Education from the communities to the world
Dr Kithsiri Edirisinghe
MBBS , MSc MD( Medical Administration ), PhD ( Health Sciences) , IVLP ( USA) , T & A ( Australia ) , Master Trainer ( Australia )

CEO / Co Founder , International Institute of Health Sciences (IIHS ) , Sri Lanka


Education from the communities to the world
Dr Kithsiri Edirisinghe
MBBS , MSc, MD( Medical Administration ), PhD ( Health Sciences) , IVLP ( USA) , T & A ( Australia ) , Master Trainer ( Australia )
CEO / Co Founder , International Institute of Health Sciences (IIHS ) , Sri Lanka



About us at IIHS



International Institute of Health Sciences, Sri Lanka


Finding solution to Local , Regional and Global “Healthcare work force crisis”

Contemporary education ; Augmented & Hybrid learning

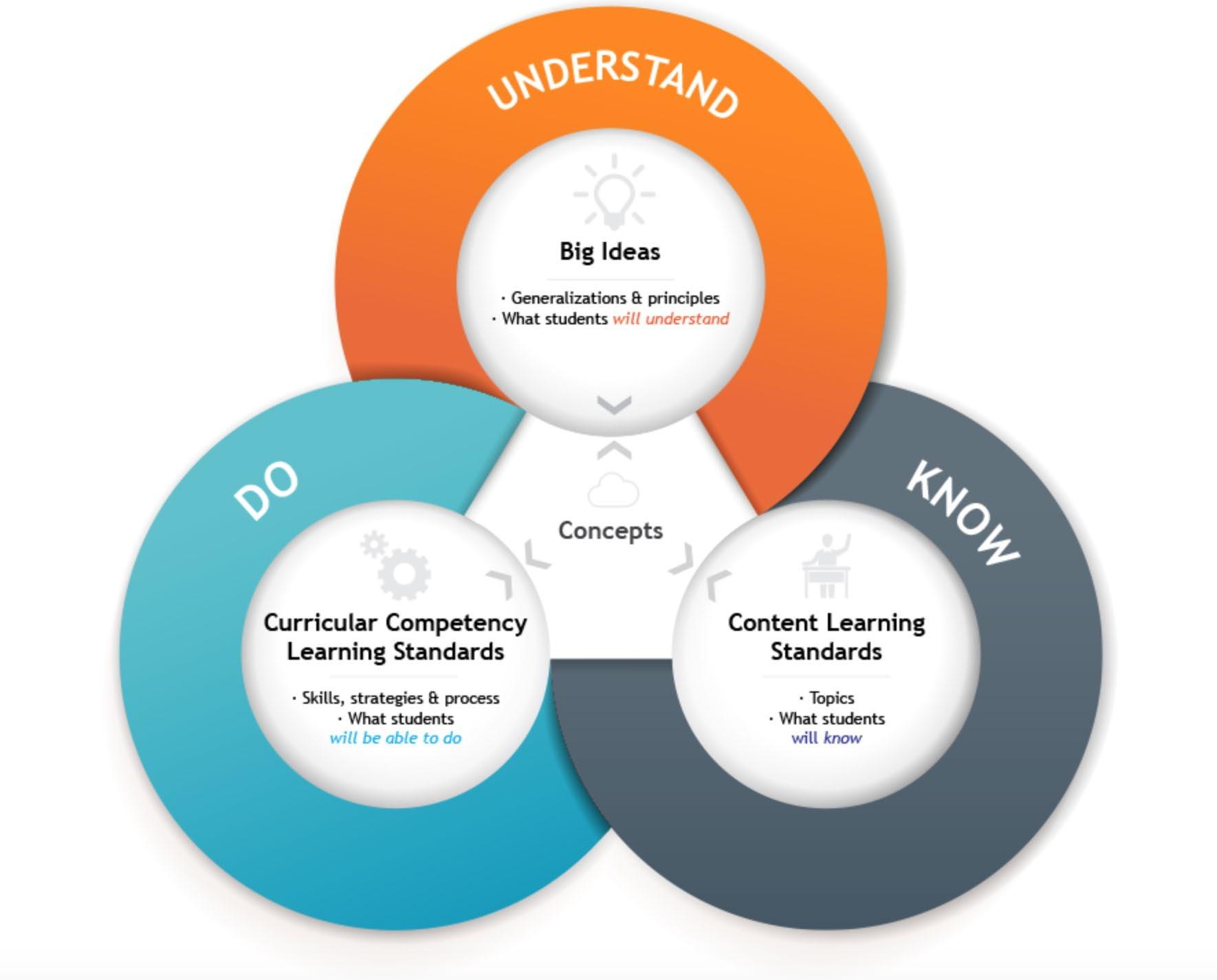
1. Curriculum design
2. Innovative teaching methods
3. Digital curriculum production

