10
5
Quaqtat Duplex Nunavik, 2019
Row Houses Nunavik, 2017
4
2010s Duplex Nunavik, 2017
3
Kikkaluk Cabin Nunavik, 1990-2015
2
Single House Nunavik, 1987
1
80s Duplex Nunavik, 1980
6
Quonset Hut Alaska, 1944
7
Sisimiut Duplex Greenland, 1960-1985
8
9
Arviat House Nunavut, 2017
DublDom Shelter Russia, 2018
11
Nordic House Nunavik, 2017
12
13
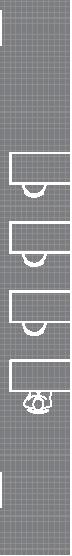
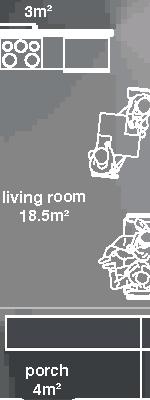
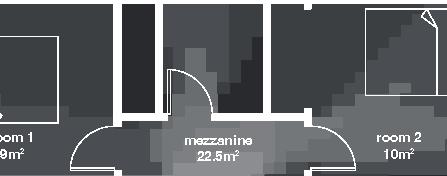
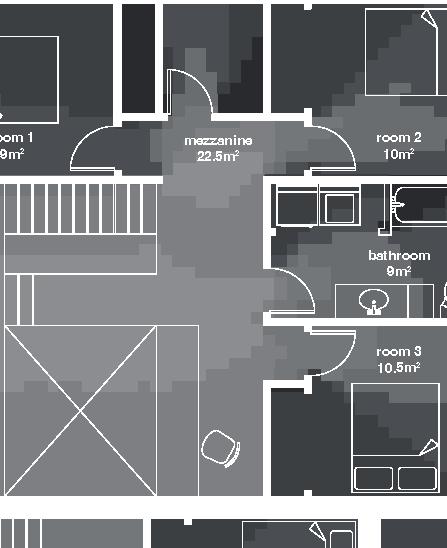
Small Community Nunavik, 2017
Tundra Camp Nunavik, 2018
14 their characteristics and their construction Doing Things Differently An atlas of best practices and opportunities for culturally acceptable and sustainable living environments in Nunavik • 2019-23 Funded by the Sentinel North program of Université Laval Canada First Research Excellence Fund 14 NORDIC HOUSES
Container Cabin Nunavik, 2018
Understanding the 14 nordic houses
Each one-pager file includes a series of information describing a house or group of houses. While some are rather factual and explicit, others are more qualitative in nature, as they are inspired by Inuit values and ways of life. Here are some keys to understanding the qualities and characteristics of each house.
Nordic House 11
Characteristics and qualities
Unbuilt (student) project which includes innovative and emerging ideas.
2017,

Prototype or built project whose promising ideas have yet to be validated over a long period of time.
Type of project that has been built regularly for several years.
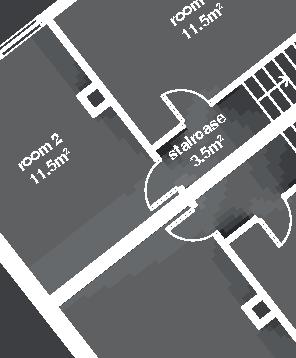
Organization of rooms
Some rooms are accessible through others.
linear
central
Rooms are distributed around a central core space.
Distinctive features
Culture appropriation
family life relationships
Families’ changing need and aspirations can be accommodated and met.
The house allows the inhabitants to occupy it and live in it as they wish.
Rooms are configured as to offer gathering spaces and quiet refuge, when needed.
seasons transitions
Investigators: Myriam Blais, Geneviève Vachon
Research associates: Samuel Boudreault, Gilles Rocheleau
Research assistants: Arianne Côté, Victor Demers, Flavie Martineau, Melaine Niget, Anthony Présumé, Maxime Vaillancourt-Cossette, Charlie Wenger









