










Academic Authors: Jatinder Kaur, Ayushi Jain
Book Production: Rakesh Kumar Singh
Project Lead: Jatinder Kaur
VP, Learning: Abhishek Bhatnagar
All products and brand names used in this book are trademarks, registered trademarks or trade names of their respective owners.
© Uolo EdTech Private Limited
First published 2025
This book is sold subject to the condition that it shall not by way of trade or otherwise, be lent, resold, hired out, or otherwise circulated without the publisher’s prior written consent in any form of binding or cover other than that in which it is published and without a similar condition including this condition being imposed on the subsequent purchaser and without limiting the rights under copyright reserved above, no part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in or introduced into a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of both the copyright owner and the above-mentioned publisher of this book.
Book Title: Hexa ICSE Computer Science Teacher Manual 6
ISBN: 978-93-49697-29-4
Published by Uolo EdTech Private Limited
Corporate Office Address:
85, Sector 44, Gurugram, Haryana 122003
CIN: U74999DL2017PTC322986
Illustrations and images: www.shutterstock.com, www.stock.adobe.com and www.freepik.com
All suggested use of the internet should be under adult supervision.
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, computer science has become an essential field of study, shaping the world around us in countless ways. From the smartphones in our pockets to the vast networks that connect people across the globe, computer science drives innovation and progress in nearly every aspect of modern life. In today’s fast-paced digital world, understanding the basics of computer science is as important as learning to read, write, or solve maths problems.
Recognising this imperative, the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 has strongly recommended the integration of coding skills, computational thinking, critical analysis, and problem-solving abilities into the curriculum.
Inspired by these insights, Uolo has introduced a comprehensive program, Hexa, for grades 1 to 8, to empower young minds with the knowledge and skills they need to thrive in the digital age. From the basics of how computers function to the tools that shape our digital landscape, this series opens the door to a world of endless possibilities.
We believe that learning computer science should be an engaging and accessible experience for all children. This series takes a project-based approach, allowing students to learn by way of concurrently applying acquired knowledge and skills. As they progress through the course, they will build strong foundations in computational thinking, coding basics, and digital literacy. Our program focuses on three key areas:
1. Computer Science Fundamentals: Core concepts are introduced step by step, ensuring a solid grasp of how computers function, and how information is processed and stored.
2. Latest Computer Tools: Various computer tools relevant to today’s world are included, equipping students with the confidence to thrive in the digital age.
3. Introduction to Coding: The series offers an introductory look into coding, preparing students for more advanced learning in the future.
To support teachers in delivering effective and engaging lessons, we offer a thoughtfully designed Teacher Manual to enhance the teaching and learning experience. Rather than prescribing teaching methods, the manual provides examples and demonstrates how and why teachers can apply these examples in their classes.
Each chapter in this manual is structured to provide a comprehensive lesson plan. The chapters are divided into multiple sessions, each following the Warm up, Engage, Build, and Sum up (WEBS) strategy.
• The Warm up phase sets the stage for learning by connecting to prior knowledge and building curiosity.
• The Engage phase captures the students’ attention and motivates them to participate actively.
• In the Build phase, questions from various sections are discussed to build the understanding of the students.
• Finally, the Sum up phase reinforces learning through easy-to-recall activities and questions.
Time duration for each section has been suggested based on the requirements of the students. Additionally, an answer key for every chapter is provided to assist teachers in assessing their students’ understanding and guiding their learning effectively.
We hope this Teacher Manual empowers educators to implement the curriculum effectively, support diverse student learning, and create interactive, engaging environments tailored to their students’ needs and interests.
Computer Languages
Translator Programs Categories of Computers
Popular Services on the Internet
Potential
Advanced Features of Google Slides and Viewing a Presentation
CSS Font Properties
CSS Border Property

This chapter is divided into the following sessions
1. Computer Languages
2. Translator Programs
3. Categories of Computers
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● define computer languages.
● describe first-generation languages and their advantages and disadvantages.
● describe second-generation languages and their advantages and disadvantages.
● describe third-generation languages and their advantages and disadvantages.
● describe fourth-generation languages and their advantages and disadvantages.
● describe fifth-generation languages and their advantages and disadvantages.
Keyword
● Computer languages: It can be defined as a set of instructions that computers can understand and follow.
Ask the students about different communicating languages.
Explain to the students the concept of computer languages and five generations of computer languages. Also, discuss their advantages and disadvantages.
Group discussion Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
● Ask the students about different communicating languages.
5 mins
● Now, build the concept by discussing that as humans communicate using different languages, computers also have their own languages to understand and follow instructions.
15 mins
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Explanation
Define computer languages. Tell the student that a computer language can be defined as a set of instructions that computers can understand and follow, as given on page 1.
Describe first-generation languages and their advantages and disadvantages.
Describe second-generation languages and their advantages and disadvantages.
Describe third-generation languages and their advantages and disadvantages.
Describe fourth-generation languages and their advantages and disadvantages.
Describe fifth-generation languages and their advantages and disadvantages.
Tell them that a first-generation language is also called machine language or low-level language. Also, tell about its advantages and disadvantages, as given on page 1.
Tell them that second-generation language is also called assembly language. It is also a low-level language. Also, tell about its advantages and disadvantages, as given on page 2.
Tell them that third-generation languages are called high-level languages. Also, tell about its advantages and disadvantages, as given on page 2.
Tell them that fourth-generation languages are called non-procedural languages. They are very high-level languages. Also, tell about its advantages and disadvantages, as given on page 3.
Tell them that fifth-generation languages are used for creating programs for Artificial Intelligence. Also, talk about its advantages and disadvantages, as given on page 3.
Ask the following questions to the students to check their understanding:
● Give some examples of third-generation languages.
Correct Responses: FORTRAN, COBOL, C, C++, Java, C#, etc.
● Which generation language uses simple mnemonic code?
Correct Response: Second-generation languages
● What is the advantage of 5GL?
Correct Response: 5GLs require less code to accomplish tasks.

● Conduct a group discussion in the class among students on the topic 'Evolution of Computer Languages From Fourth Generation to Fifth Generation'.
Possible Response: Fourth-generation languages are very high-level languages. These languages were created to reduce the time, expense, and effort required for creating various software applications. Whereas fifth-generation languages are used for creating programs for Artificial Intelligence.
● Conclude the session by summarising that computer language can be defined as a set of instructions that computers can understand and follow. Also, revise the students about all the generations of computers.
● Assign the following from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 4 and 5
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 1, 2, 4, and 5
C. Who Am I?: Questions 1 and 2
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 5
E. Answer the Following: Questions 1 and 5
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 1 and 4
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe what a translator program is.
● differentiate between compiler, interpreter, and assembler.
Keywords
● Compiler: A compiler is a language processor that reads the source programs written in high-level language and converts them into an equivalent program written in machine code in one go.
● Interpreter: Interpreter is a translator program that converts high-level language code to machine language line by line as the program runs.
● Assembler: A translator, called an assembler, is used to convert assembly language code into machine language code.
Ask the students the meaning of translation. Tell them about translator programs. Also, discuss about the three main types of translator programs: compiler, interpreter, and assembler.
Group discussion Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
Action Plan
Warm Up
● Ask the students the meaning of translation then introduce them to translator programs.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Describe what a translator program is.
Differentiate between compiler, interpreter, and assembler.
Explanation
Tell the students that a translator program for computer languages is similar to a unique tool that enables the computer to understand user requests, as given on page 4.
Tell students about three main types of translator programs namely, compiler, interpreter, and assembler, as given on page 4.

● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 1A section and encourage students to solve them. Instruct them to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses:
1. a. Assembler b. Fifth-generation
2. a. T b. F
● Conduct a group discussion in the class on the topic: 'The Difference Between a Compiler and an Interpreter'.
Correct Response: Interpreter is a translator program that converts high-level language code to machine language line by line as the program runs. Whereas a compiler is a language processor that reads the source programs written in high-level language and converts them into an equivalent program written in machine code in one go.
Sum Up
● Conclude the session by summarising that a translator program converts instructions written in a computer language into something the machine can understand. A compiler translates the source code written in a high-level language into machine language in one go. An interpreter is a translator program that converts high-level language code to machine language line by line as the program runs. An assembler is used to convert assembly language code into machine language code.
● Assign the following from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
B. Tick the Correct Option: Question 3
C. Who Am I?: Question 3
E. Answer the Following: Question 4
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 5
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe supercomputers and their advantages and disadvantages.
● describe mainframe computers and their advantages and disadvantages.
● describe minicomputers and their advantages and disadvantages.
● describe workstations and their advantages and disadvantages.
● describe personal computers and their advantages and disadvantages.
● describe tablets and smartphones and their advantages and disadvantages.
Keywords
● Supercomputers: These are super-fast and large computers. They have huge storage space. They can do lots of tasks very quickly, like a billion tasks in just one second.
● Personal computers: PCs are the most common type of computer and are designed for individual use. They include desktop computers and laptops.
Ask the students about different types of computers they have seen such as laptops, desktops, tablets, etc.
Describe different categories of computers such as supercomputers, mainframe computers, minicomputers, etc.
Group discussion Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
● Ask the students about different types of computers they have seen such as laptops, desktops, tablets, etc. Then, discuss the different categories of computers.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Describe supercomputers and their advantages and disadvantages.
Explanation
Tell the students that supercomputers are super-fast and very big computers with huge storage space. Also, tell about its advantages and disadvantages, as given on page 5.

Describe mainframe computers and their advantages and disadvantages.
Describe minicomputers and their advantages and disadvantages.
Describe workstations and their advantages and disadvantages.
Tell the students that mainframe computers are also big and super-fast, but smaller than supercomputers. Also, tell about its advantages and disadvantages, as given on page 6.
Tell the students that minicomputers are smaller than mainframes but still offer significant computing power. Also, tell about its advantages and disadvantages, as given on pages 6 and 7.
Tell the students that workstations are high-performance computers used for specialised tasks like professional photo and video editing, 3D design, scientific modelling, and software development. Also, tell about its advantages and disadvantages, as given on page 7.
Describe personal computers and their advantages and disadvantages.
Describe tablets and smartphones and their advantages and disadvantages.
Tell the students that PCs are the most common type of computer and are designed for individual use. Also, tell about its advantages and disadvantages, as given on pages 7 and 8.
Tell the students that tablets and smartphones are portable devices that combine computing capabilities with touchscreens. Also, tell about its advantages and disadvantages, as given on page 8.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 1B section and encourage students to solve them. Instruct them to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses:
Tablet and smartphones
Supercomputer
Mainframe computer
Minicomputer
Build
Smaller than mainframes
Need a lot of power and specialised cooling to stay cool
Can be carried anywhere
Performance is meaured in FLOPS
7 mins
● Ask the students to give the answer to the question “What other tasks can be performed using personal computers?" asked in the Think and Tell section on page 8.
Possible Responses: Finding information on a topic, listening to songs, watching films, organising data, etc.
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among students on the topic 'Why Tablets and Smartphones Are More Popular?'.
Possible Response: You can carry tablets and smartphones anywhere you want, they serve as phones, cameras, music players, and more, etc.
● Conclude the session by summarising that the supercomputers are super-fast and very big computers with huge storage space; mainframe computers are also big and super-fast, but smaller than supercomputers. Minicomputers are smaller than mainframes but still offer significant computing power. Workstations are high-performance computers used for specialised tasks like professional photo and video editing, 3D design, scientific modelling, and software development. PCs are the most common type of computer and are designed for individual use. Tablets and smartphones are portable devices that combine computing capabilities with touchscreens.
● Assign the following from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1, 2, and 3
C. Who Am I?: Questions 4 and 5
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 1, 2, 3, and 4
E. Answer the Following: Questions 2 and 3
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 2 and 3

This chapter is divided into the following sessions
1. File Management I
2. File Management II
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● explain file management.
● move data from one drive to another.
● copy or move data between storage devices.
Keyword
● File management: It is the way by which we organise and handle our digital documents and files on a computer or a device.
Ask the students how they manage their different items, such as toys, books, and drawings, in their home.
Explain the concept of file management by giving real-life examples.
Tell the students about how to move data from one drive to another.
Tell them how to copy or move data from one storage device to another.
5 mins
Warm Up
● Ask the students how they manage their different items, such as toys, books, and drawings, in their daily lives. You can encourage the students to share their views and experiences in the class.
● Now, relate the concept of managing things to file management using the appropriate examples.
15 mins
Explain the following concepts:
Explain file management. Describe to the students that file management is the way by which we organise and handle our digital documents and files on a computer or a device, as given on page 12.
Move data from one drive to another.
Copy or move data between storage devices.
Tell them that moving data from one drive to another means taking files and folders from one place to another, as given on page 12. Also demonstrate the various steps to move data from one drive to another by using the cut and paste method, as given on pages 12 to 14. Also, demonstrate the various steps to move data from one drive to another by using the drag and drop method, as given on page 14.
Tell them that moving or copying data between storage devices means transferring information like files or documents from one place, such as a computer, to another, like a USB drive or external hard disk, as given on page 14. Discuss with them the various steps to copy data between storage devices, as given on page 15. Demonstrate the various steps to move data between storage devices, as given on page 15. Also, demonstrate the various steps to move files from an external device to a PC, as given on page 16.
Ask the following questions to the students to check their understanding:
● Ask the students ‘Is file management about keeping your digital space tidy and organised?’
Possible Responses: Yes/No
Correct Response: Yes. When the files are managed properly, the digital space becomes organised.
7 mins
Build
● Conduct a group discussion in the class based on the topic “Why is File Management Important?” provided in the Discuss section on page 16.
Correct Response: File management is important because it helps to organise, locate, and access digital files efficiently.