4. Management related to Aged care & Nursing

1. Curriculum design

• Process of Education Services

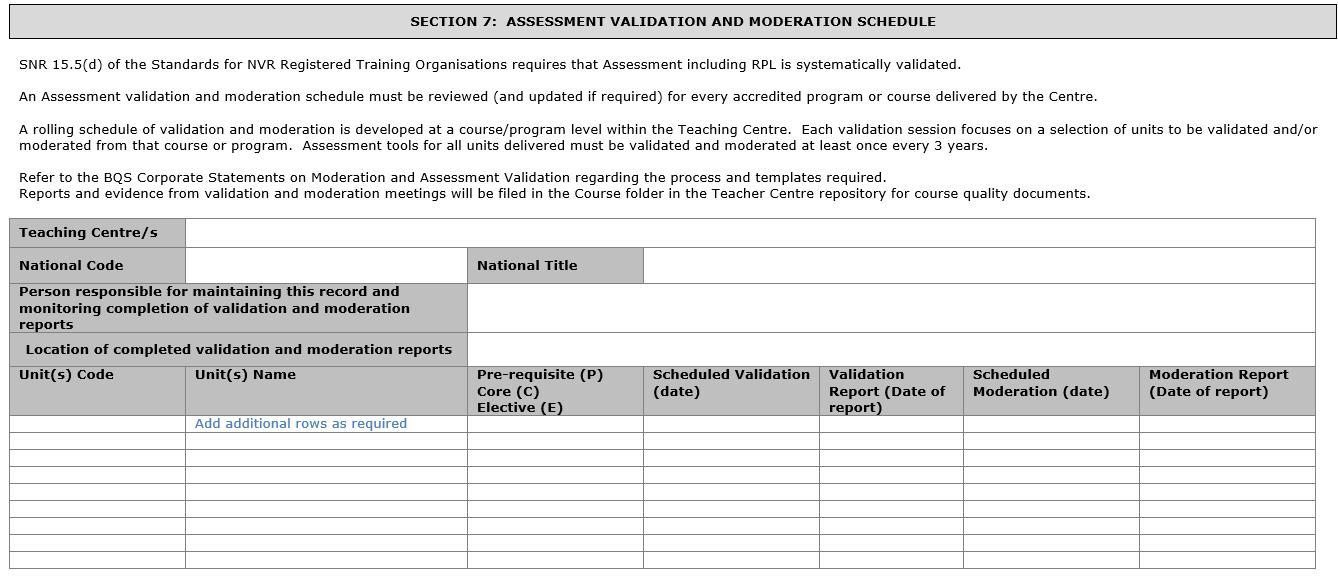
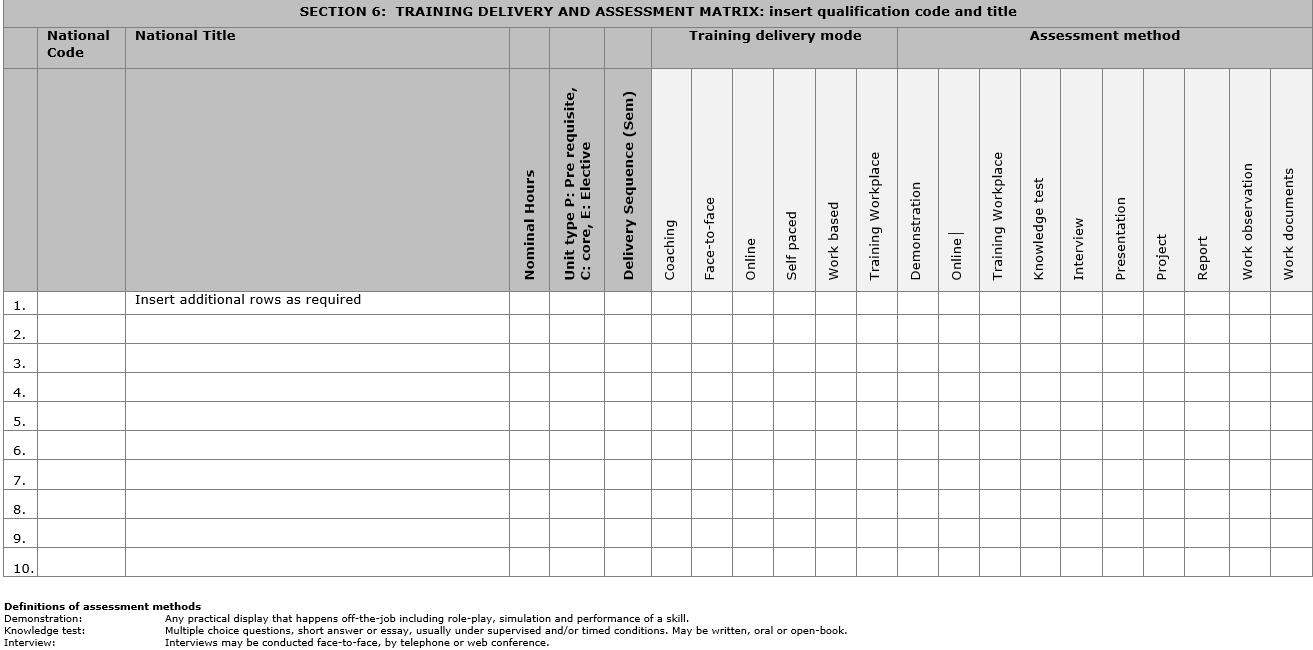
• Programme Development; Training & Assessment strategy (TAS)

