







Get access to animated learning videos, interactive quizzes, projects and more — all on the Uolo Learn app!


Melanie Grobler is a seasoned education professional with experience spanning over three decades in the field of ELT curriculum development and assessment. She has worked in senior advisory positions in India for 10 years and has developed several K-8 ELT products. In South Africa, she served as national examiner for the Class 12 Exit Examination and worked as a teacher, college and university lecturer and subject advisor.

Chandani Goyal is an English Language Teaching (ELT) educator with over 9 years of experience in renowned schools like Heritage Xperiential Learning School, Ahlcon International School and Amity International School. She is also a published author of articles on classroom intervention and pedagogy. She brings a deep understanding of methodology and approaches to language learning into the compilation of this book, enhancing its effectiveness for educators and learners alike.
Academic Authors: Melanie Grobler, Kashika Parnami, Simran Singh, Arpit Agarwal, Simran Nagpal
Book Production: Rakesh Kumar Singh, Tauheed Danish
Project Lead: Chandani Goyal
VP, Learning: Abhishek Bhatnagar
All products and brand names used in this book are trademarks, registered trademarks or trade names of their respective owners.
© Uolo EdTech Private Limited
First edition 2026
This book is sold subject to the condition that it shall not by way of trade or otherwise, be lent, resold, hired out, or otherwise circulated without the publisher’s prior written consent in any form of binding or cover other than that in which it is published and without a similar condition including this condition being imposed on the subsequent purchaser and without limiting the rights under copyright reserved above, no part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in or introduced into a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of both the copyright owner and the above-mentioned publisher of this book.
Book Title: Ignite English Grammar Book 3
ISBN: 978-81-992630-9-3
Published by Uolo EdTech Private Limited
Corporate Office Address:
91Springboard, 3rd Floor
145, Sector 44, Gurugram, Haryana 122003
CIN: U74999DL2017PTC322986
Printed by: Saurabh Printers Pvt Ltd
Illustrations and images: www.shutterstock.com, www.stock.adobe.com and www.freepik.com
All suggested use of the internet should be under adult supervision.

In today’s connected world, the ability to use language effectively is more than just a skill—it is a key to meaningful communication, personal expression and academic and professional success. While vocabulary and comprehension form the foundation of language acquisition, it is grammar that gives structure to thought and clarity to expression. However, grammar is best understood—not by memorising rules—but by using it in real situations. When learners experience grammar in context, they are able to apply what they have learnt in their speaking and writing.
Ignite Grammar series is based on the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 and the National Curriculum Framework (NCF) 2022–23. The programme reimagines how children engage with grammar. It shifts away from decontextualised drills and mechanical exercises to an approach that is contextualised, discovery-driven and embedded in real-life communication. Learners are encouraged to notice patterns in language, infer rules and apply them meaningfully across functional tasks.
This approach not only builds a natural understanding of language and communicative competence but also aligns with the NEP’s vision of nurturing 21st-century skills—critical thinking, creativity, collaboration and effective communication. By providing learners with contexts that are familiar, age-appropriate and socially relevant, Ignite Grammar series supports learners in becoming confident, expressive and skilled communicators.
In keeping with the NEP 2020 and NCF 2022–23, the programme integrates different dimensions of learning that enrich the learners’ overall growth—such as emotional well-being (SEL), cultural rootedness, artistic expression and awareness of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). These perspectives ensure that grammar is not learnt in a vacuum, but as part of a broader journey that prepares children to think ethically, collaborate meaningfully, appreciate their heritage and engage actively with the world around them.
Designed with the diverse classroom realities across India in mind, the programme is inclusive and easy to implement. Learners are supported with visual cues and scaffolded learning tasks to ensure that grammar instruction remains purposeful, engaging and accessible. The package comes with digital content, provided free of cost, to ensure a seamless and holistic learning experience for children.
Above all, this grammar series is grounded in the belief that language learning is a lived experience. Grammar is not a set of rules to be remembered—it is a way of making meaning, a toolkit for expressing ideas clearly and creatively.
We extend our warmest wishes to educators, parents and learners as they embark on this journey. May it be filled with enjoyment, exploration, expression and empowerment.
The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, introduced by the Government of India, represents a transformative shift in the country’s education system. It focusses on building conceptual understanding, skills, values and competencies that align with the demands of the 21st century, while also preserving India’s rich cultural heritage. UOLO is committed to actualising the vision of NEP 2020 by meticulously adhering to its outlined recommendations.











1. Language skills building
2. 21st-century skills, values and dispositions
3. Creative and critical thinking
4. Application in real life

5. Holistic and integrated learning
6. Learning by doing
7. Enjoyment and engagement
8. Collaboration and exploration
9. Technology–based solutions
10. Knowledge of India
11. Assessment of, as and for learning
CompetencyBased Education
NEP Pages 12, 17, 22
Teaching and Learning Pedagogy
NEP Pages 3, 11, 12, 27
National Pride
NEP Pages 15, 16, 43
Assessments
NEP Pages 12, 18, 22

The National Education Policy (NEP) outlines essential skills, values, dispositions and learning approaches necessary for learners to thrive in the 21st century. Ignite Grammar series incorporates these elements throughout. Referred to as ‘NEP Tags’, they are defined as follows:



INTEGRATED

Bringing creativity and fun into learning by combining music, drama and art with other subjects
Using physical activities, sports and games to make learning active and fun
Cross-curricular and skills linkages to make the learning experience more holistic, joyful and meaningful
Texts and tasks are rooted in the Indian context and culture to develop a sense of national pride

TEAMWORK

SDG
SEL

HANDS-ON
Embracing the spirit of mutual collaboration and cooperation while working together or engaging in a guided conversation
Unwavering commitment to generating awareness of a green, peaceful, prosperous, equitable and inclusive world
Developing the skills to understand and manage emotions, build positive relationships and make responsible choices
Engaging actively in hands-on experiences to acquire knowledge and skills
HOTS
Tasks encourage higher-order skills such as analysing, evaluating, problem-solving and fostering deep understanding

Learning Outcome Learners will be able to:
Self-Assessment
• identify common, proper, collective, countable, uncountable, singular and plural nouns.
• apply understanding of these noun types in reading and writing tasks.
• use apostrophe ’s to show belonging in age-appropriate contexts.
• distinguish between nouns that show male, female or have no gender.
• use a and an correctly with words beginning with vowel and consonant sounds.
• use the with proper nouns such as the names of rivers, mountains, well-known buildings, trains and ships.
• identify pronouns as words that replace nouns and use them correctly in context.
• distinguish between personal and possessive pronouns and apply them appropriately.
• r ecognise that every sentence contains a verb –an action verb, a verb of being ( is , are , am ) or a verb showing belonging ( have / has ).
• use these verbs appropriately in simple contexts. Review Test 1
• identify describing words as adjectives and understand how they indicate quality or quantity.
• identify words that give more information about verbs as adverbs.
Verbs in a Sentence
• use adjectives to compare nouns using -er and -est . 7 Adverbs
• use adverbs in appropriate contexts.
• use pr epositions that indicate position and time correctly in sentences.
• use prepositions of time and place in familiar and new contexts.
• identify conjunctions as linking words and use them to connect words or ideas in sentences.
• differentiate between and , or , but , so and because in meaning and use.
• identify and use interjections such as Oh! , Wow! , Yay! , Aha! , What! , Oh no! and Hurrah! in sentences.
• capitalise and punctuate interjections correctly in context.
Review Test 2
• differentiate between can , cannot , should and shouldn’t .
• use these modal verbs correctly in context.
• recognise sentences as groups of words that have meaning, and structure them correctly.
• identify subject and predicate in sentences.
• form Yes/No questions and understand changes in word order.
• use do , does , did and question words ( who , what , where , which , when , how and what ) correctly in context.
• use capital letters, full stops, question marks and exclamation marks correctly.
• use apostrophes for belonging and contractions and commas in lists and yes/no questions.
• use is , are and am in the simple present tense to talk about what or who something is.
• apply subject–verb agreement rules in the simple present tense.
Review Test 3
8 Prepositions
9 Conjunctions
10 Interjections
11 Can, Cannot, Should, Shouldn’t
12 Sentences
13 Questions
14 Punctuation
15 Is, Are, Am
• use was and were in the simple past tense to describe how or what something was.
• apply basic subject-verb agreement rules in the past tense.

Was, Were
16
• use has , have and had to describe belonging in the present and past tense.
• apply subject-verb agreement rules with these verbs in different contexts.
• identify time words such as every day , usually , sometimes and never and use the simple present tense correctly.
• form negatives and questions using is , are , am , do and does
• identify time words such as now , at the moment and busy and use the present continuous tense correctly.
• form negatives and questions in the present continuous tense.
• identify time words such as yesterday , last year and a week ago and use the simple past tense correctly in context.
• describe actions that were continuing at a specific time in the past and use the past continuous tense correctly.
• identify time words such as tomorrow and next week and use the simple future tense correctly.
• describe actions that will take place in the future. Review Test 4
• identify basic functions of prefixes and suffixes to create new words.
• use common prefixes ( -un , -re ) and suffixes ( -ess , -ful , -less , -ness , -ly , -ors ) correctly.
• identify common synonyms and antonyms in contexts.
• use synonyms and antonyms appropriately to show meaning in sentences.
• use homophones correctly in sentences to show meaning.
• identify and use homonyms correctly in different contexts.
• recognise and use common compound words in appropriate contexts.
• create new compound words through guided activities.
• identify phrasal verbs in contexts.
• use common phrasal verbs in speaking and writing.
17 Has, Have, Had
18 Simple Present Tense
Present Continuous Tense
19
20 Simple Past and Past Continuous Tense
21 Simple Future Tense
Vocabulary 1: Roots, Prefixes and Suffixes
Vocabulary 2: Synonyms and Antonyms
Vocabulary 3: Homophones and Homonyms
Vocabulary 4: Compound Words
Vocabulary 5: Phrasal Verbs
Reading Comprehension–1
Reading Comprehension–2
Reading Comprehension–3
Reading Comprehension–4
• write a story based on a picture.
• organise ideas into a clear beginning, middle and end.
• write a short paragraph on a topic with given prompts.
• use correct sentence structure to express ideas.
• complete or write a simple invitation for an event.
• include all key details clearly.
• write a diary entry about a personal experience.
• use prompts to structure ideas clearly.
• write a simple informal letter using prompts.
• organise ideas in the correct format.
Writing 1: Picture Composition
Writing 2: Paragraph Writing
Writing 3: Invitation
Writing 4: Diary Entry
Writing 5: Informal Letter

Set
Look at the picture and read the story.








We cannot/can’t
Look at the picture and read the story.















Look at the picture and read the story.

It is a warm afternoon. Rajni and her three children are having a picnic at the river. They have four apples, two bananas and three sandwiches to eat. She also brought water and a bowl of rice to share. The children are excited. They love eating outside.
Think about and discuss these questions.
1. How many children are there in the picture?
2. Name the things that you can count.
Note: We use may to ask for permission Sir, may I please leave the Should and Should Not Should and should not are
Get Set: A short and engaging warm-up to spark observation and set the context for learning to support the grammar concept
We should not/shouldn’t feed You should put your litter in We should sit on a mat at the
Guided prompts to help learners reflect, observe and prepare for concept discovery
3. Name the things that you cannot count.
Chapter 3 • Countable and Uncountable Naming Words
How It Works: Concept explanation through relatable examples and visuals that show grammar in use

Can and Cannot
These are used to talk about what someone/something is able/not able to do
For example:
How It Works
Can and Cannot
These are used to talk about what someone/something is able/not able to do
Note: The short form of cannot The short form of should Cannot is one word but should
These are used to ask for/refuse permission in an informal situation
For example: Mom, can I go to the zoo?
I can see the birds in the tree. Grandma can make snacks. We cannot/can’t travel together.
Ask your dad if you can go. Dad says I cannot/can’t go.
It is a warm afternoon. Rajni and her three children are having a picnic at the river. They have four apples, two bananas and three sandwiches to eat. She also brought water and a bowl of rice to share. The children are excited. They love eating outside.
It is a warm afternoon. Rajni and her three children are having a picnic at the river. They have four apples, two bananas and three sandwiches to eat. She also brought water and a bowl of rice to share. The children are excited. They love eating outside.
Think about and discuss these questions.
1. How many children are there in the picture?
Fun with Grammar: Interactive activity/game that enables learners to explore grammar through hands-on play and real-time collaboration
Think about and discuss these questions.
1. How many children are there in the picture?
2. Name the things that you can count.
3. Name the things that you cannot count.
Time

2. Name the things that you can count.
3. Name the things that you cannot count.
Note: We use may to ask for permission in a formal situation. Sir, may I please leave the room?
Should and Should Not
For example: I can see the birds in the tree. Grandma can make snacks. We cannot/can’t travel together.

Should and should not are used to give advice or say what is right or wrong We should not/shouldn’t feed the animals. You should put your litter in the garbage can. We should sit on a mat at the picnic.
Note: We use may to ask for permission in a formal situation. Sir, may I please leave the room?
Should and Should Not
Chapter 3 • Countable and Uncountable Naming Words
NEP Tags: To showcase alignment with NEP skills and values
SEL
Should and should not are used to We should not/ You should put your litter in the garbage can. We should sit on a mat at the picnic.

Use It for Real

(a) We can
Note: The short form of cannot is can’t The short form of should not is shouldn’t Cannot is one word but should not is two words.
Good Friends, Good Choices
Note: The short form of The short form of Cannot is one word but
Fun with

with Grammar
Good Friends, Good
We can run and play all We can’t be birds and fly share and be leave our help and we can
QR Code: Interactive quizzes for learners to practise
Let’s meet at 4 o’clock. at I will meet you on Monday. on The sun rises in the morning.
(b) We can’t
(c) We should


Good Friends, Good Choices

We can run and play all day, We can’t be birds and fly away. We should share and be so kind, We shouldn’t leave our friends behind. We can help and we can learn, We shouldn’t fight or break or burn. We should listen, we should care, Good friends shouldn’t be unfair!
Let’s meet at 4 o’clock.
1. Match the following. One has been done for you.
Let’s meet at 4 o’clock. at I will meet you on Monday. on The sun rises in the morning.
• help our teacher.
We can run and play all day, We can’t be birds and fly away. We should share and be so kind, We shouldn’t leave our friends behind. We can help and we can learn, We shouldn’t fight or break or burn. We should listen, we should care, Good friends shouldn’t be unfair! SEL
We

• push our friends.
Use It for Real: Practice tasks rooted in real-life contexts to help learners apply grammar meaningfully across situations you can count. One has been done for you. ribbons oil shoes water pens bags picnic basket. Draw two countable foods and two you can pack. Also, write their names.
(d) We shouldn’t
Error Alert! Highlights common learner mistakes to reinforce accurate grammar usage
lift heavy boxes.
Good
fight or break
should listen, we should
friends shouldn’t

atUse at for the exact time. I go to school at 8 on Use on for the day or date. My birthday is on inUse in for a broad time in a day.We play in the evening.
all swim well.
atUse at for the exact time I go to school at 8 o’clock.
atUse at for the exact time I go to school at 8 o’clock. on Use on for the day or date. My birthday is on 2 July.
2. Fill in the blanks with can or can’t.
Error Alert!
on Use on for the day or date. My birthday is on 2 July.
inUse in for a broad time in a day.We play in the evening.
Uncountable
(a) Most birds fly.
Error Alert!
Error Alert!
inUse in for a broad time in a day.We play in the evening.
(b) Birds swim underwater like fish.
(c) Ostriches run very fast.
Remember! Gives learners key takeaways and important rules to keep in mind for quick recall
We use in with morning, afternoon, and evening but NOT with night. For example: I go to school in the morning. We play in the afternoon. We rest in the evening. We sleep at night. Time
(d) Penguins fly like other birds.
(e) Parrots talk and copy sounds.
3. Fill in the blanks with should or shouldn’t.
We use in with morning, afternoon, and evening but NOT with night. For example: I go to school in the morning. We play in the afternoon. We rest in the evening. We sleep at night.
Some position words can be used to show both place and time like at …at school …at 3:30
Think and Tell: Thinking prompts and questions for teachers to assess learners’ attention and understanding of concepts
(a) We throw plastic bottles in the ocean.
(b) We clean up garbage on the beach.
Think and Tell Remember!
Think and Tell Remember!
(c) People use less plastic.
(d) We leave food wrappers behind.
We use in with morning, afternoon, and evening but NOT with night. For example: I go to school in the morning. We play in the afternoon. We rest in the evening. We sleep at night. Fun with Grammar
Some position words can be used to show both place and time like at …at school …at 3:30

Look around you. What is in front of you?
Look around you. What is in front of you?


(e) We tell others to keep the ocean clean.
Think and Tell Remember!
Some position used to show time like at …at school …at
Look around you. front of you?




1. Read the story and do the following:
• Colour ANY TWO naming words blue.
• Colour ANY TWO doing words green.
• Colour ANY TWO describing words yellow.
One sunny morning, when Arnav arrived at school, there was a huge poster saying, ‘Today is Reading Day!’
‘ We will not write tests today. We will only read books and play games!’
said Defne, Arnav’s friend. Each classroom had soft carpets and colourful pillows. The children sat in a big circle while Ms Nagpal read to them. The children laughed and clapped and had a lovely day at school.

2. Tick ( ) the correct options to complete each sentence.
(a) Arnav went to school. carried his bag.
• She
• He • They
(b) Defne and Arnav sat on the soft carpet. laughed a lot.
• We
• You
• They
(c) There was a huge banner. said, ‘Today is Reading Day.’
• It
• She
• You
(d) Ms Nagpal asked the class, ‘Are ready for a story?’
• they
• you
• he
3. Circle the correct words to complete the sentences.
(a) The school (is / are) big and clean.
(b) Arnav and Defne (has / have) colourful books.
(c) Listen, the bell (is ringing / rang) loudly.
(d) Defne (listen / listens) carefully.

