







The Great Redemption Arc: From Ridiculous to Reasonable
Remember when Big Tech spent a decade trying to convince us that strapping what looked like a microwave to our heads was the future? From Google's original "Glasshole" fiasco in 2013 to Meta's brick-sized VR headsets, tech giants seemed determined to make us look like extras from a low-budget sci-fi movie. Apple even had the audacity to release a $3,500 Vision Pro that made users look like they were cosplaying as a deep-sea diver (long way since MIT lab in 1995-image)

But somewhere between 2020 and 2025, sanity prevailed. The tech overlords finally realized what fashion designers have known for centuries: if you want people to wear something on their face all day, it better not make them look like a rejected Transformer. And thus, the age of actually wearable smart glasses began. Today's AI-powered smart glasses promise hand-free access to digital assistants, real-time information overlays, and translation on the fly all while looking like ordinary glasses. It took Big Tech a decade and billions of dollars to figure out that normal-looking eyewear might actually work. 30 years of research!.Who could have predicted that?
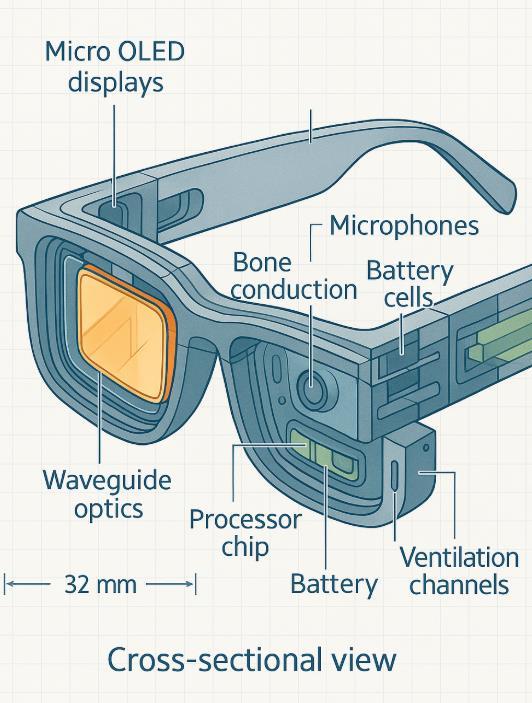
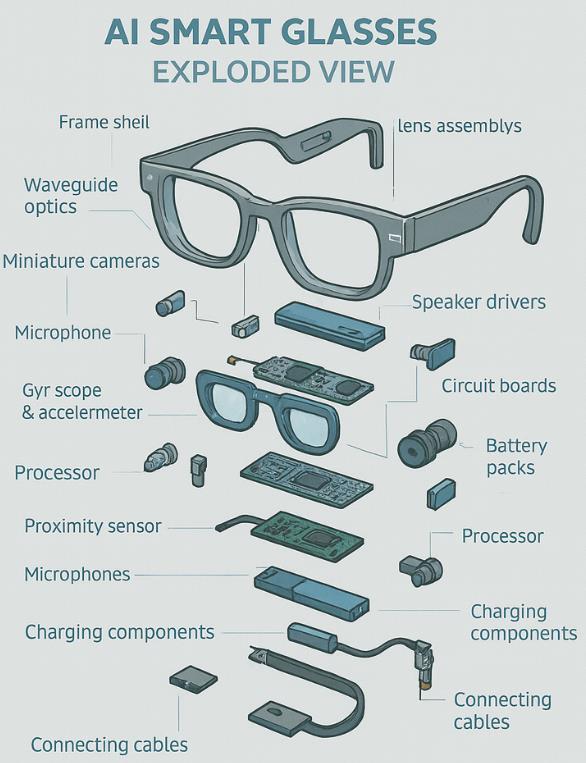
The U.S. tech giants have been aggressively exploring smart glasses, learning from early missteps and leveraging AI to make glasses smarter and more appealing. Three major players lead the charge:

Meta (Facebook/Oculus) – Ray-Ban Meta Smart Glasses: Meta partnered with eyewear brands like Ray-Ban and Oakley to create stylish smart glasses that people might actually want to wear.
The Ray-Ban Meta glasses look like classic sunglasses but house cameras, microphones, and speakers. The latest generation adds an AI voice assistant ("Meta AI") and better hardware – the new Meta/Oakley model can record 3K video and lasts about 8 hours on a charge, a big improvement over the ~4 hours of the first-gen Ray-Bans.
In 2025, Meta expanded with Oakley Meta Smart Glasses, targeting athletes and outdoor enthusiasts with rugged designs, PRIZM lens technology for enhanced contrast during sports, and the same AI features optimized for active lifestyles – perfect for recording POV action shots or getting pace updates during runs.
They don't yet project a digital display, but they can take photos, play music, handle calls, and even answer questions about what you're looking at or translate text by leveraging AI in the cloud.

Pros: Fashionable designs from Ray-Ban plus athletic performance from Oakley, proven demand (over 2 million units sold as of 2025), and growing AI capabilities.
Cons: No true AR display (you must check your phone for visuals), short battery life on heavy use, and potential privacy concerns.
Apple – Vision Pro & the Road to "`": Apple's first step was the Vision Pro, a high-end mixed reality headset launching in 2024 but it's more bulky goggles than everyday glasses. Behind the scenes,
Apple is reportedly fast-tracking development of lightweight AR smart glasses aimed for 2026, which could eventually replace the iPhone 10 years from now hinting that wearable display could take over.

The rumored Apple glasses would likely use a power-efficient chip and run on Siri and "Visual Intelligence" AI for context awareness.
Pros: Apple's strengths are sleek hardware and integrated ecosystem –their glasses will surely tie into iOS seamlessly.
Cons: The technology to pack an iPhone's power into normal-looking glasses isn't fully ready yet. Also, expect a premium price – some forecasts say a version with transparent AR display could cost up to $1,400.
Google (Alphabet) – From Google Glass to Project Moohan: Google knows better than anyone how early hype can backfire – its original Google Glass in 2013 was a consumer flop (society wasn't ready for "Glassholes" sporting face cameras). However, Google didn't give up.
At Google I/O 2025, Google showcased prototype smart glasses running Android XR featuring Google's powerful Gemini AI assistant.

The demo impressed with built-in micro-displays showing notifications and navigation prompts in your field of view – something Meta's RayBans currently lack. Google is also recruiting fashionable eyewear brands to design the frames, directly targeting Meta's strategy.
Pros: Google's forte is AI and data – their glasses leverage Google Lens, Translate, Maps, and Assistant.
Cons: Still prototype stage in 2025, with Google hinting at a 2026 launch. They must overcome trust issues from the original Glass.
Overall, U.S. smart glasses emphasize software smarts and all-day integration with our digital lives, positioning themselves as the eventual successor to the smartphone – "the must-have computer of the 2030s."
China's tech companies are in an all-out race to dominate smart eyewear, fueled by huge domestic demand and government support for AI. Chinese firms have rolled out consumer smart glasses at aggressive prices:
Xiaomi – Xiaomi AI Glasses: Launched in June 2025, priced from ¥1,999 (~$280), Xiaomi's glasses undercut many Western rivals while packing serious tech. They use Qualcomm's Snapdragon AR1 chipset and feature a 12MP ultra-wide camera. They leverage audio and phone
connection for AI features like live speech translation and control of other Xiaomi smart home devices and EVs.

Impressively, Xiaomi touts 8.6 hours of battery life – about double Meta's glasses. They even offer optional electrochromic lenses that switch from clear to sunglass tint at the tap of a button. Within a month of release, Xiaomi sold ~50,000 units with "enthusiastic" consumer reception.
Pros: Excellent bang-for-buck, long battery life, tight ecosystem integration.
Cons: Lacks AR visual overlay relies on audio or phone for outputs.
Alibaba – Quark AR Glasses: Showcased in July 2025, these are true AR eyewear with a display, built on Qualcomm's AR1 chip. Demoed with use-cases tightly integrated into Alibaba's services: scan a product and see its Taobao price, scan QR codes to pay via Alipay, get AR navigation via Amap.
Essentially, Alibaba is turning its entire ecosystem into a hands-free experience.
Pros: Rich real-time environmental interactions thanks to AR visuals and Alibaba's cloud AI.
Cons: Still in preview with no announced launch date or price.

Lenovo: Lenovo launched Legion AR Smart Glasses featuring dual 120 Hz micro-OLED screens aimed at gamers. Meanwhile, budget players like Rollme offer AirView glasses at just $80 with 8MP camera, voice assistant, and real-time translation – essentially a cheap "AI secretary" on your face.

Pros: Affordability and feature innovation, quick AI integration. Cons: Many devices lack polish or global ecosystem support, with fragmentation across brands.
South Korea: The Component Kings may not have headlinegrabbing launches, but plays a pivotal behind-the-scenes role leveraging strengths in hardware and partnerships:
LG and Component Suppliers: LG's display division likely supplies tech to others, while Korean startups like LetinAR specialize in AR optics used in Japan's NTT Docomo "MiRZA" AR glasses. Korean innovation often appears inside others' glasses, giving Korea an edge in quietly shaping the industry.
South Korea's approach emphasizes strategic partnerships and leveraging high-tech manufacturing.

Pros: Korean technology helps make smart glasses lighter, brighter, and more stylish.
Cons: Brands have yet to establish distinct identity in the AI glasses market.
Taiwan not to forget - still in the race
HTC Vive Eagle (Taiwan) – The AR Innovator: Best for cutting-edge features. Shows what's coming next by integrating high-end Zeiss optics, transparent display, on-board ChatGPT AI, and camera-based environmental recognition.

It merges voice assistant, translator, and navigator with visual AR beginnings. The "tech enthusiast's choice" for pushing the envelope with AI vision features.
Japan's contributions skew toward enterprise and R&D, reflecting a tech culture valuing precision and practical use-cases:
NTT Docomo & Sharp – MiRZA AR Glasses: In 2024, Japan's biggest telecom unveiled "Mirza" AR glasses a lightweight headset aimed initially at businesses and developers.
Uses Qualcomm's latest AR2 chipset and advanced optics to project digital screens in the wearer's view.
However, with chunky appearance and ~$1,700 price, it targets enterprise and early adopters.

Pros: Cutting-edge optics giving wide field of view, renowned Japanese build quality.
Cons: Extremely expensive and not consumer aimed.
Sony, Panasonic & Others: Japanese electronics giants continue developing micro-displays and sensors relevant to smart glasses, while focusing on enterprise solutions like AR for tourism, translations, and emergency response.
Japan's stance is cautious but technically deep, seeing AR glasses as part of "Society 5.0" vision – integrating cyberspace and physical space to solve social issues like aging workforce training.
Pros: Ultra-high-quality components and practical enterprise focus. Cons: Lack of big consumer push might make Japan appear behind in the hype cycle.
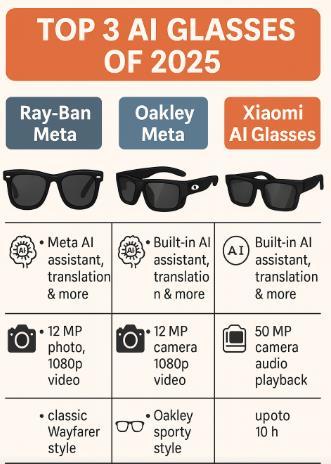
After surveying the global landscape by specialists, I agreed with, here are the picks for the four best contenders:
1. Meta Ray-Ban (USA) – The Lifestyle Trendsetter: Best for mainstream appeal. With millions sold and a head start in real-world usage, Meta's Ray-Ban glasses set the bar for consumer expectations. They nail the fundamentals: stylish designs, easy camera capture, and conversational AI assistance.

