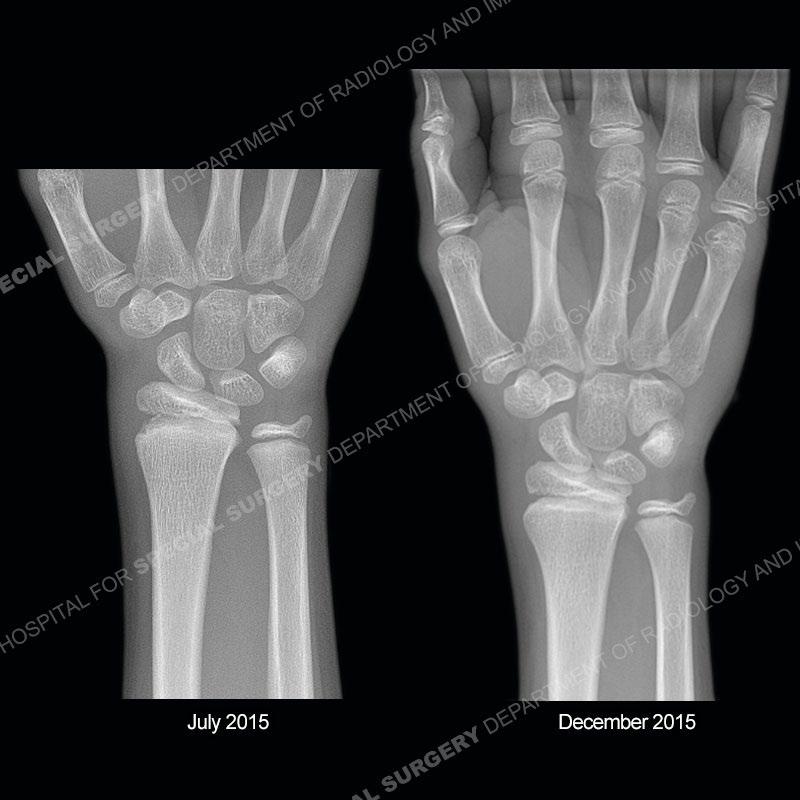
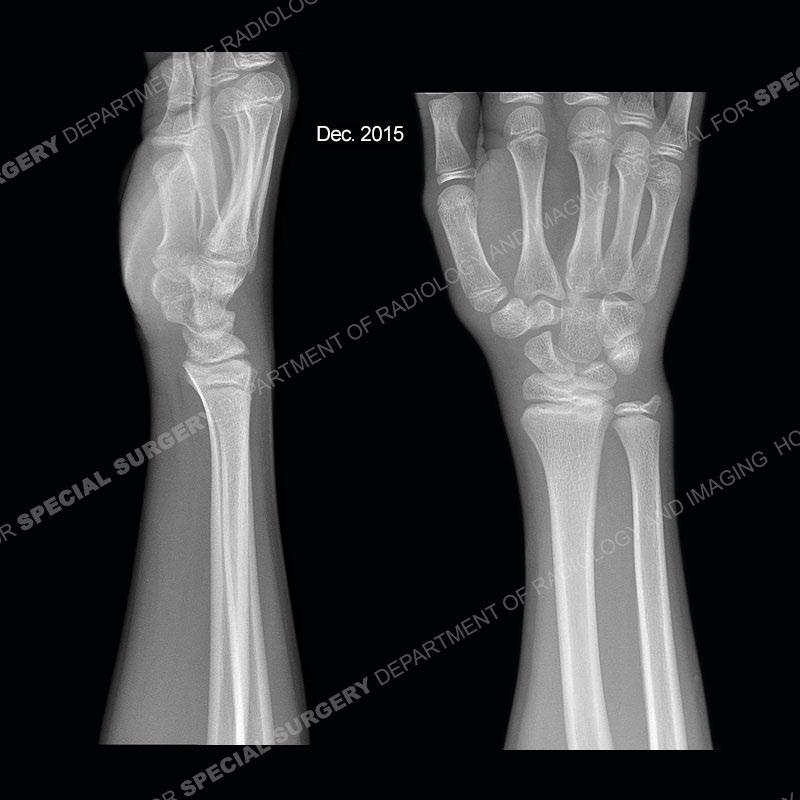
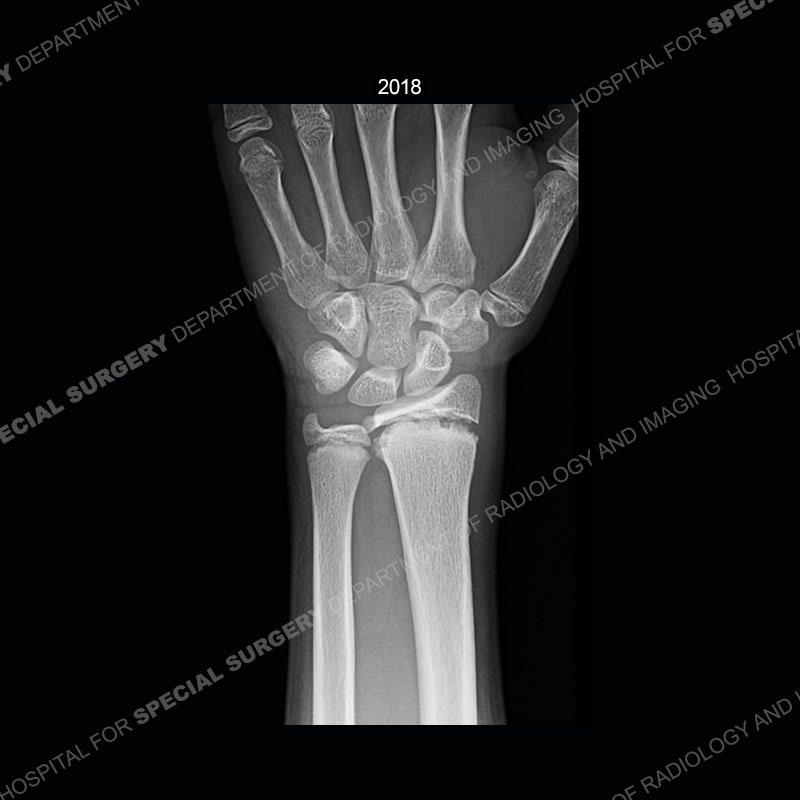
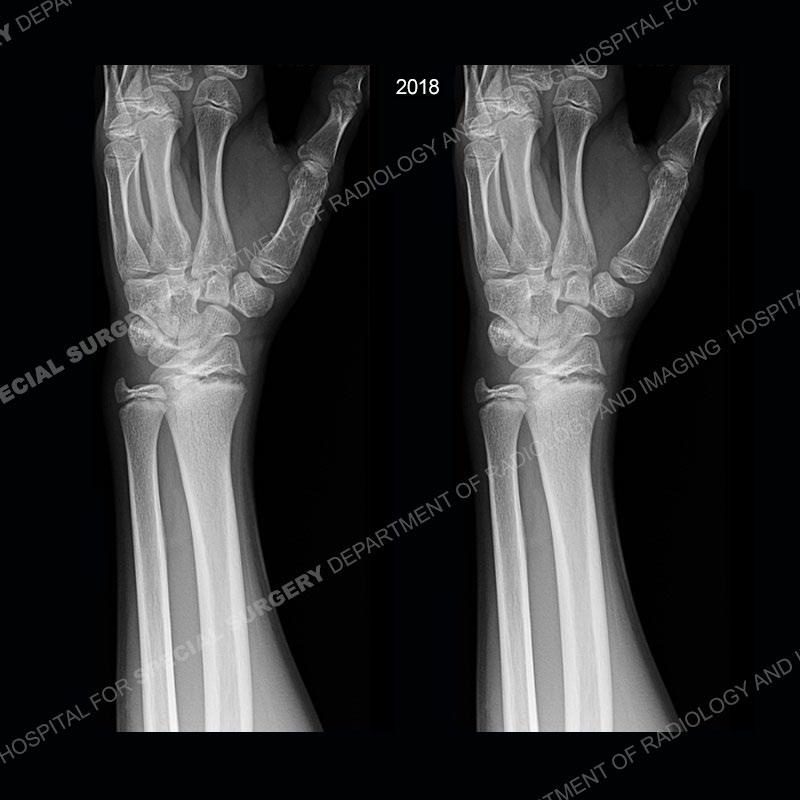
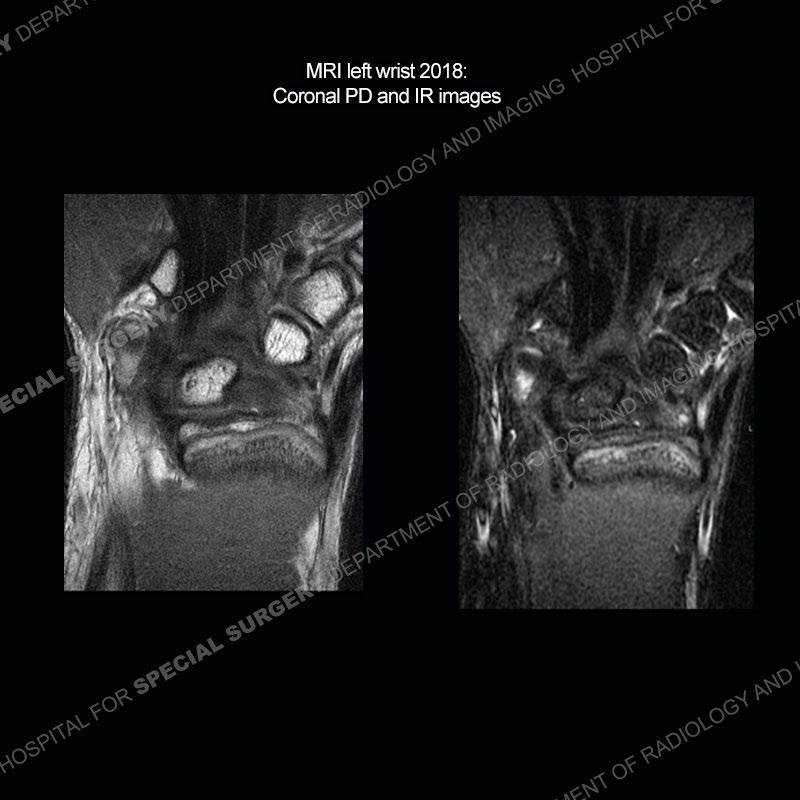
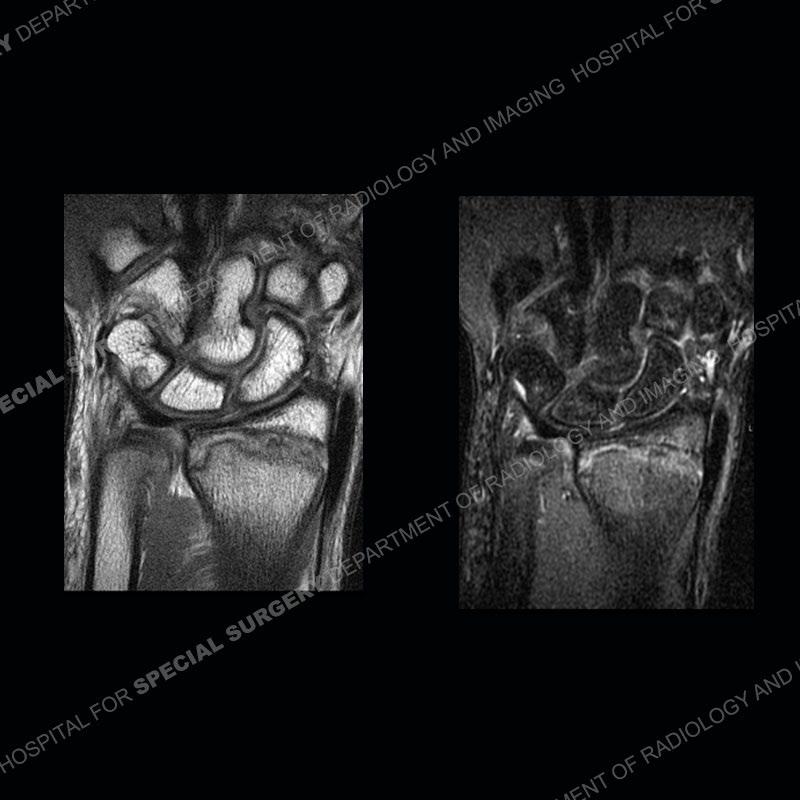
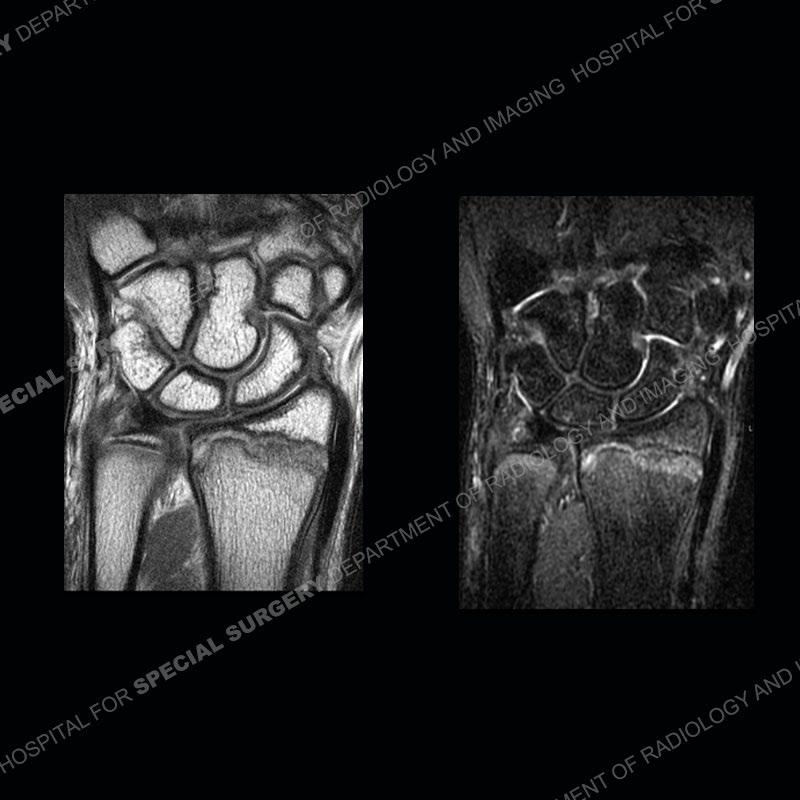
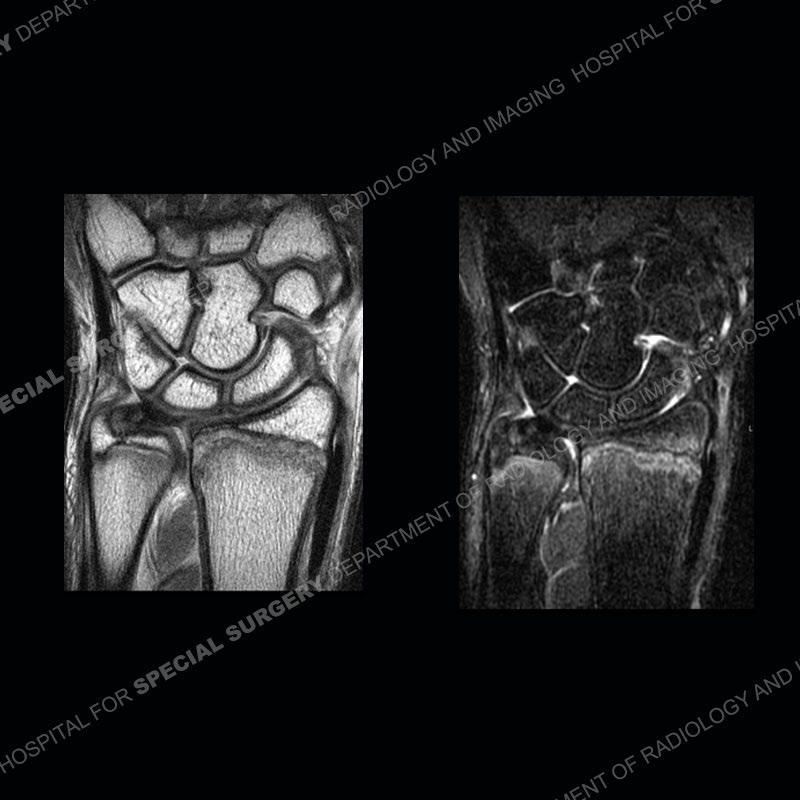
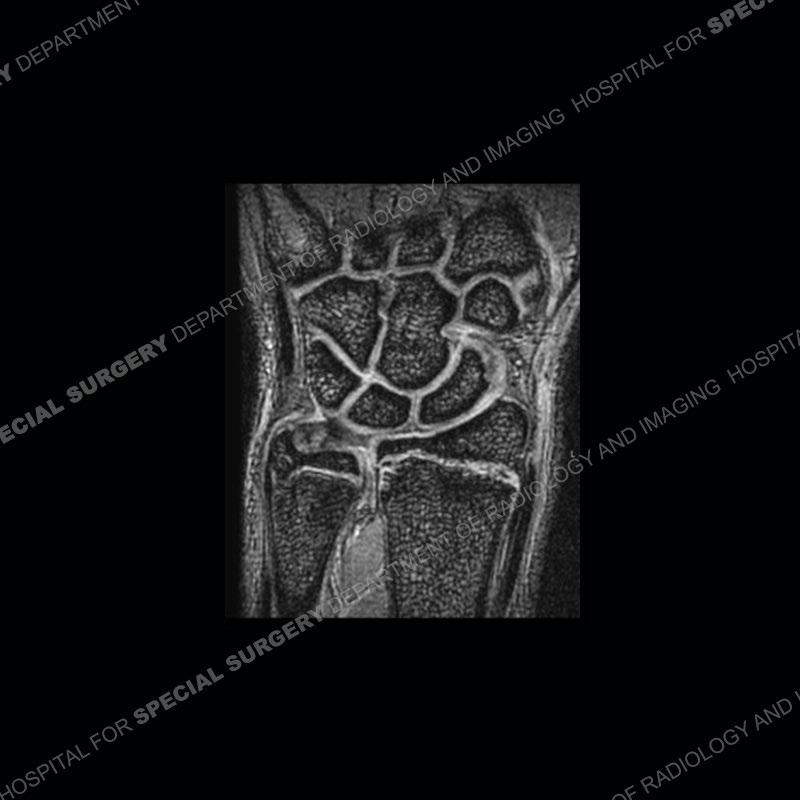
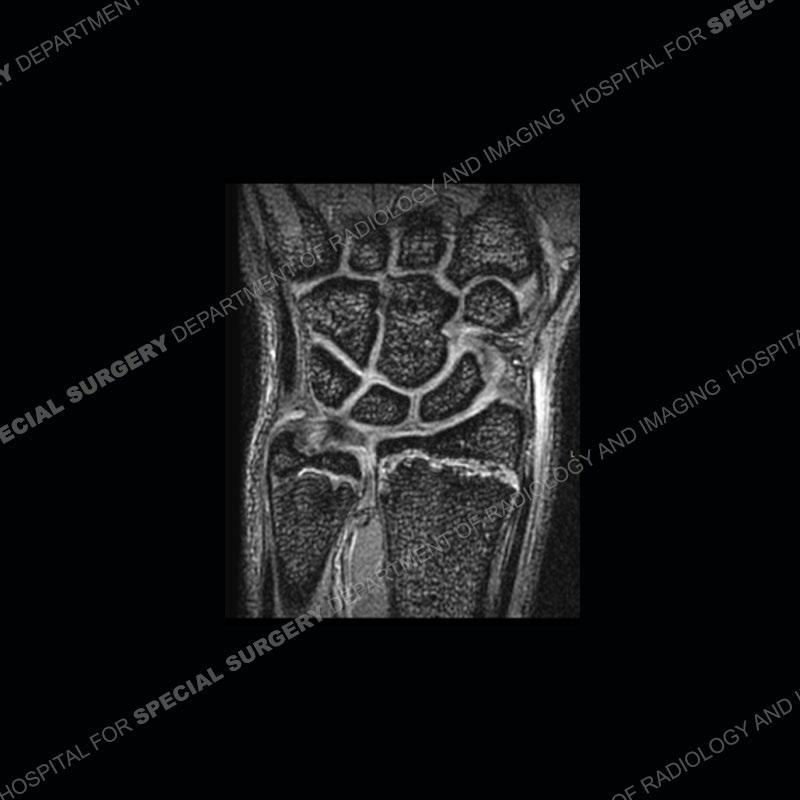
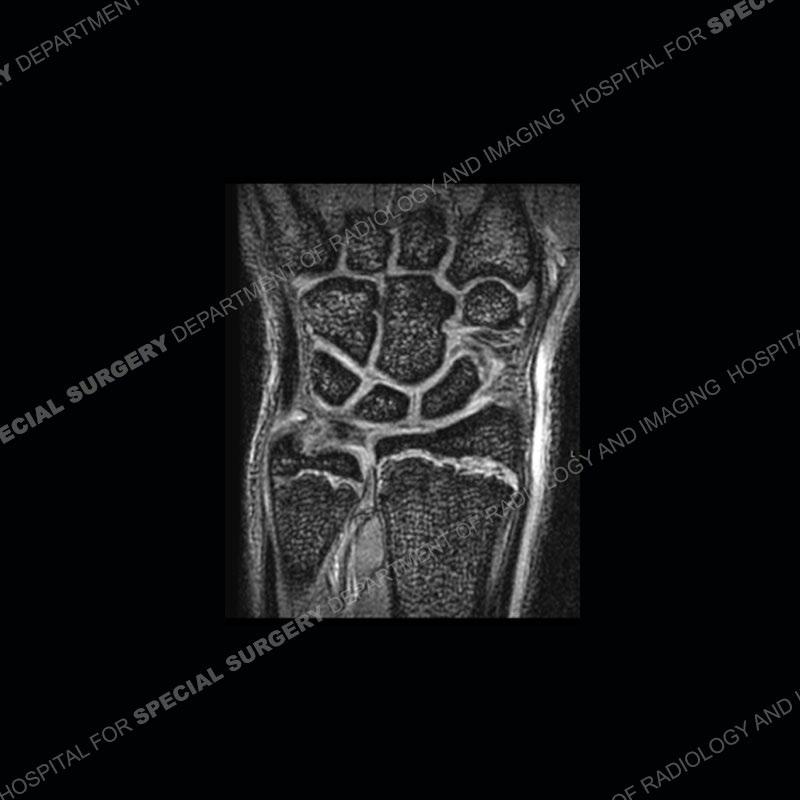
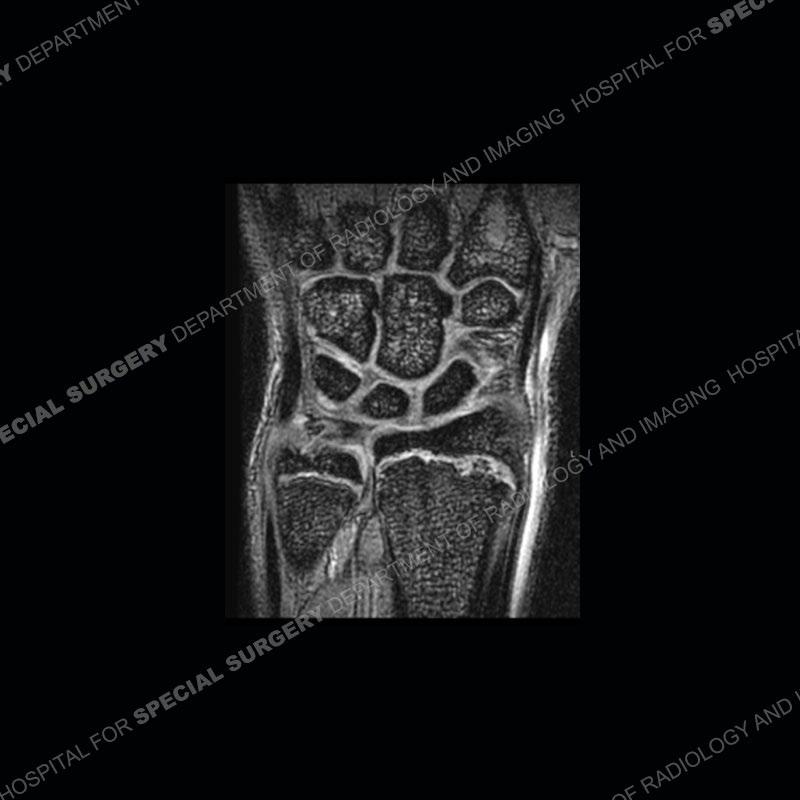
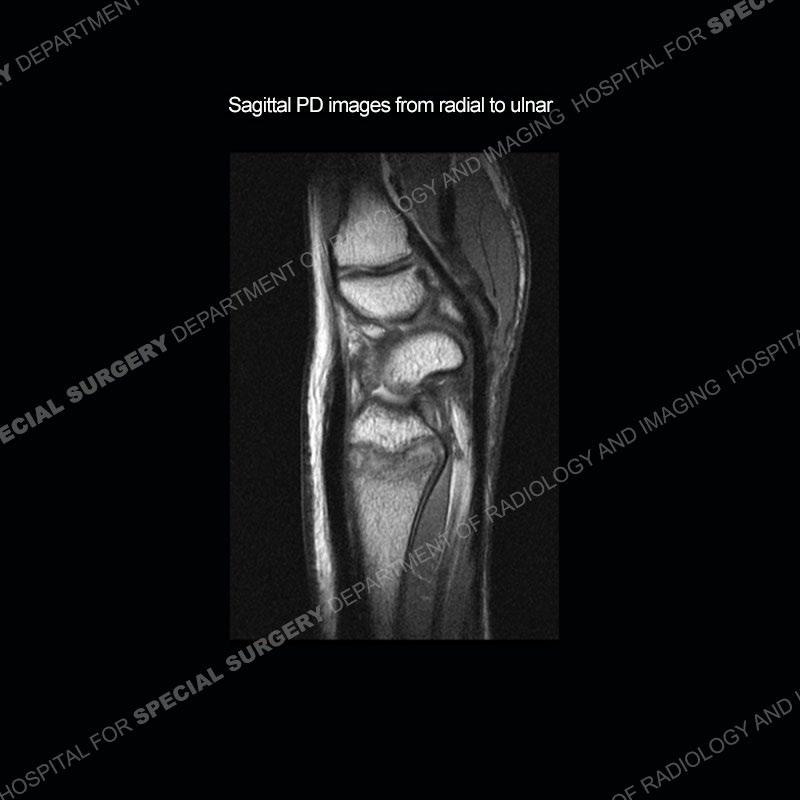
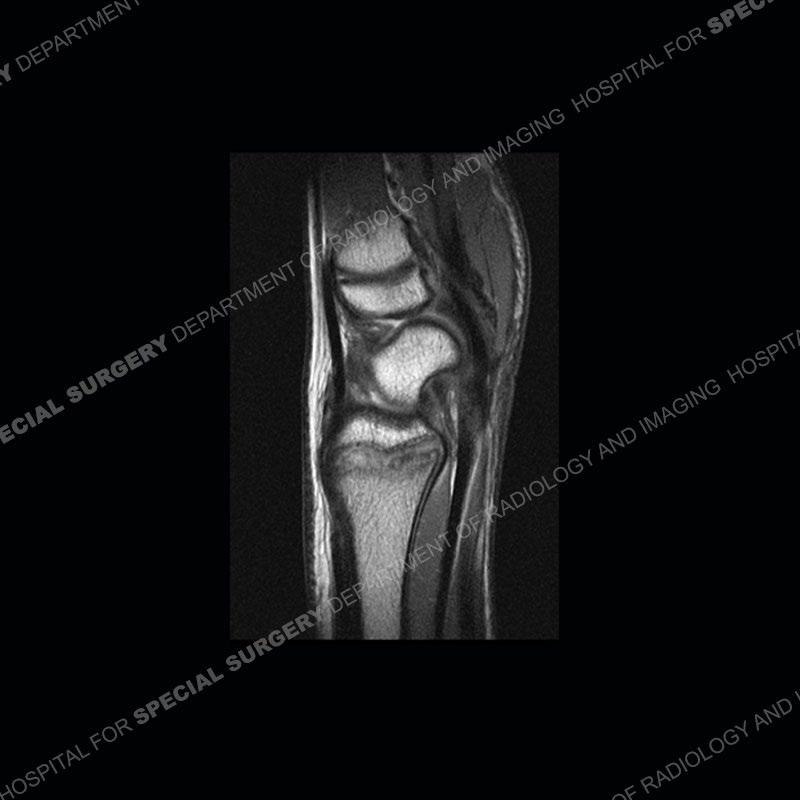

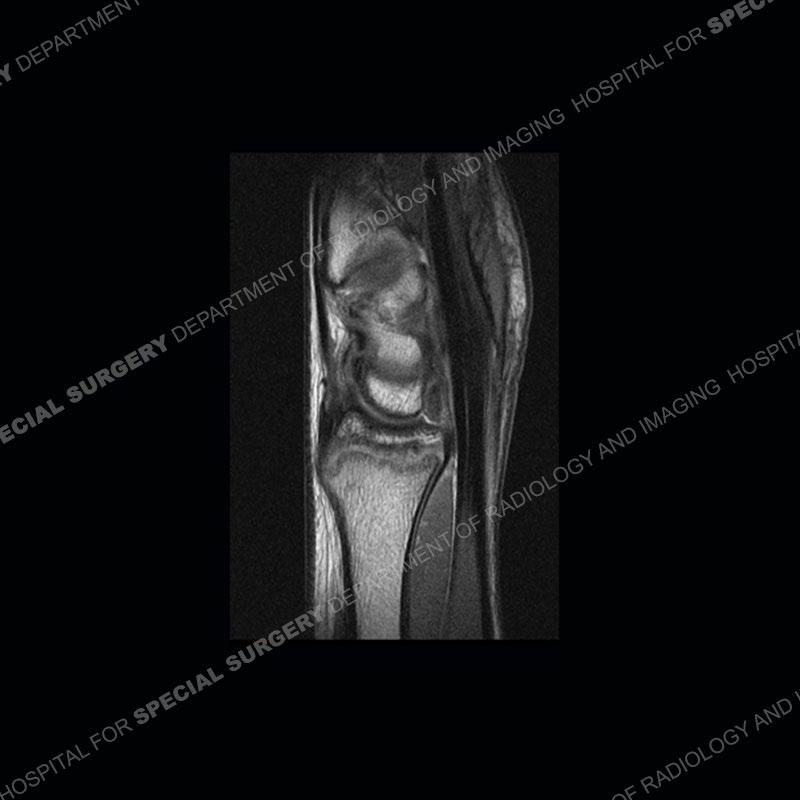