(e) The children (was / were) very excited about the Reading Day.
4. Choose the correct position word to complete each sentence.
(a) The children sat (on / in / at) a big circle.
(b) Arnav was standing (under / over / at) the school gate.
(c) The children put their bags (over / under / in) their chairs.
(d) Arnav was sitting (behind / on / at) Defne.
(e) The fun started early (in / at / on) the morning.








Read the conversation between Tara and her father. Help them become Noun Detectives!
Dad: Tara, do you want to play a quick game before dinner?
Tara: Yes! Let’s find naming words. The one who finds the most gets a hug!
Dad: I see apples in a bowl, and Riya’s hat on the chair.
Tara: Good one! I see a jug of water and a flock of birds outside.
Dad: I see the book Cinderella.
Tara: Mom is cooking rice. I see and smell it!

Dad: And there are vegetables on the table too! Great job, Tara! You win. Here’s your hug!
Remember!
Naming words are also called nouns.
Think about and discuss these questions.
1. Can you help Tara and Dad list the naming words they found?
Common Names Special Names Names for One Names for More Than One Countable Naming Words Uncountable Naming Words
2. Tara says, ‘Mom is cooking rice.’ Can you count rice ? What kind of noun is rice ?
3. Name five things you see in the picture.
4. What do you understand by ‘flock of birds’?

Tara and Dad used many naming words in their game—some were the names of things, some were names of people and some even named a group!
Nouns are the names of people, places, animals and things.
Now let us learn about the different types of nouns.
1. Common Nouns—A common noun is the name of any person, place, animal or thing.
For example: I see vegetables on the table. (any kind of vegetables/table)
2. Proper Nouns (Special names) A proper noun is a specific name that begins with a capital letter.
For example: Tara studies at Sunrise School.
Special names given to roads, mountains, festivals, rivers, newspapers and books are also proper nouns.
For example: • I made a card for my teacher for Christmas.
• The Times of India is a famous newspaper.
• Mount Everest is the highest peak in the world.
3. Countable Nouns—A countable noun names things that can be counted.
For example: I see apples in a bowl.
4. Uncountable Nouns—An uncountable noun names things that cannot be counted easily.
For example: Mom is cooking rice.

5. Singular Nouns—A singular noun is a noun that names one thing, person, animal or place.
For example: There is a vase on the table.
6. Plural Nouns—Plural nouns name more than one thing, person, animal or place.
For example: There are apples in the basket.
7. Collective Nouns—A collective noun is one word that stands for many people, animals or things together.
For example: A flock of birds flew outside.
Collective NounGroup of
team players


The team won the match. bunch bananas, grapes I bought a bunch of grapes.
class students
The class is picking up the litter.
bouquetflowers She carried a bouquet of flowers. swarm bees, insects
A swarm of bees came out of the hive. pride lions
We saw a pride of lions. fleet ships
family people (family)
school fish
herd sheep
A fleet of ships sailed away.
My family is lovely.
We saw a school of fish.
A herd of sheep is resting under the tree.
Note: Some nouns fit in more than one group. For example: Apples is a common noun, a plural and a countable noun!


Listen closely and use your brain—guess the noun, it’s fun, not plain!
1. I shine brightly in the sky during the day.
2. You sit on me and I have four legs.
3. I am full of words and stories.
4. I am white and cold and fall from the sky.
5. You carry your books to school in me.
6. I take you to places. I have wheels and an engine.
7. I am a group of lions.
8. I am red and strong, a fort with fame, in Delhi town, you all know my name!
9. We fly together in the sky. With flapping wings, we soar up high.
10. Many legs, they march in rows—tiny creatures with busy minds.

1. Underline the countable nouns and circle the uncountable nouns in each sentence. One has been done for you.
(a) The children ate an egg and drank some milk.
(b) There was bread on the plate.
(c) Sanya spilt her juice on the table.
(d) The children shared some butter and a banana.
(e) Sia had a bottle of water and a sandwich.
2. Fill in the blanks with suitable common nouns from the box. river bags bullock cart garden house roads well
(a) Last Sunday, the children packed their and went to visit their grandpa’s in the village.
(b) The journey was fun as they rode in a along the dusty .
(c) At grandpa’s house, there was a big full of colourful flowers and butterflies.
(d) Grandpa showed them how to draw water from the old .
(e) In the afternoon, they went swimming in the .
3. Rewrite the sentences by capitalising only the proper nouns.
(a) On sunday, we went to the zoo with aunt meera.
(b) My cousin, aarav, pointed at the elephant.
(c) We had lunch near the lion’s cage at nehru zoo park.
(d) After lunch, uncle anil bought us ice cream from mr rao’s cart.
4. Fill in the blanks using the correct noun form.
Simran and her family go for a picnic to the riverside.
Remember!
Proper nouns are special names.
(a) They take two (basket / baskets) with them.
(b) Simran packed some (sandwich / sandwiches) for the picnic.
(c) Simran took a blue (hat / hats) with her.
(d) There were (apple / apples) in a basket.
(e) Simran saw a (monkey / monkeys) in a tree.
(f) There were many (child / children) at the picnic spot.
5. Tick ( ) the correct collective noun given in the brackets.
(a) The (team / pack) won the cricket match.
(b) I bought a (bunch / pride) of grapes at the market.
(c) A (class / swarm) of students is going on a school trip.
(d) She carried a (bouquet / packet) of flowers for her teacher.
(e) A (swarm / school) of bees flew out of the hive.
(f) We saw a (pride / fleet) of lions near the lake.
(g) A (fleet / bunch) of ships was sailing in the sea.
(h) We saw a (school / herd) of fish in the pond.

6. Complete the paragraph with the correct collective noun. Mahi and Tarun’s grandparents’ house is in Jim Corbett. Their entire gathered at Grandma’s house for the wedding. Mahi gave the bride a beautiful of roses.
There was a of bananas in the kitchen. A loud of bees flew in the garden during the haldi ceremony! The guests visited a wildlife park on their way back. They were amazed to see a of lions.









Read the poem.
The drummer played and beat the drum, The dancer twirled and made it fun.
The prince rode by on a shiny bike, The princess waved—she looked so nice!
The lion yawned and took a nap,
The lioness watched, then gave a clap. The waiter served a plate of snacks, The waitress smiled and gave them back.
The actor told a funny tale,
The actress laughed—it didn’t fail!
Boys and girls all came to play, Learning new words along the way!

Think about and discuss these questions.
1. List the people and animals in the poem.
2. Circle the words for a male and underline the words for a female.
3. Look at the word pair prince and princess. Can you find more such word pairs?

Some nouns change when we talk about a male (boy/man) or a female (girl/woman). These are called gender nouns.
We use:
• Masculine nouns for males (like prince, actor)
• Feminine nouns for females (like princess, actress)
Here are some masculine nouns and their feminine nouns.
MasculineFeminine
fathermother
uncleaunt
husbandwife
bridegroombride sondaughter
brothersister nephewniece
kingqueen
princeprincess
emperor empress godgoddess
MasculineFeminine
lion lioness
drake duck fox vixen
cock hen bull cow peacockpeahen
stallion (horse)mare tiger tigress ram ewe
stag/buck (deer)doe gander goose
Words for things that are not alive are called neuter gender nouns. They are neither male nor female.
For example: bike, plate, drum, etc.
Belonging
Read what happened next in the poem.
‘My sister’s hat is gone!’ one said.’
‘My uncle’s watch was by the bed!’
They searched the ground and all the stalls,
But couldn’t find their things at all.
The hero’s shield rolled far away,
The tiger’s drum was in the hay.


The waiter’s snacks, the prince’s bike. Did all these things go for a hike?
The magician smiled, gave a wink, And magic worked in just a blink!
Think about and discuss these questions.

4. Who does the watch belong to? It is my watch.
5. How do we know the shield belongs to the hero? The poem calls it the shield.
6. Who does the drum belong to? It is the drum.
7. What tells you that the snacks and the bike belong to the waiter and the prince?
When we want to show that something belongs to one person, place, animal or thing, we use ’s (apostrophe (’) + s).
For example: My sister’s hat → The hat belongs to my sister.
Plural nouns that do not end in -s also take ’s.
For example: The children’s shoes are neat and clean.
Sometimes, we use ’s to show that something is about or linked to someone.
For example:
The teacher’s room is next to the library. → The room is used by the teacher.
Error Alert!
Don't add ’s to a word that already ends in s when you're talking about more than one person or animal.
Wrong: The birds’s nests were high up in the tree.
Correct: The birds’ nests were high up in the tree.


Unscramble the letters to form the correct word. Colour the gender opposite nouns in the same colour. One has been done for you.








1. Put the following nouns in the correct columns based on their gender. One has been done for you.
Actor Emperor Fox Empress Ewe Gander Pencil Table Actress Chair Vixen Boy Glass Girl Goose Ram
Masculine Nouns
Actor Feminine Nouns Neuter Nouns

2. Find the feminine nouns of the masculine nouns in the grid. One has been done for you.
Tiger Stallion Peacock Grandfather Nephew Uncle Sir Husband


3. Change the gender of the underlined nouns in each sentence and rewrite the sentences correctly.
(a) My sister is reading a storybook.
(b) Her nephew won a big award.
(c) The waitress served us cold drinks.
(d) The empress was kind to the people.
4. Look at the word in brackets and fill in the blanks. Add (’s) or (’) to show who something belongs to.
(a) The (children) eyes widened when they saw the jellyfish.

(b) The (shark) teeth looked very sharp.
(c) The (visitors) tickets were checked at the entrance.
(d) The (octopus) arms moved quickly in the water.

5. Choose two nouns from the list and draw them in the space provided. Write your own sentences adding ’s to show who they belong to. One has been done for you. book kite cat toy ball hat pen bag doll brush
The cat’s paws are soft.

6. Change the underlined words to nouns with an apostrophe to show belonging. Then rewrite the sentence. One has been done for you.
(a) The whistle of the umpire signalled the start of the match. The umpire’s whistle signalled the start of the match.
(b) The catch of the fielder was amazing.
(c) The instructions of the coach helped the players.

(d) The captain of the team lifted the trophy.








Read the conversation between Meera and Arjun.
A Hat, an Apple and the Magic!
Meera: What are you doing, Arjun?
Arjun: I’m trying a magic trick! Watch this.
Meera: Is that an old hat?
Arjun: Yes! It’s a magician’s hat.
Meera: What’s inside the hat?
Arjun: I put in an apple, a coin and a feather.
Meera: All right, so what happens now?

Arjun (waves his hand): Abradora Alakazoom! Bring the magic to the room!
Meera: Look! The apple has turned into a rabbit!
Arjun: And the coin is flying!
Meera: That’s amazing! Can I try a spell too?
Think about and discuss these questions.
1. What did Arjun put into the hat? He put in apple, coin and feather.
2. Which word is used when we talk about something for the first time?
3. Why do we say an apple but a coin ?
4. Why did Meera say the hat the second time, not a hat?

A, an and the are called articles. They help us talk about things clearly.
A and An are used when we talk about any one person, place, animal or thing—not a special one.
We use an before words that start with a vowel sound. For example: an apple, an insect, an ox.
We use a before words that start with a consonant sound.
For example: a hat, a coin and a table
We use an before words that begin with a vowel sound (a, e, i, o, u) and not a vowel letter.
✘ Wrong: an one-rupee note, an university ✔ Correct: an honest man, an hour, an X-ray
The is used when we talk about something special or about what is already known.
For example: Arjun has a black hat. The hat is old. He puts a coin in the hat. The coin turns into a bird.
We also use the with the names of special places, rivers, mountain ranges, books, etc. that are one of a kind.
1. River: We sailed in a boat on the Yamuna.
2. Mountain Ranges: We saw snow on the Himalayas.
3. Famous Places, Buildings or Towers: The Red Fort is made of red sandstone.
4. Famous Books: The Bhagwat Gita is a well-known book.
5. Celestial Bodies: The sun sets in the west.
6. Nationalities: The Chinese are very hardworking.








1. Play in pairs.
2. Roll the dice and move your token forward on the railway track.
3. If you land on a box with a noun, say the correct article (a, an or the) and say one sentence using the article and the noun. For example: An elephant has big ears.
4. If you land on a box with instructions, do as directed.

1. Match the nouns with the correct articles. One has been done for you.

2. Fill in the blanks with a, an or the. One has been done for you.
(a) One day, Oswald planted a banana tree in his backyard.
(b) He watered it every day with special blue bottle.
(c) Many years later, tree had many bananas.
(d) Oswald’s family had idea: ‘Why not have banana party in town hall?’
3. Read each sentence about the Surajkund International Crafts Mela. Underline the incorrect article and write the correct one.
(a) We went to an mela in Faridabad last weekend.
(b) I saw a statue of a elephant.
(c) My sister wanted to try out a food stalls.
(d) We bought a ice cream shaped like a flower.
(e) We saw a artist perform a traditional dance.

4. Each sentence is missing a, an or the. In your notebook, rewrite the sentences correctly.
(a) We saw elephant at zoo.
(b) Monkey was sitting in tree.
(c) We saw owl sleeping.
(d) We watched parrot talk.
(e) Zookeeper told us story about tiger.












Read the conversation between Rahul, Sneha and Sunil.
Sneha: You had a birthday celebration, Rahul. What did you get?
Rahul: Dad gave me a robotics kit. Sunil, it is almost like yours. Look!
Sunil: Yes, it is like mine.
Sneha: I would love one too! Can you buy them from any toy store?
Rahul: I will ask Dad. Someone ordered it for him. He will have to ask.
Sneha: Please ask him to find out soon.
Rahul: In the meantime, you can play with mine.
Think about and discuss these questions.

1. Look at Sneha’s first words. Who does she mean when she uses you?
2. What does them refer to?
3. Which words show that things belong to someone? Tick ( ) the answer. • you, we, it, they • yours, mine • me, her


Hi Rahul. What birthday gift did you get?
Pronouns are words that can be used in the place of naming words.
We use pronouns so that we do not repeat the naming words again and again. Pronouns help us understand who and what we are talking about.
For example: Dad knows I love robotics, so he got me the kit.
I, he, she, it, you, we and they are used at the beginning of a sentence
I wanted a robotics kit.
Me, him, her, it, you, us and them are used after the doing word (verb) in a sentence.
The teacher gave me a robotics kit. He (Rahul) wanted a robotics kit.The teacher gave him a robotics kit. It (the robotics kit) is fun to play with.They gave it (the kit) to him. You want a robotics kit too.
The teacher gave you a robotics kit. We (Rahul and Sneha) wanted robotics kits.
The teacher gave them robotics kits.
Pronouns can also be used to show possession/belonging. Mine, his, hers, its, yours, ours and theirs show who owns or possesses something.
For example: The robotics kit is mine. This kit is his/hers. These kits are ours. Those kits are theirs.

What is missing from this story?
He said he would fix it, but it blinked twice and ran into her. She screamed, ‘It did it again!’ He could not stop it.


Pronouns can only be used in the place of nouns once the nouns have been given.
For example: Mr Singh lives in Delhi. He says it is a beautiful city. That beautiful house is his.

• Form teams of three to four students.
• Each team will get paper slips with sentences that have pronouns.

• In front of the class, there will be three baskets labelled ‘Subject’, ‘Object’ and ‘Possession’.
• Work as teams to look at the pronouns in the sentences and race to sort the pronouns correctly in the baskets.
• The first team that sorts all the pronouns correctly, wins!

1. Match the pronouns in the columns. One has been done for you.

2. Tick ( ) the correct options. Write ‘S’ for subject pronouns, O for object pronouns and P for possessive pronouns. One has been done for you.
(a) feed the birds every morning.
• We • Us • Our
(b) Mia will give water.
• they • them • their
(c) This bird feeder is . • I • me • mine

(d) Mia says, ‘Ruhan helps clean the bird house’
3. Circle the correct option.
(a) Virat Kohli is a famous cricketer. (He / Him / His) plays for India.
(b) Many fans cheer for (he / him / his) at the stadium.
(c) The lucky bat is (him / he / his).
(d) Children love to watch (he / him / his) on TV.
(e) Virat Kohli says to his fans, ‘All my wins are (you / your / yours).’

4. Replace the underlined words with correct pronouns.
(a) Ravi throws the waste in the garbage can. keeps the park clean.
(b) Ravi and Sita put wrappers in the bin. We thank for keeping the place clean.
(c) It is Ravi’s idea to clean the place. The idea to place dustbins in the park is .
(d) My classmates and I clean the playground every week. work together to keep it tidy.
(e) Our teachers have put out many dustbins. teach us to throw away our garbage properly.
5. Fill in the blanks with the correct pronouns. My family loves ice cream.(a) go to the ice cream shop every Sunday. Last week, Dad took (b) there after lunch. My sister chose chocolate. (c) favourite flavour is vanilla. The biggest cone was (d) . Mom said (e) would buy (f) different flavours next time. The man at the shop gave (g) extra sprinkles. We thanked (h) and enjoyed (i) ice creams together.








Read the conversation between Aryan and his father.
Zappy and the Missing Word
Right in Aryan’s living room stood a shiny silver robot.
Aryan: Papa, is that a real robot?
Papa: Yes, its name is Zappy. He listens, he moves and he even talks.
Aryan: Can I try? Please?
Papa: Go ahead. Just give him a command.
Aryan: Zappy, jump like this!
(Zappy jumps up and down.)
Aryan: Zappy has ears. There are cookies in the kitchen. Bring them to me.
(Zappy does not move.)
Aryan: Huh? Why won’t you bring the cookies, Zappy?
Zappy: I have sensors not ears!
Aryan: I am sorr y! Will you please use your sensors and bring me the cookies?
(Zappy turns around and glides to the kitchen.)


