
























































































































































Goodfix Industrial’s contact: Ms. Cece Ma Email: info@fixdex.com
Goodfix Industrial operates 4 modern production bases covering over 300,000 square meters, featuring 20 fully automated digital anchor production lines with impressive annual capacity. The company has established its own R&D workstations and holds 33 patents, focusing on innovation in concrete anchoring, architectural hardware connections, and support systems. The product range spans photovoltaic mounting systems, post-installed concrete reinforcement anchors, specialized anchors for nuclear power plants and subways, as well as small-packaged household fasteners like self-tapping screws and expansion bolts—meeting the demand in large infrastructure projects all the way to home repairs.
Among these, its photovoltaic mounting system, a one-stop solution, uses high-strength aluminum alloy and galvanized steel, capable of withstanding winds up to category 12 and customizable for various scenarios, accelerating the completion of renewable energy projects. Its nuclear-grade anchors, successfully manufactured within China, have greatly reduced cost and obtained national S1-level certification, offering high temperature and radiation resistance and providing double-layer safety assurance for major national projects. These achievements have positioned the company as a leader in the Chinese and global construction fastener market.
Goodfix Industrial’s international brand FIXDEX is registered in over 60 countries and holds certificates including ETA, ICC, FM, UL, and CE. With in-house environmental impact assessment and multiple surface treatment production lines, every product is traceable from material to the finished state, ensuring manageable performance. This cross-industry and closed-loop production enables the company to deliver highquality products with short lead times, favored by the world. By the end of 2026, the company plans to establish overseas branches and warehouses in Southeast Asia, the Middle East, Europe, Latin America, and Africa to strengthen global supply chain deployment.
Annually, about 6% of sales are reinvested into R&D. The company’s 2,300-square-meter R&D center is equipped with 60 advanced instruments and 7 pilot production lines to offer standard and customized products. Solutions are available for sub-markets such as curtain walls, elevators, seismic resistance applications, rail transit, and photovoltaics, helping partners stand out in their fields.
The company is committed to turning wastewater into clean water through its established large treatment facilities and recycling processes. It holds ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and OHSMS 18001 certificates and has passed national-level clean production audits. From material sourcing to waste disposal, it implements full-chain green manufacturing, making it the preferred environmentally responsible supplier for overseas buyers.
Supplying products for Huawei, BYD, and the Xi’an subway, Goodfix Industrial—now a firm cornerstone of Chinese constructions— continues to advance integration of ERP, CRM, and CAM systems, blending digitalization with automation to evolve into a world-class smart manufacturing facility. Guided by the principles of Strength, Durability, and Safety, it is dedicated to advancing construction hardware technology and installation methods to build a first-class Chinese brand on the world stage.



海迅:不銹鋼緊固件的全球基石


I
n today’s rapidly changing global market, quality and a stable product supply are crucial across all industries. Hisener, a leading fastener trader from China, is becoming an indispensable cornerstone for overseas countries in securing major infrastructure, public facilities, and industrial installations with its excellent stainless steel products and strong technical support.
Hisener: "We are continuing expansion and innovation in 2025!"
Since the launch of its automated smart factory, overseas demand for Hisener’s stainless steel products has steadily increased. To meet this, Hisener has added workshops to expand production. The company mainly uses high-quality 304, 316, and 410 series stainless steel materials, covering a wide range of specifications for various applications. It also innovates to enhance product performance according to overseas industrial needs. Notably, the bi-metal screws developed by Hisener achieve a maximum penetration strength of 12.5mm and possess strong pull-out resistance. Under equivalent performance conditions, the bi-metal screws offer better cost-effectiveness, earning positive feedback from many users. Hisener’s stainless steel screws are widely used in construction, solar energy, and machinery equipment sectors. Such demand from these industries continues to grow in 2025, driving Hisener’s participation in trade shows in Germany and other key international events to provide global buyers with one-stop purchasing services.
Contact: Simon Liang, General Manager
Email: simon@hisener.com
Hisener’s stainless steel deck screws have obtained CE certificate, while its stainless steel wood structural screws hold the ETA 22/0584 certificate. These certificates reflect the company’s strict quality standards and provide reliable assurance to customers.Their stainless steel products perform exceptionally well in harsh climates and corrosive environments. The company is equipped with salt spray and acid rain testing facilities, conducting continuous 24-hour tests on each batch to ensure corrosion resistance standards are met. These test data and laboratory reports fully demonstrate Hisener’s practical application capabilities of stainless steel products.

Beyond technology, Hisener’s stainless steel and bi-metal screws create multiple added values for users. Their strengths lie in quality and cost control, balancing price competitiveness with performance to attract buyers from both advanced and emerging countries. Especially in economic downturns, offering the most cost-effective products is the greatest value for buyers. Moving forward, the company will continue to increase R&D investment and seek high-quality talents to enhance customer experience.
Hisener is fully committed to global product promotion and sales, actively expanding wherever there is demand. This strategy reflects its emphasis on the global supply chain and its determination to provide excellent Chinese products worldwide. Starting in May, it intermittently releases product information on social media platforms and increases customer interaction to improve service satisfaction, further strengthening its position in the global supply chain and establishing Hisener as the cornerstone to count on.














































Since moving to Dongguan in 2002, Tobon Screws, a major manufacturer of precision screws benefited from the well-developed industrial cluster and the proximity to customers, has showed significant improvement in its manufacturing capacity and quality standards year after year. Its systematic and intelligent lean production has also enabled it to achieve great success in its development and cooperation with customers around the world. In order to further respond to the adjustments of its major customers' global deployment strategies and strengthen the development of a wider range of customer base, Tobon determined to set up its first overseas factory at the industrial park near Hanoi in mid-2024, and has already started mass production since H2 2024. The Vietnam factory not only replicates the management and manufacturing experience of the Dongguan factory, but also complies with many of the stringent requirements of a modern factory.
“Vietnam Tobon Screws is our 1st overseas factory. It is not only a complete replicate of the Dongguan HQ's operation with a higher standard, but also our first step to serve the overseas market from our overseas base,” said Vice General Manager Barry Liu.
Occupying an area of 2,500 sq m, Vietnam Tobon Screws is located in the Frasers Real Estate Industrial Park, which is home to a large number of international leading manufacturers, and is only 30 km away from the downtown of Hanoi. The spacious facility is equipped with more than 60 screw manufacturing machines from Japan and Taiwan, 6 full-size optical sorting machines, and 3 precision lathes. Like the Dongguan factory, which has 200 sets of production equipment, the Vietnam factory also focuses on the production of precision screws, with a maximum monthly capacity of 100 million pcs. These two factories not only share resources, but also work together to develop new products to expand the market, and the complementary nature of each other has allowed Tobon to ship from both the China and Vietnam factories to meet customers’ needs.
Many of Tobon's customers have established factories in Vietnam for years or are planning to invest in Southeast Asia. Considering customer needs, market potential and competitive advantages, Tobon has decided to locate its 1st overseas factory in Vietnam. Tobon also plans to process 1/2 of its capacity in Vietnam in the future to satisfy customers' needs with localized services.


With more than 30 years of experience in customer cooperation, Tobon understands what customers need. The product design & type database accumulated over the years enables Tobon to provide better fastening solutions for customers' needs such as low volume and high variety. Professional cold heading technology, advanced ERP/MES systems and automated equipment also allow it to help customers reduce cost and improve efficiency to ensure higher quality performance.
“We once served a customer with +600 types of products, half of which had an annual demand of less than 10,000 pcs. Not only did we provide support for their factories in Europe, America and Asia, but we also helped them reduce the management costs by more than 20% and their cost of products with improved performance by more than 40%,” said Liu.
“The Vietnam factory was established not only to respond to the changes in international trade and customer needs, but also as a demonstration of our optimism for the future of Vietnam's economy and manufacturing,” said Liu.
As a quality enterprise with social responsibility, Vietnam Tobon not only strictly complies with local environmental regulations, but also plans to transfer the experience of the Dongguan factory in implementing the CBAM reporting to itself. Vietnam Tobon will continue to deepen its cooperation with local manufacturing to provide better products. In 2025, it also plans to participate in important exhibitions in the U.S., Mexico, and Vietnam, hoping that its high-quality precision screws will be seen by customers around the world.
Tobon's contact: Barry Liu, Vice General Manager









The construction of Jinan Railway Line 6 was constructed a few years ago and the products it used to anchor the critical rail system were the high-strength, safe S-class anchor bolts supplied by Handan Tedun Fastener. Tedun’s anchor bolts feature advantages such as excellent resistance to vibration/tensile/shear, fireproof, fatigue-proof, and adaptability to cracking concrete, making them repeatedly specified in many large construction projects.

Tedun's anchor bolts have demonstrated high strength and load resistance in accordance with international standards. Not only has it passed the mechanical performance test of CNAS, the test of associate companies, and the strict EU ETA certification, but it has also passed the fire and seismic performance test, greatly enhancing the installation efficiency, saving the construction time of users, and ensuring the safety of use of products. Such innovative and practical products have been widely used in the reinforcement of curtain walls, railways, highways, subways, bridges, and other important projects.
”We once cooperated with a light rail construction project in Macau, mainly supplying them heavy duty anchor bolts. Every time, they would give us great recognition and praise that the quality of our products had been on par with the international standards,” said General Manager Xuan Wang.
Born for the R&D and production of innovative construction anchor solutions, Tedun Group's products include chemical anchors, mechanical anchors, heavy-duty anchors, self-tapping anchor bolts, wedge anchors, expansion anchors, etc. Currently it has 3 workshops with a total area of about 12,600 sq m and 2 warehouses with a total area of 4,500 sq m. 25 automated production lines in the factory are equipped with 46 sets of production machines and 13 sets of inspection instruments, creating a monthly production of 4,600,000 sets. 歐盟ETA認證 「特盾」錨栓
Anchor bolts, though small in size, are a key element in maintaining construction safety. In spite of the competition and challenges from industry counterparts, the domestic involution and varying quality on the market, Tedun still adheres to the principle of high-cost manufacturing and ensures the high safety and reliability of products for customers through various QC methods (including establishing a lab and carrying out QC control in each process) to reduce the defective rate.
Contact: Xuan Wang, General Manager
Email: sales05@tedunzg.com
“Strict quality control has enabled us to successfully obtain certificates from relevant fastener associations and provincial units,” added Wang.
Tedun currently sells nearly 90% of its products in the Chinese market, with the remaining 10% going to Dubai in the Middle East, Russia, France, Canada and other countries, making it a particularly important support for domestic and overseas customers in their pursuit of high quality, high technology and the creation of additional brand value. In 2025, Tedun also actively participated in the Fastener Fair Global in Germany, hoping to accelerate the expansion of overseas markets and expand the customer base.
“With the ETA certification as a new starting point, we will accelerate the R&D of new products and optimize the anchor solutions, so that we can work together with global construction customers to strengthen the foundation of construction safety,” said Wang.
Copyright owned by Fastener World / Article by Gang Hao Chang, Vice Editor-in-Chief






Founded in 2005, CHINFAST boasts two wholly-owned factories, namely Joystart Automotive Parts (Zhejiang) Co., Ltd. and Haiyan Yousun Enterprise Co., Ltd., with an export volume of 8,000 containers in 2023. Deeply rooted in the fastener industry, CHINFAST has established business relationships with more than 500 enterprises worldwide. To further strengthen its connection with the demands of first-tier retailers and distributors in Europe and the United States, CHINFAST Co., Ltd., which has been specializing in industrial fastener production for nearly 20 years, has actively expanded its business over the past five years. It has extended its business from the original focus on the manufacturing of multi-purpose wood screws, timber screw and decking screws to DIY fastener packaging services, aiming to create a new milestone for the sustainable development of the enterprise in the ever-changing global market.
The main products of CHINFAST are multi-purpose wood screws, trumpet head wood screws, and various window fastener series. Its patented pointed tail design offers superior speed performance compared to ordinary screws. Meeting the 1,200-hour salt spray requirement allows customers with anti-corrosion and rust-proof requirements to use them with greater peace of mind. CHINFAST is currently developing a product with a double-cut tail, which is in the trial production stage. The patented double-cut tail design elevates the product's performance


to a new level. This product combines the advantages of wood screws, self-tapping screws, and self-drilling screws, providing customers with a brand-new and efficient user experience.

The ERP smart factory management system ensures the traceability of all products from production to packaging. CHINFAST is equipped with double first-class laboratories, and the production process strictly follows the ISO9001 system. With 15 QC personnel, each batch of products must undergo initial inspection, process inspection, warehousing inspection, packaging inspection and final inspection, with records kept online for each step to ensure traceability. The responsibility of CHINFAST's QC team is to prevent any defective products reaching customers. CHINFAST is equipped with advanced cold heading equipment imported from Taiwan, China, which has more stable performance. At the same time, the workshop is equipped with automatic high-rise warehouses, automatic packaging lines and AGV robots, which play an important role in the company's production and packaging of high-quality fasteners.
Europe is one of the main markets of CHINFAST. In the future, CHINFAST will continue to develop deeply in Europe and expand into the South American and Australian markets. It is believed that with the expansion of these markets, CHINFAST's export volume will reach a new high.
As the president of Jiaxing Fastener Import and Export Association, General Manager Yu Fengming has spared no effort to develop the fastener export business. CHINFAST is an enterprise with 20 years of experience in fastener exports, holding ETA and CE certifications, as well as SMETA and BSCI reports. The automated production and packaging standards of JOYSTART also provide a guarantee for CHINFAST to explore


emerging markets. At the same time, as a factory with an average antidumping tax rate in Europe, YOUSUN benefits a larger number of European customers. CHINFAST is familiar to the needs of various markets and can quickly and accurately meet customer requirements, providing customers with high-quality after-sales service. In addition, CHINFAST has an experienced DIY packaging team, which has unparalleled competitiveness in terms of both financial strength and product professionality.
Contact: Mr. George Yu
Email: george@chinfast.com
Article by Gang Hao Chang, Vice Editor-in-Chief of Fastener World
Copyright owned by Fastener World

















































































































惠達特搜全球新聞
CMCA Fastener Subdivision President Xue Kang-Sheng Continues Term & Visits AoZhan Aviation
薛康生續任中國機械通用零部件工業協會緊固件分會會長並參訪奧展航空
The member assembly held in Hangzhou from March 21 to 22 saw Mr. Xue Kang-Sheng re-elected as president of the ninth council through voting, witnessed by key leadership representatives and industry professionals in attendance. He expressed deep gratitude for the support and trust bestowed by the representatives, pledging to continue guiding the fastener industry toward high-quality development. During the same period, he led a delegation from CMCA Fastener Subdivision to visit Aozhan Aviation Fasteners, gaining insights into their production quality control and manufacturing technologies. Through this exchange, they charted new development targets for the high-quality upgrade of Chinaese fastener industry.
Foshan Fastener Manufacturing Industry Association Anniversary Celebration and Members' Meeting
佛山市緊固件製造行業協會周年慶暨會員大會
On March 27, association members gathered to witness this significant event advancing Foshan's fastener industry development. President Mr. Heh Jian-Wei reviewed the resilience and innovation demonstrated by industry peers over the past year amid complex market conditions, highlighting breakthroughs in technological innovation, green transformation initiatives, supply chain collaboration, and global market expansion. Executive President Mr. Zhang Yong announced the association’s annual work plan, emphasizing efforts to promote collaborative development across the fastener supply chain and strengthen partnerships with upstream and downstream sectors such as steel, automotive, and machinery manufacturing.
Hong Kong Screw & Fastener Council (HKSFC) Kicks Off New Leadership with Grand Inauguration Ceremony
香港螺絲業協會以盛大就職典禮揭開新領導層

On March 28, 2025, HKSFC held its 11th Council Inauguration Ceremony and Spring Gala, marking the official commencement of the new council. Chairman Mr. Tsui Ping Fai expressed gratitude for societal support and underscored the critical role of fasteners in modern industry. He urged members to actively integrate AI technologies into industry practices to drive innovation and emphasized the association’s commitment to uniting stakeholders in elevating Hong Kong’s fastener industry to new heights.
China and US Reach Major Trade Breakthrough, Slash Tariffs 中美達成重大貿易突破,雙方大幅削減關稅
In a surprising and significant development, the United States and China announced on May 12, 2025, a major breakthrough in their ongoing trade conflict by agreeing to drastically reduce tariffs on each other’s goods for an initial 90-day period. This move marks a critical step toward de-escalating a trade war that has disrupted global markets, supply chains, and economic growth.
According to a joint statement, both nations acknowledged the importance of a sustainable, long-term, and mutually beneficial economic and trade relationship. Under the agreement, the US temporarily cut its overall tariffs on Chinese goods from 145% to 30%, while China
reduced its levies on American imports from 125% to 10%. These tariff reductions have been implemented since May 14. However, certain US tariffs related to fentanyl remain in place. China also agreed to suspend or cancel several nontariff countermeasures imposed on the US, including export restrictions on rare-earth minerals and blacklisting some American companies.

Economic pressures have mounted on both sides: the US recently experienced its first quarterly GDP contraction since 2022, and China’s exports to the US sharply declined, impacting its manufacturing sector. The agreement is viewed as a "best case scenario" start to broader negotiations aimed at further tariff reductions. Both countries will continue talks through a newly established mechanism led by Chinese Vice Premier He Li-Feng and US Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent, with discussions alternating between China, the US, or a third country. US officials emphasized a mutual desire to avoid economic decoupling and promote balanced trade. This breakthrough signals hope for improved US-China economic relations and global market stability in the months ahead.

