4 minute read
6.3CASESTUDY1
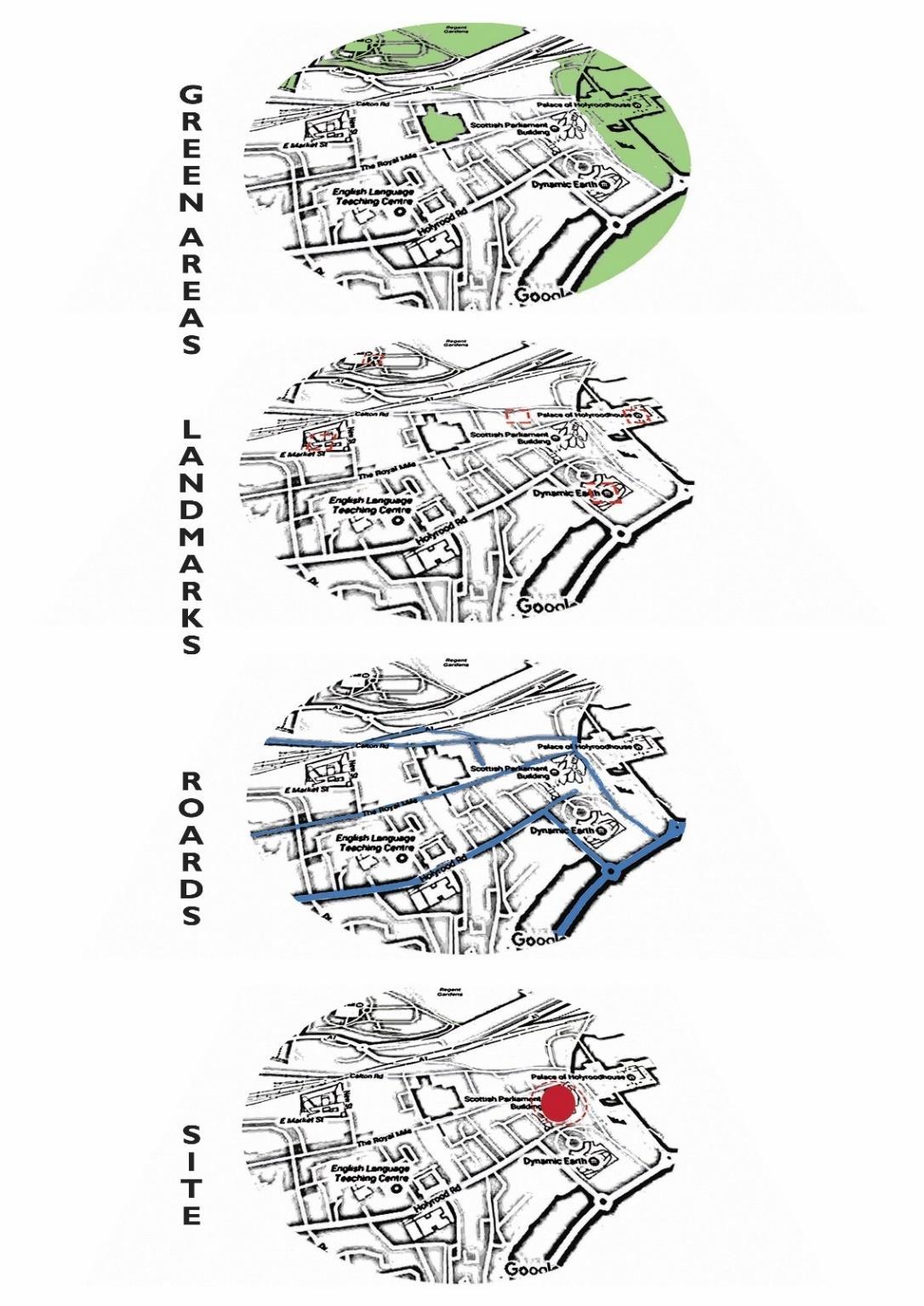
Scottish Parliament Building
Architects: Enrique Mirales
Advertisement
Location: Old town, Edinburgh, Scotland
Area: 322917.3125 sft
Project Year: 2004
In July1998, the architects EMBT of Barcelona and Scottish partners RMJM Scotland, won a competition to design the new building for the Scottish Parliament at Holyrood. The team presented a series of charts showing where the design of Parliament: as a leaf and branch, with a strong symbolic meaning. This drew the attention of the jury and led to winning the proposal
Before the parliament house the site belong to brewery company they had their factory there then the building was not in use for many years and because of its historical context it was given for the parliament
6.3.1 History of Edinburgh old town
The Old Town of Edinburgh stretches from the gates of Edinburgh Castle, down the length of the Royal Mile, and outwards from that cobbled ‘spine’. The narrow ‘closes’ originating from Royal Mile give this part of Edinburgh it’s character. In the 16th century one of the high-rise buildings, that the area was then dominated by, collapsed. At present there is a plaque in its place that commemorates the victims. Edinburgh is not only famous for the castle, but also for Edinburgh’s ‘Underground City’. “Mary Kings Close’is the most famous of these excavated areas that attracts visitors.
The building is located on land owned by a brewery of 1.6 hectares, where he was the QueensberryHouse (a historic mansion that is used as a militaryhospital) and is an area that is surrounded by Dutchman style buildings.
6.3.4.1 CONCEPT
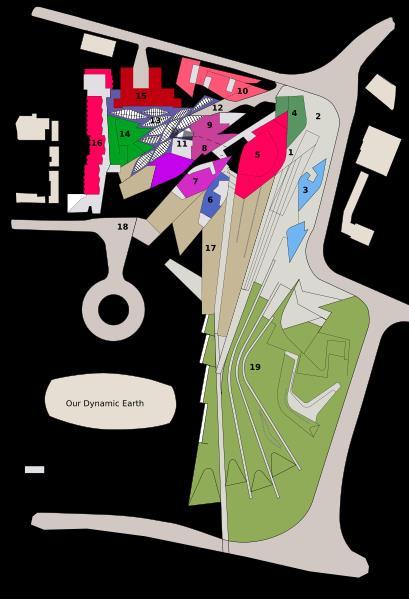
The design has a very strong symbolic basis: one thinks a building that reflects the land on which it arises.
The study based its proposal on three points: the Scottish landscape, its people and its culture. That’s whythe building is situated like a small town, with streets and buildings of varying scale, and allowed to go through different feelings while it runs.spacesthe buildings are arranged in two groups, container buildings, which form an “L” and contains a group of three buildings: the mansion Queensberry, the Royal Mile and Cannongate tower and the south wes tby the contents of buildings “ L” a series of leafshaped towers that house services for parliamentarians. Before them lies the great hall of parliament, crowned by a group of naturally lit skylights and give identity to space.
In the east side are the most important buildings: the tower of the press and the House debates, and before they have a pergola that connects the building with the outside. Towards the south will feature a series of gardens worked by Miralles.
6.3.5 STRUCTURE
Each space has a different structure. The entrance building endings are characterized bytheirhighqualityconcreteandhas threedomes dottedwith crosses (takingtheimage of the Scottish flag). The columns invade apparently arbitrarily.
In the debating chamber, the roof consists of three large wooden trusses with 120 knots, and fabricated stainless steel connectors inAberdeen especially for the building.
The elements comprising the structure are laminated European oak compression elements and stainless steel for the elements in tension. The assembly buildings have been designed in prestressed concrete to get lights for more than 14 m.
6.3.6 MATERIAL
It is used largely for banana timber Scottish European oak and banana, as well as concrete and stone.Although each sector has materials that characterize them:
In the towers of the assembly, using reinforced concrete frames, covered Kemnay granite, from Aberdeenshire. There are decorative panels made of oak and black and gray granite. The roofs are covered with stainless steel.
On the west side, the representative office, there are windows of stainless steel. Some of the windows have exterior design with a lattice of oak. In the debating chamber, all based coatings are made from European oak and banana. The western side of the camera has 1000 m2 of laminated glass panels. Each panel has a sheet of banana strips placed in horizontal layers between two glass and shaping the forms that mimic human forms. The furniture was held in banana and oak.
6.3.7Sustainability
The Parliament’s heating and hot water systems are all highly efficient and air conditioning is limited to the IT server rooms, all of which minimize emissions of carbon dioxide. In the majority of areas, instead of air conditioning, a central system controls a large number of windows which can open at night during warm weather to allow the building to cool. This system is supplemented with air handling units.("Scottish Parliament - Data, Photos & Plans - Wikiarquitectura")
6.3.9Conclusions
1) The main parliament block of the building is attached with the old building but it doesn’t dominate the old building as its elevation height is lower than the old buildings elevation so it respects the historic building