Remember!
When we talk about he, she, or it, we add an -s or -es to the verb.
I / You / We / They Jahnvi and Rohan (They) walk to school. He / She / It Jahnvi (She) walks to school.
Think about and discuss these questions.
1. Which actions does Zappy do? He listens, .
2. Does Zappy have ears? No, Zappy says he sensors.
3. Ar yan says, ‘I am sorry!’ What would we say if we apologised to Zappy? We sorry, Zappy.

A sentence always has a verb. If there is no verb, it cannot be a sentence.
We know that verbs can be action words that tell us what people, animals or things do.
For example: Aryan claps loudly. Zappy jumps up and down. The verbs is, are and am can be used to tell us who or what someone or something is. These are forms of the verb ‘to be’. That means they tell what something is, who someone is or how someone feels.
I am Zappy says, ‘I am only a year old.’
He/She/It/This/That is Zappy is a robot. That is a cute name. You/We/They/These/ Those/There are There are cookies in the kitchen. Dad and I are excited!
Has and have can be used to show belonging or a special quality. I/You/We/They/These/Those have I have a robot.
Robots have big eyes. You have sensors, Zappy.

He/She/It/This/That has Arjan has a big smile. Zappy has fingers like a human.
Note: Is, are, am, has and have are the only verbs in these sentences.
Some verbs are made of more than one word. There can be a main verb (like looking, running or dancing) and a helping verb (like is, are or am)
For example: I am looking at Zappy now. They are dancing happily now.

Remember!
The form of the verb tells us when an action takes place. For example: Zappy jumps around every day. Yesterday, Zappy jumped around. Zappy is jumping up and down at the moment.

Roll the dice and use an eraser, a sharpener or a coin as a token to move along the blocks. Identify the actions in the blocks and make sentences using correct form of the verbs.

He finishes the song. They play the games together.


1. Underline the verb (one word or two words) that shows what is happening. One has been done for you.
(a) I am showing my magnet experiment.
(b) My friend is building a model of a rocket.
(c) Rakesh and Riddhi are testing their windmill outside.
(d) Anu wears safety glasses.
(e) The volcano erupts with red foam.
(f) Zoya paints a diagram of the solar system.
(g) These children are good at science.


2. Read the story and fill in the blanks using the correct verbs from the help box. Add -s or -es to the verbs where needed. watch get meet fall practise cheer smile
Tara loves to dance. Every day, she (a) in her room before school. She and her friends (b) during the lunch break to talk about their routines. On the day of the big competition, Tara steps onto the stage. She begins to dance, but suddenly she slips and (c) ! Her friends in the audience (d) her on.

Tara quickly (e) up and starts again. Her friends (f) her performance with big smiles. At the end, Tara bows and (g) proudly.

3. Circle the correct word in the brackets to complete the paragraph.
Ayan (is / are / am) not feeling well today. He (has / have) a sore throat and a runny nose. His parents take him to the clinic. They (has / have) an appointment with Dr Sen.
Ayan and his father (is / are / am) sitting in the waiting area. Ayan says, ‘I (is / am / are) a little scared.’

His father smiles and says, ‘Don’t worry. It (are / is) okay.’
Soon, the nurse comes out. She says, ‘Ayan, you (is / are / am) next.’
The doctor checks him and says, ‘He (has / have) a mild cold. It is nothing serious.’ ‘We (has / have) some medicine to help you feel better,’ he adds.
4. Read the poem below. Choose the correct verbs from the help box and fill in the blanks. cheer am bend is are clap run jumps
The sun is bright, the sky is blue, I ready—how about you?
The field there, the tracks are wide, The teams marching side by side.
We warm up fast, we stretch and , Then take our places with our closest friends. The whistle blows—we with might, One child and lands just right!
We laugh and from where we sit, We for those who do not quit.

Time: 40 mins
Total: 25 Marks
1. Match the group names and the correct pictures. (5 × 1 = 5 marks)
(a) A swarm of • • i.
(b) A pride of •
ii.


(c) The teeth of a •
(d) A school of
(e) A bouquet of

2. Change the gender of the underlined nouns and rewrite the sentences. (5 × 1 = 5 marks)
(a) The actor wore a funny wig and made everyone laugh.
(b) The robe of the empress was stitched with golden stars.
(c) The waitress forgot to bring juice for the guests.
(d) I borrowed the boy’s cap for my role.
(e) The lead role was played by my uncle in last year’s play.
3. Read the passage. Fill in each blank with a, an or the. (5 × 1 = 5 marks)
(a) One morning, Englishman came to quiet railway station.
(b) He was carrying umbrella and wearing hat.
(c) Englishman looked around and sat on bench.

(d) He opened bag and took out apple and book.
(e) Soon, train arrived, and he boarded with a smile.
4. Fill in the blanks with the correct pronouns. (5 × 1 = 5 marks)
(a) Rahul and I love robotics. built a robot together.
(b) Sneha lost her screwdriver, so Rahul gave a new one.
(c) This is my kit. That one is . (Rahul’s)
(d) The robot danced! Did you see spin?
(e) Papa helped Rahul and Sneha. He gave new batteries for their robot.

5. Circle the correct word in the brackets to complete the paragraph.
It is Monday morning. Diya (is / are / am) ready for school. She (has / have) her bag and tiffin. Diya and her brother (is / are / am) at the table.
At the bus stop, the driver (pick / picks / picked) up the children on time. All the children (has / have / had) their science projects with them for the science fair.
(5 × 1 = 5 marks)








Look at the picture and read the description.

The picture shows a bright and fun art class. The five children are happy and busy. Mia and Mohan are working together. They are painting a big yellow sun. One boy is building a tall tower with many small square blocks. There are three large alphabet blocks next to the window. The classroom is neat and clean.
Think about and discuss these questions.
1. What do the words like big, yellow, square, small and clean do in these sentences?
2. Look at the picture and fill in the blanks with the correct adjectives.
(a) The children are sitting at a (round/green) table.
(b) The children are drawing a (yellow/black) sun.
(c) The boy is stacking (small/round) colourful blocks.
(d) There are (three/two) large alphabet blocks near the window.
3. Give a sentence about each child. Use describing words (adjectives) to talk about their clothes or the things they are using. For example: The girl in the red top is painting with a small brush.

Adjectives tell us more about the nouns. They tell us what things are like (special quality). They also tell us about number (quantity).
Adjectives describe the quality of things. What kind?
Adjectives describe the quantity (number) of things. How many?
colour size shape other quality a yellow sun big blocks a round table a neat classroom a white cap a tall tower square blocks happy children
Adjectives help us compare things. Arjun’s tower was tall.
Riya’s was taller than Arjun’s. (comparing two)
five children three blocks many blocks a few blocks
Zoya’s tower was the tallest of all! (comparing more than two)
We add -er at the end of adjectives when comparing two things. It is called the comparative form.
We add -est at the end of adjectives when comparing three or more things. It is called the superlative form. We add the before the adjective.
Positive FormComparative (-er) Form Superlative (-est) Form big bigger the biggest long longer the longest heavy heavier the heaviest clean cleaner the cleanest bright brighter the brightest fast faster the fastest small smaller the smallest

Circle the describing words. Look for words that describe a quality or quantity. Then, write them in the correct column in the table below.


1. Fill in the blanks with suitable describing words. loud two pink many big
(a) The fair was full of colourful lights.
(b) We saw clowns making everyone laugh.
(c) There were stalls selling toys and sweets.
(d) I bought a balloon shaped like a star.
(e) There was music. (quality) (quantity) (quantity) (quality) (quality)

2. The students visit the school garden for Van Mahotsav. Read the sentences. Circle the adjectives and underline the nouns they describe. One has been done for you.
(a) We walked into a peaceful garden filled with plants.
(b) The gardener handed us long spades to dig holes.
(c) We sat on the dry grass before we started planting.
(d) We hoped the plants would become big trees.
(e) The air felt cool and fresh after watering the plants.
3. Fill in the blanks with the -er or -est form of adjectives.
(a) My dog is than your dog. (small) Rohan’s dog is the of all. (small)
(b) Today is than yesterday. (hot)
Today is the day of the week. (hot)
(c) This puzzle is than the last one. (easy) This puzzle is the of all the puzzles. (easy)
(d) Nisha is than Neeta. (tall)
Sam is the in our class. (tall)
4. Read each sentence and rewrite it using the correct adjectives.
(a) The soup in the hotel was loud and tasty.
(b) I wore a delicious jacket to stay warm.
(c) We saw a tiny mountain covered in snow.
(d) The view from our room was noisy.
(e) There was a dull breeze after the rain.

5. Complete the sentences using the -er or -est form of the adjectives in brackets.
(a) The Howrah Bridge lies between Kolkata and Howrah. Howrah is a city than Kolkata. (small)
(b) It is the bridge in Kolkata. (long)
(c) The Howrah Bridge is one of the bridges in India. (busy)

(d) The traffic is in the evening than in the morning. (heavy)
(e) Among all the bridges I have seen, the Howrah Bridge is the . (pretty)

6. Match each describing word and the correct naming word. In your notebook, use each pair to write sentences about what Samar is doing.
Describing Word








Read the poem carefully.
Lilly and Polly
Lilly walked slowly down the lane, Polly skipped happily out in the rain. Lilly whispered softly, ‘Let’s go and play.’ Polly nodded quickly and they ran away.
They laughed loudly in the park so wide, And cheered and screamed excitedly on the ride.
They waved cheerfully, ‘We had such fun!’
Then walked home calmly, the day was done.
Think about and discuss these questions.

1. How did Lilly walk? Lilly walked .
2. How did Polly skip? Polly skipped .
3. How did Lilly and Polly laugh? They laughed .
4. Look at the words laughed, skipped, nodded and whispered. What kind of words are they?
5. Look at the words loudly, excitedly, softly and happily. With which letters do these words end?

Words like happily, quietly, beautifully and calmly are adverbs.
An adverb is a word that tells us more about a verb. An adverb ADDS to the verb.
For example: Lilly walked slowly down the lane. (Slowly tells us more about the verb walked.) They laughed loudly. (Loudly tells us more about the verb laughed.)
Some adverbs tell us how something is done. We add -ly at the end of the words to make adverbs.
For example: Lilly and Polly waved cheerfully. How did Lilly and Polly wave? cheerfully
Some adverbs tell us where something is done. For example: Polly sat here. Where did Polly sit?here



Here are more adverbs that tell us about the place. there above up in here below down out
Some adverbs tell us when something happens.
For example:
Lilly and Polly played yesterday. When did Lilly and Polly play? yesterday

Here are more adverbs that tell us about the time. today soon now tomorrow yesterday early late ago


Adverbs are clever, they help us explain How, when and where—again and again!
They tell us when things take place, Like now, today or soon we’ll race! They show us where things go, Like here, there, above, below ! They tell us how it’s done, Like slowly, quickly, happily run! So, always tell yourself this rhyme, Adverbs give how, where and time!

1. Fill in the blanks using the adverbs in the box. One has been done for you. happily loudly excitedly cheerfully brightly
It was Kashika’s birthday. All her friends came wearing party hats and brought presents.
(a) The children danced happily to the birthday music.
(b) She opened the gifts to see what was inside.
(c) She smiled when her friends sang for her.
(d) Balloons popped as the children jumped around.
(e) The candles burnt on the birthday cake.
2. Choose the adverb that tells you when things happened.
(a) I visited my grandmother’s house . (yesterday / gently)
(b) We will go shopping . (tomorrow / happily)
(c) Grandma baked a cake . (today / quickly)
(d) We will watch a film . (now / slowly)
3. Circle the correct adverb that tells where the action happens.
(a) The children played (outside / inside) because the weather was pleasant.
(b) Father sat (below / inside) reading a newspaper.
(c) My baby sister slept (inside / outside) in her cosy cot.
(d) The birds flew (under / away) when I made a noise.
4. Use adverbs from the box to complete the diary entry. happily loudly cheerfully brightly quietly today late outside (date) (time) (day)
Dear Diary,
(a) was such a fun day! It was a holiday, so I woke up (b) . I ran (c) to play in the park. The sun was shining (d) . I met my friends and we played (e) on the slide and swings. We shouted (f) while running around. I sat (g) on a bench to eat my snacks. Then, I rode my bicycle (h) along the path.
(your name)








Read the conversation between Shalini and her mother.








Shalini, you promised to go to bed at 9 p.m. today! You have an exam in the morning.
But mom, how can I sleep with so many stars shining in the sky?
If you don’t go to sleep now, you will fall asleep on your desk during the paper!
You are right. Let me bring my mat here and sleep next to the window!
Think about and discuss these questions.
1. What word does Shalini use to talk about the position of the stars?
2. Where will Shalini sleep?
3. When does Shalini have her exam?
4. Why do we use words like in, on and next to?






Remember!
Position words tell us the place something or someone is. They can also tell us the time.

Prepositions (position words) tell us the position of things. They help us to know the ‘where’ and ‘when’ of things.
These words tell us where something is.
(Position words)
Place Time
On: Used when something is touching the top of a surface The book is on the table.
Under: Used when something is directly below or beneath another object The dog is under the bed.
Behind: Used when something is at the back of another thing, usually hidden by it
The dog is standing behind the kennel.
In front of: Used when one thing is placed ahead of another and can be seen easily She is standing in front of the box.
Next to: Used when something is very close to another person or object Ram sat next to his sister.
Above: Used when something is higher but not touching The clock is above the window.
Below: Used when something is lower but not touching The window is below the clock.
At: Used for a specific point/place They are at the bus stop.
In: Used when something is inside a space The toys are in the box.
Near: Used when something is close by The bench is near the shop.
Between: Used when something is in the middle of two things
Esha is siting between Rohan and Rahul.
These words tell us when something happens.
At: Used for exact time
On: Used for days and dates
He woke up at 7 a.m.
The party is on 21 February.
In: Used for parts of the day, months and years We play in the evening.
Before: Used when something happens earlier than another
After: Used when something happens later than another
Brush your teeth before breakfast.
We cleaned the park after lunch.
Think and Tell
Look at these sentences: The ball is under the bed. The clouds are below the aeroplane. Why do we use under in the first sentence and below in the second?
We use in with morning, afternoon and evening but NOT with night.
For example: We sleep in the morning / afternoon. We sleep at night. ✗ We sleep in night.

Name three things in your bag. Draw something on the table.

Name one thing behind you and one thing next to you.
Say two things you do before coming to school.
Say a sentence using ‘under’.


1. Match the sentences and the correct images.
(a) The cat is next to the boy. i.
(b) The window is behind the curtain. ii.
(c) The puppy is under the stool. iii.
(d) The clock is above the blackboard. iv.

(e) The bicycle is in front of the tree. v.
2. Fill in the blanks with the correct option from the help box. behind next to on above between
(a) An aeroplane is flying the house.
(b) Sameer was sitting his friend.
(c) Our exams begin Friday.
(d) The girl is the bookcase.
(e) The ball is the trees.



3. There is a mistake in each sentence. Write the correct word in the space.
(a) The football match is played after two teams.
(b) The football is on the net.
(c) The goalpost is before the goalkeeper.
(d) India won gold in the Asian Games at 1951 and 1962.

4. Look at the picture and fill in the blanks using the correct prepositions in the brackets.
This is a picture of a happy family garden. The father is standing (a) (behind / under) the plants, holding a hose. The water falls (b) (on / in) the plants. A little boy is also watering the plants (c) (between / next to) his father. A butterfly is flying (d) (below / above) the flowers. The mother is holding a baby. The house is (e) (before / behind) the family, and there are trees (f) (in front of / after) the house.










Read the story.
Good morning, class! We won’t have outdoor games today because it’s raining outside.

I brought my colour pencils and my new sketchbook!

Yes Diya, you may choose either one.
Can we read our favourite books or draw quietly?

Raghav, please share your colour pencils with Zoya, so she can also colour in.
I want to colour in too, but I forgot my pouch.
Think about and discuss these questions.

Sure, ma’am!
1. Diya asks a question and gives two choices. What does she say?
2. Raghav shows what he has brought to class. What does he say?
3. The teacher wants the children to help each other. What does the teacher say?


Conjunctions are joining words. They help us join words, ideas or sentences. Conjunction Use Example Sentence and joins two words, ideas and sentences
I brought my colour pencils and my new sketchbook!
I went to my grandma’s house and she gifted me the colour pencils. or shows a choice or option
Can we read our favourite books or draw quietly? but joins sentences with opposite meanings I want to colour in too, but I forgot my pouch. so shows a result or purpose
Please share your pencils with Zoya, so she can also colour in. because shows a reason
We won’t have outdoor games today because it’s raining.
The use of so and because is often confused.
Wrong: I wore a jacket so it was cold.
Correct: I wore a jacket because it was cold.
Use because to give a reason.

Wrong: I was cold because I wore a jacket.
Correct: I was cold, so I wore a jacket.
Use so to show the result.

1. Get in to pairs and take turns to roll the dice and move forward.
2. When you land on a square, fill in the blank with the correct conjunction. If your answer is incorrect, go back one space.
3. Land on FINISH with the correct answer to win the game!