Programme Development; Training & Assessment strategy (TAS)





1. Industry analysis > Job Description 2. Leaner analysis > Learner profile 3. Programme organization 4. Resources 5. Training & assessment resources 6. Training & Assessment modes 7. Evaluation > Validation
2. Innovative teaching methods


 • The Learner
• The Teacher
• The Learner
• The Teacher
The student
How about the student ?



The main consumer ?
The main customer ?
The learner


• A good exclusion


2. People > ……the traditional look
• Inculcating Knowledge , Skill , Attitude, Aptitude , Values
• Behavioral change was expected with Strict rules & punishment
• Education was then considered sacred

• Objective > to be the best and teachers happy
• Convergent thinking was the name of the game

>>>> Objectively oriented learners > professionals with a tunnel vision

Contemporary Learner & Education

• Change in the learner profile

• Information overload

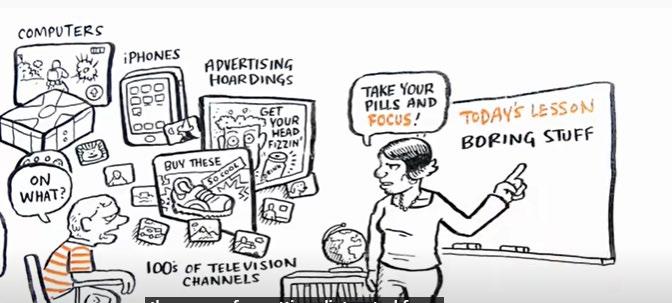
• Loosing power in the scared place
• More learner rights
• Needed a paradigm shift in education
• Creating an Aesthetic environment .. Moving away from Anesthesia

• Sir Ken Robinson -International Educator-



Including Learners

• Multiple intelligence Theory

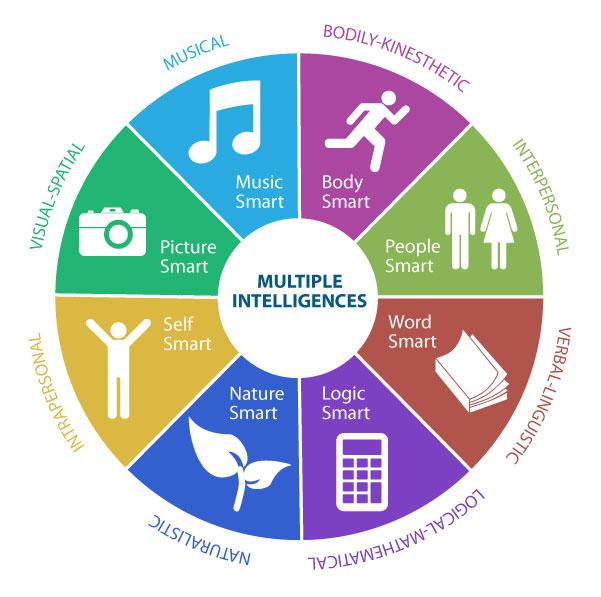

- Dr Howard Gardner

• Variety in learning and teaching
• The best fit
• Learning pyramid
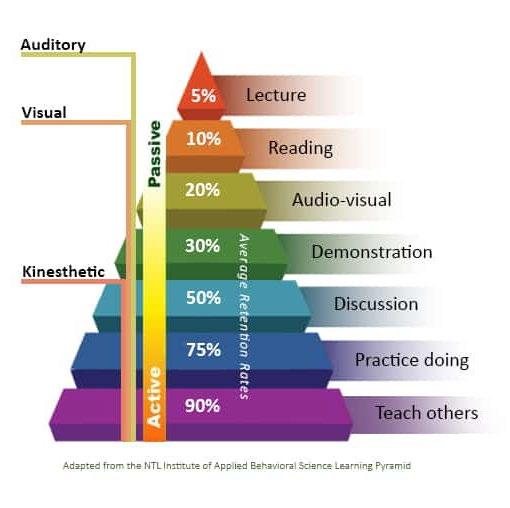
Paradigm shift in education