LAST MINUTE FROM META – September 30 2025
Breakthrough EMG Technology Enables Hands-Free Interface Control Through Muscle Signals
MENLO PARK, CA – September 30, 2025 – Meta today announced the launch of its groundbreaking Ray-Ban Display smart glasses, featuring an innovative neural interface system that transforms how users interact with augmented reality technology.
The complete system, priced at $799, combines advanced display glasses with Meta's proprietary Neural Band wristband for unprecedented hands-free control.
The centerpiece of this innovation is the Meta Neural Band, a sophisticated wristband equipped with Surface Electromyography (sEMG) sensors.
This cutting-edge device detects minute electrical signals generated by finger muscle movements, translating subtle gestures into precise digital commands without requiring visible hand motions. Users can click, scroll, and navigate interfaces through nearly imperceptible finger movements.
"This represents a fundamental shift in human-computer interaction," said [Meta spokesperson]. "By reading the electrical signals your muscles naturally produce, we've eliminated the barrier between thought and digital action."
Advanced Smart Glass Capabilities The Ray-Ban Display glasses deliver a comprehensive suite of features designed for seamless daily integration:
• AI-Powered Visual Assistant – Engage with Meta AI and receive realtime visual information overlaid on your field of view
• Immersive Communication – Conduct video calls through popular applications with hands-free operation
• Instant Content Access – Stream Reels and multimedia content directly through the display
• Universal Translation – Real-time language translation with onscreen subtitles for global connectivity
Market Availability The complete Meta Ray-Ban Display system, including both the smart glasses and Neural Band, is available today for $799. This launch represents Meta's most ambitious integration of AI technology with wearable devices, positioning the company at the forefront of next-generation augmented reality experiences.
2. Xiaomi AI Glasses (China) – The Value Champion: Best for feature-packed affordability. Xiaomi's glasses deliver impressive value with good camera, multi-language translation, music playback, and all-day battery (8+ hours).
They cleverly cater to lifestyle needs from QR payments to electrochromic lenses. Xiaomi has democratized smart glasses in China, proving you don't need to spend a fortune for a taste of the future.
3. Oakley Meta Smart Glasses (USA) – The Athletic Champion: Best for active lifestyles. Oakley's Meta glasses fill the sports and outdoor niche that Ray-Ban couldn't touch.
With rugged designs, PRIZM lens technology for enhanced contrast during sports, and the same Meta AI features optimized for active use, they're perfect for athletes who want to record POV action shots or get real-time performance data.
Finally, here we are with smart glasses that can keep up with your morning jog without flying off your face.

Imagine a future where the world’s information and digital layers are projected seamlessly into your vision not through glasses or bulky headsets, but with the comfort and subtlety of soft contact lenses. That’s the radical innovation that
InWith Corporation, a U.S.-based tech startup, is racing to bring to life. Their “smart” contact lenses promise to merge vision correction, augmented reality (AR), and even health monitoring into something millions wear daily, quietly reshaping how we see and interact with our environment.
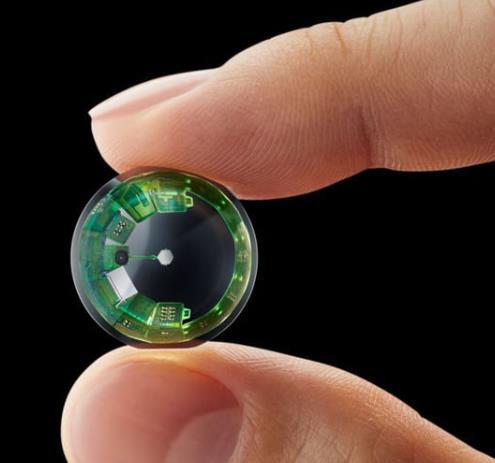
At the heart of InWith’s breakthrough is patented technology for embedding microscale computer circuits and display chips directly inside soft hydrogel lenses, like those from household brands such as Bausch & Lomb. This extraordinary leap means the lenses remain as soft and flexible as conventional contacts yet are now augmented with solid-state microelectronics.
If successful, this approach could make AR visuals, think GPS directions, fitness stats, or contextual text appear directly in the field of vision, all while maintaining everyday comfort and appearance.

But InWith’s ambitions reach beyond flashy digital overlays. The first expected application is “tunable vision” lenses. Imagine dynamically adjusting your visual correction for farsightedness or nearsightedness, all controlled via smartphone, banishing the need for reading glasses or progressive lenses.
By wirelessly linking to mobile devices, these smart contacts could deliver personalized, fine-tuned eyesight changes on demand. For the nearly two billion people worldwide who wear contacts, this could be a true revolution in optical health.
InWith envisions its platform as the ultimate discreet gateway to the convergence of real and virtual worlds. Unlike current AR devices, which are often cumbersome and conspicuous, these soft lenses are virtually invisible.
Technologeven harvests energy from the natural blinking of the eye, aiming for all-day power without external batteries. Embedded biosensors may one day monitor health markers in tears, opening new frontiers in noninvasive medicine and personal wellness.
While prototypes have dazzled at tech shows, and InWith boasts hundreds of patents, these lenses remain in advanced development. The company is pursuing U.S. FDA clearance, with initial “tunable vision” medical products likely preceding full AR versions.
Still, the promise is profound: comfortable, everyday lenses connecting humans to information, entertainment, and health like never before.
InWith’s vision is clear: a future where seeing really is believing, and reality becomes what you make of it.

The Orion cortical stimulation system represents a revolutionary advancement in restoring vision for the profoundly blind. This investigational device bypasses damaged eyes entirely, transmitting visual information directly to the brain's visual cortex to help users perceive motion and light patterns.
The system comprises three integrated components working seamlessly together. Video glasses equipped with a miniature camera capture real-world visual scenes. A body-worn visual processing unit (VPU) then translates these captured images into precise electrical signals optimized for brain stimulation.
Finally, a wireless transceiver sends this processed data to an implanted cortical array, creating visual perceptions without requiring functional eyes.
Recent findings from March 2025 demonstrate remarkable stability and safety. Participants in the extended feasibility study continue using Orion devices at home and in their communities with zero major malfunctions reported after five years of continuous use. This realworld performance validates the system's durability and practical viability for daily life.
The feasibility study has been extended to six years to further evaluate long-term safety and explore effectiveness improvements.
While participants experience meaningful vision restoration, the system remains investigational and not yet FDA-approved for commercial use. Access is currently limited to clinical trial participants.

The unchanged core hardware design featuring camera-integrated glasses, body processor, and wireless implant interface suggests a mature, stable platform ready for the next phase of development.
This advance offers genuine hope for the millions of people living with profound blindness worldwide.

Imagine losing your sight, then having technology help you see again. It sounds like science fiction, but two groundbreaking approaches are making this reality for people with eye diseases that destroy vision.
Bionic Eyes: Artificial Sight Think of bionic eyes as tiny computers for your retina. The most advanced system, called Argus II, works by implanting a grid of microelectrodes directly onto the back of the eye. These electrodes act like artificial photoreceptors, sending electrical signals to the brain when they detect light.
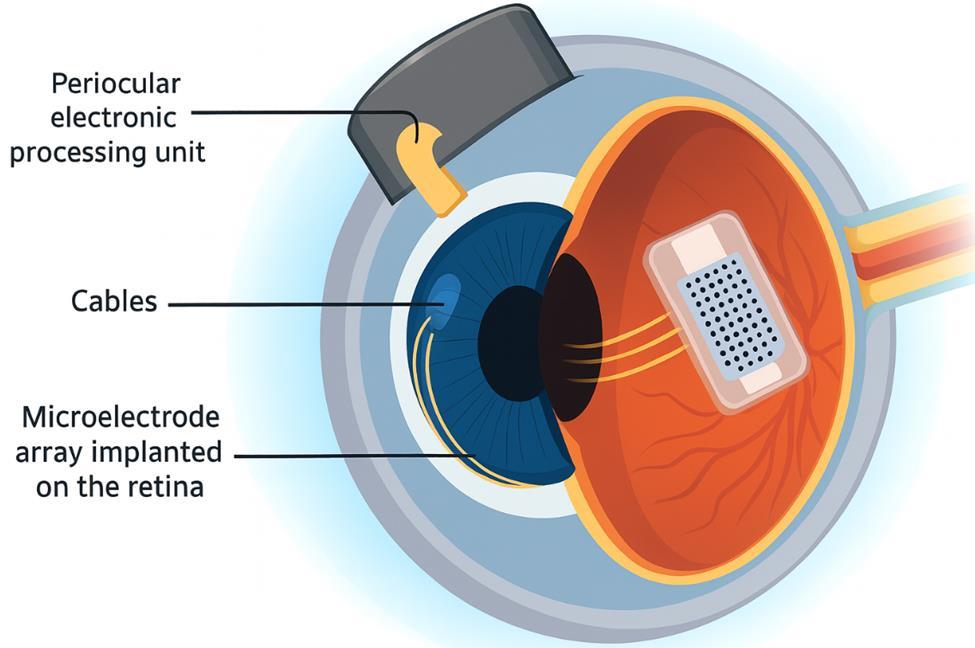
Here's how it works: a camera captures images and sends them to the implant, which then stimulates the remaining healthy nerve cells in the retina. While patients can't see in full color or detail, they can detect light, recognize shapes, and even track movement.
For someone who was completely blind, being able to navigate a room or see a loved one's silhouette is life changing.
Optogenetics: Reprogramming Cells to See.
The second approach sounds even more futuristic. Scientists are genetically modifying eye cells to make them light-sensitive, essentially turning ordinary cells into biological light detectors.
They inject harmless viruses carrying special genes that produce proteins called opsins. The same proteins that help us see naturally.
Recent clinical trials have shown remarkable progress. Patients with retinitis pigmentosa, a disease that gradually destroys vision, have regained the ability to identify shapes and objects after receiving optogenetic treatments.
Companies like Science Corp are pushing boundaries further, combining genetic modifications with sophisticated devices that translate visual information into signals the brain can understand.

