
1 minute read
Design and Operation
from Volvo Penta TAD1240GE TAD1241GE-VE TAD1242GE-VE, TWD1240VE Group 22-26 Workshop Manual_381897674
Lubrication system
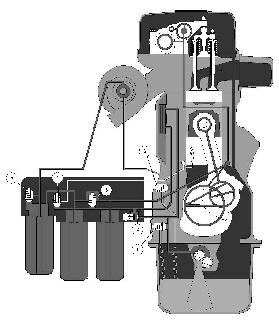
The engine is pressure-lubricated via a gear pump coupled to the engine transmission. The oil flow is regulated by six valves.
The oil pump pumps the oil to two full-flow filters and one by-pass filter, where the oil to the turbocharger is also filtered by about 5%. From the full-flow filter the oil is passed to the engine block and distributed through passages to the engine lubrication points. The oil cooler is of the plate type and is located under a cast-iron cover on the right-hand side of the engine block.
1Safety valve
2Bypass valve for oil cooler
3Bypass valve for oil filter
4Piston cooling valve
5Bypass valve for bypass filter (turbocharger)
6Reducing valve
1 Safety valve
When the oil pressure across the safety valve exceeds 8.6 bar (125 psi), the valve opens and returns the oil to the oil pan.
2 Bypass valve for oil cooler
When the pressure across the oil cooler is low, for example, when the oil temperature is low immediately after start-up, the bypass valve opens and the oil bypasses the cooler. When the oil temperature rises and the pressure drop across the oil cooler falls (<3.0 bar, 45 psi), the valve closes and the oil flows through the oil cooler before being pumped into the lubrication system.

3, 5 Bypass valve for oil filter/bypass (turbo-
The bypass valve opens (>2.1 bar, 30 psi) to maintain lubrication when the filter is clogged.
4 Piston cooling valve
The piston cooling valve opens (3.0 bar, 45 psi) when the engine speed reaches just above idle. The oil flows through the piston cooling passages to the six piston cooling nozzles, where oil is sprayed onto the underside of the pistons.
6 Reducing valve
The reducing valve controls the oil pressure by opening at high pressure (5.7 bar, 80 psi) and returns the excess oil to the oil pan.



