LettertotheEditor(Casereport)
doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kez012
Reversibleeruptionofneurofibromatosisassociatedwithtofacitinibtherapyforrheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatologykeymessage
. Ongoingclinicalvigilanceisessentialtoidentifyunrecognizedcomplicationsofnewbiologictherapies inRApatients.
SIR,A45-year-oldfemalepresentedwithwidespread neurofibromasaftercommencingtofacitinibforRA.
Shewasdiagnosedwithneurofibromatosistype1aged 5yearsduetomultiplecutaneouscafe ´ aulaitspots,associatedwithaxillaryandinguinalfreckling.Therewereno neurofibromasatdiagnosis,butshedevelopedintermittentforearmandbackmassesthatfluctuatedinsize throughoutherteenagelife,beforeresolving.Themutationwaspresumedtohavearisen denovo duetoanegativefamilyhistory.
HerseropositiveRAwasdiagnosedinherearly twenties,initiallywell-controlledformanyyearsby theDMARDsulfasalazine.MTXandHCQwerelater addedtocontrolongoingactivedisease,beforeescalationtobiologicDMARDtherapywasrequired. Tofacitinib5mgtwicedailywascommencedinearly 2017withmarkedsymptomaticandbiochemicalimprovement.Heronlyotherpastmedicalhistorywas well-controlledasthma.
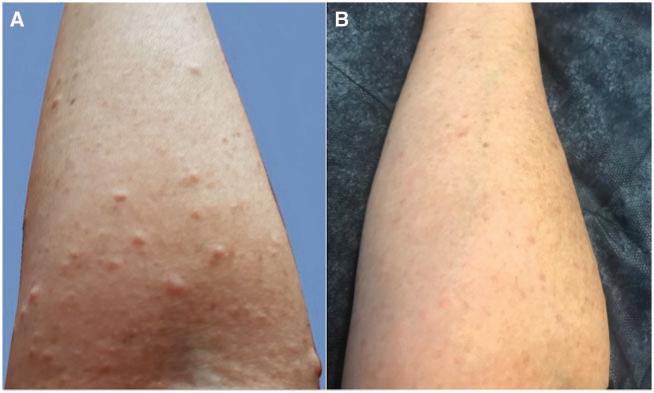
Approximately6weeksafterstartingtofacitinib,thepatientpresentedwithawidespreaderuptionofcutaneous neurofibromasonherarms,trunkandface(Fig.1).Aclinicalneurogeneticistconfirmedthepresenceofneurofibromas.Giventheapparenttemporalrelationshipto biologicaltherapy,tofacitinibwasceased,andthecutaneousneurofibromassubsequentlyregressedoverthe followingmonths.
Thiscaseisthefirstreportedintheliteratureofageneralizederuptionofneurofibromatosisfollowingtreatment withabiologicortargetedsyntheticDMARDandmore specificallyajanuskinase(JAK)inhibitor.Thereisone previouslypublishedcaseofa78-year-oldwomanwith RAwhodevelopedsegmentaleruptiveneurofibromatosis inthesettingofinfliximab[1].
Neurofibromatosistype1isanautosomaldominant geneticdisordercausedbyanalteredgeneonchromosome17. NF1 isatumoursuppressorgenethatcodes fortheproteinneurofibromin,expressedinmanycells includingprimarilyneurons,glialandSchwanncells [2]. NF1 alsoaffectsearlymelanocytedevelopment. Neurofibrominisanegativeregulatorofthe RAS oncogenepathway,therebycontrollingcellproliferation[3]. Thelinkbetweenneurofibromatosistype1andthe RAS pathwayhasbeenwellestablished[4].Individualswith neurofibromatosishavereducedneurofibromin,making thempronetouncontrolled RAS activationandthedevelopmentofbenignandmalignanttumoursofthecentral andperipheralnervoussystems,aswellasmalignantdiseaseelsewhere[5].