The recent surge in tariffs on steel and aluminum imports, reinstated by the Trump administration at a 25% rate, has sharply increased the prices of screws and other industrial fasteners, affecting both manufacturers and everyday consumers. An example comes from a recent encounter at a Home Depot, where a customer wearing a T-shirt with an American flag lamented, “Screws are so expensive right now,” highlighting how tariff-driven price increases are felt by ordinary Americans trying to complete simple projects like building a chicken coop. This anecdote underscores how tariffs ripple down to everyday purchases, not just large industrial buyers.
The tariffs have forced manufacturers and suppliers to either absorb higher costs or pass them on to customers, pushing up prices for construction firms and small businesses reliant on screws and bolts. Some contractors warn that rising fastener prices may delay projects or force cancellations, tightening margins in an already challenging economic environment. The Federal Reserve noted tariffs have contributed to a 0.3% rise in consumer prices this year, with many companies selectively raising prices on affected items to offset increased import costs. While tariffs aim to protect domestic industries, the unintended consequence is inflationary pressure on essential components like screws, impacting both industry and consumers alike.
受美國關稅影響,韓國3月對美鋼鐵出口同比下降近19%
The Korea International Trade Association (KITA) released data showing that South Korea's steel exports to the United States in March 2025 were USD 340 million, representing an 18.9% year-on-year decline. The export volume also decreased by about 14.9%. This drop was mainly due to the U.S. government's imposition of a 25% tariff on all imported steel starting March 12, which also abolished the duty-free quotas previously granted to South Korea and other countries.

Industry insiders noted that since most transactions are completed several months in advance, it is still difficult to fully assess the tariff's impact, but initial effects have already begun to appear. In response to the tariffs, South Korean steel companies plan to increase their production within the United States. Hyundai Steel announced a USD 5.8 billion investment to build its first overseas electric arc furnace steel mill in Louisiana, expected to begin operations by 2029. The U.S. tariffs have raised concerns about rising costs in construction, automotive, and manufacturing sectors, potentially affecting supply chains and product prices.
福特因關稅影響調漲墨西哥製車款價格

Ford has announced immediate price increases on three of its Mexico-produced models effective May 2, 2025. Some models will see price hikes of up to USD 2,000, marking one of the clearest examples of how US auto tariffs are affecting consumers. The price adjustments follow President Trump's imposition of a 25% tariff on imported auto parts, which Ford estimates will cost the company USD 2.5 billion annually. Ford plans to absorb USD 1.5 billion of these costs but will pass on about USD 1 billion to customers through higher vehicle prices. Spread over the 2.08 million vehicles Ford sold in the US last year, this translates to roughly USD 480 added to the price of US-built SUVs and trucks.
Ford noted the company's reliance on foreign parts, such as carpeting and fasteners not sufficiently produced in the US, that are subject to tariffs. Despite this, Ford's strong US manufacturing base limits its exposure compared to rivals like General Motors, which expects USD 4-USD 5 billion in tariff costs.

歐洲ENVI支持歐盟碳邊境調整機制重大簡化方案
On May 12, 2025, the European Parliament's Committee on Environment, Climate Change and Food Safety (ENVI) endorsed the European Commission's proposal to simplify the EU CBAM. This simplification package, known as ‘Omnibus I,’ was introduced in February 2025 to improve the efficiency and accessibility of CBAM. MEPs approved several technical clarifications aimed at streamlining the implementation of CBAM. A significant change is the introduction of a new de minimis threshold of 50 tons of CO2 emissions per year, exempting around 90% of importers (who are mostly small and medium-sized enterprises and individuals who import small quantities) from CBAM obligations. Despite this exemption, the mechanism will continue to cover approximately 99% of CO2 emissions from imports in sectors such as iron, steel, aluminum, cement, and fertilizers.
The proposal also simplifies the authorization process for declarants, enhances emissions calculation methods, and improves the management of financial liabilities. Additionally, it strengthens measures to prevent abuse of the system, ensuring its integrity and effectiveness. Rapporteur Antonio Decaro emphasized the importance of balancing simplification with maintaining the environmental integrity of CBAM to effectively prevent carbon leakage. The full European Parliament voted on the negotiation mandate on May 22, 2025. Looking ahead, the European Commission plans to review the possibility of extending CBAM's scope to other high-risk sectors in early 2026. This ongoing development reflects the EU's commitment to driving global climate ambition and supporting a just transition to a lowcarbon economy.

歐盟鋼鐵業呼籲提前準備CBAM以防2026年貿易中斷
With the EU Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) set to begin on January 1, 2026, European steel industry players remain unprepared for its gradual implementation, warns Alexander Julius, president of EUROMETAL, in a presentation in Milan on May 8. Although CBAM's fiscal impact will start in May 2027, companies must register on the EU platform and declare emissions from Scope 1 and 2, with Scope 3 emissions to follow. Julius highlights a major cash flow challenge: importers will pay for only 2.5% of embedded emissions in 2026, rising to 100% by 2034, meaning financial reserves must be built well in advance. The complexity and extra costs, estimated at €56 per tonne for high-emission steel, could overwhelm smaller businesses and disrupt supply chains. Stronger collaboration across the supply chain and emission surcharges in contracts are recommended. The European Commission plans to propose amendments in late 2025, including expanding CBAM's scope downstream and anti-circumvention measures to protect EU manufacturing industries from carbon leakage through steel derivatives.


Suzhou Taicang Launches High-End Aerospace Fastener Production Project 蘇州太倉航空高端緊固件生產項目 正式啟動
On April 26, 2025, the project officially commenced construction in Taicang, Suzhou. The project is invested and built by China Aviation Industry Standard Parts Manufacturing Co., Ltd., a subsidiary of the Aviation Industry Corporation of China. The company specializes in the development and production of highend aerospace fasteners, providing professional connection technology solutions and integrated services for aerospace equipment construction. Once completed and fully operational, the project is expected to achieve an annual output value exceeding RMB 1 billion and generate over RMB 40 million in annual tax revenue. It is anticipated to inject new vitality into the local economy and promote the upgrade of the aerospace industry. Furthermore, the project aims to set a new benchmark for the expansion of the fastener industry in high-end fields, strengthening Taicang's position as a key hub for aerospace manufacturing.

永年區首席品質官培訓大會成功舉辦
On February 15, the Yongnian District Market Supervision Bureau organized the 2025 Chief Quality Officer Training Conference, attended by over 170 quality officers. The event focused on enhancing corporate quality management capabilities. Mr. Zheng Zhongwei, head of the bureau’s quality department, delivered an analysis of China’s Product Quality Law, using practical cases to clarify legal responsibilities. Deputy Director Mr. Gao Deju conducted specialized training on the roles and functions of chief quality officers, sharing advanced quality management methodologies.
浙江東明在泰國設立首家海外分公司
On April 21, 2025, the company opened its first overseas branch in Bangkok, Thailand, marking a major step in its global expansion. After 300 days of preparation and cooperation between its headquarters and the Thai team, the company aims to shift from exporting products to building a global ecosystem in stainless steel fasteners. This move responds to ongoing US-China trade tensions and rising US tariffs that disrupt supply chains. By localizing production and diversifying markets, the company seeks to reduce risks from unilateral trade policies and boost its international competitiveness. The Thai branch will focus on cross-border technical collaboration, innovative logistics, and deep market development to strengthen the company's presence in Southeast Asia and the world. This strategic step lays the foundation for further global growth amid changing trade dynamics.




江蘇法思特獲得汽車構件高強度緊固件螺栓專利
This innovation provides enhanced protection for fastening bolts, improving their durability and reliability in vehicle applications. The patented technology addresses common issues such as bolt loosening and corrosion, which are critical for ensuring the safety and performance of automotive assemblies. By leveraging advanced materials and precision manufacturing techniques, this new bolt offers superior mechanical strength and resistance to harsh environmental conditions. This development is expected to strengthen the company's position in the automotive fastener market and meet the increasing demand for high-quality, reliable fastening solutions in the automotive industry.
飛沃科技與貝克休斯簽署燃氣輪機C類零部件戰 略合作協議

On March 25, 2025, at the Baker Hughes Asia-Pacific Supplier Conference, Finework Technology was invited as a core supplier of gas turbines and signed a strategic collaboration agreement for gas turbine C-parts with global energy giant Baker Hughes. On March 31, Leo Di Filippo, Baker Hughes' Director of Rotating Parts Procurement, led a delegation to visit Finework and signed a procurement framework agreement. During the visit, Finework introduced the company's development and expansion plans. The delegation toured Finework's offshore hex bolt production base, aerospace industrial park, and CNAS laboratory, gaining deep insights into Finework's manufacturing strength and advanced testing capabilities. The agreements mark a milestone for Finework in the international gas turbine supply chain, positioning it for rapid growth in high-end equipment

manufacturing globally. Finework will supply core gas turbine components, including fasteners, to Baker Hughes worldwide. The partnership enhances Finework's global reputation and opens broad overseas markets. Finework plans to continue investing in R&D and deepen collaboartion with Baker Hughes to create more successful projects in global energy equipment.
新能源汽車市場帶動增長,超捷股份2025年第一季業績強勁

On April 24, 2025, Essence Fastening Systems released its Q1 financial report, showing revenue of RMB 189 million, up 38.36% year-on-year, and net profit of RMB 15.99 million, a 27.18% increase. Adjusted net profit excluding non-recurring items rose 47.22% to RMB 15.64 million. The company's main products include high-strength precision fasteners and special connectors used in automotive turbochargers, transmission parking control, exhaust systems, seats, lighting, and mirrors. In new energy vehicles, products are applied in battery trays, chassis, body, inverters, and battery swapping systems.
The company's 2024 annual report showed RMB 137 million in new revenue and RMB 212 million in orders. The company is actively developing new energy vehicle clients such as BYD, Tesla, and Xiaomi Auto, and key battery and motor system customers. Overseas expansion focuses on Mexico, targeting clients including Magna and Bosch. The company also formed a dedicated humanoid robot business team and secured commercial aerospace contracts for rocket structural parts. In 2025, the company plans to expand automotive export business, promote aerospace deliveries, and enhance profitability.

美國關稅衝擊,Tree Island Steel 公司2025年第一季營收下滑
Tree Island Steel, a leading North American wire and fastener products manufacturer, announced a significant revenue drop in the first quarter of 2025, citing the impact of new U.S. tariffs on imported steel and wire products. The company reported that Q1 revenues fell to USD 52.4 million, down from USD 60.7 million a year earlier. Management attributed the decline to reduced demand and higher costs caused by the tariffs, which have disrupted supply chains and increased the prices of raw materials. CEO Remy Stachowiak noted that the company is working to mitigate these challenges by optimizing operations and seeking alternative supply sources. The company's outlook for the rest of 2025 remains cautious as tariff uncertainties continue to weigh on the industry.


B&F Fastener Supply, a Minnesota-based distributor founded in 1988, announced it has changed its name to “BFirst Industrial.” The rebranding reflects the company’s dedication to providing top-quality products and services in the fastener industry. Despite the new name, existing contracts, orders, and accounts remain unaffected. BFirst Industrial emphasized that its commitment to customer support and operational excellence continues unchanged. Over recent years, the company has expanded by acquiring firms like TPI and Northern States Supply and now operates 17 locations across Minnesota, Wisconsin, Iowa, Nebraska, and the Dakotas.

Howmet Aerospace is well positioned to benefit from the recently announced US-China trade agreement, which aims to reduce tariffs and ease the trade tensions that have affected global supply chains and manufacturing costs. The aerospace sector, a critical market for Howmet, stands to gain as tariffs on key raw materials and finished aerospace components are lowered. Howmet, a leading manufacturer of advanced metal parts used in aircraft engines and structures, could see increased demand and improved profit margins as a result of reduced costs and expanded export opportunities. Industry analysts emphasize that the easing of trade barriers is expected to facilitate smoother cross-border transactions and reduce expenses for manufacturers like Howmet. The positive outlook reflects broader optimism about the easing of trade barriers and renewed growth prospects in aerospace manufacturing.


日本三住集團以3.5億美元收購Fictiv


Portland Bolt
In late April 2025, Portland Bolt & Manufacturing Co., a leading fastener supplier based in Oregon, announced the acquisition of Vermont-based Applied Bolting Technology. Applied Bolting is renowned for its industry-leading direct tension indicating washers, which are critical components in structural and industrial bolting applications. Portland Bolt's CEO Blake Ray expressed enthusiasm about the acquisition, highlighting that Applied Bolting's innovative products, strong customer relationships, and commitment to industry education complement Portland Bolt's existing business. The acquisition is expected to enhance Portland Bolt's product offerings, expand its geographic reach, and strengthen its manufacturing capabilities. John Cummings, President of Applied Bolting, added that the combined strengths of both companies will enable them to grow their market presence and continue delivering high-performance bolting solutions globally. This acquisition follows Portland Bolt's earlier purchase of Southern Anchor Bolt in South Carolina, reflecting the company's strategic efforts to broaden its portfolio and footprint in the fastener industry.


On April 17, 2025, Tokyo-based Misumi Group Inc. announced the acquisition of San Francisco-headquartered Fictiv Inc. in a USD 350 million all-cash deal. Fictiv, founded in 2013, provides on-demand procurement services for custom mechanical components to the U.S. manufacturing industry and operates in the U.S., China, India, and Mexico with about 400 employees and a global network of 250 manufacturing partners. Misumi said the acquisition will enhance its digital services and expand its customer base by integrating Fictiv's advanced technology and supply chain innovation. This move aims to elevate Misumi's value proposition from traditional production equipment to upstream product development in the value chain. Misumi's U.S. presence includes a supplier network with manufacturing and distribution centers. Fictiv's CEO Dave Evans called the deal a milestone, highlighting the shared vision to make a manufacturing platform that is smarter, faster, and more scalable. compiled by Fastener World














供應鏈重組覓生機 歐洲採購人潮湧現2025司徒加特螺絲展
As a bellwether for the European fastener industry, Fastener Fair Global is embracing its tenth edition in 2025. The show spanned halls 1, 3, 5, and 7, covering 52,000 square meters of exhibition space, showcasing over 1,000 exhibitors from more than 40 countries. The event also featured an innovation display area showcasing many creative new products for the year.
According to the organizer’s press release, the majority of exhibitors came from major fastener-manufacturing countries/regions, with high participation from Germany, Italy, Taiwan, China, India, Turkey, the Netherlands, the UK, Spain, and France. Fastener World (the Taiwan sales representative for Fastener Fair Global) led over 160 Taiwanese exhibitors there to participate, forming a highlight at the event. Additionally, exhibitors from other Asian countries like India, Indonesia, Vietnam, and Japan booked large booths to showcase products, aiming to secure more partnerships and competitive advantages in a challenging market environment.


Fastener World sent many exhibition specialists to our two booths in halls 5 and 7 (5-2621 and 7-4260). Besides matching visitors with fastener suppliers from various countries, we were interacting with other exhibitors to gather the latest market intelligence from European suppliers. Our specialists revealed that from the first day of the show, there was a surge of visitors, mostly European distributors and importers. We had many visitors flocking at our booths, including fastener manufacturers, buyers and distributors who mentioned that the global fastener supply chain is undergoing a "restructuring" in 2025, and that many importers are seeking to establish additional sources beyond their current suppliers and are building more robust and intimate supplier partnerships to face future challenges such as tariffs, carbon reduction targets, as well as potential economic and supply chain risks.
The organizer has announced that the next Fastener Fair Global will be held on April 6-8, 2027 at Messe Stuttgart. For more information, check out Fastener World’s website at www.fastener-world.com















GUANGQINGCHANG










As the world's largest and most leading international exhibition within the fastener industry, Fastener Fair Global not only attracts a great number of leading European and American fastener manufacturers and distributors (such as Sacma, Eurobolt, Ambrovit) to participate every year, but also draws the attention of many fastener businesses from Asia (Taiwan, China, India, Japan and S. Korea, for example) which regard the Fair as their first choice and a shortcut to entering the European market and expanding the market share in Europe. The exhibitors and visitors of the Fair are highly international. Not only did we see many familiar frequent exhibitors, but we also met many new faces on-site. Through face-to-face interaction at the Fair, exhibitors and visitors can accelerate the exchange of technical and industrial info between each other on the one hand, and open up unlimited possibilities for future bilateral cooperation on the other hand.