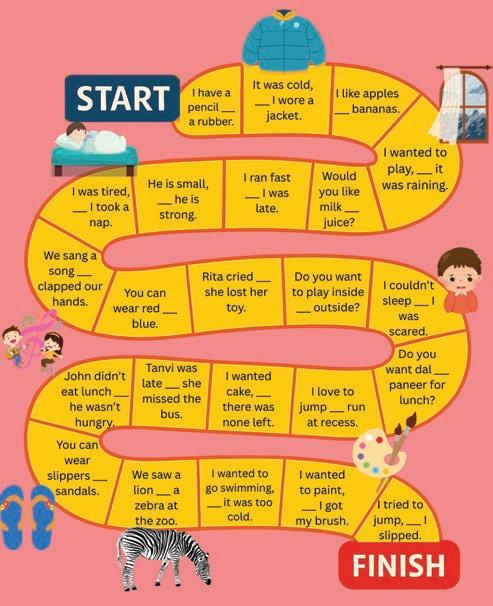


1. Fill in the blanks with and, but, or, so or because.
(a) We cleaned the house decorated it with lights. (but / because / and)
(b) My grandmother made Kada Prasad, the whole house smelled sweet. (so / or / and)

(c) I wanted to help in the kitchen, the stove was too hot. (but / or / and)
(d) My father asked, ‘Do you want to light a candle hang the decorations?’ (so / because / or)
(e) We listened to kirtan it makes us feel peaceful. (so / because / and)
(join) (result) (opposite) (choice) (reason) (join)
(f) The whole family sat together we said a prayer. (but / so / and)
2. Fill in the blanks with the correct conjunctions from the box. but or because so and
(a) The class went to the history museum they were learning about the past.
(b) They saw a knight’s sword a golden crown in the first room.

(c) There was a giant dinosaur skeleton, some students felt a little nervous.
(d) The guide asked, ‘ Would you like to see the old coins the ancient clothes first?’
(e) Jay wanted to write notes, he forgot his notebook.
3. In your notebook, join the sentences with suitable conjunctions (and, but, or, so, because).
(a) We packed our towels. We packed our sunglasses.
(b) I wanted to build a sandcastle. The sand was too dry.
(c) The sun was shining. We wore our hats.
(d) Do you want to swim in the sea? Do you want to look for shells?

(e) We brought a beach umbrella. We wanted to sit in the shade.

4. Rani is a kind girl who helped her friend. Complete the story by filling in the appropriate conjunctions.
It was the last period at school, (a)
Rani was not ready to go home. Her friend, Riya, looked around the classroom (b) saw that Rani was sitting alone. Rani had hurt her arm during lunch, (c) she wasn’t able to pack her bag. Riya quickly walked over to help her.

‘Do you want me to carry your bag (d) do you want to carry it yourself?’ Riya asked. Rani nodded happily, (e) she felt better with her friend by her side. As the bell rang, they waved goodbye to the teacher (f) left the classroom together.









Read the passage.
Riya and Aman were watching the science experiment when Riya exclaimed, ‘ Wow! It’s perfect. Our volcano erupted.’
Aman leaned in too close and said, ‘Oops! There is some of the stuff on my coat.’ Their model worked perfectly and Riya cheered, ‘Hurrah! We did it!’
But then Aman noticed the judges walking away and cried, ‘Oh no! They have already passed our table!’
Think about and discuss these questions.
1. What do you say when something falls?
2. What do you say when you are surprised or excited?
3. What do you say when you win a game?


Words like ‘Oops!’, ‘ Wow!’, ‘Hurrah!’, ‘Oh no!’ express strong feelings like happiness, sadness, excitement or shock.
Interjections are words that help us express strong feelings. They are followed by an exclamation mark (!).
For example: Hurrah! I won the game. (happiness)
Oh no! I dropped my lunch. (sadness)
Note: The first letter after the exclamation mark (!) always begins with a capital letter. For example: Alas! The little bird could not fly.
Let us now look at some common interjections.
Interjections
Hurrah! Wow!joy/happinessErr! Yuck! Eww!disgust/dislike
Ouch! Oh! Ow!pain Oh no! Oops! Alas!sadness
Aha! Oh! What!surprise
Hey! Look! Listen!call attention to

Fun with Grammar

Fill in this fun poem using interjections. Then, read it aloud with expression. Oh no! Hurrah! Ouch! Yuck! Aha!
! I won the game, I danced around and called my name.
! I tripped and hurt my toe, My tears came fast and wouldn’t slow.
! My toy is lost, I’ll have to find it, at any cost.
! What is that smell?
Something’s rotten, I can tell!
! That magician made things fly, I watched him with a blinking eye.

1. Match the interjections and the correct sentences. One has been done for you.

(a) Yuck! •
• I left my homework at home.

(b) Hurrah! •
(c) Oh no! •
(d) Oops! •
• I spilt my juice.
• This milk tastes bad.
• We are going on a picnic.
2. Read the situations and choose the correct expression to match the feeling.
(a) The teacher gave us extra homework.
• Hey!
• Oh no!
(b) We are going on a field trip!
• Yippee!
(c) I left my tiffin in the bus.
• Oops!
(d) We have a quiz today.
• What!
• Eww!
• Hurrah!

• Oops!
3. Complete the comic using suitable interjections.

(a) (b)

! We found a treasure box. ! It is locked.
Time: 40 mins
Total: 25 Marks
1. Read the passage below. Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the adjective in brackets. Add -er or -est as needed. (5 × 1 = 5 marks)
It was a sunny day, and Class 3 went to the park for a picnic.
(a) Ayaan ran than his brother. (fast)
(b) Zoya brought the sandwich I have ever seen! (big)
(c) Ziya’s water bottle was than Ishaan’s bottle. (heavy)
(d) We sat under the tree we could find. (tall)
(e) Everyone agreed that Soham told the joke of all! (funny)
2. Read the sentences and fill in the blanks using adverbs from the box. Adverbs tell us how, when or where something happens. (5 × 1 = 5 marks) happily loudly today outside quickly
(a) We saw a magic show . (When?)
(b) The children laughed at the funny puppet. (How?)
(c) Priya ran to reach her seat before the next trick. (How?)
(d) The magician performed his tricks under a colourful tent. (Where?)
(e) Arjun clapped after the magician made a rabbit appear! (How?)
3. Read each sentence carefully. Fill in the correct preposition from the options given. (5 × 1 = 5 marks)
(a) The paintbrushes are kept the drawer. (on / in / behind)
(b) The large clay model is placed the wooden table. (in / above / next to)
(c) Our school’s art exhibition is 12 August. (in / at / on)
(d) Meera stood her two classmates as they explained their painting to the visitors. (between / over / under)
(e) We washed our hands lunch before working on our canvas. (after / in / at)

4. Join the sentences with suitable conjunctions (and, but, or, so, because).
(5 × 1 = 5 marks)
(a) I cut the paper. I glued it to the cardboard.
(b) We wanted to use glitter. We couldn’t find any.
(c) The paint was wet. We waited for it to dry.

(d) Should we add buttons to the robot? Should we use beads instead?
(e) Shravan used a glue gun. It was quicker and easier.
5. Fill in the blanks with the correct interjections from the help box.
(5 × 1 = 5 marks)
(a) I found my toy! It fills my heart with so much joy!
(b) I slipped and fell. My knees now hurt—they will surely swell!
(c) I see a bird in the tree. It sings a song just for me.
(d) I passed the test! I tried so hard and did my best!
(e) My balloon went pop! I tried to catch it—but had to stop.








Read the conversation between Sherry and Aman.
Sherry: Hi Aman! Are you coming on the school trip tomorrow?
Aman: Yes! My mom says I can come. I am so excited!
Sherry: So am I! We can see the animals and we can have a picnic.
Aman: Yes! But we should not feed the animals.
Sherry: That’s right. My mom said I can take snacks. Should I bring some for you too?
Aman: Sure. Tomorrow will be so much fun. I cannot wait!
Think about and discuss these questions.
Tick ( ) the correct answers.
1. Aman’s mom says he can go to the zoo. She has given him . • permission • a warning • advice
2. Sherry says they can see the animals. In this sentence can means they will .
• not be allowed to • be able to • have to
3. We should not feed the animals. This means that they to feed the animals.
• are not allowed • have permission • not be able to


These are used to talk about what someone/something is able/not able to do
For example:
I can see the birds in the tree. Grandma can make snacks. We cannot/can’t travel together.
These are used to ask for/refuse permission in an informal situation For example: Mom, can I go to the zoo? Ask your dad if you can go. Dad says I cannot/can’t go.
Note: We use may to ask for permission in a formal situation. Sir, may I please leave the room?
Should and should not are used to give advice or say what is right or wrong. We should not/shouldn’t feed the animals. You should put your litter in the garbage can. We should sit on a mat at the picnic.
Note: The short form of cannot is can’t. The short form of should not is shouldn’t. Cannot is one word but should not is two words.


We can run and play all day, We can’t be birds and fly away. We should share and be so kind, We shouldn’t leave our friends behind. We can help and we can learn, We shouldn’t fight or break or burn. We should listen, we should care, Good friends shouldn’t be unfair!


1. Match the following. One has been done for you.
(a) We can • • help our teacher.
(b) We can’t • • push our friends.
(c) We should • • lift heavy boxes.
(d) We shouldn’t • • all swim well.

2. Fill in the blanks with can or can’t.
(a) Most birds fly.
(b) Birds swim underwater like fish.
(c) Ostriches run very fast.
(d) Penguins fly like other birds.
(e) Parrots talk and copy sounds.

3. Fill in the blanks with should or shouldn’t.
(a) We throw plastic bottles in the ocean.
(b) We clean up garbage on the beach.
(c) People use less plastic.
(d) We leave food wrappers behind.
(e) We tell others to keep the ocean clean.

4. Fill in the blanks with can, can’t, should or shouldn’t.
Mom said, ‘You (a) come out of your room until it is tidy.’ We (b) all keep our rooms clean and tidy. We (c) throw our toys on the floor. We (d) put books back on the shelf.
We (e) leave clothes on the bed. We (f) ask our family for help if we need it. We (g) find things easily in a messy room.








Read the lines below.
breakfast everyday
everyday breakfast eat We eat breakfast every day.
Think about and discuss these questions.
1. Whose line makes the most sense to you?
2. Why do you think that is?

A group of words arranged so that they make sense is a sentence.
For example: My brother and I eat breakfast every day.
Remember!
A sentence starts with a capital letter and ends with a full stop.
A sentence has two parts.
It tells us who or what the sentence is about. It tells us what the subject does or is. My sister and I + have breakfast. The dog + is hungry. It (The dog) + looks at our plates. I + give the dog some biscuits. A sentence must have a verb (an action word).

A sentence is a bunch of words, That share a thought so clear.
It starts a letter capital and bright, So everyone can read it right.
It ends with a full stop, neat and true, That’s what sentences always do!
It has a subject—who or what, Like Sam, or Mom, or dogs or hut.
It has a predicate—what they do, Like runs or jumps or sings so true.
So, write your sentences, neat and bright, Just make sure they are built just right!

Sentence Challenge
Colour in no more than 3 words in each verse that will remind you what a sentence is. Choose the most important words!

1. Tick ( ) the groups of words that make complete sense.
(a) Early in the morning
(b) I run downstairs.
(c) We pack our bags.
(d) Oats eat
(e) My mother takes me to school.
Remember!
Ask these two question. Subject: Who/What does the action?
Predicate: What does the subject do?
2. Read each sentence. Circle the subject and underline the predicate. One has been done.
(a) We go shopping together.
(b) My sister picks a red dress.
(c) Dad pays the bill at the counter.
(d) The shopkeeper gives us a big smile.
(e) The bags are heavy.

3. Match the subjects and the correct predicates.
Subject
Predicate
(a) The Taj Mahal • • is made of white marble.

(b) It • • is a famous building in Agra, India.
(c) Shah Jahan • • visit the monument every year.
(d) Many tourists • • built the Taj Mahal long ago.
4. Make sentences using the pictures and the words as clues.
(a) (Ana / book)
(b) (jumping / trampoline)
(c) (family / picnic)
(d) (Arpit / kite)
5. Rewrite the paragraph using capital letters and full stops where needed. yesterday, i made a bird house with my dad we used some wood, nails and paint we cut the wood into pieces and nailed them together we made a small door for the birds i painted the bird house blue and yellow we hung the bird house from a tree in our garden now, i am waiting for little birds to come and make it their home








Read the two sentences below.
This apple is sweet. Is this apple sweet?

Is, am, are, was, were, has and have can be the main verb in a sentence. For example: I am a girl. I have an apple. The apple was sweet.
Think about and discuss these questions.
1. Which is a question? Which is a statement?
2. Look at the verb is in the statement and in the question. How has the position of the verb changed?

Questions are sentences that ask for information about something. They start with a capital letter and end with a question mark. For example: This apple is sweet. (Statement – gives information) Is this apple sweet? (Question – asks something)
In sentences that have is, are, am, was, were, has or have as the only verb, we move the verb to the beginning to form questions.
Statement
Question
This apple is sweet. Is this apple sweet?
In sentences where is, are, am, was, were, has or have help another verb, we move only the helping verbs to the beginning to form questions.
Statement Question
She is/was eating an apple. Is/Was she eating an apple? They have eaten their apples. Have they eaten their apples?
If there is no helping verb in the sentence, we add do or does in the present tense and did in the past tense.
Present Tense I eat an apple every day. She eats an apple every day. Do I eat an apple every day? Does she eat an apple every day?
Past Tense I ate an apple yesterday Did I eat an apple yesterday?
Note: Does, do and did are superhero helpers – they take the load off the main verb! Look at how does takes the load of the -s off the main verb. Did shows that the question is in the past tense, so the main verb goes back to the present tense form (eat).
We can also add question words if we need more detailed information.
Wh-Question
Words
Why Why is the apple sweet? Asks for a reason
What What are they eating? Asks about the person or thing
Where Where does she eat an apple? Asks about a place
When When do you pick apples? Asks about the time
How How do you bake an apple pie? Asks about the way something is done
Which Which apple should I eat? Asks about choice
Who Who bought you these apples? Asks about the person



1. Form a group of three to four students.
2. On a piece of paper, each player secretly writes the name of a person that everyone playing the game knows.
3. Take turns to make others guess the name you are holding. The other group members must ask not more than 5 questions to guess the name.
4. You may only answer Yes or No to their questions. No Is the person in class?
Does the person play sport?


1. Form questions by changing the position of the underlined words. One has been done for you.
(a) This is the entrance to the zoo.



(b) The giraffe and the hippo are standing still.
(c) The zookeeper is feeding the monkeys.
(d) I am here to see all the animals. Is this the entrance to the zoo?



2. Change each statement into a question using do, does or did. One has been done for you.
(a) You always turn off the lights when you leave the room.
Do you always turn off the lights when you leave the room?
(b) He saves electricity at home. Does
(c) They switch off the fan every evening. Do
(d) We turned off the TV last night.
Did
3. Fill in the blanks with wh-question words.
Sara: Hi Meena! (a) are you doing right now?
Meena: I am doing my homework.
Sara: (b) gave you so much homework?
Meena: Our English teacher did.
Sara: (c) homework are you doing first?
Meena: I am doing Maths first.
Sara: (d) will you finish all your homework?
(asks about a person/thing) (asks about a person) (asks about choice) (asks about time)
Meena: By evening, I think!
4. Frame one question about each of these situations.
(a) (b)











Read the conversation between Ravi and Aman.
Ravi: Hi Aman! Do you want to play cricket today?
Aman: Of course. Where’s your bat?
Ravi: It’s in my brother’s bag.
Aman: Let’s take a ball, stumps and gloves too.
Ravi: Good idea! Did you see yesterday’s match?
Aman: No, I didn’t. Was it fun?
Ravi: Yes, it was great.
Think about and discuss these questions.
1. Whose brother has the bat? brother.
2. List the items the kids will need to play cricket. They will need , , and .
3. Colour in the punctuation mark that is used to separate things in a list.
4. When do we use a full stop?
• In between a sentence
• At the end of a sentence
5. When do we use a capital letter? Think of two reasons.


Capital Letters
• At the start of a sentence
• For I or the name of a person and place
• For the name of festivals, months or days in a week
Full Stop (.) At the end of statements
Question Mark (?) At the end of questions
Comma (,)
Note: We don’t add comma (,) before ‘and’ in a list.
Apostrophe (’)
Exclamation
Mark (!)
• For a list of people or things
• After Yes / No in yes/no answers
• To show belonging
• To shorten two words (contractions)
• To express strong emotions
• I am going to Delhi on Monday.
• I will celebrate Diwali with my family.
• I play cricket every day.
• When will you return?
• I need a ball, a bat, stumps and gloves.
• No, I didn’t see the Red Fort.
• This is my brother’s bag.
• I can’t find my bat.
• Good idea!
Note: When we shorten words we use an apostrophe to show that a letter/letters have been left out:
did not – didn’t cannot – can’t do not – don’t
I will – I’ll madam – ma’am of the clock – o’clock


1. Divide the class into 2 teams.
2. One student from each team runs to the board.
3. They take a slip with an incorrect sentence from the bowl and rewrite it correctly on their team’s side of the board.
4. Teammates cannot help. Instead, they should keep a team score of all the correct sentences.
5. Finally, the team with the most correct sentences wins.
Prepare slips that have sentences with no punctuation in a bowl—one slip per student. For example: my sisters bag is red where is my hat lets play hide and seek i like apples bananas and grapes did you see the dogs bone yes i did no i didn’t



1. Read each sentence. Circle the punctuation mark that best completes the sentence. One has been done for you.
(a) How does your robot work ( . / ? / ! )
(b) Look at my new robot ( . / ? / ! )
(c) Robots are very smart ( . / ? / ! )
(d) Can robots do my homework ( . / ? / ! )
(e) Wow, your robot is amazing ( . / ? / ! )
2. Underline the words that should start with capital letters. In your notebook, rewrite the sentences correctly.
(a) we celebrate independence day on 15 august.
(b) our national flag is called the tiranga.
(c) many people visit red fort in delhi.
(d) i love my country, india.
3. Read the sentences below and use a green pencil to put in commas correctly.
(a) Yes I am very excited about the vacation.
(b) We packed clothes shoes hats and sunglasses.
(c) We will visit beaches museums and markets.
(d) No we did not forget anything.
4. Rewrite the words/phrases using apostrophes.
(a) does not →
(c) we are →


(b) The toys of Ajay →
(d) The tail of the dog →
5. Rewrite each sentence correctly. Use capital letters, full stops, question marks, exclamation marks, commas and apostrophes where needed.
(a) our groups project is about animals
(b) yes we brought glue paper and colouring pencils
(c) I dont know how to draw a lion
(d) Wow anils poster is great








Let us meet Ravi, a student in Grade 3.