• Shift from teacher centric education to student centric, and now Student driven education (Choice)
• Shift in training methods aiming at Divergent thinking



• Shift from fragile learner to an agile learner

The Teacher

• The luckiest job in the world
• Staying young and thinking young
• Easiest job in the world
• Downloading the transferring information


• Attention
• Center of attraction
• Dependability
• Power
• Standardized curriculum
• Standardized delivery and assessment methods
• Teachers way of teaching
• Black board > White board > Smart board

• Text book > Note book > scrap book
• Teachers way of assessment / examinations
• Request only one answer question f


• Two answers >>>> “ get outta hear !
• Three -->>>>>
• TEACHER CENTRIC EDUCATION system
• Creates a tunnel vision !!!!
The Teacher
2. Choice

7.


1. Centricity
3. Collaboration
4. Consistency
5. Creativity 6. Critical thinking
Caring
the
> the 07 Cs
Innovative teaching methods
ingredients
1. CENTRICITY
Moving from central attention
Moving from the front / center
Presents as less important
But in reality more important
Work as a guide on the side
More free time to interact

Teacher centricity >>>>> Student centricity

Teaching Vs. facilitation
Less attention but more connection> One on one connection> Effective communication > Effective attention > Effective education
Transfer the power to the student
17
2 . CHOICE
The inclusion
The best match – delivery and assessment methods
Matching Learning styles
Choice
Students love choice
Menu for learning


Activity based learning > What ever the activities chosen > must achieve the outcome/ objective of the unit – same for everyone
Activities are chosen according their learning styles
Menu for assessments ?
ADD - Arts and entertainment > non traditional
Student centric vs. driven education
Making and agile learner Vs. a fragile learner
18
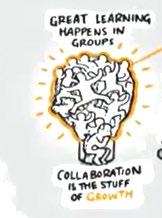
3. COLLABORATIVE LEARNING
Many brains together Vs. one brain
Open >> minds
Creating many ideas
Helps to have well rounded learning styles >> well rounded personality
Introverts >>> virtual world >>> extroverts >> real world >> real people
Evolution of Collaborative Learning center> Physical > Hybrid >


Virtual with LMS ( break up groups)

19
4. CONSISTENCY
Air tight lesson plan
Well organized Consistent disciplined plan
Effective use of technology is important
Learner management systems (LMS)

ICT
Digital library
Standards are important but do not let it kill the creativity
All modules are at LMS

Delivery > Just in time
Assessments
Tests > MCQs to Structured essay
High quality > Un biased > paper less education
Cost effective
Mobile friendly education
20
5. CREATIVITY
• Improving divergent thinking

• Stimulating to think differently
• Out of the box thinking > Breaking the box
• Innovation
• Community engagement

21
6. CRITICAL THINKING

• Essential >>> most important thinking

• Analytical thinking
• Logical thinking
• Evidence based study
• Case studies
• Simulations
• Reflections
22
7. CARE
Two loves
Teachers love for the subject and the passion for the subject > Passion to do good for the others


Genuine love for the kids
Decisional / put the others first kind of love
Motivates and inspires in a powerful way
You can love the kids even they are not likable
Not emotional but decisional
Most effective , powerful , inspiring way of teaching
Getting their attention, motivating them inspiring them
Look them in their eyes and ask of their extra curricular activities/ part time jobs
They will remembers most
Asked them how they are doing

Working hard in the first few weeks to learn their names
Going their athletic or other events
Transparent , real and humorous and laugh with them and not at them
Worked for their achievements
23
3. Digital curriculum production



• Process of course development
• SDG > Sustainable education > two aspects


• Description of the process
• Planning > Implementation > monitoring > evaluation
Physical curriculum