● Conclude the session by summarising that file management is the way by which we organise and handle our digital documents and files on a computer or a device. Also tell them that moving data from one drive to another means taking files and folders from one place to another. Tell them that moving or copying data between storage devices means transferring information from one device to another. Also, tell them that in moving data, the data gets removed from the original location while copying duplicates it.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 1
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 1 and 2
C. Who Am I?: Questions 1, 3, and 5
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 1 and 2
E. Answer the Following: Questions 1 and 2
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● sort files and folders.
● describe the guidelines for file management.
● search files and folders.
● explain file formats.
● work with multiple applications.
Keywords
● Sorting files: It means to arrange the files in a particular order.
● Searching files: It means looking for specific documents or data on a computer or a device.
● Wildcards: It refers to special symbols that are used to narrow down your search results.
● File format: It defines how information is organised and stored for a specific program’s use.
Ask the students if having their belongings sorted and organised helps them find them more easily.
Explain the concept of sorting file by giving real-life examples.
Tell the students about the general guidelines that needs to be followed while managing files or folders on the computer.
Describe the various steps to search files in the computer.
Discuss the concept of file format.
Explain to them how to work with multiple applications.
Think and Tell Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
● Multitasking: It allows you to switch between apps without closing them. 5
● Ask the students if it’s easy to find an item when everything is sorted and well-organised.
● Relate the same concept of sorting and searching in computers.

Explain the following concepts:
Sort files and folders. Explain to the students that sorting files means arranging the files in a particular order. Discuss with the students that ascending order means to arrange the files in increasing order of their size, and descending order means to arrange the files in decreasing order of their size. Also, demonstrate how to sort files on a computer, as given on pages 16 and 17.
Describe the guidelines for file management.
Discuss the basic guidelines for file management with the students, as given on page 17.
Search files and folders. Tell them that searching files means looking for specific documents or data on a computer or a device, as given on page 18. Discuss with them that wildcards are the special symbols that are used to narrow down your search results, as given on page 18. Demonstrate the steps to use the asterisk and question mark to search files, as given on pages 18 and 19.
Explain file formats. Tell them that file format defines how information is organised and stored for a specific program’s use, as given on page 19. Discuss with them different types of file formats, such as JPEG, PNG, MP4, MP3, DOCX, etc., as given on page 20.
Work with multiple applications.
Tell them working with multiple applications means using several software programs or apps on a computer or a device at the same time, as given on pages 20 and 21. Also, discuss with them multitasking allows you to switch between apps without closing them. Demonstrate how to work with multiple applications, as given on pages 20 and 21.
● Read aloud the question provided in the Do It Yourself 2A section and encourage the students to solve the question. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses:
The steps to observe how data transfer works are:
1. Plug the USB drive or external hard disk into an available USB port on your computer.
2. Open File Explorer and navigate to the location of the files you want to transfer.
3. Select and copy the files you want to transfer.
4. Open another File Explorer and navigate to the external storage device.
5. Paste the selected file.
6. Wait until the transfer process is complete.
7. Before physically disconnecting the device, make sure to safely eject. This ensures all data is written properly on the drive and it is ready for removal.
8. Unplug the USB drive or external hard disk from the computer.
9. Plug the external storage device back into the computer.
10. Open File Explorer and navigate to the external storage device.
11. Select the files on the external storage device and copy them.
12. Paste the copied file into the desired location on your computer.
13. Monitor the transfer progress, and once completed, your files should be on your computer.
7 mins
● Ask the students to give the answer to the question “What are some other file formats that you have seen?” asked in the Think and Tell section on page 20.
Possible Responses:
Some common file formats that you might see are:
● .txt: Plain text file.
● .docx, .doc: Microsoft Word documents.
● .pdf: Portable Document Format, widely used for documents that should look the same on all devices.
● .xlsx, .xls: Microsoft Excel spreadsheets.
● .pptx, .ppt: Microsoft PowerPoint presentations.
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that sorting files means arranging the files in a particular order, either in ascending order or descending order. Tell them that searching files means looking for specific documents or data on a computer or a device. Revise the various symbols used for searching the files and folders. Also, conclude that file format defines how information is organised and stored for a specific program’s use, along with the steps of how to work with multiple applications.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1, 3, 4, and 5
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 3, 4, and 5
C. Who Am I?: Question 2 and 4
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 3, 4, and 5
E. Answer the Following: Questions 3, 4, and 5
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 1 and 2 Build

This chapter is divided into the following sessions
1. What is the Internet?
2. Popular Services on the Internet
3. Potential Threats of Using the Internet and Netiquette
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● define what internet is.
● describe history of internet.
● elaborate advantages of internet.
● discuss disadvantages of internet.
Keyword
● Internet: The internet is a network that connects computers all over the world.
Think about your favourite online game or app. Do you ever wonder how did it get to your device? Elaborate with the students about History of the internet, advantages and disadvantages of the internet.
Think and Tell Conclude the concepts Assign homework
5 mins Warm Up
● Think about your favourite online game or app. Do you ever wonder how did it get to your device?
● Now, relate the concept that these games or apps are available because of the Internet.
Explain the following concepts:
15 mins
Define what internet is. Discuss with the students, internet is a network that connects computers all over the world, as given on page 25.
Describe history of internet. Tell the students that in the early 1960s, the U.S. military laid the groundwork for the internet by creating ARPANET, a network for sharing information between universities, as given on page 25.
Communication: The internet has revolutionised the way we communicate. It allows people to connect instantly through email, social media, video calls, and messaging apps, making it easy to stay in touch with family, friends, and colleagues worldwide.
Communication: The internet has revolutionised the way we communicate. It allows people to connect instantly through email, social media, video calls, and messaging apps, making it easy to stay in touch with family, friends, and colleagues worldwide.
Elaborate advantages of internet. Tell them various advantages of the internet from instant connections across continents to virtual classrooms and convenient shopping, the internet has irrevocably changed how we communicate, learn, navigate, shop, and manage finances, as given on page 26.
Discuss disadvantages of internet.
Communication: The internet has revolutionised the way we communicate. It allows people to connect instantly through email, social media, video calls, and messaging apps, making it easy to stay in touch with family, friends, and colleagues worldwide.
Online Learning: The internet offers access to a vast number of educational resources and online courses. Students and learners of all ages can acquire new skills, take courses, and earn degrees from the comfort of their homes.
Online Learning: The internet offers access to a vast number of educational resources and online courses. Students and learners of all ages can acquire new skills, take courses, and earn degrees from the comfort of their homes.
Describe the different disadvantages of the Internet: that it leads to addiction and neglecting personal health; unsecured connections expose us to cyber threats; while misinformation and cyberbullying can have emotional impacts, as given on pages 26 and 27.
Online Learning: The internet offers access to a vast number of educational resources and online courses. Students and learners of all ages can acquire new skills, take courses, and earn degrees from the comfort of their homes.
Maps and Navigation: Online maps and GPS services help people find addresses, get directions, and navigate unfamiliar places effortlessly. Services like Google Maps provide real-time traffic updates and even public transportation options.
Maps and Navigation: Online maps and GPS services help people find addresses, get directions, and navigate unfamiliar places effortlessly. Services like Google Maps provide real-time traffic updates and even public transportation options.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 3A section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses:
Online Shopping: E-commerce platforms have made shopping more convenient than ever before. People can browse and purchase products from a wide range of retailers, without leaving their homes. Online shopping also offers the advantage of comparing prices and reading reviews.

Maps and Navigation: Online maps and GPS services help people find addresses, get directions, and navigate unfamiliar places effortlessly. Services like Google Maps provide real-time traffic updates and even public transportation options.
Online Payment: The internet has streamlined financial transactions through online payment systems like PayPal and Paytm, and digital wallets. Such services make it secure and easy to send and receive money, pay bills, and make online purchases.
Online Shopping: E-commerce platforms have made shopping more convenient than ever before. People can browse and purchase products from a wide range of retailers, without leaving their homes. Online shopping also offers the advantage of comparing prices and reading reviews.



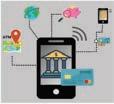
Online Shopping Communication Maps & Navigation Online Payment
Online Payment: The internet has streamlined financial transactions through online payment systems like PayPal and Paytm, and digital wallets. Such services make it secure and easy to send and receive money, pay bills, and make online purchases.
Online Shopping: E-commerce platforms have made shopping more convenient than ever before. People can browse and purchase products from a wide range of retailers, without leaving their homes. Online shopping also offers the advantage of comparing prices and reading reviews.
Despite many advantages, the internet has some disadvantages too. Wastage of Time: The internet has a lot of information that can kill people’s time while surfing the internet. Impact on Health: People may become addicted to using the internet. It can disturb their minds and affect their physical health in the long run. Spending an excessive amount of time on phones, laptops, or other such devices can cause health problems such as reduced eyesight, lower backache, and neckache.

Build 7 mins
Cybersecurity Threats: The internet, if not used correctly, can be a bit like leaving your front door unlocked. Some not-so-nice people may try to sneak into your personal networks and systems and cause harm for their gain or just for fun. If your computer is not secured, they can gain unauthorised access to your personal documents and other information such as stealing your bank account details and using them for their benefit.
● Ask the students to give the answer of the question “Is using the internet an advantage or a disadvantage?” asked in the Think and Tell section on page 27.
Online Payment: The internet has streamlined financial transactions through online payment systems like PayPal and Paytm, and digital wallets. Such services make it secure and easy to send and receive money, pay bills, and make online purchases.
Despite many advantages, the internet has some disadvantages too.
Wastage of Time: The internet has a lot of information that can kill people’s time while surfing the internet.
Possible Response: The internet has advantages, aiding quick information access for school projects, but it can also be a distraction, requiring a balance in usage to ensure effective learning without neglecting other tasks.
Impact on Health: People may become addicted to using the internet. It can disturb their minds and affect their physical health in the long run. Spending an excessive amount of time on phones, laptops, or other such devices can cause health problems such as reduced eyesight, lower backache, and neckache.


Cybersecurity Threats: The internet, if not used correctly, can be a bit like leaving your front door unlocked. Some not-so-nice people may try to sneak into your personal networks and systems and cause harm for

● Conclude the session by summarising that the internet is a network that connects computers all over the world. The history of the internet goes back to the early 1960s when the U.S. military laid the groundwork for the Internet by creating ARPANET, a network for sharing information between universities. The internet has irrevocably changed how we communicate, learn, and navigate. The internet’s vast amount of information can be a time sink, leading to addiction and neglecting personal health. Unsecured connections expose us to cyber threats.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1 and 4
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 1
E. Answer the Following: Question 1
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 1
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe about email and its features, advantages, and disadvantages.
● define Google Drive.
● explain about e-commerce.
● elaborate online payments.
● describe blogging.
● define podcasting.
Keywords
● Email: Email stands for electronic mail. It is a way to send messages over the internet to other people.
● Google Drive: It is a cloud storage service that lets you store files online and access them from anywhere using the internet.
● E-commerce: It refers to buying and selling of products and services online.
● Blog: It is a website where people can write about their thoughts, experiences, and interests.
● Podcasting: It involves creating and sharing audio content.
Ask the students about some earlier methods of sending messages to friends or relatives.
What’s your favourite store? Could you ever buy something from them without leaving your house?
Tell the students about different services of the internet like email, Google Drive, e-commerce, podcasting, blogging. Also describe about the online payments.
● Ask the students about some earlier methods of sending messages to friends or relatives.
● What’s your favourite store? Could you ever buy something from them without leaving your house?
● Now, relate the concept by describing different services of the internet.