Hi! I am Ravi. My school is big. Ananya is my best friend. We are in Class 3. There are swings in the garden. We play on them. Our teacher is kind. There is a green board in the class. There are many books in the class.

Think about and discuss these questions.
1. Who is your best friend?
2. What are the children playing on in the garden?
3. Look around your class. How many bags are there?

Remember! We use is, are and am to tell who someone is or what something is.
We use is, are and am to talk about who someone is or what something is in the present time. They help us talk or write about people, animals, places or things. For example:
Is: We use is when we talk about a person, place, animal or thing in the present time. We use is for he, she or it.
Rupak (He) is a student at Rainbow Public School.
The school is big. His pet (It) is Tuffy.

We use is for he, she or it.
big. His pet (It) is Tuffy.
Am: We use am when we talk about ourselves. I am in Class 3. I am happy today.
Are: We use are with you, we and they.
A collective noun stands for one group or a single unit, so we use is with it.
For example: The team is ready.
Error Alert!
You are a dear friend We/They are good friends.
Note: We use is when any two items go together as one idea or one dish.
For example: Rice and curry is my favourite lunch. We use is because it is one combined meal.
Correct: My brother or my sister is at home.
Wrong: My brother or my sister are at home.
‘Or’ means one of them—so we use is.

Correct: My brother and my sister are at home.
Wrong: My brother and my sister is at home.
‘And’ means both—so we use are.

Roll a dice and start from the START box. Move forward by the number you get. Read the sentences and fill in the blanks with is, am or are.
What your address? START END
My mom and I in a shop. My cousins in London. Ben tall? He not at home. The kids busy. this a giraffe? I a painter. you happy?


The toys colourful. it raining today?



1. Use is or are to complete the sentences. It is Diwali today.
(a) Mother and father in the living room. They are hanging lanterns for the dinner party.
(b) I excited. We video-calling our grandparents.
(c) Chanchal or Salma coming home. Only one of them will join us for dinner tonight.
(d) There poori and aloo sabzi for dinner.

2. Complete the dialogue to learn what Zaid and Rani are talking about.
Rani: Oh no, Zaid! My socks (a) soaking wet!
Zaid: Mine too! This rain (b) so sudden.
Rani: Where (c) your umbrella?
Zaid: It (d) at home. I forgot to bring it.
Rani: I (e) feeling cold now.
Zaid: Let’s run! We (f) near the school gate.



Rani: Look! Our friends (g) waving from the window!
3. Complete the story by filling in the blanks with is, are or am.
My name (a) Divya. I (b) 9 years old. Today (c) Sunday and the weather (d) sunny. My friends Tara and Dev (e) waiting for me at the park. Soon, I reach the park. There (f) a lot of plastic wrappers on the ground. The park (g) not clean. Tara says, ‘It (h) not good to litter like this! There (i) a dustbin nearby. We should start picking up papers.’ Helping others and keeping our community clean (j) important. Kindness and cleanliness (k) good habits.


Time: 40 mins
Total: 25 Marks
1. Read the story and circle the correct options. (5 × 1 = 5 marks)
One day, Anya was painting a poster for her class. She was using her friend Riya’s special markers. When Anya pressed too hard on one of them, the tip broke. Anya felt bad.
She thought, ‘Should I tell Riya the truth or just keep quiet?’
(a) Anya (should / shouldn’t) tell Riya what happened.

(b) She (can / can’t) hide the truth and still feel good inside.
(c) We (should / shouldn’t) be honest even when we’re scared.
(d) Riya (should / shouldn’t) get upset if Anya tells the truth.
(e) Friends (can / can’t) stay close when they are honest with each other.

2. Read the sentences. Circle the subjects and underline the predicates. (5 × 1 = 5 marks)
(a) We visited Qutb Minar last Sunday.
(b) Many tourists take pictures near the tall tower.
(c) The guide explained the histor y of the monument.
(d) Our class walked around the beautiful carvings.
(e) The Qutb Minar stands tall in the heart of Delhi.

3. Fill in the blanks with what, where, which, who, when or how. (5 × 1 = 5 marks)
Avi: Hi Riya! (a) is packing your bag for the trip?
Riya: I’m doing it myself. (b) do we have to bring for the trip?
Avi: Please bring a water bottle, lunch box and your cap.
Riya: Hmm, (c) are we stopping first?
I forgot the plan.

Avi: At the science museum—it’s going to be fun!
Riya: Cool! (d) bus are we taking again? The red or the blue one?
Avi: The blue one—the same as last time.
Riya: Right! And (e) will we reach there?
Avi: At 10 o’clock!

4. Rewrite the sentences using capital letters, full stops, question marks, exclamation marks, commas and apostrophes where needed. (5 × 1 = 5 marks)
The class is rehearsing for the Independence Day celebration.
(a) our class is making posters flags and badges
(b) did you see anils drawing of the indian army
(c) no we cant practise the dance without the music
(d) wow your peacock costume looks amazing

(e) dont forget to bring rajiv and aarushs props tomorrow

5. Complete the story by filling in the blanks with is, are or am. (5 × 1 = 5 marks)
My name is Arjun. Penguins are my favourite flightless birds. A penguin (a) black and white and it is very cute. Penguins (b) not able to fly, but they swim very well.

There are many kinds of flightless birds. Ostriches and emus (c) very big. The kiwi (d) a small bird from New Zealand. I think flightless birds are amazing! I (e) planning to make a poster about them for our classroom.









Read the imaginative poem titled ‘Last Night in My Drawer’.
Last night in my drawer, when the moonlight was bright, My socks were dancers, twirling left and right. My pencil was a soldier, brave and bold, My old crayon box was full of gold.
My ruler was a rocket, zooming through the air, The eraser was a cat meowing—I swear!
My brother and I were princes ready to play, There was my sister, a queen dressed in grey.
When I awoke and the sunlight came in, My drawer was quiet, neat and thin.
The socks were folded, the pencil was straight— No princes, no cats, no rocket or gate.
Think about and discuss these questions.
1. Which words in the poem tell you that the events happened in the past?
2. Which highlighted word is used with My pencil (It)?
3. Which word is used with My socks (They)?

We use was with only one thing. For example: The ruler was a rocket.
We use were with more than one thing. For example: The paper clips were tigers.

We use was and were to tell who or what something was in the past.
We use was for I, he, she and it and with this, that and there.
For example:
My sister (She) was a queen. My pencil (It) was a soldier. There was my sister, a queen dressed in grey.
We use were for you, we and they and with these, those and there.
For example:
My brother and I (We) were knights. The socks (They) were folded. There were many tigers.

Fun with Grammar

You are locked in a vault! Use was or were to crack the 4-digit code and escape!
Each correct answer gives you a code number. Write the correct code to unlock the vault!
1. The kittens asleep on the rug. was → Code: 4 were → Code: 7
2. My backpack heavy yesterday. was → Code: 3 were → Code: 6

3. That my favourite book when I was little. was → Code: 5 were → Code: 0
4. The students excited about the school trip. was → Code: 2 were → Code: 9

1. Zayn went on a trip to the mountains with his family. Circle the correct options. One has been done for you.
(a) The weather (was / were) cold and windy.
(b) My jacket (was / were) warm and cozy.
(c) The trees (was / were) tall and green.
(d) There (was / were) snow on the mountain top.
(e) Our guide (was / were) very kind and funny.
(f) The rocks (was / were) slippery near the stream.
2. Fill in the blanks with was or were.

Last night, we went to watch a new cartoon film. We (a) excited. The theatre (b) full of children and families. My favourite characters (c) on the poster outside. The popcorn (d) warm and buttery. There (e) funny scenes that made us laugh loudly. The best part (f) when the robot danced with the cat!

3. The picture shows a village as it was long ago. In your notebook, describe the picture in 4–5 sentences using is, are, was and were. Start your picture description with ‘Long ago... ’.









Read this passage about celebrating Chhath Puja.
Shanvi’s family has a festival today. It is called Chhath Puja. People in Bihar and nearby states have this festival to thank the Sun God. The sun gives us light and helps plants grow.
It is the first day of the puja. Shanvi’s family has fruit, flowers and lamps for the prayer. Shanvi has a basket. It has bananas, coconuts and sugarcane. Her mother has sweets called thekua. They are yummy! People have to stand near the river to pray.
Yesterday, Shanvi had a busy day. She had a long list of things to do. Her mother had a lot of work in the kitchen.
Shanvi has happy memories of Chhath Puja. Her family has love and joy in their hearts.
Think about and discuss these questions.
1. What items has Shanvi’s family brought for Chhath Puja?
2. What does Shanvi have in her basket?
3. What sweet dish does Shanvi’s mother have?
4. What did Shanvi have to do yesterday?
Remember!
We use has and have for things that happen in the present.
We use had for things that happened in the past.


Let us learn how to use has, have and had, when they are the only verbs in a sentence.
has We use has with he, she or it:
• to talk about the present.
• to show belonging/ possession.
• to show a special quality.
He (Dad) has a lamp for the prayer. She (Shanvi) has a basket.
It (The sun) has importance in our lives. have We use have with I, you, we or they:
• to talk about the present.
• to show belonging/ possession.
• to show a special quality.
had We use had to talk about something in the past, to show belonging and to a show special quality.

I/We have a lamp. You have a basket of fruit.
They (Temples) have peaceful surroundings.
I/You/We had a good time yesterday. He/She had a cheerful smile yesterday. It (The day) had a happy end.
They (Shanvi and her family) had a puja.

1. Imagine a silly or magical pet—it could be a dinosaur dog, a glitter fish or a robot bird!
2. In your notebook, draw your pet and describe it using fun sentences with has, have and had. Give your pet a fun name!
3. Now, tell everyone about your pet.
My pet’s name is Dragoman. It has a long tail. I have a bed for my pet. Yesterday, it had fun flying around.


1. Look at the picture of the toy shop. Circle the correct word to complete each sentence. One has been done for you.
(a) The girl in the picture (has / have) a new doll in her hands.
(b) The boys (has / have) two remote-control cars.
(c) The children (has / have) happy smiles.
(d) When I was little, I (have / had) a soft toy that I loved.

(e) Last year, the shopkeeper (had / has) even more toys in his shop.
2. Fill in the blanks with has, have or had.
(a) Rahul knows that ants (They) six legs.
(b) Butterflies (They) two pairs of wings.
(c) A grasshopper (It) long legs to help it jump.



(d) A spider (It) eight legs and makes a web.


(e) Insects different body parts like a head, a thorax and an abdomen.



(f) Last year, Rahul a science teacher who gave many projects.
3. Read the story. Correct the underlined words by writing has, have or had in the blocks.
It is Sunday morning. Ayaan have a big smile on his face. He has a gift for his best friend, Mira. Mira and her sister has planned a party in their garden. The girls has a colourful mat for everyone to sit on.Yesterday, Ayaan has a cold and said he couldn’t come. They are hopeful that he may come today. They has packed some biscuits for him.








Read the poem.
Let’s Sing, Hop and Shine
She sings when the morning sun shines, He hops on the stones and never whines. It rains a little, then the rainbow glows, Nature gives us joy wherever it goes.
They watch the clouds as they float in the sky, You point at the birds as they fly by. The sun sets, and the evening grows, The world rests calmly as the firefly glows.
Think about and discuss these questions.
Remember!
When a sentence tells us what happens every day, it is in the simple present tense.
1. Underline all the action words in the poem that end with -s or -es.
2. When do these verbs end in -s or -es?
3. Are the actions in the poem happening right now, or do they happen regularly?

When we talk about actions that someone does every day/regularly or as a habit, we use the base form of the verb.
We do not add -s or -es when we talk about I, You, We, They.
For example: I ride my bike. You / We / They point at the birds.
Remember!
Some doing words need an -es because they end with the letters -ch, -sh, -x, -s and -o.
We add -s or -es to the base form of the verb when we talk about he, she or it.
For example:
He / She watches the clouds. It barks loudly.
Some time words in the simple present tense are every day, usually, sometimes, often, always or never.
For example: I usually eat lunch at 1 o’clock. We/They sometimes go for a walk in the evening.
We use is, are and am to ask questions.

For example: I am happy every day. Am I happy every day? The sun (It) is often bright. Is the sun (It) often bright? You are always jolly. Are you always jolly?
If there is only an action verb in the sentence, we add the helping verbs do or does. Does or doesn’t takes the -s and the verb goes back to its plain form.
For example: She/He/It sings in the morning. Does she/he/it sing in the morning?
I/You/We point at the birds. Do I/you/we point at the birds?
Why don’t the action verbs for he, she and it have an -s in the questions? Which word is the super helper that shows the tense?
We use isn’t, aren’t, am not, don’t and doesn’t to say that something does not happen every day.
NegativesPronounsStatementsNegative Statements
am not I I am happy today. I am not happy today.
Note: Am not does not have a short form.
is not (isn’t) He, She, It
are not (aren’t) We, You, They
He/She is angry. It is a bright day. He/She isn’t angry. It isn’t a bright day.
We/They/You are tired. We/They/You aren’t tired.
don’t I/You/We/ They I/You/We/They like loud noises. I/You/We/They don’t like loud noises.
doesn’t He, She, It
He/She paints often. It rains in summer
He/She doesn’t paint often. It doesn’t rain in summer.


Simple Present Tense Fun with I, You, He, She, It, They
1. Make a team of two players. Decide who goes first. 2. Roll a dice. Each number gives you a pronoun.

3. Start from the START box and move forward as many steps as the number on your dice.
4. Make three sentences in the simple present tense – one statement, one negative and a question.
For example:
You roll a 1 → Pronoun: I Block: go to bed early every evening I go to bed early every evening. I don’t go to bed early every evening Do I go to bed early every evening?

1. Fill in the blanks with the correct options. One has been done for you.
(a) My uncle always runs a food stall at the village fair. (run / runs)
(b) Do you your cousins at the fair every year? (see / sees)
(c) They sell handmade toys anymore. (don’t / doesn’t)


(d) She like loud music, so she skips the stage area. (doesn’t / don’t)
(e) What time the fair usually open? (do / does)
(f) I wait in long queues for the rides. (don’t / am not)

2. Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verb in brackets. Add -s or -es as needed. One has been done for you.
(a) Every weekend, Arjun visits (visit) a new place with his parents.

(b) His father usually (take) photos.
(c) His mother (carry) food for them.
(d) They (like) to visit historical monuments.
(e) The guide (tell) them all about the place.

3. Look at the picture. These children help out in the classroom in different ways. Read and complete the questions using: is, are, am, do or does.
(a) she ring the bell after break?
(b) you carry the books to the shelf?
(c) she your class leader?
(d) you in charge of collecting the notebooks?
(e) I the cleanliness in-charge?
4. A student is the media announcer at the school fest . He asked Nitish some questions—but oops! Some helping verbs were incorrect! Correct the helping words. Imagine that you are Nitish and write the answer.
(a) Does you enjoy dancing on stage?
Correct Question: .
Nitish’s Answer: Yes, .
(b) Is you excited about the performance?
Correct Question: .
Nitish’s Answer: Yes, .
(c) Does your friends cheer for you?
Correct Question: .
Nitish’s Answer: Yes, .
(d) Does the teachers tell you to practise every day?
Correct Question: .
Nitish’s Answer: No, .








Read what is happening in the mall.
I am holding a skateboard.
My mother is holding my new football.
My father is looking for a new tie.
My grandfather and my aunt are sitting on the bench.
Jay and I are hoping that grandfather will buy us an ice cream too.

Are the people in the bookshop talking to each other?
No, they aren’t talking.
Think about and discuss these questions.
1. Which part of the verbs in red show real actions?
2. How do all these action verbs end?
3. Which verbs help the action words?
4. How are the last two sentences different from the rest?

A tense is the form of a verb that tells us when an action takes place. Verbs in the present continuous tense tell us that an action continues (is happening) at a time in the present.
The verb form used: is, are or am + verb + -ing. (helping verb) + (main verb)
For example:
At this moment:
I am watching my aunt and grandpa on the bench. My aunt is wearing a yellow saree.
We use am with the pronoun I. We use is with he, she and it. We use are with you, we and they.
Time words are like signals that tell us which tense to use. now: I am watching grandpa right now. at the moment: The shop assistant is speaking at the moment. busy: The people in the bookshop are busy reading.



Note: The helping verb moves to the beginning of the sentence in a question. We can also add question words like How, Where, When, Who, What and Why.
You already know that the helping verbs is, are and am help us to form questions.
I am thinking about ice cream right now.
Am I thinking about ice cream right now?
Why am I thinking about ice cream right now?
Dad is holding a shirt. Is Dad holding a shirt? What is Dad holding? They are visiting the mall. Are they visiting the mall? Why are they visiting the mall?

The helping verbs is, are, am + not help us say what is not happening.
For example:
I am holding a skateboard. I am not holding a skateboard. My aunt is sitting next to GrandpaMy aunt is not sitting next to Grandpa. We are buying things at the mall. We are not buying things at the mall.
Th ink and Tell
1. How can we use contractions in these negative sentences?
My aunt is not sitting next to Grandpa. We are not buying things at the mall.
2. Can we use a contraction in this sentence?
I am not holding a skateboard.

1. Divide the class into two (or more) teams.
2. One team selects a student to mime an action silently (like brushing teeth, riding a bicycle, flying a kite).
3. The other team watches and tries to guess the action by forming complete sentences in the present continuous tense.
4. The team only gets a point if they guess the actions correctly and says the sentences accurately.
5. Switch roles so each team gets a chance to mime and guess.
A Team B

Tina is combing her hair.
• Use action cards if students need help choosing actions.
• Give each team a time limit (30 seconds) to guess.
• Keep a scoreboard to track points and encourage participation.


