often resulting in continuous valve emissions. The L2t Liquid Level Controller addresses these and other issues by using a displacer to measure level and level interface, while executing a single loop control algorithm to drive an electrically-actuated control valve. Emerson www.emerson.com

The new KOBOLD MIS electromagnetic flowmeter was developed for measuring and monitoring medium-sized flow of conductive liquids in pipes. The electromagnetic measurement principle is as follows. According to Faraday’s Law of magnetic induction, a voltage is induced in a conductor moving through a magnetic field. The electrically conductive measuring agent acts as the moved conductor. The voltage induced in the measuring agent is proportional to the flow velocity and is therefore a value for the volumetric flow. The flowing media must have a minimum
Thomson Industries, Inc. has announced the availability of a rotating-nut stepper motor linear actuator (SMLA) with a rotary encoder as a standard option. Machine designers with applications requiring positional feedback can now specify the full line of SMLAs integrated with this enhancement. Thomson SMLAs use a stepper motor and lead screw shaft to translate rotary motion to linear motion for all three configurations: linear actuator, rotating screw and rotating nut. As machine designers are developing more complex applications requiring monitoring for speed, distance and position, the integration of encoders has been the most requested SMLA customization for Thomson. This strong demand led the company to offer encoders as a standard option for all three SMLA configurations. Thomson Industries www.thomsonlinear.com



PSG Biotech recently announced the availability of the new Quattroflow QB2-Standard (QB2-SD) Single-Use Precision Micropump. This model is the smallest size in the family of single-use, lightweight and compact rotary microdosing pumps designed for precision and can be used to transfer delicate biologics. The QB2-SD has a minimum resolution of 25 μl and flow rates up to 2.7 liters per hour (91.3 fluid ounces per hour), which makes the QB2-SD pump ideal for liquid-handling operations requiring precise and delicate dosing of products that can be found in cell and gene therapy, laboratory and small-scale upstream and downstream applications. The QB2-SD works on the positive displacement principle where fixed cavities of liquid are transferred from inlet to outlet around a rotor. This creates high vacuum levels of -0.6 bar (-9 psi) and exhibits back-pressure capabilities up to 0.2 bar (2.9 psi). Lightweight at 6.4 g (0.013 lb.), this single-use pump is highly compact at 38 mm wide (including barbs) and 30 mm high with a depth of only 17 mm, which offers a very low hold-up volume. This micropump features a bi-directional pumping motion, is compatible with gamma irradiation, and can handle viscosities up to 500 cP.
PSG Biotech
www.psgdover.com/biotech

HEMCO’s Acid Storage Cabinet is specifically designed for the storage of corrosive chemicals and is available in 12”, 18”, 24”, 30”, 36”, 42”, and 48” widths. Standard size is 35” high and 22” deep. The molded onepiece fiberglass liner inserts directly in the cabinet and is sealed on all edges for ease of cleaning. Interior features a containment lip, on the front bottom edge to hold spills. The front access doors have air inlet vents, are lined, and the edges are sealed. No metal is exposed to corrosive vapors. Shelf is removable for smaller container storage.
HEMCO
www.HEMCOcorp.com




