• It is one of the four essential components of physical education.
• It is the written, clearly articulated plan for how standards and education outcomes will be attained.
• Schools should have a written physical education curriculum for grades that is sequential and comprehensive.
• The physical education curriculum should mirror other school curricula in its design and schedule for periodic review.
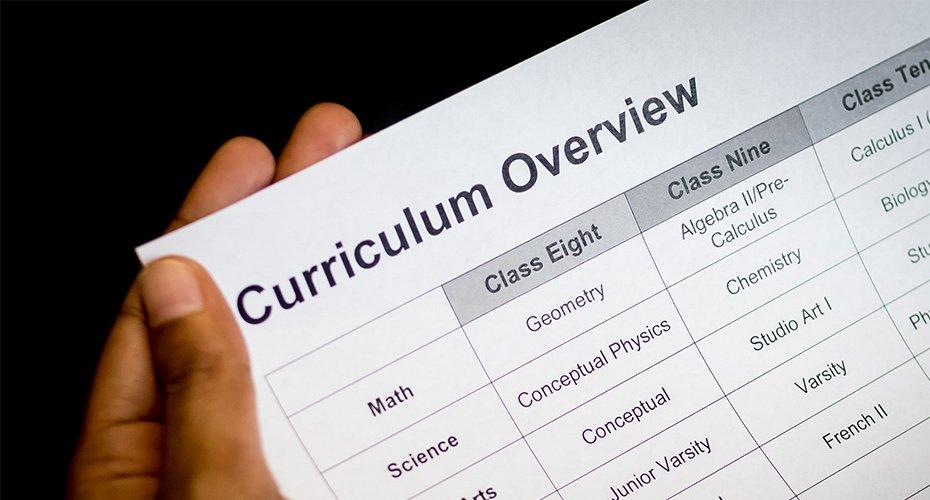
Physical curriculum

• It is comprehensive.
• Also customizable collection of resources.
• Digital resources come in a variety of formats, texts, video, images, audio, and interactive media.
• Can use these resources to better individualize.
• Also personalize the learning experience for their students.
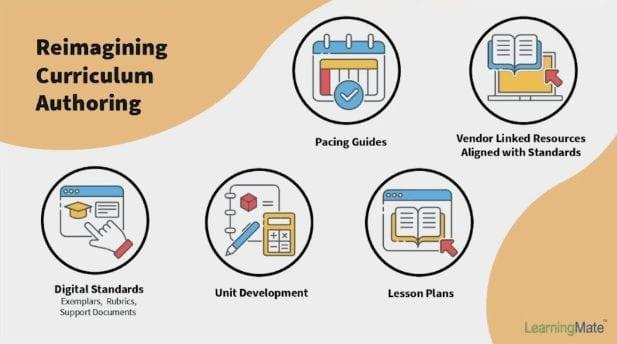

Planning > Digitalization of the Curriculum

• Digitize the Content
• Choose a Delivery Platform
• Create Interactive Content


• Make lesson plans clear and accessible.
• Let standards drive the curriculum – not the other way around
• Foster curiosity
• Take advantage of existing resources.
Implementation > Digital Curriculum

• The first step is to digitize the content.

• This may involve scanning textbooks, handouts, and other materials to create digital copies.
• The content may need to be rewritten in a digital format, such as a Word document or a PDF. More…

Implementation > Digital

Curriculum
• The next step is to choose a delivery platform.
• This may involve using a learning management system (LMS).


• A digital curriculum can incorporate various interactive elements, such as videos, animations, simulations, and quizzes.
• Creating interactive content requires specialized skills and software
• Teachers, curriculum staff and IT personnel must collaborate from the beginning.
Monitoring > Digital Curriculum
• it's important to test it thoroughly and get feedback from users.
• This feedback can be used to refine the curriculum and improve its effectiveness.
• Once the digital curriculum is launched, it's important to monitor its usage and effectiveness.
• This may involve tracking metrics such as engagement, completion rates, and assessment scores.