1. Match the people and the jobs they are doing in the city at this moment.
A banker • • is teaching the students.
A builder • • is counting money.
A professor • • is making delicious chocolates.
A mechanic • • is building a wall.
A cartographer • • is fixing a truck.
A chocolatier • • is drawing a map.

2. Correct the underlined word in each line by writing the correct word in the blank.
(a) Anuj and his friends is helping the community.
(b) Simran am smiling happily.
(c) Kashika are picking up a plastic bottle.
(d) ‘We is saving the environment,’ says Kashika.
(e) ‘I is doing my part,’ says Raj.

3. Fill in the blanks using the words in brackets.
Teacher: What (a) you all (work) on for the water project?
Bhanu: We (b) (test) the water to see if it is clean.
Dhanush: I (c) (make) a poster about the importance of trees.

Shanti: Ravi (d) (colour) in the flyers we made.
Teacher: Shanti, why (e) (not) you (help) Ravi?
Shanti: He (f) just (finish) ma’am.
Teacher: You (g) (do) a great job.

4. Use the picture and the clues to write the sentences in the present continuous tense.
Statement: (children, run)
Question: Is ? (Danish, win)
Negative: No, (Danish, win)
Statement: (Gaurav, try)
5. In your notebook, write a description of what is happening in your classroom at this moment. Use is, are and am and -ing verbs in your description. Write five sentences.









Read the passage aloud. Look at the highlighted words.
Last Sunday morning, my friends and I took part in a cleanliness drive in our neighbourhood. It started at 10 o’clock in the morning. Rohan was sweeping the streets, while Jaspreet and I were picking up plastic bottles and papers. A group of parents was planting small trees along the roadside. The shopkeepers were helping us too. They were arranging dustbins outside their shops. Ali and Nancy were putting up posters about keeping the area clean. Everyone was busy working together to make the neighbourhood neat and beautiful.
Think about and discuss these questions.

1. What was Rohan doing during the cleanliness drive?
2. What were the shopkeepers doing?
3. What were Ali and Nancy doing?
4. Were these actions happening in the past or present?
Encourage learners to answer the questions in complete sentences.

We use the simple past tense to talk about actions that happened in the past. The basic form of the verb takes an -ed or changes completely to show actions that happened in the past.
every day/every year/sometimes/ usually, etc.
I/We/They pick up litter every day.
He/She usually starts in the morning.
I/We/They take part in every cleanliness drive.
He/She goes home with a happy heart.
Remember!
Verbs show the tense (time) of the action.
yesterday/last week/last year/ a week ago, etc.
Verb + -ed
I/We/They picked up litter yesterday. He/She started last week/last year. Verbs that change completely Last year, I/we/they took part in every cleanliness drive.
He/She went home with a happy heart.
Here are more verbs that change in the simple past tense. Every Day Yesterday Every Day Yesterday
am/is/are was/were see saw run ran take took make made have had come came buy bought give gave find found go went swim swam catch caught throw threw meet met write wrote feel felt think thought win won sing sang
We also use was and were as main verbs in the simple past tense to show what something was like. For example: The sun was bright.
Had is used in the simple past to show belonging. For example: The shopkeepers had dustbins.
Verbs in the past continuous tense – was sweeping, were picking up, was planting, were arranging – show actions that were happening at a certain time in the past.
Use was + verb + ing with I, he, she or it
Use were + verb + ing with you, we or they Sunday morning at 10 o’clock, he/she/I was busy sweeping the streets.
Sunday morning at 10 o’clock, they/we/ you were helping clean the streets.
Look at the time words that show how the actions were continuing at a certain time in the past.
At 10 o’clock (any specific time)
At that moment
They were putting up posters at 10 o’clock last Sunday. Rohan was sweeping the street at that time.
The shopkeepers were helping us at that moment.
The past continuous tense is also used with another action in the simple past that indicates a specific time.
For example: We were cleaning the street when it started to rain. I was arranging the bins when my mother called me.


1. Place your token on START.
2. Roll the dice and move your token forward.
3. Look at the time on the block where you land.
4. Say or write what you were doing at that time last Sunday.

For example: At 3:00 p.m. last Sunday, I was playing cricket.


1. Fill in the blanks by changing the verbs in the brackets to the simple past tense.
(a) Last Sunday, my mother (make) soft puris and spicy chole.
(b) My grandmother (cook) tasty vegetable biryani.
(c) My father (buy) fresh paneer from the market.
(d) We all (eat) together and shared stories.
(e) My cousin (sing) a funny song while we ate.
(f) We (feel) full and happy after the meal.
(g) We all (have) a great time.

2. Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verb in brackets (Simple Past or Past Continuous).
(a) One spring morning, we (decide) to decorate the garden.
(b) It (be) a sunny day.
(c) We (take) our tools and (go) outside.
(d) When we stepped out in the garden, the squirrels (play) in the trees.
(e) While we busy (plant) flowers, it suddenly (start) to rain.
(f) When we (come) into the house, my mother and grandma (make) hot chocolate for us to drink.
4. Rewrite Kanak’s story in the past tense, using the simple past or the past continuous. Use the verbs in brackets to help you.
(a) I (visit) Uttarkashi with my family last year. (simple past)
(b) We (arrive) there early in the morning, and my brother and I (walk) to the riverside. (simple past)
(c) I (take) photographs of the snow-covered mountains. (simple past)
(d) When we (get) back, my parents (drink) hot tea at a small stall. (simple past, past continuous)
(e) Many people (sell) caps and shawls at the market. (past continuous)
(f) I (meet) some children who (play) near the temple. (simple past, past continuous)








Read the story given below.
One day, Ridhi sat next to her papa and asked, ‘Papa, how will I go to school in Kanchanpura?’
Papa smiled and said, ‘First, you will wake up early, before the birds! You will brush your teeth with cool river water. Then, you will ride a boat to cross the big river. A crocodile will wave at you—don’t be scared! Next, you will climb a tall mountain. Then, you will sit in a golden bus. The bus will carry goats, hens and happy children. The driver will sing old songs and share funny stories. Finally, you will reach the school just as the bell rings!’

Ridhi’s eyes grew big. She asked, ‘Really, Papa? Will I do all this?’
Papa laughed and said, ‘Of course not, my dear! You will take the school van like you always do!’
Think about and discuss these questions.
1. What will Ridhi brush her teeth with?
2. What will the crocodile do when Ridhi crosses the river?
3. Who will sing old songs?
4. Imagine that your way back home is full of fun and surprises—just like the events Ridhi’s papa told her about! How will you go home after school?


Look at these sentences from the story:
You will wake up early.
The crocodile will wave at you.
You will take the school van like you always do!

Each sentence above has will + a verb. This helps us talk about things that will happen in the future.
To talk about something that will not happen in the future, we use will not + the base form of a verb.

I will play with my car. She will sing a song. We will not watch a film today.

Imagine that you are a superhero! On an A4 size sheet, draw your superhero self in action. Show your cape, mask and powers.
• What powers will you have?
• What will your costume look like?
• What will be your superhero name?




1. Complete the sentences using will + verb.
(a) The jungle team (observe) colourful birds tomorrow.
(b) Rohan (collect) leaves for his project.


(c) Saina (look at) insects with a magnifying glass.
(d) We (learn) about different types of soil.
(e) The whole class (write) reports in their science journal.
2. Read the situations. Tick ( ) the correct option: will or will not to complete the sentence.
(a) There is a test next week.
I (will / will not) work hard to achieve my goal.
(b) Your parents are busy cleaning the house.
I (will / will not) help my parents at home.
(c) Your friend breaks a vase and asks you to lie to the teacher.
I (will / will not) tell lies.
(d) You are brushing your teeth and the tap is open.
I (will / will not) waste water.


3. Read what Riya and Kabir do every weekend. Now in your notebook, rewrite the sentences to say what they will do NEXT weekend.
Riya and Kabir like to help their family.
(a) Riya waters the plants every weekend.
(b) Kabir cleans his room.
(c) Riya bathes her dog.
(d) Kabir helps his mother clean the dishes.





Time: 40 mins
Total: 25 Marks
1. Rewrite the sentences by correcting the underlined words. (5 × 1 = 5 marks)
(a) The students was planting flowers near the wall.
(b) The gardener were helping them dig holes.

(c) The seeds was kept in a small box near the shed.
(d) The watering can were right next to the bench.
(e) Our teacher’s idea were to grow herbs and flowers.
2. Fill in the blanks with has, have or had. (5 × 1 = 5 marks)
(a) My friend Vanya a beautiful voice for singing.
(b) The singers matching costumes for their group performance.
(c) Our teacher told us yesterday that she a list of performances ready.
(d) I to practise my dance steps.

(e) Look, the magician a box full of amazing props!

3. Complete the story with the correct form of the verbs in brackets. Add -s or -es if needed. (5 × 1 = 5 marks)
One day, Pankhuri finds a pencil that can make anything real. She (a) (draw) a bowl of ice cream, and it appears in front of her. Her brothers (b) (ask) her to draw a football. Pankhuri (c) (smile) and draws it quickly. The football and ice cream (d) (look) real. The children (e) (plan) to make a treehouse next.



4. Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verbs in brackets to show that the action is happening now. (5 × 1 = 5 marks)
Teacher: What (a) you all (prepare) for the space exhibition?
Zoya: We (b) (make) a 3D model of the solar system.

Ravi: I (c) (paint) the planets using different colours.
Meera: Arjun (d) (collect) facts about astronauts.
Teacher: (e) You (do) excellent work!
5. Your family is planning a trip to your favourite place. Write five sentences to say what you will or will not do there. (5 × 1 = 5 marks)
A root is the base form of a word. It has its own meaning.
A prefix is a group of letters added to the beginning of a word. It changes the meaning of the root.
A suffix is a group of letters that also changes the meaning or tense and is added to the end of a root word.
For example: play They play with toy cars.
For example: replay Hit the replay button to hear the instructions again.
For example: player and played.
He is a football player. He played a match yesterday.
PrefixesRoot WordNew WordMeaning
un- means not happy unhappy not happy fair unfair not fair
re- means again do redo do again write rewrite write again
SuffixesRoot WordNew WordMeaning
-ful means full of helphelpfulfull of help carecarefulfull of care
-less means without hopehopelesswithout hope carecarelesswithout care
-ness means the state of being kindkindnessbeing kind darkdarknessthe state of being dark
Roots, Prefixes and Suffixes
-ly suggests in a way
quickquicklyin a quick way slowslowlyin a slow way
-ess suggests a female princeprincessfemale of prince lionlionessa female lion
-or or -ors shows a person who does something actactora person who acts inventinventorspeople who invent things
1. Underline the root word and circle the prefix/suffix.
(a) repaint (b) spotless (c) thankful (d) repack
(e) weakness (f) happily (g) director (h) tigress
2. Write the correct prefix (un-, re-) or suffix (-ful, -less, -ness, -ly, -ess, -ors) in each blank to complete the word.
(a) help (without help)
(b) kind (not kind)
(c) power (full of power)
(d) neat (in a neat way)
Note: Check the spelling when you add suffixes to the root words.
(e) good (the state of being good)
(f) invent (people who invent things)
(g) poet (a female poet)
(h) enter (enter again)
3. Fill in the blanks using the correct words with prefixes or suffixes. help care kind happy waiter quick act play
(a) I danced on my birthday.
(b) Can you the video one more time?
(c) That was a answer! Now, I understand.
(d) You should not be when you cross the street.
(e) His made everyone feel welcome.
(f) The played his part very well.
(g) Please bring the water . I am thirsty.
(h) The served a hot meal.
Synonyms are words that mean the same. Antonyms are words that mean the opposite. For example:
Synonyms: big and huge
Note: Small and tiny are also synonyms!
Antonyms: huge/big – tiny/small
SynonymsAntonym/sSynonymsAntonym/s angry/cross/upsetcalm/peaceful/ happy brave/courageousscared/afraid fast/quick/swiftslow/unhurriedwet/soakeddry active/energetic/ lively lazy/idle/inactivehappy/glad/ cheerful sad/unhappy excited/thrilled/ delighted bored/ disappointed bright/shiny/sunnydull/dark/dim/ rainy kind/caring/sweetmean/cruel/nastybeautiful/pretty/ lovely ugly/plain tired/sleepyrested/alertdifficult/tough/ hard easy/simple cold/chilly/icyhot/warmnoisy/loudquiet/silent old/aged/elderlyyoung laugh/giggle cry/sob clean/neat/ spotless dirty/messy/ untidy enemy/foefriend/pal begin/startend/finish/stop love/affectionhatred/dislike
1. Compare the pictures of Zoya and Shanta getting up. Fill in the blanks using words from the box.
tidy easy lazy rainy energetic bright tough messy
Zoya wakes up.

Shanti wakes up.

(a) It is a morning when Zoya gets up. It is a morning when Shanti wakes up.
(b) Zoya is after a good night’s sleep, but Shanti feels .
(c) Zoya finds it to get up in the morning, but Shanti finds it .
(d) It may be because Zoya’s room is , but Shanti’s room is and she knows she will have to clean it up.
2. Fill in the blanks with synonyms of the words given in brackets.
Yesterday, I went to the fair with Sarah, my best friend. It was a (a) (warm) day, but we had enough (b) (icy) water to keep us cool. We saw a (c) (huge) wheel with (d) (small) seats hanging from it.
Sarah was (e) (scared) but I told her we should be (f) (courageous) and go for a ride. The lady at the ticket office was very (g) (sweet), not like the man at the gate who was a bit (h) (nasty).
As we went up, we could see the whole fair! The view was (i) (lovely) from up there!
Homo means ‘same’ and phone means ‘sound.’ So, homophones are words that sound the same but have a different meaning, spelling or both.
The pail is empty. He was pale with fever.
The maid works hard. I made this painting.
I rub my heel with ointment.Doctors heal the patients.
She read the story aloud in classI was allowed to go to the picnic.
Do not stare!
Stop! Pause the game.
Go up one stair at a time.
Dogs have four paws.
These are words that have the same spelling and the same pronunciation, but they have a different meaning.
She is a kind girl. What kind of juice do you want?
This is a heavy rock. Rock the baby to sleep.
He went on a trip to the mountainsDid you trip over your own feet?
This is my mom’s nail. Hammer the nail into the wall.
India won the cricket match.My shoes match my pants.
1. Tick ( ) the correct spelling for the objects in the pictures. (a) pail pale

blew blue
pour paw
stare stair
(e) allowed aloud (f) pair pear

2. Draw a next to the wrong meaning of the words given.
(a) Leaves
i. parts of a plant
ii. a person joining a group
iii. to go from a place
(c) Match
i. a tool for digging
ii. a sports game
iii. a pair that goes well together
(e) Park
i. a green play area
ii. to stop and leave a vehicle
iii. a wild animal
(b) Nail
i. a small metal pin
ii. a fruit from a tree
iii. the hard part on the end of a finger
(d) Fair
i. light in colour
ii. a village carnival
iii. a shopping mall
(f) Right
i. something that is correct
ii. to travel to a place
iii. a direction to turn
3. Fill in the blanks using the appropriate words in brackets.
(a) She went to (buy / by) a dress that matched her shoes.
(b) She injured her (heal / heel) during the sports period. It will take time to (heal / heel).
(c) Our (maid / made) has (maid / made) halwa for me.
(d) I was running on the (stair / stare) when I saw my teacher (stare / stair) at me.
Sometimes, when two words are joined together, they make a new word with a new meaning. Such words are called compound words. For example: tooth + brush = toothbrush
1. Match the words in column A and column B to make a compound word. Write the new words in the space provided.
Column A
Column B door
ring paint
box butter
book mail
bell ear
fly story
brush
2. (a) Use words from the box to write a compound word for each picture. book gold fire snow shelf fish man




(b) In your notebook, use the words in sentences of your own.
A phrasal verb is usually a verb combined with a preposition or an adverb. When you put the words together, they mean something different.
For example:
Turn on/turn off means to start/stop something.
Please turn on the TV.
(verb + preposition = phrasal verb)
Run away means to move away from, usually in fear. The boy ran away from the bully. (verb + adverb = phrasal verb)
1. Fill in the blanks with the correct words in each sentence.
(a) The teacher said, ‘Please before we begin.’ (stand up / dry up)
(b) We will do a exercise together. (take up / warm up)
(c) Exercise our lungs so that we get enough fresh air. (opens up / closes up)
(d) At the end of the day, we our belongings. (pack up / wake up)

2. Fill in the blanks with the correct phrasal verbs from the box. look for hide behind count down come out give up ran off
(a) We always start the game when the seeker says, ‘I will from 10!’
(b) I saw Sneha a big tree.
(c) The seeker had to all the hidden players.
(d) Uri so quickly that the seeker could not catch him.
(e) After 5 minutes, the seeker said, ‘I ! I can’t find anyone!’
(f) ‘Okay, time’s up! Everyone, from your hiding places.’
My friend and I play in the sun, We laugh together, we always have fun. We help each other every day, We find new games and love to play.
Yesterday we shared my kite, It flew so high—a lovely sight. We ate some cookies under the tree, We talked and smiled, and felt so free.
Tomorrow we’ll build a fort so tall, We will hide inside and call to all. A friend like him stays by my side, In every game and every ride.
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
(a) Where do the friends play?
• In the rain
• In the snow
(b) What did the children share?
• A toy car
• A kite
• In the sun
• In the dark
• A sandwich
• A ball
(c) The kite flying is a pretty sight, so it is pretty to…
• hold on to.
• to play with.
• to hear.
• look at.
(d) Which word in the poem means the same as biscuits?
• cakes
• pizzas
• cookies
• sandwiches
2. Fill in the blanks.
(a) The words that rhyme in the first verse (stanza) are: sun and fun and day and .
(b) The opposite of the word ‘low’ from the poem is .
(c) A good friend stays by my .
3. Write the answers in one to two sentences.
(a) Name two things the friends do every day.
(b) Which two things did the two friends do yesterday?
(c) What will they do tomorrow?