China, the world's most populous nation, experienced a demographic shift in 2024, with its population decreasing by approximately 1.39 million to reach 1.408 billion by the year's end. This figure represents about 17.2% of the global population, underscoring China's significant presence on the world stage. Economically, China maintained its position as the second-largest economy globally, with a Gross Domestic Product (GDP) estimated at US$17.8 trillion in 2023. In 2024, the country reported a GDP growth rate of 5.0%, reflecting its ongoing economic resilience and development. This growth trajectory highlights China's pivotal role in shaping global economic trends and underscores its influence within the international marketplace.1
China's fastening tool industry, encompassing products such as electric screwdrivers, rivet guns, nail guns, and torque wrenches, plays a pivotal role in both domestic manufacturing and global supply chains. In 2024, the sector demonstrated notable trends in production, exports, and imports, reflecting broader economic dynamics and market demands.
In 2024, China's production of interchangeable tools for hand tools, a category that includes various fastening tools, was estimated at approximately 939,000 tons, maintaining levels similar to the previous year. This steady output indicates the industry's resilience amidst fluctuating global demand and supply chain challenges. The production value was estimated at US$10.5 billion, reflecting a consistent performance over the period.
China's import of interchangeable tools for hand tools saw significant activity in 2024. The country imported approximately 34,000 tons of these tools, marking a 29% increase from the previous year. This surge suggests a
growing domestic demand for specialized or high-quality fastening tools not readily available through local production. In value terms, imports totalled around US$1.1 billion, indicating a modest increase. Germany emerged as the leading supplier, accounting for 41% of the total import volume, followed by Japan and Taiwan.
◆ The fastening tool trade between the European Union (EU) and China:
It is characterized by regulatory complexities and import restrictions, which often serve as challenges for Chinese exporters. The EU has stringent environmental and quality standards, which require Chinese manufacturers to meet specific certifications for their fastening tools to enter the market. Moreover, tariffs and anti-dumping measures have occasionally made Chinese products less competitive compared to those from European or other international suppliers. Despite these barriers, China’s cost-effective production remains an attractive selling point, particularly in construction and automotive industries, where there is continuous demand for affordable yet durable tools. China can explore opportunities by aligning its products with EU standards, focusing on eco-friendly manufacturing practices, and expanding partnerships within the EU’s large-scale infrastructure projects, which are expected to rise in the coming years.
◆ The trade of fastening tools between China and Japan:
It presents unique challenges due to Japan's preference for highquality and precision tools, a demand that often outpaces what Chinese manufacturers currently offer. Additionally, Japan’s robust domestic industry limits reliance on imports for certain types of fastening tools, particularly those requiring high precision or innovation. However, this presents a significant opportunity for China to tap into a niche market by providing cost-effective solutions for basic and medium-precision tools. As Japan looks to modernize its manufacturing sectors and pursue more automated solutions in industries like automotive, electronics, and robotics, China can expand its market share by offering innovative, efficient, and competitively priced fastening tools that help streamline production processes. The key opportunity lies in adapting to Japan’s high standards while leveraging affordable production capabilities to cater to growing automation demands.
1https://www.statista.com/statistics/263616/gross-domestic-product-gdp-growth-rate-in-china/ 2https://app.indexbox.io/table/8207/156/
◆ The relationship between Taiwan and China in fastening tool trade:
It is influenced by the political dynamics and competitive pressures between the two economies. Taiwan boasts a highly advanced manufacturing sector, with its local tool production often setting the standard for quality and innovation. Chinese manufacturers face stiff competition from Taiwan’s established brands, especially in high-end tools for precision industries like electronics. However, Taiwan’s demand for affordable, mass-produced fastening tools opens the door for China to provide cost-effective alternatives. By focusing on technological upgrades and providing tools that complement Taiwan’s high-tech industries, Chinese manufacturers can strengthen their position as suppliers of value-oriented fastening solutions. Additionally, trade agreements between China and Taiwan could help facilitate smoother trade flows, creating potential for increased market penetration in the Taiwanese market.
In 2024, China’s fastening tool industry demonstrated strong export growth, reinforcing its position as a key supplier in the global market. The country exported approximately 449,000 tons of interchangeable tools for hand tools, including fastening tools such as electric screwdrivers, rivet guns, and nail guns. This marked a 9.4% increase compared to the previous year, highlighting the sector's expanding international demand. The total export value of these tools reached US$4.8 billion, reflecting China's competitive pricing and large-scale manufacturing capabilities. The primary destinations for these exports included the United States (57,000 tons), Russia (33,000 tons), and India (27,000 tons), collectively accounting for 26% of China’s total fastening tool exports. This steady growth indicates China's continued dominance in the fastening tool trade, driven by its extensive production capacity and ability to meet diverse market needs.
◆ The trade relationship between China and the United States in fastening tools remains complex:
Shaped by tariffs, technological competition, and shifting supply chains. One of the biggest challenges is the ongoing U.S.-China trade tensions, which have led to high tariffs on Chinese-made fastening tools, making them less competitive in the U.S. market. Additionally, the United States has been actively reshoring manufacturing and investing in domestic tool production to reduce reliance on Chinese imports. However, despite these obstacles, China remains the largest supplier of fastening tools to the U.S., benefiting from its cost-effective production and large-scale manufacturing capabilities. The growing demand for electric fastening tools in the U.S. construction and automotive sectors presents an opportunity for Chinese manufacturers to innovate and produce higherquality, precision fastening tools that align with U.S. industry standards.
◆ The fastening tool trade between China and Russia:
It has seen significant growth, particularly as Russia shifts its supply chain away from Western countries due to sanctions and geopolitical tensions. The primary challenge in this trade relationship is logistics and payment difficulties, as international banking restrictions have affected transactions. Additionally, Russia’s preference for European-quality tools poses a challenge for Chinese manufacturers, who must meet stringent performance expectations. However, China has a
major opportunity to expand its market share in Russia by offering cost-effective, high-quality fastening tools, particularly for the infrastructure, energy, and defense industries. With Russian companies looking for reliable suppliers outside of Europe, Chinese fastening tool manufacturers can capitalize on this demand by establishing local partnerships and improving product reliability.
◆ The fastening tool trade between China and India:
It faces hurdles related to import restrictions and local manufacturing policies. The Indian government has implemented measures to boost domestic production under the "Make in India" initiative, leading to higher import duties on Chinese tools. Additionally, political tensions and border disputes occasionally disrupt trade flows. However, China remains a dominant supplier of fastening tools to India, given its competitive pricing and ability to supply in bulk. The rapid growth of India’s construction, infrastructure, and automotive sectors presents a major opportunity for Chinese fastening tool manufacturers. By investing in localized production units, joint ventures, or technology transfer agreements, Chinese firms can strengthen their foothold in the Indian market while navigating trade restrictions more effectively.

The Chinese fastening tool industry is poised for transformation, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 2.2% through 2035. This anticipated growth is likely to be driven by increased investments in research and development, a focus on producing high-end tools, and strategies aimed at reducing reliance on foreign technology. Additionally, the expanding domestic and international demand for advanced fastening solutions presents opportunities for Chinese manufacturers to innovate and capture larger market shares. Addressing challenges related to high-end tool manufacturing and leveraging growth opportunities.
Looking ahead, China's fastening tool industry is poised for transformation:
• Technological Innovation: Continued emphasis on R&D is expected to yield more advanced and specialized products, catering to evolving global demands.
• Market Diversification: Expanding into emerging markets and reducing reliance on traditional partners will mitigate risks associated with geopolitical tensions.
• Environmental Compliance: Adhering to stringent environmental regulations.














RMB 1,141.448 million in 2023.
1,203.135 vs. 1,141.448
5,181.470 vs. 5,219.639
Gem-Year Industrial’s 2024 revenue was RMB 2,369.711 million, up 2.3% from RMB 2,314.182 million in 2023. Net profit was RMB 130.141 million in 2024, compared to net profit loss of RMB 19.285 million in 2023. Total assets decreased to RMB 5,181.470 million in 2024 from RMB 5,219.639 million in 2023.
14,065 vs. 14,155
Alcoa's 2024 net sales were USD 11,895 million, up 12.7% from USD 10,551 million in 2023. The company ended the year with a net income of USD 60 million in 2024,









Chicago Rivet & Machine's 2024 net sales were USD 26.986 million, down 14.3% from USD 31.507 million in 2023. Net loss was USD 5.615 million in 2024, down from a net loss of USD 4.401 million in 2023. Total assets decreased to USD 23.370 million in 2024 from USD 27.830 million in 2023.
Fastenal's 2024 net sales were USD 7,546.0 million, up 2.7% from USD 7,346.7 million in 2023. Net income was USD 1,150.6 million in 2024, down 0.3% from USD 1,155.0 million in 2023. Total assets increased to USD 4,698.0 million in 2024 from USD 4,462.9 million in 2023.
Grainger's 2024 net sales were USD 17,168 million, up 4.1% from USD 16,478 million in 2023. Net income was USD 1,909 million in 2024, up 4.3% from USD 1,829 million in 2023. Total assets increased to USD 8,829 million in 2024 from USD 8,147 million in 2023.
4,698.0 vs. 4,462.9
8,829
8,147
2,330.503 vs. 2,331.101
2,737.350 vs. 2,704.724
1,324.180 vs. 1,341.660
Hillman Group's 2024 net sales were USD 1,472.595 million, down 0.2% from USD 1,476.477 million in 2023. Net income was USD 17.255 million in 2024, down from a net loss of USD 9.589 million in 2023. Total assets decreased to USD 2,330.503 million in 2024 from USD 2,331.101 million in 2023.
Simpson Manufacturing's 2024 net sales were USD 2,232.139 million, up 0.8% from USD 2,213.803 million in 2023. Net income was USD 322.224 million in 2024, down 8.9% from USD 353.987 million in 2023. Total assets increased to USD 2,737.350 million in 2024 from USD 2,704.724 million in 2023.
Trimas’ 2024 net sales were USD 925.010 million, up 3.5% from USD 893.550 million in 2023. Net income was USD 24.250 million in 2024, down 39.9% from USD 40.360 million in 2023. Total assets decreased to USD 1,324.180 million in 2024 from USD 1,341.660 million in 2023.









CHF)
Bossard's 2024 net sales were CHF 986.4 million, down 7.7% (in CHF) or down 5.8% (in local currency) from CHF 1,069.0 million in 2023. Europe, at 567.5 million, registered the largest sales portion generated within the group in 2024, but down 3.2% from the previous year. America registered the largest drop margin within the group, while Asia registered a sales gain both in CHF and local currency.


9,191 vs. 8,600



2,210.283 vs. 2,058.566
1,436.628 vs. 1,493.278
2,612.2 vs. 2,546.8

Bufab's 2024 net sales were SEK 8,035 million, down 7.4% from SEK 8,680 million in 2023. Net profit was SEK 551 million in 2024, down 4.0% from SEK 574 million in 2023. Total assets increased to SEK 9,191 million in 2024 from SEK 8,600 million in 2023.
1,490.8 vs. 1,392.7
Bulten's 2024 net sales were SEK 5,807 million, up 0.8% from SEK 5,757 million in 2023. Net profit was SEK 135 million in 2024, up 31.0% from SEK 103 million in 2023. Total assets increased to SEK 5,099 million in 2024 from SEK 4,852 million in 2023.

Lisi Group's 2024 revenue was EUR 1,794.050 million, up 10.0% from EUR 1,630.444 million in 2023. Net profit was EUR 56.006 million in 2024, up 49.2% from EUR 37.533 million in 2023. Total assets increased to EUR 2,210.283 million in 2024 from EUR 2,058.566 million in 2023.
Norma Group's 2024 revenue was EUR 1,155.128 million, down 5.5% from EUR 1,222.781 million in 2023. Net profit was EUR 14.696 million in 2024, down 47.1% from EUR 27.832 million in 2023. Total assets decreased to EUR 1,436.628 million in 2024 from EUR 1,493.278 million in 2023.
SFS Group’s 2024 net sales were CHF 3,031.1 million, down 1.3% from CHF 3,073.0 million in 2023. Net profit was CHF 241.3 million in 2024, down 9.2% from CHF 266.0 million in 2023. Total assets increased to CHF 2,612.2 million in 2024 from CHF 2,546.8 million in 2023.
Vossloh's 2024 revenue was EUR 1,209.6 million, down 0.38% from EUR 1,214.3 million in 2023. Net profit was EUR 63.2 million in 2024, up 63.3% from EUR 38.7 million in 2023. Total assets increased to EUR 1,490.8 million in 2024 from EUR 1,392.7 million in 2023.
Würth's 2024 sales were EUR 20,214 million, down 0.8% from EUR 20,396 million in 2023. Net income was EUR 672.4 million in 2024, down 40.2% from EUR 1,124.9 million in 2023. Total assets increased to EUR 19,272.9 million in 2024 from EUR 17,995.2 million in 2023.



16,450 in
vs. 16,683 in
Amatei’s 2025 revenue was JPY 5,583 million, up 0.9% from JPY 5,533 million in 2024. The company ended the year with a net profit of JPY 142 million in 2025, up 6.5% from JPY 133 million in net profit in 2024. Total assets decreased to JPY 5,231 million in 2025 from JPY 5,357 million in 2024. The company forecasts 2026’s revenue at JPY 5,700 million, up 2.1%.
JPF's 2024 revenue was JPY 5,040 million, down 1.3% from JPY 5,108 million in 2023. The company ended the year with a net profit of JPY 509 million in 2024, compared to a loss of JPY 108 million in net profit in 2023. Total assets decreased to JPY 5,785 million in 2024 from JPY 7,459 million in 2023. The company forecasts 2025’s revenue at JPY 5,330 million, up 5.7%.



in

in 2023
in
in

Mitsuchi’s 2024 revenue was JPY 13,147 million, up 4.7% from JPY 12,555 million in 2023. The company ended the year with a net profit of JPY 419 million in 2024, compared to a loss of JPY 32 million in net profit in 2023. Total assets decreased to JPY 16,450 million in 2024 from JPY 16,683 million in 2023. The company forecasts 2025’s revenue at JPY 13,872 million, up 5.5%.
Nifco’s 2025 revenue was JPY 353,038 million, down 5.0% from JPY 371,639 million in 2024. The company ended the year with a net profit of JPY 44,767 million in 2025, up 145.3% from JPY 18,252 million in 2024. Total assets decreased to JPY 379,816 million in 2025 from JPY 380,405 million in 2024. The company forecasts 2026’s revenue at JPY 348,000 million, down 1.4%.
Nitto Seiko's 2024 revenue was JPY 47,069 million, up 5.2% from JPY 44,744 million in 2023. The company ended the year with a net profit of JPY 2,199 million in 2024, up 26.8% from JPY 1,734 million in 2023. Total assets increased to JPY 55,604 million in 2024 from JPY 53,344 million in 2023. The company forecasts 2025’s revenue at JPY 50,100 million, up 6.4%.
Sanko Techno’s 2025 revenue was JPY 21,250 million, up 0.5% from JPY 21,142 million in 2024. The company ended the year with a net profit of JPY 1,122 million in 2025, down 35.5% from JPY 1,740 million in 2024. Total assets increased to JPY 26,558 million in 2025 from JPY 24,629 million in 2024. The company forecasts 2026’s revenue at JPY 22,000 million, up 3.5%.
Torq’s 2024 revenue was JPY 22,409 million, up 3.0% from JPY 21,757 million in 2023. The company ended the year with a net profit of JPY 895 million in 2024, up 5.9% from JPY 845 million in 2023. Total assets increased to JPY 33,680 million in 2024 from JPY 32,689 million in 2023. The company forecasts 2025’s revenue at JPY 23,100 million, up 3.1%.



662,367
653,167






全新SBW4軌道緊固系統

Voestalpine Fastening Systems has launched the SBW4 rail fastening system, an innovative upgrade to the long-standing SBW3 system widely used in Poland’s railway infrastructure. Building on decades of experience, the new SBW4 addresses key

This advanced wood screw by Hillman features a dual thread design that enables 30% faster installation while maintaining strong holding power. Tim Ferguson, Hillman’s VP of Product and Engineering, highlighted the fastener’s ability to eliminate pre-drilling with a selfstarting tip and optimized threads that reduce wood splitting. The screw also includes a star drive to prevent cam-out, integrated countersinking blades for clean finishes, and a no-split twist shank for durability.



challenges such as assembly ergonomics, electrical resistance, material weight, and automation compatibility The SBW4 features a redesigned SB3/5 cast iron anchor and WIW60C insulating clamp that standardize clamp positioning and simplify manual installation. A hollow anchor head reduces weight by 20%, cutting production and transport costs while lowering environmental impact. The PWE6094R rail pad’s improved lateral ribs enhance electrical resistance, consistently exceeding safety standards (EN 13481-2). The system is designed for integration into automated assembly lines, boosting efficiency and reducing errors. Tested rigorously at the Railway Institute in Warsaw, the SBW4 meets stringent quality and safety criteria, with all components patented for innovation. This system promises faster, more reliable track laying with a smaller carbon footprint, offering economic and ecological advantages for rail construction and maintenance.
Designed for decks, subfloors, framing, and fences, the Power Pro fasteners improve speed and efficiency in wood construction. Hillman plans to release complementary accessories in Q3 2025, such as magnetic tool holders and TrapJaw® spring-loaded pouches, along with durable beams and joist tapes.


太陽能支架用的隱藏式緊固件
Martin Roofing and Solar has won a prize from the U.S. Department of Energy’s Solar Energy Technologies Office (SETO) as a semifinalist in the American-Made Solar Prize program. The company’s innovation, the Hidden-Fastener Solar Mount (HFSM), is designed for asphalt shingle and composite slate roofs and eliminates the need to drill holes in the exterior roofing layer.

Unlike traditional solar mounts that penetrate all roof layers, HFSM installs beneath the roofing layer by attaching through the nail strip. This method avoids removing shingles; installers simply lift the shingle seal, install the mount, then reseal the shingles to cover fasteners. It can be used on existing roofs or integrated during reroofing, a common time for solar installation.
Constructed from durable, U.S.-made 5052-grade aluminum, each mount weighs just 0.6 lbs. Preston Nelson, Martin Solar’s director, highlights HFSM’s ability to virtually eliminate leak risk, offering installers greater confidence in rooftop solar installations.




















超低推力單軸自動螺絲鎖付機
Nitto Seiko (Japan) officially announced the new "FEEDMAT® FM513 Series Ultra-Low Thrust SingleSpindle Automatic Screw Driving Machine." This new product is designed for industries with stringent component performance requirements such as the automotive sector. It effectively reduces the thrust applied during screw fastening, minimizing the risk of damage to screws and substrates, thereby enhancing product quality.
The new model employs digital thrust control technology to finely adjust the thrust during the fastening process, preventing excessive pressure that could cause screw seizing or substrate deformation. It also increases fastening speed by 40% compared to traditional products, significantly shortening production cycles. It is especially suitable for fastening screws in deep or specially shaped parts, meeting the demands for both "finer" and "faster" fastening.
Nitto Seiko emphasizes that this product integrates a screw feeder, fastening unit, and controller into a comprehensive system. Combined with last year's high-precision low-torque NX driver, it creates a rare complete screw fastening solution in the industry, providing a more efficient and reliable technological platform for automated production lines.



K&K Engineering’s new inspection machine, the “QV-7100AI,” utilizes AI to distinguish between good and defective products, while also enhancing the user operation experience. The goal is to reduce the workload of on-site inspection tasks.

The QV series inspection machines are centered around “High Quality Vision System,” offering customized models tailored to different inspection targets and building a solid track record. The newly launched “QV-7100AI” emphasizes operational efficiency and user experience on the shop floor. Through repeated research, the AI-based recognition function is integrated with an intuitive user interface, enabling quick setup and precise inspection. This model further expands the QV series product line and strengthens the company’s technological presence in the field of automated inspection.