Explain the following concepts:
Describe about email and its features, advantages, and disadvantages.
An email is a short form for electronic mail which lets you share messages across the internet. Also tell about its features, advantages and disadvantages as given on pages 27 and 28.
Define Google Drive. Tell the students that Google Drive is their personal vault, which lets you store any file online and access it from anywhere with an internet connection as given on page 28.
Explain about e-commerce. Define that e-commerce is an online shopping wonderland which lets you browse and buy anytime, anywhere, as given on pages 28 and 29.
Elaborate online payments. Explain to the students that online payments are the convenient way to pay for goods and services over the internet without the need for cash or checks, as given on page 29.
Describe blogging. Discuss with the students that a blog is your own corner of the internet, a platform where you can share your thoughts, experiences, and passions with the world, as given on page 30.
Define podcasting. Tell students that podcasts are like radio on demand, but with a twist. Instead of one-size-fits-all broadcasts, you get to choose your own story, as given on pages 30 and 31.
Ask the following questions to the students to check their understanding:
● What is an email?
Correct Response: Email stands for electronic mail. It is a way to send messages to other people over the internet.
● Name some of the online modes of payment.
Correct Responses: Credit Card, Debit Card, Net Banking, Mobile Wallet, UPI
Build 7 mins
● Ask the students to give the answer of the question “Is using email a more convenient way to send or receive messages than the traditional mail?” asked in the Think and Tell section on page 28.
Possible Response: An email offers quick communication, while traditional mail takes longer. Preferences depend on the situation, with email for speed and traditional mail for meaningful experiences.
● Conclude the session by summarising Email is a short form for electronic mail, which lets you share messages across the internet. Google Drive is their personal vault, which lets you store any file online and access it from anywhere with an internet connection. E-commerce is an online shopping wonderland which lets you browse and buy anytime, anywhere. Online payments are a convenient way to pay for goods and services over the internet without the need for cash or checks. A blog is your own corner of the internet, a platform where you can share your thoughts. Podcasts are like radio on demand, but with a twist. Instead of one-size-fits-all broadcasts, you get to choose your own story.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 2, 3, and 5
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 1, 2, 3, and 5
C. Who Am I?: Questions 1, 2, 3, and 5
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 2, 3, 4, and 5
E. Answer the Following: Questions 2, 3, and 5
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 2, 3, and 4

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● define various potential threats and risks.
● describe netiquette.
Keyword
● Netiquette: It refers to a set of rules and regulations for behaving politely and respectfully online.
Can you think of a situation where someone might try to trick you into sharing personal information online? How would you recognise and avoid such a scenario?
If you accidentally come across inappropriate content while using the internet, what steps would you take, and why is it important to report such incidents?
Tell the students about the potential threats and risks associated with the use of internet.
Also tell them about the netiquette.
Group discussion Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
Warm Up
● Can you think of a situation where someone might try to trick you into sharing personal information online? How would you recognise and avoid such a scenario?
● If you accidentally come across inappropriate content while using the internet, what steps would you take, and why is it important to report such incidents?
● Now, build the concept that there are various potential threats when you use the internet, and to avoid them you should follow certain guidelines.
Explain the following concepts:
Define various potential threats and risks.
Describe netiquette.
15 mins
Tell students that there are various risks related to the use of the internet, starting from malware hiding in the shadows to fake links phishing for your personal information, the online world can be a minefield for the unwary, as given on page 31.
Discuss with them netiquette refers to a set of rules and regulations for behaving politely and respectfully online, that means being polite, avoiding unnecessary drama, and respecting privacy, as given on pages 31 and 32.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 3B section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses: 1. B 2. G 3. B 4. B 5. B
Build
7 mins
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among students based on the topic ‘What is personal information and why it’s important to keep it private online?’
Possible Response: Personal information includes details like name and address. Keeping it private online is vital to stay safe, preventing issues like identity theft and unwanted attention from strangers.
3 mins
Sum Up
● Conclude the session by summarising that the internet is as vast and wonderful as it is, comes with its own set of dangers. From malware hiding in the shadows to fake links phishing for your personal information, the online world can be a minefield for the unwary. Netiquette refers to a set of rules and regulations for behaving politely and respectfully online, which means being polite, avoiding unnecessary drama, and respecting privacy.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
B. Tick the Correct Option: Question 4
C. Who Am I?: Question 4
E. Answer the Following: Question 4
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 5

This chapter is divided into the following sessions
1. Creating a Table, Entering, and Editing Data
2. Formatting Tables in Google Docs
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● create a table in Google Docs.
● enter data into a table.
● edit a table.
Keywords
● Table: A table is a grid made up of rows and columns.
● Cell: A cell refers to the intersection of a row and a column.
Ask the students to observe the structure of the timetable of their class.
Explain to the students what a table is and how we can create it. Also, tell them how to enter data into the table and how to edit it.
Warm Up
● Ask the students to observe the structure of the timetable of their class.
● Build the concept that a table is like a grid made up of rows and columns.
Explain the following concepts:
Create a table in Google Docs.
5 mins
15 mins
Tell the students that a table is like a grid made up of rows and columns, as given on pages 36 and 37. Also, explain the steps to create a table.
Enter data into a table. Explain the steps to enter data into a table to the students, as given on pages 37 and 38. Explain how to use the Tab key to move to the next cell and Shift + Tab key to move to the previous cell.
Edit a table.
Discuss with the students that editing a table means making some modifications to the table structure or changing the data in it, as given on page 38.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 4A section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their books.
Correct Responses:
1. Ask the students to solve this question by themselves. Responses may vary.
2. a. Editing a table means making some modifications to the table structure or changing the data in it.
b. Shift + Tab
● If you want to create a table in Google Docs, what steps would you take?
Possible Response: Click Insert > Table > Select the size
● If you want to go to the next cell in a table, which key of the keyboard will help you do so?
Possible Response: Tab
Note: Ask the students the additional questions, if time permits.
Build
7 mins
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among students on the topic ‘How to Edit Data in a Table?’. Possible Response: Locate the cell, click on it to edit, and make the required changes.

● Conclude the session by summarising that a table is like a grid made up of rows and columns. The intersection of a row and a column is called a cell. Tables can be created using the Table option from the Insert menu. After creating a table, you can enter data in it. Editing a table means making some modifications to the table structure or changing the data in it. You can click on a cell to edit its data.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1 and 2
B. Tick the Correct Option: Question 1
C. Who Am I?: Question 2
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 1 and 2
E. Answer the Following: Questions 1 and 2
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 1, 2, 3, and 4
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● format a table.
● change row height and column width in a table.
● split and merge cells in a table.
● add and remove rows and columns in a table.
● apply border and shading to a table.
● align the text horizontally and vertically.
Keywords
● Formatting: It means to change the overall appearance of a table.
● Row: A horizontal arrangement of cells is known as a row.
● Column: A vertical arrangement of cells is known as a column.
● Border: The border refers to a dark outline around any text or picture that makes it look a little standout.
● Shading: Shading means to set the background colour of a cell.
● Cell padding: Cell padding refers to the space between the edges of the cell and the content of the cell.
Ask the students whether they can modify the height of the rows and the width of the columns once the table is drawn on paper or not.
Explain about different types of formatting options for tables like changing row height/column width and splitting/merging cells. Also, discuss how to add and remove rows or columns to and from a table.
Group discussion Conclude the concepts
Assign homework

● Ask the students to draw a table in their notebooks. Now, ask them whether they can modify the height of the rows and the width of the columns once the table is drawn on paper or not.
● Now, relate the concept that while you cannot change the row height and column width of a table created on paper, Google Docs allows you to alter the overall appearance of a table. This includes the ability to modify row heights, column widths, and perform actions, such as merging and splitting cells.
Explain the following concepts:
Format a table. Explain to the students that formatting means to change the overall appearance of a table, as given on page 39.
Change row height and column width in a table.
Split and merge cells in a table.
Discuss with the students that row height is the vertical distance between the top and bottom borders of a row in a table, as given on pages 39 and 40. Also, demonstrate the steps to do so. Also, define that column width is the horizontal distance between the left and right borders of a column in a table, as given on pages 41 and 42. Also, demonstrate the steps to do so.
Explain to the students that splitting cells in a table can help us separate and categorise information in a clear and structured way, as given on pages 42 and 43. Also, discuss with the students that merging cells is like combining two or more cells in a table to create a single, larger cell, as given on pages 43 and 44.
Add rows and columns to a table.
Apply borders and shading.
Align text horizontally and vertically.
Tell the students that after creating a table, they can add more rows and columns by right-clicking on the row/column and selecting the appropriate option, as given on page 44. Similarly, they can remove the rows and columns also, as given on pages 44 and 45.
Describe that applying borders and shading to a table in Google Docs can enhance its visual appeal and make it stand out, as given on pages 45 and 46.
Tell them that horizontal text alignment refers to how the text is positioned within a cell, deciding whether it aligns with the left, centre, or right margins, as given on page 47. Also, discuss with them that vertical alignment refers to the position of a text within the top and bottom edges of a cell in a table, as given on pages 47 and 48.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 4B section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their books. 15 mins
Correct Responses:
1.
Merging cells is like combining two or more cells in a table to create a single cell.
Splitting cells in a table can help you separate and categorise information in a clear and structured way.
2. The border is like a dark outline around any text or picture that makes it look a little standout.
7 mins
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among students on the topic ‘The significance of changing the row height and column width’
Possible Response: You can change the height of the rows and width of the columns to make things easier to read and more organised.
3 mins
Sum Up
● Conclude the session by summarising that formatting means to change the overall appearance of a table which includes changing row height, column width, and merging and splitting cells. Tell them how to change the row height and column width. Also, discuss with them the process of splitting and merging cells in a table.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 3, 4, and 5
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 2, 3, 4, and 5
C. Who Am I?: Questions 1, 3, 4, and 5
E. Answer the Following: Question 3
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 5

This chapter is divided into the following sessions
1. Mail Merge I
2. Mail Merge II
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe Mail Merge and its two documents.
● create the main document.
● create a datasource.
Keywords
● Mail Merge: Mail Merge is a tool in Google Docs that helps you send the same letter or document to many people.
● Datasource: A datasource is the list of recipients to whom you want to send the invite.
Tell the students about Gmail and ask them if they have ever sent an email.
Explain Mail Merge to the students. Also, elaborate about the main document and datasource.
● Tell the students about Gmail and ask them if they have ever sent an email. Then, introduce them to the mail merge.
Explain the following concepts:
15 mins
Describe Mail Merge and its two documents. Tell the students that mail merge is a tool in Google Docs that helps you send the same document to many people. Describe its two documents, as given on page 52.
Create the main document. Describe to the students that the main document is the primary file in a mail merge that contains the layout and structure of the document. The steps to create the main document include launching Google Docs on your computer and selecting the Blank option to create a new document for your invitation, as shown on pages 53 and 54.
Think and Tell
In the Mail Merge pane, you will see the List of Friends is the name of the selected sheet, which is currently active for Mail Merge. What can be the recipient list if you are sending a report card through Mail Merge?
Create a datasource. Describe to the students that the datasource is a file or database containing the information that needs to be merged into the main document during a mail merge. The steps to create the datasource include launching Google Docs on your computer and selecting the Blank option to create a new sheet to create a list of ten friends. Then, provide a unique title for the sheet, such as “List of Friends,” as given on pages 54 to 58.

● Read aloud the question provided in the Do It Yourself 5A section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses:
1 Find these words in the word grid.
1.
2. The main document is the document which contains the text that is to be sent to all recipients.
2 Answer the following questions.
a What is the main document in Mail Merge?
3. The Extension menu is used to add the mail merge extension.

b Name the menu used to add the Mail Merge extension.
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students based on the topic “What would be a better idea—writing an invitation by yourself or doing this job using Mail Merge?” provided in the Discuss section as mentioned on page 52.
Possible Response: Handwritten invitations are more personal when you only need a few; however, mail merge can save you time and allow you to customise each one when you have many to send.
● Ask the students to give the answer of the question “What can be the recipient list if you are sending a report card through Mail Merge?” asked in the Think and Tell section on page 58.
Possible Response: The recipient list can include the names of the students or their parents.
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that the Mail Merge is a tool in Google Docs which helps to send a single document to multiple people at the same time. Describe its two documents and how we can create them.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1, 2, and 3
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 1 and 2
C. Who Am I?: Questions 1, 2, and 3
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 1, 3, and 4
E. Answer the Following: Questions 1, 2, and 3
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 1, 2, and 4
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● define how to insert merge fields.
● describe how to view merge fields.
● print the letter.
Keyword
● Merge field: A merge field is an area within a main document where data from a spreadsheet document or another data source is inserted.
Imagine you’re writing invitations for your birthday party. You want to send each guest a personal invitation with their name and other details. Would it be easier to write each one by hand, or could there be a quicker way?
Explain to the students the steps for inserting and viewing merge fields. Also, elaborate on how to print the letters.
Group discussion Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
5 mins
Warm Up
● Imagine you’re writing invitations for your birthday party. You want to send each guest a personal invitation with their name and other details. Would it be easier to write each one by hand, or could there be a quicker way?
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Define how to insert merge fields.
Explanation
Describe what a merge field is and then tell the students the steps to insert merge fields as given on pages 58 to 60.