The sun is a big, bright star. It gives us light and heat. Without the sun, we would not have day and night. The sun rises in the east and sets in the west. Plants need sunlight to make their food. Animals and people also need the sun. Sunlight helps us stay warm and healthy. Too much sunlight can be harmful, so we must wear hats and sunglasses. The sun is very far from the Earth, but it looks big because it is so close compared to other stars. People use the sun’s energy in many ways. Solar panels change sunlight into electricity. This helps us save other energy sources. The sun is important for life on Earth. The sun helps us in many ways, so we should use its light and take care of our Earth.
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
(a) What is the sun?
• A planet
• A star
(b) Where does the sun rise?
• In the west

• In the north
(c) Why do plants need sunlight?
• To make food
• To drink water
(d) What changes sunlight into electricity?
• A lamp
• A solar panel
2. Circle the option that is NOT correct.
(a) The sun warms the earth.
(b) The sun causes night and day.
(c) Animals and humans need the sun.
(d) The sun is small because it is far away.
• A moon
• In the east
• To grow roots
• A heater
3. Fill in the blanks with the words from the passage.
(a) The word rises is the opposite of .
(b) The word in the passage means the same as dangerous.
4. Write the answers in one to two sentences.
(a) Why should we wear hats and sunglasses?
(b) Write two ways in which people use the sun’s energy.
Last Sunday, Aarav went to an amusement park with his parents and sister. The weather was perfect—it was sunny but not too hot. As they entered, Aarav saw a huge Ferris wheel turning slowly in the sky. First, he and his sister rode the spinning teacups and laughed as they twirled around.
Next, they tried the roller coaster. As it zoomed up and down, there were loud screams and big smiles. Aarav felt a little scared but also excited! Then, they visited the bumper cars. Aarav drove one and gently bumped into his dad’s car.








They also saw a sparkling water fountain and ate some yummy cotton candy. Before leaving, they watched a funny clown perform tricks and saw a man making animals from balloons.
It was a day full of fun, laughter and memories. Aarav said, ‘This was the best day ever!’
1. Fill in the names of the rides next to the adjectives that describe them. Match the description and the correct picture.
(a) Bumpy
(b) Fast
(c) Spinning
(d) Huge




2. Tick ( ) the correct option.
(a) Which ride did Aarav find a little scary but exciting?
• The bumper cars
• The roller coaster
• The spinning teacups
(b) What did Aarav and his sister do on the spinning teacups?
• Fell asleep
• Laughed and twirled
• Cried loudly
3. Find the opposites of the words from the story.
(a) tiny
(b) cried
4. Write the answers in one to two sentences.
(a) What did Aarav eat at the amusement park?
(b) How can you tell Aarav enjoyed his day?

Penguins are birds, but they cannot fly. Instead, they are great swimmers. Penguins have short wings that help them move quickly in water. They use their wings like flippers to swim and catch fish. Most penguins live in cold places like Antarctica. They have thick feathers and a layer of fat to keep them warm. Some penguins, like the African penguin, live in warmer places.

Penguins walk in a funny way because of their short legs. They can also slide on their bellies across the ice. They live in groups called colonies, and they help each other stay safe and warm.
Penguins eat fish, squid and small sea creatures. They catch their food in the ocean. Baby penguins are called chicks. The parents take turns to keep the eggs warm until they hatch. They also share the duty of feeding the chicks.
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
(a) What helps penguins swim?
• Their tails
• Their wings
(b) Where do most penguins live?
• Antarctica
(c) What do penguins eat?
• Grass and leaves
• Fish and squid
• Insects and worms
• The desert
• Their beaks
• The jungle
2. Write true or false.
(a) Penguins can’t fly.
(b) Only their feathers keep them warm.
(c) All penguins live in cold places.
3. Fill in the blanks.
(a) The collective noun for a group of penguins is a of penguins.
(b) Kitten – cat, lamb – sheep, – penguin
4. Write the answers in one to two sentences.
(a) Why do penguins walk in a funny way?
(b) How do you know that penguins are good parents?
A picture composition is when you look at a picture and write a few sentences or a story about it. You look at the picture to know what’s happening, and then use your imagination and words to tell others about it. You can write about the people, animals, things or even what the weather is like in the picture.
One sunny day, a family had a picnic in the park. The parents sat on a big mat under the bright sun. They brought a yummy pizza to share.
There were fruits like watermelon, apples and kiwi. A black and white cat watched them happily. The children rode bicycles on the green grass. Birds and bees flew around. The park was full of colourful flowers. Everyone smiled and enjoyed the fresh air.
Look at the pictures carefully and write 6–8 sentences to describe each picture. (a) (b)


Look at the picture, think about what’s happening, choose how you want to write about it, and use your own ideas to make it fun and creative. Tip!
A paragraph is a group of sentences about the same topic. All the sentences are connected and follow each other in a way that makes sense.
Title
Topic Sentence
Supporting Details Closing Sentence
My favourite person is my mother. She takes care of everyone in the family and always makes me feel loved. She helps me with my homework and tells me interesting stories at bedtime. My mother is kind, hardworking and is always ready to help others. Sometimes, she bakes my favourite cake and we enjoy eating it together. I like spending time with her because she makes me happy. My mother is very special to me and I want to be like her when I grow up.
1. Write about a fun family celebration that you had recently. You can use these questions to help you. What was the celebration? Who was there? Where did it happen? What did you do? How did you feel? What was the best part?
2. Write a paragraph on ‘My First Time on Stage’. Write about what you did, how you felt before and after and what made the experience exciting or memorable.
3. Write a paragraph on ‘If I Could Fly’. Use your imagination to share where you would go, what you would see and how it would feel.
An invitation is a message that asks someone to come to a special event like a birthday party, wedding or school program. It says what the event is, when and where it will happen and who is invited.
An invitation has five sections:
• Event Name
• Date and Time • Location
• Details about the activities • Images (optional)
Model Answer
Event Name
Date and Time
Location
Details
Invitation
Art Mela
Date: Saturday, 15 July 2025
Time: 2 to 4 p.m.
Where: Blue Meadows School Auditorium
We are excited to invite you to our fun and colourful Art Mela! Come and enjoy a day filled with creativity, colours and amazing art! There will be:
• Painting and drawing displays • Fun art games
• A make-your-own craft corner • Prizes for the best artwork!
1. Invite your friends and their parents to a Diwali celebration at your home. Give your invitation a heading and use the correct format.
2. Invite your friends to a storytelling session at your neighbourhood library. Mention who the storyteller is (like your grandmother), the date, time and place. Say what makes the event special.
3. Invite your friends to a Green Day celebration where you will be planting trees in the nearby park. Include the date, time, place and give your invitation a heading.
4. Write an invitation to your cousin for a film night at your house. Include what film you will watch, what snacks there will be and what fun activities you have planned.
A diary entry is like writing a letter to yourself. You write about what happened during your day, how you felt or something you want to remember.
Model Answer
15 July 2025
9 p.m.
Monday
Dear Diary,
Today was a really fun day! We had a drawing competition at school. I drew a big, colourful garden with butterflies. My teacher liked it and gave me a sticker.
Date, Time and Day
Thoughts, Activities and Feelings Greeting
I felt proud and happy. I want to draw even better next time!
Good night, Shivam
Closure
Your Name
1. Write a diary entry describing a visit to a park, zoo, mall or even Grandma’s house. Write about what you saw, heard and felt during the visit. Was there something fun or surprising?
2. Write a diary entry about a time you felt proud. Share a moment when you did something brave or kind—like helping someone, speaking up or learning something new.
3. Write a diary entry about a rainy day adventure. What happened when it rained? Did you splash in puddles, stay cozy inside or curl up with a good book?
4. Write a diary entry about a time you lost or found something. How did you feel? Were you worried, happy or surprised?
• A diary is your special book, so use words like ‘I did,’ ‘I saw’ and ‘I felt.’
• Be honest with your diary.
• Keep it short and simple. Tip!
An informal letter is a letter you write to someone you know well, like a friend or someone in your family. It is friendly and personal.
123, Block B
Raj Garden Road Hyderabad 500001
15 July 2025
Dear Uncle Ravi,
Your home address with the pincode
Date of writing the letter
Greeting
How are you? I hope you are doing well. I miss you a lot! We had a fun day at school yesterday. It was Tree Planting Day. We planted small saplings and watered them. My teacher told us how trees help keep the air clean and cool. I also joined the drawing club last week. I love making colourful posters. I made one about saving nature. Take care and see you soon.
Love, Avinash
Thoughts, activities and feelings
Closing and your signature
1. Write a letter to your aunt thanking her for a gift she gave you. Mention what the gift was, why you liked it and how you are using it.
2. Write a letter to your grandfather asking him to visit during the holidays. Tell him what plans you have and why you want him to come.
3. Write a letter to your friend telling them about a book you read recently. Mention the title, the characters and why you liked the story.
4. Write a letter to your friend telling them about a new hobby you have started. Explain what it is, why you enjoy it and what you have learnt so far.
2. We use an or a
1. He put in an apple, a coin and a feather.
Get Set
Chapter 3 • Articles
(d) The team’s captain lifted the trophy.
(c) The coach’s instructions helped the players.
(b) The fielder’s catch was amazing.
(a)6. The umpire’s whistle signalled the start of the match.
The kite’s tail is long. The doll’s dress is pink.
The cat’s paws are soft.
5. (Answers may vary.)
(a)4. children’s (b) shark’s (c) visitors’ (d) octopus’s
(d) The emperor was kind to the people.
(c) The waiter served us cold drinks.
(b) Her niece won a big award.
(a)3. My brother is reading a storybook.
HAUNTBISNAD AMVANASATUR TNARPEAHEND AUHEEDMISYA
IDSHEKCSHAN
MAREHBAEZYX
PMQCRSTRUVW
ONMELKJGIHG
ABCIDEWIFEF
GRANDMOTHER
Neuter Nouns: Table, Chair, Glass, Pencil 2.
Feminine Nouns: Actress, Empress, Vixen, Girl, Ewe, Goose
Masculine1. Nouns: Actor, Emperor, Fox, Boy, Ram, Gander
Use It for Real
7. The ‘s added to the words ‘waiter’s’ and ‘prince’s’ tell us that they belong to them.
6. It is the tiger’s drum.
5. The poem calls it the hero’s shield.
4. It is uncle’s watch.
How It Works
3. lion – lioness; waiter – waitress; actor – actress; boys – girls
Underline: princess, lioness, waitress, actress, girls
Circle:2. prince, lion, waiter, actor, boys
Animals – lion, lioness, tiger, tigress
People1. – drummer, dancer, prince, princess, actor, actress, waiter, waitress, boys and girls
Get Set
Mahi gave the bride a beautiful bouquet of roses. There was a bunch of bananas in the kitchen. A loud swarm of bees flew in the garden during the haldi ceremony! The guest visited a wildlife park on their way back. They were amazed to see a pride of lions.
6. Mahi and Tarun’s grandparents’ house is in Jim Corbett. Their entire family gathered at Grandma’s house for the wedding.
(e) swarm (f) pride (g) fleet (h) school
(a)4. baskets (b) sandwiches (c) hat (d) apples (e) a monkey (f) children (a)5. team (b) bunch (c) class (d) bouquet
(d) After lunch, Uncle Anil bought us ice cream from Mr Rao’s cart.
3. (a) On Sunday, we went to the zoo with Aunt Meera. (b) My cousin Aarav pointed at the elephant. (c) We had lunch near the lion’s cage at Nehru Zoo Park
1. (a) Underline: egg, children Circle: milk (b) Underline: plate Circle: bread (c) Underline: table Circle: juice (d) Underline: children, banana Circle: butter (e) Underline: bottle, sandwich Circle: water (a)2. bags, house (b) bullock cart, roads (c) garden (d) well (e) river
9. Birds/A flock of birds 10. Ants/A colony of ants Use It for Real
7. Pride (a group of lions) 8. Red Fort
3. table, sofa, lamp, curtain, cards, flower pot (Answers may vary.) 4. many birds Fun with Grammar 1. Sun 2. Chair/Sofa 3. Book/Story book 4. Snow 5. Bag (or School bag) 6. Car/Bus/Train
2. No, we cannot count rice. Rice is an uncountable naming word.
1. Common Names Special Names Names for One More Than One Countable Naming Words Uncountable Naming Words game, apples, bowl, chair, jug, water, birds, book, rice, vegetables, table Tara, Dad, Riya, Mom, Cinderella game, bowl, chair, jug, hat, table apples, vegetables, birds apples, bowl, chair, jug, birds, vegetables, table water, rice
Chapter 1 • Types of Nouns Get Set
4. (a) in (b) at (c) under (d) behind (e) in
3. (a) is (b) have (c) is ringing (d) listens (e) were
2. (a) He (b) They (c) It (d) you
Doing ords:W is, write, read, sat, laughed (Any 2)
escribingD Words: sunny, huge, soft, big, lovely (Any 2)
amingN Words: Arnav, school, Defne, pillows, Ms Nagpal (Any 2)
1. (Answers may vary.)
Self–Assessment
(a)3. smaller smallest (b) hotter hottest (c) easier easiest (d) taller tallest
(e) Circle: cool, fresh Underline: air
(d) Circle: big Underline: trees
(c) Circle: dry Underline: grass
(b) Circle: long Underline: spades
2. (a) Circle: peaceful Underline: garden
1. (a) big (b) two/many (c) many/two (d) pink (e) loud
Use It for Real
with Grammar
2. (a) round (b) yellow (c) small (d) three 3. The boy wearing a white hat is building a tall tower.
Get Set 1. They describe things.
5. tI is Monday morning. Diya is ready for school. She has her bag and tiffin. Diya and her brother are at the table. At the bus stop, the driver picks up the children on time. All the children have their science projects with them for the science fair.
(a)3. an, a (b) an, a (c) The, a (d) a, an, a (e) the (a)4. We (b) her (c) his (d) it (e) them
(e) The lead role was played by my aunt in last year’s play.
(d) I borrowed the girl’s cap for my role.
(c) The waiter forgot to bring juice for the guests.
(b) The robe of the emperor was stitched with golden stars.
(a)2. The actress wore a funny wig and made everyone laugh.
(a)1. (v) (b) (i) (c) (iv) (d) (ii) (e) (iii)
Review Test 1
We clap for those who do not quit.
eW laugh and cheer from where we sit,
One child jumps and lands just right!
The whistle blows — we run with might,
Then take our places with our closest friends.
eW warm up fast, we stretch and ,bend
The teams are marching side by side.
The field is there, the tracks are wide,
4. The sun is bright, the sky is blue, I am ready — how about you?
‘We have some medicine to help you feel better,’ he adds.
The doctor checks him and ,says ‘He has a mild cold. It is nothing serious.’
oon,S the nurse comes out. She says, ‘Ayan, you are next.’
His father smiles and says, ‘Don’t worry. It is okay.’
3. Ayan is not feeling well today. He has a sore throat and a runny nose. His parents take him to the clinic. They have an appointment with Dr Sen. Ayan and his father are sitting in the waiting area. Ayan says, ‘I am a little scared.’
(a) We (b) us (c) My (d) mine (e) she (f) us (g) us/me
Chapter 4 • Pronouns Get Set 1. She means Rahul 2. ‘Them’ refers to the robotics kits. 3. yours, mine Think and Tell The naming words/ nouns are missing from the story, so the story does not make sense. Use It For Real 1. Subject Object Object I her its You me his He you hers She him mine It us ours We them theirs They it yours 2. (a) We (S) (b) them (O) (c) mine (P) (d) me (O) 3. (a) He (b) him (c) his (d) him (e) yours 4. (a) He (b) them (c) his (d) We (e) They
4. (a) We saw an elephant at the zoo. (b) A monkey was sitting in a tree. (c) We saw an owl sleeping. d)( We watched a parrot talk. )e( The zookeeper told us a story about a .tiger
2. (a) a (b) a (c) the (d) an, a, the (a)3. a mela (b) an elephant (c) the food stalls (d) an ice cream (e) an artist
1. tree • A • violin Lotus empleT • artist• ant • An Eiffel• Tower man • • igloo
4. Meera said ‘the hat’ because she and Arjun had already spoken about that same hat—it was a specific hat Use It for Real
3. eW say ‘an apple’ because ‘apple’ begins with a vowel sound, and ‘a coin’ because ‘coin’ begins with a consonant sound.
• • eW are going on a picnic.
• • This milk tastes bad.
• • I spilt my .juice

(d) ops!O
(c) hO no!
• • I left my homework at home. (b) Hurrah!