Various seasonal activities can take place in flexible and adaptable spaces.
Climatic and temperature variations between inside and outside are mitigated by a variety of thresholds and transition spaces.
A variety of orientations allows privileged and rich contacts with landscapes and neighborhoods.
sight
Materials and techniques are simple to implement, while being efficient and durable.
The house includes innovative and frugal bioclimatic strategies, as well as energy-efficient systems
Careful relationships with the ground and topography allows their qualities to be preserved.
siting
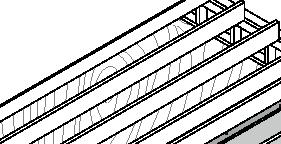
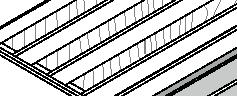
Construction Construction comfort systems
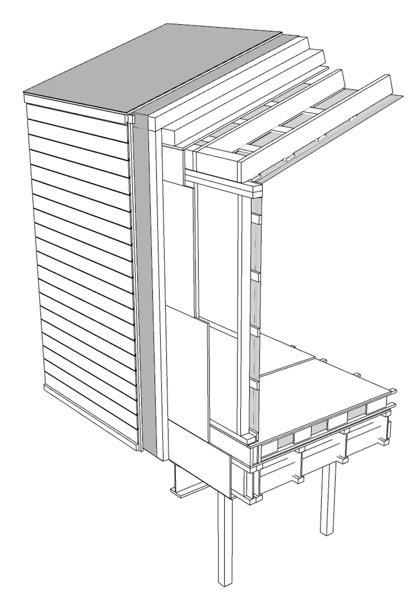
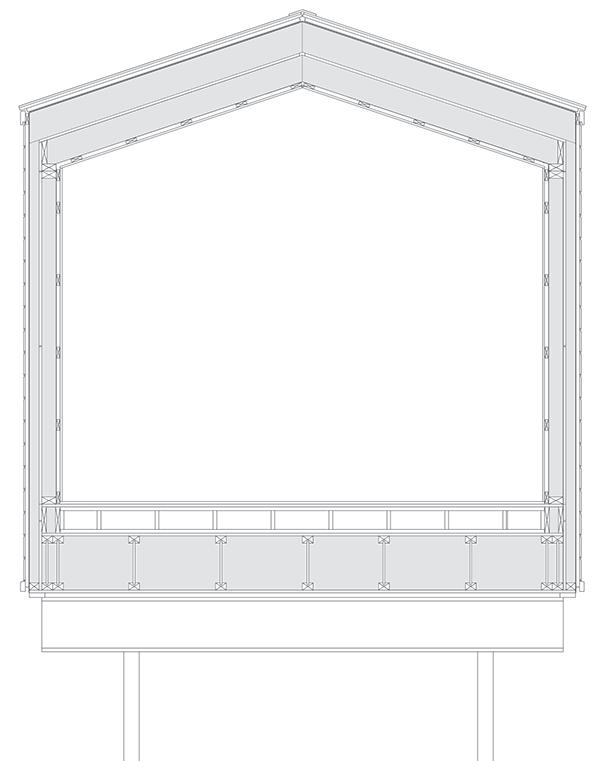
+0.46m +3.00m +6.38m permafrost (active layer) (x) 12.8m 3.7m 3.7m 1m Second Floor first floor attic storage balcony 0,5m Foundation Detail - base structure (steel) W 170x128 beam - bearing piles (friction, to bedrock) Wall detail - exterior cladding (wood) 19 mm (3/4 in.) - horizontal nailing strips (wood) 19x64 (1x3 in.) fixed to vertical furring - vertical furring strips (wood) 19x64 mm (1x3 in.) fixed to framing studs - insulation (extruded polystyrene) 235 mm (9 1/4 in.) - vapor and air barrier (fully adhered membrane) - interior lining (plywood or other) 19 mm (3/4 in.) - exposed framing studs (wood) 38x140, 610 mm oc (2x6, 24 in. oc) Roof detail - roofing (corrugated metal sheet) - weatherproofing (fully-adhered membrane) - underlay (plywood) 12 mm (1/2 in.) - insulation (extruded polystyrene) 310 mm (12 1/4 in.) in 2 layers - vapor and air barrier (fully adhered membrane) - structural underlay (plywood)19 mm (3/4 in.) - framing rafters (wood) 38x235, 610 mm oc (2x10, 24 in. oc) - interior lining (board 19 mm (3/4 in.) Floor detail - floor finish - subfloor (plywood) 19 mm (3/4 in.) - vapor barrier (polyethylene sheet or aluminium foil) - insulation (extruded polystyrene) 75 mm (3 in.) - underlying panel (plywood) 19 mm (3/4 in.) - framing joists (wood) 38x140, 610 mm oc (2x6, 24 in. oc) - insulation between joists (extruded polystyrene) 140 mm (5 1/2 in.) - weatherproofing (non-woven polyolefine house wrap) - exterior underside (plywood) 19 mm (3/4 in.) - seam-cover (wood-battens) 19x75 mm (1x3 in.) Student project, U. Laval by Alexandre Morin
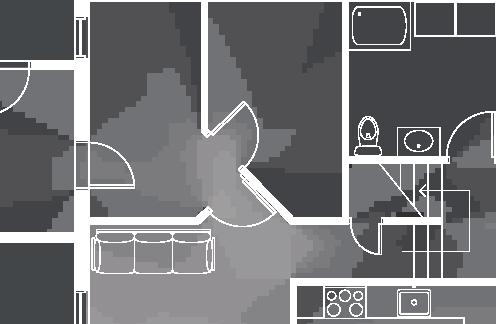
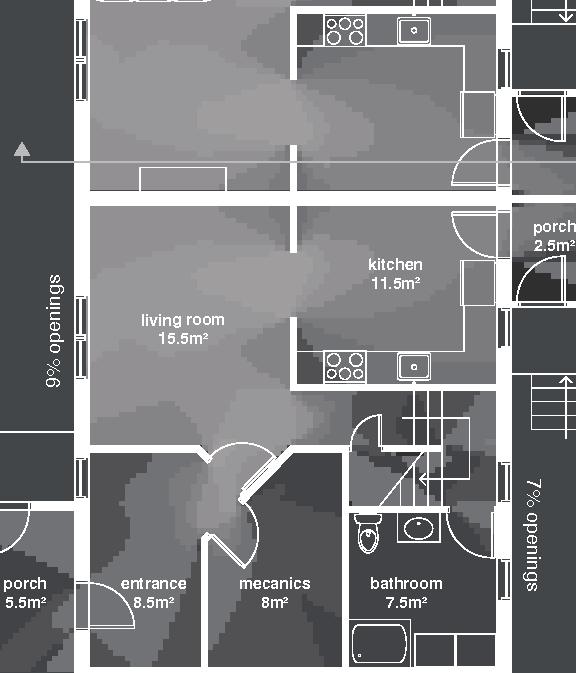
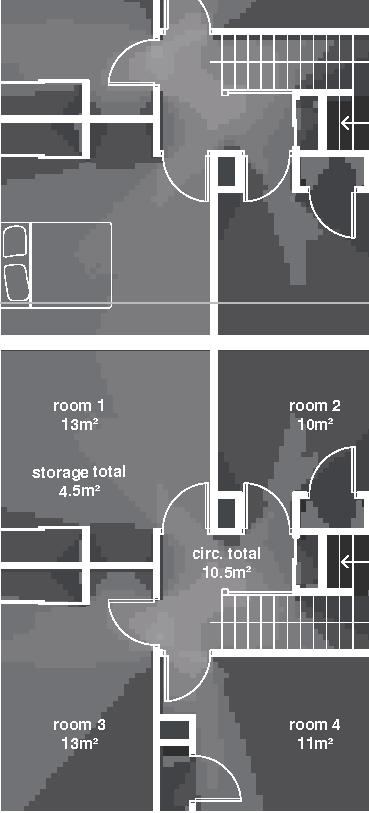
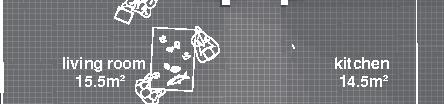
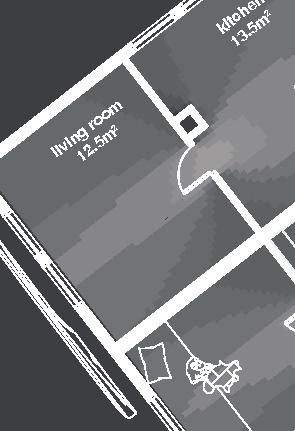
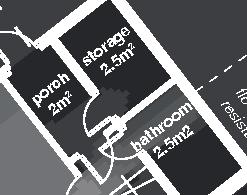
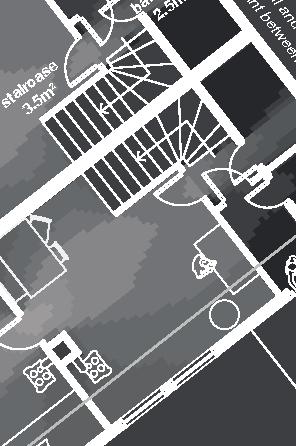
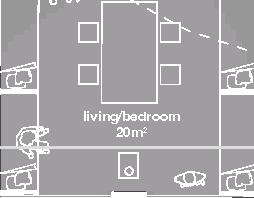
Nunavik unit area 104m2 58°N emerging Distinctive features latitude Culture Doing Things Differently An atlas of best practices and opportunities for culturally acceptable and sustainable living environments in Nunavik • 2019-23 Funded by the Sentinel North program of Université Laval Canada First Research Excellence Fund Characteristics and qualities Space Construction comfort systems seasons family life transitions appropriation siting sight relationships semi-detached house floors•rooms 2•7 central
Space
Status emerging common promising
Construction principles in Northern territory: about the building envelope
The term “envelope” refers to the exterior walls, roof, and windows of a building. In Nunavik, raised ground floors are also part of the building envelope. The envelope is a boundary, as well as a filter, which aims to control the effects of the environment (the climatic conditions) as well as air, vapor, and heat flows, between inside and outside.
A review of current knowledge about building envelope
• An efficient building envelope has to meet five requirements: 1) control heat flow, 2) control air flow, 3) control water vapor (moisture) flow, 4) control rain penetration, and 5) be durable.
• Air flow control is the most important because, due to temperature differences between indoor and outdoor environments, air flows will transport both water vapor and heat.
• Water vapor generally seeks to escape either by diffusion (migration through contiguous materials) or air leakage (exfiltration through an opening or a hole or any discontinuity in materials) (see image on the right).
• As water vapor passes through the envelope to the outside, it encounters colder and colder materials, eventually reaching a cold surface on which it will condense or even freeze, thus risking damage to water-sensitive materials like wood, gypsum, cardboard, or insulation batts.
• Air leakage through an opening in the envelope (even a very small one) allows a much greater quantity of water vapor to escape than through diffusion: damage to watersensitive materials is therefore much greater.
• This observation underpins the principle of the absolute necessity that the envelope forms an effective air barrier (one that is continuous, strong, and flexible at joints), in order to prevevvt warm water vapor from coming into contact with cold surfaces. This means achieving airtightness – without neglecting the fact that water vapor migration by diffusion must also be controlled, as well as heat flow.
Achieving airtightness and water vapor diffusion control
There are generally two ways to install air and vapor barriers :
1. The most common practice
Contextual note: The one-pager files presented in this booklet describe construction methods dating from the 1950s and beyond: they thus account for knowledge, principles and processes that have significantly evolved over time. The perception of comfort with regard to climatic conditions also changed during this period. This can explain certain construction decisions illustrated in the files.
diffusion air leakage
Main characteristics
• Air flow and water vapor flow controls are fulfilled by two distinct membranes: an air barrier (such as polyolefin) and a vapor barrier (such as polyethylene or aluminum film).
• These two membranes are located on different sides of the structural frame: the vapor barrier is always on its warmest side.
• Heat flow control is usually met by a combination of insulating materials (such as mineral wool batts and rigid foam-based panels), within and outside the structure.
Practical aspects
• The vapor barrier is often not supported and thus subject to tearing and puncturing, even after construction is completed.
• Its continuity is not easy to ensure where horizontal and vertical framings meet, thus requiring multiple sheets.
• Multiple steps are required to ensure continuity, creating a possibility for a humidity traps.
• It is not fully visible, thus difficult to inspect and repair.
• The air barrier plan on the most exterior side of the wall makes it subject to wear by wind.
2. An emerging practice, known as the “perfect wall”
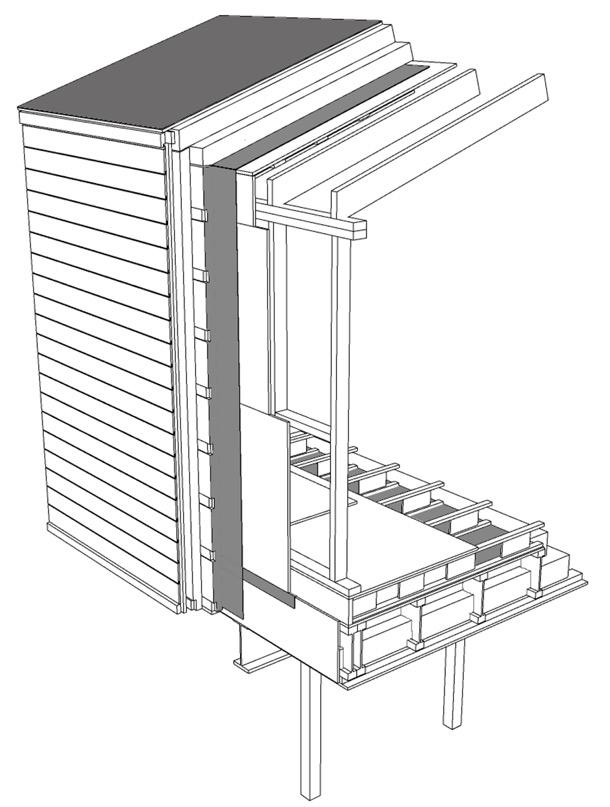
Main characteristics
• Air flow and water vapor flow controls are fulfilled by a single membrane: an air-vapor barrier (such as self-adhesive rubberized asphalt or polypropylene film).
• This membrane is located on the exterior side of the structural frame (sheeting); it has to always be on the warmest side.
• Heat flow control is usually met by a single insulating material (such as semi-rigid mineral wool panels), in one layer or more.
Practical aspects
• The air-vapor barrier is fully supported, thus protected from wear during construction and after its completion.
• Its installation is easy, just like wrapping a gift box: the continuity and integrity of the membrane are ensured.
• It is fully visible, easy to inspect and repair.
• Since there is only one membrane, it is impossible for humidity traps to be created inside the wood structure.
• This emerging practice is more efficient and durable, although (possibly) more costly.
by Bernard Sicotte