When devastating accidents destroy facial features, cutting-edge technology is offering new hope for reconstruction. Scientists are combining DNA analysis with artificial intelligence to help surgeons rebuild faces, creating a powerful bionic approach that could transform reconstructive medicine.
Traditional facial reconstruction relies heavily on photographs, witness descriptions, or the surgeon's best judgment. But what happens when no photos exist, or when trauma is so severe that original features are completely unrecognizable? This is where bionic reconstruction steps in, using the patient's own genetic blueprint as a guide.

The process begins with DNA extracted from the patient's blood or tissue samples. Advanced AI algorithms analyze thousands of genetic markers linked to facial characteristics bone structure, nose shape, eye spacing, and jaw dimensions. These systems can predict how features
should naturally appear, providing surgeons with a genetic roadmap for reconstruction.
AI as Surgical Assistant Machine learning networks process vast databases of genetic-facial feature correlations, identifying patterns invisible to human analysis. The AI doesn't just predict individual traits it understands how multiple genes interact to shape overall facial architecture. This creates comprehensive 3D models that surgeons can use as templates during complex reconstructive procedures.
Deep learning algorithms are particularly valuable for processing the millions of genetic variations that influence appearance. They can weigh the relative importance of different genetic factors, helping surgeons prioritize which features to focus on during lengthy reconstruction surgeries.
Current Applications Several medical centers are beginning to integrate this technology into their reconstructive programs.
Patients with severe burns, traumatic injuries, or congenital facial differences can benefit from having their genetic "original blueprint" guide surgical planning. The technology is especially valuable for restoring symmetry and proportion critical factors in successful facial reconstruction.

While technology cannot yet create photorealistic predictions, it provides surgeons with scientifically grounded starting points rather than guesswork. As AI systems become more sophisticated and genetic databases expand, bionic facial reconstruction may eventually offer near-perfect restoration of original features, giving accident survivors not just function, but their genetic identity back.

In a groundbreaking advancement, researchers have successfully developed a technique to 3D bioprint living skin with hair follicle precursors, potentially revolutionizing reconstructive surgery and wound healing. This innovative approach utilizes fat tissue as a key component, allowing for the creation of multiple skin layers, including the hypodermis, which plays a crucial role in wound healing and hair follicle cycling.

The bioprinting process involves three main components: extracellular matrix extracted from human adipose tissue, stem cells obtained from the same adipose tissue, and a clotting solution to facilitate proper binding. These components are loaded into separate compartments of the bioprinter, enabling precise control over their deposition. The technique allows for intraoperative printing, meaning it can be applied directly during surgery to repair damaged skin more seamlessly.
This new method represents a significant leap forward in skin regeneration technology. Unlike previous attempts that only produced thin layers of skin, this technique creates a full, living system of multiple skin layers. The printed hypodermis has shown the presence of downgrowths, which are the initial stages of hair follicle formation.
The potential applications of this technology are vast, including more natural-looking reconstructive surgery outcomes, improved wound healing, and possible hair growth treatments. Researchers are now working to refine the process, aiming to mature the hair follicles with controlled density, directionality, and growth
The team is also exploring ways to match pigmentation across various skin tones, which could further enhance the aesthetic outcomes of reconstructive procedures. This breakthrough in 3D bioprinting technology holds promise for transforming the fields of dermatology, plastic surgery, and regenerative medicine, offering hope for more effective and aesthetically pleasing treatments for patients with skin injuries or diseases.

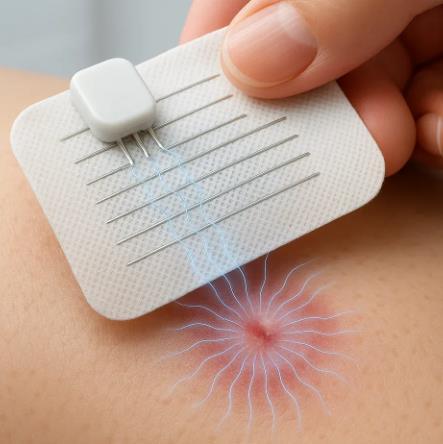
Scientists have created a revolutionary bandage that literally shocks wounds back to health. This water-activated electric dressing heals chronic wounds 30% faster than traditional bandages, offering hope for millions suffering from stubborn injuries that refuse to heal.
The Problem with Chronic Wounds Chronic wounds plague diabetic patients and others, creating open sores that heal slowly or never fully close. These persistent injuries dramatically increase amputation risk and can be life-threatening. Current treatments are prohibitively expensive and often require lengthy clinic visits, making patient compliance difficult.
How Electric Healing Works The ingenious bandage contains electrodes on one side and a small biocompatible battery on the other. Simply adding a drop of water activates the device, generating a gentle electric field for several hours. This electrical stimulation is the keyscientists have proven that electric fields naturally accelerate wound healing processes.
The flexible electrodes bend and conform to irregularly shaped wounds, ensuring the electric field flows from the wound's edges toward its center. This precise targeting optimizes the healing environment where it's needed most.
Remarkable Results Testing in diabetic mice revealed impressive outcomes. The electric bandages promoted faster wound closure, encouraged new blood vessel growth, and reduced harmful inflammation. Most importantly, wounds treated with electric stimulation healed 30% faster than those receiving standard care.
Game-Changing Advantages Beyond superior healing rates, these bandages cost just a few dollars each - a fraction of existing treatments.
Patients can apply them at home and continue daily activities, eliminating expensive clinic visits and improving treatment compliance.
Technology represents the first major advancement in diabetic wound care approved in over 25 years, potentially revolutionizing treatment for chronic wounds affecting millions worldwide.

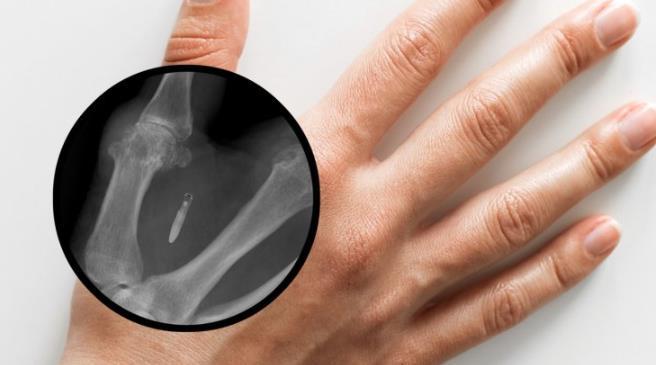
In a world where technology is rapidly evolving, Sweden stands at the forefront of a biohacking revolution: microchip implants that allow people to pay with a simple wave of their hand.

This tiny device, no larger than a grain of rice, is transforming the way Swedes interact with their environment, blurring the lines between humans and machine.
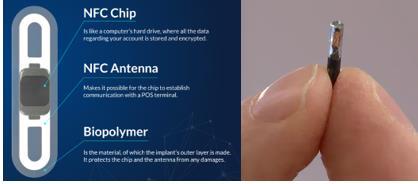
Sweden, known for its early adoption of cashless technologies, has embraced this futuristic payment method with open arms. Over 4,000 Swedes have already taken the plunge, replacing their wallets with a simple hand gesture.
But the implications of this technology extend far beyond convenience in payments. These microchips are also being developed to store crucial medical information.
In emergency situations, healthcare professionals could potentially scan a patient's hand to instantly access their medical history, allergies, and current medications, potentially saving precious time and lives.
The adoption of this technology in Sweden has been facilitated by a culture of trust in institutions and a willingness to embrace technological innovations. However, as the trend spreads to other parts of Europe and beyond, it raises important questions about privacy, data security, and the potential for misuse.
Despite these concerns, proponents argue that the benefits outweigh the risks. They envision a future where carrying physical cards or keys become obsolete, replaced by the ultimate all-in-one device: our own bodies.
As this technology continues to evolve, Sweden's experience serves as a real-world laboratory, offering valuable insights into the potential and pitfalls of integrating technology so intimately with the human body.

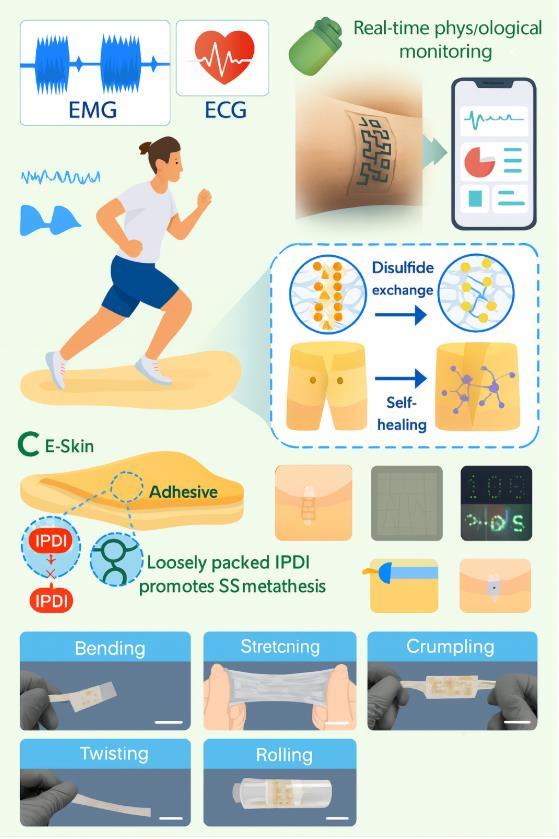
Electronic Patches That Fix Themselves in 10 Seconds will Transform Health
Imagine wearing a health monitor that repairs itself when damaged. Researchers have created the world's first electronic "skin" that heals within 10 seconds without any outside help—a breakthrough that could revolutionize wearable health technology.