1. (a) Yuck!
It for Real
1. I say, ‘Oops!’ 2. I say, ‘Wow!’ 3. I say, ‘Hurrah!’
Get Set
.4 (a) but (b) and (c) so (d) or (e) because (f) and
(d) Do you want to swim in the sea or look for shells? (e) We brought a beach umbrella because we wanted to sit in the shade.
.3 (a) We packed our towels and our sunglasses (b) I wanted to build a sandcastle but the sand was too dry. (c) The sun was shining, so we wore our hats.
.2 (a) because (b) and (c) so (d) or (e) but
1. (a) and (b) so (c) but (d) or (e) because (f) and
23. I iedtr to jump, but I slipped.
22. I wanted to paint, so I got my brush.
21. I wanted to go swimming, but it was too cold.
20. eW saw a lion and a zebra at the zoo.
19. ouY can wear slippers or sandals.
18. ohnJ didn’t eat lunch because he wasn’t hungry.
17. anviT was late because/so she missed the bus.
16. I wanted ,cake but there was none left.
15. I velo to jump and run at recess.
14. Do ouy want dal or paneer for lunch?
13. I ’tcouldn sleep because I was scared.
12. Do ouy want to play inside or outside?
11. Rita iedcr because she lost her toy.
10. ouY can wear red or blue.
9. eW sang a song and clapped our hands.
8. I was ed,tir so I took a nap.
7. eH is small, but he is strong.
6. I anr fast because I was late.
Chapter 9 • Conjunctions Get Set .1 Can we read our favourite books or draw quietly? 2. I brought my colour pencils and my new sketchbook! 3. aghav,R please share your colour pencils with Zoya so that you both can work together. Fun with Grammar .1 I ehav a pencil and a rubber. 2. tI was cold, so I wore a jacket. 3. I like apples and bananas. 4. I wanted to ,play but it was raining. 5. ouldW you like milk or juice?
(a) behind (b) on (c) next to (d) above (e) behind (f) in front of
(a) above (b) next to (c) on (d) behind (e) between 3. (a) between (b) in (c) behind (d) in
iii (b) v (c) i (d) iv (e) ii
The ball is under the bed.– Under is used when something is directly beneath another object. Below is used when something is at a lower level but not necessarily directly underneath or touching. The clouds are below the aeroplane. – The clouds are far beneath the plane. They are lower but not touching.
4. These words show the position of something or someone. Think and Tell
3. She has an exam in the morning.
2. Next to the window.
1. Shalini says they are in the sky
Tina Chapter 8 • Prepositions Get Set
7 ulyJ 2025 9:00 pm Monday earD Diary, (a)Today was such a fun day! It was a holiday, so I woke up (b) late. I ran (c) outside to play in the park. The sun was shining (d) brightly. I met my friends at the playground and we played (e) happily on the slide and swings. We shouted (f)loudly while running around. I sat (g) quietly on a bench to eat my snacks. Then, I rode my bicycle (h) cheerfully along the path.
4. (Answers may vary.)
3. (a) outside (b) inside (c) inside (d) away
2. (a) yesterday (b) tomorrow (c) today (d) now
5. They end with ly.Use It for Real (a)1. happily (b) excitedly (c) cheerfully (d) loudly (e) brightly
3. They laughed loudly. 4. They ear action words.
1. Lilly walked slowly. 2. Polly skipped happily.
Chapter 7 • Adverbs Get Set
(e) His mother said he should have clean hands.
(d) He used a wooden spoon to mix the batter.
(c) He used sweet icing to decorate the cake.
(b) He mixed the batter in a big bowl.
(a) Samar baked a soft cake for the party.
6. Describing Word Naming Word soft spoon big cake sweet hands wooden icing clean bowl (Answers may vary)
(d) heavier (e) prettiest
5. (a) smaller (b) longest (c) busiest
(e) There was a cool breeze after the rain.
(d) The view from our room was calm.
(c) We saw a huge mountain covered in snow.
(b) I wore a woollen jacket to stay warm.
4. (a) The soup in the hotel was hot and tasty.
3. There are twenty bags. (Answers may vary.)
1. My best friend is Tina. (Answers may vary.) 2. They are playing on the swings.
Get Set
(d) Wow, Anil’s poster is great!/Wow! Anil’s poster is great.
5. (a) Our group’s project is about animals. (b) Yes, we brought glue, paper and colouring pencils. (c) I don’t know how to draw a lion.
4. (a) doesn’t (b) Ajay’s toys (c) we’re (d) The dog’s tail
(c) We will visit ,beaches museums and markets. (d) ,No we did not forget anything.
(b) We packed ,clothes ,shoes hats and sunglasses.
3. a)( ,Yes I am very excited about the vacation.
(b) Our national flag is called the Tiranga (c) Many people visit Red Fort in Delhi (d) I love my country, India
2. (a) We celebrate Independence Day on 15 August
(e) Wow, your robot is amazing!
(d) Can robots do my homework?
(c) Robots are very smart.
(b) Look at my new robot.
1. (a) How does your robot work?
5. eW use a capital letter at the start of a sentence and for someone’s name. Use It For Real
4. At the end of a sentence
2. They will need a ball, a bat, stumps and gloves. 3. We use comma (,) to separate things in a list.
Get Set 1. Ravi’s brother.
(b) Which dress should I wear?
(a) Who are you talking to?
.4 (Answers may vary.)
.3 (a) What (b) Who (c) Which (d) When
(d) Did we turn off the TV last night?
(c) Do they switch off the fan every evening?
(b) Does he save electricity at home?
.2 a)( Do you always turn off the lights when you leave the room?
(d) Am I here to see all the animals?
(c) Is the zookeeper feeding the monkeys?
(b) Are the giraffe and the hippo standing still?
. (a) 1Is this the entrance to the zoo?
2. It has moved from the middle of the sentence to the beginning.
1. Question: Is this apple sweet? Statement: This apple is sweet.
Get Set
5. Yesterday, I made a bird house with my dad. We used some wood, nails and paint. We cut the wood into pieces and nailed them together. We made a small door for the birds. I painted the bird house blue and yellow. We hung the bird house from a tree in our garden. Now, I am waiting for little birds to come and make it their home.
(d) Arpit loves flying kites.
(c) My family is having a picnic.
(b) The boy is jumping on the trampoline.
(a) Ana is reading a book.
4. (Answers may vary.)
(d) Many tourists • built• the Taj Mahal long ago.
3. Subject Predicate (a) The Taj Mahal • • is made of white marble. (b) It • is• a famous building in Agra, India. (c) Shah Jahan • visit• the monument every year.
(c)d Da pays the bill at the counter. (d) The pershopkee gives us a big smile. (e) The gsba are heavy.
(b) My ersist picks a red dress.
2. (a)e W go shopping together.
(e) My mother takes me to school.
(c) We pack our bags.
1. (b) I run downstairs.
2. I think so because the sentence is complete and the dswor are in order. Use It for Real
1. The mother’s line makes the most sense.
Get Set
Chapter 12 • Sentences
2. (a) can (b) can’t (c) can (d) can’t (e) can 3. (a) shouldn’t (b) should (c) should (d) shouldn’t (e) should 4. (a) cannot (b) should (c) shouldn’t (d) should (e) shouldn’t (f) can (g) can’t
1. (a) We can • • help our .teacher (b) eW can’t • • push our iends.fr (c) eW should • • lift heavy xes.bo (d) eW shouldn’t • • all swim ell.w
1. permission 2. be able to 3. are not allowed Use It for Real
Chapter 11 • Can, Cannot, Should, Shouldn’t Get Set
5. (a) Yay!/Hurrah! (b) Ouch! (c) Look! (d) Hurrah!/Yay! (e) Oh no!
(d) Should we add buttons to the robot or use beads instead? (e) Shravan used a glue gun because it was quicker and easier.
(c) The paint was wet, so we waited for it to dry.
(b) We wanted to use glitter, but we couldn’t find any.
4. (a) I cut the paper and glued it to the cardboard.
3. (a) in (b) next to (c) on (d) between (e) after
2. (a) today (b) happily/loudly (c) quickly (d) outside (e) loudly/happily
(a)1. faster (b) biggest (c) heavier (d) tallest (e) funniest
Review Test 2
3. (a) Hurray!/Wow! (b) Oh no!
.2 (a) Oh no! (b) Yippee! (c) Oops! (d) What!
We are writing in our notebooks. The teacher is walking around to help us. Rohan is asking the teacher a question. Anshul and Abhishek are whispering quietly. I am doing my best.
5. Answers( may vary.)
Statement: Gaurav is trying his best. (Answer may vary.)
Negative: No, Danish is not winning.
Question: Is Danish winning?
Statement: The children are running a race.
4. (Answers may vary.)
(e) aren’t helping (f) is just finishing (g) are doing
(a)3. are working (b) are testing (c) am making (d) is colouring
(a)2. are (b) is (c) is (d) are (e) am
• • is drawing a map.
A chocolatier
A cartographer • • is fixing a truck.
A mechanic • • is building a wall.
A professor • • is making delicious chocolates.
A builder • • is counting money.
Use It For Real 1. A banker • • is teaching the students.
4. All the eviouspr sentences are statements but the last two sentences are a question and a negative statement.
3. The verbs is, are and am help the action words.
2. They all end with an -ing.
1. The second tpar of the verb shows an action, for example, holding, buying and looking.
Get Set
No, the teachers do not/don’t tell me to practise every day.
(d) Do the teachers tell ouy to practise every day?
Yes, they cheer loudly!
(c) Do oury friends cheer for you?
Yes, I am excited about the performance.
(b) eAr you excited about the performance?
Yes, I enjoy dancing on stage.
4. (a) Do ouy enjoy dancing on stage?
3. (a) Does (b) Do (c) Is (d) Are (e) Am
2. (a) visits (b) takes (c) carries (d) like (e) tells
1. (a) runs (b) see (c) don’t (d) doesn’t (e) does (f) don’t
Use It For Real
When we form questions in the Simple Present Tense for the pronouns he, she and it, the helping verb does takes the load of -s (or -es) from the main verb.
Think and Tell
3. The actions happen regularly, not right now.
(Answers may vary.) 1. ,sings shines, hops, whines, rains, glows, gives, goes, sets, grows, rests, glows 2. When ew talk about he, she and it, we add an -s or -es in the simple present tense.
Get Set
Chapter 18 • Simple Present
They has packed some biscuits for him.
It is Sunday morning. Ayaan have a big smile on his face. He has have a gift for his best friend, Mira.Mira and her sister has planned a have party in their garden. The girls has a colourful mat for everyone had to sit on. Yesterday, Ayaan has a cold and said he could not come. have
has
2 (a) have (b) have (c) has (d) has (e) have (f) had
.1 (a) has (b) have (c) have (d) had (e) had
Use It For Real
3. She has thekua. 4. She had a long list of things to do.
1. They have brought fruit, flowers and lamps for the prayer. 2. She has bananas, coconuts and sugarcane in her basket.
Chapter 17 • Has, Have, Had Get Set
Long ,ago life in a village was simple. The houses were made of mud and straw. Wood was used to cook food. Bullock carts were used to carry things. In the picture, the woman is carrying water from the well. The children are playing with spinning tops.
2. (a) were (b) was (c) were (d) was (e) were (f) was .3 (Answers may vary.)
1. Circle: (a) was (b) was (c) were (d) was (e) was (f) were
The final code to escape the vault: 7-3-5-9. Use It for real
Fun with Grammar
2. Was is used with my pencil. 3. Were is used with my socks.
1. Last night tells us that the event happened in the past.
Chapter 16 • Was, Were Get Set
5. (a) is (b) are (c) are (d) is (e) am
(e) Don’t forget to bring Rajiv and Aarush’s props tomorrow.
(d) ow!W Your peacock costume looks amazing./Wow, your peacock costume looks amazing!
(c) No, we can’t practise the dance without the music.
(b) Did you see Anil’s drawing of the Indian Army?
3. (a) Who (b) What (c) Where (d) Which (e) When 4. (a) Our class is making posters, flags and badges.
(e) The Qutb narMi stands tall in the heart of .Delhi
(d) Our sscla walked around the beautiful carvings
(c) The eguid explained the history of the monument
(b) Many ststouri take pictures near the tall tower
2. (a) eW visited Qutb Minar last Sunday
1. (a) should (b) can’t (c) should (d) shouldn’t (e) can
Review Test 3
(h) is (i) is (j) are (k) are
(a)3. is (b) am (c) is (d) is (e) are (f) are (g) is
2. (a) are (b) is (c) is (d) is (e) am (f) are (g) are
(a)1. are (b) am, are (c) is (d) is
Use It for Real
(c) easy, tough (d) tidy, messy
(b) The entspar take turns keeping the eggs warm and feeding the chicks.
4. (a) enguinsP walk in a funny way because their legs are short and close to their bodies.
(a)3. colony (b) chick
(a)2. True (b) False (c) False
(a)1. Their wings (b) Antarctica (c) Fish and squid
4. (a) avAar ate some yummy cotton candy. (b) eH had fun rides, good food and made happy memories with his family. He said it was his best day ever. (Answers may vary.)
1. (a) Bumpy cars (b) Fast roller coaster (c) Spinning teacups (d) Huge Ferris wheel 2. (a) The roller coaster (b) Laughed and twirled 3. (a) huge (b) laughed
4. (a) eW should wear hats and sunglasses in the sun because the sun can harm our eyes and skin. (b) eopleP use the sun’s energy to dry clothes and make electricity. (Answers may vary.)
3. (a) sets (b) harmful
1. (a) A star (b) In the east (c) To make food (d) A solar panel 2. (d) The sun is small because it is far away.
(b) They flew a kite and they ate some cookies. (c) They will build a fort, call out and hide from others.
3. (a) The iendsfr play, laugh, have fun, help each other and play games every day. (Any 2)
2. (a) play (b) high (c) side
1. (a) In the sun (b) A kite (c) look at (d) cookies
e)( give up (f) come out
2. (a) count down (b) hide behind (c) look for (d) ran off
1. (a) stand up (b) warm up (c) opens up (d) pack up
The emanfir helped people during the fire.
The arylibr has a big bookshelf full of storybooks.
yM brother has a pet goldfish in a bowl.
I made a wmansno with my friends in winter.
Doorbell, paintbrush, butterfly, mailbox, earring, storybook 2. (a) snowman, goldfish, bookshelf, fireman (b) (Answers may vary.)
Vocabulary 4 • Compound Words
(a) Leaves: a person joining a group (b) Nail: a fruit from a tree (c) Match: a tool for digging (d) Fair: a shopping mall (e) Park: a wild animal (f) Right: to travel to a place 3. (a) buy (b) heel, heal (c) maid, made (d) stair, stare
Vocabulary 3 • Homophones and Homonyms
may vary.)
(a) happily (b) replay (c)
painter (b) slesspot c)( l futhank(d) packer (e) snesweak (f) lyhappi (g) rodirect (h) sestigr 2. (a) lesshelp (b) kind un(c) fulpower (d) lyneat (e) nessgood (f ) orsinvent (g) esspoet
I will not getfor to buy souvenirs for my friends.
I will not spend too much time on my phone
I will take lots of photos to ememberr the trip.
I will eat my ouritefav food with my family.
I will play on the beach and collect .seashells
5. (Answers may vary.)
4. (a) are preparing (b) are making (c) am painting (d) is collecting (e) are doing
2. (a) has (b) have (c) had (d) have (e) has (a)3. draws (b) ask (c) smiles (d) look (e) plan
1. (a) The students were planting flowers near the wall. (b) The gardener was helping them dig holes. (c) The seeds were kept in a small box near the shed. (d) The watering can was right next to the bench. (e) Our teacher’s idea was to grow herbs and flowers.
.3 (a) Riya will water the plants every weekend. (b) abirK will clean his room. (c) Riya will bathe her dog. (d) Kabir will help his mother clean the dishes. Review Test 4
.2 a)( will (b) will (c) will not (d) will not
4. (Answers may vary.) I will fly on a rainbow bird. Then I will slide down a chocolate hill. Next, I will ride a scooter driven by a robot. I will reach home just in time for snacks! Use It For Real (a). 1 will observe (b) will collect (c) will look at (d) will learn (e) will write
3. The driver will sing old songs.
2. The crocodile will wave at her.
1. Ridhi will brush her teeth with cool river water.
Get Set
(f) I met some children who were playing near the temple.
(e) Many people were selling caps and shawls at the market.
(d) When ew got back, my parents were drinking hot tea at a small stall.
(c) I took photographs of the snow-covered mountains.
(b) We arrived there early in the morning, and my brother and I walked to the riverside.
3. (a) I visited Uttarkashi with my family last year.
2. a)( decided (b) was (c) took, went (d) were playing (d) were planting, started (e) came, were making
(a)1. made (b) cooked (c) bought (d) ate (e) sang (f) felt (g) had
Use It For Real
4. These actions were happening in the past.
3. Ali and ancyN were putting up posters about keeping the area clean.
2. The shopkeepers erew helping us. / They were arranging dustbins outside their shops.
1. Rohan was sweeping the streets during the cleanliness drive.
Chapter 20 • Simple Past and Past Continuous Tense Get Set
The Ignite English Grammar Book is Uolo’s thoughtfully designed grammar programme that aims to help learners go beyond memorising rules to applying grammar in real-life contexts. In line with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 and the National Curriculum Framework (NCF) 2022–23, the grammar programme reimagines learning grammar as a meaningful, discovery-driven journey. Learners explore grammar through contextualised activities that build confidence, expression and communicative competence. The programme supports overall learner development by integrating 21st-century skills— critical thinking, creativity, collaboration and communication—while nurturing social and emotional growth.
• Contextualised Grammar: Learners engage with grammar in real-life situations, which helps them apply patterns, infer rules and use language meaningfully
• Discovery-Driven Learning: A shift from drills to activities that encourage exploration, expression and creativity
• 21st-Century Skills Development: Focusses on critical thinking, creativity, collaboration and effective communication
• Scaffolded Support: Visual cues, structured tasks and step-by-step guidance make grammar instruction accessible to all learners
• Holistic Growth: Encourages learners to apply language to express themselves ethically, collaborate meaningfully, appreciate cultural heritage and connect learning with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
• Gamified Quizzes: Interactive quizzes and challenges motivate learners, reinforce concepts and make grammar practice enjoyable and engaging
• Review Test Papers: Periodic review papers help learners to consolidate their knowledge, assess progress and measure their own learning
Uolo partners with K-12 schools to provide technology-enabled learning programs. We believe that pedagogy and technology must come together to deliver scalable learning experiences that generate measurable outcomes. Uolo is trusted by over 15,000+ schools across India, Southeast Asia and the Middle East.
ISBN 978-81-992630-9-3