Roof Detail
-
dimensions to needs
- insulation (mineral wool batts) 150 mm (6 in.)
- insulation (mineral wool batts) 180 mm (7 in.)
- insulation (polystyrene board) 12 mm (1/2 in.)
- vapor barrier (polyethylene sheet or aluminum foil)
- furring strips (wood) 19x89 mm (1x4 in.)
- interior lining (cardboard or gypsiumboard) 300x300 mm (12x12 in.)
Wall detail
exterior cladding (horizontal pressed wood) - furring strips (wood) 19x65 mm (1x3 in.)
- air barrier (black building paper)
- sheating (plywood) 9 mm (3/8 in.)
- external framing studs (wood) 38x89 406 mm oc (2x4 16 in. oc)
- insulation between studs (mineral wool) 89 mm (3 1/2 in.)
- sheating (plywood) 12 mm (1/2 in.)
- internal framing studs staggered (wood) 38x89 406 mm oc (2x4 16 in. oc)
- insulation in between studs (mineral wool) 89 mm (3 1/2 in.)
- lining (plywood) 9 mm (3/8 in.)
- vapor barrier (polyethylene sheet or aluminum foil)
- interior lining (pressed wood sheet) 6 mm (1/4 in.)
Floor detail
- flooring (PVC)
- subfloor (plywood) 19 mm (3/4


(6x6
second floor 8.7m 8.7m 7.8m first floor 0% openings road setback lot road drainage 5m 3m 1m porch v
gravel
-
sheeting - treated wooden blocks
- pressed
raft
wheelbase from 8 pieces with treated wood 150x150 mm
in.) - 19 outdoor plywood
190x330x1280 mm
-
- Roofing (asphalt shingles)
air barrier (black building paper) - structural underlay (plywood) 12 mm (1/2 in.) - framing trusses (wood)
in.) - joists (wood) 38x184 mm (2x8 in.) - vapor barrier (aluminium foil) - underlying panel (plywood) 9 mm (3/8 in.) - insulation (extruded polystyrene) 38 mm (1 1/2 in.) - structural underlay (plywood) 9 mm (3/8 in.) - framing joists (wood) 38x184 mm (2x8 in.) - insulation in between joists (mineral wool) 184mm (7 1/4 in.) - exterior underside (outdoor plywood) 9 mm (3/8 in.) +4.9m +1.1m +0.0m permafrost (active layer) (x) 3m 2m 1m .5m granular pad (0,85x) Doing Things Differently : An atlas of best practices and opportunities for culturally acceptable and sustainable living environments in Nunavik 2019-2023 Funded by the Sentinel North program of Université Laval Canada First Research Excellence Fund Société d’habitation du Québec
architecte model J2.4
Duplex
Characteristics and qualities 121m2 58°N 2•7 Distinctive features unit area semi-detached house central common latitude floors•rooms Culture Space Construction relationships comfort systems seasons transitions appropriation siting sight family life relationships
80s
1 1980, Nunavik
Roof detail
- roofing (asphalt shingles)
- structural underlay (plywood) 13 mm (1/2 in.)
- framing trusses (wood) height and spacing to needs
- insulation (mineral wool batts) 200 mm (8 in.)
- insulation








-
- underlying panel (plywood)
mm (3/8 in.)
- vapor barrier (polyethylene sheet or aluminum foil)
- insulation (extruded polystyrene) 38 mm (1 1/2 in.)
- structural underlay (plywood) 9 mm (3/8 in.)
- framing joists (wood) 38x184 mm (2 x 8 in.) spacing to needs
- insulation between joists (mineral wool batts) 2x 89 mm (3 1/2 in.)
- air barrier (non-woven polyolefine house wrap)
- exterior underside (plywood) 9 mm (3/8 in.)
- seams-cover (wood-battens) 19x64 mm (1x4 in.)
Foundation detail
- base structure (W 360x33 metallic beam)
- adjustable metallic screwjack
- base of screwjack (2 treated wooden parts) 200x200 mm (8x8 in.) bearing the efforts form the screwjack
- wheelbase (8 treated wood pieces) 150x150 mm (6x6 in.)

m 5 3 1 8.5m s g n n e p o % 0 2 6 10% openings 0.01% openings road setback lot s g n n e p o % 5 5m 3m 1m road drainage granular pad (1,5x) permafrost (active layer) (x) +0.0m +1.1m +1.8m 3m 2m 1m 0.5m
flooring (PVC)
subfloor (plywood) 16
in.)
Floor detail -
-
mm (5/8
joists
38x184
8
spacing
supported
(wood)
mm (2 x
in.)
to needs,
by short trusses (wood) 38x89 mm (2x4 in.)
9
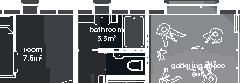
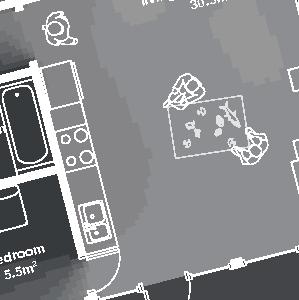
(mineral wool batts) 89 mm (3 1/2 in.) - insulation (extruded polystyrene) 38 mm (1 1/2 in.) - vapor barrier (polyethylene sheet or aluminum foil) - furring strips (wood) 19x64 mm (1x4 in.) - interior lining (gypsum board) 13 mm (1/2 in.) Wall detail - exterior cladding (main : vertical wood planks, headband : corrugated steel sheet) - furring strips (wood) 16x64 mm (1x3 in.) - air barrier (non-woven polyolefine house wrap) - sheating (plywood) 9 mm (3/8 in.) - framing studs (wood) 38x140, 406 mm oc (2x6, 16 in. oc) - insulation between studs (fiberglass wool) 140mm (5 1/2 in.) - insulation (rigid extruded polystyrene) 38 mm (1 1/2 in.) - vapor barrier (polyethylene sheet or aluminum foil) - sheating (plywood) 9mm (3/8 in.) - furring strips (wood) 38x64 mm (2x3 in.) - interior lining (gypsum board) 13 mm (1/2 in.) Société d’habitation du Québec model U3 Single House 2
Nunavik unit area 113m2 58°N 1•5 common Distinctive features latitude floor•rooms linear detached house Culture Doing Things Differently An atlas of best practices and opportunities for culturally acceptable and sustainable living environments in Nunavik • 2019-23 Funded by the Sentinel North program of Université Laval Canada First Research Excellence Fund Characteristics and qualities Space Construction comfort systems seasons family life transitions appropriation siting sight relationships relationships
1987,
Kikkaluk Cabin 3
1990 to 2015, Nunavik
designed and builded by Inuit community members of Salluit

Distinctive features
62°N
Roof detail
- roofing (nailed asphalt sheets)
- structural underlay (plywood) 16 mm (5/8 in.)
- (in some construction) insulation (mineral wool or recuperated solid insulation)
- framing rafters (wood) height and spacing to needs
Wall detail
- exterior cladding (exposed plywood ) 16 mm (5/8 in.)
- framing studs (wood) 38x89, 610 mm oc (2x4, 24 in. oc)
- (in some/most construction) insulation between studs (mineral wool or recuperated solid insulation) - (in some construction) interior lining (plywood) 16 mm (5/8 in.)
Floor detail
- flooring (exposed plywood) 16 mm (5/8 in.)
- insulation (rigid insulation)
- underlying panel (plywood) 16 mm (5/8 in.)
- joists (wood) 38x184, 610 mm oc (2x8, 24 in. oc)
Foundation detail
- wood pieces and concrete wheelbases manually adjusted on the ground




