Intelligence in Healthcare: Exploring AI in Mobile Health Applications
Student: Silvia Mancini | Faculty Advisor: Dr.
Frank G. Zarb School of Business, Hofstra University, Hempstead, NY 11549

Abstract & Introduction
The purpose of this study is to examine and explore how artificial intelligence (AI) is used in healthcare, specifically in mobile health (mHealth) applications that support clinical and consumer health functions.
• This study defines AI-embedded mHealth apps as those incorporating AI techniques such as natural language processing (NLP), convolutional neural networks (CNNs), decision trees, generative AI, and others – all used to support health-related tasks across diverse health domains.
• It analyzes 17 peer-reviewed academic journals in which empirical studies were conducted and published between 2020 and 2025 and features 16 unique AI-driven apps.
• The papers selected exemplify a comprehensive sample of how AI is becoming more prevalent in healthcare, namely, through chatbots providing mental health support and image-based diagnostic tools.
• This research seeks to determine commonalities, distinguish differences, and provide meaning to how AI contributes to personalized, patient-centered care –particularly in outpatient, preventative, or self-managed settings where traditional healthcare services may be limited or become unnecessary.
• It highlights the patterns in AI integration and offers insights into how these technologies are shaping the future of healthcare.
• Focuses on apps using AI to enhance diagnosis, patient education, and conversation modalities.
• Underscores AI’s potential in improving patient access, particularly in regions where resources are limited.
• Reveals the progress in the mHealth sphere, broader trends in continued AI integration, and future growth areas.

Methods
Literature Review:
• Literature search and review conducted between January - March of 2025.
• Via the ScienceDirect research database using keywords:
• “AI Mobile Apps” yielded 38 papers
• “mHealth Apps AI” yielded ten (10) papers
• Initial results were screened for relevance to AI’s use in mHealth apps.
Screening & Inclusion Criteria:
• Papers required to be from peer-reviewed journals.
• Apps must use AI as a core embedded feature (not a backend tool or add-on).
• Apps had to be mobile-accessible and support user-directed interaction.
• Apps needed to contribute to patient-centered care (i.e., diagnosis, education, or conversation).
Final Sample:
• Of the 48 downloaded articles, 17 were included in the final sample.
• Excluded papers used only traditional statistics or lacked exact healthcare relevance.

• Articles were tracked using a structured Excel spreadsheet with fields for title, medical condition, AI method/how it is used, and summary notes.
Analysis:
• Apps were categorized and analyzed by core functionality, AI methodology, and user engagement strategy.
• Cross-referencing was performed to ensure consistency and accuracy using a generative AI model (LLM).







Discussion
• mHealth apps with AI-embedded algorithms show strong potential to enhance patient-centered care, notably by expanding access in settings where support should be accessible 24/7.
• Privacy and data security remain critical, especially for mental health apps where users may unknowingly share sensitive personal information
• The reliability and accessibility of these apps raise questions about overdependence, particularly for emotionally vulnerable users who may be adversely affected by technical failures or inconsistent performance when seeking timely support.
• Image -based diagnostic apps such as SkinHealthMate and cobbAngle Pro demonstrated high accuracy and clinical consistency, reinforcing AI’s added value in visual diagnostics when trained on well-structured datasets, which will improve over time.
• While this research is limited to one database and a narrow set of search terms, the results illustrate a growing integration of AI in health tools that promote individualized care experiences.
• The findings confirm an increasing global adoption of AI in mHealth applications. Its capabilities are vast if placed in healthcare systems with thoughtful consideration of equity, privacy, and trust.