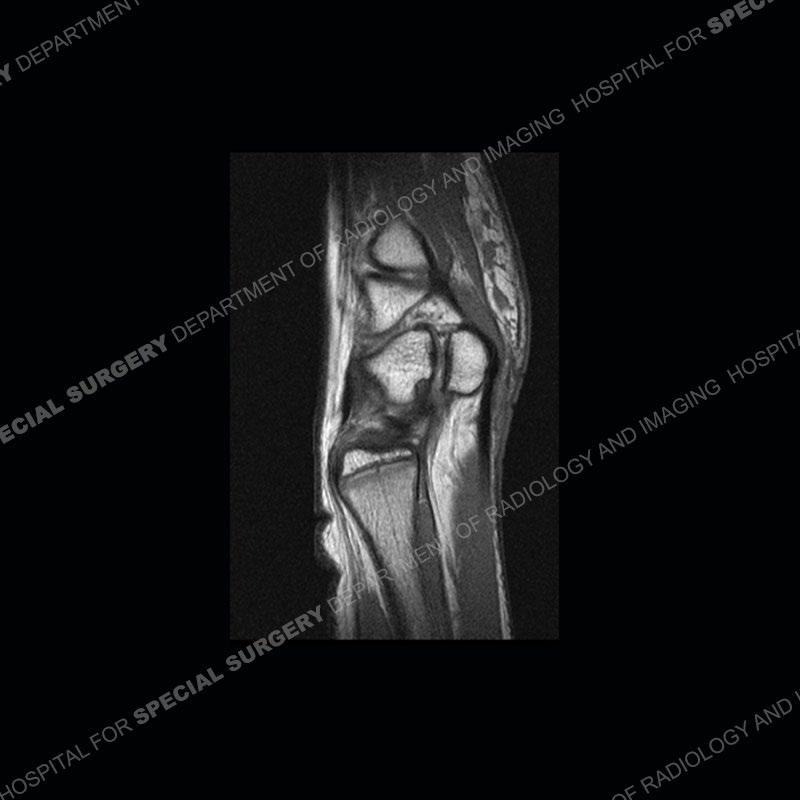
Findings
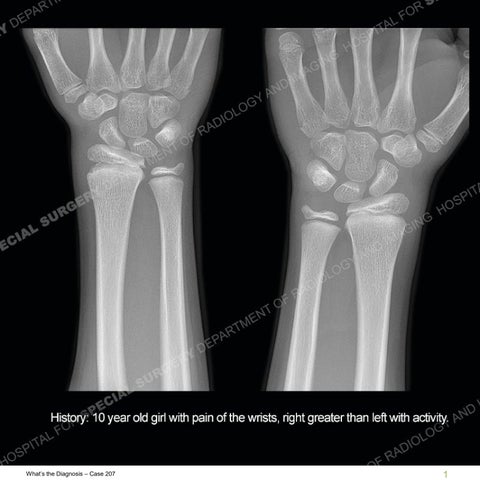
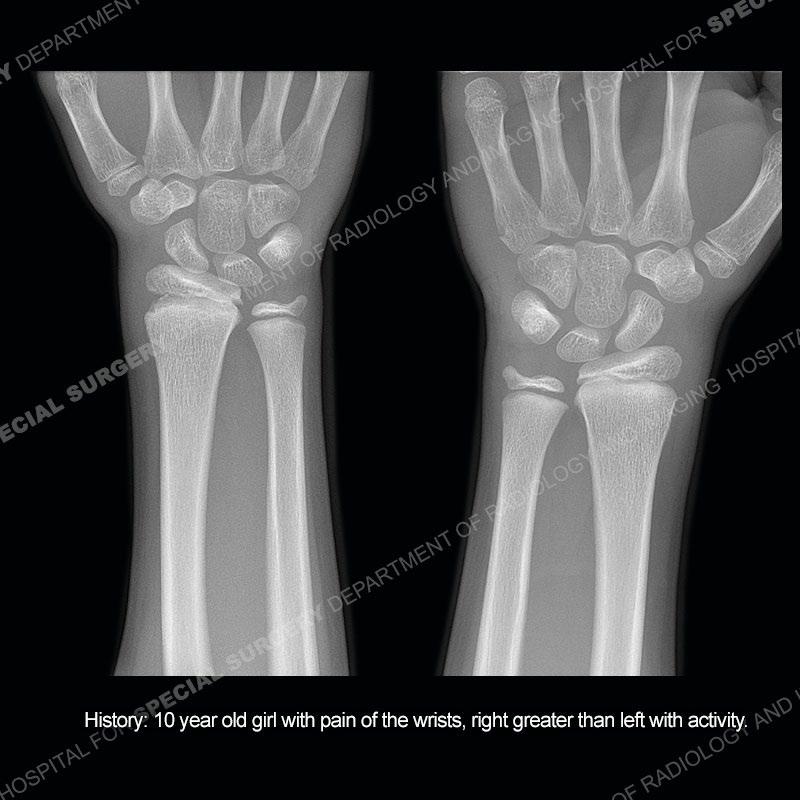
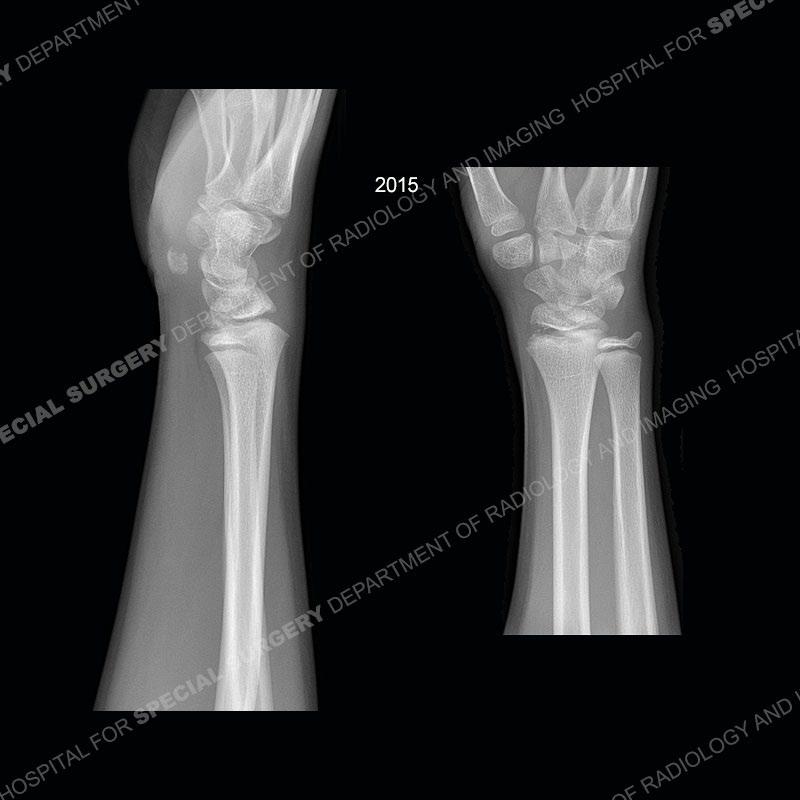
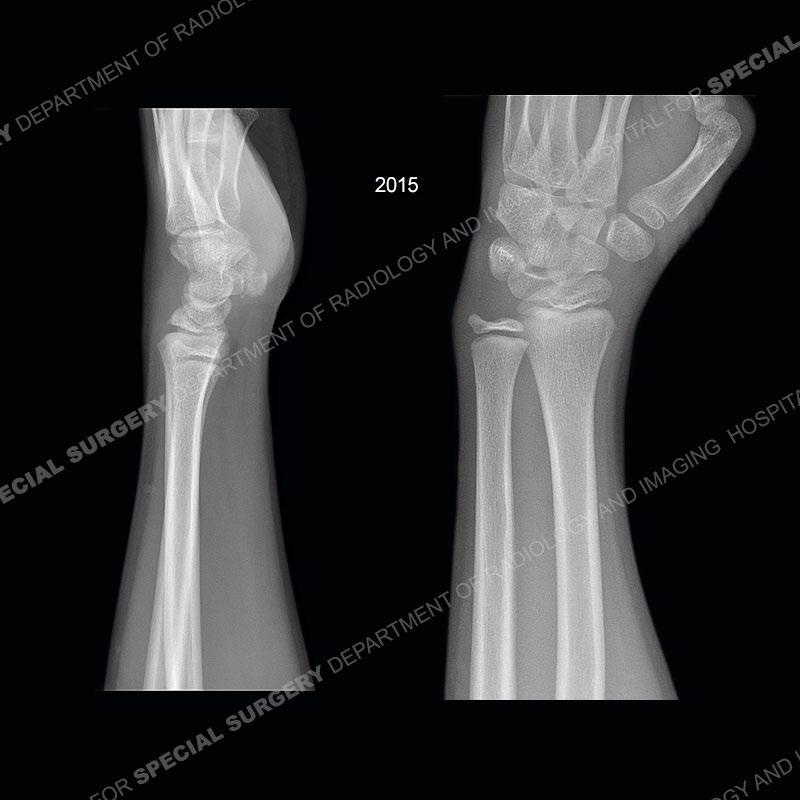
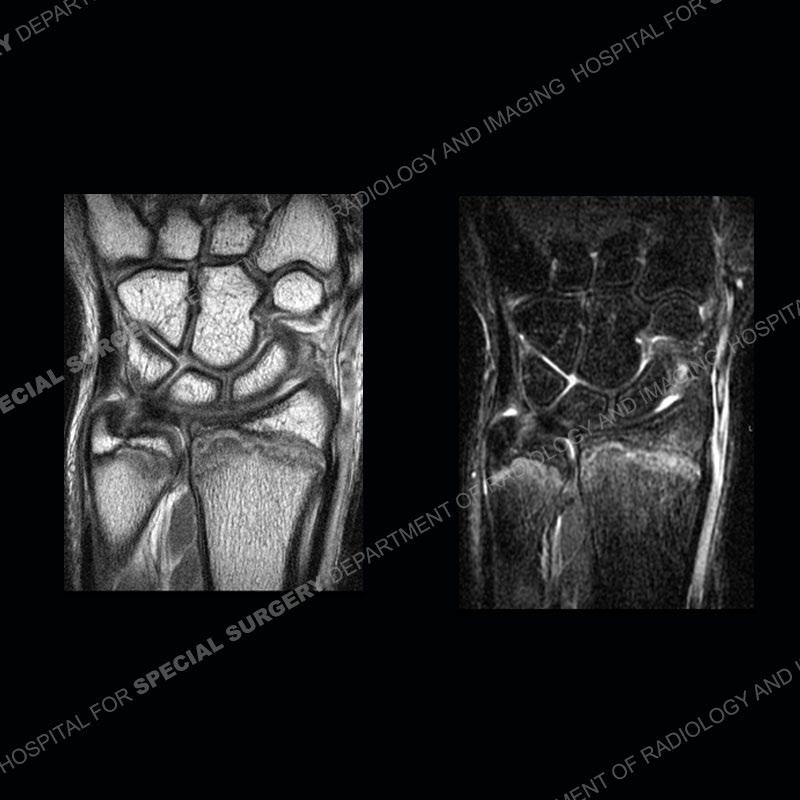
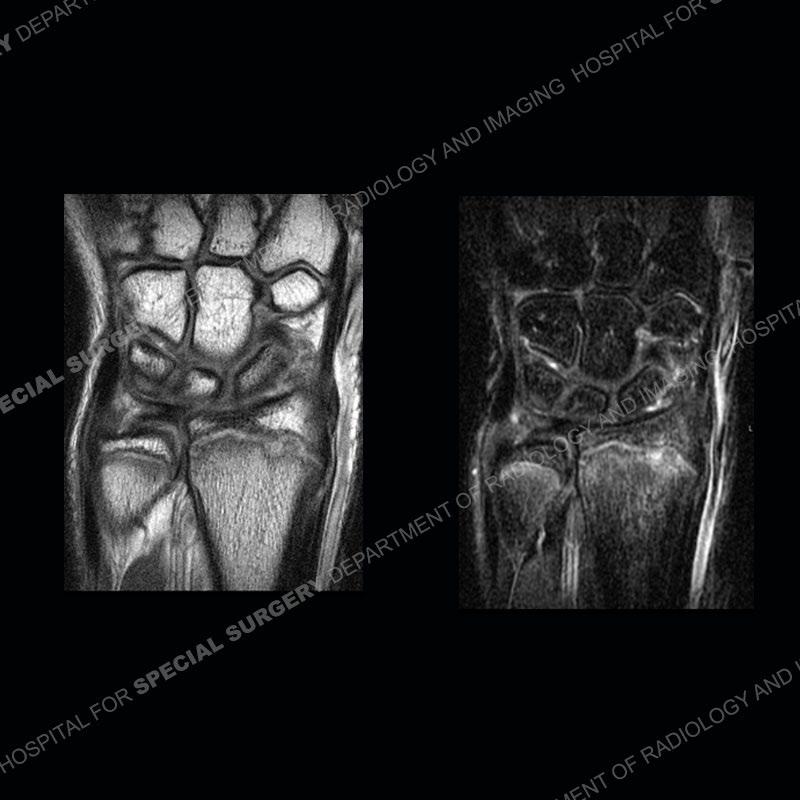
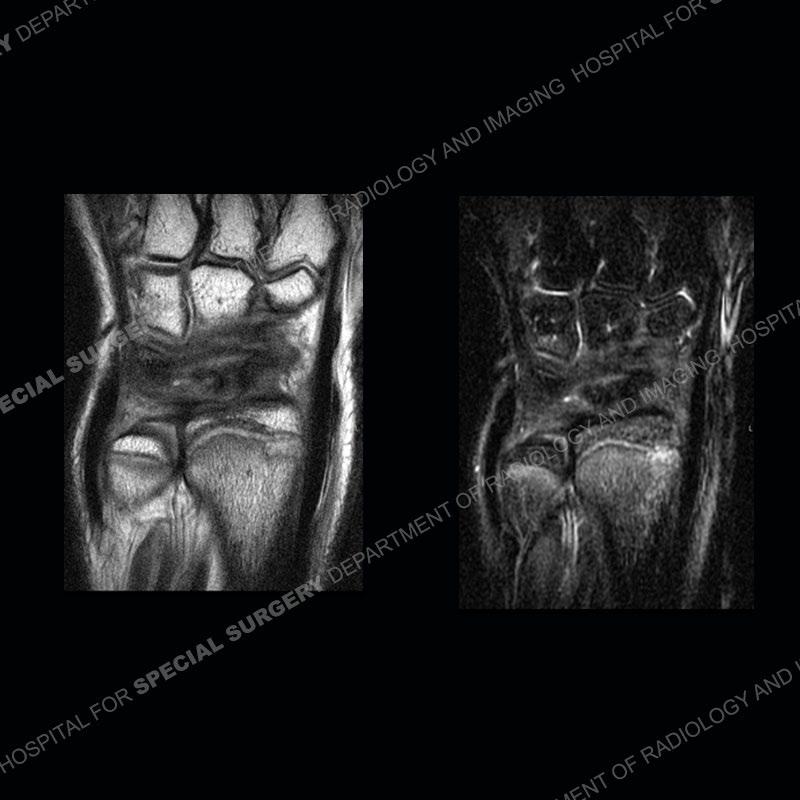
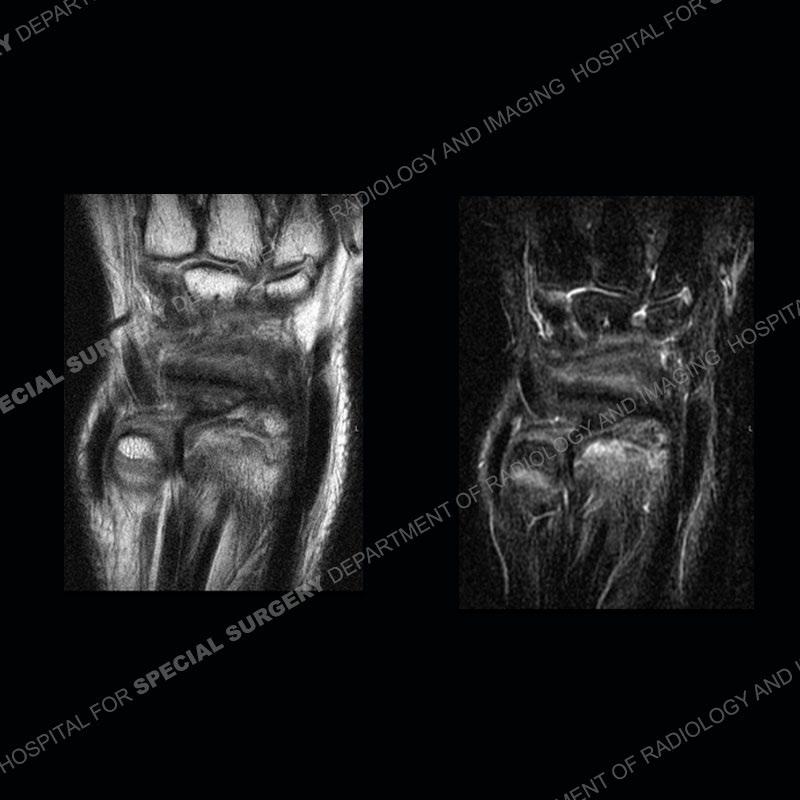
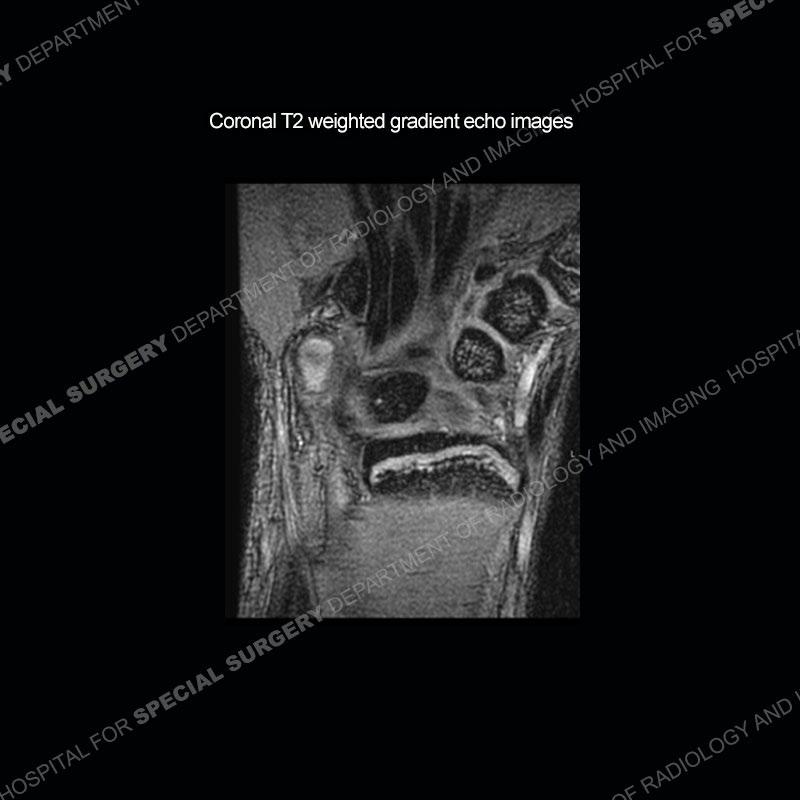
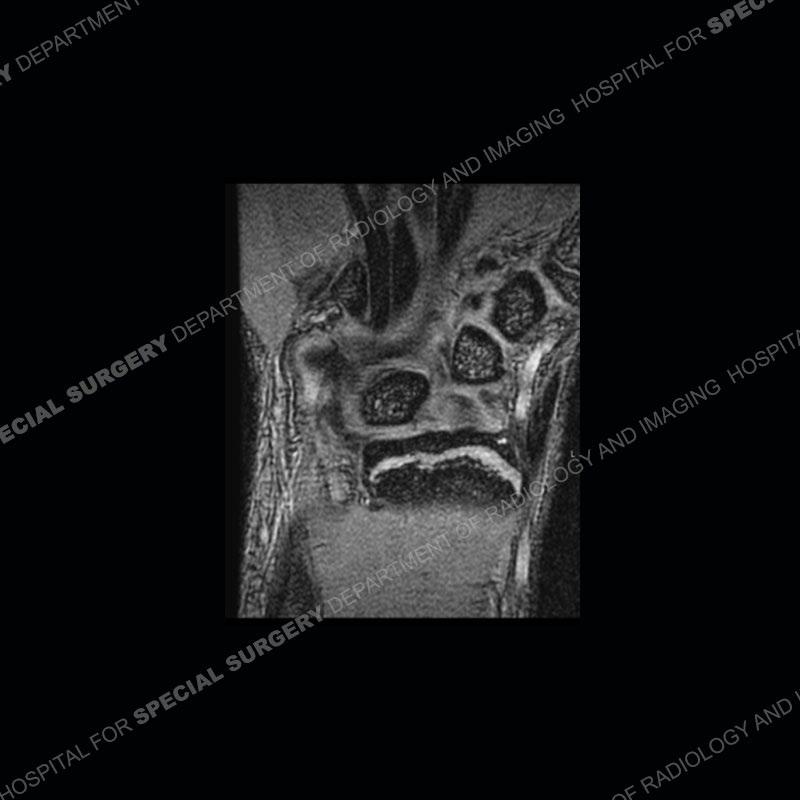
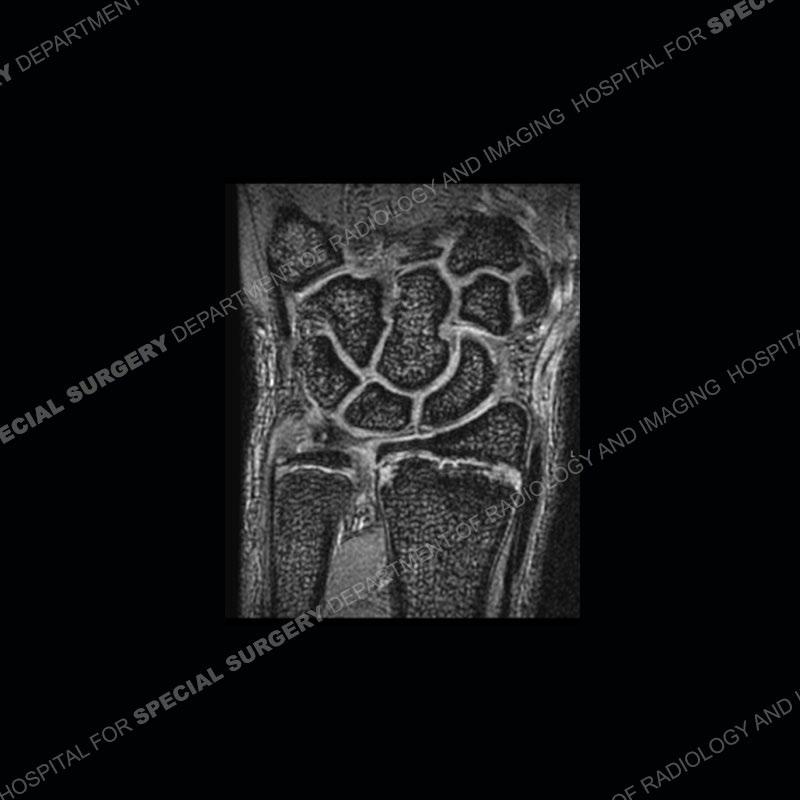
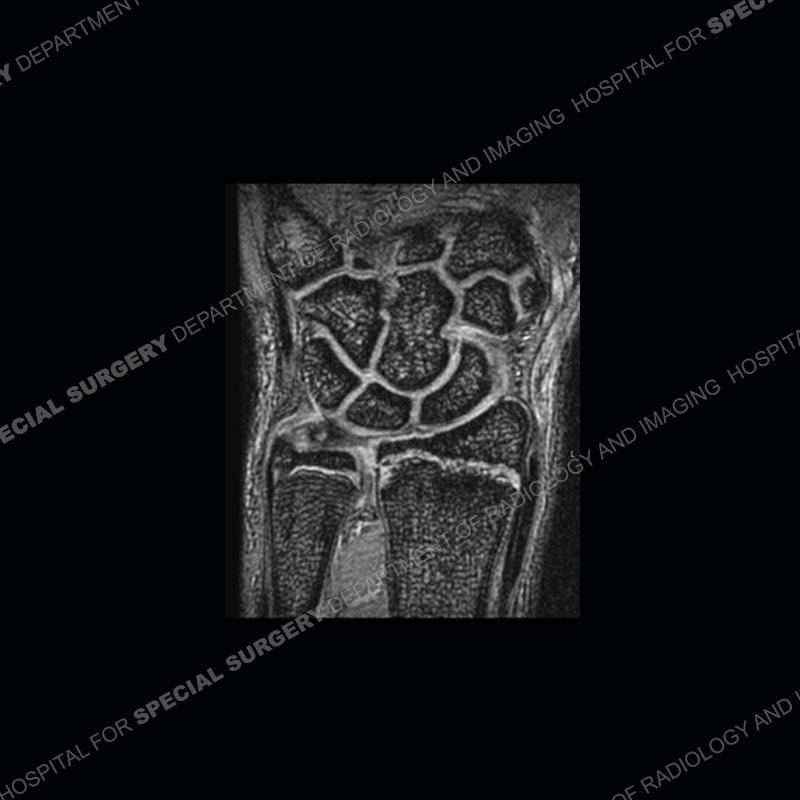
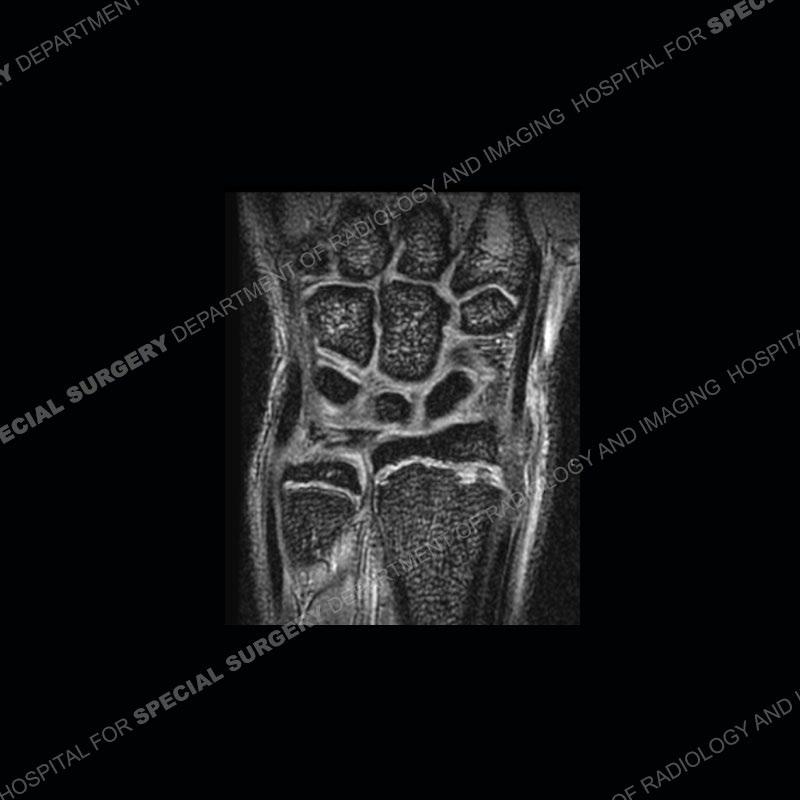
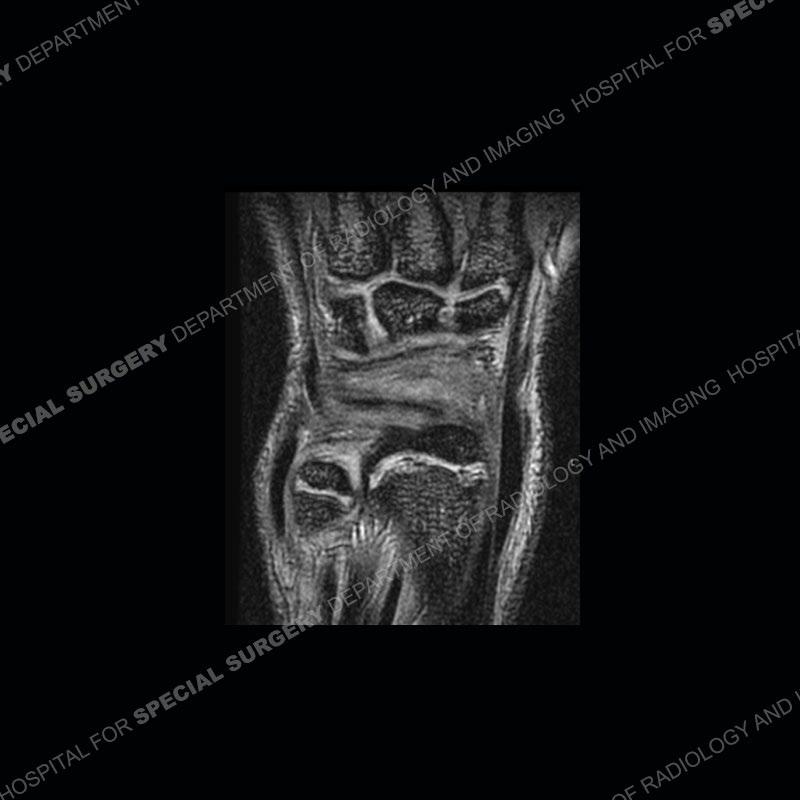
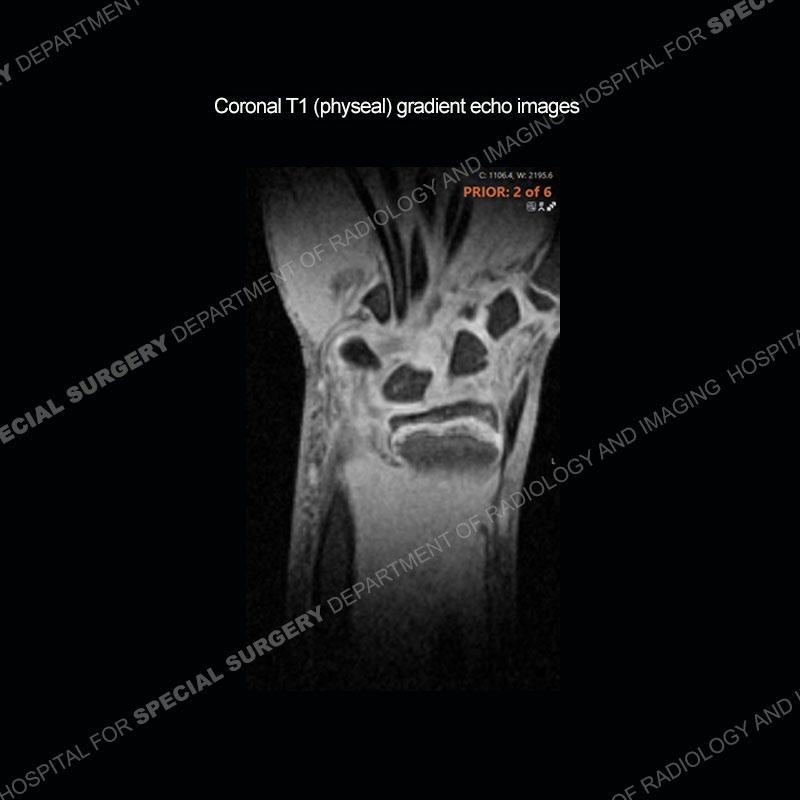