6m 8m 7.5m 3.5m 3.8% openings openings2.8% 3.8% openings fjordfaçade 2.8%openings 0%openings 13% openings entrance facade 26%
fjordfacade 27%openings 5m 3m 1m openspace kitchen m openspace deck 4m deck 13m storage 2m
openings
+0.6m +0.0m bedrock 1.5m 1m .5m
Culture Doing Things Differently An atlas of best practices and opportunities for culturally acceptable and sustainable living environments in Nunavik • 2019-23 Funded by the Sentinel North program of Université Laval Canada First Research Excellence Fund Characteristics and qualities Space Construction family life comfort systems seasons transitions appropriation siting sight relationships unit area 50m2
1•2 emerging latitude floor•rooms linear cabins
Roof
-
- structural underlay (plywood) 16 mm (5/8 in.)
- framing trusses (wood) dimensions to needs - insulation between trusses

Wall detail
- exterior cladding (horizontal wood planks)
- furring strips (vertical wood) 19x64 mm (1x4 in.)
- air barrier (non-woven polyolefine house wrap)
- insulation (extruded polystyrene) 38 mm (1 1/2 in.)
- sheating (oriented strand board) 11 mm (7/16 in.)
- framing studs (wood) 38x140, 406 mm oc (2x6, 16 in. oc)
- insulation between studs (mineral wool) 140 mm (5 1/2 in.)
- vapor barrier (polyethylene sheet or aluminum foil)
- furring strips (horizontal wood) 19x64 mm (1x4 in.)
- interior lining (gypsum board) 13 mm (1/2 in.)
Floor detail
- flooring (PVC sheets)
- subfloor (plywood) 16 mm (5/8 in.)
- joists (wood) 38x140 mm (2x6 in.) spacing to needs
- vapor barrier (polyethylene sheet or aluminum foil)
- structural underlay (oriented strand board)16 mm (5/8 in.)
- framing web trusses (wood) 280mm (12 in.) spacing to needs
- insulation between trusses (blown-in cellulose) 280 mm (11 in.)
- air barrier (non-woven polyolefine house wrap)
- exterior underside (plywood) 13 mm (1/2 in.)
- seams-cover (wood-battens) 19x64 mm (1x4 in.)
Foundation Detail
- beam (metallic) W 310x39 or W 310x21 spacing to needs
- metallic adjustable columns anchored in concrete
- 250 mm (10 in.) thick Reinforced Concrete wheelbase


detail
shingles)
- roofing (asphalt
air barrier underlay sheet (black building paper)
(blown-in cellulose) 280 mm (11 in.) - vapor barrier (polyethylene sheet or aluminum foil) - furring strips (wood) 19x89 mm (1x4 in.) - interior lining (gypsum board) 13 mm (1/2 in.) +4.7m +1.9m +0.0m permafrost (active layer) (x) granular pad (1,5x) 3m 2m 1m 0.5m road drainage 10m 10m 10m 11% openings 3% openings 7% openings road setback lot 5m 3m 1m living room m Doing Things Differently An atlas of best practices and opportunities for culturally acceptable and sustainable living environments in Nunavik 2019-2023 Funded by the Sentinel North program of Université Laval Canada First Research Excellence Fund Makivvik by EVOQ architecture
J2.2 2010s Duplex 4 2010, Nunavik Characteristics and qualities 80m2 58°N 1•3 Distinctive features unit area semi-detached house central common latitude floor•rooms Culture Space Construction comfort systems seasons family life transitions appropriation siting sight relationships
model
Roof detail - roofing (fully-adhered elastomeric membrane)
- base panel (layered with elastomeric membrane) 16mm (5/8 in.)
- structural underlay (plywood) 16 mm (5/8 in.)
- framing joists (wood) 38 x 235 mm (2x10 in.) spacing to needs
- insulation between joists (mineral wool batts) 235mm (9 1/4 in.)
- insulation (extruded polystyrene with sealed joints) 38 mm (1 1/2 in.)
- vapor barrier (polyethylene membrane)
- furring strips (wood) 38x64, 400 mm oc (2x4, 16 in. oc)
- interior lining (gypsum board) 13mm (1/2 in.)

38x140 mm (2x6 in.) spacing to needs
- insulation between studs (mineral wool batts) 140mm (5 1/5 in.)
- vapor barrier (polyethylene sheet or aluminum foil)
- furring strips (horizontal wood) 19x64 mm (1x4 in.)
- interior lining (gypsum board) 13 mm (1/2 in.)
Floor detail
- flooring (PVC sheet)
- subfloor (plywood) 16 mm (5/8 in.)
- vapor barrier (self-adhesive plastic sheet or aluminum foil)
- underlying panel (plywood) 16 mm (5/8 in.)
- framing joists (wood) 38 x 235 mm (2x10 in.) svpacing to needs
- insulation between joists (mineral wool batts) 235mm (9 1/4 in.)
- air barrier (non-woven polyolefine house wrap)
- insulation (extruded polystyrene) 38 mm (1 1/2 in.)
- exterior underside (plywood)13 mm (1/2 in.)
- seam-cover (wood-battens) 19 mm (1 1/2 in.)





site set back Culture Construction Doing Things Differently An atlas of best practices and opportunities for culturally acceptable and sustainable living environments in Nunavik 2019-2023 Funded by the Sentinel North program of Université Laval Canada First Research Excellence Fund Kativik Ilisarniliriniq by EVOQ architecture
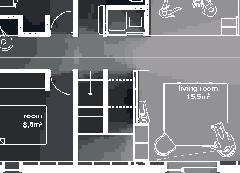
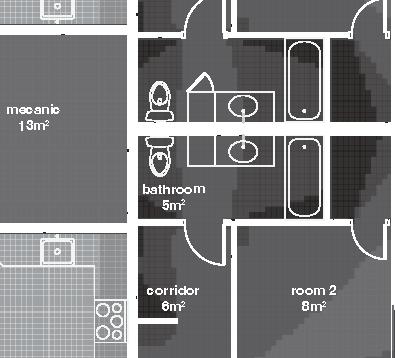
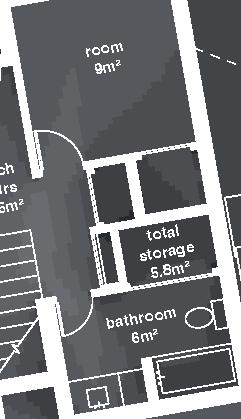
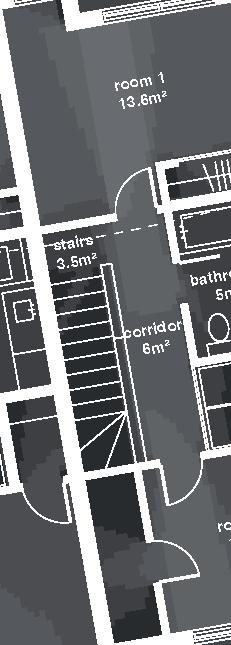
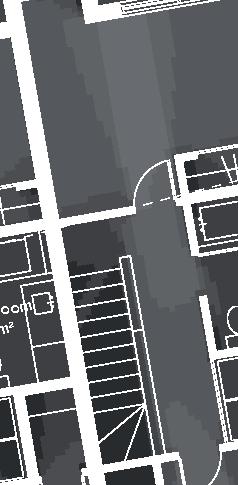
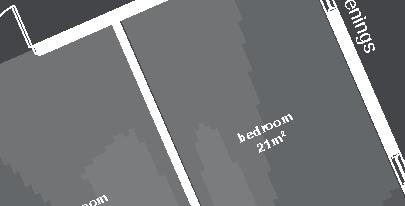
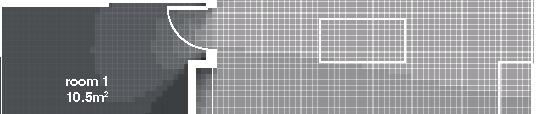
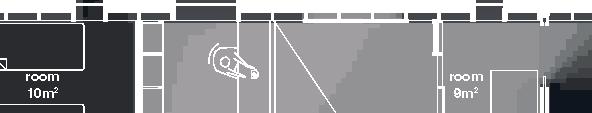
Nunavik Characteristics and qualities unit area 75-90m2 58°N common Distinctive features latitude 2•4 floors•rooms row houses linear Space comfort systems seasons family life transitions appropriation siting sight family relationships 4.5m 12.1m porch stairs 10.5m bathroom 5m room 2 10m second floor first floor 5m 3m 1m granular pad (1,5x) permafrost (active layer) (x) +4.7m +1.9m +0.0m 3m 2m 1m .5m Foundation Detail - beams (W 310 x 39 or W 310 x 21) spacing to needs - metallic adjustable columns - 250 mm thick reinforced concrete wheelbase Wall detail - exterior cladding (corrugated galvanized steel) 22 mm (7/8 in.) - furring strips (vertical wood) 19x64 mm (1x4 in.) - insulation (extruded polystyrene insulation) 38 mm (1 1/2 in.) - air barrier (non-woven polyolefine house wrap) - sheating (plywood)16mm (5/8 in.) - framing studs
Row Houses 5 2014,








granular pad (1,5x) permafrost (active layer) (x) +0.0m +1.2m +4.3m 4.5m 11m 5.8m 16.5m 5m 3m 1m 1.5m 1m .5m Roof and wall detail - roofing (corrugated galvanized steel sheets) - framing curved ribs and purlins (steel) - insulation (corrugated paper) 25 mm (1 in.) - interior lining (masonite) 32 mm (1/8 in.) or 64 mm (1/4 in.) Floor detail - flooring (exposed plywood) - underlying strips (wood) staggered with ribs - framing crossbeams (steel) 62 mm (2 5/16 in.) - framing beams (steel) 84 mm (3 5/16 in.) Foundation detail - wood sills - metallic adjustable columns - 250 mm thick reinforced concrete blocks
States Navy by
Quonset Hut 6
Alaska 40-100 m2 60°N 1•1-3 Distinctive features Culture Doing Things Differently An atlas of best practices and opportunities for culturally acceptable and sustainable living environments in Nunavik • 2019-23 Funded by the Sentinel North program of Université Laval Canada First Research Excellence Fund Characteristics and qualities Space Construction comfort systems seasons family life transitions appropriation siting sight relationships unit area promising latitude floor•rooms cabins central
United
Otto Brandenberger architect
1944,
Roof detail (retained existing elements in italic)
7
1960, Greenland