FIG.1 Rightforearm(A)showingthecutaneousneurofibromatosiseruption;(B)regressionafterwithdrawaloftofacitinib therapy
! TheAuthor(s)2019.PublishedbyOxfordUniversityPressonbehalfoftheBritishSocietyforRheumatology.Allrightsreserved.Forpermissions,pleaseemail:journals.permissions@oup.com
Tofacitinibisanoralreversiblecompetitiveinhibitorof theJAKfamilyoftyrosinekinases,approvedforthe treatmentofRA.Tofacitinibpreventstheactivationof thesignaltransducersandactivatorsoftranscription andthereforemodulatestheimmuneresponseby decreasingcytokineproductionviatheJAK-signaltransducersandactivatorsoftranscriptionpathway[6]. TofacitinibmoststronglyinhibitsJAK3.Inadditionto theJAK-signaltransducersandactivatorsoftranscriptionaxis,JAKscanalsoaffectothersignallingpathways throughaprocessknownasintracellularcrosstalk[7].
The RAS pathwayhasbeendemonstratedtobeoneof theothermajorsignalsthatcanbeaffected[7].Through crosstalk,tofacitinibcouldpotentiallyaffectthe RAS pathway.
Theexactmechanismleadingtoourpatient’sneurofibromatosiseruptionisunknown.Shehasbeenmanaged onMTXandHCQwithnonewneurofibromasoccurring. DuetoincreasingRAdiseaseactivity,sherequiresuptitrationofimmunosuppressivetherapyagain.Theriskof neurofibromarecurrencewiththeotherbiologicDMARDs beingconsideredisunclear.
Thetemporalrelationshipbetweencommencingtofacitinibandtheeruptioninapatientthathadhadno neurofibromasfortheprevious25yearsmakesaconnectionbetweenthesetwoeventslikely.Inmostscenarios,anyunintentionaleffectofJAKinhibitiononthe RAS pathwaymaybeunrecognizedduetonosignificant clinicalimpact.Neurofibromatosispatientsmaybethe exceptionduetotheirreducedneurofibrominandresultantsusceptibilityto RAS overactivation.Laboratorystudieswouldbeneededtoassessthislinkandany causalityfurther.
Biologicandtargetedsynthetictherapies,includingJAK inhibitors,arehighlyeffectiveforRA,withincreasinguse worldwide.Thisuniquecasehighlightsararecomplicationoftofacitinib,andtheneedforongoingawarenessby rheumatologistsofpotential,unrecognizedimmunerelatedcomplications.
Funding:Nospecificfundingwasreceivedfrom anyfundingbodiesinthepublic,commercialornot-for-
profitsectorstocarryouttheworkdescribedinthis manuscript.
Disclosurestatement:Theauthorshavedeclaredno conflictsofinterest.
AdamRischin 1,*,ThilinieDeSilva1,*and KimLeMarshall1,2
1DepartmentofRheumatology,WesternHealthand 2Western ClinicalSchool,UniversityofMelbourne,Melbourne,Victoria, Australia
Accepted21December2018
*AdamRischinandThilinieDeSilvacontributedequallytothis study.
Correspondenceto:AdamRischin,Departmentof Rheumatology,FootscrayHospital,160GordonStreet, Footscray,Victoria3011,Australia.
E-mail:adamrischin@gmail.com
References
1DragoF,PastorinoC,CecchiF,ParodiA.Segmental eruptiveneurofibromatosisinfliximab-induced.JEurAcad DermatolVenereol2016;30:356 7.
2StockerKM,BaizerL,CostonT,ShermanL,CimentG. Regulatedexpressionofneurofibromininmigratingneural crestcellsofavianembryos.JNeurobiol1995;27:535 52.
3KorfBR,RubensteinAE.Neurofibromatosis:ahandbook forpatients,families,andhealthcareprofessionals,2nd edn.NewYork,NY:Thieme,2005.
4TidymanWE,RauenKA.TheRASopathies:developmental syndromesofRas/MAPKpathwaydysregulation.Curr OpinGenetDev2009;19:230 6.
5BoydKP,KorfBR,TheosA.Neurofibromatosistype1.J AmAcadDermatol2009;61:1 14.
6GhoreschiK,JessonMI,LiX etal.Modulationofinnate andadaptiveimmuneresponsesbytofacitinib(CP-690, 550).JImmunol2011;186:4234 43.
7BousoikE,MontazeriAliabadiH.‘‘Doweknowjack’’ aboutJAK?AcloserlookatJAK/STATsignalinpathway. FrontOncol2018;8:287.
https://academic.oup.com/rheumatology