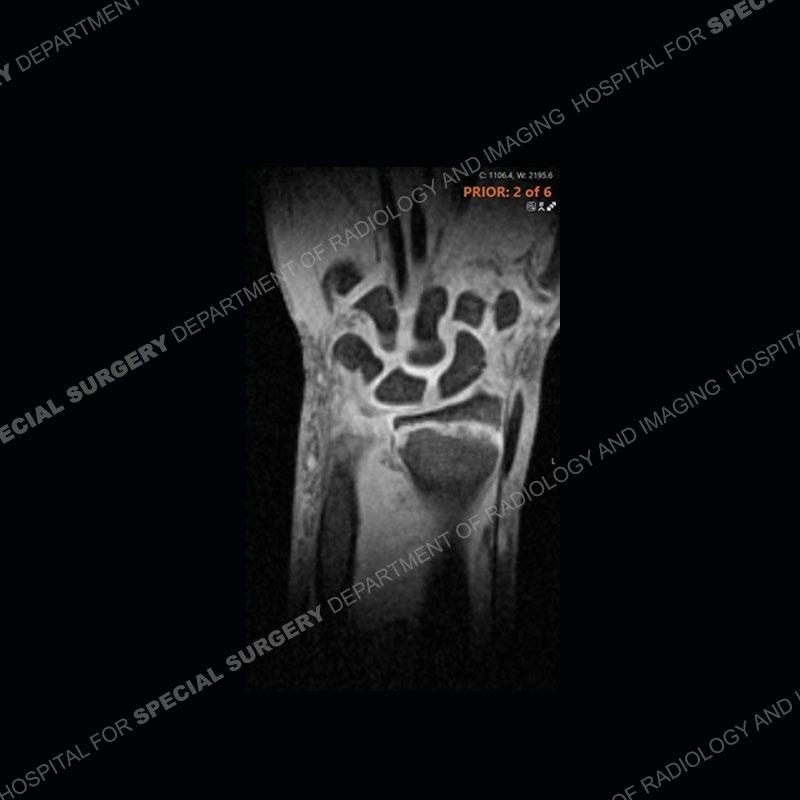
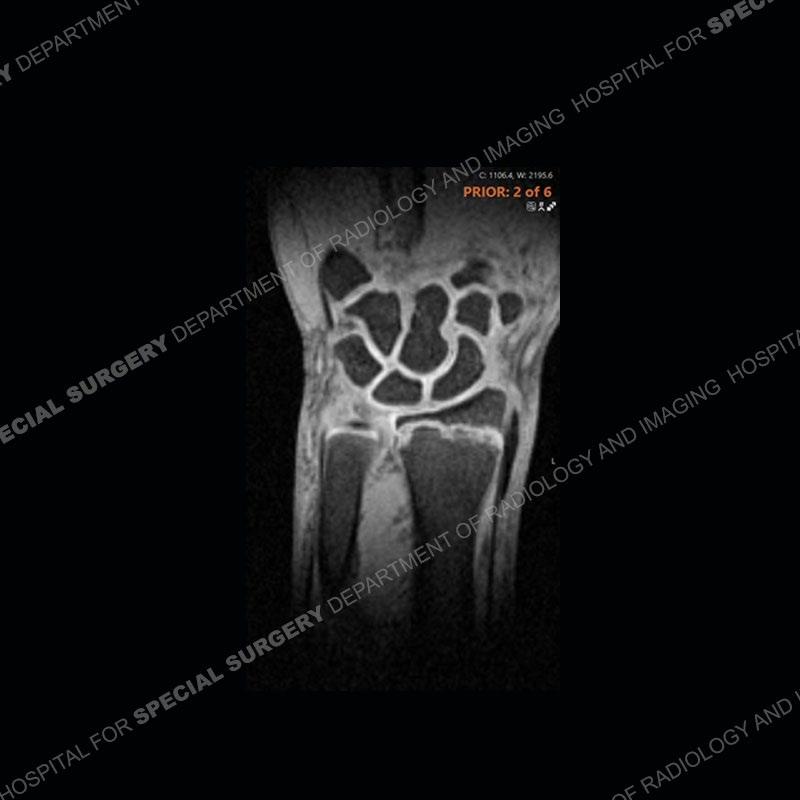
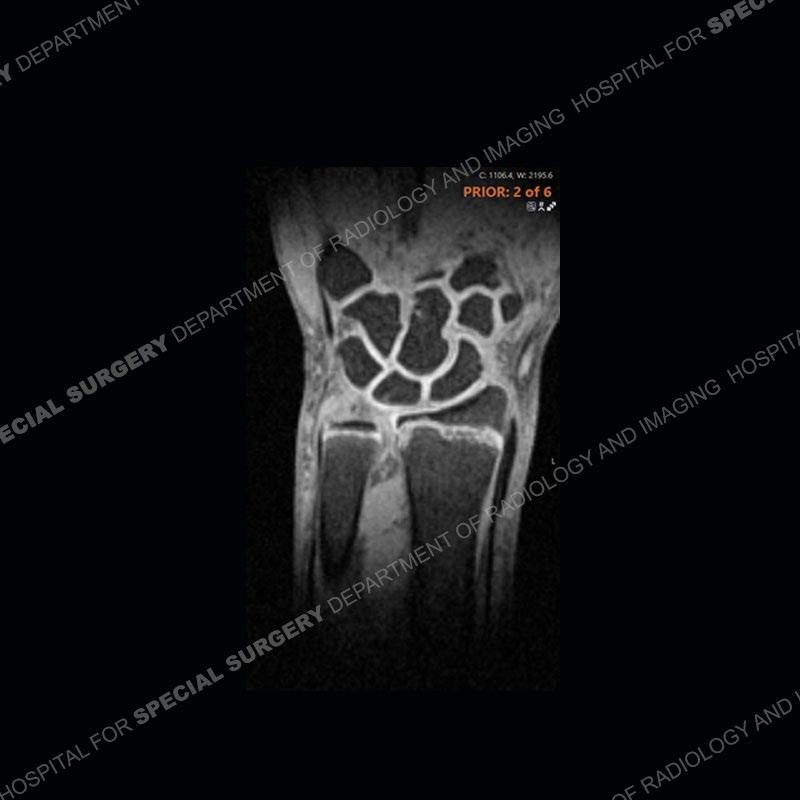
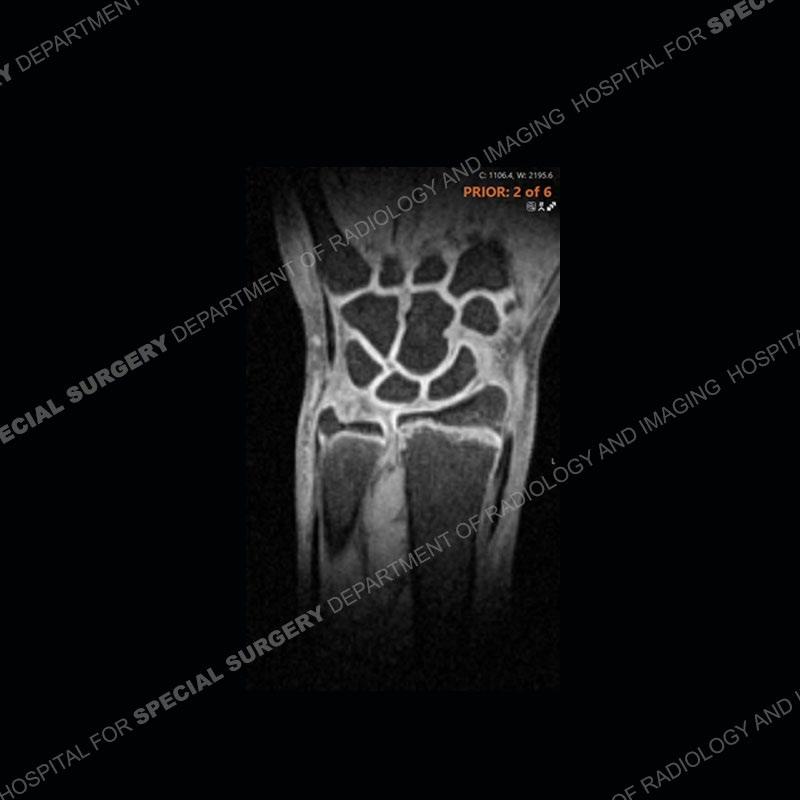
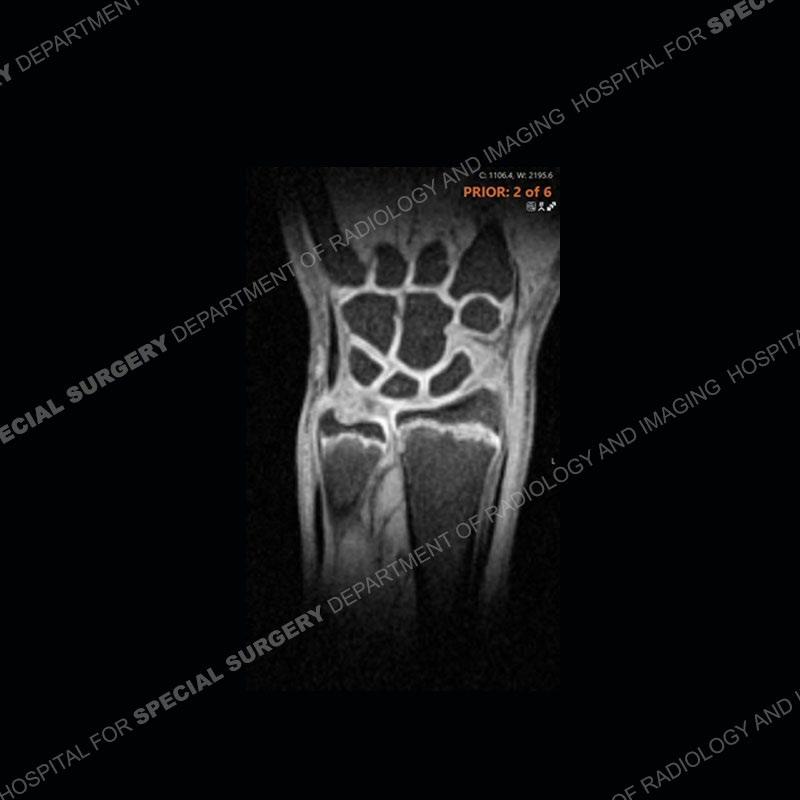
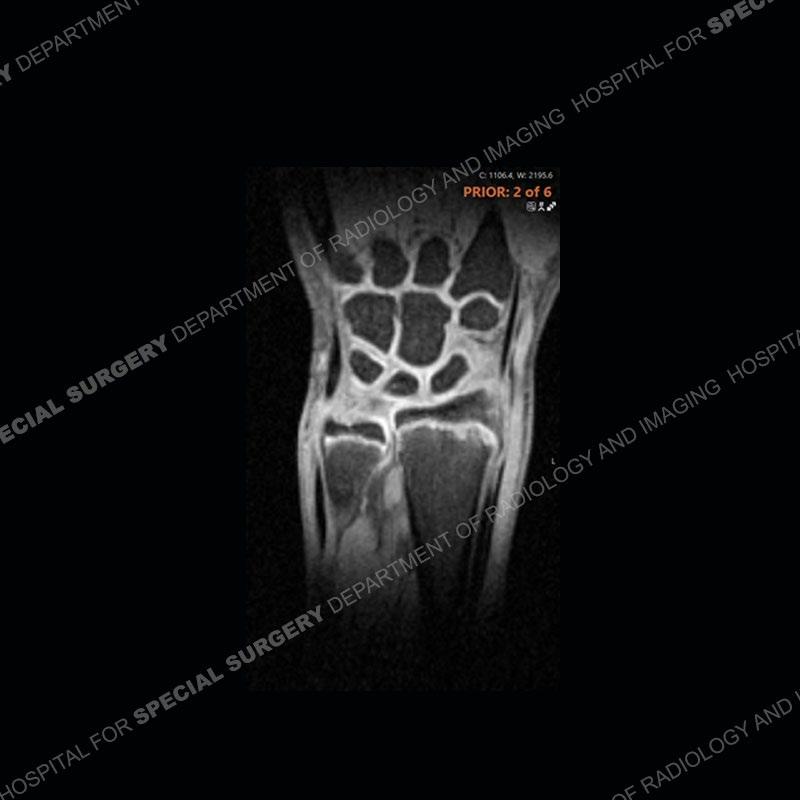
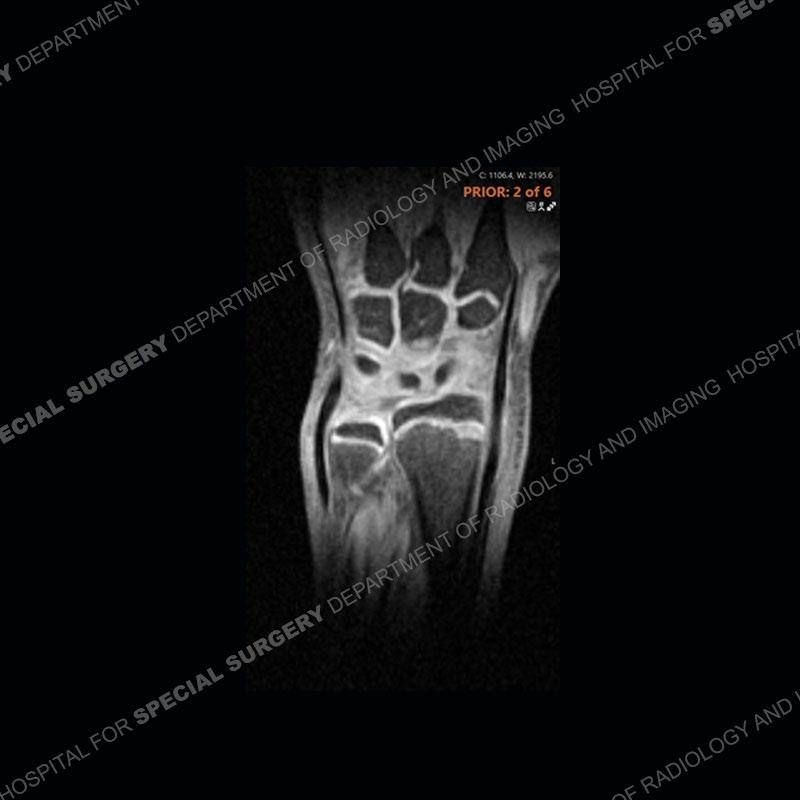
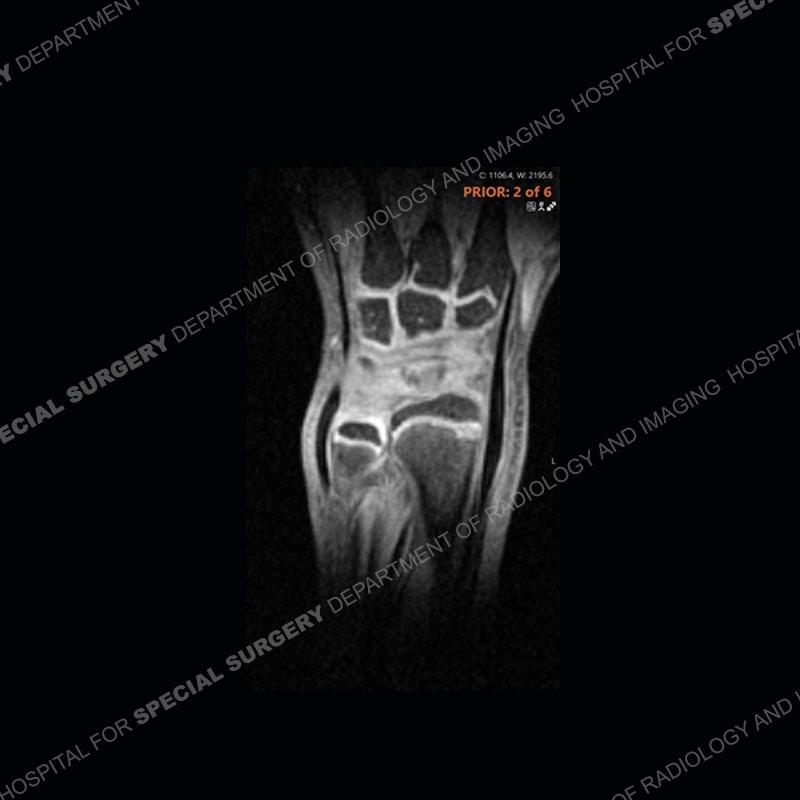
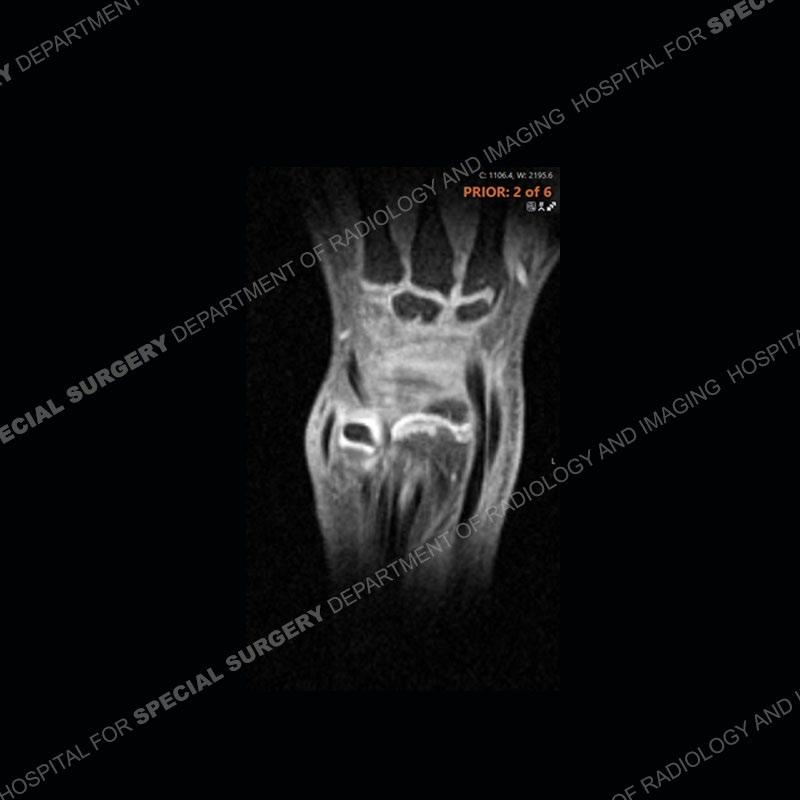
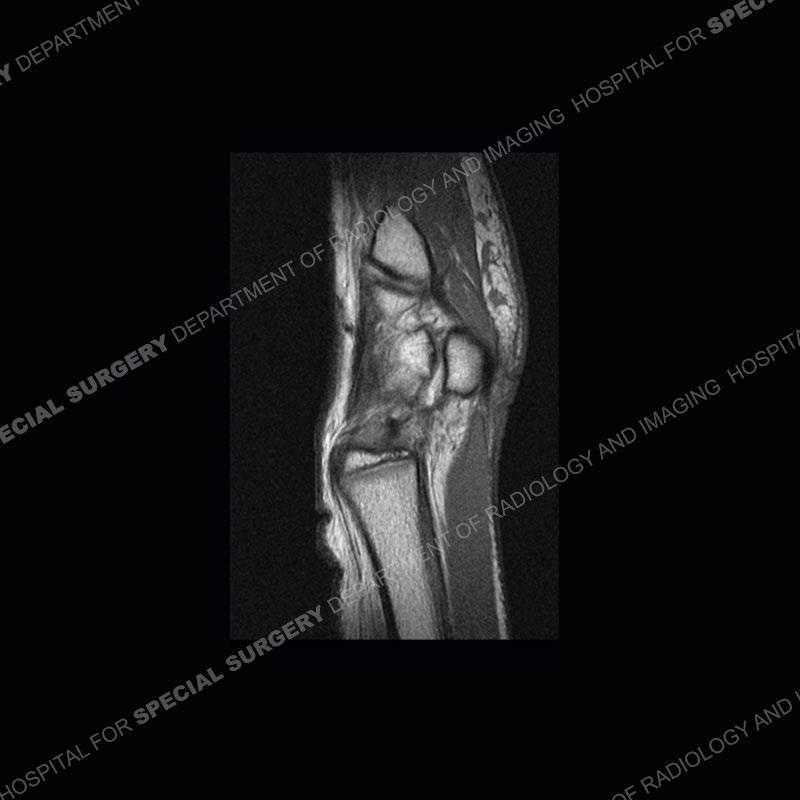
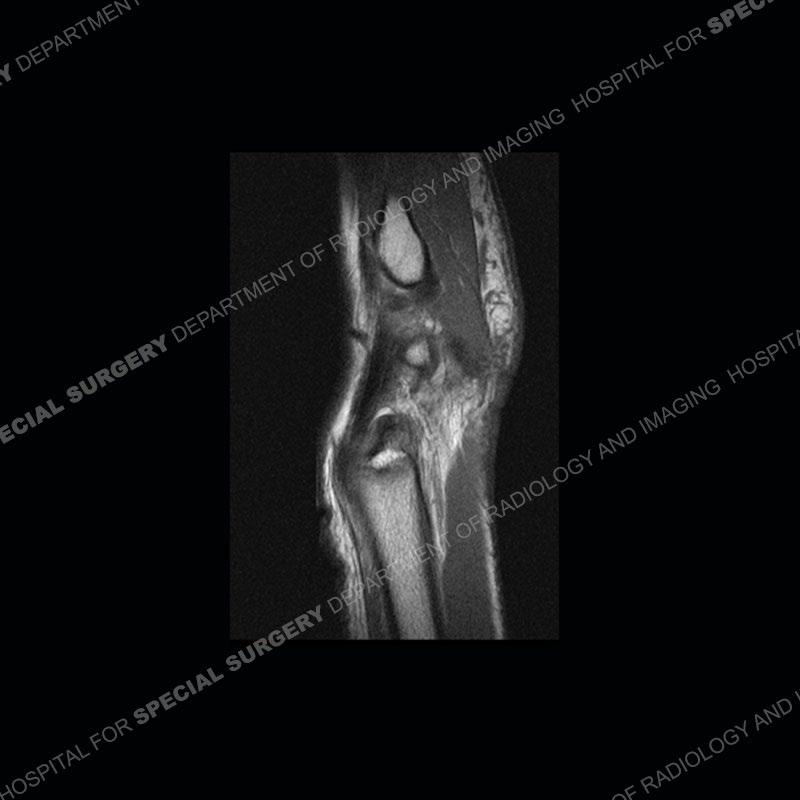
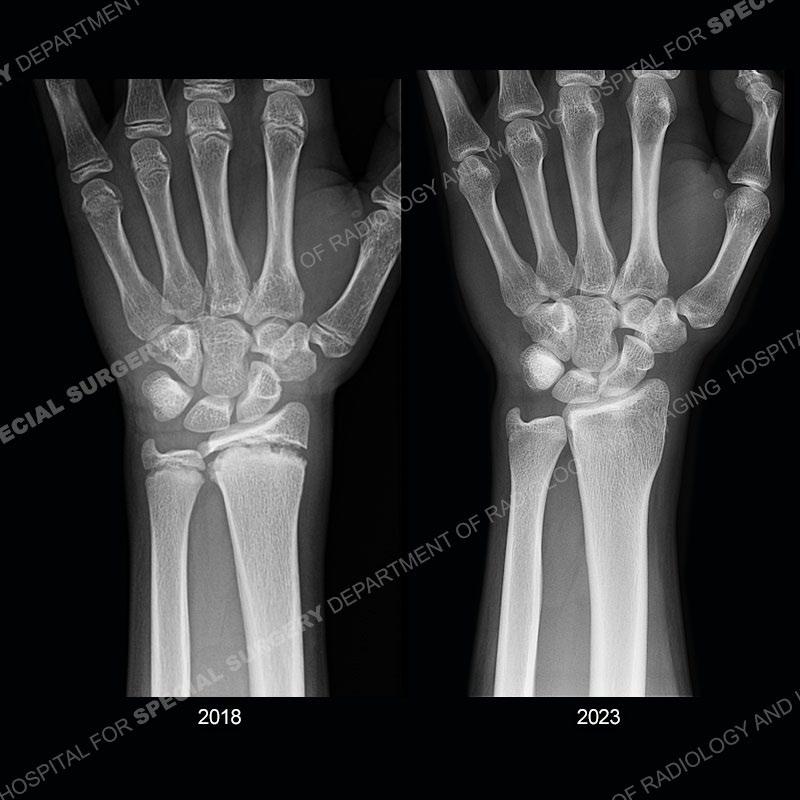
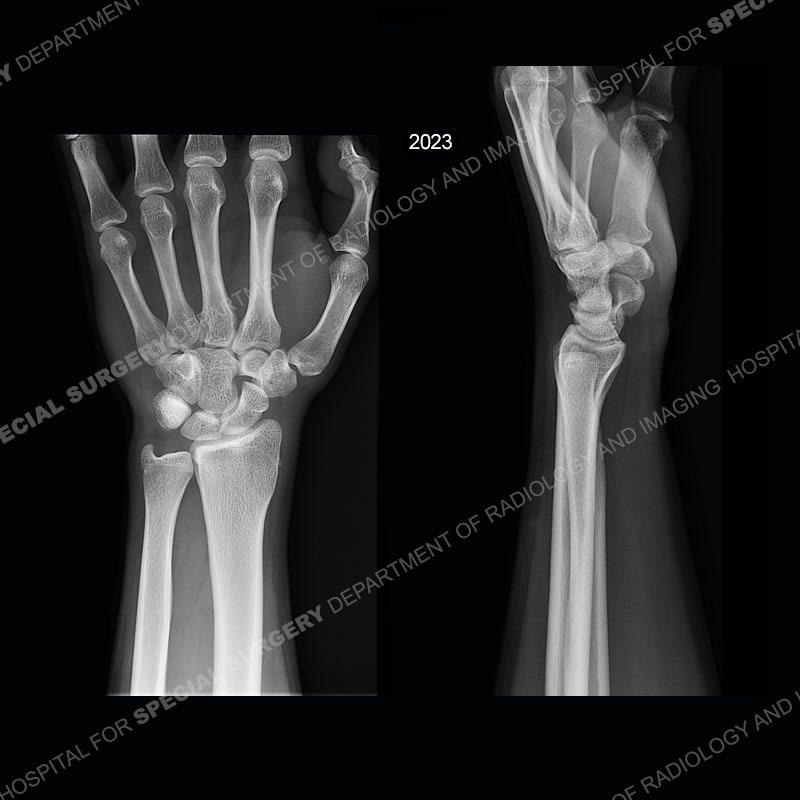
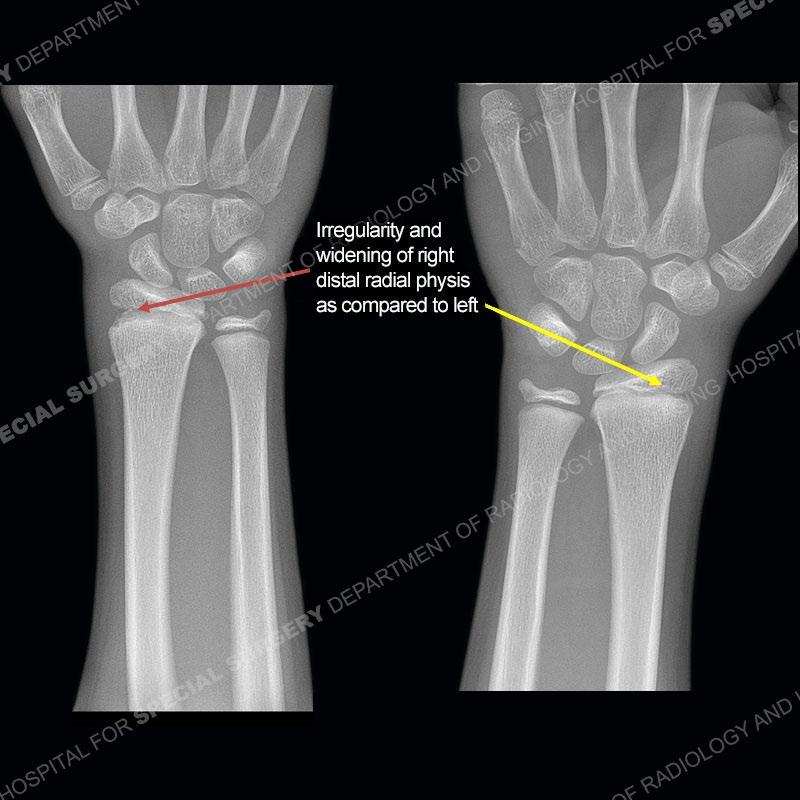
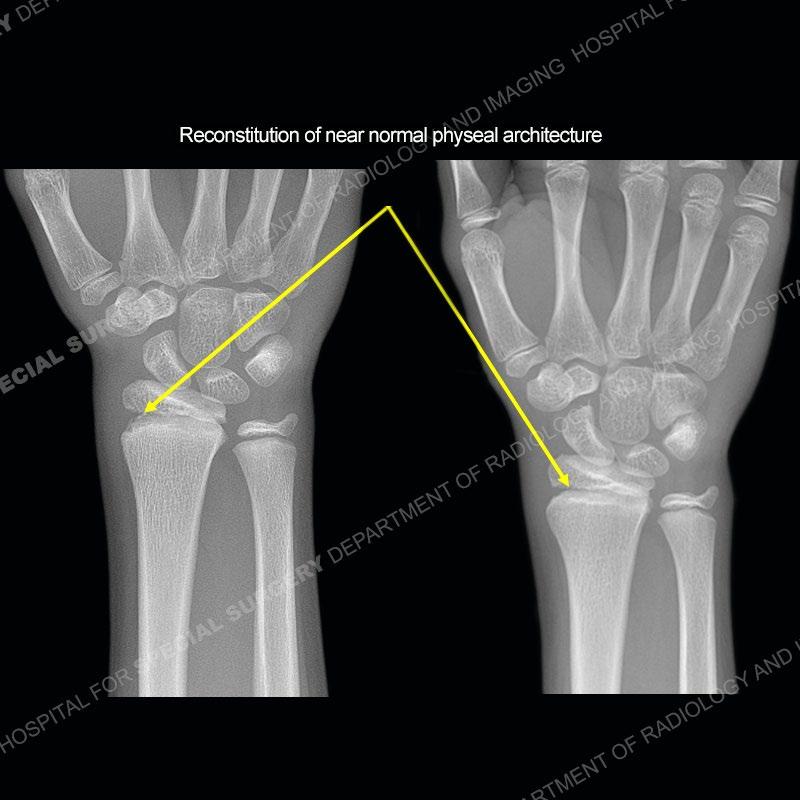