Tsukimori Kougyo developed this product to enable visual confirmation of fastening completion while ensuring stable axial force. Testing on M20 specifications under 280Nm tightening torque showed that after a 17-minute NAS vibration test, traditional hexagonal 4.8 bolts retained only 180Nm (64% of the original torque), whereas this product maintained 260Nm (93%), improving the axial force retention by 44%. The technology originated from a 2021 R&D project subsidized by Japan's Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, and secured a patent in 2022. Combining specialized wrenches with cold forging techniques, it streamlines installation while ensuring torque accuracy, supporting specifications up to M36 and offering innovative solutions for anti-loosening needs in construction parts.
Compiled by Fastener World



Data note: The data for this article is derived from the US Census trade statistics. US Census trade statistics analyze imports and exports on all modes of transportation. That value is calculated in USD by general FOB for imports and FOB for exports. Fasteners in this article are defined as any product under HS Code 7318 (screws, bolts, nuts, coach screws, screw hooks, rivets, cotters, cotter pins, washers and similar articles, of iron or steel). The volume in terms of mass is recorded in Gross Weight (KG).
The ongoing trade tensions between the United States and China have sent ripple effects throughout the global fastener supply chain, fundamentally reshaping trade flows, manufacturing practice and strategic planning across multiple industries. These dynamics are beginning to be seen in the first few months of 2025 through statistical trade data and the shift in fastener trade between these two major economic powers. Additionally, the escalation of tariffs and regulatory measures are beginning to have immediate impacts on trade policies and international market strategies. Ultimately, the manufacturers and importers are managing operational pressures including rising costs and logistical disruptions deepening the economic divide between the U.S. and China.
Looking at the fastener supply chain on a holistic level, the U.S. primarily sources from Taiwan and China. Historically, Taiwan has maintained upwards of 30% of the market share of fastener trade to the U.S., followed by China that has maintained anywhere from 17% to 20% of the total market share in FOB value (Table 1-1 to 1-2). Countries such as Japan, Canada and Germany follow suit, accounting for upwards of 5% to 10% of the total market share. In February 2025, U.S. fastener imports from China totaled USD Table 1-1. U.S. Import Origins of Fasteners (2022-2023)
95 million (Table 1-3), down from USD 121 million in January – a sharp 21% decline ( Table 1-2). This stark decline in February 2025 can be attributed to the tariff threats of late 2024 following the presidential election results where U.S. importers may have begun to shift to a more conservative mindset. Overall, there was a near 11% decline in total fastener imports into the U.S. in February 2025 compared to January 2025.
Table 1-2. U.S. Import Origins of Fasteners (2024-Jan. 2025)
Table 1-3. U.S. Import Origins of Fasteners (Feb. 2025)
Table 2-1. Fasteners Imported from China to the U.S. by Category (2022-2023)
731811 - Coach Screws, Threaded, Of Iron Or Steel
731814 - Self-Tapping Screws, Threaded, Of Iron Or Steel
731815 - Threaded Screws And Bolts Others, With Or Without Their Nuts Or Washers, Of Iron Or Steel
731816 - Nuts, Threaded, Of Iron Or Steel
731819 - Threaded Articles Of Iron Or Steel Others
731821 - Spring Washers And Other Lock Washers, Of Iron Or Steel
731822 - Washers, Other Than Lock Washers, Of Iron Or Steel 731823 - Rivets Of Iron Or Steel
731824 - Cotters And Cotter Pins, Of Iron Or Steel
731829 - Nonthreaded Articles (Fasteners) Others, Of Iron Or Steel
Table 2-2. Fasteners Imported from China to the U.S. by Category (2024-Feb. 2025)
731811 - Coach Screws, Threaded, Of Iron Or Steel
731814 - Self-Tapping Screws, Threaded, Of Iron Or Steel
731815 - Threaded Screws And Bolts Others, With Or Without Their Nuts Or Washers, Of Iron Or Steel
731816 - Nuts, Threaded, Of Iron Or Steel
731819 - Threaded Articles Of Iron Or Steel Others
731821 - Spring Washers And Other Lock Washers, Of Iron Or Steel
731822 - Washers, Other Than Lock Washers, Of Iron Or Steel
731823 - Rivets Of Iron Or Steel
731824 - Cotters And Cotter Pins, Of Iron Or Steel
731829 - Nonthreaded Articles (Fasteners) Others, Of Iron Or Steel
Table 3-1. Fasteners Exported from the U.S. to China (Jan. – Feb. 2025)
The U.S. primarily imports fasteners from China within HS 731815 (threaded screws and bolts), 731816 (nuts, threaded), and 731814 (selftapping screws) ( Table 2-1 to 2-2). These are all common components in the automotive industry for engine assembly and suspension systems. However, these are also components used for manufacturing machinery equipment, electronics and appliances. In February 2025, U.S. imports from China fell by 21.6% for HS 731815, 17% for HS 731816, and nearly 27% for HS 731814. In addition to the decline in market share by value, February 2025 also saw a significant drop in fastener import volumes, with a 24% decrease recorded (Table 2-2).
Table 3-2. Fasteners Exported from the U.S. to China (Jan. – Feb. 2025)
731812 - Wood Screws Other Than Coach Screws, Threaded, Of Iron Or Steel
731814 - Self-Tapping Screws, Threaded, Of Iron Or Steel
731815 - Threaded Screws And Bolts Others, With Or Without Their Nuts Or Washers, Of Iron Or Steel
731816 - Nuts, Threaded, Of Iron Or Steel
731819 - Threaded Articles Of Iron Or Steel Others
731821 - Spring Washers And Other Lock Washers, Of Iron Or Steel
731822 - Washers, Other Than Lock Washers, Of Iron Or Steel
731823 - Rivets Of Iron Or Steel
731824 - Cotters And Cotter Pins, Of Iron Or Steel
731829 - Nonthreaded Articles (Fasteners) Others, Of Iron Or Steel
In relation to U.S. fastener exports, China has remained strong as its third largest trading partner accounting for 5% of the total market share. Ahead of China are Canada and Mexico which together account for over 50% of the total market share. Due to the USMCA trade agreement, U.S. trade with its immediate neighboring partners is beneficial for several reasons including advantages on tariffs. In February 2025, there was a slight decrease of 9% in total fastener exports from the U.S. to China ( Table 3-1 to 3-2). Amongst the fasteners exported from the U.S. to China are 731815, 731816, and 731829 (non-threaded articles of fasteners) (Table 4).
In 2025, the U.S.-China trade relationship intensified sharply, beginning in February when the United States imposed a 10% tariff on all Chinese imports of goods, citing national security concerns. This was quickly followed by a second increase in March which raised the tariff to 20%. By early April, a more aggressive stance was taken as the U.S. implemented an additional 34% tariff, bringing the cumulative rate to 54%, and immediately increased it further to 125% with a clarification pushing the effective rate to 145%. In response, China launched a series of retaliatory measures beginning in February where the imposed tariff ranging from 10-15% on key U.S. exports including commodities such as crude oil, LNG, agricultural machinery, and vehicles. In March, this expanded to agricultural goods such as soybeans, port and cotton. By mid-April, China escalated its retaliation, first raising tariffs on all U.S. goods to 84%, and then to 125%. It also suspended exports of critical minerals and magnets essential to high-tech manufacturing, signaling a strategic shift beyond tariffs. These actions combined marked a severe escalation in trade tensions, with profound implication for industries reliant on U.S.-China supply chains, including fasteners.
Higher tariffs sharply increase the price of Chinese fasteners leading to a higher landed cost for US Importers and consumers. This will more than likely cause a rise in production costs for U.S. manufacturers who rely on Chinese fasteners. Let alone the number of supply chain disruptions that will be seen considering how fasteners are a critical component. These disruptions could lead to delays or cost fluctuations, and ultimately cause inventory planning issues for companies relying on Chinese suppliers.
The 2025 escalation in U.S.-China trade tensions has had immediate, tangible effects on manufacturing and procurement operations across the fastener supply chain. With import costs rising sharply due to elevated tariffs, U.S. manufacturers face mounting pressure to manage tighter margins, especially in cost-sensitive sectors like automotive, electronics, and industrial equipment. Procurement teams are contending with increased lead times, limited availability of specific fastener types, and greater volatility in pricing. The uncertainty around future policy shifts has led many companies to adjust purchasing strategies such as placing earlier or larger orders, increasing safety stock levels, or renegotiating supplier contracts to include contingency clauses. Operationally, manufacturers are also absorbing the impact of supply delays from China, forcing adjustments to production schedules and occasionally leading to stalled assembly lines. These pressures are not only straining supplier relationships but also reshaping how manufacturers evaluate risk and resilience within their global sourcing strategies.
In summary, the 2025 tariff escalation has created a costlier, riskier and less predictable trade environment for fasteners moving between the U.S. and China, with consequences for both immediate operations and long-term supply planning.
Copyright owned by Fastener World / Article by Sabrina Rodriguez




In 2025, President Donald Trump’s return to the White House has ushered in a fresh wave of trade policies under the renewed "America First" banner. These policies have immediate and far-reaching consequences for global trade dynamics—especially for export-intensive sectors such as the fastener industry.
With the declaration of a national economic emergency, implementation of a blanket 10% import tariff, and a growing list of bilateral tensions, fastener exporters around the globe are navigating a dramatically altered trade landscape.
The most pivotal and controversial trade policy changes introduced in early 2025 include a universal 10% tariff on all imports, announced on April 5, 2025, by the Trump administration under the IEEPA. This measure applies to all imported goods, including fasteners, regardless of the country of origin. Additionally, countries with significant trade surpluses with the U.S.—such as China, Mexico, and Germany—now face increased tariffs on selected product categories. Compounding these measures, the administration has also eliminated the de minimis threshold, which previously allowed small-value shipments under USD 800 to enter the U.S. duty-free. This exemption has been revoked for all parcels originating from China and Hong Kong, significantly affecting e-commerce and small-scale industrial supply chains.
Fasteners—ranging from screws and nuts to industrial bolts— are fundamental in manufacturing, construction, defence, and automotive sectors. The U.S. is both a major importer and user of fasteners, relying heavily on suppliers from Asia and Europe.
Key Figures
• In 2024, the U.S. imported USD 7.1 billion worth of fasteners, with over USD 2.3 billion from Taiwan, USD 1.3 billion from China, USD 660 million from Japan, and USD 440 million from Germany, and so on.
• The average price per ton of imported fasteners is expected to rise by 18–30% in 2025 due to tariff-driven price inflation.
• According to the Industrial Fasteners Institute (IFI), U.S. domestic production capacity is insufficient to meet short-term demand, especially in high-spec industrial and aerospace-grade fasteners.
Rising import costs are forcing U.S. buyers to reassess their supplier networks, particularly as tariffs and logistical expenses make international sourcing less predictable and more expensive. Exporters who demonstrate pricing stability or absorb part of the tariff burden are better positioned to retain their market share in this shifting landscape. Buyers are increasingly valuing consistency and reliability, prompting a re-evaluation of long-standing partnerships in favor of those who can offer more resilient pricing strategies amid global uncertainty.
At the same time, major sectors like construction and automotive are grappling with significant supply chain disruptions. Delivery delays and cost overruns have become common due to the need to reroute shipments and renegotiate prices. In response, many U.S.-based Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) are accelerating efforts to onshore production or source from tariff-exempt countries. This shift is opening up new trade opportunities for nations with favorable bilateral agreements, positioning them as attractive alternatives for U.S. companies seeking more stable and cost-effective supply solutions.
Trump Administration (2017–2020): Trade War and Tariff Impact
During Trump's first term, U.S. fastener imports from China (Figure 1) experienced significant fluctuations due to the escalating U.S.-China trade war and the implementation of tariffs on Chinese goods.
• 2017–2018: Imports rose from USD 1.23 billion to USD 1.62 billion, likely due to front-loading before tariffs took effect.
• 2019–2020: A sharp decline followed— dropping to USD 1.19 billion in 2019 and further to USD 898 million in 2020— reflecting the impact of tariff enforcement and supply chain disruptions, compounded by the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic.
This period illustrates how protectionist trade policy and rising geopolitical tensions significantly reduced the attractiveness of Chinese fasteners for U.S. importers.
Under Biden, imports rebounded to USD 1.26 billion in 2021 and peaked at USD 1.85 billion in 2022 as demand surged post-pandemic. However, the resurgence was temporary.
• 2023–2024: Imports dropped again to USD 1.18 billion and then slightly up to USD 1.32 billion, likely due to efforts to diversify supply chains, increased interest in reshoring or nearshoring, and lingering uncertainties around tariffs and global logistics.
Biden retained most of Trump's tariff policies while signaling openness to allied supply chains, leading U.S. importers to adopt a more cautious and diversified sourcing strategy rather than relying heavily on China.

▲ Figure 1
Based on historical trends and the likelihood of new or sustained tariffs, U.S. fastener imports from China are expected to decline gradually over the next four years. In 2024, imports was USD 1.32 billion. Assuming a moderate impact from future trade policy, projections indicate a year-over-year decrease of 1–5%:
• 2025: ~USD 1.26 billion
• 2026: ~USD 1.22 billion
• 2027: ~USD 1.20 billion
• 2028: ~USD 1.18 billion
This trend reflects a combination of tariffdriven cost increases, ongoing efforts by U.S. buyers to diversify away from China, and the strategic relocation of sourcing to tariff-free or nearshore countries. While imports will likely remain substantial due to China’s production scale, its share of the U.S. fastener market is projected to shrink steadily unless future trade agreements shift the current direction.
With fastener imports from China expected to gradually decline over the next four years, the geopolitical and policy environment is shaping not just trade volumes but also the structure of global sourcing strategies. Following a peak of approximately USD 1.85 billion in 2022, imports dropped to USD 1.32 billion by 2024 and are projected to fall further to USD 1.18 billion by 2028, driven by rising tariffs, supply chain diversification, and geopolitical tension.
China is set to face the harshest trade conditions, including a high tariff rate and the removal of de minimis provisions for small shipments. This policy shift directly impacts over 1,800 fastener companies, significantly increasing the cost of doing business with U.S. buyers. As a result, Chinese exporters must now adapt quickly—either by partnering with U.S.-based distributors, investing in U.S.-based assembly operations, or losing ground in one of their largest export markets. The forecasted decline in Chinese imports aligns with this pressure, as U.S. companies increasingly seek stable and tariff-free sources.
European countries such as Germany, Italy, and France are not spared. Fasteners from the EU are subject to a 25% tariff (as of midMay), making them less competitive. German exporters, in particular, could lose 10–12% of their U.S. market share in 2025 alone, a major blow given their established presence. This tariff impact reinforces the broader trend of American importers diversifying away from higher-cost and policy-risk markets.
In contrast, countries like Taiwan, Vietnam, and India are emerging as preferred alternatives. They are perceived as low political risk and are not currently targeted by high U.S. tariffs. Taiwan, with its high-quality value-added industrial fastener industry, is especially well-positioned to capture demand that’s shifting away from China and the EU. Vietnam and India, meanwhile, offer both cost-efficiency and a growing manufacturing base, making them strategic supply sources for U.S. buyers.




The next four years will likely see a strategic realignment of U.S. fastener sourcing, with imports from China decreasing year-over-year, European players losing competitive edge due to tariffs, and Asia-Pacific exporters—especially Taiwan—absorbing the redirected demand. This reconfiguration will not only affect trade volumes but also accelerate supply chain restructuring, joint ventures, and localized assembly operations as exporters race to retain access to the U.S. market.
The ripple effects of rising tariffs on fasteners will vary significantly across industries, but some sectors are poised to absorb a heavier impact—most notably automotive, aerospace, and construction/infrastructure. These industries depend heavily on reliable and cost-efficient fastener supply chains, and the new pricing pressures threaten to erode margins, disrupt timelines, and force strategic shifts in sourcing and production.
The U.S. automotive industry is especially vulnerable. A typical American-made vehicle uses over 3,000 fasteners, embedded throughout safety systems, structural components, and internal assemblies. With the new tariffs and price hikes on imported fasteners, per-vehicle manufacturing costs could rise by as much as USD 190. While this figure may seem moderate at first glance, the impact is compounded at scale, especially for mass-market carmakers operating on thin profit margins. The result could be a combination of reduced profitability, delays in production schedules, and increased pressure to localize or renegotiate supplier contracts. The policy shift might also accelerate investments in domestic fastener production, though ramping up capacity will take time.
The aerospace sector faces a more specialized challenge. Many aerospace-grade fasteners are precision-engineered components that are predominantly imported from European suppliers. The imposition of a 25% tariff on EU imports will disproportionately impact this sector, which already bears high R&D and compliance costs. As a result, both commercial aviation programs and U.S. defence contracts may experience cost inflation. In response, aerospace firms may be driven to invest in domestic manufacturing capabilities for fasteners, or explore niche suppliers in politically neutral countries. However, due to strict certification standards and long qualification cycles, any shift will be gradual and logistically complex.