Evaluation > Digital Curriculum
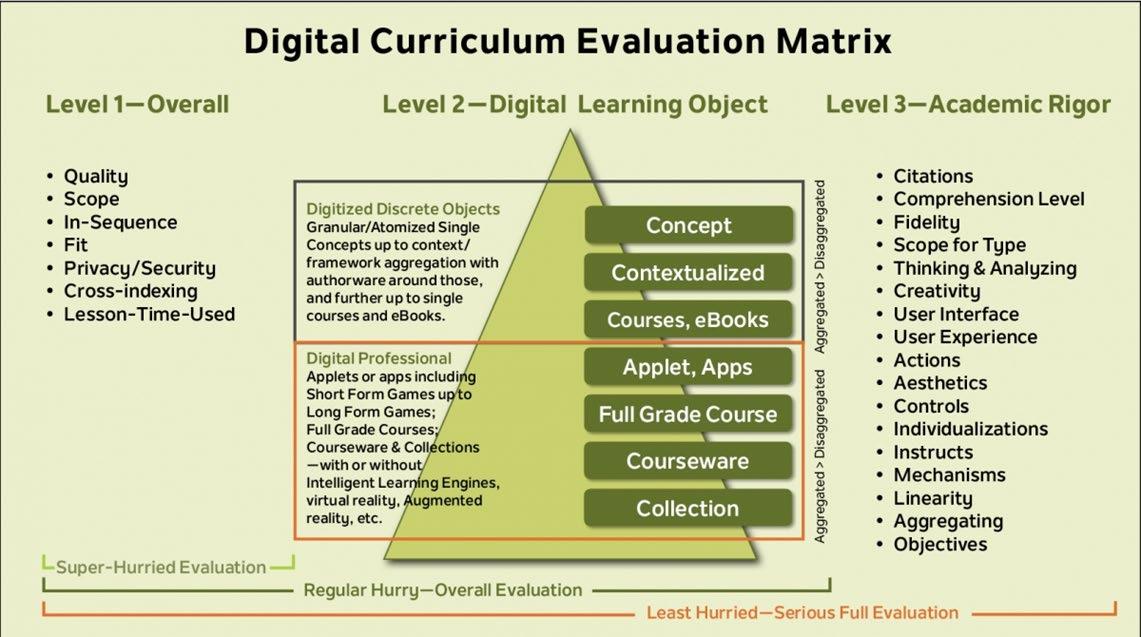
• It's important to ensure that the digital curriculum is accessible to all learners, including those with disabilities.
• This may involve adding captions to videos, using alt tags for images, and creating accessible PDFs.


• Clearly identify the outcomes expected of the curriculum.
• Understand the underlying model, pedagogy, and process used to develop the curriculum.
Our success stories