Describe how to view merge fields.
Explain to them that viewing the merge field is to check whether the letter has been created with all recipients on the list. Also, describe the various steps involved in viewing merge fields as given on pages 60 and 61. Print the letter. Tell the students that after merging the letters, you can take printouts of the letters. Then discuss the steps to print the letter as given on page 61.
● Read aloud the question provided in the Do It Yourself 5B section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses:
1. 1. Prepare the invite 2. Prepare the list of friends 3. Insert the merge fields
4. View the letter 5. Print the letter
2. a. F b. T c. F Build 7 mins
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among students based on the topic “Share some real-life scenarios where you can use mail merge.” provided in the Discuss section as mentioned on page 62.
Possible Responses:
1. You can use mail merge for a school project, like making personalised letters to invite people to a class event.
2. If you’re in a club and need to send the same information to lots of members, mail merge helps make it easier.
3. Maybe for a family party, sending invites with everyone’s names using mail merge saves time.
4. Teachers could use mail merge to send report cards or announcements to all students and parents.
● Conclude the session by summarising that a merge field is an area within a main document where data from a spreadsheet document or another data source is inserted. Discuss the steps to insert merge fields, view fields, and print a letter.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 4 and 5
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 3, 4, and 5
C. Who Am I?: Questions 4 and 5
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 2 and 5
E. Answer the Following: Questions 4 and 5
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 3 and 5
This chapter is divided into the following sessions
1. Applying Animation and Transitions
2. Inserting Multimedia
3. Advanced Features of Google Slides and Viewing a Presentation
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe animation and apply animation effects in Google Slides.
● determine the use of transitions and how to apply them in Google Slides.
Keywords
● Animation: Animation is a special visual effect that you add to text and different objects on a slide.
● Transition: Transition is the way one slide follows the other on the screen in a presentation.
Ask the students if they have ever thought about how moving effects are added to the objects and slides in a presentation.
Explain to the students what animation is and how it can be applied in Google Slides. Also, tell them how to apply transition effects.
Group discussion
Conclude the concepts
Assign homework

5 mins
Warm Up
● Ask the students if they have ever thought about how moving effects are added to the objects and slides in a presentation.
● Now, build the concept that animations are used to add moving effects to the objects on the slides in a presentation.
● Also discuss with the students that they can also apply special effects to slides which are known as slide transition effects.
Explain the following concepts:
Describe animation and apply animation effects in Google Slides.
Determine the use of transitions and how to apply them in Google Slides.
15 mins
Tell the students that the animations are special visual effects that they add to the text and different objects on a slide, as given on pages 67 and 68.
Discuss with the students that the way one slide follows the other on the screen in a presentation is called a transition, as given on pages 69 and 70.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 6A and 6B sections and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses: (Do It Yourself 6A)
1. False 2. True
Correct Responses: (Do It Yourself 6B)
1. You can preview the transition by clicking the Play button in the Transition sidebar.
2. The Apply to all Slides Button is used to apply the same transition effect to all slides in the presentation.
Build 7 mins
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among students on the topic “How do animations add life to videos and presentations?” as given in the Discuss section on page 68.
Possible Response: Animations add life to videos and presentations by making content more visually appealing, emphasising key points, improving clarity, and enhancing overall engagement.
● Conclude the session by summarising that animation effects are computer magic for making things on the screen move, change size, or appear and disappear in a fun way. In Google Slides, you can add animations by choosing an effect, deciding when it starts (on click, after previous, or with previous), and even make text appear one part at a time. Transitions are moves between slides in presentations.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 3
B. Write T for True and F for False: Question 2
D. Answer the Following: Question 4

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● explain the use of multimedia in a presentation.
● determine how to insert audio and video in a presentation.
● Multimedia: It refers to the combination of multiple forms of content such as text, audio, video, images, etc.
Ask the students what they think about the importance of videos and audios in their learning.
Explain the process of inserting audio and video into the presentation.
Think and Tell Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
● Ask the students what they think about the importance of videos and audios in their learning.
● Now, relate the concept that we can insert multimedia in Google Slides to convey information or engage the audience.
Explain the following concepts:
Explain the use of multimedia in a presentation.
Determine how to insert audio and video in a presentation.
Explain to the students that multimedia refers to the combination of multiple forms of content, such as text, audio, video, images, etc., as given on page 71.
Discuss with the students that sound can capture the audience’s attention and make the presentation more engaging and memorable. Explain that videos can break the monotony of text and static images, making the content more engaging, as given on pages 71 to 74.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 6C and 6D sections and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses: (Do It Yourself 6C)
1. The speaker icon on the slide indicates that the audio file is attached to your presentation.
2. Sound can capture the audience’s attention and make the presentation more engaging and memorable.
Correct Responses: (Do It Yourself 6D)
1. Insert, Video 2. URL
7 mins
● Ask the students to give the answer to the question, “What is the importance of videos? Should they be used or avoided? Present your opinion”, asked in the Think and Tell section given on page 74.
Possible Response: Videos can break the monotony of text and static images, making the content more engaging. While videos can make your presentation unique and interesting, it is important to use them thoughtfully, and ensure they are relevant to your topic, and add meaning to your message.
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that multimedia means using different things like text, audio, video, and images together. In Google Slides, we can make our presentations more interesting by adding sounds and videos.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 4
B. Write T for True and F for False: Question 3
D. Answer the Following: Question 3

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● explain how to use action buttons in a presentation.
● import external data into a presentation.
● describe how to add comments into a presentation.
● explain the use of a dictionary in Google Slides.
● use ink annotations in a presentation.
● illustrate how to zoom a slide and arrange slides in the Slide sorter view.
● describe how to view a presentation.
Keywords
● Comments: The comments facilitate collaboration among multiple authors or reviewers working on the same presentation.
● Action buttons: Buttons that are used to make the presentation more interactive.
Ask the students: Have you seen buttons in presentations which make the presentation more interactive? Explain to them the process of inserting action buttons into the presentation. Think and Tell Conclude the concepts Assign homework
● Ask the students: Have you seen buttons in presentations which make the presentation more interactive?
● Now, relate the concept that we can insert action buttons to make presentations more interactive. We can also write at the time of slideshow, add comments, zoom slides, etc.
Explain the following concepts:
Explain how to use action buttons in a presentation.
Import external data into a presentation.
Describe how to add comments into a presentation.
Explain the use of a dictionary in Google Slides.
Use ink annotations in a presentation.
Illustrate how to zoom a slide and arrange slides in the Slide sorter view.
Describe how to view a presentation.
Explain to the students that action buttons in a presentation are like magic buttons. Also, tell them that it is used to make the slides more interactive, as given on pages 74 to 76.
Discuss with the students that importing data into a presentation is the process of bringing external content or data into your own presentation, as given on pages 76 and 77.
Define that comments facilitate collaboration among multiple authors or reviewers working on the same presentation, as given on pages 78 and 79.
Describe to the students that they can learn more about words or phrases used in the presentation with the help of a dictionary, as given on pages 79 and 80.
Elaborate to them that ink annotations in presentations is like drawing or writing on the slides with colourful pens, just like we do on paper, as given on page 81.
Discuss with the students that slide zoom in presentations makes a small part of the slide look enlarged on the screen. Also, tell them that rearranging slides means changing the order of your slides in your presentation, as given on pages 82 and 83.
Discuss with the students that viewing a presentation means to watch the slides in action, as given on page 84.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 6E, 6F, 6G, 6H, and 6I sections and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses: (Do It Yourself 6E)
1. Insert
2. With the button selected, click on Insert in the menu bar. Choose Link from the drop-down menu. In the Link dialog box, you can add a link to a specific slide, such as the previous slide or slide 1, in your presentation.
Correct Responses: (Do It Yourself 6F)
1. T 2. F
Correct Responses: (Do It Yourself 6G)
1. Insert, Comment 2. Comment
Correct Responses: (Do It Yourself 6H)
1. T 2. F

Correct Responses: (Do It Yourself 6I)
1. Open your presentation in Google Slides
2. Running a slideshow
3. Navigate through slides
4. End the presentation
5. Close Google Slides Build
7 mins
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students on the topic, “If you are given the option to choose the shape for an action button you would like to insert in your presentation, which one would you select, and why do you think it will be suitable?” given in the Discuss section on page 76.
Possible Response: Arrow shapes are more suitable as they denote the direction.
● Ask the students to give the answer to the question, “In what ways can importing data benefit the presenter?” in the Think and Tell section given on page 77.
Possible Response: Importing slides helps to add slides from another presentation to your current presentation. You can also import data from Google Sheets into your Google Slides presentation.
3 mins
Sum Up
● Conclude the session by summarising that we can set action buttons to open external content, such as a website, another PowerPoint presentation, a document, a spreadsheet, and much more. Also, tell the students that there are many interesting tools in Google Slides that are used to import data, add comments, search for information about a word, and many more.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1, 2, and 5
B. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 1, 3, and 5
C. Explain the Functions of the Icons: Questions 1, 2, 3, and 4
D. Answer the Following: Questions 1, 2, and 5
E. Apply Your Learning: Questions 1, 2, 3, and 4
This chapter is divided into the following sessions
1. Introduction to Scratch 3.0 and Its Components
2. Adding and Duplicating a Sprite and Adding Backdrops
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● explain what coding is.
● describe block-based coding.
● explain about Scratch 3.0.
● start Scratch 3.0.
● identify the components of the Scratch window.
Keywords
● Coding: The process of creating sets of instructions that a computer can understand and execute.
● Scratch: An application program that lets you create your own games, stories, and animations.
● Stage: The area where sprites interact and display the results of your code.
Ask the students to think about how they give instructions to a friend to complete a task, like making a sandwich— step by step.
Explain to them what coding is; tell them about block-based coding; introduce them to Scratch 3.0; demonstrate them how to start Scratch and explain the components of the Scratch window. Attempt the given activity.
Conclude the concepts
Assign homework

● Ask the students to think about how they give instructions to a friend to complete a task, like making a sandwich—step by step.
● Then connect this same concept to how coding works in a similar way to give instructions to a computer.
Explain the following concepts:
Explain what coding is. Tell the students that coding is the process of creating sets of instructions that a computer can understand and execute, as given on page 87.
Describe block-based coding. Tell the students that block-based coding is like putting together a fun and colourful jigsaw puzzle, as given on page 87.
Explain about Scratch 3.0.
Introduce the students to Scratch 3.0. Tell them it is an application program that lets you create your games, stories, and animations, as given on page 88.
Start Scratch 3.0. Demonstrate the steps to start Scratch 3.0 to the students, as given on page 89.
Identify the components of the Scratch window.
Introduce students to the various components of the Scratch window such as block panel, blocks palette, coding area, stage, etc., as given on pages 90 and 91.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 7A and 7B sections and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their books.
Correct Responses: Do It Yourself 7A
1. software, websites, mobile apps
2. block-based coding
3. block-based
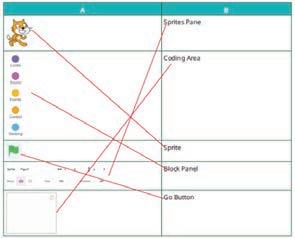
● Describe the functions of three main components of the Scratch window.
Correct Response:
The three main components of Scratch window are: Stage – where the animation happens. Sprite list – shows the characters or objects in the project. Blocks palette – where coding blocks are found and selected.
● Conclude the session by summarising that coding is the process of creating sets of instructions that a computer can understand and execute. Block-based coding is like putting together a fun and colourful jigsaw puzzle. Scratch 3.0 is a free platform where you can show your creative skills. Also, revise them on how to start Scratch and its various components.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 3, 4, and 5
B. Who Am I?: Questions 1, 2, 4, and 5
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 1 and 4
E. Answer the Following: Questions 1, 2, and 4

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● add a sprite and change its costume.
● animate a sprite.
● duplicate a costume and a sprite.
● add a backdrop.
● change a backdrop.
Keyword
Warm Up
Ask the students to imagine designing a character and setting for their own cartoon story.
Demonstrate how can a new sprite be added, animated and duplicated. Demonstrate how can the costume of the sprite be changed and duplicated.
● Sprite: The main character that performs all the actions in your project. 5 mins
Action Plan
Attempt the given activity.
Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
Warm Up
Ask the students to imagine designing a character and setting for their own cartoon story. Then connect it to how in Scratch, we can use sprites and backdrops to bring that story to life. 15 mins
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Add a sprite and change its costume.
Explanation
Explain to the students that they can change or add more sprites to their project as per their choice. Also, they can change the costume of their sprite to give it a different look, as given on pages 91 to 93.
Animate a sprite. Demonstrate to them the steps to animate a sprite, as given on pages 93 and 94.
Duplicate a costume and a sprite. Demonstrate to the students the steps to duplicate a costume and a sprite, as given on pages 95 and 96.
Add a backdrop. Tell the students that you can add backgrounds, also known as backdrops, to your project to create various settings or scenes for your sprites to interact with, as given on pages 97 and 98.
Change a backdrop. Tell the students that if they want to change the background while their project is running, they can use special code blocks to do it, as given on page 98.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 7C and 7D section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their books.
Correct Responses: Do It Yourself 7C
1. Sprite 4. Sprite
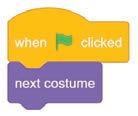
2. next costume 5. When clicked, next costume
3. Choose a sprite Do It Yourself 7D
1. You can switch between costumes using the switch costume to block. You need to specify the names of the costume in this block.
2. next costume block is used to change the costume of a sprite.
3. These blocks are used to animate a sprite.
Build
● Create a Scratch project. Add a new sprite and switch to a different costume.

7 mins

● Conclude the session by summarising how to add a sprite, change a costume, animate a sprite, duplicate a costume, and duplicate a sprite. Also summarise that the students can add backdrops to their project to create various settings or scenes for their sprites to interact with. Revise with them on how to add a backdrop. Also tell them if they want to change the background while their project is running, they can use special code blocks to do it.
● Assign the additional activity given on the panel to the students as homework.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1 and 2
B. Who Am I?: Question 3
C. Explain the Function of the Icon: Questions 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 2, 3, and 5
E. Answer the Following: Questions 3 and 5
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5
This chapter is divided into the following sessions
1. Using Control Blocks
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
2. Using Sensing Blocks
● describe control blocks and their various categories.
Keywords
● Scratch: It is a special computer language that helps us think and solve puzzles.
● Control blocks: These blocks allow a program to perform a test based on a given condition and then take actions based on the result of that test.
Ask students to list steps in their morning routine and identify which ones repeat, which depend on conditions (like weather), and which happen only once.
Explain to them what control and sensing blocks are. Discuss various control blocks.
Attempt the given activity.
Conclude the concepts
● Ask students to list steps in their morning routine and identify which ones repeat, which depend on conditions (like weather), and which happen only once.
● Now, tell them that just like our daily routines have steps that repeat or depend on certain conditions, control blocks in Scratch help us create smart instructions for our sprites.