2) Colors of materials used in the outer façade of the building matches with the other buildings surrounding it
3) Use of materials is same as buildings around
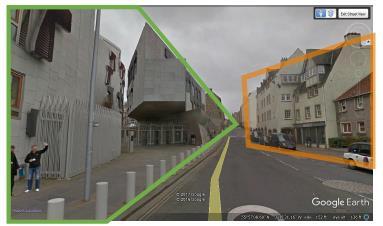
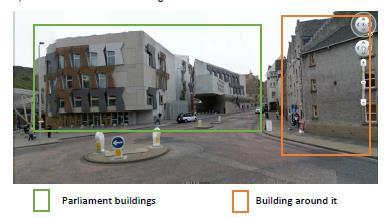
4) The residential building is very close to the building around now known as THE PARK BUILDING which has residential plus other functions such as dental practices etc. so the parliament buildings section is not much ornamented, elevated or strange in manner but it is more simpler towards this side the only element is the use of window shape is same as that of the rest of the building
6.3.9.1RESIDENTIAL BUILDING

5) The elevation of the building is with varying heights to match the terrain of the area which helps in creating feel` of the place
6.4 CASE STUDY 2
Theacropolis Museum


Architects: Bernard TschumiArchitects
Location:Acropolis,Athens, Greece
Area: 21000.0 sq.ft
Project Year: 2009
Exhibition space: 90,000 square feet
The Museum is conceived as a base, a middle zone and a top, taking its form the archeological excavation below and from the orientation of the top floor toward the Parthenon.The Museum stands less than 1,000 feet southeast of the Parthenon.The topfloor Parthenon Gallery offers a 360-degree panoramic view of the Acropolis and modern AthensAt street level the building is a 21st century architectural wonder. Its glass reflects a 1940s Romantic Byzantine building, and it is designed to maximize the light pouring in through the giant windows.("New Acropolis Museum / Bernard Tschumi Architects")
6.4.1LOCATION
It sits on the site of ancient Makrygianni and the ruins of Roman, and early Byzantine, Athens. The site is still being excavated today and large columns hold the new museum above the ruins where archeologists are still digging and revealing
SOCRATES PRISON
PANTHEON
HADRIANSARCH
OLYMPIOS DIOS
THEATRE OF DINOSES CISTER
SOLDIERS SAILORS MONUMENT TEMPLE OF HEPHAESTUS
Table 2.2