The Problem Current fitness trackers and health monitors break easily from scratches, cuts, or daily wear. For athletes, construction workers, or patients needing continuous monitoring, device failure isn't just inconvenient it's potentially dangerous. A broken heart monitor during medical procedures or damaged fitness tracker during training could miss vital health warnings.
The Solution The secret lies in revolutionary materials that mimic how living skin heals. Scientists created their "E-Skin" using flexible plastic enhanced with special chemical bonds that automatically reconnect when broken.
Think of it like molecular Velcro. When damaged, broken bonds seek out their partners and reconnect, restoring strength and electrical conductivity. The healing happens at room temperature without external energy no heat, pressure, or special conditions needed.
Lightning-Fast Recovery While most self-healing materials take hours to repair, this E-Skin recovers over 80% strength in just 10 seconds.
The researchers demonstrated by completely cutting through a patch powering an LED light within seconds, the light flickered back on as electrical pathways reconnected
The Self-Healing Breakthrough In 2025, scientists made a leap forward with e-skin that can heal itself in just seconds after being damaged.
Using materials inspired by the stretch and softness of human skin like thermoplastic polyurethane these electronic patches recover over 80% of their sensing power in less than ten seconds.
No longer fragile, the new e-skin can survive the bumps and scrapes of real life, whether used for health monitoring or as sensitive robotic fingertips.
The secret lies in specially designed polymers that can reconnect their molecular bonds when damaged. Think of it like biological tissue repair, but engineered at the microscopic level. When a cut or tear occurs, the material automatically begins healing, restoring both its physical integrity and electrical conductivity without any external intervention.
Nature's Inspiration Meets Digital Innovation What makes this wearable so powerful? Embedded in each patch are ultra-thin sensors and circuits that act like tiny nerves.
These can continuously measure body signals such as heartbeat, muscle movement, or even joint position, sending the data wirelessly to a smartphone for real-time health feedback.
Technology draws inspiration from human skin's remarkable abilities its sensitivity to pressure, temperature changes, humidity, and even chemical molecules in the environment.
Modern e-skin can detect pressure as light as a feather's touch while remaining durable enough for athletic activities. Advanced versions incorporate pH sensors that monitor the acidity of sweat, temperature gauges that track body heat regulation, and even biomolecule detectors that could identify early signs of illness through skin secretions.
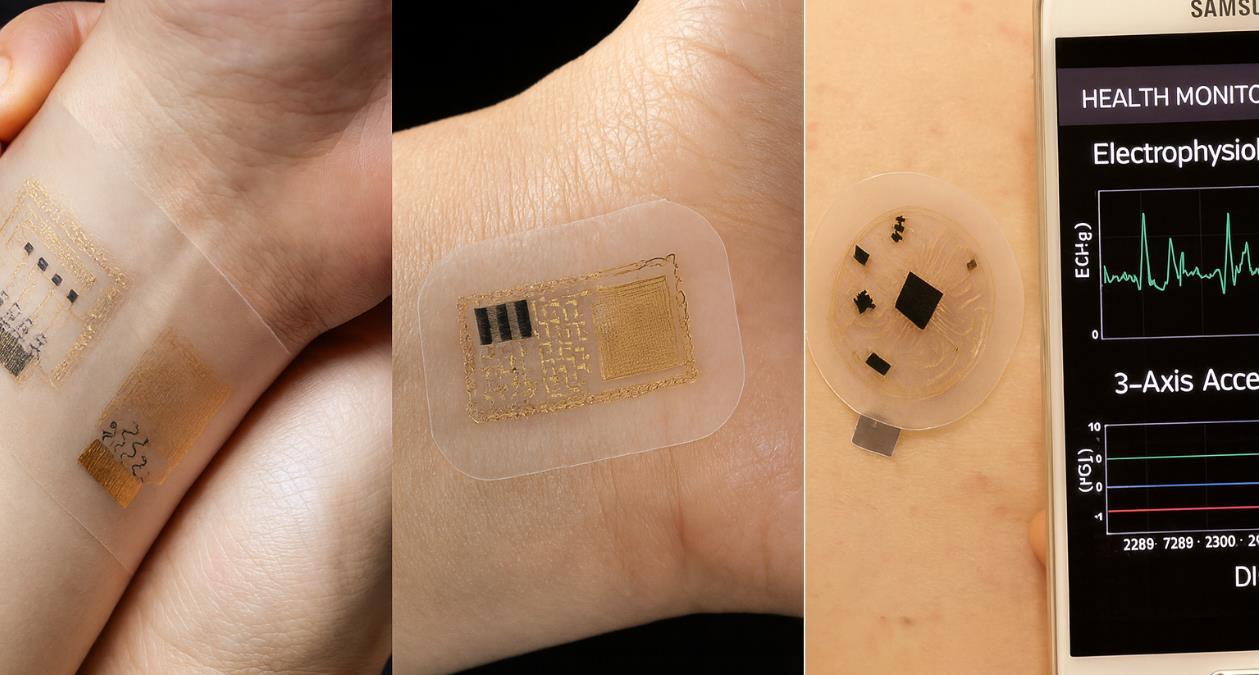
Intelligence That Adapts Powered by cutting-edge machine learning, these e-skin systems can now spot muscle fatigue, detect subtle health changes, and adapt to the user's needs all while sticking comfortably
to the skin. Artificial intelligence learns individual patterns, becoming more accurate over time at predicting health events or optimizing performance metrics.
Recent innovations have made e-skin truly human-adaptable. New printing techniques allow the technology to be customized and applied directly onto skin surfaces, creating seamless integration with the body. Some versions are even designed to be comfortably worn underwater or during sleep, expanding their potential applications.
Tested for Real Life Researchers have put the latest e-skin through tough tests: not just in the lab, but also underwater, during intense motion, and through temperature changes proving its strength for daily use.
These stress tests simulate years of wear in accelerated conditions, ensuring technology can handle everything from morning jogs to surgical procedures.
Tomorrow's Applications Looking ahead, e-skin offers big potential for wearable health tech, advanced prosthetics, and giving robots the gentlest human touch. Medical applications could include continuous monitoring of chronic conditions, early detection of skin cancer, or providing sensory feedback for prosthetic limbs. In space exploration, astronauts could use e-skin to monitor their health during long missions, while the self-healing properties ensure functionality in harsh environments.
Soon, we might all wear a little piece of the future, one that feels just like our own skin—only smarter, stronger, and impossible to outgrow.

Imagine controlling a robotic arm with your thoughts while actually feeling what it touches. This science fiction scenario just became reality for people with spinal cord injuries, thanks to breakthrough research that's rewriting the rules of artificial limbs.
Scientists have cracked the code for creating artificial touch sensations by directly stimulating the brain. Using tiny electrodes implanted in sensory regions, researchers can now "type" complex tactile messages straight into a person's consciousness. Participants report feeling object edges, textures, and motion across phantom fingertips sensations they haven't experienced in years.
"We are in another level of artificial touch now," explains lead researcher Giacomo Valle from Chalmers University. His team achieved what seemed impossible: transmitting the rich, nuanced world of human touch through electronic signals.
Previous brain-controlled prosthetics could only respond to mental commands—like a remote control for robot arms. This new system creates a two-way conversation between brain and machine. When the bionic hand grasps an object, sensors relay contact information back to the brain, enabling users to feel shapes, curves, and movement.
Two participants with brain implants demonstrated remarkable abilities, manipulating objects with unprecedented precision. The secret lies in sophisticated micro stimulation patterns that mimic natural nerve signals, fooling the brain into experiencing genuine tactile sensations.

The Bigger Picture This research addresses a crucial gap in prosthetic technology. Without sensory feedback, even the most advanced robotic limbs feel disconnected and clumsy. Touch provides the nuanced information needed for delicate tasks distinguishing between grasping an egg versus a tennis ball, or feeling when an object is slipping.
Future developments will integrate artificial skin and more sophisticated sensors, expanding the vocabulary of artificial touch. The ultimate goal: restoring the full richness of human tactile experience to those who've lost it

Imagine having an extra thumb at your disposal, controlled by your toes and capable of enhancing your hand's capabilities. This isn't science fiction; it's the reality of motor augmentation, exemplified by the innovative "Third Thumb" project developed at the University of Cambridge.
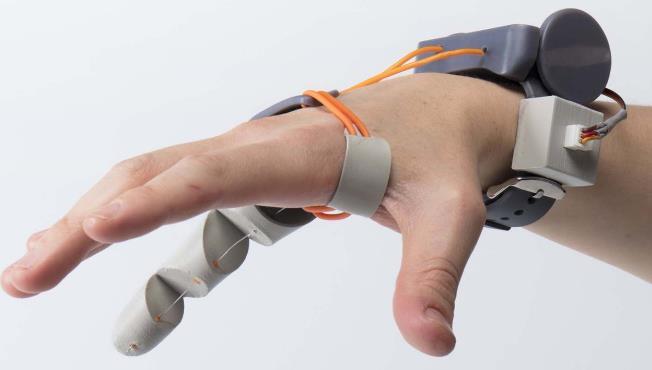
The Third Thumb is a 3D-printed robotic digit that attaches to the side of the hand opposite the natural thumb. Users control it through pressure sensors under their big toes ,the right toe moves the thumb side to side, while the left toe directs it up and down. This seamless integration of technology with the human body represents a significant leap in the field of motor augmentation.
What's truly remarkable about the Third Thumb is how quickly people adapt to using it. In a study involving nearly 600 participants aged 3 to 96, an astounding 98% were able to manipulate objects with the device
within just one minute of wearing it. This rapid adoption showcases the human brain's incredible plasticity and our ability to incorporate new "body parts" into our motor repertoire.
Video to watch : Testing the Third Thumb (youtube.com)

The implications of such technology are far-reaching. For individuals with disabilities, devices like the Third Thumb could offer new ways to interact with their environment, potentially improving their quality of life.
In the workplace, it could enhance productivity by allowing users to perform complex tasks more efficiently or handle objects that typically require two hands.
However, the Third Thumb isn't just about practical applications. It challenges our very conception of what the human body is capable of and pushes the boundaries of human-machine integration.
As we continue to explore and refine motor augmentation technologies, we may be on the cusp of redefining human physical capabilities.
The success of the Third Thumb also underscores the importance of inclusive design in technological development. By testing the device on a diverse range of participants, researchers ensure that such innovations can benefit everyone, regardless of age or background.
As we move forward, motor augmentation technologies like the Third Thumb promise to open up exciting new possibilities, potentially transforming how we interact with our world and expanding the limits of human ability.

Your arm is gone, but your brain still remembers how to move it. That phantom limb sensation, once a cruel reminder of loss, has become the key to bionic resurrection.
The Neural Connection
Modern bionic arms don't just strap on—they plug in. Surgeons now perform targeted muscle reinnervation, redirecting severed nerves to healthy muscle tissue.

When you think "close fist," those rerouted nerves fire, and sensors detect the electrical signals. The prosthetic hand obeys instantly, translating thought into titanium grip.
At the University of Utah, researchers have achieved something that borders on supernatural: they've given amputees the ability to feel through artificial fingers. Electrodes implanted in residual nerves send touch sensations directly to the brain.
Users can distinguish between cotton and concrete, feel the weight of an egg, and adjust their grip without crushing it.
These aren't just replacement parts they're upgrades. Bionic hands can exert crushing force that would shatter bone yet delicately thread a needle moments later.

Some designs incorporate multiple grip patterns programmed through machine learning, adapting to each user's unique neural signatures.
The LUKE arm, inspired by Star Wars, features multiple joints and can be controlled by muscle contractions, joysticks, or even foot pedals. Users learn to operate it intuitively, their brains adapting to command mechanical fingers as naturally as biological ones.
Scientists are developing arms with built-in screens, temperature regulation, and even modular attachments.
imagine swapping your hand for a drill or welding torch. Neural implants could eventually eliminate external sensors entirely, creating a direct brain-to-machine interface.
The boundary between humans and machine grows thinner with each breakthrough. Soon, losing a limb might mean gaining capabilities that flesh, and blood never could. The age of the enhanced human begins with a handshake half neural impulse, half silicon dream.