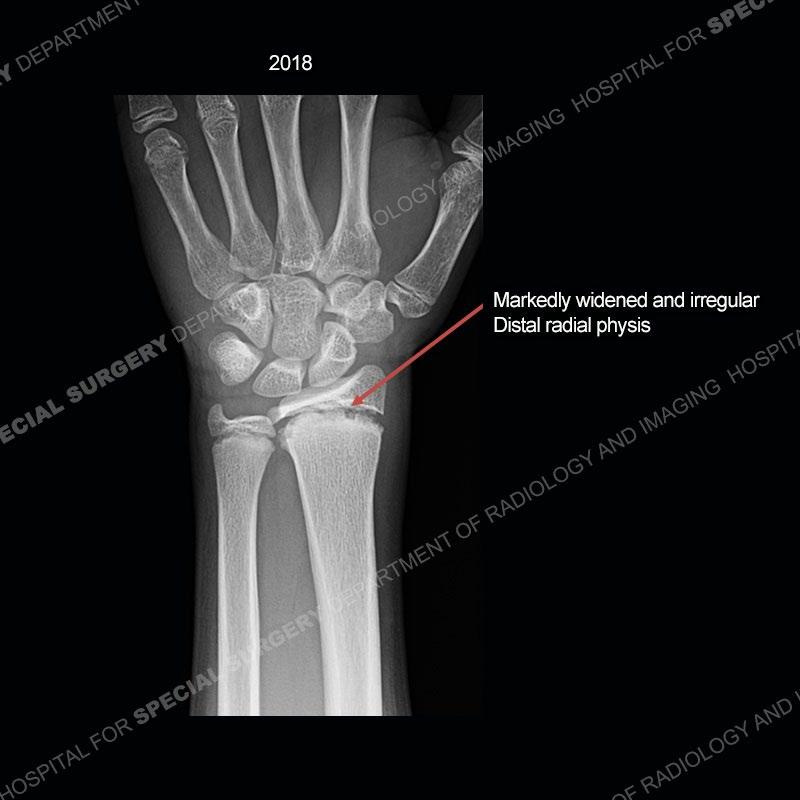
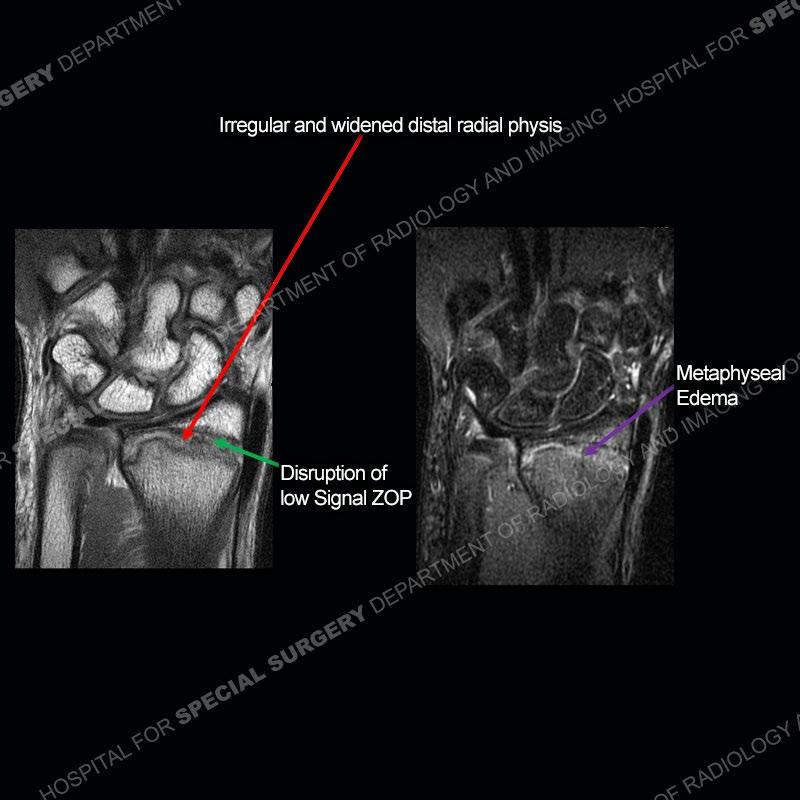
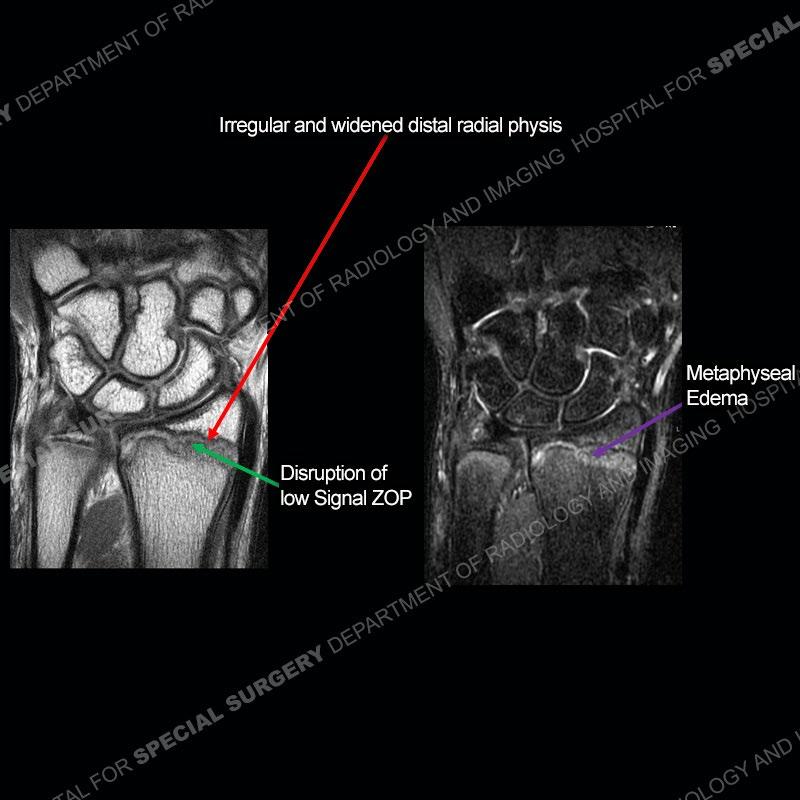
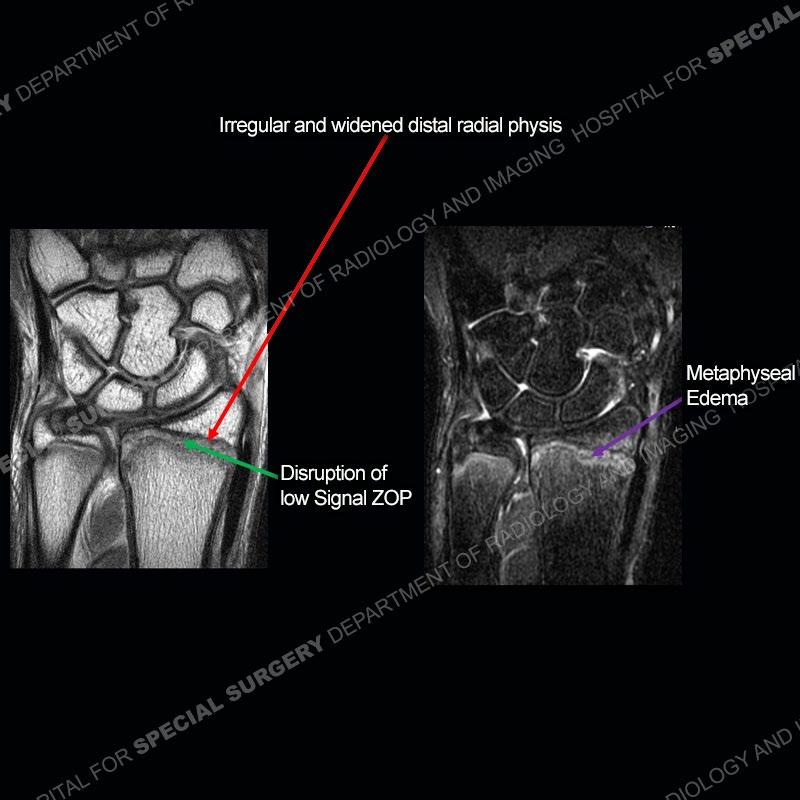
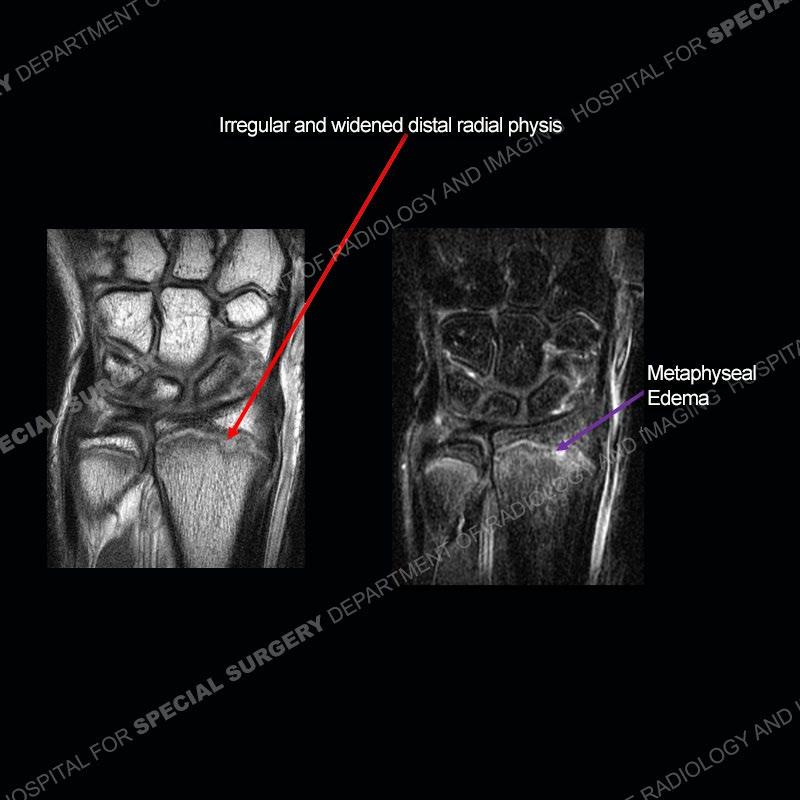
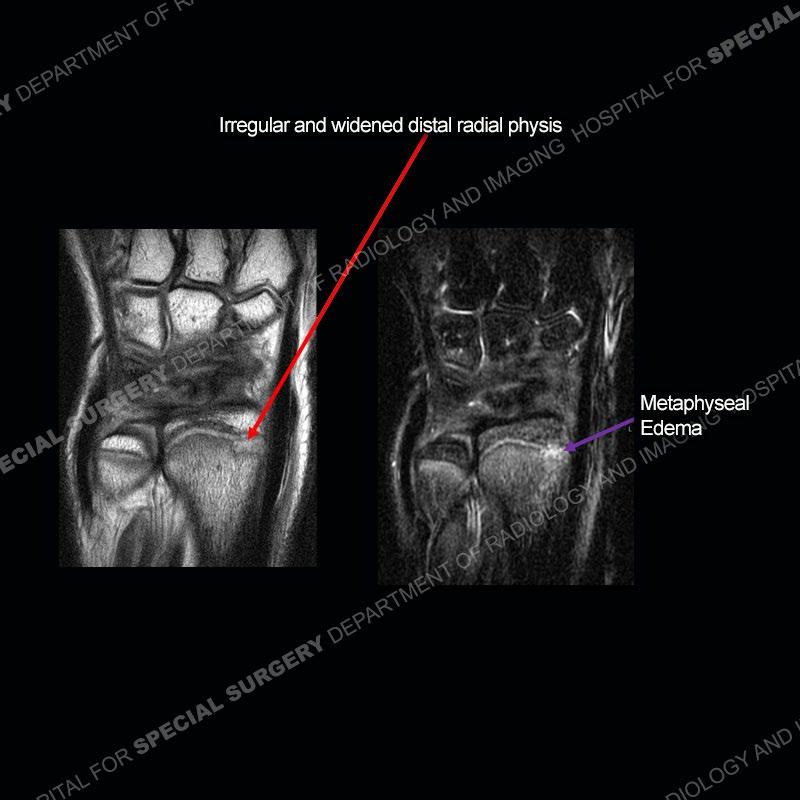
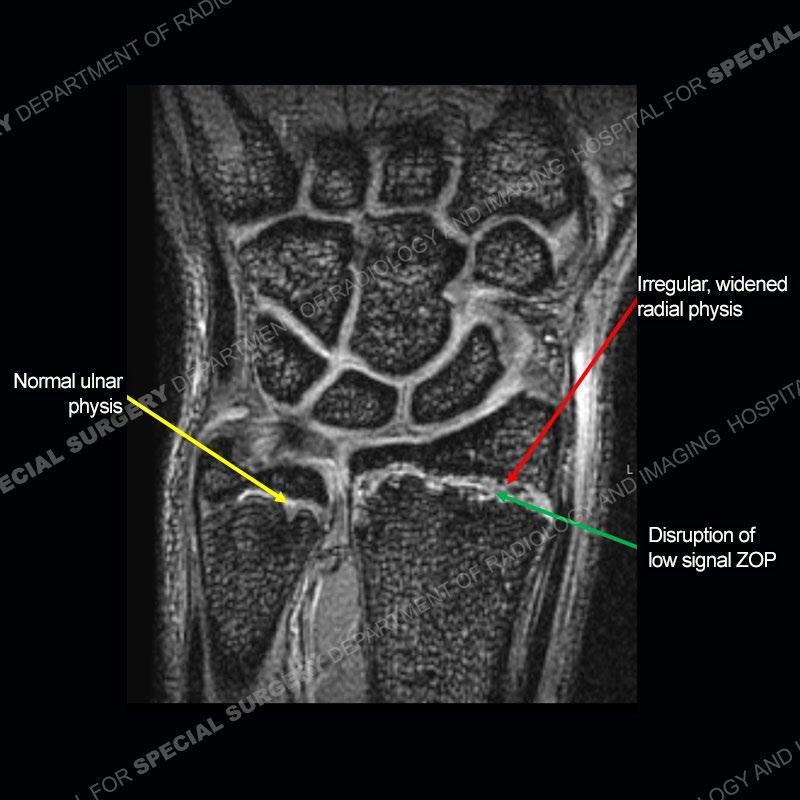
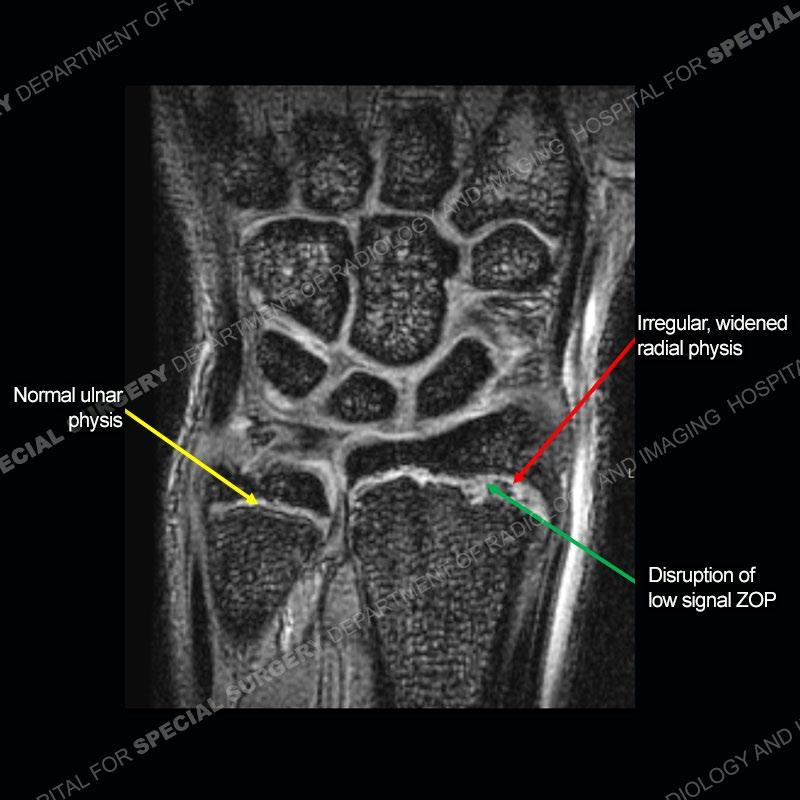
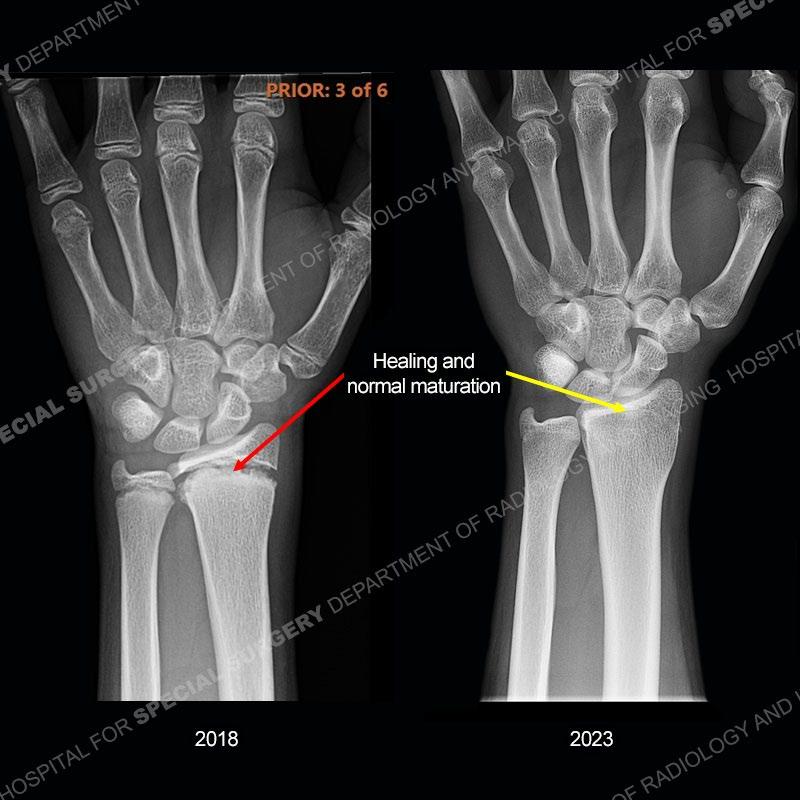
Initial radiographs demonstrate a marked widening and irregular architecture of the distal right radial physis. On the imaging 5 months later, the architecture has reconstituted to nearly normal . Three years later, there is a marked widening and irregular architecture of the distal left