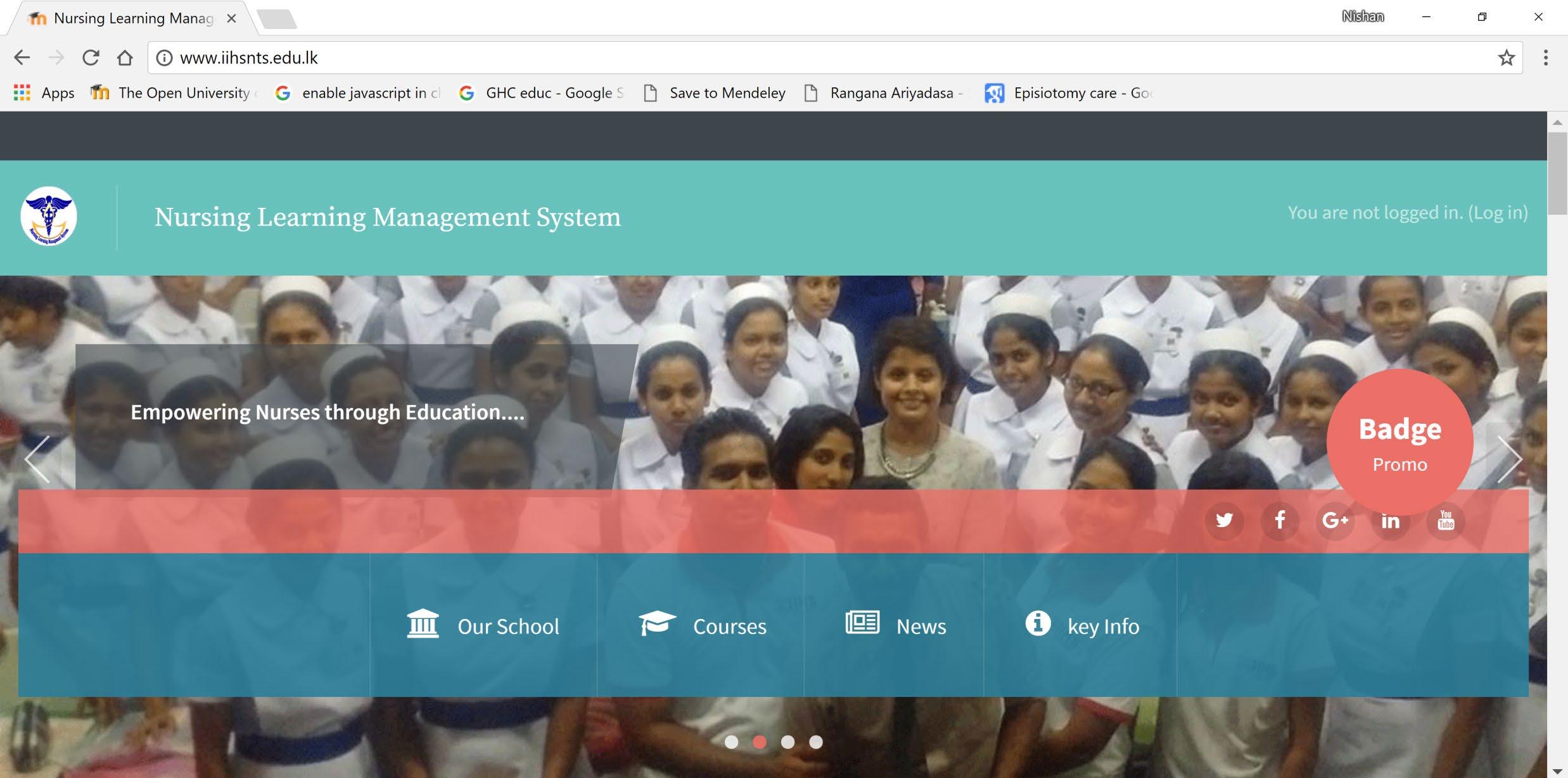



4. Management related to Aged care & Nursing
1. Developed the first ever HIS module in South Asia, 2010
2. Developed the First module on managing aged care services , 2010

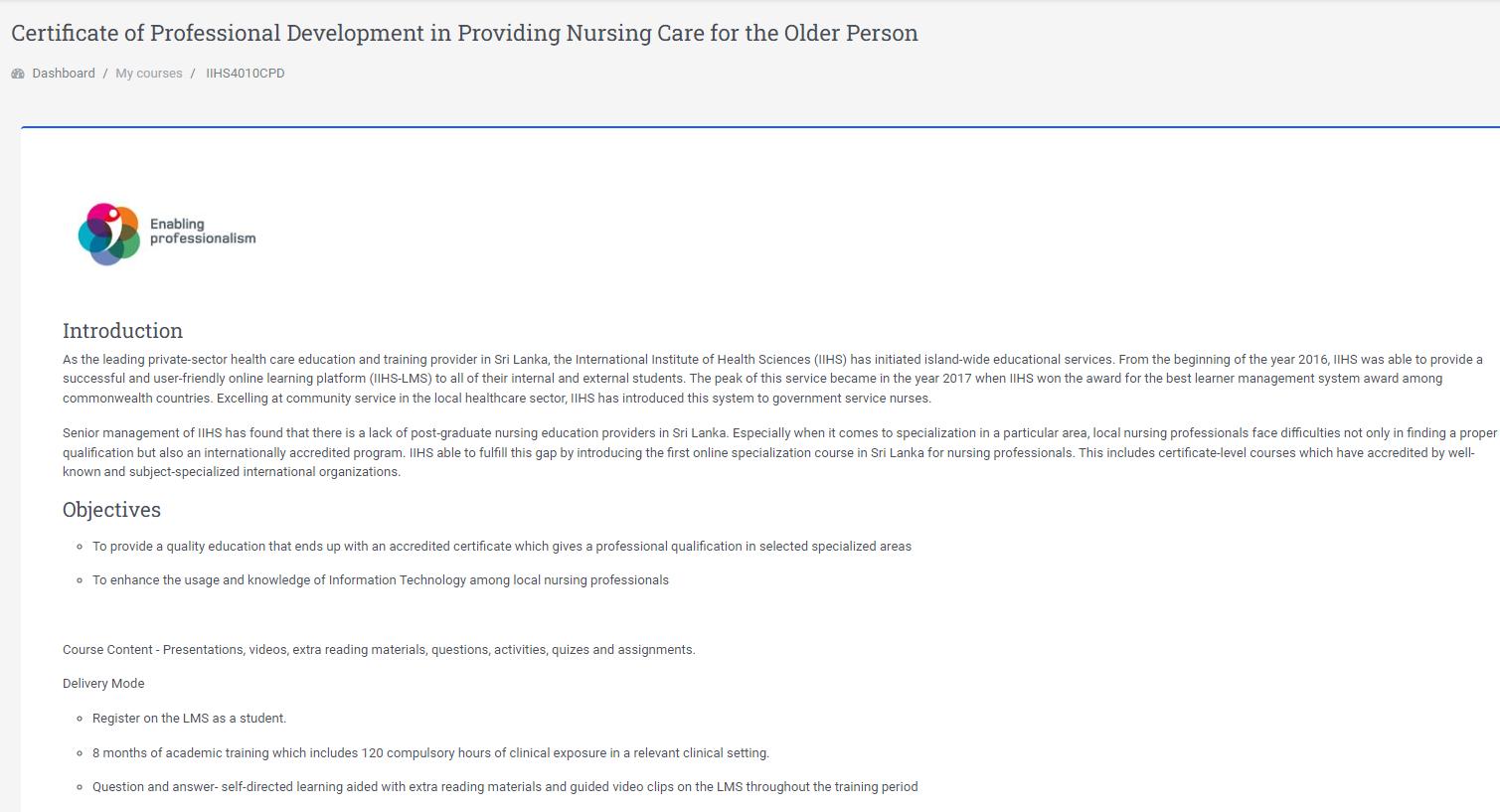
3. Developed frost CPD programme for Nurse for managing Elderly care, 2015
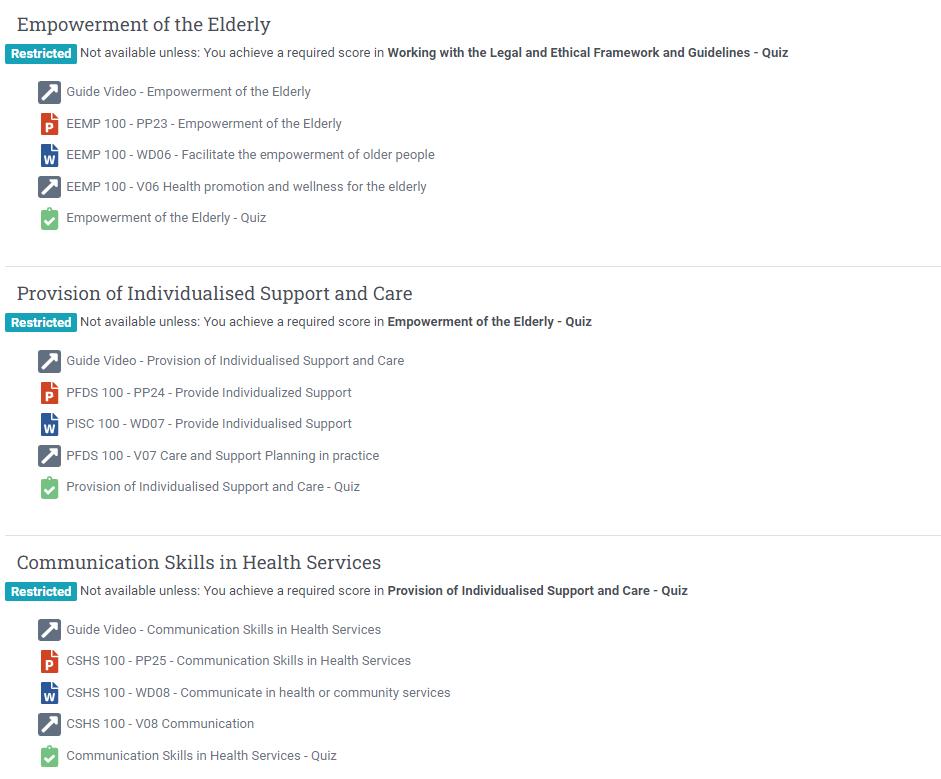