- furring strips (wood) 50x50 mm (2x2 in.)
- insulation (mineral wool batts) 50 mm (2 in.)
- vapor barrier (polyethylene sheet)
- interior lining (wooden fiber board)12mm (1/2 in.)
Wall detail (retained existing elements in italic)
- air cavity between existing and renovated enveloppe 25 mm (1 in.)
- furring strips (horizontal wood) 50x50 mm (2x2 in.)
- insulation (mineral wool batts) 50 mm (2 in.)
- vapor barrier (polyethylene sheet monarflex brand)
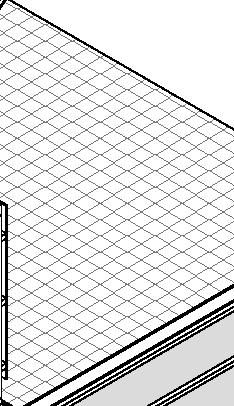
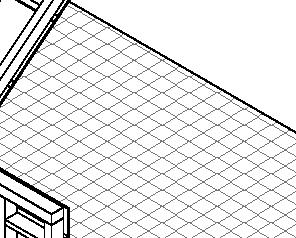
- interior lining (wooden fiber board)12mm (1/2 in.)
Floor detail (retained existing elements in italic)
- flooring (mosaic tile) 50x50x5 mm (2x2x1/4 in.)
- subfloor (chipboard) 22 mm (7/8 in.)
- vapor barrier (aluminum foil)
- floor joists (wood) 87.5x150 mm (3 1/2x6 in.)
- insulation (rockwool) 100mm (4 in.) and air cavity
37mm (1 1/2 in.)
- air barrier (bitumen felt)
- air cavity between existing and renovated envelope
12mm (1/2 in.)
- exterior floor joists (wood) 50x125mm (2x5 in.)
- insulation (mineral wool batts) 100 mm (4 in.)
- exterior underside (planks) 25x100 mm (1x4 in.)
- seam-cover (wood-battens)
Foundation detail (retained existing elements in italic)

secondfloor

resistantfloor,wallandrooffire

firstfloor

5m 3m 1m
m8,3 m9,9
kitchen staircase
bedrock (x) 3m 2m 1m 0.5m
+0.0m +1.2m +3.6m +5.9m
betweendwellings - joint cover on seams (vertical wood-battens) 15x45 mm (5/8x 1 3/4 in.) - exterior clading (water resistant boards) 12 mm (1/2 in.) - air barrier (black bitumen felt) - studs (wood) 75x100, 550 oc mm (3x4, 23 in.) - horizontal struts (wood) 50x100 mm (2x4 in.) - insulation between studs (rockwool) 100 mm (4 in.) - exterior lining (bitumen roofing felt) - air barrier (black building paper) - underlay (mineral wool cardboard) - structural underlay (wood planks) 25x125 mm (1x5 in.) - frame rafters, 50x125 mm (2x5 in.) spacing to needs - insulation between rafters (rockwool) 100 mm (4 in.) - concrete dwarf walls directly anchored in the bedrock (forming ventilated crawlspace)
Duplex
Greenlandic Technical Organization Sisimiut
unit area
common
features latitude linear Culture Doing Things Differently An atlas of best practices and opportunities for culturally acceptable and sustainable living environments in Nunavik • 2019-23 Funded by the Sentinel North program of Université Laval Canada First Research Excellence Fund Characteristics and qualities Space Construction comfort systems seasons family life transitions appropriation siting sight relationships semi-detached house 2•4 floors•rooms renov. 1985
60m2 56°N
Distinctive
Roof detail
- roofing (corrugated metal sheets)
- furring strips (wood) 19x89, 600 mm oc (1x4, 24 in. oc)
- structural underlay (plywood)15 mm (5/8 in.) self-adhered bituminous membrane on seams, width 150 mm (6 in.)
- framing joists (wood/OSB I joists) height 457 mm (18 in.)
spacing to needs
- insulation between joists (mineral wool batts) 450 mm (18

Wall detail - exterior cladding (composite siding)
- air barrier (non-woven polyolefine house wrap)
- sheating (plywood) 9.5 mm (3/8 in.)
- external framing studs (wood) 38x140, 600 mm oc (2x6, 24 in. oc)
- insulation between studs (mineral wool) 140mm (6in.)
- nailing strips (wood) forming air cavity 12 mm (1/2 in.)
- internal framing studs (wood) 38x89, 600 mm oc (2x4, 24 in. oc) (staggered to exterior studs)
- insulation between studs (mineral wool) 89 mm (3 1/2 in.)
- sheating (plywood ) 9.5 mm (3/8 in.)
- vapor barrier (polyethylene sheet or aluminum foil)
- insulation (rigid polystyrene) 38 mm (1 1/2 in.)
- furring strips (wood) 38x38, 600 mm oc (2x2, 24 in. oc)
- interior lining (gypsum board) 13 mm (1/2 in.)
Foundation Detail
- beam (laminated timber) 140x 394mm (5 ½ x15 ½ in.) spacing to needs, protected by structural skirt and wall siding
- stakes HSS metallic, dimension to needs, reaching bedrock



+0.0m
+1.5m pad 0.5m
permafrost (active layer)
3m 2m 1m 0.5m
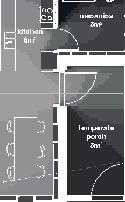
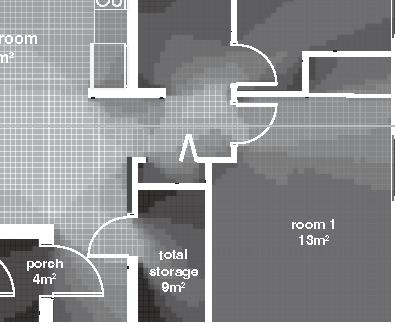
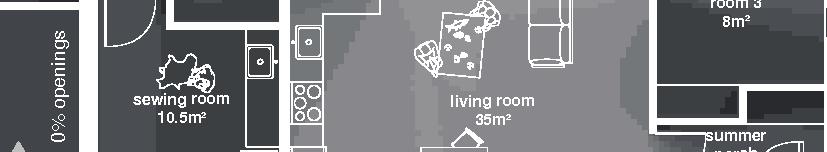
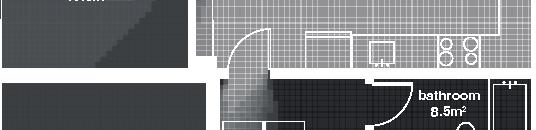
in.) 3 layers of 150mm (6 in.) - vapor barrier (polyethylene sheet or aluminum foil) - furring strips (wood) 19x89, 400 mm oc (1x4,16 in. oc) - interior lining (gypsum board) 13 mm (1/2 in.) Floor detail - flooring - subfloor (plywood glued and screwed) 19 mm (3/4 in.) - framing joists (TJI beams) height 305 mm (12 in.), 600 mm (24 in.) oc - insulation between joists (mineral wool batt) 305 mm (12 in.) - furring strips (wood) 38x38, 600 mm oc (2x2, 24 in. oc) - insulation (polystyrene semi-rigid) 38 mm (1 1⁄2 in.) - air barrier (spun bonded polyolefin) - exterior underside (OSB) 11 mm (7/16 in.) - seam-cover (wood-battens) 19x89 mm (1x4 in.) 14m 2m 9.5m 1.5m 1% openings 11% openings south facade 5% openings road lot 5m 3m 1m room 3 porch Nunavut Housing Corporation Arviat House 8
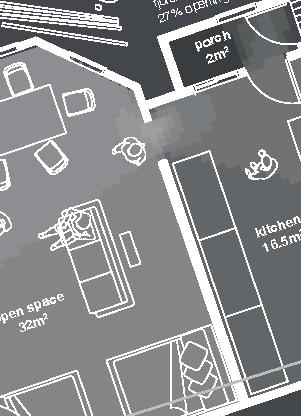
Nunavut unit area 124m2 61°N promising Distinctive features latitude linear Culture Doing Things Differently An atlas of best practices and opportunities for culturally acceptable and sustainable living environments in Nunavik • 2019-23 Funded by the Sentinel North program of Université Laval Canada First Research Excellence Fund Characteristics and qualities Space Construction comfort systems seasons family life transitions appropriation siting sight relationships floor•rooms detached house 1•5
2017,
2018, Russia
by BIO architects





