
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 07 | Jul 2025 www.irjet.net


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 07 | Jul 2025 www.irjet.net
p-ISSN:2395-0072
Shreyas
Paimode1, Shreyash Girge2, Dr. Mugdha Kango3, Dr. Anil Shirsat 4
1,2,3,4Electronics & Tele. Dept., PES Modern College of Engineering, Shivajinagar, Pune
Abstract - The current project focuses on developing a hand gesture-controlled robot that functions in real time, utilizing the OpenCV library for the detection and interpretation of hand gestures. A camera captures visual data, which is subsequently processed to identify and analyze hand movements. The robot's actions are controlled by precise commands that are based on the movement that was detected. The main goal is to make an interface that is easy to use and doesn't require hands. This will improve the interaction between people and robots, which is especially helpful for people with physical disabilities or in situations where traditional input methods would be impractical. This paper examines pertinent research on gesture recognition and control, outlining key challenges and results.
Key Words: Gesture recognition, Human-robot interaction, OpenCV, Real-time control, Robotics.
1. INTRODUCTION
Robotics has made a lot of progress in the last few decades, especially with the use of smarter and more creative control systems like gesture recognition. Gesture control is an even more natural way to interact with machines than traditional methods that involve direct physical contact or remote controls. You can do it with simple hand gestures. This not only improves the overall userexperience,butitalsomakesthetechnologyeasierto use,especiallyforpeoplewithdisabilitieswhocan't touch thedevices.So,thisgivespeoplemorefreedomandmakes iteasiertouse.
Wewereabletomakearobotthatcanbecontrolledby hand gestures in this project. The system is built on the powerful OpenCV library, which is the main part that recognizes and interprets hand gestures through a live video feed. The main goal was to teach the robot how to read gestures correctly so that it could move in different directionsbasedonthesignalsitsaw.Thistechnologyhas a lot of potential for many uses, from helping patients in hospitalstomakingsmarthomeautomationandindustrial processespossiblewithtouchless,easy-to-usecontrols.
A robot arm system was created by Chong et al. with the purpose of handling hazardous materials in facilities such as nuclear power plants and poisonous waste treatment facilities. The system makes use of a glove
equipped with accelerometers and flex sensors to record hand movements, which are then wirelessly transmitted to the robot device through NRF24L01 transceivers. Although such an arrangement is feasible and effective, it has limitations that can impair its operational performance,suchassignalinterferenceandsensornoise.
A Virtual Blackboard Operating Through Hand Gestures Soroni has developed a new virtual blackboard system in which users can write on a virtual screen with their hand gesture alone, which is recorded using a webcam. It recognizes and processes the gesture using OpenCVandthereforeisquitesuitedtovirtualclassrooms orvirtual learningenvironments.Butitishighlysensitive to light, which can limit its use in other environmentsofcontexts.
A control mechanism where a robot tracks hand movementsonthepalmwasproposedbyFloerschandLi. The system uses accelerometers and infrared cameras to detect hand movements in real time. Even though the systemissimpleandremarkablyaccurate,ithasproblems when used with low-power processors, particularly when morecomputationisneeded.
UsingaRaspberryPi3andaPiCamera,EmmaKaufman and Chloe Kuo developed a robot that recognizes hand gestures. The robot has an accelerometer to improve movement accuracy, pressure sensors to improve interaction,andanultrasonicsensortopreventcollisions. It is also fed gesture commands via Bluetooth. Although the design is usable, its accuracy in detecting gestures is affectedbylightingvariations,makingitunreliable.
In order to enable movement control, Harish Kumar Kaura and his colleagues created a robotic system that could recognize hand gestures through a webcam and process them using OpenCV. The system can effectively translate gestures into commands and exhibits outstanding real-time response. But like the majority of vision-based systems, it struggles to recognize more complexgesturesandisaffectedbychangesinlighting.