In the construction and infrastructure sectors, which rely on high volumes of general-purpose fasteners for structural steel, utilities, and civil engineering, the impact will be broad-based but particularly damaging to large-scale projects. Many infrastructure developments budgeted in 2024 did not anticipate a spike in fastener costs. As tariffs take effect, these projects now face margin erosion, potential delays, or forced redesigns to stay within cost constraints. Governments and private developers may need to request strategic waivers for critical imports or fast-track local sourcing initiatives to avoid disruptions. This dynamic could also revive interest in U.S.-made fasteners, especially for federally funded infrastructure under “Buy American” provisions.
In conclusion, the renewed "America First" policies under President Trump's administration are reshaping the global fastener export landscape. The introduction of a blanket 10% import tariff and increased duties on fasteners from key trading partners, including China and Europe, is expected to drive up prices and create significant disruptions in supply chains. These changes will disproportionately affect industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction, which heavily rely on fasteners for production and infrastructure projects. As the U.S. increasingly looks to diversify its sourcing strategies, countries like Taiwan, Vietnam, and India are emerging as viable alternatives, potentially reshaping the global fastener supply network in the years ahead.
The long-term impact of these trade policies will likely result in a decline in U.S. fastener imports from traditional suppliers like China and the EU, as U.S. companies seek more stable and cost-effective sourcing solutions. While domestic production capacity may eventually rise, it will take time to meet the demand for specialized fasteners, particularly in high-specification sectors. As a result, the fastener industry faces a period of volatility, with exporters needing to adjust quickly to the changing dynamics of U.S. trade policy. For those who can adapt, this shift presents an opportunity to capture market share in a restructured, tariff-conscious trade environment.
Copyright owned by Fastener World
Article by Dr. Sharareh Shahidi Hamedani, UNITAR International University





Over the past two decades, the global economic landscape has undergone a dramatic transformation. At the heart of this change stands the shifting balance of power between two economic giants: the United States and China. Since the early 2000s, China has risen from a low-cost manufacturing hub to the world’s second-largest economy, expanding its influence through massive infrastructure investments, technological development, and global trade initiatives such as the Belt and Road Initiative. Meanwhile, the United States has maintained its position as the world’s leading economy, driving innovation, financial dominance, and global consumer markets.
The turning point came with the presidency of Donald Trump. In a sharp departure from previous administrations, Trump launched a full-scale tariff war against China, accusing Beijing of unfair trade practices and economic aggression. This marked the beginning of a new era — one where tariffs, sanctions, and economic nationalism would become the tools of a broader geopolitical contest.
The origin of trade conflicts can be traced back to 2018, when the Trump administration launched Section 301 investigations accusing China of unfair trade practices, intellectual property theft, and forced technology transfers. In response, a sweeping set of tariffs were introduced, affecting more than USD 550 billion worth of Chinese goods, including fasteners.
The U.S. imposed tariffs on a broad range of Chinese fasteners including steel screws, hex bolts, self-tapping screws, washers, and structural fasteners. According to the data from the U.S. International Trade Commission (USITC), the value of Chinese fastener imports dropped by 31% between 2018 and 2021, a dramatic signal of disruption in the trade flow.
The Chinese government responded with its own retaliatory tariffs, but for fastener exporters, the pain was already acute. China accounted for more than 23.5% of all U.S. fastener imports in 2017, a dominance that began to shrink post-2018. In 2024, China accounted for 19% of all U.S. fastener imports.
To offset the direct impact of U.S. tariffs, many Chinese fastener companies began offshoring production to Southeast Asian countries. Nations like Vietnam, Malaysia, and Thailand have seen a surge in investment from Chinese firms eager to maintain U.S. market access.
According to the China Fastener Association (CFA), more than 15% of tier-one fastener manufacturers in Guangdong and Zhejiang provinces have moved partial operations offshore since 2019. This trend, known as "transnational rerouting," has allowed exporters to re-label their products under countries not targeted by U.S. tariffs.
However, during the second term of the Trump administration, the U.S. government responded to this rerouting tactic by significantly increasing tariffs on several Southeast Asian countries suspected of serving as intermediaries for Chinese goods. By expanding the scope of trade enforcement and tightening rules of origin, the administration aimed to close loopholes exploited through transnational rerouting. This policy escalation pressured Chinese manufacturers to explore even more complex offshore strategies or shift focus to non-U.S. markets.
Firms that couldn’t relocate turned inward—streamlining operations and investing in automation. Automation upgrades in fastener production plants help reduce labor costs, partially compensating for lost export revenue.
Automation also improves product consistency and reduces delivery delays—key elements when competing globally. A growing number of Chinese companies are integrating robotic arms, CNC machinery, and AI-based defect detection into their lines.
By reducing dependence on third-party raw material suppliers and adopting vertical integration, companies are lowering internal cost structures. The integration of steel processing, galvanizing, and packaging within one facility is becoming increasingly common among top players
To remain price competitive in the U.S. despite tariffs, exporters have slashed their margins. Data from the China Chamber of Commerce for Import and Export of Machinery and Electronic Products (CCCME) shows that average gross margins in the fastener export industry have fallen from 12% to 6% since 2019.
Some exporters have been absorbing a portion of the tariffs themselves to maintain long-standing relationships with U.S. buyers. For example, Hangzhou-based Tianbao Fasteners reportedly subsidized tariff costs in major B2B deals, a move that helped retain contracts but led to sharp declines in net profits.
In 2025, the situation worsened with the introduction of a new wave of sweeping U.S. tariffs targeting a broader range of industrial goods, including fasteners, under the revived "America First Trade Reinforcement Act." These punitive tariffs, which in some cases doubled previous rates, pushed many Chinese exporters into an impossible cost squeeze. Already operating on thin margins, firms were forced to either exit the U.S. market or dramatically restructure their pricing and supply chains. The industry now faces a pivotal moment, with some companies turning to higher-value products or alternative markets in Europe and Latin America to survive.
As price competition intensifies and profit margins shrink, Chinese manufacturers are shifting focus from pure cost strategies to long-term brand development. Rather than solely segmenting by price, leading companies are investing in brand identity and positioning to overcome the persistent global perception that "Made in China" equates to cheap and low-quality products.
This strategic pivot involves creating differentiated product lines—basic, mid-tier, and premium—not just by functionality, but by brand promise, reliability, and perceived value. In critical industries such as automotive and aerospace, where trust and certification matter, strong branding allows manufacturers to justify higher prices and reduce the risk of substitution. However, building a credible brand takes time, consistency, and significant marketing investment—something many Chinese firms are only now beginning to prioritize.
Exporters are transitioning from mass-producing low-value fasteners to developing custom, high-precision fasteners with higher barriers to entry. This strategic pivot reduces exposure to price-based competition and adds stickiness to client relationships.
For instance, manufacturers that have launched a series of corrosion-resistant, heat-treated titanium bolts for aerospace clients, doubling their average selling price per unit from USD 0.06 to USD 0.14 between 2020 and 2023.

In addition to tariffs, U.S. importers are increasingly demanding ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) compliance. Factories with carbon footprints or poor waste disposal standards risk being blacklisted.
Leading exporters are investing in zinc-free coatings, water treatment systems, and ISO 14001 certifications to align with buyer expectations. This "green compliance" not only preserves access to high-paying Western markets, but may eventually become a competitive differentiator.
To hedge against U.S. dependence, Chinese fastener exports to Europe and "Belt & Road" countries have expanded rapidly. From 2019 to 2024, fastener exports to the EU rose by 50%. This growth is partly aided by the China-Europe Railway Express, which reduces transport time from 45 days by sea to 15 days by rail, boosting the attractiveness of Chinese fasteners in European markets. Exports to Asia increased over 52% between 2019 to 2024.
As part of China's broader "dual circulation" strategy, policymakers are pushing manufacturers to balance export revenue with growing domestic consumption. Infrastructure spending and urbanization projects are fuelling domestic demand for fasteners in construction and transportation sectors.
In 2024, China’s domestic demand for industrial fasteners grew by 11%, and local government subsidies further incentivized homegrown sourcing, reducing reliance on volatile foreign markets.



Conclusion
The U.S. tariffs on Chinese fasteners represent more than just a tax—they’ve catalyzed a transformation. Exporters who once thrived on volume and cost advantage are now focused on agility, value creation, and market agility. From shifting manufacturing bases to reengineering product lines and embracing automation, China’s fastener industry is in the midst of a profound strategic evolution.
In this optimistic scenario, tariff negotiations ease under a new administration, and Chinese fastener makers regain part of their lost U.S. market share. Innovation and diversification continue, but trade normalization gives companies breathing space.
In this scenario, Chinese companies reduce U.S. focus permanently, treating it as a high-risk, low-margin market. Investment shifts to the EU, Africa, and South America, with partial reshoring to ASEAN as a buffer.
3. Global Consolidation
The most aggressive future includes consolidation within the Chinese fastener industry, with smaller players being acquired or driven out. The survivors will be larger, vertically integrated, and export-agnostic powerhouses.
Copyright owned by Fastener World / Article by Behrooz Lotfian

On April 9, 2025, the Trump administration launched a sweeping trade offensive dubbed “Liberation Day,” escalating reciprocal tariffs on all Chinese imports to a minimum of 145 percent. This move builds on previous tariff layers of 20 percent (Section 301) and 34 percent (reciprocal duties), and now deals a major blow to Chinese fastener exporters who had long dominated the U.S. market.
China swiftly responded with countermeasures: first announcing an 84 percent retaliatory tariff on U.S. goods on April 10, followed by an increase to 125 percent by April 12. As tensions escalate, Chinese exporters, particularly those in the fastener sector, are facing a dramatically altered global trade environment.
This article analyses the new tariff landscape, highlights key shifts in demand, and explores strategic responses by Chinese fastener manufacturers, including market diversification efforts in Europe, Southeast Asia, and Latin America. Recent trade data also illustrate how these geopolitical shocks are reshaping export volumes and value.
The latest U.S. tariff hike effectively doubles down on protectionist trade policies, further limiting the access of Chinese products, including fasteners, to the American market. In 2024 alone, Chinese exporters had shipped roughly USD 9.6 billion of fasteners (HS Code 7318) to the U.S. These flows are now severely disrupted, with immediate pricing disadvantages for Chinese products and uncertainty for long-term contracting.
U.S. original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and contractors are rapidly adjusting by increasing domestic output and sourcing from alternative low-cost suppliers. However, production bottlenecks, labour constraints, and inflated costs have limited these efforts, exacerbating supply delays. Meanwhile, Chinese manufacturers are deferring planned capital investments in automation and R&D due to the volatile policy climate.

2.1 High-Value Markets, Strategic Shifts
Despite a 5% drop in EU imports from China between January 2023 and December 2024, Europe remains a strategic market for Chinese fastener exporters. Germany (USD 468.1 million) and Russia (USD 568.3 million) stood out in 2024 as key destinations, particularly for automotive, construction, and aerospace-grade fasteners.
In response to U.S. tariffs, Chinese firms are expanding operations in Germany, France, and Italy, often through partnerships or acquisitions, to gain access to sophisticated buyers and to reposition their brand within Europe’s industrial ecosystem.
2.2 Regulatory and Logistical Considerations
Europe’s extensive network of Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) and customs unions offers preferential duties for locally assembled products, incentivizing Chinese firms to establish production or finishing facilities within EU member states. Some exporters are exploring joint ventures in Poland and the Czech Republic to leverage lower labour costs and tariff exemptions for EU-origin goods.
3.1 Vietnam and the New Manufacturing Frontier
At the 137th Canton Fair, multiple suppliers unveiled plans to scale operations in Vietnam and Cambodia. These investments are not only a workaround for U.S. tariffs, but part of a broader reindustrialization strategy that aligns with nearshoring trends.
Vietnam, in particular, offers well-developed export infrastructure, favourable investment policies, and a growing labour pool. This makes it a prime location for transshipment and light manufacturing of fasteners, though scrutiny around rules of origin is tightening.
3.2
To maintain credibility and avoid blacklisting, Chinese investors are increasingly shifting from “label swapping” operations to establishing deeper production footprints in Southeast Asia. This ensures better compliance with origin requirements and helps sustain access to Western markets.
4.1
Latin America, especially Mexico, Brazil, and Colombia, continues to present growth opportunities for Chinese fastener exporters due to expanding infrastructure projects and industrial demand. Mexico, in particular, has been a focal point for Chinese firms aiming to access both domestic and North American markets. Investments in warehousing and distribution centres have supported "Made in Mexico" strategies, facilitating regional integration under the USMCA framework.
However, recent policy shifts under the Trump administration have introduced significant challenges. Effective March 4, 2025, the U.S. imposed a 25% tariff on all imports from Mexico, citing concerns over illegal immigration and drug trafficking. This move marks a departure from previous trade agreements and has raised concerns about the stability of the USMCA. The tariffs apply broadly, affecting a wide range of products, including industrial fasteners, and are in addition to existing duties such as the 25% tariffs on steel and aluminium imports from Mexico due to Section 232.
These developments have prompted Chinese exporters to reassess their strategies in Mexico. While the country remains a vital hub due to its proximity to the U.S. and established manufacturing infrastructure, the new tariffs have increased operational costs and introduced uncertainty. Companies are now exploring alternative markets and considering adjustments to their supply chains to mitigate the impact of these trade barriers.
Beyond Mexico, Brazil and Colombia are emerging as potential markets for Chinese fastener exports, driven by infrastructure development and industrial growth. However, these markets come with their own set of challenges. In Brazil, local manufacturers have advocated for anti-dumping measures against Chinese imports, leading to increased scrutiny and potential tariffs. Colombia, while offering opportunities, has complex regulatory frameworks that require careful navigation.
Chinese exporters looking to enter these markets must conduct thorough due diligence, understand local regulations, and build strong relationships with local partners to succeed. Diversifying export destinations remains a critical strategy in the face of evolving global trade dynamics.
Recent export data underscore a significant shift in China's fastener trade dynamics, reflecting both the impact of U.S. tariffs and the strategic diversification of export markets.

Figure 1 illustrates the export values (in USD million) of Chinese fasteners to the top five importing countries over the past five years:
• USA: Despite a decline in 2023 due to initial tariff implementations, exports rebounded slightly in 2024 to USD 1.36 billion. However, the market remains volatile amid ongoing trade tensions.
• Russia: Exports to Russia have shown resilience, increasing to USD 568.3 million in 2024. This growth is attributed to strengthened bilateral relations and Russia's demand for industrial components amid Western sanctions.
• Vietnam: Serving as both a manufacturing base and transshipment point, Vietnam's imports of Chinese fasteners rose to USD 518.7 million in 2024, reflecting its strategic role in regional supply chains.
• Germany: As a key player in Europe's automotive and machinery sectors, Germany imported USD 468.1 million worth of Chinese fasteners in 2024, maintaining its position as a significant European market despite slight fluctuations.
• Japan: While imports have slightly decreased, Japan remains a stable market with USD 336.3 million in imports in 2024, reflecting consistent demand in its manufacturing industries.
References:
• WTO Reports on trade barriers and regional trade flows
• UN Comtrade Database
• International Trade Centre (ITC) – Trade Map
• Office of the United States Trade Representative (USTR)
• South China Morning Post
The data indicates a strategic pivot by Chinese fastener exporters:
• Diversification: Reduced reliance on the U.S. market has led to increased focus on emerging and resilient markets like Russia and Vietnam.
• Regional Integration: Engagement with neighbouring Asian markets supports China's regional trade objectives and mitigates risks associated with Western markets.
• Adaptation to Trade Policies: Exporters are adjusting to global trade dynamics by exploring markets with favourable trade agreements and less restrictive tariffs.
This realignment reflects a broader strategy to ensure stability and growth amid an evolving global trade landscape.
China’s fastener export industry is undergoing a major transformation shaped by shifting geopolitics, trade policies, and regional reconfiguration. While the United States remains a key destination, the combination of tariffs, nearshoring strategies, and bilateral tensions, including frictions even with regional partners like Mexico, has catalysed a more diversified export strategy.
Emerging markets such as Russia, Vietnam, and Brazil are absorbing a growing share of Chinese exports, reflecting a deliberate effort to de-risk from overdependence on any single market. At the same time, countries like Mexico are increasingly acting as strategic buffers, simultaneously importing, reprocessing, and re-exporting fasteners under “Made in Mexico” strategies that align with USMCA benefits and Chinese logistical interests.
This evolving trade matrix marks not just a geographic shift, but a strategic recalibration. Chinese exporters are no longer just reacting to global pressure, they’re reshaping global supply chains in their favour, integrating logistics hubs, and adapting to complex regulatory landscapes. The result is a more resilient, multipolar trade structure with broader regional anchoring, particularly in Latin America and Southeast Asia, and a reduced vulnerability to any political or economic shock.





Copyright owned by Fastener World
Article by Shervin Shahidi Hamedani













中國電動車產業發展政策與緊固件商機(上)


New Energy Vehicles (NEVs), including electric vehicles (EVs), have gained widespread attention and rapid development globally in recent years as a crucial alternative to gasoline vehicles. NEVs include battery electric vehicles (BEVs), plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), and hydrogen fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs). With technological advancements and policymaking, NEVs in the Chinese market have demonstrated significant progress in market share, technological innovation, and development in supply chains.
The rapid growth of the NEV market benefits from multiple factors. To address environmental pollution and energy crises, governments worldwide have formulated a series of policies supporting NEV development, such as providing purchase subsidies, tax incentives, and building charging infrastructure, actively promoting the adoption of NEVs. In addition, increased consumer environmental awareness and the demand for energy conservation have further boosted the expansion of the NEV market.
Technological innovation is the core driving force behind NEV development. Continuous breakthroughs in battery technology, such as increased lithium-ion battery energy density, reduced costs, and faster charging speeds, provide a solid guarantee for the performance improvement and market acceptance of NEVs. Advancements in electric motors and their control systems, lightweight materials, and intelligent driving technology have also significantly improved the overall performance and user experience of NEVs. For example, some high-end vehicles widely use autonomous driving technology and have gradually gained an important position in the electric vehicle market.
The improvement of the supply chain is an important support for the sustainable development of NEVs. With the growth of market demand, the integration of upstream and downstream manufacturers in the NEV supply chain has become a trend. This integration extends from the mining and supply of key raw materials such as lithium and cobalt in the upstream, to the manufacturing of core components such as power batteries and electric motors in the midstream, and then to the production and sales of whole vehicles in the downstream, forming a complete and efficient industrial ecosystem. As the world's largest NEV (including EV) market, China has a complete supply chain layout, attracting a large amount of capital and manufacturer investment, which has driven the rapid development of the industry and the market.
Despite the significant progress of NEVs, their development still faces many challenges. For example, the recycling and environmental protection of power batteries, the imperfect construction of charging infrastructure, and range anxiety are important issues that need to be addressed. In addition, global economic uncertainties and supply chain risks also have a potential impact on the NEV industry. With the further release of market demand and the continuous improvement of the supply chain, NEVs will usher in a more brilliant stage of development.
The 2010s were the heyday for the rapid development of China's NEV industry. In 2012, China issued the "Energy Saving and New Energy Vehicle Industry Development Plan (2012-2020)", which clearly proposed that the cumulative production and sales of NEVs should reach 5 million vehicles by 2020. To achieve this goal, the government expanded its support for NEVs, including providing purchase subsidies, reducing purchase taxes, and accelerating the construction of charging infrastructures. Meanwhile, leading Chinese manufacturers such as BYD, BAIC BJEV, and NIO actively invested in R&D, launching a series of competitive NEVs.
With the growth of market demand and the improvement of technological level, China's NEV industry occupies an important position in the global market. As of 2024, China's NEV ownership has exceeded 6.5 million vehicles, making it the world's largest NEV market. Concurrently, China's NEV supply chain has been formed. From the supply of power battery materials in the upstream to the manufacturing, assembly, and sales of whole vehicles in the downstream, a large number of manufacturers are involved in all aspects and demonstrate competitiveness in the international market.
In recent years, with the proposal of the dual carbon goals (carbon peaking and carbon neutrality), China's NEV industry has ushered in new development opportunities. The government continues to expand its policy support for NEVs, promoting connectivity of NEVs and making them smart. Meanwhile, the construction of charging infrastructure has been further expanded, and the convenience of using NEVs has been significantly improved. In 2024, China's NEV sales at home and abroad reached a new high of 4.75 million vehicles, accounting for 55.2% of the global market.