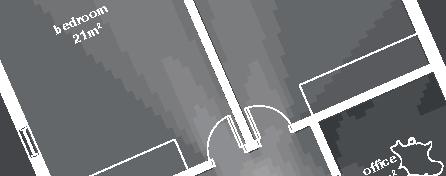
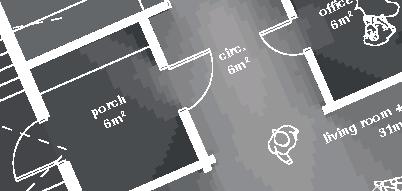
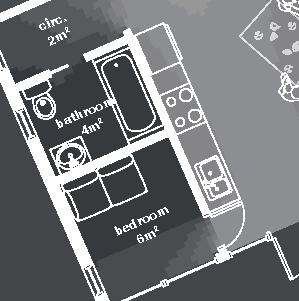
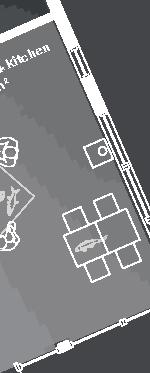


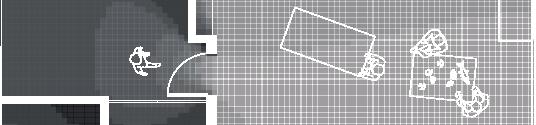
7.5m 5m 86.4% openings 6,4m 12m 12m 19,5m 7.5m 90.3%openings 41.2%openings 22.7% openings 90.3% openings 10.7% openings 40.6% openings 11.6% openings 8.7% openings 25.3% openings 5.9% openings 5.9% openings 5m 3m 1m bedroom 14.5 bathroom bedroom veranda 23.5m veranda 11m office veranda 23.5m livingroom+kitchen m porch + storage +0.0m +0.9m rock (x) 1.5m 1m 0.5m 0.25m
DublDom Shelter 9
unit area 27-100m2
promising Distinctive features latitude Culture Doing Things Differently An atlas of best practices and opportunities for culturally acceptable and sustainable living environments in Nunavik • 2019-23 Funded by the Sentinel North program of Université Laval Canada First Research Excellence Fund Characteristics and qualities Space Construction comfort systems seasons family life transitions appropriation siting sight relationships cabins floor•rooms 1•1-5 central Roof detail - roofing (metal sheets) 1 mm (1/32 in.) - furring strips (metallic z-bar) 95mm (3 3/4 in.) forming ventilated air cavity - waterproofing (breathable membrane) - framing rafters (wood) 38x184mm (2x8 in.) spacing to needs - insulation between rafters (mineral wool batt) 184 mm (7 3/4 in.) - vapor barrier (polyethylene sheet or aluminum foil) - furring strips 20 mm (3/4 in.) - interior lining (wood) 19 mm (3/4 in.) Wall detail - exterior cladding (metal sheets) 1 mm (1/32 in.) - furring strips (metallic z-bar) 95mm (3 3/4 in.) forming ventilated air cavity - waterproofing breathable membrane - framing studs (wood) 38x184mm (2x8 in.) spacing to needs - insulation between studs (mineral wool batt) 184 mm (7 3/4 in.) - vapor barrier (polyethylene sheet or aluminum foil) - furring strips 19x75 mm (1x3 in.) - interior lining (wood) 19 mm (3/4 in.)
detail - flooring (wood planks) 35 mm - vapor barrier (polyethylene sheet
aluminum foil) - framing joists 38x184
in.) - insulation between joists
wool) 184mm
in.) - waterproofing breathable membrane - exterior underside (plywood) 16mm
in.) - seams cover (wood) 19x75 mm (1x3 in.)
detail - steel beams - metal pillars directly on the ground - on bedrock
67°N
Floor
or
mm (2x8
(mineral
(7 3/4
(5/8
Foundation
-
Roof detail
- structural underlay (plywood) 16 mm (5/8 in.)
web joists (wood) height 420mm (16 in.) spacing to needs
- insulation between joists (mineral wool batts) 420mm (16 in.) x2 layers of 210mm (8 in.)
- vapor barrier (polyethylene sheet or aluminum foil)
- insulation (extruded polystyrene)

- interior lining (gypsum board) 13 mm (1/2 in.)
in.)








Permarfrost (active layer) (x) +0.0m +3.0m +1.0m 21m 22% openings 10m 5% openings 7% openings5m 3m 1m balcony 6.5m 3m 2m 1m 0.5m Société d’habitation du Québec by EVOQ Architecture
Duplex 10
Quaqtaq
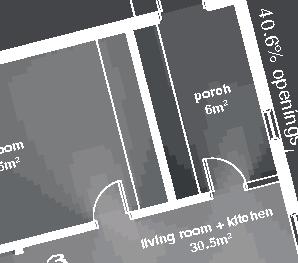
unit area 88m2 61°N promising Distinctive features latitude Culture Doing Things Differently : An atlas of best practices and opportunities for culturally acceptable and sustainable living environments in Nunavik • 2019-23 Funded by the Sentinel North program of Université Laval Canada First Research Excellence Fund Characteristics and qualities Space Construction comfort systems seasons family life transitions appropriation siting sight family life relationships semi-detached house floor•rooms 1•3 central Foundation detail - base structure (W steel beams) height 160mm (6 1/3 in.) spacing to needs - adjustable metallic screwjack in between welded steel plates - concrete filled metallic HSS posts 144 mm (5 2/3 in.) dia. reaching bedrock through permafrost (2 meters deep min.) Wall detail - exterior cladding (wood planks) - furring strips (vertical wood) 19x64 mm (1x4 in.) - air barrier (non-woven polyolefine house wrap) - insulation (extruded polystyrene) 50 mm (2 in.) - sheating (plywood) 13 mm (1/2 in.) - external framing studs (wood) 38x140, 600 mm oc (2x6, 24 in. oc) - air cavity 50 mm (2 in.) - internal framing studs staggered (wood) 38x89, 600 mm oc (2x4, 24 in. oc) - insulation (blown-in fiberglass wool) 280mm (11 in.) filling the wall cavities - vapor barrier (polyethylene sheet) - furring strips (horizontal wood) 19x64 mm (1x4
2016, Nunavik
vapor
- roofing (metal sheet ) -
and air barrier (fully adhered membrane)
framing
50 mm (3 in.) - furring strips 19x64 mm (1x4 in.) - interior lining (gypsum board)13 mm (1/2 in.) Floor detail - flooring (PVC) - subfloor (plywood) 16 mm (5/8 in.) - floor joists (wood) 38x184 mm (2x8 in.) spacing to needs - vapor barrier (polyethylene sheet or aluminum foil) - underlying panel (plywood) 16 mm (5/8 in.) - framing web joists (wood) height 312 mm (14 in.) spacing to needs - insulation between web joists (blown-in cellulose) 280mm (11 in.) - insulation (extruded polystyrene) 50 mm (2 in.) - air barrier (non-woven polyolefine house wrap) - exterior underside (plywood) 16 mm (1/2 in.) - seam-cover (wood-battens)
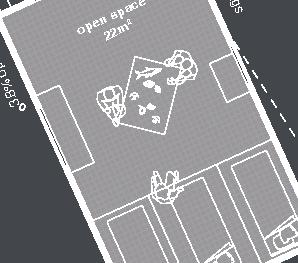
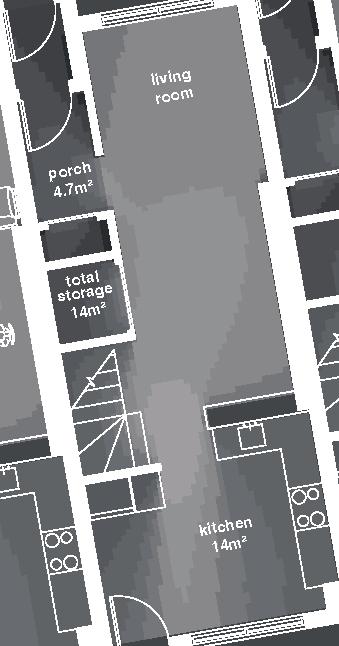
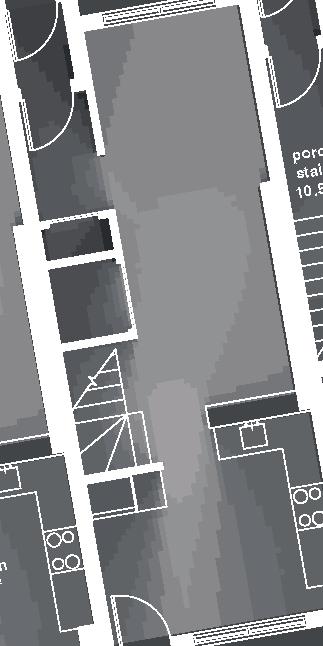
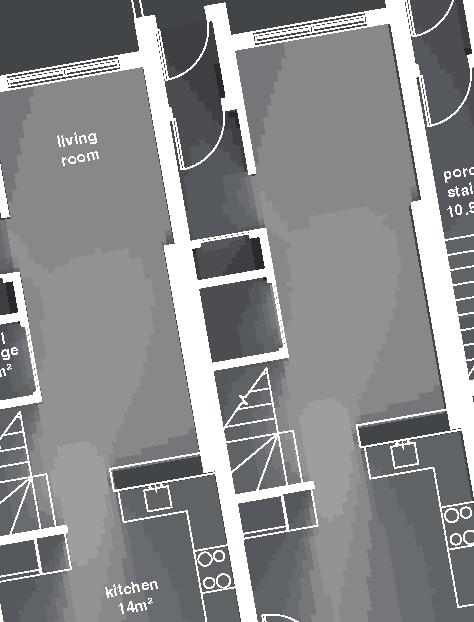
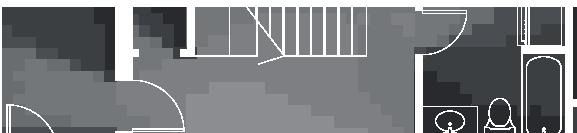
Nordic House 11
2017, Nunavik
Student
by Alexandre Morin