radial physis. The MRI demonstrates a marked widening of the distal radial physis, edema pattern of the adjacent metaphysis, and areas of loss of the normal low signal band of the zone of provisional calcification (ZOP). Noted is there is no edema in the adjacent soft tissue and no disruption of the perichondrium or periosteum.



Diagnosis: Gymnast’s Wrist
The activity of the patient was kept vague on purpose. This patient was an avid gymnast from an early age. The stress placed on the wrist from gymnastics can lead to overuse injuries as shown in this case. The distal radial physis responds to the chronic overuse with widening and irregular architecture. The physis that we perceive on MRI typically has a trilaminar appearance with a high signal physeal cartilage, low signal ZOP, and then high signal primary spongiosa. With overuse, there are areas of disruption of the ZOP as shown in this case. An acute traumatic injury would have a different history and although the physis may be widened it is not as irregular. Also, in trauma the ZOP may be disrupted but is found to be disrupted slightly more frequently in overuse injuries. Also, in acute traumatic injuries, the low signal periosteum/perichondrium at the periphery will show an area or areas of disruption.
In this case, when the patient presented with pain rest/immobilization was prescribed and the physis was able to remodel. Typically, conservative measures are all that is needed. However, if rest/immobilization are not adhered to or the injury is allowed to progress too far, then premature closure of the radial physis may occur precipitating removal of bony bars. If even greater physeal closure occurs than ulnar epiphysiodesis and shortening osteotomy may be necessitated. Thankfully in this case the patient adhered to the prescribed rest/immobilization when indicated and was able to achieve normal skeletal maturation.

References
Bedoya MA, Jaramillo D, Iwasaka-Neder J, Laor T. Stressed or fractured: MRI differentiating indicators of physeal injury. Skeletal Radiol. 2024 Nov;53(11):2437-2447. doi: 10.1007/s00256-024-04670-y. Epub 2024 Apr 1. Erratum in: Skeletal Radiol. 2025 Mar;54(3):643. doi: 10.1007/s00256-02404847-5. PMID: 38557698.
Ana Carolina de Lima Augusto, Paola Cecy Kuenzer Goes, Dyan V. Flores, Maria Alice F. Costa, Marcelo Straus Takahashi, André C. O.
Rodrigues, Luiz C. Padula, Taisa Davaus Gasparetto, Marcello H. NogueiraBarbosa, and André Yui Aihara. Imaging Review of Normal and Abnormal Skeletal Maturation RadioGraphics 2022 42:3, 861-879