Ahead-controlledwheelchairwascreatedbyPathanet al. to help people with physical disabilities. The system makes use of an RF module for wireless communication and a number of sensors, including the MPU6050 sensor for movement detection. The innovation increases the system's operational flexibility by enabling it to switch between head gesture control and joystick control.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 07 | Jul 2025 www.irjet.net
Althoughheadgesturesaretheprimaryfocusofthepaper, italsoshowshowgesturecontrolandwirelesstechnology can be used in a variety of contexts. This approach aligns with the goals of our hand gesture-controlled robot system,particularlyinassistivetechnology.
A. Overview of the System
Our system is a hand-gesture-controlled robot that can follow certain movement instructions and react to hand gestures.Therearethreemainpartstoit:
• Webcam: Continuous live video capture of hand movements.
• OpenCV-based Gesture Recognition:identifiesvarious hand gestures from video streams by using image processing techniques made possible by the OpenCV library
The ESP32 microcontroller: it receives the recognized gesture data and transforms it into the appropriate movementcommandsfortherobot.
B. Components of Hardware
The following are the system's fundamental hardware components:
• ESP32: The robot's brain, this component takes input fromthegesturerecognitionmoduleandusesittocontrol theappropriatemotors.
• Cytron Motor Driver (MD30C series): Regulates the robot'sDCmotors'speedanddirection.
• DC motors: Give the robot mechanical movement so it canmoveinresponsetocommands.
• The webcam provides input for the visual processing system by continuously recording the user'shandmovements.
C. Software Design
It is intended for accurate command execution and efficientgesturerecognition:
• OpenCV Gesture Recognition: OpenCV helps the system process the webcam images. Hand shapes are detected and recognized using methods such as contour detection, skincolorfiltering,andbackgroundsubtraction.
• Command Mapping and Execution: After a gesture is identified,itismappedtoaspecificrobotcommand,which may include turning left and right, moving forward, or
p-ISSN:2395-0072
movingbackward.TheESP32microcontrollerreceivesthe commandandusesittoregulatetherobot'smotion.
D. System Architecture
The entire framework comprises a series of connected elementseachwithacertainrole:
•GestureDetectionModule:Utilizesthewebcamtotakea steady stream of photographs, which are analyzed employingOpenCVforidentifyingcertainhandgestures.
• Command Processing Module: Converts the identified gesturesintoadirectcontrolcommandthattherobotcan readandfollow.
•MovementControl Module:Passestheinstructionsafter processing to the Cytron Motor Driver (MD30C series), which subsequently drives the motors to execute the intendedmovement
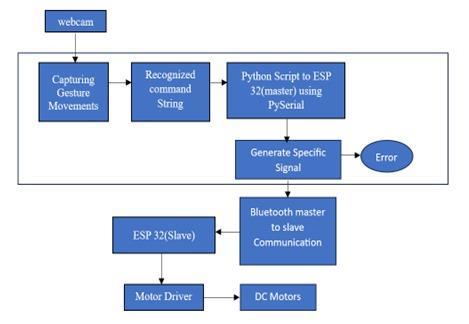
Fig -1:BlockDiagram
Awebcammoduleoracameramodulemustfirstcapture videoframes.
Gesture Motion Capture: Hand gestures are recognized by processing the captured images. Included are hand detectionandusertracking.
Hand Gesture Detection: OpenCV allows the system to recognize thehandregionineachpicture.Featuressuch aspalmorientation,handshape,andfingerlocationsare used.
Command Identification Using a Designated Methodology: Certain gestures (such as the thumbs up, closed fist, and open hand) are associated with the features that have been extracted. The robot can be controlledusingthesegesturesasinstructions.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 07 | Jul 2025 www.irjet.net
Create Individual Signals: The system creates individual control signals after detecting the gestures. These signals telltherobotwhattodo(e.g.,turnleft,moveforward).
BluetoothCommunication:TheESP32receivesthecontrol signals remotely via Bluetooth technology. The ESP32 servesasaninterfacebetweentheroboticsystemandthe computer.