Roof detail
- roofing (corrugated metal sheet)
- weatherproofing (fully-adhered membrane)
- underlay (plywood) 12 mm (1/2 in.)
- insulation (extruded polystyrene) 310 mm (12 1/4 in.) in 2 layers
- vapor and air barrier (fully adhered membrane)
- structural underlay (plywood)19 mm (3/4 in.)
- framing
Wall detail
- exterior cladding (wood) 19 mm (3/4 in.)
- horizontal nailing strips (wood) 19x64 (1x3 in.) fixed to vertical furring
- vertical furring strips (wood) 19x64 mm (1x3 in.) fixed to framing studs
- insulation (extruded polystyrene) 235 mm (9 1/4 in.)
- vapor and air barrier (fully adhered membrane)
- interior lining (plywood or other) 19 mm (3/4 in.)
- exposed framing studs (wood) 38x140, 610 mm oc (2x6, 24 in. oc)



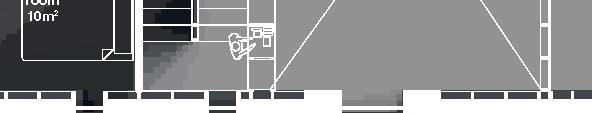


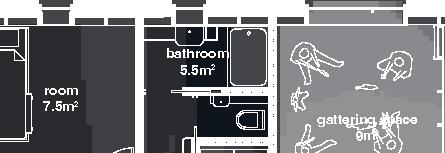
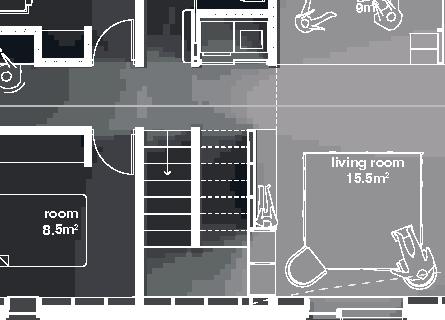
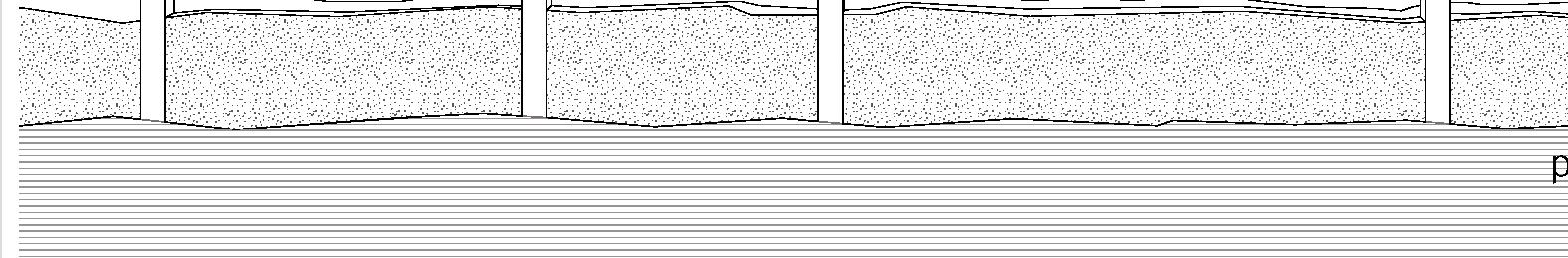



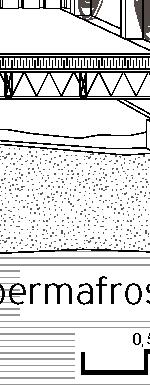
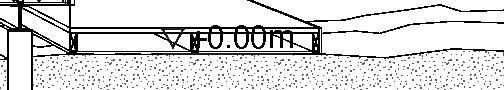
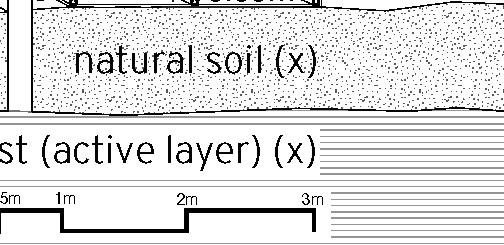
+0.46m +3.00m +6.38m permafrost (active layer) (x) 12.8m 3.7m 3.7m 5m 3m 1m Second Floor first floor attic storage balcony 28 0,5m
base structure
W
beam - bearing piles
to bedrock)
Foundation Detail -
(steel)
170x128
(friction,
rafters (wood) 38x235, 610 mm oc (2x10, 24 in. oc) - interior lining (board) 19 mm (3/4 in.) Floor detail - floor finish - subfloor (plywood) 19 mm (3/4 in.) - vapor barrier (polyethylene sheet or aluminium foil) - insulation (extruded polystyrene) 75 mm (3 in.) - underlying panel (plywood) 19 mm (3/4 in.) - framing joists (wood) 38x140, 610 mm oc (2x6, 24 in. oc) - insulation between joists (extruded polystyrene) 140 mm (5 1/2 in.) - weatherproofing (non-woven polyolefine house wrap) - exterior underside (plywood) 19 mm (3/4 in.) - seam-cover (wood-battens) 19x75 mm (1x3 in.)
project, U. Laval
unit area 104m2
emerging Distinctive features latitude Culture Doing Things Differently An atlas of best practices and opportunities for culturally acceptable and sustainable living environments in Nunavik • 2019-23 Funded by the Sentinel North program of Université Laval Canada First Research Excellence Fund Characteristics and qualities Space Construction comfort systems seasons family life transitions appropriation siting sight relationships semi-detached house floors•rooms 2•7 central
58°N
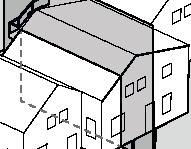
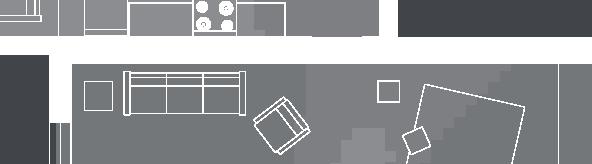
Small Community 12
2017, Nunavik
Student project, U. Laval by Marie-Jeanne Allaire-Côté