Led by government policies, China's NEV industry has experienced a process from initial start-up to rapid development. Leading manufacturers are actively expanding their domestic and international deployment and building factories. In the future, with continuous technological breakthroughs and further market maturity, China's NEV industry will continue to develop.
China's electric vehicle industry is currently experiencing significant growth and consolidating its global leadership position. Electric vehicles achieved a significant milestone in August 2024, with sales exceeding 1 million vehicles, marking a major increase in the electrification of the automotive market. This represents 30.6% of all vehicle sales in that month, highlighting the continued upward trend of electric vehicles.
Sales of new energy vehicles have exceeded those of internal combustion engine vehicles for the first time. This shift marks a major milestone in China's transition to automotive electrification, driven by increased consumer acceptance and manufacturers' aggressive marketing strategies. S&P Global Mobility predicted that NEVs would account for 46% of the passenger car market in 2024, up from 36% in 2023. In 2024, BYD sold more than 1 million new energy vehicles, strengthening its dominant market position. Other automotive brands such as Xpeng, Zeekr, and GAC Aion are also beginning to emerge.
1. Comparing Sales Volume of New Energy Vehicles (Including Pure Electric Vehicles) by Car Manufacturers
According to retail sales data released by the China Passenger Car Association, the cumulative sales volume of China's auto market in 2024 reached 22.892 million vehicles, an increase of 5.5% compared to the previous year. The cumulative sales volume of new energy vehicles was 10.749 million vehicles, an increase of 47.5% compared to the previous year, with a cumulative penetration rate of 45.8%. Among them, the sales volume of pure electric vehicles was 6.281 million vehicles, accounting for 58.5% of the market. The Chinese auto market was 2024 is highly competitive. BYD led in sales volume with 4.25 million vehicles, while Tesla's sales volume declined to 910,000 vehicles. Independent brands such as Geely and Chang'an were growing rapidly, narrowing the gap with the leading group. In 2025, BYD will accelerate the sales of smart vehicles, and Tesla will usher in for the next generation for Model Y.
China's NEV market has made significant progress in recent years, with sales continuing to reach new highs. According to data from the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers, China's NEV production in 2023 was 9.587 million vehicles, and sales were 9.495 million vehicles, an increase of 35.8% and 37.9% respectively compared to the previous year. From January to May 2024, the cumulative sales volume of new energy vehicles was 3.89 million vehicles, an increase of 32.5% compared to the previous year.
From the perspective of power sources, China's NEV market is dominated by pure electric vehicles (BEVs), and the proportion of plug-in hybrid vehicles is increasing year by year. From January to May 2024, the sales volume of pure electric vehicles was 2.407 million vehicles, accounting for 62%; the sales volume of plug-in hybrid vehicles was 1.486 million vehicles, accounting for 38%. In terms of price, the sales volume of new energy vehicles is mainly concentrated in the price range of RMB 150,000~200,000. From January to May 2024, the cumulative sales volume was 1.028 million vehicles, accounting for 27.8%. In terms of sales by vehicle model, in May 2024, the models with the highest sales volume below RMB 80,000, RMB 80,000~150,000, RMB 150,000~200,000, RMB 200,000~300,000, and above RMB 300,000, were Seagull (34,000 vehicles), Qin PLUS (49,000 vehicles), Song PLUS New Energy (33,000 vehicles), Model Y (40,000 vehicles), and AITO M9 (16,000 vehicles), respectively.
Regarding power battery technology, lithium iron phosphate (LFP) power batteries account for nearly 70% of the installed capacity in China. Low-end models mainly use LFP batteries, while high-end models mostly use ternary lithium batteries. In terms of new cars, pure electric vehicles such as Xiaomi SU7 and Zeekr 001 have shown strong market competitiveness with their excellent performance. BYD has further consolidated its leading position in the field of LFP batteries through multiple plug-in hybrid extended-range new cars. In addition, the level of autonomous
driving technology for new energy vehicles continues to improve. From January to February 2024, L2 and above-level autonomous driving new energy vehicles accounted for 62.5%, an increase of 7.2% compared to the same period last year. The installation rate of intelligent driver assistance systems is also increasing year by year. The market penetration rate of new energy vehicles is increasing year by year. According to data from the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers, the penetration rate of new energy vehicles in China reached 31.6% in 2023, an increase of 5.9% compared to 2022. From January to May 2024, the penetration rate of new energy vehicles reached 33.9%, and the penetration rate further increased to 39.5% in May.
In terms of exports, from January to April 2024, China's exports of new energy vehicles were 663,000 vehicles, an increase of 27% compared to the previous year. Among them, passenger car exports were 649,000 vehicles, an increase of 30% compared to the previous year. Among passenger car exports, BEV exports were 557,000 vehicles, an increase of 20% compared to the previous year, accounting for 86%; PHEV exports were 92,000 vehicles, an increase of 144% compared to the previous year, accounting for 14%. In April 2024, China's exports of new energy vehicles were 207,000 vehicles, of which passenger car exports were 203,000 vehicles, an increase of 59% compared to the previous year. The average price of China's new energy vehicle exports has also been increasing year by year. From January to April 2024, the average export price of new energy vehicles in China was US$23,000, a significant increase compared to 2019. The price increase reflects the increasing competitiveness of China's new energy vehicles in the international market and also demonstrates the progress in new energy vehicle technology and manufacturing. Figure 1 shows the export volume of new energy vehicles (including pure electric vehicles) in China from January to April 2024.

Source: China Association of Automobile Manufacturers; ISTI, March 2025
Source: ISTI, March 2025

Led by policies, China's pure electric vehicle industry has experienced a process from initial start-up to rapid development. Leading manufacturers such as BYD are not only actively expanding their domestic deployment, but also expanding their factories and markets in Eastern Europe, Mexico, and Central & South America, which will trigger the booming development opportunities of the electric vehicle supply chain.
Copyright owned by Fastener World Article by James Hsiao

2025年更新──北美緊固件標準
In 1841, the English engineer and inventor Joseph Whitworth presented his paper, “ A Uniform System of Screw Threads” to Great Britain’s Institution of Civil Engineers. This paper was a proposed solution to an Industrial Revolution problem vexing Great Britain and other western countries. Although it started with the burgeoning railroads, this problem was being experienced globally throughout all industries relying on newly developed mechanization. Specifically, when threaded fasteners failed or needed to be replaced, there was no uniformity among manufacturers. Without any confidence in interchangeability, replacing a broken part required going back to the original manufacturer, which often was inconvenient and sometimes impossible. Whitworth’s uniform thread design solved this problem and was quickly adopted as a national standard, propelling it into the history books as the world’s first industrial standard.
Today, there are thousands of fastener standards, including global standards like ISO, regional standards like JIS, ANSI, and DIN, and individual user standards like Boeing, Honda, and Bosch. Standards fall into one of two categories, Consensus Standards and Nonconsensus Standards. Consensus Standards are generated by Consensus Standard’s organizations, which means they are developed by a diverse and multi-talented group of experts using a formal set of procedures and rules that guarantee they reach consensus regarding the contents of the final standard. Non-consensus Standards are developed by individuals and individual organizations to best represent their specific interests.
Standards related to fasteners can be divided into several categories:
1. Product Standards: These standards provide all the requisite information to be able to produce a part or family of parts. Foremost they provide dimensional information but may have other information required to make or control the proper manufacture of parts as well.
2. Material Standards: This is a slightly broader range of standards, as it includes standards related to raw materials, performance (specifically mechanical performance), heat treating, plating and coatings, and testing.
3. Testing Standards: This is a small group of standards that are specifically written to detail one or more fastener test methods.
4. Procurement Standards: These are generally unique to aerospace and defense fasteners and provide requirements related to quality, performance, and procurement.

5. System Standards: These are broad standards that detail quality-related, business management systems, some are intended to encompass all industries and others are specific to fasteners.
In North America, there are several Consensus Standard’s organizations that generate fastener standards. The primary ones include:
• American Society of Mechanical Engineering (ASME), predominantly providing product standards. Fastener-related standards come from two different technical committees, B18 (fasteners) and B1 (threads).
• American Society of Testing and Materials (ASTM), predominantly providing material and testing standards. Fastener-related standards come mostly from the Fastener Committee F16 although a number of them are derived from the steel committee A01.
• Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), providing mostly material and a few product standards. Fastenerrelated standards come primarily from their Fastener Committee, although aerospace fastener material standards come from their Aerospace Material Division.
• National Aerospace Standards Committee (NASC), providing product, material, testing, and procurement standards for aerospace fasteners.
• International Organization for Standardization (ISO), providing product, material, and system standards. ISO is unique because it is a world organization and, thus, delegates to the fastener committee, TC2, represent different countries or regions.
• Research Council on Structural Connections (RCSC), exclusively focused on structural bolting.
• National Association of Corrosion Engineers (NACE), with several fastener standards, mostly focused on the oil and gas industry.
• American Petroleum Institute (API), with several material standards exclusively for oil and gas industry fasteners.
There is always debate over which standards, Consensus or Non-consensus are better. Good arguments can be made for both sides and, the best answer is, most likely, “it depends”. For example, if you are an automotive OEM and have some specific requirements that you wish to maintain, a company proprietary, Non-consensus Standard is probably a better choice. One of the big advantages, however, of most of the Consensus Standards is that one of the rules of the Consensus Standard’s organization is that standards must be kept up to date. Each organization has its own rules, but most require that the standard be reviewed and either updated or reapproved every five to seven years. This is good practice because it doesn’t allow these standards to fall too far behind the state of the industry. Although this is really a necessity, it can often be frustrating because it means that these standards are continuously changing, and users must be continually attentive to recent and upcoming additions and revisions.
The following are some of the current activities of these fastener committees:
The ASME fastener committee B18 meets twice a year. The last meeting was in September 2024 and the next meeting was held in April 2025 at the IFI headquarters in Cleveland Ohio. The following are highlights of some of the recent revisions and work of this committee.
• ASME B18.6.3: “Machine Screws, Tapping Screws, and Metallic Drive Screws (Inch Series)”. A new revision of this standard was published in the first half of 2024. Although it was a significant editorial update from the 2013 revision, technical changes include a reduction of the core hardness to not exceed HRC36 for case hardened tapping screws, revised guidance regarding the Hydrogen Embrittlement Test, and revised underhead thread rolling parameters on tapping screws to reduce the risk of rolling threads into the fillet radius.

• ASME B1.1 “Unified Inch Screw Threads”. This standard was revised and published in May of 2024. It corrected and revised several issues from the 2019 revision.
• ASME B18.3: “Socket Cap, Shoulder, Set Screws, and Hex Keys (Inch Series)”. The Subcommittee that is responsible for this standard is working on a major revision. Currently the only allowable material choice is to use ASTM A574. This ASTM standard provides only one strength grade, equivalent to 180,000 psi. Unfortunately, this strength level makes these specific parts susceptible to hydrogen embrittlement, especially when they receive a zinc electroplated surface finish. Although the standard recommends avoiding this practice, it does not outright disallow it, and thus, it gets commonly applied. Metric socket parts can also experience this issue, but the metric standard includes option for property classes lower than 12.9 (the metric equivalent of a 180,000 psi strength fastener). To correct this, a task group in this ASME subcommittee has been working on a revision that will include Grade 5 and 8 inch socket products. Work is proceeding but likely will not be completed until the latter half of 2025 or sometime in 2026.
The ASTM fastener committee F16 meets twice a year. The last meeting was in November 2024 and the next meeting was held in Toronto Canada in May 2025.
The following ASTM Standards were revised in 2024:
• ASTM A193/A193M: “Alloy Steel and Stainless-Steel Bolting for High-Temperature or High-Pressure Service and Other Special Purpose Applications”
• ASTM A320/A320M: “Alloy Steel and Stainless-Steel Bolting for Low-Temperature Service”
• ASTM A394: “Steel Transmission Tower Bolts, Zinc-Coated and Bare”. This standard was not changed but was reaffirmed to the last revision in 2008.
• ASTM A540/A540M: “Alloy Steel Bolting for Special Applications”
• ASTM A962/A962M: “Common Requirements for Bolting Intended for Use at Any Temperature from Cryogenic to the Creep Range”
• ASTM F880: “Stainless Steel Socket, Square Head, and Slotted Headless Set Screws”
• ASTM F593: “Stainless Steel Bolts, Hex Cap Screws, and Studs”
• ASTM F3148: “High Strength Structural Bolt Assemblies, Steel and Alloy Steel, Heat Treated, 144KSI Minimum Tensile Strength, Inch Dimensions” This standard was not changed but was reaffirmed to the last revision in 2017.
• ASTM A194/A194M: “Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel, and StainlessSteel Nuts for High Pressure or High Temperature Service or Both”
• ASTM A563/A563M: “Carbon and Alloy Steel Nuts (Inch and Metric)”
• ASTM F467: “Nonferrous Nuts for General Use”
• ASTM C1513: “Steel Tapping Screws for Cold-Formed Steel Framing Connections”
• ASTM F436/F436M: “Hardened Steel Washers Inch and Metric Dimensions”
• ASTM F3393: “Zinc Flake Coating Systems for Fasteners”
• ASTM F606/606M: “Standard Test Methods for Determining the Mechanical Properties of Externally and Internally Threaded Fasteners, Washers, Direct Tension Indicators, and Rivets”
So far, only the following ASTM Standard has been revised in 2025:
• ASTM F3125/F3125M: “High Strength Structural Bolts and Assemblies, Steel and Alloy Steel, Heat Treated, Inch Dimensions 120KSI, 144KSI,and 150 KSI Minimum Tensile Strength, and Metric Dimensions 830 MPa and 1040 MPa Minimum Tensile Strength”. This was a significant revision as it added the 144KSI strength grade for all styles and types of structural bolts.
Highlights of future activity include:
• Currently there are almost seventy work items open in the F16 Committee, impacting forty different fastener standards. Many of these are relatively simple, minor changes, but having so many open work items signifies that this committee is currently very busy, and many standards are likely to be revised in 2025 and 2026.
• A proposal is underway to provide a galvanizing option for A490 (high strength) structural bolts.
• A guideline for best practices regarding fastener test reporting has been in development for several years and may see completion in 2025 or 2026.
The SAE Fastener Committee met in September 2024 and will have its next meeting in September 2025.
Highlights of recent activity include:
• Combination of SAE J1701 and 1701M- These standards are the inch and metric versions of “Torque-Tension Tightening for Inch Series (J1701) and Metric Series (J1701M) Fasteners”. These have been combined into one standard that is expected to publish in early 2025.
• SAE J995- “Mechanical and Material Requirements for Steel Nuts”- There is currently a work project on this standard to clarify the usage of screw machining materials.
• SAE J58- “Flanged 12-Point Screws”. There is currently a work project to revise and update this standard.
• SAE J429: “Mechanical and Material Requirements for Externally threaded Fasteners”. There is a significant revision of this document currently being worked on by a task group. It was balloted in early 2024 but is currently on-hold pending the proposed addition of Grade 5 and 8 versions to ASME B18.3 Socket Products.
The ISO Fastener Committee, TC2, is not a regional Consensus Standard organization, but rather the global activity of many regional fastener organizations. In the U.S., ISO fastener activities are primarily hosted by the ASME Fastener Committee B18, Subcommittee 4. As most metric fasteners worldwide are governed by the standards under the jurisdiction of this committee, it is a very important one.
Highlights of recent activity include revisions to the following standards:
• ISO 15330: “Preloading Test for the Detection of Hydrogen Embrittlement- Parallel Bearing Surface Method”
• ISO 10684: “ Hot Dip Galvanized Coatings”
• ISO 898-1: “ Mechanical Properties of Fasteners Made of Carbon Steel and Alloy Steel- Part 1: Bolts, Screws and Studs with Specified Property Classes- Coarse Thread and Fine Pitch Thread”
• ISO 13809: “Hexalobular Socket Set Screws”
• ISO 6157-1: “Surface Discontinuities- Part 1: Bolts, Screws, and Studs for General Requirements”
• ISO 6157-3: “Surface Discontinuities- Part 3: Bolts, Screws and Studs for Special Requirements”
Unlike the other Consensus Standard’s organizations listed above, which focus on a broad range of fastener topics, the Research Council on Structural Connections (RCSC), is singly focused on user guides for structural steel bolting. Its hallmark standard, the “Specification for Structural Joints Using High-Strength Bolts”, is used worldwide by steel erectors and construction trades. This document has been undergoing a major overhaul and was expected to go out for its second ballot in the first quarter of 2025. Likely approval and publication will occur in the latter half of 2025.
As is obvious above, standards are always changing. Consensus Standard’s organizations incorporate rules within their procedures to make sure that their standards do not get stale and are evolving to incorporate the latest development and understanding in the industry. In fact, an estimated 20%-25% of all consensus standards are under review or revision at any point in time. This is a big advantage, since it helps industry stay abreast of a continuously changing environment. However, it also creates a challenge because with so many standards in use and so often changing, users must be prepared to keep abreast of the changes. That is not always as simple as one might think. Therefore, users are encouraged to find ways to stay abreast of changes and implement actions in their management systems that will keep them up to date.
Copyright owned by Fastener World / Article by Laurence Claus