The ESP 32 microcontroller decodes incoming gesture commandsandtranslatesthemintomotorcontrolactions.
TheMD30CSeriesCytronmotordriverisacontrolsignalacceptingmodule.
ItreceivesinputsfromtheESP32andusestherecognized gesturestocontroltherobot'sDCmotors.
DC Motors: Finally, the robot's DC motors respond to the control signals. The operator's hand movements are followedbytherobot
5.SOFTWARE DESIGN
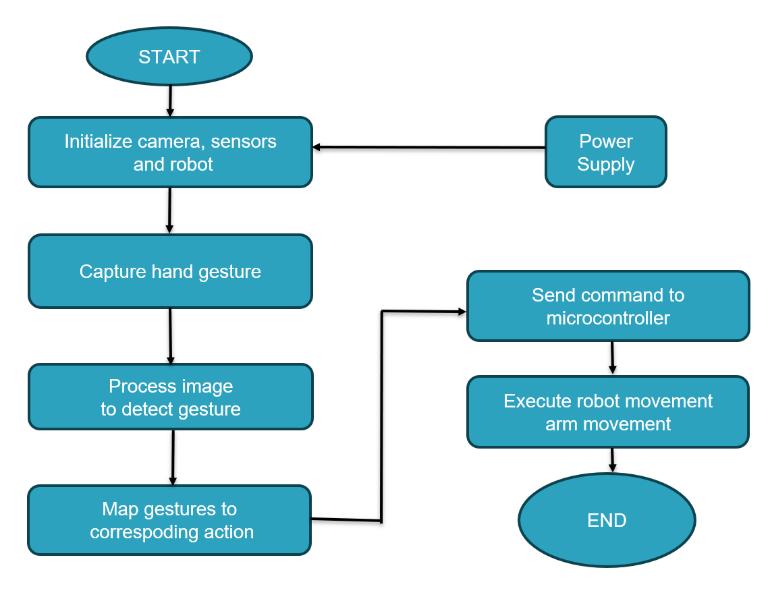
Start:Theproceduregetsstarted.
Start setting up the robotic apparatus, sensors, and camera: Every piece of hardware is turned on by the system.
Thecamerarecordstheuser'shandgesture.
Image processing to find gesture: The gesture is found by processingtheimage.
Mapgesturetocorrespondingaction:Anactionisassigned tothegesturethathasbeenidentified.
p-ISSN:2395-0072
Transmit directive to microcontroller: The robot's microcontroller receives the appropriate instruction from thesystem.
Execute robot movement (arm movement): The robot follows the gesture by carrying out the appropriate movement.
End:Theprocessisover.

Fig -1:OpenCVBasedGestureControlledRobot
The system's functionality and performance were evaluatedusinga rangeofhandmovementsandlighting conditions.
A Accuracyofgesturerecognition
In good lighting, its mean gesture recognition accuracy was about 92%; however, when the robot's gestureresponseistakenintoaccount,itperformsupto 30% worse than mean in low or excessively bright lighting.
B.InstantReaction
According to the results, the average gesture to robotic movement reaction time was 150 milliseconds, which is usually adequate for most real-world uses However, the detection and execution processes were delayed by more complex gestures that involvedfingeroverlap.
C. Robustness of the System Because the system is sensitive to variations in lighting, it performed well indoors but poorly outdoors. The system may become sensitive to variations in lighting and environmental conditionswithfurtherresearch.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 07 | Jul 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Ithasnumerousapplicationsingesture-controlledrobots.
Medical care: During a pandemic like COVID-19, a gesture-controlledrobotcanbeveryhelpful.Itstouch-free operation reduces the risk of viruses spreading through direct contact with surfaces and eliminates the need for physical contact altogether. To reduce virus exposure, medical personnel can use gesture-controlled robots to deliver supplies, food, or medication to patients without going into their rooms. Additionally, the robot can communicate with and care for patients remotely thanks to gesture navigation, making sure safer medical treatmentwithoutviolatingsocialdistancing.