Explain the following concepts:
Describe control blocks and their various categories.
Build an understanding of control and sensing blocks using the ask and answer blocks. Discuss control blocks and their various categories, such as if-then, if-then-else, repeat, forever, repeat until, wait, wait until, and stop all, with the students, as given on pages 102 and 103.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 8A section and encourage students to solve them. Instruct them to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses: 1. condition 2. repeat
● Create a simple animation where a sprite moves 10 steps and says “I love coding!” 5 times using the repeat control block. Then, explore the forever and if blocks by adding conditions or endless movements.
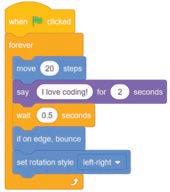
● Conclude the session by summarising that Scratch is an event-driven programming language. This means that the actions are triggered by events, such as clicking a sprite or pressing a key, making it easy to create interactive animations and games. Discuss the control blocks and their various categories, such as if-then, if-then-else, repeat, forever, repeat until, wait, wait until, and stop all, with the students.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1, 2, 3, and 4
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 1, 3, and 4
C. Who Am I?: Questions 2, 3, and 5
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 1 and 5
E. Answer the Following: Questions 1 and 3
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 2 and 5

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe the sensing blocks.
Keyword
● Sensing blocks: These blocks are used to sense conditions in the environment, such as the background colour or the sprite’s touching status.
Warm Up Engage Build Sum Up
Ask students: “Which body parts help you see, hear, or feel things around you?” and list their answers.
Explain sensing blocks to the students with the help of the given project. Attempt the given activity. Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
Warm Up
Ask students: “Which body parts help you see, hear, or feel things around you?” and list their answers. Then tell them that just like we use our senses to understand the world, Scratch sprites use sensing blocks to know what’s happening in their environment.
Engage
Explain the following concept:
Learning Outcome
Describe the sensing blocks.
Explanation
Describe sensing blocks to the students. Discuss the usage of some sensing blocks like touching colour, answering, key pressing, etc. Demonstrate the workings of the project, as given on pages 104 to 108.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 8B section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses: 1. Control, wait for 0.5 seconds 2. Message
Build
7 mins
● Create a Scratch project using a sensing block to make a sprite respond when it touches another object.


Sum Up
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that the sensing blocks are used to sense conditions in the environment, such as the background colour or the sprite touching status. Discuss the various sensing blocks. Also explain the Robo calculator project to the students.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 5
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 2 and 5
C. Who Am I?: Questions 1 and 4
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 2, 3, and 4
E. Answer the Following: Questions 2, 4, and 5
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 1, 3, and 4

This chapter is divided into the following sessions
1. Variable Blocks
2. Mathematical Blocks
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe variable blocks.
● add variables.
Keyword
● set variable values.
● change the variable values.
● Variable blocks: These are the blocks that help a computer store a value that can be changed throughout a project.
Ask the students what a variable is.
Explain to them what variable blocks are. Demonstrate how to add, set, and change variable values.
Warm Up
● Ask the students what a variable is. Give them an example of any mathematical expression having variable, then build the concept of variable blocks.
Explain the following concepts:
Describe variable blocks. Define variable blocks to the students and tell them that in Scratch, a variable can contain two types of values: numeric and textual or string, as given on page 114.
Add variables.
Describe to the students the steps to make the Robo Calculator add a variable value, as given on pages 114 and 115.
Set variable values. Describe to them the steps to make the Robo Calculator set a variable value. Tell them we can just add the set variable to the 0 block to set the variable value, as given on pages 115 to 117.
Change the variable values.
Describe to them the steps to make the Robo Calculator change a variable value. Tell them we can just edit the set variable to 0 block to change the variable value, as given on pages 117 and 118.
Ask the following questions to the students to check their understanding:
● Name the two types of values that a variable can contain.
Correct response: Numeric variable and string variable.
● Name the block that can be edited to change the variable value.
Correct response: Set variable to 0.
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students on the topic ‘Different blocks in Variables blocks category’.
Possible Responses: Set my variable to, change my variable to, my variable.
● Conclude the session by summarising that variable blocks are the blocks that help a computer to store a value that can be changed throughout a project. In Scratch, a variable can contain two types of values: numeric and textual or string. We can add, set, and change the value of a variable.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1 and 4
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 2, 3, and 5
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 1 and 5
E. Answer the Following: Questions 1 and 2
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 2, 3, 4, and 5

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe the mathematical blocks.
● add the two given numbers.
● subtract a number from another number.
● multiply two numbers.
● divide two numbers.
Ask the students to calculate how much they will spend if a pencil costs ₹10 and an eraser costs ₹5. Explain the mathematical blocks to the students. Demonstrate to them the steps to add, subtract, multiply, and divide two numbers.
Attempt the given activity.
Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
● Ask the students to calculate how much they will spend if a pencil costs ₹10 and an eraser costs ₹5.
● Then explain that just like we use math in real life to solve simple problems, we can use Math blocks in Scratch to make our programs smart with numbers.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Describe the mathematical blocks.
Add the two given numbers.
Describe the mathematical blocks to the students. Tell them about the four most commonly used mathematical blocks—addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, as given on pages 118 and 119.
Demonstrate to them the steps to make the Robo calculator add two given numbers, as given on pages 119 and 120.
Subtract a number from another number.
Demonstrate to them the steps to make the Robo calculator subtract a number from another number, as given on pages 120 and 121. Multiply two numbers. Demonstrate to them the steps to make the Robo calculator multiply two given numbers using the multiplication block, as given on pages 121 and 122. Divide two numbers. Demonstrate to them the steps to make the Robo calculator divide a number from another number, as given on pages 122 and 123.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 9A section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses:
1. Events
2. Motion blocks
3. ask and wait
4. Set my variable to 5. Variables
6. Set my variable to
Build
7 mins
● Create a Scratch project to move a sprite. Declare two variables and assign them numeric values. Then, use mathematical blocks to control the sprite’s movement by adding the two values to determine how far the sprite moves. Extend the project by using subtraction, multiplication, and division operations.
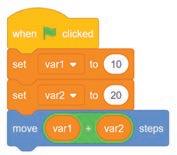
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that the mathematical blocks help a computer perform mathematical operations. These blocks are found under the Operators block category. Discuss with them the steps to add, subtract, multiply, and divide two numbers.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.

A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 2, 3, and 5
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 1 and 4
C. Who Am I?: Question 2
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 2, 3, and 4
E. Answer the Following: Questions 3, 4, and 5
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 1
This chapter is divided into the following sessions
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe HTML and its advantages and disadvantages.
Keyword
● HTML: HTML stands for HyperText Markup Language. It helps you to display colourful text, images, and attractive backgrounds to your web page.
Ask the students to list different ways they share information (e.g., talking, writing, texting).
Describe to the students what HTML is. Tell its advantages and disadvantages.
Attempt the given activity.
Action Plan
Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
● Ask the students to list different ways they share information (e.g., talking, writing, texting).
● Then relate the concept to how HTML helps share information on the internet by structuring content on web pages.

Explain the following concepts:
Describe HTML and its advantages and disadvantages.
Tell the students that we use various computer languages or technologies to create web pages. HTML is one of the technologies used to create web pages, as given on pages 128 and 129.
● Ask the following additional question to the students to check their understanding.
Why is HTML said to be the skeleton of a web page?
Possible Response:
HTML is called the skeleton of a web page because it gives the page its structure, just like bones give shape to a body.
7 mins
Build
● Provide the students with a printed screenshot of a web page (or display one on the board). Ask them to label the parts: heading, paragraph, image, link, etc.
● Then, in small groups, have the students draw their own mock web page on paper, including headings, images (as boxes), and text. Ask them to think about how HTML might help organise those parts.
Sum Up
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that HTML helps you display colourful text, images, and attractive backgrounds to your web page. Revise its advantages and disadvantages.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 3
B. Tick the Correct Option: Question 1
C. Who Am I?: Questions 1 and 4
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 1, 2, and 3
E. Answer the Following: Questions 1, 2, 3, and 5
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 2
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● explain about web browsers.
● describe the basic structure of an HTML document.
Keyword
Ask the students which application will they use to open a website.
● Web browser: A web browser is a software application that processes HTML and other web technologies to display web pages to users. 5 mins Warm
Explain to the students what a web browser is.
Describe the basic structure of an HTML document. Think and Tell Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
● Ask the students which application will they use to open a website.
● Then, tell them about the web browsers. 15 mins
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Explanation
Explain about web browsers. Describe to them what a web browser is. Tell them that Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Microsoft Edge are some common examples of web browsers, as given on page 129.
Describe the basic structure of an HTML document.
Describe the basic structure of an HTML document, which includes a header section and a body section, as given on page 129.

● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 10B section. Encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses:
● Ask the students to give the answer to the question “What type of websites do you want to create using HTML?” asked in the Think and Tell section given on page 129.
Possible Responses: Game websites, news websites, and social networking websites.
● Conclude the session by summarising what a web browser is. Also, revise that HTML contains two sections: a head section and a body section.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 3
C. Who Am I?: Question 1
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 2
E. Answer the Following: Question 2
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● design web pages in HTML.
● create the structure of an HTML document.
Ask the students to think about what parts are needed to build a house (like walls, roof, windows). Explain to the students how to design web pages in HTML. Demonstrate to them how to create the structure of an HTML document.
Attempt the given activity.
Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
5 mins
● Ask the students to think about what parts are needed to build a house (like walls, roof, windows).
● Then relate the concept to how an HTML document also needs a structure with specific parts like head, body, title, and headings to build a web page.
Explain the following concepts:
Design web pages in HTML.
Create the structure of an HTML document.
15 mins
Explanation
Describe the steps involved in designing a web page in HTML are open an editor, write HTML code, save a file, open a browser, and check the web page, as given on page 130.
Describe to them that to create an HTML document, you need to know about a few essential elements, such as doctype HTML, HTML, head, etc. To create a basic HTML document structure, refer to pages 130 and 131 for the necessary elements.

● Ask the following additional question to the students to check their understanding.
● If you leave out the <head> or <body> part of an HTML document, what do you think might happen when you open the page in a browser—and why?
Possible Response:
The web page might not display correctly or might be missing important information, because the browser would not know how to structure or describe the content properly.
● Create the basic structure of an HTML document and add simple content. Save the file with the name “index.html” and open it in a web browser to view the result.
Correct Response:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My First Web Page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to My Page!</h1>
<p>This is a simple web page created using HTML.</p>
</body>
</html>
● Conclude the session by summarising how to design web pages in HTML. Also revise how to create the structure of an HTML document.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 4
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe basic terminologies in HTML.
● explain different types of tags.
Keywords
● Tags: A tag is a keyword that tells the browser how to display a piece of text or content.
● Container tags: These tags consist of an opening tag as well as a closing tag. This start tag and end tag pair are known as the ON and OFF tags and are used to open and close the document.
● Empty tags: An empty tag is a tag without a closing tag.
Now, as the students know about the structure of an HTML document, ask them if they know about tags.
Describe to them the basic terminologies in HTML. Explain about different types of tags.
Group discussion Conclude the concepts Assign homework
5 mins
Warm Up
Now, as the students know about the structure of an HTML document, ask them if they know about tags.
Tell them before writing the HTML code, they need to know about a few terms that they can use in the HTML code.
15 mins
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Describe basic terminologies in HTML.
Explain different types of tags.
Explanation
Describe basic terminologies of HTML, such as tags, elements, attributes, as given on page 131.
Describe types of tags, such as container tags and empty tags. Also, tell them about basic tags in HTML, as given on pages 132 to 134.

● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 10C section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses:
Tag Meaning
hr Italics
br Horizontal rule
b Underline
i Line break
u Bold
Build
7 mins
● Conduct a group discussion among the students in the class on the topic “What is the difference between tags and elements?” mentioned in the Discuss section, as given on page 134.
Possible Responses: A tag is a keyword that tells the browser how to display a piece of text or content. On the other hand, an element is a building block of an HTML, which is defined by a start tag, some content, and an end tag.
3 mins
Sum Up
● Conclude the session by summarising that a tag is a keyword that tells the browser how to display a piece of text or content. Tell them about elements and attributes. Also, describe to them the various types of tags, such as paragraph, break, body, head, etc.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1, 2, 4, and 5
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 2, 3, 4, and 5
C. Who Am I?: Questions 2, 3, and 5
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 4 and 5
E. Answer the Following: Question 4
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 1, 3, 4, and 5
This chapter is divided into the following sessions
1. Structure of an HTML Document
2. Creating an HTML Document
3. Basic HTML Coding Conventions and More HTML Tags
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe the structure of an HTML document.
Keyword
● HTML: HTML stands for HyperText Markup Language. It helps you to display colourful text, images, and attractive backgrounds to your web page.
Ask the students to list the parts of a letter (like greeting, body, and closing).
Describe the structure of an HTML document to the students.
Attempt the given activity.
Action Plan
Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
● Ask the students to list the parts of a letter (like greeting, body, and closing).
● Then relate the concept to how an HTML document also has specific parts like head and body to organise content.