Robotic Suits Are Giving Paralyzed Patients Their Movement Back Stroke survivors lifting coffee cups with robotic arms. Paraplegic patients taking their first steps in years with mechanical legs. These scenes from science fiction are now medical reality, as rehabilitation exoskeletons transform how patients recover from devastating injuries.
Unlike industrial robots built for strength, medical exoskeletons focus on retraining the human body to move again. They come in two main types: upper-body devices for arms and shoulders, and lower-body suits for walking rehabilitation.
MyoPro by Myomo (USA) This powered arm brace reads faint electrical signals from a patient's muscles even when paralyzed and amplifies them into actual movement. When a stroke survivor thinks about bending their elbow, sensors detect the tiny muscle signals and motors complete the motion. The 2025 MyoPro 2x model is FDAapproved for home use, essentially functioning as a bionic prosthetic that helps users dress, cook, and regain independence.
Fourier M2 by Fourier Intelligence (China) Shanghai-based Fourier Intelligence has emerged as a global leader with their bilateral arm rehabilitation robot. The M2 uses "active motion control" it senses patient intentions and adapts in real-time, providing assistance for weak movements or resistance to build strength. At one-third the cost of Western competitors, it's making advanced arm rehabilitation globally accessible.
These devices mount to the torso and use sensors to detect what movement patients are attempting. The robot then provides just enough power to complete the motion, giving the brain feedback of success and gradually strengthening neural pathways.
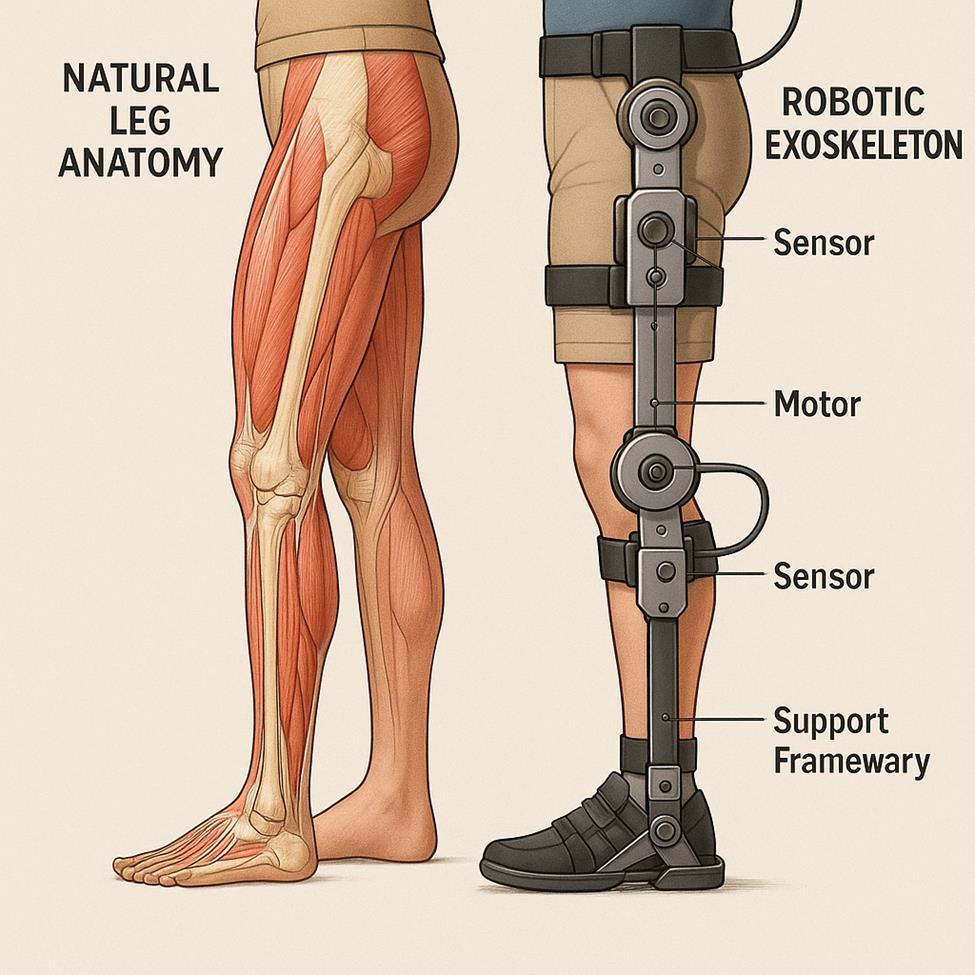
EksoNR by Ekso Bionics (USA) The first FDA-approved walking exoskeleton for stroke, spinal cord injury, and brain injury patients. This battery-powered frame supports the wearer from backpack to feet, guiding legs through natural walking patterns even when patients can't move independently. Therapists can adjust assistance levels—requiring patients to initiate steps or fully driving the legs during fatigue.

EksoNR provides real-time data on step count and gait symmetry, allowing more intensive practice than traditional therapy. Patients can take hundreds of steps per session versus the dozen possible with manual support.
HAL by Cyberdyne (Japan) The most advanced system uses the patient's own bio-electrical signals to trigger movement. When someone attempts to walk, their brain still sends nerve signals even if muscles don't respond. HAL's sensors detect these faint signals and instantly activate robotic joints to complete the intended movement.

This "cyborg suit" approach helps rewire the nervous system by enabling weak neural signals to produce actual movement, providing crucial brain feedback. Clinical trials show patients improve walking ability even without the device, suggesting genuine neural recovery.
How They Work
Upper-body exoskeletons align with natural joints and use EMG sensors to detect muscle activity or motion sensors to gauge assistance needs. The robot provides collaborative power—"helping patients do what they want to do" rather than moving them passively.
Lower-body suits strap onto legs and pelvis with motors at hips and knees. Safety systems include balance sensors and emergency stops, with therapists using overhead harnesses during training. Different modes accommodate various abilities from weight-shift activation for beginners to neural control for advanced users.
Real-World Impact Beyond retraining movement, walking exoskeletons provide crucial health benefits for paralyzed patients: improved bone density, circulation, and reduced spasticity. Psychologically, standing eye-level with others and controlling body movement proves powerfully therapeutic.
Modern devices double as digital therapy platforms, collecting data on each step and muscle activation to track progress objectively. This gamified approach motivates patients while providing therapists detailed recovery metrics.
Key developments are reshaping rehabilitation: Cost and Access: Asian competition is driving prices down dramatically. Medicare recently began covering personal exoskeletons, marking mainstream medical acceptance. Fourier's devices cost onethird of traditional alternatives.
Intelligence: AI analyzes patient data to personalize therapy programs. Fourier demonstrates group therapy scenarios where one therapist supervises multiple patients, each in adaptive exoskeletons.
Portability: Devices are shrinking rapidly. Fourier's X2 weighs just 18kg versus much heavier predecessors. Future soft exosuits using fabrics and smart materials promise easier wear.
Neural Integration: HAL's bio-electrical control represents the cutting edge—reading mind intent to drive robotic movement. This approach shows superior results in restoring voluntary function versus passive assistance.
Medical exoskeletons remain expensive (often over $100,000) and require professional supervision for most models. Battery life limits session duration, and complex fitting procedures restrict accessibility.
However, the trajectory is clear. What seemed like futuristic gadgetry a decade ago now represents standard care at leading rehabilitation centers. As technology matures, these bionic suits will likely become commonplace—giving millions of patients worldwide their first real hope of walking or reaching again.
The merger of human intention with machine strength represents more than technological achievement. It embodies the hopeful message that with proper support, the human body can recover and adapt even after devastating injury.
From high-tech labs to rehab centers globally, these robotic suits are literally helping people stand up and reclaim their lives.

Expert pianists face a frustrating reality: after years of intensive training, further practice often yields diminishing returns. This phenomenon, known as the "ceiling effect," occurs when skills plateau despite continued effort. The traditional approach of simply practicing more hours doesn't help - the brain has essentially learned all it can from repeated voluntary movements.
Researchers developed a custom robotic hand exoskeleton that can move individual fingers faster and more precisely than humanly possible. Think of it as a high-tech glove with mechanical fingers that can guide your digits through complex movements at superhuman speeds - up to 4 cycles per second, nearly twice as fast as expert pianists can voluntarily perform.
The key insight was providing pianists with sensory experiences they could never achieve on their own: experiencing impossibly fast, complex finger patterns through passive movement while their conscious mind simply observes.
The Experiment The researchers tested 118 expert pianists across three studies:
Study 1: Pianists practiced a challenging chord-trill pattern for two weeks until their performance plateaued. Then they were randomly assigned to experience either complex finger movements (mimicking advanced piano techniques) or simple movements (like basic grasping) through the robotic exoskeleton for 30 minutes.
Study 2: Different groups experienced various training conditions - fast complex movements, slow complex movements, fast simple
movements, active piano practice, or rest - to identify what specific elements drive improvement.
Study 3: Brain stimulation techniques measured neurological changes in the motor cortex before and after robotic training.


Scientists have developed a breakthrough technology that could transform everyday fabrics into personal power plants.
Triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs) made from electro spun nanofibers are turning the simple act of walking, breathing, or even typing into electricity that can power wearable devices.

The science behind this technology is elegantly simple: when two different materials rub together, they generate electrical charges through friction – the same phenomenon that makes your hair stand up after sliding down a plastic slide. Researchers have engineered ultrathin fibers, thousands of times thinner than human hair, from materials like PVDF (a special plastic) and nylon.
These nanofibers create textiles with enormous surface areas that can harvest energy from the smallest movements.
The magic happens in four main ways: contact-separation (like clapping your hands), lateral sliding (rubbing surfaces together), single-electrode mode (touching a surface), and freestanding layers that move freely. Each method captures different types of mechanical energy from human movement.
The applications emerging from laboratories worldwide are remarkable. Smart textiles can now monitor your breathing patterns, detect when you're walking versus running, and even sense your emotional state through subtle body movements.
Face masks embedded with these fibers can power air filtration systems using nothing but your breath. Athletic wear can track your performance while generating power for sensors and communication devices.
Researchers have developed self-powered medical sensors that monitor patients without batteries, smart home interfaces that respond to touch while generating their own power, and even underwater diving sensors that alert to dangerous conditions.
The breathable, washable nature of these fiber-based generators makes them ideal for integration into clothing and accessories.
The study reveals that different fiber materials excel in various applications. PVDF-based fibers work excellently for sensing and energy harvesting due to their piezoelectric properties. Nylon fibers, being naturally tribo-positive (gaining positive charge through friction), pair well with other materials.
Silk fibers offer biocompatibility for medical applications, while biodegradable options like PLA ensure environmental sustainability.
What makes these materials particularly promising is their ability to be "hybrid" – combining multiple materials at the nanoscale to create entirely new properties. Adding nanoparticles of metals, ceramics, or carbon materials can dramatically enhance performance.
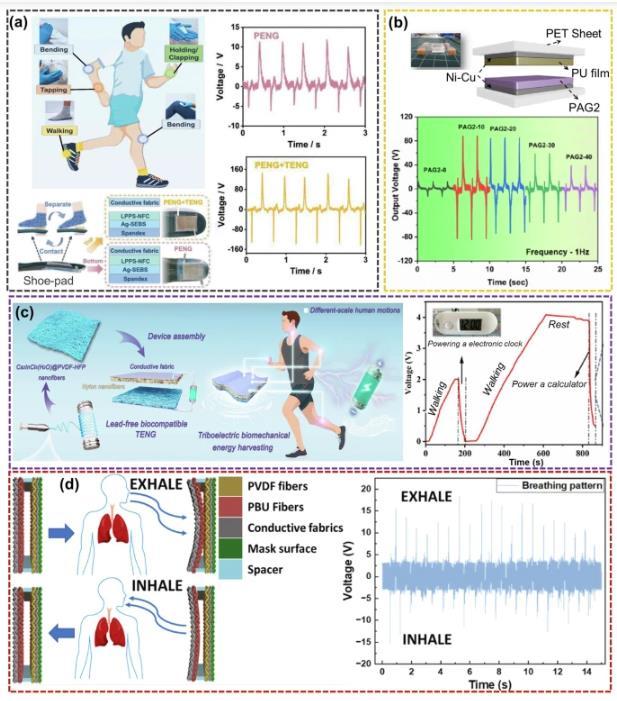
The manufacturing process, called electrospinning, is already wellestablished industrially, making large-scale production feasible. Current laboratory devices generate enough power to run small electronics like LED lights, calculators, and wireless sensors.