Conclusion
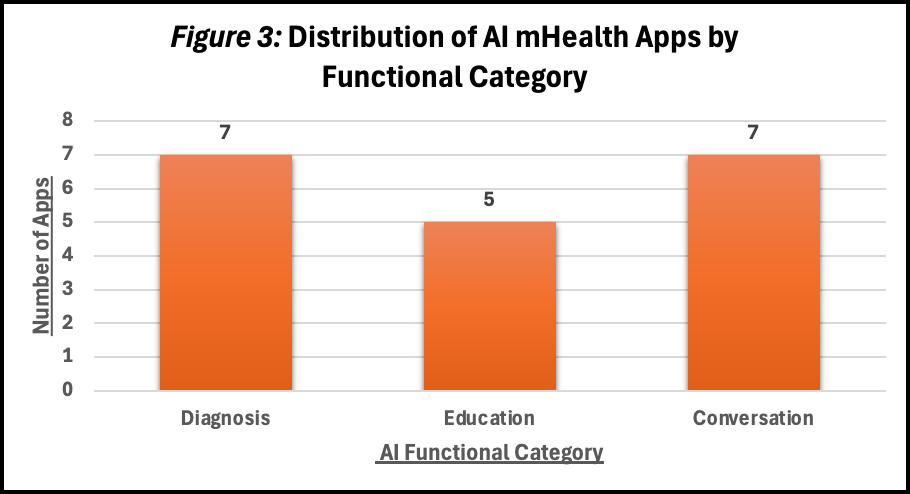
• 16 AI-embedded mHealth apps were categorized by function (diagnosis, education, conversation) (Fig 3).
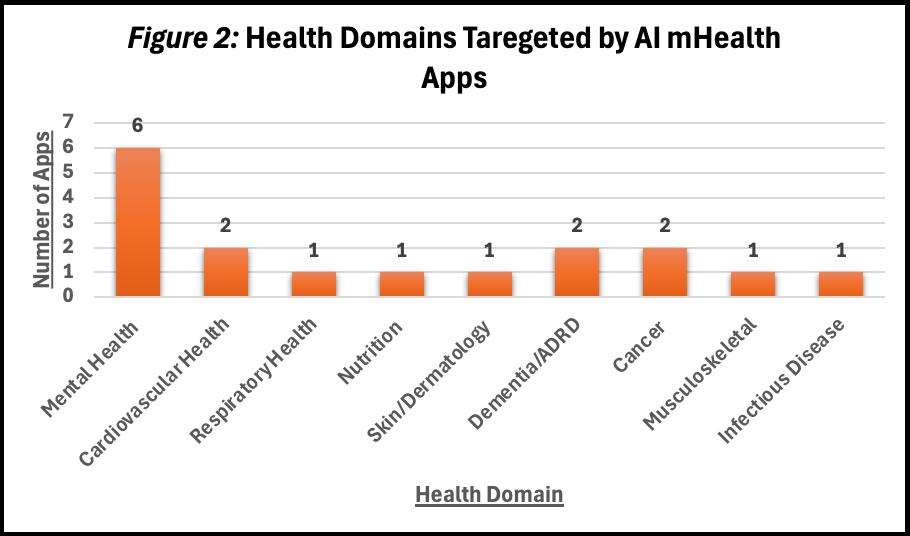
• Most apps targeted mental health (n=6), with others addressing dementia, cardiovascular disease, cancer, and niche areas like nutrition and respiratory health (Fig 2).
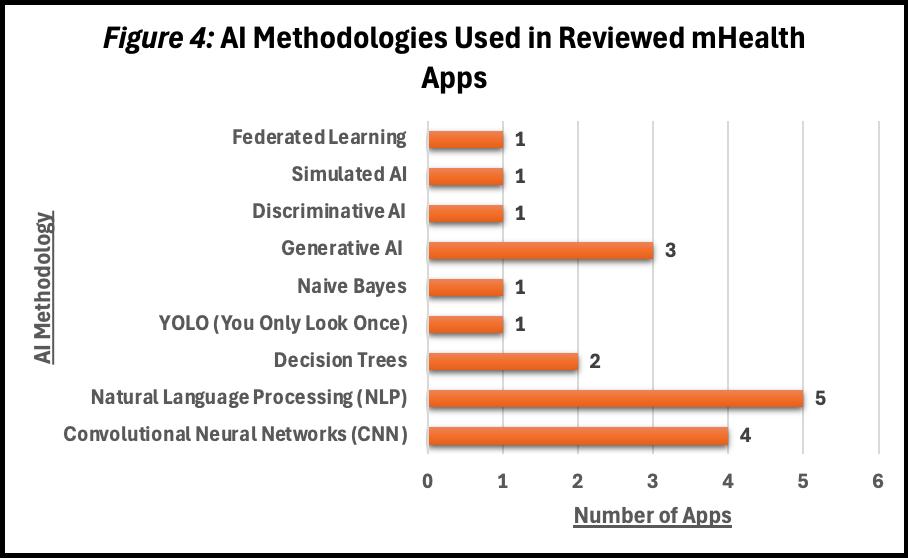
• Common AI methods included NLP (n=5), CNNs (n=4), generative AI (n=3), and specialized models like decision trees, YOLO, and Naive Bayes (Fig 4).


• This study analyzed 17 peer-reviewed empirical articles featuring 16 AI-embedded health apps, revealing how AI is actively reshaping healthcare delivery through mobile platforms.
• The research identified three primary functions: diagnosis, education, and conversation.
• Diverse use cases range from symptom triage and image recognition for diagnosis to personalized health coaching and emotional support.
• Across applications, AI significantly enhanced user engagement and autonomy.
• Organizing apps by AI methodology, health domain, and function allowed the study to uncover patterns in how models like NLP, CNNs, and generative AI are at the forefront when applied in clinical contexts.
• These findings underscore the importance of ethically guided AI development, focusing on data security, integrity, and accessibility, as foundational pillars for the continued growth of patient-centered mHealth tools.
• The adaptive nature of AI models signals that as more user data are collected, these tools will continue to self-improve. With increased precision, personalization, and convenience, this unlocks broader potential in delivering diverse healthcare aspects directly into patients' hands.