Explain the following concepts:
Describe the structure of an HTML document.
Describe to the students that the structure of an HTML document includes a header section and a body section. Tell them that the basic structure of an HTML document consists of five elements, as given on pages 138 and 139.
● Ask the following additional question to the students to check their understanding. Why do you think HTML needs a specific structure instead of just letting us write all the content freely?
Possible Response:
We need to follow a specific structure for an HTML document because the browser needs clear instructions to understand what each part of the page is and how to display it properly.
● Fill in the missing HTML tags to complete the web page structure.
<! html>
< >
< >
< >My First Page</ >
</ >
< >
< >Hello, World!</ >
<p>This is a paragraph in my first HTML page.</p>
</ >
</ >
Correct Response:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>My First Page</title> </head> <body>
<h1>Hello, World!</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph in my first HTML page.</p> </body> </html>
● Conclude the session by summarising that HTML helps you to display colourful text, images, and attractive backgrounds to your web page. Explain to them the structure of an HTML document. Also, revise them that HTML contains two sections: a head section and a body section.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 2 and 3
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 1 and 2
C. Who Am I?: Questions 2, 3, 4, and 5
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 3 and 5
E. Answer the Following: Questions 1, 2, and 3

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● create an HTML document.
● view an HTML document using a web browser.
Ask the students what type of a web page they would like to create.
Demonstrate to them how to create an HTML document and the steps to view an HTML document using a web browser. Group discussion Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
Action Plan
Warm Up
Ask the students what type of a web page they would like to create.
Then, tell them that HTML provides a lot of tags that are useful for creating a web page.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Explanation
Create an HTML document. Demonstrate the steps to create an HTML document, as given on pages 139 and 140.
View an HTML document using a web browser.
Demonstrate the steps to view an HTML document using a web browser, as given on page 141.
Ask the following questions to the students to check their understanding:
● Which type of editor can be used for creating a web page?
Correct Response: Text-based editors, such as Notepad and WordPad.
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students on the topic ‘Different web browsers in which the web page can open’.
Possible Responses: There are many web browsers which can be used to open the web pages, such as Mozilla FireFox, Microsoft Edge, Google Chrome, etc.
● Conclude the session by summarising the steps to create an HTML document. Also, demonstrate the steps to view an HTML document using a web browser.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
C. Who Am I?: Question 1

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe the basic HTML coding conventions.
● describe more HTML tags.
Ask the students to recall rules they follow when writing a school assignment (like using headings, paragraphs, bold, or italics). Describe the basic HTML coding conventions to the students. Also, demonstrate the use of various HTML tags. Attempt the given activity. Conclude the concepts Assign homework
Ask the students to recall rules they follow when writing a school assignment (like using headings, paragraphs, bold, or italics).
Then relate the concept to how HTML also has certain coding conventions and specific tags to organise and highlight content on a web page.
15 mins
Explain the following concepts:
Describe the basic HTML coding conventions.
Describe more HTML tags.
Explanation
Describe to the students that while writing HTML documents, you should follow some coding conventions, as given on page 141.
Demonstrate to them the use, syntax, and code for some more HTML tags, as given on pages 142 to 144.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 11A section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses:
1. Do it yourself 2.

Build
7 mins
● Create a basic web page on the topic “Science Notes” and include the tags that you have learnt in the chapter.
Possible Response:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Special Tags Example</title> </head>
<body>
<section> <article>
<h2>Science Notes</h2>
<p>Water is made up of H<sub>2</sub>O.</p>
<p>The formula for area is A = πr<sup>2</sup>.</p>
<p><strong>Important:</strong> Always wear safety goggles in the lab.</p>
<p><em>Note:</em> This chapter will be included in the test.</p> </article>
</section>
</body>
</html> Sum Up
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that while writing HTML documents, you should follow the coding conventions such as, always declare the document type as the first line in your document; use either small or capital letters for element names because mixing capital and small letters may be confusing and difficult to debug, etc. Then, revise the <em> tag, <strong> tag, <sub> tag, <sup> tag, <section> tag, and <article> tag. Also, demonstrate the complete project.

● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1, 4, and 5
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 3, 4, and 5
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 1, 2, and 4
E. Answer the Following: Questions 4 and 5
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5
This chapter is divided into the following sessions
1. Introduction to CSS
CSS Colour Properties 3. CSS Font Properties
CSS Border Property
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● explain what CSS is.
● describe CSS syntax.
● use inline CSS.
● use internal CSS.
● use external CSS.
Keywords
● CSS: Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) is a language used to incorporate styles like background colour, font colour, and font size in web pages.
● Selector: It is any HTML element to which you want to apply a style, like <p>.
● Property: It is like an HTML attribute, like colour, which adds additional features to an element.
Ask students if they have ever seen the look of a web page changed without recreating it.
Discuss with the students about CSS, its syntax, and different methods to use it.
Think and Tell Conclude the concepts

Warm Up
● Ask students if they have ever seen the look of a web page change without recreating it.
● Now, build the concept that CSS allows you to change the look of a website without recreating it.
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Explanation
Explain what CSS is. Explain to the students that Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) is a language used to incorporate styles like background colour, font colour, and font size in web pages, as given on page 148.
Describe CSS syntax. Explain to the students that style rules are made up of selectors, properties, and values. All style rules are enclosed within curly brackets {}, as given on page 148.
Use inline CSS. Tell students that the purpose of inline CSS is to apply CSS style rules only to a particular element in an HTML document, as given on page 149.
Use internal CSS. Tell students that they can use the internal CSS method to apply CSS style rules to multiple elements or an entire web page, as given on page 149.
Use external CSS. Explain to the students that the external CSS method allows you to apply style rules to multiple web pages of a website, as given on pages 149 and 150.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 12A section and encourage the students to solve the question. Instruct the students to write the answer in their book.
Correct Responses:
1. a. F b. F c. T
2. Values of the href and rel attributes are wrong. The correct code is: <link rel=”stylesheet” href = “style.css”>
● Conduct a group discussion among the students in the class on the topic “Which method of adding CSS to an HTML document is better in your point of view?” mentioned in the Discuss section, as given on page 150.
Possible Responses: The external CSS method is better in case if you want to apply the style to the entire web page. The internal CSS method is useful when you want to apply the style to multiple elements or an entire web page. The inline CSS method is beneficial when the style needs to be applied to a particular element in a web page.
● Conclude the session by summarising that Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) is a language used to incorporate styles like background colour, font colour, and font size in web pages. Style rules are made up of selectors, properties, and values. There are three methods to use CSS in an HTML document: inline, internal, and external.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1, 2, and 3
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 1 and 2
C. Who Am I?: Questions 1, 2, and 5
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 1, 2, 3, and 5
E. Answer the Following: Questions 1, 2, and 5
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 2

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● use CSS colour properties.
Warm Up Engage Build Sum Up
Ask the students to describe how they choose colours when decorating something (like a card, poster, or outfit).
Demonstrate how to use colour properties of CSS.
Attempt the given activity.
Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
● Ask the students to describe how they choose colours when decorating something (like a card, poster, or outfit).
● Then relate the concept to how web designers use CSS colour properties to style and beautify web pages.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcome
Use CSS colour properties.
Explanation
Demonstrate to the students how to use color and background-color properties. The color property applies colour to the text of an element. The background-color applies a colour to the background of an HTML document, as given on pages 150 and 151.
● Ask the following additional question to the students to check their understanding:
● Why do you think it is helpful to separate the content (HTML) and the style (CSS) when creating a website?
Correct Response:
It is important to separate the content (HTML) and the style (CSS) when creating a website because it makes the code easier to manage and allows you to change the look of the website without touching the content.
7 mins
Build
● Create a web page and decorate it by using the CSS color properties.
Possible Response:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Colour Practice</title>
<style>
body { background-color: lightyellow; }
h1 { color: darkblue; } p { color: green; } </style> </head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to My Colourful Page!</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph with green text on a yellow background.</p> </body>
</html>

● Conclude the session by summarising that CSS provides two colour properties: color and background-color. The color property applies colour to the text of an element. The backgroundcolor property applies colour to the background of an HTML document.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 5
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 3 and 4
C. Who Am I?: Question 3
E. Answer the Following: Question 3
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● use CSS font properties.
Ask students if they have ever wondered how the text on the web page looks well formatted.
Explain to the students the various CSS font properties.
Group discussion
Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
Warm Up
● Ask students if they have ever wondered how the text on the web pages looks well formatted.
● Tell students that they can use the various CSS font properties to format text on web pages.
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcome
Explanation
Use CSS font properties. Tell students that the CSS font properties are used to format text on web pages. Also tell them how to use the font properties like font-family, font-size, font-weight, text-align, text-decoration, and line-height, as given on pages 151 and 152.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 12B section and encourage the students to solve the question. Instruct the students to write the answer in their book.

Correct Responses: Match the CSS property with its possible value.
CSS Property Value
background-colour 14pt
font-size red
text-align double
text-decoration justify
border-style overline
Build
7 mins
● Conduct a group discussion among the students in the class on the topic ‘Different ways to format text on a web page’.
A Fill in the Blanks.
Possible Response: We can format text on a web page by setting its various font styles and sizes, changing the thickness of characters, aligning text, underlining, changing the spacing between the lines of text, etc.
Hints .css # style font-weight structure
1 The main purpose of CSS is to separate the styles from the of the web pages.
3 mins
Sum Up
2 rules are made up of selectors, properties, and values.
3 CSS file is saved with the extension.
● Conclude the session by summarising that the CSS font properties are used to format text on web pages. There are various font properties like font family, font size, font weight, text align, text decoration, and line height
4 The property of CSS specifies the thickness of characters.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
5 The symbol is used at the beginning of hexadecimal code.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 4
B Tick () the Correct Option.
B. Tick the Correct Option: Question 5
C. Who Am I?: Question 4
1 Which of the following brackets is used to enclose style rules with a selector?
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 1, 3, and 4
2 Which of the following is not a method of using CSS in an HTML document?
3 Hexadecimal codes are made up of: a six characters b four characters c two characters d eight characters
4 What does R stand for in RGB?
5 The property sets the size of the text in pixels, points, percentage, or em.
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● use CSS border property.
Ask the students to notice how frames are used around photos, signs, or posters to make them stand out.
Demonstrate to the students how to use the border property of CSS.
Attempt the given activity.
Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
● Ask the students to notice how frames are used around photos, signs, or posters to make them stand out.
● Then relate the concept to how borders in CSS can be used to highlight and separate content on a web page.
Explain the following concepts:
Use CSS border property. Tell students that the border property allows them to add a border around an HTML element. It is a shorthand property that allows them to set the width, style, and colour of the borders. Demonstrate to them how to use border property, as given on pages 152 and 153.
● Ask the following additional question to the students to check their understanding:

● Why do you think designers might use different styles of borders (like solid, dashed, or dotted) on a web page?
Possible Response:
Different styles of borders are used to make different parts of the page stand out, to show separation, or to match the style and purpose of the content.
Build
● Create a web page and apply the CSS border property to highlight and separate different sections on the page.
Possible Response:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Border Practice</title>
<style>
h1 { border: 2px solid blue; padding: 10px; } p { border: 1px dashed green; padding: 8px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This heading has a blue border</h1>
<p>This paragraph has a green dashed border.</p>
</body>
</html>
● Conclude the session by summarising that the border property allows you to add a border around an HTML element. It is a shorthand property that allows you to set the width, style, and colour of all four borders (top, right, bottom, and left).
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 4
E. Answer the Following: Question 4
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 5

Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. FLOPS 2. Mainframe 3. Personal 4. binary 5. mnemonic
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. b. A way in which computers understand instructions. 2. a. Binary 3. b. Interpreter 4. d. Fifth-generation 5. d. Fourth-generation
C. Who Am I?
1. Assembly language 2. Binary language 3. Translator program 4. Workstation 5. Personal Computer
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. T 2. F 3. F 4. F 5. F
E. Answer the Following.
1. A computer language can be defined as a set of instructions that computers can understand and follow.
2. Based on their size and capacity, the computers can be categorised into supercomputers, mainframes, minicomputers, workstations, personal computers, laptops, and tablets.
3. The features of mainframe computers are:
● Mainframe computers are big and super-fast, but they are smaller than supercomputers.
● They can do lots of jobs quickly.
● They are used in places where high precision is required, such as in banks to handle money transactions or in aeroplane guidance.
● Mainframes are super reliable, and they can work for a long time—at least 10 years.
● Examples: IBM z15, IBM z14, Unisys ClearPath Libra, Fujitsu GS21 360, and Hitachi VOS3.
4. A compiler is a language processor that reads the source programs written in high-level language and converts them into an equivalent program written in machine code in one go. On the other hand, the interpreter is a translator program that converts high-level language code to machine language line by line as the program runs.
5. Assembly language uses a simple mnemonic code to communicate with computers. On the other hand, the language that includes the use of binary codes is called binary language.
F. Apply Your Learning.
1. She must have used high-level languages, for example, C, C++, and Java.
2. Supercomputers.
3. Laptop
4. Fifth generation
5. Translator program
Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. move 2. Wildcards 3. format 4. Alt+Tab 5. Multitasking
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. c. To organise files and make them easier to access
2. c. Use the Cut and Paste method or drag and drop
3. b. To represent any number of characters
4. c. It determines how information is stored and which software can open files
5. c. Using several software programs or apps simultaneously
C. Who Am I?
1. Cut and Paste or Drag and Drop
2. Wildcards
3. Organising files and making them easier to find
4. File format
5. Copying data from one storage device to another
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. T 2. F 3. T 4. T 5. T
E. Answer the Following.
1. File management is the way by which we organise and handle our digital documents and files on a computer or a device. On a computer, you can create files using various software applications. To organise these files on your computer, it is better to keep them in separate folders. This is called file management.
2. Copying files means creating a duplicate copy of the file without removing it from the original place, while moving files means relocating the file to a new location and removing it from the original place. Choosing between them depends on whether you want to keep the file in its original place or move it to a new location.
3. In Windows 10, you can use special symbols called wildcards to narrow down your search results. The asterisk (*) symbol is used to search all the files of the same type. For example, you can type *.docx to find all the files that have the .docx extension. The question mark (?) is used to match a single character in the name of the file. For example, if you search for “document?.txt”. Windows will find both “document1.txt” and “document2.txt” because the question mark represents a single character and it can match any single character in the file name.
4. A file format defines how information is organised and stored for a specific program’s use. For example, a .docx file is a Microsoft Word document. Understanding file formats means knowing how different kinds of computer files are built and the rules they follow. These files are important because they help computers make sense of the information stored in them.
5. Working with multiple applications means using several software programs or apps on a computer or device at the same time. In multitasking, you can easily switch between applications based on what you need to do at a particular moment. Compatibility ensures that different apps can work together and share information smoothly. Both multitasking and compatibility help users complete various tasks and projects with ease.
F. Apply Your Learning.
1. By following these steps, you efficiently organise files into subfolders based on their types:
i. Create a new main folder and name it in a way that makes sense to you.
ii. Open File Explorer on your computer.
iii. Navigate to the folder containing the various types of files that need organisation.
iv. Sort the files in the folder by type.
v. Select and copy the files based on the specific type.
vi. Create a new subfolder and name the new folder based on the file type.
vii. Drag the selected files into the newly created subfolder.
viii. Repeat steps v-vii for each file type (e.g., images, spreadsheets). Create a new subfolder for each type and move the corresponding files into their respective subfolders.
ix. Double-check the subfolders to ensure the files are correctly organised.