Distinctive features
84136m2
58°N
Roof detail
- roofing (metal sheet)
- weatherproofing (fully-adhered membrane)
- underlay (plywood) 19 mm (3/4 in.)
- insulation (extruded polystyrene) 310 mm (12 1/4 in.) in two layers
- vapor and air barrier (fully adhered membrane)
- structural underlay (plywood)19 mm (3/4 in.)
- framing rafters (wood) 36x235 (2x10, 24 in.) spacing
to needs
- sheating (plywood) 19 mm (3/4 in.)
- interior lining (as wanted)
Wall detail
- exterior siding (wood) 25 mm (1 in.)
- furring strips (horizontal wood) 19x64 mm (1x3 in.)
- insulation (extruded polystyrene) 235 mm (9 1/4 in.) in two layers
- vapor and air barrier (fully adhered membrane)
- sheating (plywood ) 19 mm (3/4 in.)
- studs (wood) 38x140, 600 mm oc (2x6, 24 oc in.)
- sheating (plywood ) 19 mm (3/4 in.)
Floor detail
- flooring (concrete or other)
- subfloor (plywood) 19mm (3/4 in.)
- vapor barrier (polyethylene sheet or aluminum foil)
- insulation (extruded polystyrene) 76 mm (3 in.)
- underlaying panel (plywood) 19 mm (3/4 in.)
- joists (wood) 38x235 (2x10 in.) spacing to needs
- insulation between joists (mineral wool batt) 235mm (9 1/4 in.)
- weatherproofing (non-woven polyolefine housewrap)
- exterior underside (plywood) 19 mm (3/4 in.)
- seam-cover (wood-battens) 19x75 mm (1x3 in.)
Foundation detail
- base structure (W steel beams)
- bearing piles (steel posts) to bedrock




rock (x) 3m 2m 1m 0.5m
5m 3m 1m +1.60m +5.50m +4.90m +0.00m
unit area
emerging
latitude Culture Doing Things Differently An atlas of best practices and opportunities for culturally acceptable and sustainable living environments in Nunavik • 2019-23 Funded by the Sentinel North program of Université Laval Canada First Research Excellence Fund Characteristics and qualities Space Construction comfort systems seasons family life transitions appropriation siting sight relationships
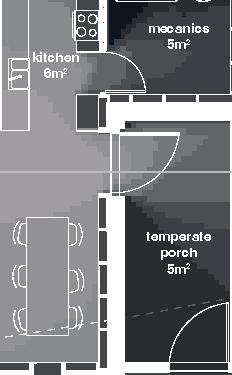
floors•rooms central row houses second floor first floor 9.5m 6.3m 10m 0% openings 6.3m porch 5.5 kitchen dining room mecanics 3m room 1 room 1 m room 10.5m courtyard facade
2•5-7
based on student project by Pierre-Olivier Demeule (2018)

Roof detail
- roofing (sheet metal) reclaimed from discarded
shipping containers
- weatherproofing (fully adhered membrane)
- underlay (plywood) 16 mm (5/8 in.)
- insulation (fibrewood) 300mm (12 in.) in two layers
- vapor and air barrier (fully adhered
Wall detail
- exterior cladding (vertical wood planks) 19mm (3/4 in.) reclaimed and charred
- horizontal furring strips (wood) 19x64 mm (1x3 in.)
- insulation (fibrewood) 150mm (6 in.) in two layers
- vapor and air barrier (fully adhered membrane)
- sheating (plywood) 16 mm (5/8 in.)
- structural composite columns (wood) 4 38x286mm
(4 2x12 in.) at 3m o.c. (9ft 10in.)
- wall studs (wood) 38x184mm (2x8 in.)
- insulation between studs (goose feather mats) 204 mm (8' in.)
- interior lining (plywood or canvas) 19 mm (3/4 in.)
Foundation detail
- continuous still-beam (treated wood) made of 186x186mm (8x8 in.)
- screw-jacks or bearing piles, hidden in dry stone gabion baskets
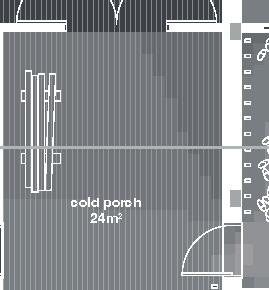
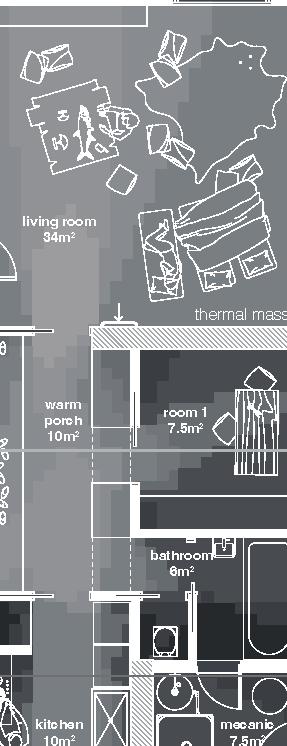


+1.80m bedrock +0.00m 5m 3m 1m 6m 4m 15m 3.7m mezzanine thermal mass first floor
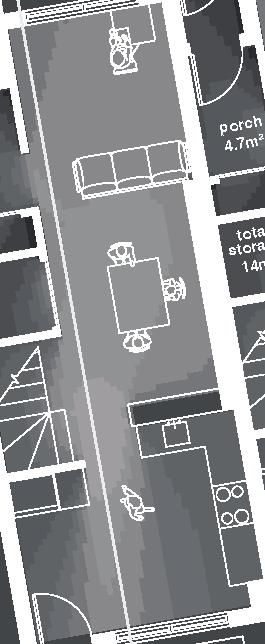
membrane) - structural roof (CLT wood) depth as needed - structural composite beams (wood) 3 38x286 mm (3 2x12 in.) at 3m o.c. (9ft 10in.) Floor detail - flooring (to wants) - subfloor (plywood) 16 mm (5/8 in.) - insulation (polystyrene) 50mm (2 in.) - vapor barrier (polyethylene or aluminium sheet) - structural underlay (plywood) 16 mm (5/8 in.) - joists (wood) 38x286 mm (2x12 in.) spacing to needs - structural composite beams (wood) 4 38x286mm (4 2x12 in.) at 3m o.c. (9ft 10in.) - insulation between joists (fiberwool batts) 286 mm (11 1/2 in.) - structural underlay (plywood) 9mm (3/8 in.) - weatherproof membrane (polyolefine sheet) - exterior underside (plywood) 9 mm (3/8 in.) - seam-cover (wood battens) 19x64mm (1x3 in.) deck 40m deck 12.5 3m 2m 1m 0,5m
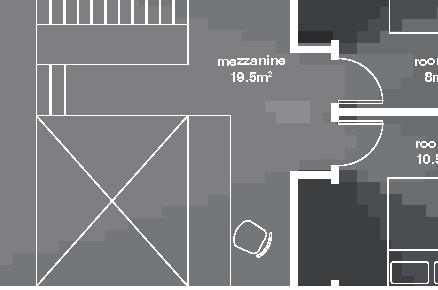
Tundra Camp 13
Nunavik unit area 75m2 62°N 1•4 emerging Distinctive features latitude floor•rooms linear detached house Culture Doing Things Differently An atlas of best practices and opportunities for culturally acceptable and sustainable living environments in Nunavik • 2019-23 Funded by the Sentinel North program of Université Laval Canada First Research Excellence Fund Characteristics and qualities Space Construction comfort systems seasons family life transitions appropriation siting sight relationships
2022,
Container Cabin
2018, Nunavik
Student project, U. Laval
by Vincent Foster

16mm (5/8 in.)
- furring 19x64mm (1x3 in.) (embedded in insulation)
- insulation (extruded polystyrene) 80mm (3 1/2 in.)
- structural underlay (plywood) 19mm (3/4 in.)
- structural rafters (wood) 38x184mm (2x8 in.) spacing at need
- insulation (mineral wool batts) 184mm (7 ¼ in.) between rafters
- vapor barrier (polyethylene sheet or aluminum foil)
- interior lining (wood planks) 13mm (1/2 in.)
Floor detail
- flooring
- subfloor (plywood) 19 mm (3/4 in.)
- insulation (extruded polystyrene) 80mm (3 ½ in.)
- structural underlay (plywood) 19mm (3/4 in.)
- joists (wood) 38x140mm (2x6 in.)
- insulation (mineral wool batts) 140mm (5 1/2 in.) between joists
- structural underlay (plywood) 19mm (3/4 in.)
- container flooring structure C-bars (Corten steel)
- exterior underside (plywood) 9 mm (3/8 in.)
- seam-cover (wood-battens) 19x64mm (1x3 in.)


5m 3m 1m 2.65m 6.26m 16.5m 16.5m 16.5m
14
unit area 16.5m2
emerging
62°N
latitude Culture Doing Things Differently An atlas of best practices and opportunities for culturally acceptable and sustainable living environments in Nunavik • 2019-23 Funded by the Sentinel North program of Université Laval Canada First Research Excellence Fund Characteristics and qualities Space Construction comfort systems seasons family life transitions appropriation siting sight relationships relationships floor•room cabins central Foundation detail - continous sill-beam (treated wood) made of 38x184 and 38x89mm (2x8 and 2x4 in.) - deck blocks (concrete) Wall detail - exterior cladding (wood planks) 19mm (3/4 in.) - vertical furring (wood) 19x64mm (1x3 in.) - horizontal furring 19x64mm (1x3 in.) (embedded in insulation) - insulation (extruded polystyrene) 80mm (3 1/2 in.) - vapor and air barrier (fully adhered membrane) - sheating (plywood) 16mm (5/8 in.) - container sidewall (Corten steel) - interior lining (wood planks) 13mm (1/2 in.) Roof detail - roofing (asphalt shingles) - underlay (plywood)
Distinctive features
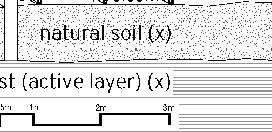
+1.00m natural soil (x) +0.00m
1•1






















































































































































