CROSSROADS SOLAR GRAZING CENTER
RADAR AND NAVIGATIONAL AID SCREENING STUDY
APRIL 23, 2025
Westslope Consulting, LLC
3940 West Tecumseh Road, Suite 200
Norman, Oklahoma 73072 (405) 310-6058
INTRODUCTION
The Crossroads Solar Grazing Center (Project) consists of a solar array at a maximum height of 20 feet above ground level (AGL) and two substations at a maximum height of 80 feet AGL located within an approximate 800-acre boundary in Morrow County, Ohio 1 This report provides the results of a radar and navigational aid screening study conducted by Westslope Consulting, LLC (Westslope) for the Project using a maximum structure height of 80 feet AGL.
This study includes the following:
• Research into radar sites and navigational aid (NAVAID) sites near the Project.
• An Air Route Surveillance Radar (ARSR) and Airport Surveillance Radar (ASR) line-of-sight analysis.
• A Terminal Doppler Weather Radar (TDWR) screening analysis.
• A Next Generation Weather Radar (NEXRAD) screening analysis for Weather Surveillance Radar1988 Doppler (WSR-88D) sites.
RESEARCH
ARSR and ASR Sites
Primary Surveillance Radar
Westslope’s research identified the following nine ARSR and ASR sites near the Project:
• Akron Airport Surveillance Radar-11 (ASR-11)
• Brecksville Common Air Route Surveillance Radar (CARSR)
• Cleveland Airport Surveillance Radar-9 (ASR-9)
• Columbus ASR-9
• Dayton ASR-9
• London CARSR
• Mansfield Airport Surveillance Radar-8 (ASR-8)
• Toledo ASR-9
• Wilmington ASR-9
1 Crossroads_Expected Site Control (leases) - 10.31.24 (5).kml, Crossroads_Project Substation.kmz, and Crossroads_Utility Substation.kmz
The Department of Defense (DoD) uses these radar sites for air defense at the North American Aerospace Defense Command, and the Department of Homeland Security uses these radar sites for homeland security at the Air and Marine Operations Center. In addition, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) uses these radar sites for air traffic control at multiple facilities, including the Cleveland Terminal Radar Approach Control (TRACON), the Cleveland Air Route Traffic Control Center (ARTCC), the Columbus TRACON, the Indianapolis ARTCC, and the Toledo TRACON
Co-Located Secondary Surveillance Radar
Westslope’s research identified the following secondary surveillance radar systems co-located with the ARSR and ASR systems:
• A Monopulse Secondary Surveillance Radar is co-located with the Akron ASR-11.
• An Air Traffic Control Beacon Interrogator-6 is co-located with the Brecksville CARSR and the London CARSR.
• A Mode S is co-located with the Cleveland ASR-9, the Columbus ASR-9, the Dayton ASR-9, the Toledo ASR-9, and the Wilmington ASR-9.
• An Air Traffic Control Beacon Interrogator-5 is co-located with the Mansfield ASR-8.
TDWR Sites
Westslope’s research identified the following three TDWR sites near the Project:
• Cleveland TDWR
• Columbus TDWR
• Dayton TDWR
The FAA uses these radar sites for air traffic control at multiple facilities, including the Cleveland TRACON and the Columbus TRACON. In addition, the National Weather Service (NWS), part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, uses these radar sites for weather operations at multiple facilities, including the Cleveland Weather Forecast Office (WFO) and the Wilmington, Ohio WFO.
The Cleveland TDWR scans at the lowest elevation angle of 0.2 degrees, the Columbus TDWR scans at the lowest elevation angle of 0.1 degrees, and the Dayton TDWR scans at the lowest elevation angle of 0.3 degrees.
NAVAID Sites
Westslope’s research shows there are no Very High Frequency Omnidirectional Range, Distance Measuring Equipment, or Tactical Air Navigation NAVAID sites near the Project
WSR-88D Sites
Westslope’s research identified the following two WSR-88D sites near the Project:
• Cincinnati WSR-88D
• Cleveland WSR-88D
The NWS uses these radar sites for weather operations at multiple facilities, including the Wilmington, Ohio WFO and the Cleveland WFO. In addition, the DoD may use these radar sites for weather operations.