2. The steps to insert an image in a word processing document are as follows:
i. Open the word processing program, such as Microsoft Word.
ii. Create a new document, type your content, and format it as needed.
iii. Save the document with a name, and it will typically be saved as a .docx file.
iv. Open an image editing program, such as Microsoft Paint.
v. Edit or create an image in it.
vi. Save the image in a commonly used format, like .png or .jpg.
vii. Switch to the Microsoft Word program and go to the location in the document where you want to insert the image.
viii. Click on the Insert tab in the Ribbon. The Insert Picture dialog box opens.
ix. Choose the image file you saved from Microsoft Paint and click the Insert button.
x. Now, the image is inserted in the document in the Microsoft Word.
The file formats associated with the word processing program are .docx, .doc, and .txt and, the file formats associated with the image editing program are .jpg, .png, and .bmp.
Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. global 2. send 3. share 4. 1960s 5. sell
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. d. Television
2. a. A writer’s thoughts and opinions on a particular topic
3. d. None of these
4. c. Share personal information about yourself or others
5. a. You can share your thoughts and experiences with the world
C. Who Am I?
1. E-mail 2. Blog 3. Podcasting 4. Netiquette 5. UPI
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. T 2. F 3. T 4. T 5. F
E. Answer the Following.
1. The internet is a network that connects computers all over the world.
2. Email stands for electronic mail. It is a way to send messages over the internet to other people. Emails can be used to send textual content, photos, documents, and others as attachments.
Following are the advantages of an email:
● Most email services are free and easy to use.
● You can send a message in real time to a person anywhere across the globe.
● Emails are personal and are secured with passwords.
3. Podcasting is a way to create and distribute the audio content. This content can include discussions, interviews, storytelling, music, and more.
4. Following are the netiquette rule one should follow while online:
● Treat others on the internet the way you want to be treated. Do not say or write mean or hurtful things.
● Write in a way that is easy to understand, and avoid using all capital letters (LIKE THIS) or unnecessary punctuation (!!!! Or *!?*#), which can seem like shouting or being rude.
5. Examples of Modes of Online Payments:
Credit Card: Customers can make online payments using their credit cards. The customers need to enter card details like their card number, expiration date, and CVV code for transactions.
Debit Card: Debit cards are another popular option for making online payments. These cards allow users to pay online by entering debit card information, and the transaction amount is deducted directly from their bank account.
F. Apply Your Learning.
1. Nishi can search for information online using the internet.
2. You can find it on the internet by browsing a web browser.
3. No, she should not share her personal information. The potential threats she can be exposed to include: financial fraud, identity theft.
4. Blogs
5. ● Write in a way that is easy to understand, and avoid using all capital letters (LIKE THIS) or unnecessary punctuation (!!!! Or *!?*#), which can seem like shouting or being rude.
● Do not be mean or make fun of others online. Cyberbullying hurts people, just like physical bullying.
● Emojis can help show emotions, but do not use too many. It can be confusing.
● Sometimes, people on the internet may not respond right away. Be patient, and give them time.
Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. grid 2. rows, columns 3. vertical 4. adjacent 5. center
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. b. Click on the Insert menu.
2. c. Dividing a cell into smaller parts.
3. c. To make the table visually appealing and stand out.
4. a. Merging Cells
5. c. By adjusting the row height value in the Table properties pane.
C. Who Am I?
1. Format 2. Column 3. Column width 4. Border 5. Cell Alignment
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. F 2. F 3. T 4. F 5. T
E. Answer the Following.
1. The intersection of a row and a column is called a cell.
2. A row is a horizontal arrangement of cells or boxes that runs from left to right. On the other hand, a column is a vertical arrangement of cells or boxes that run from top to bottom.
3. Two methods to open the Table properties pane are: Method 1:
a. Right-click on any cell of your table.
b. Select the Table properties option. The Table properties pane will appear. Method 2: Select the Format menu Table Table properties option from the menu bar.
4. The Border dash option is used to change the type of border of a table.
5. The three types of alignments available in Google Docs are: Left, Right, and Center.
F. Apply Your Learning.
1. Do it yourself.
2. Do it yourself.
3. Do it yourself.

4. Do it yourself.
5. Merging cells.
Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. Recipients 2. Main document 3. Data source 4. personalise 5. view
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. b. Sending many personalised letters at once. 2. b. Details which will be merged with the letters.
3. b. Information inserted from the data source. 4. d. All of these.
5. c. By checking the document which is created after merging.
C. Who Am I?
1. Mail Merge 2. Main Document 3. Data source 4. Insert Merge Field 5. Print Icon
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. T 2. F 3. T 4. T 5. F
E. Answer the Following.
1. i. Mail merge is important because it can save time and effort by producing mass mailings.
ii. Users can select many people at once and send them a letter easily.
iii. Users don’t have to type each recipient’s name separately in each letter.
iv. Users only need to proofread the main document.
v. Mail merge is economical.
2. A data source is a list of recipients to whom you want to send the invite. The datasource contains the details of the recipients like name, address, phone number etc. that will be used in mail merge.
3. The first file is the Main Document. The main document contains the text that is to be sent to all the recipients.
4. When you use Mail Merge, it takes information from the Google Sheets and inserts it into the empty spaces in the letter, one by one, until all the letters are ready to be sent.
5. A merge field is where you want to insert information from a spreadsheet document or data source into a main document.
F. Apply Your Learning.
1. Main Document
2. Data Source
3. The merge fields would be the personalised details like names, addresses, and any other individual information.
4. Data Source
5. Yes, it is possible for Pihu to send these letters as an email. She can use the mail merge feature in an email to personalise and send emails to her friends.
Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. View, Zoom menu 2. Dictionary 3. Play 4. Insert 5. Slide Sorter
B. Write T for True and F for False.
1. F 2. F 3. F 4. T 5. F
C. Explain the Functions of the Icons.
1. The comments facilitate collaboration among multiple authors or reviewers working on the same presentation.
2. The Shapes icon is used to select a shape that you want to use as an action button.
3. The Slide zoom feature in presentations makes a small part of your slides look enlarged on the screen.
4. The Grid View icon represents the Slide Sorter view.
D. Answer the Following.
1. Using the “Dictionary” feature in presentations can help you learn more about words or phrases used in your presentation. This allows you to quickly access definitions, explanations, and other relevant information about a word or phrase within your presentation.
2. Action buttons in a presentation are used to make your slides more interactive. You can set action buttons to open the external content, such as a website, another PowerPoint presentation, a document, a spreadsheet, and much more.
3. You can choose one of the following sources to insert a video into your presentation: YouTube: Look for a video on the YouTube by typing the keywords in the search box. Google Drive: You can also insert an uploaded video from your Google Drive.
URL: You can paste the URL of a specific YouTube video or the link of an uploaded video from the Google Drive in the search bar.
4. Animations are special visual effects that you add to a text and different objects on a slide. On the other hand, the way one slide follows the other on the screen in a presentation is called a transition.
5. Importing data into a presentation is the process of bringing external content or data into your own presentation. Importing slides helps you to add slides from another presentation to your current presentation. You can also import data from the Google Sheets into your Google Slides presentation.
E. Apply Your Learning.
1. Mahima can use the Ink Annotation feature of the Google Slides.
2. To zoom in on a presentation slide, you can use the shortcut key Ctrl + =.
3. She can use the Dictionary feature to find the meaning of the word.
4. To reply to a comment, click on it and type your response in the comment box. Click on the Reply button.
Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. Sprite 2. Backdrops library 3. Scratch 4. Stop sign 5. Sprites pane
B. Who Am I?
1. Coding 2. Blocks palette 3. Event category 4. Scratch 5. Coding area
C. Explain the Function of the Icon.
1. when (green flag) clicked – It is an Event category block. It helps the script run when the green flag is clicked.
2. Choose a Backdrop Button – The Choose a Backdrop button helps you add backgrounds to your projects.
3. Costumes – This tab allows you to customise and edit the costumes of your sprites or backdrops.
4. create clone of (myself) – This block allows you to create a clone (copy) of the sprite on the stage.
5. next costume – This block allows you to change the next costume (pose) of the sprite.
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. T 2. F 3. T 4. T 5. F
E. Answer the Following.
1. Scratch 3.0 is an application program that lets you create your games, stories, and animations.
2. The Sprites Pane contains details about sprites, including name, size, and location.
3. To add a sprite to a project, the Choose a Sprite option is used.
4. The coding area is the area where you assemble coding blocks to create scripts and make your sprites perform actions.

5. Steps to duplicate a sprite in Scratch are as follows:
● In the Sprites pane, click the sprite you want to duplicate.
● Right-click the sprite, which opens a menu.
● Select the duplicate option to create a copy of the selected sprite.
● The duplicated sprite will appear with the same name as the sprite along with the suffixes 2, 3, or so on.
F. Apply Your Learning.
1. Do it yourself.
2. Follow the given steps to upload the school’s playground as a backdrop:
● Click on the Choose a Backdrop button in the bottom right corner of the interface.
● Click on the Upload Backdrop option from the list.
● The Open dialog box appears.
● Locate the picture that you want to use as a backdrop.
● Click on the Open button.
● The selected picture will be applied to the background of your project.
3. Steps to duplicate a sprite in Scratch are as follows:
● In the Sprites pane, click the sprite you want to duplicate.
● Right-click the sprite, which opens a menu.
● Select the duplicate option to create a copy of the selected sprite.
● The duplicated sprite will appear with the same name as the sprite along with the suffixes 2, 3, or so on.
4. Tanu can use the created clone of (myself) block to add the same sprite five times.
5. To change the background while your project is running, you can use special code blocks to do it.
● Drag the when clicked block from the Events category.
● Drag the next backdrop from the Looks category and snap it below the when clicked block.
Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. Decisions 2. Sensing 3. Pause 4. Condition 5. User’s response
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. c. Control 2. a. touching colour? 3. c. It is used to make decisions based on a condition.
4. b. wait until 5. b. Use the touching edge block.
C. Who Am I?
1. ask and wait and answer block 2. if-then block 3. wait block
4. touching colour? Block 5. Control block category
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. T 2. F 3. F 4. T 5. T
E. Answer the Following.
1. The blocks from the Control category are also called conditional blocks. They allow a program to perform a test based on a given condition and then take actions based on the result of that test.
2. The Sensing blocks are used to sense conditions in the environment, such as the background colour or the sprite touching status. For example, you can use the “touching colour?” block to check if a sprite is touching a specific colour on the stage. Two commonly used sensing blocks are “touching colour?” and “ask and wait” blocks.
3. Difference between the if and if-else blocks:
If block
This block is used to check the given condition. If the condition is true, the blocks inside the if-then block are executed; if it is false, the blocks are not executed.
This block is an extension of the if-then block. If the given condition is true, then the blocks inside the if then section are executed. If the condition is false, then the blocks inside the else part are executed.
4. Sensing category blocks are used to gather information about the environment and user input hence making the games quite interactive and interesting for the users.
5. The ask and wait block displays a message or a question for the users and waits for their input.
F. Apply Your Learning.
1. Script for sprite to move left and right:
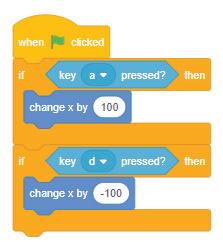
In this script, the “key pressed” block is used, which is a Sensing block.
2. For this project, you can add two sprites the cat and the mouse on the stage as shown below:

Add the following scripts for both the sprites:
Script for cat sprite:

Script for mouse sprite:
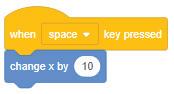

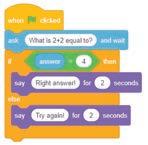
4. Script for changing the costume of a sprite when the mouse pointer is hovering on it:
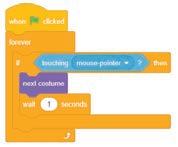
In this script, the forever block, if block, and wait block from the Control category and touching mousepointer block from Sensing category are used.
5. For traffic lights simulation, you need to paint the following sprites with different costumes:





The script for the project is as follows:


You can add a backdrop and more sprites to make your project interactive.
Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. Angular brackets 2. element 3. Microsoft Edge 4. <body> 5. Text paragraph
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. b. A markup language
2. d. All of these
3. b. To create a division
4. c. Additional information that can be added to a tag
5. a. A combination of a start tag, some content, and an end tag
C. Who Am I?
1. Web browser 2. <HR> tag 3. Attribute 4. HTML 5. <I>
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. T 2. T 3. F 4. F 5. T
E. Answer the Following.
1. HTML stands for HyperText Markup Language. It helps you to display colourful text, images, and attractive backgrounds to your web page. Some features of HTML are:
● HTML is a simple and easy language to learn.
● HTML can create web pages that run on any device (computers, mobiles, and tablets).
● HTML helps you to add videos, images, and audio files to web pages. This feature enhances the experience for website visitors.
● Using HTML, you can link various web pages with each other. It allows users to click text or images and navigate various websites.
2. A web browser is a software application that processes HTML and other web technologies to display the web pages to the users. For example, Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Edge, etc.
3. Structural Elements of HTML are:
<html>: The <html> tag is the root element of an HTML document. This tag contains all other HTML elements and is the starting point for creating an HTML page. You can see this tag at the beginning of an HTML document.
<head>: The <head> tag contains metadata (data about data) and other information about the HTML document.
<title>: The <title> tag is written inside the <head> tag and is used to define the title of the HTML document, which appears in the browser title bar or tab.
<body>: The <body> tag contains the main content of the web page, including text, images, links, and other elements visible to the user.
4. Container Tags: These tags consist of an opening tag as well as a closing tag. This start tag and end tag pair are known as the ON and OFF tags and are used to open and close the document.
Syntax: <tag_name>.......</tag_name>
Example: <B> tag is a container tag in HTML.
Empty Tags: An empty tag is a tag without a closing tag.
Syntax: <tag_name>
Example: <img> tag is an empty tag in HTML.
5. The basic structure of an HTML document is:
<!Doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My Web Page</title> </head> <body> </body> </html>
F. Apply Your Learning.
1. Shreya can use the <I> tag to make the text italics.
2. Some of the features of HTML are:
● HTML is a simple and easy language to learn.
● HTML can create web pages that run on any device (computers, mobiles, and tablets).
● HTML helps add videos, images, and audio files to web pages. This feature enhances the experience for the website visitors.
● Using HTML, you can link various web pages with each other. It allows users to click text or images and navigate various websites.
3. Anmol can use the <HR> tag as it is used to create divisions in an HTML web page.
4. Tanya can use the <BR> tag as it is used to create a line break in an HTML web page.
5. First, we will create a web page using the basic structure of HTML such as: <!Doctype html> <html> <head> <title>My Web Page</title> </head> <body>
</body> </html>
Then, we can make use of various text formatting tags, such as <B>, <I>, <U>, <BR>, <HR>, etc.
Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. .html 2. Case-sensitive 3. <HTML> 4. <strong> 5. subscript
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. c. HyperText Markup Language
2. c and d. HTML, Head, Title, Body
3. c. <sup>
4. c. <section>
5. c. <em>
C. Who Am I?
1. Web page 2. <!DOCTYPE html> 3. Body 4. <!DOCTYPE html> tag 5. <title>
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. T 2. F 3. T 4. T 5. F

E. Answer the Following.
1. An HTML document is divided into two parts:
Head part: The title and metadata of a web document are contained in the head part. Body part: The content you want to display on a web page is contained in the body part.
2. The basic structure of an HTML document consists of 5 elements.
<!DOCTYPE html>: This tag informs the browser about the document type.
<html>Tag: The <html> tag informs the browser that this is an HTML document. <head>Tag: It contains information about the HTML document.
<title>Tag: The <title> tag provides a suitable title for the entire HTML document. <body>Tag: The primary content of an HTML document that displays on the browser is specified by the <body> tag.
3. The <title> tag provides a suitable title for the entire HTML document.
4. The <em> tag is used to emphasise text and is typically displayed in italics. Whereas, the <strong> tag is used to represent strongly emphasised text and is typically displayed in bold.
5. The <sub> tag is used to represent text as a subscript. A subscript is the text that is below the baseline of the surrounding text. For example, 2 in H2O is a subscript. Whereas, the <sup> tag is used to represent text as a superscript. A superscript is the text that is above the baseline of the surrounding text. For example, 2 in E = mc2 is a superscript.
F. Apply Your Learning.
1. An HTML page containing your name, father’s name, mother’s name, school name, postal address, and contact number.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang=”en”> <head> <title>My Information</title> </head> <body> <section>
<h2>Name:</h2> <p>Your Name</p> </section> <section>
<h2>Father’s Name:</h2> <p>Your Father’s Name</p> </section> <section>
<h2>Mother’s Name:</h2> <p>Your Mother’s Name</p> </section> <section>
<h2>School Name:</h2> <p>Your School Name</p> </section> <section>
<h2>Postal Address:</h2> <p>Your Postal Address</p> </section> <section>
<p>Where r is the radius of the circle.</p>
</section>
<section>
<h2>Area of a Square:</h2>
<p>The area of a square is given by the formula:</p>
<p>Area = side<sup>2</sup></p>
<p>Where side is the length of a side of the square.</p> </section> <section>
<h2>Area of a Rectangle:</h2>
<p>The area of a rectangle is given by the formula:</p>
<p>Area = length × width</p>
<p>Where length is the length of the rectangle and width is the width of the rectangle. </p> </section>
<section>
<h2>Area of a Triangle:</h2>
<p>The area of a triangle is given by the formula:</p>
<p>Area = (base × height) / 2</p>
<p>Where base is the base of the triangle and height is the height of the triangle.</p> </section> </body> </html>
4. An HTML page to display information about the eastern states of India, often known as ‘the Seven Sisters’. <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang=”en”> <head>
<title>Eastern States of India</title> </head> <body>
<h1>Eastern States of India</h1> <section>
<h2>Arunachal Pradesh</h2>
<p>Arunachal Pradesh is known for its picturesque mountains, rich cultural heritage, and diverse tribal communities.</p> </section> <section>
<h2>Assam</h2>
<p>Assam is famous for its tea gardens, wildlife sanctuaries, and the mighty Brahmaputra River.</p> </section> <section>
<h2>Manipur</h2>
<p>Manipur is known for its vibrant culture, traditional dance forms, and scenic landscapes.</p> </section> <section>
<h2>Meghalaya</h2>
<p>Meghalaya is renowned for its stunning waterfalls, living root bridges, and lush greenery.</p>
</section>
<section>
<h2>Mizoram</h2>
<p>Mizoram is known for its peaceful atmosphere, rich tribal culture, and beautiful landscapes.</p> </section>
<section>
<h2>Nagaland</h2>
<p>Nagaland is famous for its vibrant festivals, unique tribal traditions, and beautiful handicrafts.</p> </section>
<section>
<h2>Tripura</h2>
<p>Tripura is known for its rich history, ancient temples, and diverse cultural heritage.</p> </section> </body> </html>
5. A web page showing information about your favourite sports persons.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang=”en”> <head>
<title>Favourite Sports Persons</title> </head> <body>
<h1>Favourite Sports Persons</h1>
<section>
<h2>Basketball</h2>
<p>LeBron James - LeBron Raymone James Sr. is an American professional basketball player for the Los Angeles Lakers of the National Basketball Association (NBA).</p> </section>
<section>
<h2>Football</h2>
<p>Lionel Messi - Lionel Andrés Messi is an Argentine professional footballer who plays as a forward for Paris Saint-Germain and the Argentina national team.</p> </section>
<section>
<h2>Tennis</h2>
<p>Roger Federer - Roger Federer is a Swiss professional tennis player. He has been ranked world No. 1 in the ATP rankings a total of 310 weeks – including a record 237 consecutive weeks – the most in the Open Era.</p> </section> </body> </html>

Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. structure 2. style 3. .css 4. font-weight 5. #
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. a. {} 2. b. Outline 3. a. six 4. b. Red 5. b. font-size
C. Who Am I?
1. Colon(:) 2. Inline CSS method 3. color property 4. line-height 5. External CSS method
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. T 2. T 3. F 4. T 5. F
E. Answer the Following.
1. Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) is a language used to incorporate styles like background colour, font colour, a font size in web pages. CSS is mainly used to enhance the look of web pages by applying various formatting styles to the elements or the entire web page.
2. CSS consists of style rules. Style rules are made up of selectors, properties, and values. All style rules are enclosed within curly brackets {}.
The syntax for using CSS is as follows: selector{property: value;} where,
● a selector is any HTML element to which you want to apply a style, like <p>. Always remember that an HTML element is written without angle brackets while creating CSS style rules.
● a property is like an HTML attribute, like colour, which adds additional features to an element.
● a value is similar to an attribute’s value assigned to a CSS property.
3. <style> h1 { color: #0066cc; } </style>
4. The syntax of the border property is: div { border: border-width border-style border-color; }
5. Three methods of using CSS style sheets: a. Inline CSS b. Internal CSS c. External CSS
F. Apply Your Learning.
1. Web page to display the text within the <div> tag: <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang=”en”> <head> <title>Red Div</title> <style> body { font-family: Arial, sans-serif; margin: 0; padding: 0;
} .red-div { background-color: red; color: white; padding: 20px; } </style> </head> <body>
<div class=”red-div”>
This text is inside a div with a red background and Arial font family. </div> </body> </html>
2. Sangeeta can use the External CSS method to apply the styles to the multiple web pages.
3. Romi can use the “text-align” property in CSS to align text to the right edge on a web page.
4. Create a .css file and specify the properties of the <font> element in it. First, create an external style sheet and type the following text in it: font { font-family: Arial, sans-serif; font-size: 16px; color: #333; }
Now, save this file with the name “styles.css” and then refer to this file in another document as shown below:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang=”en”>
<head>
<title>Styling the Font Element</title>
<link rel=”stylesheet” href=”styles.css”> </head>
<body>
<font>This text will be styled according to the properties specified in the CSS file.</font> </body> </html>
5. Sharvi can use the “border” property in CSS to apply a border to an HTML element.
A. Fill in the Blanks. 1. Datasource 2. Machine 3. Pictures and Photos 4. UPI
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. b. Cell Padding
2. b. Ransomware
3. d. Audio file
4. d. Alt + Tab

C. Write T for True and F for False.
1. T 2. T 3. T 4. F
D. Answer the Following Questions.
1. Following are the disadvantages of Fourth-generation Languages:
The programs written in fourth-generation languages occupy more space in memory.
They have weak hardware control.
They are not very flexible.
2. Action buttons are used to make your slides more interactive. You can set action buttons to open external content, such as a website, another PowerPoint presentation, a document, a spreadsheet, and much more.
3. When you surf the internet, your history is stored on each website that you visit. This history leaves an online data trail called a digital footprint.
4. E-commerce is the buying or selling of goods and services online.
E. Apply Your Learning.
1. Sidharth’s situation is an example of phishing.
2. Ayan can use cut and paste commands to move them efficiently.
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. HyperText Markup Language 2. Scripts Area 3. four 4. External CSS
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. a. Control blocks
2. a. font-family
3. a.

4. b. Bold
C. Write T for True and F for False.
1. T 2. T 3. F 4. T
D. Answer the Following Questions.
1. <!DOCTYPE html>: Tells the browser that this is an HTML5 document. <html>: The root element that wraps all the content of the web page. <head>: Contains meta-information about the page like the title, styles, and scripts. <title>: Sets the title of the page that appears on the browser tab. <body>: Contains the visible content of the web page like text, images, links, etc.
2. Container tag consist of an opening tag as well as a closing tag. This start tag and end tag pair are known as the ON and OFF tags and are used to open and close the document. Whereas, n empty tag is a tag without a closing tag.
3. The Sprites Pane is below the stage. It shows all the details of sprites, like their name, location, and size. You can use it to add, upload, edit, or delete sprites.
4. Sensing blocks are used to detect when two characters touch each other.
E. Apply Your Learning.
1. Aryan should use the <title> tag inside the <head> section of his HTML document to make the webpage title appear in the browser tab.
2. Vinayak should use a block from the Sensing category in Scratch.
Uolo has introduced a comprehensive program, Hexa, for Grades 1 to 8, aimed at empowering young minds with essential knowledge and skills for the digital age.
To support the effective implementation of Hexa in classrooms, this Teacher Manual has been thoughtfully designed. It provides structured lesson plans for each chapter, guiding teachers through both classroom instruction and computer lab activities. Every lesson follows Uolo’s research-based WEBS framework, which simplifies teaching methodologies and enhances lesson delivery, making learning more engaging and impactful for students.
• Sharp Lesson Planning: Each lesson plan focuses on specific sub-learning outcomes within a chapter and are designed for delivery within the stipulated class or lab time.
• Real-life and Application-based Questions: Additional questions that link Computer Science to real-life contexts and assist teachers to develop learners' conceptual understanding and application skills.
• Support and Detailed Solutions: In-depth solutions for in-class and post-class activities to reinforce learning.
Uolo partners with K-12 schools to bring technology-based learning programs. We believe pedagogy and technology must come together to deliver scalable learning experiences that generate measurable outcomes. Uolo is trusted by over 15,000+ schools across India, South East Asia, and the Middle East.
ISBN 978-93-49697-29-4