Now imagine this technology scaled to a billion people: Every step taken, every gesture made, every breath drawn could contribute to a vast, distributed energy network.
A billion people walking to work could theoretically generate gigawatts of clean, renewable energy. Your morning jog could power your smart home devices. A crowded subway car could become a mobile power station.
This vision represents more than just technological advancement, it's a paradigm shift toward truly sustainable, human-powered technology.
Rather than depleting Earth's resources, we'd be harvesting the inexhaustible energy of human activity itself.
The future may well be one where we are not just consumers of energy, but generators of it, turning every human movement into a contribution to our collective power needs.
Technology is advancing rapidly, and the first commercial applications are already emerging. We're standing at the threshold of an era where humans become their own renewable energy source

Your muscles don't particularly care whether the signal to contract comes from your brain or from a device that looks like it belongs in a mad scientist's laboratory. This insight has led researchers to investigate whether adding electrical muscle stimulation to traditional weight training can supercharge your gains.
What Is Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation? Neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) uses small electrical currents to trigger muscle contractions.
Think of it as temporarily hijacking your body's electrical systeminstead of your brain sending "contract now" signals through your nerves, a device does it for you.
These aren't the medieval torture devices you might imagine. Modern NMES units are user-friendly gadgets that deliver controlled electrical pulses through electrodes placed on your skin. Athletes and physical therapists have used them for decades for rehabilitation and recovery.
The Research Question Dr. Sudip Bajpeyi and his team at the University of Texas at El Paso wondered: what happens when you combine electrical stimulation with traditional resistance training? Instead of using NMES as a standalone treatment or for recovery, could it enhance actual workouts?
The Study Design The researchers conducted a meta-analysisessentially a study of studies - examining 13 different research projects that compared two groups:
• Control group: Traditional resistance training (
• Enhanced group: The same exercises while using NMES devices

Participants performed standard weight training routines - typically 812 repetitions, rest, repeat - over periods ranging from 2 to 16 weeks. The longer training periods showed better results, which makes intuitive sense.
:Strength gains: Adding electrical stimulation produced significantly greater strength improvements compared to traditional training alone (effect size: 0.31, meaning a moderate but meaningful difference).
Muscle mass: Similarly, the combination approach led to superior muscle growth compared to conventional weight training (effect size: 0.26).In practical terms, this means people who used electrical stimulation during their workouts saw meaningfully better results in both getting stronger and building muscle mass.
Under normal circumstances, your brain decides how many muscle fibers to activate during exercise. Even during intense training, you typically don't recruit all available muscle fibers simultaneously.
NMES changes this equation by providing an additional recruitment mechanism. While your brain activates muscle fibers through the nervous system as usual, the electrical device simultaneously triggers additional contractions. This creates a "superimposed" effectessentially forcing more muscle fibers to work than your brain would normally activate.
The result is more comprehensive muscle engagement during each repetition, leading to greater training stimulus and improved adaptations.
Dr. Bajpeyi's research extends beyond bodybuilding applications. His team is investigating how NMES might help people who cannot engage in traditional exercise, including those with mobility limitations or metabolic conditions like type 2 diabetes.
Since muscle tissue plays a crucial role in glucose metabolism, building muscle mass through NMES could help improve blood sugar regulation. The approach could be particularly valuable for populations who face barriers to conventional exercise.

The technology is surprisingly accessible. NMES devices range from clinical-grade equipment used in physical therapy to consumer versions available for home use. The key is proper application - electrode placement, stimulation intensity, and timing relative to exercise movements.
Training periods in the studies ranged from 2-16 weeks, with longer durations producing better results. This suggests that like any training adaptation, the benefits of combined NMES and resistance training accumulate over time. After decades of fitness enthusiasts searching for the perfect workout supplement, training protocol, or recovery method, it turns out one of the most effective enhancements might be literally shocking your muscles into submission.


Neko Health has secured $260 million in Series B funding to expand its AI-powered body scanning technology across new locations. The preventative healthcare company, co-founded by Spotify founder Daniel Ek and Hjalmar Nilsonne, has now raised over $325 million in total funding from investors including Lightspeed Venture Partners and General Catalyst.
How Technology Works the Neko Body Scan uses artificial intelligence to analyze millions of health data points during a non-invasive examination that takes just minutes to complete. Priced at £299, the scan evaluates multiple health indicators simultaneously, checking for early signs of various conditions before symptoms appear.
Technology can detect skin abnormalities that may indicate cancer, assess metabolic factors related to stroke and heart attack risk, measure blood sugar levels for pre-diabetes screening, identify early cardiovascular disease markers, and spot potential blood disorders. The AI system processes this information to provide patients with a comprehensive health assessment.
Current Operations Since launching in February 2023, Neko Health has completed 10,000 scans across facilities in Stockholm and London.
The company reports an 80% retention rate, with most patients scheduling follow-up appointments before leaving their initial scan. A global waiting list of over 100,000 people indicates continued demand for the service.
The scanning process appears to meet patient expectations, as evidenced by the high return rate and expanding waitlist. Technology has received recognition from medical experts as a useful tool for early detection and disease prevention.

Development of the AI platform will continue, with improvements to scanning capabilities and data analysis. The approach aligns with healthcare industry trends toward preventative care rather than reactive treatment.

Imagine checking your blood pressure as easily as putting on a BandAid. This futuristic vision is becoming reality as revolutionary wearable patches transform how we monitor one of our most critical health metrics. Gone are the days when bulky cuffs and clinic visits were the only way to track blood pressure the future of cardiovascular monitoring is literally sticking to our skin.
The Problem with Traditional Monitoring Current blood pressure measurement relies on inflatable cuffs that provide only snapshot readings. This approach misses the dynamic fluctuations that occur throughout our daily lives—the stress-induced spikes during meetings, the drops during relaxation, or the changes during exercise. For the 1.3 billion people worldwide living with hypertension, this limitation means missing crucial data that could prevent heart attacks and strokes.
A Wave of Innovation The year 2025 has witnessed an unprecedented breakthrough in wearable blood pressure technology. Companies like Novosound unveiled miniaturized ultrasound monitors at CES 2025, using thin-film sensors that detect arterial wall movement with clinical accuracy. Meanwhile, Biobeat's artificial intelligence-powered patches earned FDA clearance, proving that continuous monitoring can meet rigorous medical standards.
These devices employ sophisticated technologies like photoplethysmography (PPG), a technique that uses light to detect blood volume changes and advanced machine learning algorithms that learn your unique cardiovascular patterns. European research teams have developed patches capable of 14-day continuous monitoring, creating unprecedented datasets for personalized healthcare.
Seoul's Scientific Breakthrough At the forefront of this revolution stands Seoul National University, where Professor Seung Hwan Ko's team has achieved something remarkable: a blood pressure monitor that truly acts like a bandage.
Their innovation centers on a ingenious principle measuring the time difference between electrical signals from your heartbeat (electrocardiogram) and the mechanical pulse reaching your wrist.
The secret lies in liquid metal technology. This extraordinary material remains liquid at room temperature while conducting electricity perfectly, matching skin's natural elasticity. However, liquid metal's high surface tension makes it nearly impossible to shape into precise circuits.
The Seoul team solved this with laser sintering, a process that uses focused laser beams to fuse liquid metal particles exactly where needed, creating flexible electronics without chemicals.
The results are astounding: their patch maintains accuracy even when
stretched to 700% of its original size and survives over 10,000 stretching cycles.
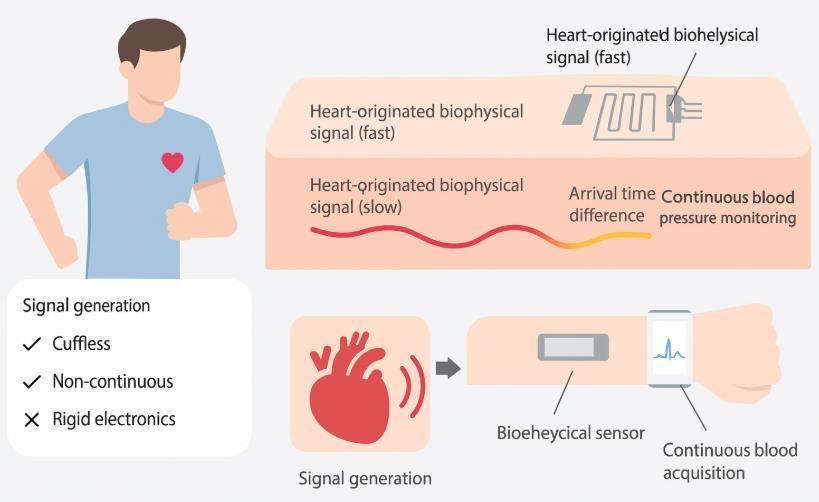
The Healthcare Revolution Ahead This technology promises to transform cardiovascular care from reactive to predictive. Patients with hypertension often called the "silent killer" can now monitor their condition continuously, detecting dangerous patterns before they become life-threatening events.
Athletes can optimize performance by tracking cardiovascular responses in real-time, while everyday users gain unprecedented insights into how stress, diet, and activity affect their heart health.
Seoul National University's breakthrough represents more than just a technological achievement—it's a glimpse into a future where preventing disease becomes as natural as checking the time on your smartwatch.
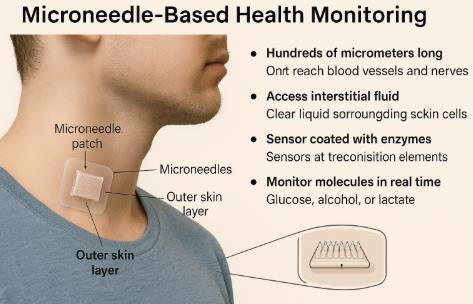
Imagine a future where a patch on your skin quietly streams critical health data no needles, no fuss, barely a pinch. That's the promise of microneedle-based wearables, a breakthrough that blends painless technology with powerful health insights.
Unlike standard needles, microneedles are just hundreds of micrometers long so small they penetrate only the outer skin layer with minimal discomfort, avoiding blood vessels and nerves entirely.
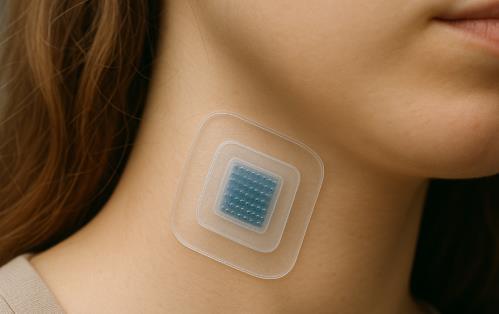
Crafted from advanced polymers, biocompatible metals, or even smart hydrogels, these tiny spikes form precise arrays that painlessly access interstitial fluid, the clear liquid surrounding your skin cells that's rich with clues about your body's chemistry.
On the tip of each microneedle sits a sophisticated sensor coated with specialized enzymes or molecular recognition materials, creating a miniature laboratory that tracks specific molecules like glucose, alcohol, or lactate in real time. This represents a fundamental shift from surface-level monitoring to true biochemical surveillance.
What sets microneedle wearables apart is their unique ability to deliver "molecular" monitoring—not just heart rate or step counts, but deep insights into your metabolism, hydration status, and even medication levels circulating through your system.
Research teams have already demonstrated continuous blood sugar monitoring and muscle fatigue detection, transmitting this vital information directly to smartphone apps for instant feedback and trend analysis.
Clinical trials reveal these devices rival traditional laboratory tests in accuracy while offering all-day comfort and seamless wireless connectivity. As material science advances, the newest microneedle patches are increasingly flexible, sometimes even self-healing, and engineered for extended wear without skin irritation or performance degradation.