The NWS, and possibly the DoD, use data from the lowest elevation angle scanned by these radar sites to monitor hazardous weather conditions. The Cincinnati WSR-88D scans at the NWS’s standard lowest elevation angle of 0.5 degrees.
For the Cleveland WSR-88D, the NWS reduced the lowest elevation angle to improve radar coverage. As a result, this radar site scans at the lowest elevation angle of 0.4 degrees.
ANALYSIS
ARSR and ASR Line-of-Sight Analysis
Westslope conducted an ARSR and ASR line-of-sight analysis using the 4/3rd Effective Earth’s Radius Model and United States Geological Survey (USGS) 1/3rd arc-second 3-Dimensional Elevation Program (3DEP) bare-earth data 2 The 4/3rd Effective Earth’s Radius Model accounts for the refraction of radio waves as these waves propagate through the lowest layer of the atmosphere under standard atmospheric conditions. Westslope’s analysis shows whether structures in the Project at a maximum height of 80 feet AGL will be within line-of-sight of and will interfere with ARSR or ASR sites.
Westslope conducted the line-of-sight analysis for the following nine ARSR and ASR sites:
• Akron ASR-11
• Brecksville CARSR
• Cleveland ASR-9
• Columbus ASR-9
• Dayton ASR-9
• London CARSR
• Mansfield ASR-8
• Toledo ASR-9
• Wilmington ASR-9
The Project is beyond the instrumented range of the Akron ASR-11, the Cleveland ASR-9, the Dayton ASR-9, the Toledo ASR-9, and the Wilmington ASR-9. As such, Westslope did not consider any additional analysis necessary for these radar sites.
Brecksville CARSR
The line-of-sight analysis results show that structures located in the Project will not be within line-ofsight of and will not interfere with the Brecksville CARSR at a maximum height of 80 feet AGL. As a result, Westslope does not expect any radar effects at or below this structure height.
Columbus ASR-9
The line-of-sight analysis results show that structures located in the Project will not be within line-ofsight of and will not interfere with the Columbus ASR-9 at a maximum height of 80 feet AGL. See Figure 1. As a result, Westslope does not expect any radar effects at or below this structure height.
2 The USGS 1/3rd arc-second 3DEP bare-earth data has a vertical accuracy of approximately 2.7 feet root mean square error. [1]
London CARSR
The line-of-sight analysis results show that structures located in the Project will not be within line-ofsight of and will not interfere with the London CARSR at a maximum height of 80 feet AGL. As a result, Westslope does not expect any radar effects at or below this structure height.
Mansfield ASR-8
The line-of-sight analysis results show that structures located in the Project will not be within line-ofsight of and will not interfere with the Mansfield ASR-8 at a maximum height of 80 feet AGL. As a result, Westslope does not expect any radar effects at or below this structure height.