2025中國上海國際緊固件工業博覽會
On May 22-24, roughly one thousand Chinese and a few overseas fastener-related exhibitors gathered at the Shanghai World Expo Exhibition & Convention Center (SWEECC) to participate in the annual IFS China. This year, two halls were open (one for raw materials, equipment, molds/dies, and consumables, and the other for finished fasteners) with the total exhibition area of about 40,000 square meters.
The exhibitors this year were mainly Chinese companies focusing on domestic sales, but there were also a few European and U.S. machineryrelated companies (e.g. SACMA and National Machinery) wishing to expand their domestic sales in China. In addition, about 10 well-known Taiwanese machinery & equipment brands, such as Chun Zu, Jiancai, Tong Ming, and Jern Yao, as well as some punch/die/wire suppliers also participated in this year's show to enhance their exposure. According to the observation of Fastener World’s staff on-site, the visitors this year, facing the influence of new regulations and tariff barriers from the EU and the U.S., were mainly buyers from China, India and Russia (not many from the EU and the U.S.), and most of them were buyers focusing on domestic sales in China. Visitors came mainly on the first day of the three-day exhibition, and the second day's crowd was less because of heavy rain.
Some local manufacturers revealed to Fastener World’s staff on-site that the turmoil in the global market over the past few months has caused a great impact on the export performance of Chinese suppliers, so many of them have turned to strengthen domestic sales and shifted to India, Brazil, Central & South America, and other emerging markets to cope with it. One Chinese manufacturer mentioned that as Russia recently put out a lot of post-war reconstruction programs ushering in increased demand for fasteners, many Chinese companies received a lot of inquiries and orders from Russian buyers, many of which could not even be handled by a single manufacturer and had to be divided into separate orders to be processed by 2-3 downstream factories in order to ensure punctual delivery. While the EU and the U.S. continue to exert economic pressure on China at the time,

such orders do bring a ray of hope to Chinese manufacturers having encountered significantly decreased orders from Europe and the U.S. and ease the cost pressure on their operation. In addition, a number of industry experts were invited to hold trend seminars and industry summits focusing on CBAM and U.S. tariffs. They mentioned that although CBAM and U.S. tariffs had increased the short-term pressure on Chinese enterprises, the layout of export sales should be continuously strengthened in order to mitigate the involution of the Chinese market.
As there will be another international fastener expo in Shanghai this June, some exhibitors said that, considering the scale of both big shows, they will still actively participate in one of these industry events or both on the premise of expanding market opportunities. However, they suggested that with the dates of both shows being so close to each other, it might be better to combine them into one bigger show, thereby attracting more visiting overseas buyers and expanding the benefits of participation.
The organizer has announced that the next show will be held on May 20-22, 2026 at SWEECC.

















U.S. President Trump signed an executive order on February 10th this year to impose a 25% tariff on all steel and aluminum imports to the U.S., which has come into effect since March 12th, including downstream finished products such as fasteners. The move has put even more pressure on Chinese fastener manufacturers and U.S. importers. This article details China's imports and exports of various fastener items in the first quarter of 2025, and summarizes the top 5 trading partners for each item, as well as which items have a higher import and export demand share. It is hoped that the data in these tables will help readers see whether China's trade in fasteners has changed differently under the pressure of U.S. tariffs.
Note: The fastener items included in this article are: Screws, coach, iron or steel (731811); Screws, wood, iron or steel, nes (731812); Screw hooks and screw rings, of iron or steel, threaded (731813); Screws, self-tapping, iron or steel (731814); Bolts or screws, nes, with or without their nuts or washers, iron or steel (731815); Nuts, iron or steel, nes (731816); Threaded articles of iron or steel, nes (731819); Washers, spring or lock, iron or steel (731821); Washers, non threaded, of iron or steel, nes (731822); Rivets, of iron or steel (731823); Cotters and cotter-pins, iron or steel (731824); Non-threaded articles, of iron or steel, nes (731829).
China exported US$2.317 billion of fasteners to the world in the first quarter of 2025, up 10.65% from US$2.094 billion in the same period of 2024. The top 5 export destinations were the U.S., Vietnam, Russia, Germany and Japan. The export portion to the U.S. increased by about 5%.
China imported approximately US$508 million of fasteners from the world in the first quarter of 2025, a decrease of 9.7% from US$558 million in the same period of 2024. The top 5 sources of imports were Japan, the U.S., Germany, Taiwan and France.
China's exports of various fasteners in the first quarter of 2025 are ranked in the table below. The export value of bolts or screws, nes, with or without their nuts or washers, iron or steel (731815) was over US$ 1 billion. The export value of nuts, iron or steel, nes (731816) was nearly US$ 0.4 billion. The export value of threaded articles of iron or steel, nes (731819) was nearly US$ 0.25 billion. The export value of washers, non threaded, of iron or steel, nes (731822) also reached nearly US$ 0.15 billion.
China's Exports of Various Fasteners in The First Quarter of 2025

China's Exports of Various Fasteners in The First Quarter of 2025
The table on the right hows the ranking of China's imports of various fasteners in the first quarter of 2025. The import value of bolts or screws, nes, with or without their nuts or washers, iron or steel was over US$ 0.2 billion. The import value of nuts, iron or steel, nes was also over US$ 0.1 billion. The import value of washers, non threaded, of iron or steel, nes was nearly US$ 60 million.
The tables below show the top 5 export destinations for individual items. The data show that the U.S. remained China's top export destination for most items, which might be related to the anticipation of US importers to stock up early due to the imminent implementation of tariff measures. Russia was also one of the main export destinations. However, Kyrgyzstan, Germany, Taiwan and Vietnam were the most important export destinations for items 731811, 731813, 731814, and 731823 respectively.
The tables show below the top 5 sources of imports of individual items. Taiwan, Germany, Japan, the U.S., and France were the main sources of imports for China. However, Slovenia topped the list at 731813. In addition, Turkey, Denmark, the UK, Spain, Italy, Sweden, S. Korea, and Indonesia were also major sources of imports. Top 5 Sources of

Although the U.S.-China reciprocal tariff negotiations have seen more positive developments, and the previous high tariff rates have been substantially reduced for the time being under the coordination of the U.S. and Chinese representatives; however, fasteners are subject to the steel and aluminum tariffs under Section 232, and therefore China's fastener exports to the U.S. are still subject to the 25% tariff plus the basic tariff rate. At present, although some Chinese enterprises affected by the U.S.-China trade war have chosen to temporarily shift to other markets to ease the pressure of tariffs, if we view the export data of the first quarter, China's high dependence on the U.S. market for fastener exports may not change much in the near future.
In addition, in terms of imports, the U.S., Germany, Japan, Taiwan, and France were still China's most important sources for fastener imports. Apparently, in terms of some of the higher value-added fasteners, the products from these import partners still have a great deal of attraction to the Chinese buyers.
2024全球汽車產銷分析
產量增長略顯停滯,銷售增幅較顯著

Overthe past 6 months, the global automotive supply chain has been in a state of chaos, with the EU imposing a high countervailing duty of up to 45.3% in October 2024 on Chinese EVs sold to Europe. However, at a time when Trump's tariffs are slashing at the two major sources of automotive exports, the market has also been reporting that the EU and the Chinese government are negotiating and the EU is considering replacing the duties by setting a minimum price for EVs from China. On the other hand, many carmakers have either held off on exporting their cars to the U.S. or suspended customs clearance procedures for cars that were originally planned to be shipped to the U.S. or have already arrived at U.S. ports in order to cope with the huge losses that may be caused by Trump's “ever-changing” tariff policies. The negative effects of the high cost of manufacturing in the U.S. have also begun to emerge, such as layoffs at large European and U.S. car makers, and the dilemma faced by many car makers relying on globalized component supply chains due to the difficulty of accessing non-Chinese-made parts that can avoid the high tariffs in the short term. These market uncertainties will not only affect the expansion plans of global automakers, but also the willingness of consumers to purchase and replace their vehicles in the short term, which will add more uncertainties to the global automobile sales and production situation in the future. This article will analyze the production and sales figures of major car manufacturing countries in 2024, and compare them with the figures in 2022 and 2023, so as to help readers understand the current market situation and development prospects of the automotive industry.
Table 1 shows the amount of cars produced in major countries on each continent over the past 3 years. Over 92.5 million cars were produced globally in 2024, a small decrease of only 1% from 2023 and still more than the 2022 production.
In Europe, the total production amounted to more than 17 million units, down 5% from 2023. The top 5 producing countries were Germany, Spain, Czech Rep., France, and Slovakia. Germany accounted for about 23.6% of the total, producing more than 4 million units. Among the top 5 producers, only the Czech Rep. showed a positive YoY growth of 4%, while the rest 4 had negative growth. Among the 18 major European car manufacturing countries, the Netherlands experienced the largest YoY contraction of 94%.
In the former CIS countries, Belarus and Ukraine are excluded from the comparison as they have not published any vehicle production data for the past 3 years. In 2024 Russia led the way with more than 980,000 units, a 35% increase over 2023. Uzbekistan was in the 2nd place with nearly 430,000 units, a small increase of 1% over 2023. Kazakh production remained at around 140,000-150,000 units, down 2% year-on-year. Azerbaijan, with an annual output of less than 10,000 units, was up 43% year-on-year.
The annual automobile production of Turkey, which spans Europe and Asia, is roughly the size of all production in the former CIS countries. Turkish production once approached 1.5 million units in 2023, but dropped by 7% to just over 1.36 million in 2024.
The Americas is the world's 2nd largest car production region, with its total production reaching nearly 19.2 million units in 2024, almost unchanged from the 2023 figure. 55% of the production was in the U.S., which produced more than 10 million units in 2024, but shrank slightly by 1% year-over-year. Mexico ranked the 2nd with about 4.2 million units, up 5% year-on-year. Canada's decline was significant, shrinking 14% to 1.34 million units, less than Brazil's 2.54 million units. Brazil, the leading producer of automobiles in South America, was the best performer in the Americas with a 10% YoY increase. Argentina and Colombia contracted by 17% and 32% from 2023 respectively.
About 60% of the world's car production is in Asia (incl. the Oceania). Roughly 54.9 million units were produced in Asia (incl. the Oceania) in 2024, not much change from 2023. The top 5
producing countries were China, Japan, India, S. Korea, and Thailand. China's production volume was about 31.28 million units, up 4% year-on-year, while India's volume also grew by 3% to more than 6 million units. Japan, S. Korea, and Thailand shrank by 9%, 3% and 20% respectively compared to 2023. Indonesia, ranked the 6th, also saw a 14% decrease in production compared to 2023.
The major car producing countries in Africa are South Africa, Morocco, Algeria, and Egypt, but Egypt has not announced any production data in the past 3 years, so it is not included in this analysis. Although South Africa has long been the most important car producer in Africa, it produced nearly 600,000 units in 2024, a decrease of 5% from 2023. Morocco has been on the rise in the past 3 years, with a 4% increase to nearly 560,000 units in 2024, and will probably have a golden crossover with South Africa in 2025. Algeria, although producing fewer units, showed impressive growth in 2024 compared to 2022 or 2023 figures.
Estimate
CARS: Audi, BMW, JLR, Mercedes not reported
COMMERCIAL VEHICLES: SINCE Q1 2025: Scania, Daimler Trucks, Volvo Buses not reported
N/A : Non Available Source: OICA

Table 2 shows the car sales in major countries on all continents over the past 3 years. In contrast to the trend of “boom-and-bust” in the global car production over the past 3 years, car sales have increased for 3 consecutive years, growing by 2.7% in 2024 to more than 95.3 million units.
In Europe, the top 5 countries with the highest sales in order in 2024 were Germany, the UK, France, Italy, and Spain. Germany led the list with nearly 32 million units sold, but with a slight YoY decrease of 0.4%. Among the top 5 countries, Spain had the most significant YoY growth of 8.1%, followed by the UK with a 2.6% YoY growth. Poland, the Netherlands, Hungary, Croatia, and Bulgaria all recorded double-digit growths. Only Finland experienced a double-digit contraction.
In 2024, Russia's sales exceeded 1.8 million units, slightly higher than Turkey's 1.28 million units. However, compared to 2023, Russia's sales greatly increased by 39.2%, while Turkey's remained flat. In addition, although Ukraine is suffering from the war, its car sales in the past 3 years still showed stable growth, and in 2024 its sales reached 83,000 units, a YoY growth of 13.4%.
The Americas (incl. the U.S./Canada/Mexico + South America) accounted for more than 24.15 million units of sales in 2024, but N. America alone accounted for more than 80% of the total (about 19.8 million units). Sales in the U.S. in 2024 reached 16.34 million units, up 2.1% year-over-year. Brazil (reaching about 2.63 million units, the 2nd highest sales by volume), with a 14.1% YoY increase, also outperformed Canada, Mexico, and the South American countries in the region. Only Chile, Peru, and Ecuador showed signs of contraction.
In the Asia/Middle East/Oceania region, its total sales in 2024 exceeded 51.4 million units, a small YoY increase of 1.5%. The top 5 countries with the highest sales in order were China, India, Japan, S. Korea, and Australia. China's sales amounted to 31.43 million units, up 4.5% year-on-year. Although India's sales were only about 17% of China's, there was still also a 2.9% YoY increase. Pakistan had the highest YoY increase of 52.1% (other double-digit increases were recorded in the Philippines, UAE, and Uzbekistan as well), while the worst was Thailand at -26.2%.
In Africa, the sales in 2024 totaled about 1 million units, a small YoY contraction of 0.3%. South Africa led the pack with 515,000 units, followed by Morocco and Egypt (which showed the best YoY growth of 9.2% and 12.6%, respectively).


Summarizing the above changes in production and sales data, it can be seen that the growth of the global car production in 2024 was slightly stagnant, especially in Europe. Sales in all regions had a certain degree of growth, especially in Russia, Latin America and the EU, showing that the market's purchasing power continued to show a steady upward trend. However, it should be noted that after U.S. President Trump's announcement of a 25% tariff increase on global cars on April 2, 2025, the global car production, shipment and sales have begun to be chaotic, and the prices of new vehicle sales may be pushed up significantly, and low-priced models in the market may no longer be available. Although there is unofficial news that the 25% tariff on auto parts may be exempted, it is estimated that the market sentiment will remain conservative for the time being, as many uncertainties have yet to be fully eliminated.