IndustrialAutomation:Tominimizehumaninteraction with hazardous machinery, gesture-controlled robots can beusedinfactoriesorotherhazardoussettings.
The most critical issues encountered during the project are:
Lighting Sensitivity: A lot of light affects how well a system works. This significantly affects gesture recognitionaccuracy.Futuredesignsshouldthereforetake into account algorithmic adaptation to varying light intensities. Complex Gesture Recognition: When fingers overlap, the system is unable to recognize complex gestures. CNN and other machinelearning algorithms can significantlyincreasetheprecisionofgesturerecognition.
EnvironmentalRobustness:Thesystemhasundergone a great deal of indoor testing. To test the system as a whole, it needs to be tested in industrial settings or outdoors.Inthefuture,thesystemwillbestrengthenedby adding depth sensors such as Kinect or Intel RealSense, enhancing the gesture recognition algorithm, and expanding the number of gestures to accommodate increasinglycomplexcommands.
Thispaperpresentsreal-timehandgesturerecognition using OpenCV and a gesture-controlled robot. It has been difficult for the system to manage intricate gestures and lighting changes because of the desire to showcase these systems to the world in an attempt to develop gesturebased control for applications like home automation, healthcare, and industrial automation. These limitations will be addressed in future studies to produce a reliable andflexiblegesture-controlledrobot
[1]F. Soronietal.,“Handgesturebasedvirtualblackboard using webcam,” Proc. IEEE 12th Ann. IEMCON, 2021. researchgate.net+3smartquantai.com+3
[2] B. Zain, S. Hassan, B.Mir, and R. H. Dar, “Robotic hand control using hand gesture recognition,” Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol.,vol. 6,no. 2,Feb.2019.studylib.net+1irjet.net+1
[3]A.Budhiraja,“Gesturecontrolledroboticarmforsocial distancing,”Int.J.Res.Anal.Rev.,2023.
[4] S. Dasgupta and A. Ghosh, “Bluetooth controlled Arduinobasedroboticarm,”IRJET,2020.
[5] R. R. Prabhu and R. Sreevidya, “Design of robotic arm based on hand gesture control system using wireless sensornetworks,”Int.Res.J.Eng.Technol.,2017.
[6] N. Anughna, V. Ranjitha, and G. Tanuja, “Wireless robotic arm using flex and gyroscopic sensors,” Int. J. RecentTechnol.Eng.,vol. 8,no. 5,Jan.2020.
[7]S.M.K.Pathanetal.,“Wirelessheadgesturecontrolled robotic wheelchair system,” J. Sensor Technol., vol. 10, pp. 47–59,2020.
[8]H.K. Kauraetal.,“Gesturecontrolledrobotusingimage processing,”Int.J.Adv.Res.Artif.Intell.,vol. 2,no. 5,2013
[9]C. K. Wen,L. C. Yong,andC. Nataraj,“Gesturecontrolled robotic arm for handling hazardous chemicals,” J. Appl. Technol.Innov.,vol. 6,no. 3,pp. 47–54,2022.
[10] J. Paterson and A. Aldabbagh, “Gesture-controlled roboticarmutilizingOpenCV,”Proc.IEEEIEMCON,2021.
[11] J. Qi et al., “Computer vision–based hand gesture recognitionforHRI,”Int.J.Mach.Learn.Comput.,2023
[12]S.A. HandeandN.R. Chopde,“Automatingindustrial applications using gesture-controlled robotic arms,” Int. J. Innov.Res.Sci.Technol.,2020.
[13] N. Chaudhari et al., “Hand gesture control for robotic armsusingOpenCV,”2023.
[14]A.Naleetal.,“Gesture recognitionsystemfor robotic cars,”2015.
[15] E. Kaufman and C. Kuo, “Gesture-controlled educationalrobotprototype,”2020.
[16] J. Floersch and J. Li, “Palm-steered point-and-follow control system using accelerometers and IR cameras,” 2019.