The human brain generates constant electrical activity as millions of neurons fire in coordinated patterns. For decades, scientists have used electroencephalography (EEG) to monitor these neural signals, but the technology has remained confined to clinical settings with cumbersome scalp electrodes and tangled wires.
Now, researchers are exploring a different approach: monitoring brain activity through earbuds.
The Ear as a Neural Gateway The concept might seem counterintuitive the ear canal sits relatively far from the brain compared to scalp electrodes. However, the ear offers unique advantages. It provides a stable, enclosed environment naturally shielded from electrical interference, while sensors maintain consistent skin contact unlike scalp-based systems that can shift with movement, hair, or sweat.
More importantly, the ear canal lies surprisingly close to the temporal lobe, which governs memory, emotion, and auditory processing, making it an unexpectedly valuable monitoring location.
Technical Challenges Brain signals detected through the ear are extraordinarily faint measured in microvolts, thousands of times weaker than heart activity. This requires extremely sensitive sensors that can filter out electrical noise from muscles, heartbeat, and electronic devices.
Advanced algorithms and machine learning help extract meaningful patterns from this noisy environment,
Identifying electrical signatures of different brain states like deep sleep, REM sleep, focused attention, or stress responses.
Sleep research has emerged as the most promising application. Our brains cycle through distinct sleep stages, each with unique electrical patterns.
While traditional sleep studies require overnight lab stays with dozens of electrodes, in-ear EEG could bring analysis into homes, collecting data over weeks rather than single nights.
Technology enables real-time optimization detecting deep sleep phases to adjust temperature, lighting, or audio stimulation for better rest. Some researchers explore targeted audio interventions synchronized with brain waves to enhance sleep quality.
Forget bulky fitness trackers the future of health monitoring might fit on your finger. Smart rings are transforming how we track wellness, packing sophisticated sensors into a device smaller than a bottle cap that you can wear 24/7 without anyone noticing.
Tiny Device, Big Data These miniature powerhouses monitor everything your smartwatch does: heart rate, sleep patterns, blood oxygen levels, and stress indicators. But their real advantage lies in their invisibility.
Unlike chunky wristbands that scream "fitness enthusiast," smart rings blend seamlessly into daily life, making continuous health tracking effortless and socially acceptable.
Recent models have pushed boundaries further. Advanced temperature sensors can detect early signs of illness a feature that proved invaluable during the pandemic for fever monitoring. Some rings now track body temperature variations to predict menstrual cycles or identify optimal workout recovery times.
Intelligence That Learns The magic happens through artificial intelligence. These devices don't just collect data—they learn your patterns.
The AI analyzes weeks of information to provide personalized insights: "Your sleep quality drops when you exercise after 7 PM" or "Your stress levels spike every Tuesday morning." This personalized coaching helps users make meaningful lifestyle changes.
Battery life has dramatically improved, with top models running for a full week on single charge. This reliability is crucial for accurate health tracking, eliminating the data gaps that occur when devices die overnight.

The smart ring market is exploding with innovation. Companies are racing to add features like contactless payments, medication reminders, and even blood glucose monitoring for diabetics.
Some experimental models can detect early signs of depression through subtle changes in movement patterns and sleep. As sensors shrink and become more sophisticated, smart rings are positioning themselves as the ultimate health companions—unobtrusive, intelligent, and always watching over your wellbeing.
The question isn't whether you'll wear one, but which finger you'll choose.

A profound leap in breast cancer detection is emerging from the laboratories of MIT, where scientists have developed a revolutionary wearable ultrasound scanner that fits discreetly into a standard bra.
This conformable device, inspired by the personal experience of lead researcher Canan Dağdeviren, enables women especially those at high risk to check for suspicious tissue changes in the comfort of their own homes, providing frequent, user-friendly monitoring without the need for hospital visits.

Technology centers on a flexible, palm-sized patch equipped with miniaturized ultrasound sensors. Magnets secure the device to any bra, with strategically positioned openings that allow direct skin contact.
Users can move the scanner to cover six key regions of breast tissue and rotate for imaging from multiple angles, capturing data comparable in resolution to traditional hospital imaging systems.
Initial clinical studies show the patch can detect cysts and tumors as small as 0.3 centimeters, matching the performance of conventional ultrasounds and reaching up to 8 centimeters deep
What makes this innovation truly transformative is its accessibility and ease of use. Unlike standard mammograms, which are recommended every two or three years and require specialized radiological equipment,
The MIT scanner offers the possibility of non-invasive, routine checks for interval cancers tumors that arise between scheduled screenings and can be more aggressive.
Check Video https://youtu.be/Tn-cgYAnAGs
The design also aims to reduce global disparities in breast cancer detection, making frequent, reliable screening available even to those in underserved communities or remote locations.
The research team is now working to miniaturize the interface so it can be connected to a smartphone for instant imaging and analysis.
By leveraging advances in materials science, low-power circuitry, and artificial intelligence, this wearable device has the potential to redefine breast cancer care worldwide turning everyday clothing into a lifesaving medical tool.

Your throat knows exactly when you swallow that cookie or sip of coffee, and now a smart neckband can eavesdrop on those signals with startling accuracy.

This sleek device wraps around your neck like a high-tech choker, using three sensors to decode the subtle movements of your thyrohyoid muscle, the tiny muscle that contracts every time you swallow.
Combined with a microphone that catches acoustic signatures and an accelerometer detecting head tilts, the neckband creates a complete picture of your eating and drinking habits.
The magic happens through machine learning algorithms that distinguish between different throat activities.
Talking to a friend? The device knows that it’s not eating. Taking a sip of water while walking? It can tell the difference between your footsteps and your swallowing.
Beyond Calorie Counting Traditional food tracking relies on memory and honesty both notoriously unreliable. Users forget snacks, underestimate portions, or simply can't be bothered to log every bite.
This neckband eliminates human error by automatically detecting consumption events with 96% accuracy for single activities and 89% when you're multitasking.
The implications extend far beyond simple calorie counting. For people with diabetes, precise tracking helps optimize insulin timing. Athletes can monitor hydration without breaking stride.
Anyone trying to understand their eating patterns gets objective data instead of fuzzy recollections.
Comfortable Technology Unlike clunky previous attempts, this device prioritizes wearability. The mesh textile band stretches and twists naturally, while the sensor module curves gently against your throat
A rechargeable battery provides over 18 hours of monitoring, and the whole system connects wirelessly to your smartphone.
The researchers achieved something rare in wearable technology: a device that actually feels comfortable enough to wear all day while providing genuinely useful information about one of our most basic behaviors.
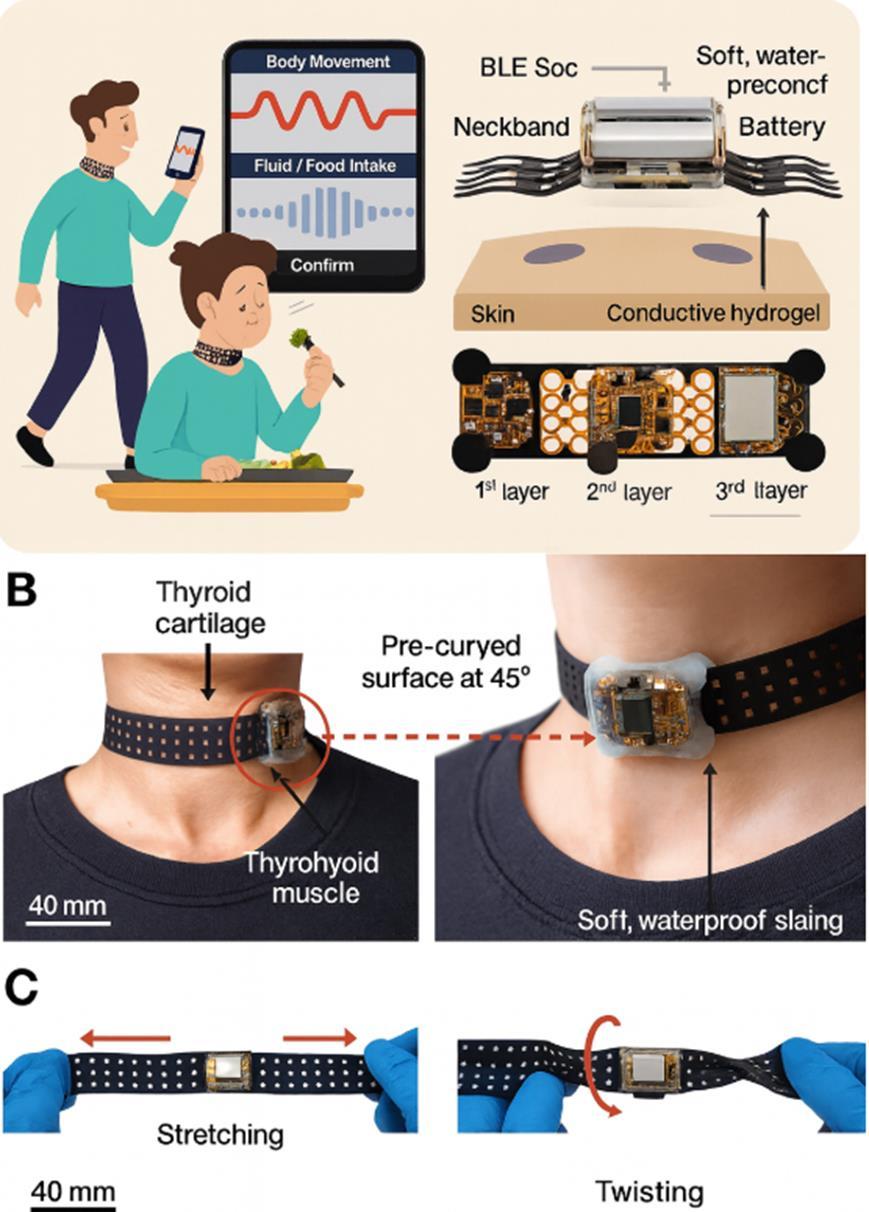