According to the "World Economic Outlook" report published by the IMF on July 16, 2024, the economic growth forecast for India in the fiscal year 2024-25 was raised from 6.8% to 7%. This adjustment is primarily attributed to sustained increases in private consumption, particularly in rural areas, which have driven India's economic growth beyond expectations.
The Asian Development Bank (ADB), in its recently released "Asian Development Outlook" report, stated that strong demand in manufacturing and construction sectors is expected to drive robust growth in India's industrial sector. Investments led by public infrastructure projects remain strong, maintaining the economic growth forecast at 7% for the fiscal year 2024-25 and projecting a growth rate of 7.2% for FY2025-26.
Globally, the IMF forecasts a growth rate of 3.3% for 2025. The Economic Counselling and Research Department of IMF noted that emerging economies in Asia remain the primary engines of global economic growth, with India's contribution representing a significant percentage of global growth. Over the next five years, global economic prospects are expected to weaken. "By 2029, China's economic growth is projected to slow to 3.3%, far below current levels," said IMF. China's economic momentum is weakening and shows a sign of cooling. With a narrowing demand-supply gap, India's economic growth potential is worth continuous attention.
As India strives to realize its economic development potential, it accounts for over 15% of the MSCI Emerging Markets Index, up from 6.7% in 2009, ranking second only to China in index weight. Consequently, India is rapidly becoming an indispensable large market. Significant progress has also been observed in addressing supply-demand gaps within its fastener market.
India is a developing economy with the world's largest population of approximately 1.4 billion people. In 2021, its GDP totaled around USD 3.1 trillion, ranking sixth globally. Although per capita income remains relatively low at about USD 2,200, India's domestic market is vast and highly promising, making it one of the most important emerging markets globally. India's future development will primarily rely on several key factors, including demographic dividends, digital economy advancements, promotion of localized manufacturing, and enhanced connectivity with other countries. Promoting manufacturing localization is also a critical component of India's future development strategy under the "Make in India" initiative.
India's economic development includes transforming into a global manufacturing hub and creating more job opportunities while enhancing competitiveness in its manufacturing sector. On January 30, 2024, India's Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) announced mandatory inclusion of various fastener products under "Quality Control Orders" (QCOs) to strengthen quality standards for fasteners. Government notifications S.O. 3267(E), dated
July 21, 2023, and S.O. 2771(E), dated July 12, 2024, listed fastener products under ISI mark certification frameworks (refer to Fastener World Magazine No. 210). These measures aim to prevent circulation of substandard fasteners in the Indian market and avoid accidents or loss of life while attracting investments and promoting upgrades in fastener products.
From 2022 to 2024, export statistics by Taiwan's Bureau of Foreign Trade indicate challenges faced by Taiwan's fastener export market after the world walked out of COVID-19 (refer to Fastener World Magazine No. 209). India is actively developing its automotive industry, leading to a significant increase in demand for automotive fasteners. Additionally, as India undergoes urbanization and industrialization with plans to construct 100 smart cities, industrial fasteners are in demand due to significant rise in infrastructure and construction needs. It is predicted that India's vigorous promotion of the automotive industry and other industrial sectors, along with increased use of construction fasteners, presents a considerable opportunity for high-quality and high-value fasteners. It is worth observing whether the Indian fastener market will become a new blue ocean for the high-quality and high-value fastener industry.
According to trade statistics on steel fasteners, India exported USD1.06 billion worth of steel fasteners in 2023, ranking as the world's 9th largest exporter of such products. Steel fasteners were the 74th most exported item in India that year. The primary export destinations included the United States (USD 217 million), Germany (USD 126 million), the Netherlands (USD 81.5 million), the UK (USD 62.8 million), and Saudi Arabia (USD 44.6 million). Between 2022 and 2023, the fastest-growing export markets for Indian steel fasteners were the UAE (USD 7.74 million), Saudi Arabia (USD 6.9 million), and Italy (USD 6.71 million). In 2023, again India imported USD 1.06 billion worth of steel fasteners, ranking as the world's 12th largest importer of such products. Steel fasteners were ranked as the 94th most imported product in India. The main import sources were China (USD 306 million), Japan (USD 131 million), South Korea (USD 123 million), Germany (USD 109 million), and the United States (USD 78.4 million). Thailand (USD 29.7 million) was India's fastest-growing import origin for steel fasteners between 2022 and 2023. (Figure 1)
▼ Fig. 1. Proportion of India’s Fastener Export Destinations and Import Origins in 2023 (in Percentage by Trading Value)
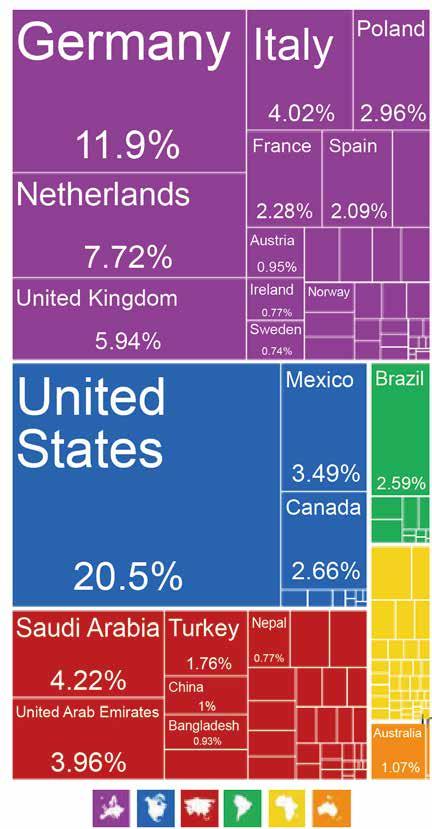
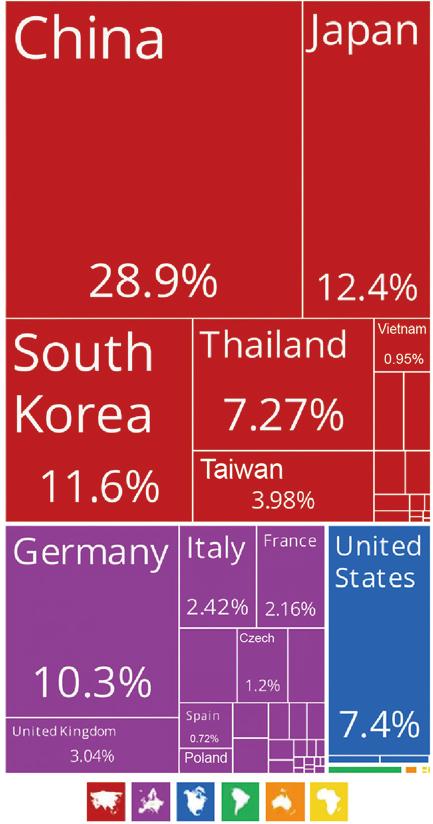
Source: https://oec.world/en/profile/bilateral-product/iron-fasteners/reporter/ind?yearExportSelector=exportYear1&tradeValueExport=tradeScale0#historical-data
Based on India's 2023 fastener statistics, the export and import of various fastener products are categorized using the international goods classification system (HS code), as shown in Table 1. Table 2 compares export and import data from 2021 to 2024. Following the end of COVID-19, India's fastener exports declined due to reduced global demand, showing negative growth, while imports increased, reflecting positive growth.
According to trade statistics compiled by India's Ministry of Commerce and Industry based on H.S. codes, Table 3 compares the total weight and price of steel fasteners exported in 2023 and 2024, while Table 4 compares the total weight and price of steel fasteners imported during the same period. The result of calculations of average unit prices and overall average unit prices is listed in Table 5 in terms of export and in Table 6 in terms of import.
Trade statistics indicate that in 2024, both individual unit prices and average unit prices of imported fasteners in India significantly exceeded those of exported fasteners. From 2022 to 2024, products classified under H.S. code 73181500 accounted for the largest weight percentage in India's market (95,713.19 metric tons in 2022, 1,841,891.59 metric tons in 2023, and 94,502 metric tons in 2024). The average import unit price for this category was USD 4.45/kg in 2022, USD 0.26/ kg in 2023, and USD 5.01/kg in 2024. India's overall average import price for fasteners during this period was USD 4.4758/ kg in 2022, USD 0.55/kg in 2023, and USD 3.45/kg in 2024. This suggests that the quantity of imported fasteners in India in 2024 returned to levels close to the market demand observed in 2022, with unit price variations depending on product type. Therefore, from a supply-demand perspective, except
for products under H.S. codes 73181190, 73181200, 73181400, and 73182400, other categories of fasteners remain essential for India's market among reduced global demand for fasteners. Observing growth trends for products priced above the overall average unit price can help assess future demand for specific types of fasteners in India.
Comparing export unit prices with countries such as Vietnam and Thailand (refer to Fastener World Magazine No. 204 and No. 201), the average unit price of India's steel fastener export is lower or similar to Vietnam's prices, offering competitive advantages over countries such as Vietnam and Thailand in international trade due to lower costs. However, compared to ASEAN countries, India exhibits a stronger demand for high-value imported fasteners. A statistical analysis suggests that India primarily exports lower-value fasteners produced domestically or resold internationally, while importing higher-value fasteners to meet domestic market shortages or high demand.

Loosening nuts and bolts during operation has been a problem since their invention. Wedge Locking Washers are currently considered in professional circles to be one of the most reliable locking systems for bolted joints. In this sense, they are presented not only by manufacturers, but also by distributors. They gained their popularity mainly after the spread of the so-called Junker vibration test, which is used to check the reliability of locking systems. This vibration test, according to DIN 65151, is considered the most severe vibration test for bolted connections. To testify to the complete properties of this locking method and to help designers is the task of this contribution. It is important to note that the article is of a strictly technical nature and has no ambition to interfere with the distribution network.
Wedge locking washers (WLW) are two washers glued together in a pair with external ribbing and internal wedge surfaces (Fig. 1). The wedge-locking method is based on tension instead of friction. A typical bolted joint assembly with WLW application is shown in Fig. 2 According to the manufacturer's recommendation, a pair of wedge washers should be in the case of nut connections installed under the bolt head as well as under the nut. The pair of washers use cam-geometry. Any attempt from the bolt/nut to rotate loose should be blocked by the wedge effect of the cams.
Considering that WLWs belong to the group of locking elements whose locking effect depends on the preload of the bolted joint pA → f(FM ) (Fig. 3), the existence of up to 7 interfaces (Fig. 2) is unpleasant. Fig. 2 also shows that by installing two pairs of WLW, the clamping length of the joint increases by 2x h.
Depending on the roughness of the surface and the hardness of the steel, each interface manifests itself in material settling. The rougher the surface of the material and the greater the number of interfaces, the more significant the resulting settlement value and the decrease in preload. It is also proven by the Junker test in Fig. 4. From this figure it is clear that only one washer, i.e. not a pair, causes a lower settling value while still showing the same locking effect. However, this fact needs to be examined more closely, as it may also depend on the strength of the material of the parts being joined.
It was already stated at the beginning that wedge locking washers are considered in professional circles to be one of the most reliable locking system for bolted joints. This is also proven by Fig. 4. But is it true in every case? The answer to this question requires a more detailed analysis. First, the known shortened quote from C.O. Bauer:
“For each bolting stress another locking dress!”
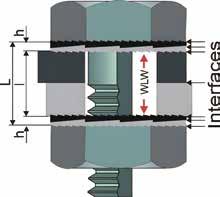
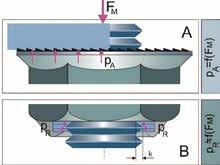
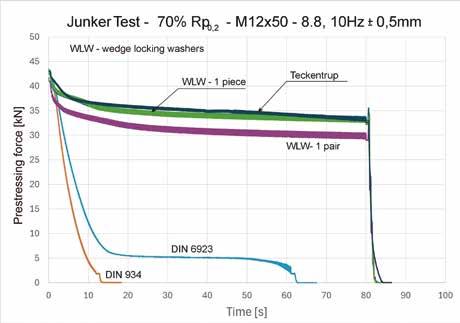
This bolting axiom is based on the principle that during operation, screw joints are exposed to mainly two various mechanical effects (Fig. 5, 6 and 7). This serious fact cannot be disputed, but is fully respected. This also applies to the choice of the relevant locking of screw joints and their vibration testing methods.
The different locking effect of WLW at different stresses is clearly documented in Fig. 8a with an associated Fig. 8b
These pictures show that wedge locking washers were the best at resisting transverse vibrations, moderately resistant to axial vibrations loading, and according to Hard Lock Technical Report, 2007, vol. 2, completely failed when NAS 3354 was applied.
The Junker vibration test (Fig. 9) itself gradually gained such popularity that the DIN 65151 standard was assigned to it. This has earned it the credit of a generally valid standard for any type of stress. However, such a function belongs to it wrongly, because it does not respect the different stress conditions of bolted joints (s. Dominik, J.: Polemic About Junker Test Standard in: Hardware & Fastener
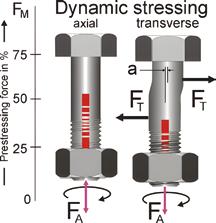


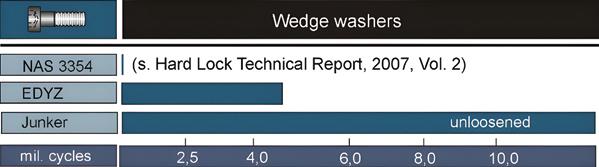
Components No. 62, May 2024). For that reason, there should be a revision of the standard in the sense that only transverse dynamic load applies.
It is obvious that the hook on the wagon (Fig. 10) is subjected to tensile cyclic stress and an axial pulsator must be used to test the strength bolts that secure it (Fig. 11). The Junker test would not be objective.
It must be objectively admitted that for the given type of stress, WLW is a good option. However, the locking effect is not the only criterion for its selection. Here are the next: Price, Logistic (number of parts), Assembly difficulty, Repeatability, Number of interfaces, Ability to seal, Damage of contact surface.
Therefore, it does not hurt to remember some other options for securing screw joints. The current market offers a wide choice of external locking elements. Among the many options, at least flange nuts with ribs (Fig. 12) should be mentioned (there are also similar head screws with an integrated ribbed flange). The benefits would be at hand: fewer interfaces, simpler logistics, easy assembly, safe for use in food machinery from a health point of view.
The article uncompromisingly confirmed the truth of C. O. Bauer that there is no universal type of bolting that would be equally effective for all types of stress. It should be added that there is also no universal method of testing the resistance of threaded bolting to vibration. For the designer, this is a clear signal for the individual choice of method for securing bolted joints against spontaneous loosening. Of course, this only applies to cases that require external securing. The basic prerequisite for this is a thorough knowledge of the conditions (type of stress, aggressiveness of the environment, etc.) under which the future construction will operate.






緊固件 帶狀組織
Copyright owned by Fastener World Article by Chang Hsien-Ming

With the development of the automotive industry, especially new energy vehicles and technology improvement, the mechanical properties of fasteners have been increasingly emphasized. The mechanical properties of general fasteners include yield ratio, hardness, fatigue life, and other key indicators, of which the fatigue life is the most direct response to the physical properties of a fastener under external loading.
In the production of fasteners, after the use of a batch of raw materials, it is inevitable that another batch of raw materials will be used. The composition of raw materials from different steel mills and different furnace lot numbers of the same steel mills is different, and such a difference will lead to a serious impact on the quality of heat treatment. Even the same material grade, specifications and performance of products with different furnace lot numbers (in the same process), processed with the same equipment and heat treatment, will appear inconsistent tensile strength, hardness value and deformation, and may even appear serious deviation or quench cracks. Hence, it is necessary to make corresponding adjustments in the heat treatment process for products of different furnace lot numbers.
Low alloy steel is one of the key materials widely used in automobiles, railway, engineering machinery, etc. It is an important raw material to ensure the safety of core component connection. “Band” is a common harmful structure of low alloy steel. Common band types are ferrite/pearlitic, ferrite/martensitic, etc. In terms of low alloy steels, band generally refers to ferrite/pearlitic structure formed under slow cooling of hot rolling (see Fig. 1).
According to the formation mechanism of banded structure, it can be divided into primary banded structure (caused in the solidification process of steel due to selective crystallization and dendritic segregation) and secondary banded structure (which is caused in the heat treatment of steel and is parallel, layered, strip-like along

▲ Fig. 1 Ferrite/Pearlitic Structure

the machining direction). Banded structure is a common structural defect formed in the hot rolling process of coil and bar billets, which seriously affects the subsequent processing and performance of the steel.
In the automotive industry, there is no need for control of banded structure in high grade bolt steels. However, the conditions, control requirements and rationale for its creation need to be reasonably understood and are discussed below:
Micro segregation of alloys is the reason for the formation of banded structure, and reasonable control of alloy composition, dendritic morphology and thermal processing technology is also an important way to inhibit banded structure. The larger the temperature difference between the Ar3 region transformation within and between the dendrites caused by micro segregation, the easier the formation of banded structure. The cooling rate and grain size during austenite decomposition are the main factors influencing the formation of banded structure, and higher cooling rate and larger grain size will inhibit the occurrence of banded structure.
There are two general reasons for the formation of banded structure:
① Banded Structure Caused by Component Segregation
In terms of low carbon bolt steel, when more impurities exist, processing deformation will result in the streamlined distribution of impurities. When the steel cools from the heat processing temperature, these impurities can be used as the core of the nucleation of the proeutectoid ferrite, which will generate around the impurities first, while the remaining austenite will turn into pearlite, making proeutectoid ferrite and pearlite distribute in bands, thus forming banded structure, which is difficult to eliminate by heat treatment.
② Banded Structure Caused by Improper Heat Processing
Temperature
In forging, when the forging-stopping temperature of the medium carbon alloy bolt steel is in the phase between Ar1-Ar3, ferrite will precipitate from the austenite in the form of bands along the direction of metal flow, and the austenite which hasn’t decomposed yet will be cut into bands. When the temperature cools down to Ar1, the austenite will be transformed into banded pearlite, which can be eliminated by normalizing or annealing.
The existence of banded structure will make the mechanical properties of bolt steel anisotropic, and those along the banded structure will be obviously better than those perpendicular to it. Materials are prone to crack from the junction during the forging process. Since the banded structure is different from the adjacent microstructure, there are also differences in performance, and the uneven distribution of stress between the strong and weak bands will result in the overall reduction of mechanical properties, especially the significant reduction in the plastic toughness of the bolt steel; the anisotropy of structure and performance is prone to lamellar tearing along the banded structure under external force, often laying a hidden danger for the early failure of bolts.
2.1
Since there is a lack of research on automotive fastener banded structure in China, banded structure should be the industry's attention in view of its increasing impact on the production and performance of steel. Banded structure in high-end fasteners used in the aviation/aerospace, marine engineering, advanced rail transportation, and other key areas should especially receive urgent attention. Comment on the solutions of formation, hazards, and control of banded structure in common fastener steel, and raise key issues in the study and control of banded structure.
The banded structure of steel for fasteners can only be evaluated visually in the annealed equilibrium state (see Fig. 2). Fig. 2 shows the banded distribution of ferrite/pearlitic 45 steel.

The more serious the banded structure is, the more serious the alloy segregation is, and the hardenability varies greatly in different areas. Largesize bolts after head forging, if not annealed or normalized, will be prone to granular bainite organization and thus affect the mechanical processing performance; in addition, during the quenching process of bolts, the hardenability of the areas with low alloy content (ferrite banded areas) is lower, making it hard to guarantee the quality of quenching. The core of the bolt is prone to banded hardened bainite, resulting in greater fluctuations in tensile loading, affecting the stability of the mechanical properties. In short, the quality of the relevant heat treatment technology of fasteners has a significant impact.
During the cooling process, the first ferrite precipitation area is where the austenite is relatively unstable. Such a unstable condition is due to the low alloy content in the region. The pearlitic region with the high alloy content will lead to stable austenite. The relative content (%) of ferrite and pearlite depends on the carbon content of the material. At the same time, to promote the uniform diffusion of alloys and reduce the micro segregation in the solidification structure of coil, bar and billet is the main way to reduce or eliminate the banded structure. Elongated inclusions may be present in the banded structure, however, the effect of the size, morphology and distribution of inclusions in the steel on the banded structure has not been clear so far. The detailed characterization and quantitative evaluation of banding and its harmful effects are important tasks that need to be carried out urgently. In addition, the influence of the heating system of coil and bar billets on the elimination of banding and the control of the grain size also needs to be studied.