Research










Way forward Global , regional , local collaboration
• EDUCATON
• Physical ,hybrid digital learning
• 10 CPDs for nursing specialization
• Bachelors in Nursing

• CPD MBA in Healthcare management
• Master in Nursing
• Doctorate in nursing

• Merging education with Sustainable education
• Bio Inquirer
• Research collaboration
• Research conference
• Staff / student exchange
• Industry placement > UK, Australia ,USA
• Contact details
• drkithsiri@iihscinences.edu.lk
1. Redefining Learning & Teaching using Technology. | Jason Brown | TEDxNorwichED
2. Can Technology Change Education? Yes!: Raj Dhingra at TEDxBend
3. A different way to think about technology in education: Greg Toppo at TEDxAshburn
4. Why Technology Can't Fix Education | Mary Jo Madda | TEDxChicago
5. Technology in Education - From Novelty to Norm | Joel Handler | TEDxHIllsboroughLibrary
6. Exploring the potential of the will, skill, tool model in Ghana: Predicting prospective and practicing teachers’ use of technology, Douglas D. Agyei a, Joke M. Voogt b
7. Measuring Teachers’ Technology Uses, Damian Bebell, Michael Russell & Laura O’Dwyer
8. Effects of Technology Integration Education on the Attitudes of Teachers and Students, Rhonda Christensena, a University of North Texas Published online: 24 Feb 2014.
9. BARRIERS TO THE EFFECTIVE USE OF TECHNOLOGY IN EDUCATION: CURRENT STATUS, DEE L. FABRY, University of Colorado at Denver , JOHN R. HIGGS,
10. No Access, No Use, No Impact, Cathleen Norrisa, Terry Sullivana, James Poirota & Elliot Solowayb a University of North Texas, b University of Michigan, Published online: 24 Feb 2014.
11. EFFECTIVE TEACHING WITH TECHNOLOGY IN HIGHER EDUCATION: FOUNDATIONS FOR SUCCESS, A. W. Bates and Gary Poole.

36

























































