A new generation of wearable device is taking health monitoring in a different direction literally around your neck. Smart neckbands emerge as practical tools for tracking eating and drinking habits, offering detailed insights into nutrition patterns that were previously difficult to measure outside medical facilities.
The device combines three key technologies: muscle sensors that detect swallowing motions, motion detectors that track head and neck movement, and a small microphone that picks up sounds from eating and drinking. Positioned over the throat muscles, the neckband can distinguish between different activities like sipping water, chewing food, or simply talking.
The flexible design adapts to various neck sizes and daily movements. Researchers have focused on making the device comfortable enough for extended wear, addressing concerns about skin pressure and temperature that can make wearables irritating over time. Data is transmitted wirelessly to a smartphone for analysis and storage.
Intelligent Recognition A machine learning system processes the collected information, learning to identify specific patterns associated with different activities. Technology can recognize when someone is eating while walking or distinguish between drinking water and consuming thicker liquids. This level of detail provides a more complete picture of daily consumption habits.
Practical Applications The device shows promise for various health management scenarios. People with diabetes could better track their food intake timing and portions. Athletes might use it to monitor nutrition during training periods. Those following specific dietary plans could gain objective data about their eating patterns rather than relying on memory or manual logging.
Testing has confirmed the device's durability and safety for regular use, including resistance to sweat and daily movement.

While still in development, smart neckbands represent an interesting approach to nutrition monitoring. They could provide healthcare providers and individuals with more accurate information about eating habits, supporting better health decisions rather than guesswork.

A simple bracelet developed in France is making waves as a discreet tool to combat drink spiking, offering real-time detection of GHB one of the most commonly used substances in drink tampering cases.

How It Works The bracelet contains four test zones with reactive strips. Users simply place a drop of their drink on a test patch, and if GHB is present, the strip turns blue within moments. The device can be worn on the wrist, carried in a pocket, or kept in a purse, making it accessible when needed most.
Filling a Critical Gap GHB presents unique detection challenges—it disappears from blood within 6-8 hours and from urine in under 10 hours. This narrow window often leaves victims without biological proof when they seek medical help. The bracelet circumvents this timing issue by providing immediate on-site detection with 96% accuracy.
Real-World Impact Since launching in July, over 150,000 units have sold across 4,000 French pharmacies. At roughly six euros for a twobracelet set (testing eight drinks total), the device has already
prevented at least one confirmed poisoning attempt, according to user testimonials received by the company.
While women comprise 82.5% of victims according to French health data, the creators emphasize that men are also targeted sometimes for theft rather than assault.

Looking Ahead The company is developing an enhanced version capable of detecting five substances: GHB, cocaine, ketamine, scopolamine, and flunitrazepam. Beyond individual protection, widespread adoption could serve as a deterrent, potentially discouraging would-be perpetrators who know their targets can quickly test suspicious drinks.
This technology represents a significant step forward in personal safety, putting detection power directly into potential victims' hands.

Your brain produces a constant electrical symphony and now a simple headband can tune into that neural music to teach you the art of meditation. The Muse headband transforms invisible brainwaves into something you can actually hear. Using EEG sensors pressed against your forehead, it detects the electrical chatter of billions of neurons firing.

When your mind wanders during meditation, you hear stormy weather sounds. When you find your focus, peaceful birdsong fills your ears.
This isn't science fiction t's neurofeedback in real time. Your brain generates different patterns when calm versus distracted, and Muse translates these patterns into immediate audio cues that guide you back to tranquility.
The original Muse launched in 2014 as a meditation trainer, but Muse 2 expanded the concept in 2018. Beyond brain monitoring, it now tracks your heart rate through pulse oximetry and uses accelerometers to detect breathing patterns and body movement.
This multi-sensor approach creates a complete picture of how your physiology responds during meditation practice.The device isn't just for wellness enthusiasts—researchers use it to study Buddhist monks and investigate how meditation affects pain perception. It's bringing laboratory-grade brain monitoring to your living room.
Making the Invisible Visible Traditional meditation leaves you guessing whether you're improving. Muse eliminates that uncertainty by quantifying your mental state. Think of it as a fitness tracker for your mind instead of counting steps, it measures moments of calm.
Users consistently praise its simplicity and the app's engaging features, including progress tracking, goals, and meditation journals. The battery lasts about a week, and setup takes minutes rather than the complex calibration you might expect from brain-monitoring equipment.
The Reality Check
At $199 to $249, Muse represents a significant investment in your mental wellness. The basic device works well, but many guided sessions require ongoing subscriptions. Some advanced meditators find the feedback less useful once they've developed their practice, while beginners often discover it accelerates their learning curve dramatically.

The hardware can feel delicate, and the ongoing costs add up. But for those struggling to establish a meditation routine or wondering if they're making progress, Muse offers something invaluable: objective confirmation that your mind is indeed learning to find stillness in an increasingly chaotic world.

The Nix Hydration Biosensor has achieved a major milestone in 2025, receiving official approval from the Union Cyclist Internationale (UCI) for use in competitive cycling races.
This breakthrough allows professional teams to monitor hydration levels during actual competition, not just training sessions.
Race-Day Game Changer Previously restricted to training environments, the sensor can now be used in UCI-sanctioned events starting January 2025. This represents a fundamental shift in competitive cycling, where real-time hydration data can influence race strategy and prevent performance-limiting dehydration during critical moments.
How It Works The lightweight system combines a disposable skin patch with a clip-on sensor that measures fluid and electrolyte loss in real time.
Using AI-enabled sweat analysis, it provides instant personalized recommendations through a smartphone app, accounting for exercise intensity and environmental conditions. The technology integrates with Apple, Garmin, and soon Strava, Wahoo, and Zwift platforms.
Professional Adoption Elite teams like EF Pro Cycling have equipped all riders with the technology, reporting significant improvements in hydration management and overall performance. The non-invasive sensor proves particularly valuable for endurance athletes, though it's not yet suitable for swimming.

Expanding Reach Beyond competitive approval, the biosensor is now directly available to consumers in the UK and Ireland, expanding beyond its original North American market. This broader accessibility allows recreational athletes to benefit from the same precision hydration technology used by professionals.
The approval marks a pivotal moment where real-time physiological monitoring becomes integral to competitive strategy, potentially preventing heat-related issues and optimizing athletic performance across professional cycling and other endurance sports.


From restoring sight to enhancing strength, from tracking vital signs to predicting health outcomes, technology is redefining the boundaries of human capability.
What began as tools designed to heal impairments retinal implants, smart bandages, biosensors, and exoskeletons has evolved into a new paradigm of optimization. (Yes, we're officially upgrading humans now. Please check your warranty.)
Artificial intelligence now acts as an invisible partner, transforming streams of biological data into actionable insights, accelerating rehabilitation, and enabling devices to anticipate our needs before we voice them.
It's like having a mind reader, except this one actually wants to help you rather than judge your Netflix choices.
The convergence of neural interfaces, skin sensors, and adaptive wearables is no longer just compensating for lost functions; it unlocks new dimensions of perception and performance essentially turning us into superheroes, minus the cape and the questionable fashion choices.
Yet, amid this surge of innovation, one constant remains: the human identity at the center of it all. Because let's face it, no matter how smart our patches get or how many sensors we strap on, we're still the species that can't remember where we put our keys five minutes ago.
The true measure of progress is not in replacing human faculties but in extending them preserving our delightful quirks while expanding our potential to do amazing things (and possibly find those keys faster).
As these tools continue to evolve, they form a bridge between biology and intelligence, between healing and enhancement. Think of it as evolution with a tech support hotline.
The destination is not a future where humans are outpaced by machines, but one where technology exists to augment our strengths, restore our senses, and safeguard our humanity
while hopefully not judging us too harshly when we still choose pizza over salad despite our glucose monitor's gentle protests.
The goal remains unchanged: extending capability while preserving identity. After all, what's the point of having superhuman abilities if we lose our fundamental human talent for creative procrastination?
But guess what!... more fun … will be what this is going to happen in 10 years …. for sure…next page…

As we stand in 2025, smartphones still reign supreme but cracks are showing in their digital dominance. Will AI smart glasses eventually stage a coup against our pocket-sized overlords? The signs are promising, and frankly, it's about time.
Act I: The Denial Phase (2025-2028) "My phone isn't going anywhere!" insist the smartphone loyalists, clutching their devices like digital security blankets. "How will I doom-scroll TikTok with glasses?" they cry, not realizing that their glasses will soon doom-scroll for them, whispering "you've been watching cat videos for 47 minutes" directly into their ears.
Act II: The Bargaining Phase (2028-2032) Phones start getting smaller as glasses get smarter. People begin carrying "backup phones" – tiny devices that do nothing but exist in pockets, like a digital appendix. "I still need it for... um... emergencies?" they mumble, while their glasses handle calls, texts, navigation, and that crucial task of finding their keys (spoiler: they're in the fridge) and sensors patch are all the rage !
Act III: The Acceptance Phase (2032-2035) By 2035, pulling out a physical phone will be like whipping out a flip phone in 2015 –technically functional but socially mortifying. Your Gen Alpha kids will witness you actually touching a screen and gasp in horror: "Parent, why are you poking that rectangle? Are you having a stroke?"
The transformation will be swift and merciless. One day you're arguing that phones are irreplaceable; the next, you're explaining to your granddaughter why people once walked into fountains because they were staring at tiny screens instead of having information gracefully floating in their peripheral vision.
Your next upgrade won’t fit on your pocket… it will sit on your nose or on your sensor patch!

interesting engineering popular mechanics
Inverse mckinsey
technology review azoai scientific american the conversation
neuroscience news medium live science eetimes
investorplace spectrum scmp robb report science post serverobotics future sciences futurism spectra we forum gates notes azorobotics
Business insider wired technology review arstechnica new atlas trust my science robotics and automation phonandroid silicon india freethin