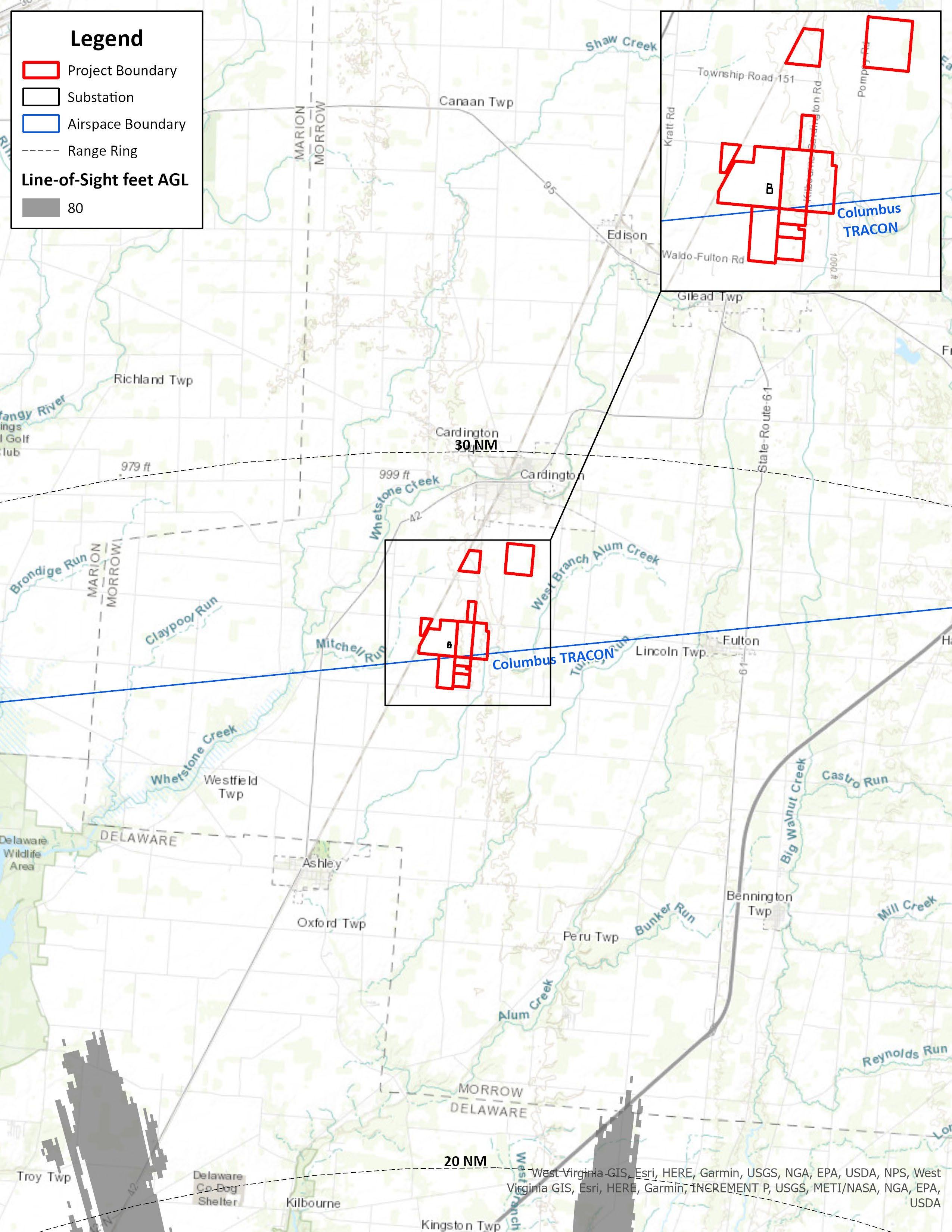

1 Line-of-Sight Analysis Results for the Columbus ASR-9
TDWR Screening Analysis
Westslope conducted a TDWR screening analysis using an antenna beamwidth of 0.55 degrees, the 4/3rd Effective Earth’s Radius Model, and USGS 1/3rd arc-second 3DEP bare-earth data. Westslope’s analysis shows whether structures in the Project at a maximum height of 80 feet AGL will be within line-of-sight of a TDWR site and penetrate the lowest elevation angle scanned by the radar site.
Westslope conducted the TDWR screening analysis for the following three radar sites:
• Cleveland TDWR
• Columbus TDWR
• Dayton TDWR
These radar sites scan at the lowest elevation angles of 0.2 degrees, 0.1 degrees, and 0.3 degrees, respectively.
Westslope’s TDWR screening analysis results show that, at a maximum height of 80 feet AGL, structures located in the Project will not be within line-of-sight at the lowest elevation angle scanned by the Cleveland TDWR, the Columbus TDWR, or the Dayton TDWR. As a result, Westslope does not expect any impacts to Cleveland TDWR operations, to Columbus TDWR operations, or to Dayton TDWR operations at or below this structure height.
