
• Surgical scalpel blades
• #10 – medium rounded – opening chest, bridged leg incision, commonly called “skin blade”
• #15 – small rounded – EVH incision, chest tube incision
• #11 – pointed straight – ‘Stab and Grab’ incision
• Disposable – bed-side procedures

Forceps
• Forceps are used throughout the case to handle tissues
• Type of forceps varies depending on tissues being handled
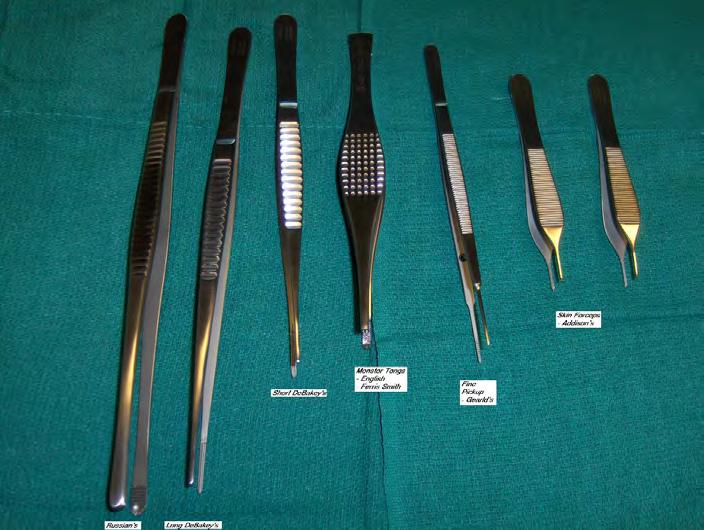
Instruments from Left to Right:
- Russian's - Long DeBakey's
- Ferris Smith, "English", or "Monster Tongs"
- Gerald's vascular pickups
- Addison's skin forceps (2)
• Russian’s – normally used for larger tissues and to handle clot removal

• Gerald’s – these are vascular forceps, used to handle blood vessels
• Very fine tip
• Peg in handle reminds holder of forces being applied to tissue

• If you can feel or see the peg you’re holding on too tight
• Singly’s – normally used for larger, friable or fragile tissues
• Typically used to handle the atria, or lungs

• Ferris-Smith’s – normally used for larger, non-friable tissues
• Also called ‘English’ forceps or ‘Monster Tongs’
• Typically used to handle skin during chest closure

• Diamond Dust – these are vascular forceps, used to handle blood vessels
• Very fine, diamond dusted tip

• Ring Tipped Gerald’s– these are vascular forceps, typically used to handle the thoracic (mammary) arteries
• Very fine, ring tip

• DeBakey – general purpose tissue forceps
• Tip has interlocking grips that are kind to tissues
• Depending on tip size, can be used as vascular forceps

• There are other types of forceps
• Titanium versus stainless steel
• Can be curved (see “curved De Bakey’s” below)
• Selection is often surgeon preference based on how they’re used

Needle Drivers
• Needle drivers are based on the size needles that will be driven
• The smaller the needle, the finer the driver

• Berry – heavy driver used for chest wires

• Ryder – general purpose needle driver

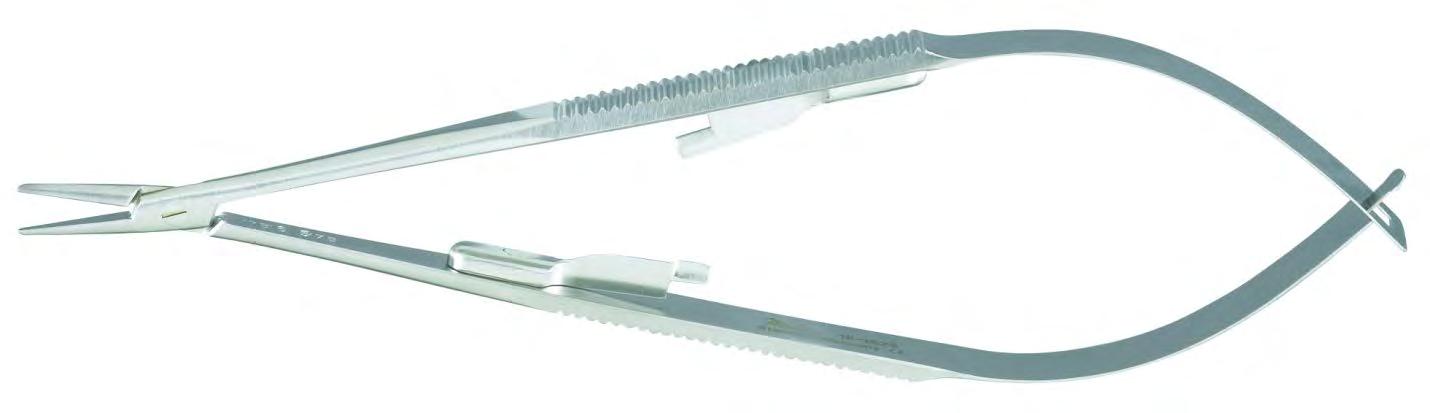
• Castroviejo – for fine vascular needles that are selected based on size of needle and surgeon preference
• Can have flat or rounded handle
• Locking or non-locking
• Stainless steel or titanium
• Straight or curved tip
Scissors
• Metzenbaum (‘metz’) – general purpose tissue scissors
• Come in various lengths
• 18 cm is a ‘standard’ length and are used as a ‘length of vein’ for bypass

• Cooley (‘My’) – general purpose tissue scissors
• 20 cm is a ‘standard’ length
• Blunt tip
• Good for dissecting the vein tunnel, or open/bridged harvest

• Potts’ – vascular scissors
• Used for arteriotomies

• Come in differing angles (e.g. ‘straight’, ‘forward’, ‘reverse’)
• Castroviejo (‘Castro’) – vascular scissors, used to trim thoracic (mammary) artery

• Straight or curved (pictured) tip

Clips / Appliers
• Used to ligate small vessels such as tributaries (branches) of vein or IMA
• Clips are titanium, stainless steel, or plastic (less common)
• Clips come in ‘micro’, ‘small’, ‘medium’, ‘large’ and ‘extra-large’ sizes
• Sizes are color coded, and appliers match color scheme Retractors
•Army/Navy (‘USA’) – General purpose retractor
• Tunnels
• Sternal edges, Sternal notch, Xiphoid dissection

• Rake – typically used for sternal edges
• Sharp or rounded tines
• Use with care on other tissues