NEXRAD Screening Analysis
Westslope conducted a NEXRAD screening analysis using an antenna beamwidth of 1.31 degrees, a 1.21 effective earth’s radius model, and USGS 1/3rd arc-second 3DEP bare-earth data. Westslope’s analysis shows whether structures in the Project at a maximum height of 80 feet AGL will be within line-of-sight of a WSR-88D site and penetrate the lowest elevation angle scanned by the radar site.
Westslope conducted the NEXRAD screening analysis for the following two WSR-88D sites:
• Cincinnati WSR-88D
• Cleveland WSR-88D
The Cincinnati WSR-88D scans at the NWS’s standard lowest elevation angle of 0.5 degrees. For the Cleveland WSR-88D, the NWS reduced the lowest elevation angle to improve radar coverage. As a result, this radar site scans at the lowest elevation angle of 0.4 degrees.
Westslope’s NEXRAD screening analysis results show that, at a maximum height of 80 feet AGL, structures located in the Project will not be within line-of-sight at the lowest elevation angle scanned by the Cincinnati WSR-88D or the Cleveland WSR-88D. As a result, Westslope does not expect any impacts to Cincinnati WSR-88D operations or to Cleveland WSR-88D operations at or below this structure height.
CONCLUSIONS
ARSR and ASR Line-of-Sight Analysis
Westslope conducted an ARSR and ASR line-of-sight analysis for the following nine radar sites:
• Akron ASR-11
• Brecksville CARSR
• Cleveland ASR-9
• Columbus ASR-9
• Dayton ASR-9
• London CARSR
• Mansfield ASR-8
• Toledo ASR-9
• Wilmington ASR-9
The Project is beyond the instrumented range of the Akron ASR-11, the Cleveland ASR-9, the Dayton ASR-9, the Toledo ASR-9, and the Wilmington ASR-9. As such, Westslope did not consider any additional analysis necessary for these radar sites.
Westslope’s ARSR and ASR line-of-sight analyses for the Brecksville CARSR, the Columbus ASR-9, the London CARSR, and the Mansfield ASR-8 show that structures located in the Project will not be within line-of-sight of and will not interfere with these radar sites at a maximum height of 80 feet AGL As a result, Westslope does not expect any effects to these radar sites at or below this structure height.
TDWR Screening Analysis
Westslope conducted a TDWR screening analysis for the following three radar sites:
• Cleveland TDWR
• Columbus TDWR
• Dayton TDWR
Westslope’s TDWR screening analyses for the Cleveland TDWR, the Columbus TDWR, and the Dayton TDWR show that, at a maximum height of 80 feet AGL, structures located in the Project will not be within line-of-sight at the lowest elevation angle scanned by these radar sites As a result, Westslope does not expect any impacts to Cleveland TDWR operations, to Columbus TDWR operations, or to Dayton TDWR operations at or below this structure height.
NEXRAD Screening Analysis
Westslope conducted a NEXRAD screening analysis for the following two WSR-88D sites:
• Cincinnati WSR-88D
• Cleveland WSR-88D
Westslope’s NEXRAD screening analyses for the Cincinnati WSR-88D and the Cleveland WSR-88D show that, at a maximum height of 80 feet AGL, structures located in the Project will not be within line-ofsight at the lowest elevation angle scanned by these radar sites. As a result, Westslope does not expect any impacts to NWS WFO operations or to DoD weather operations at or below this structure height.
Contact Information
If you have any questions regarding this analysis, please contact Geoff Blackman at (405) 816 -2604 or via email at gnblackman@westslopeconsulting.com.
REFERENCES
[1] USGS, “What is the vertical accuracy of the 3D Elevation Program (3DEP) DEMs?,” 2022. (https://www.usgs.gov/faqs/what-vertical-accuracy-3d-elevation-program-3dep-dems). Last accessed April 23, 2025.
