











































































































































































































As the global manufacturing industry shifts toward high quality and low pollution, Chin Tai Sing Precision Manufactory (CTSP) leverages its technical strength and diverse supply capabilities to deepen its presence in Europe’ s high-end market and emerging Asia Pacific markets, showcasing strong overseas competitiveness. The company supplies global clients with costeffective threaded inserts and clinching fastener solutions.
CTSP integrates IoT equipment on production lines with AI and machine learning to precisely monitor production data. It has developed a smart demand forecasting system and a process selfoptimization mechanism while enforcing strict batch number management. These initiatives enhance traceability, production efficiency, and quality stability. Environmentally, CTSP holds RoHS certification and actively promotes low-carbon manufacturing. It carries out carbon inventories and provides carbon footprint reports with CBAM data, helping clients meet international environmental and carbon reduction standards. Energy optimization and waste management further drive CTSP’s green smart manufacturing goals.
CTSP develops high-precision products with a tolerance accuracy of ±0.01 mm to meet stringent performance and reliability needs from clients in Europe, America, and Japan. It has entered supply chains in automotive, aerospace,

electronics, telecommunications, construction, and defense sectors. Equipped with automated machinery and experienced teams, the company achieves a monthly output of over 20 million pieces and a near-zero PPM ultra-high yield rate. Besides brass, it offers customized stainless steel, aluminum, and other material designs, responding flexibly to varied market demands and becoming a trusted partner for global high-end industries.
serves clients in 50 countries, with 80% from Europe & America and 20% from Asia. Its European focus targets advanced economies like Germany, France, and the UK, where strict environmental regulations and green technology standards present strong business opportunities. CTSP collaborates with leading automotive and aerospace manufacturers in Europe, capitalizing on its green energy and high-performance parts expertise. Rapid urbanization and infrastructure growth in Asia-Pacific and other emerging markets fuel demand in automotive, electronics, and machinery sectors. Strategic markets also include India and Japan. Leveraging geographic and supply chain advantages, CTSP meets local demands and steadily grows market share.
Focusing on cost-effectiveness and competitive pricing, CTSP provides global clients with high-performance products at affordable prices. Automated production lowers manufacturing costs, while R&D innovations optimize materials and processes to ensure quality and price balance. This cost-performance strategy extends product applicability and supports one-stop customized design, production, and inspection services. CTSP strengthens long-term client partnerships, maintains leadership in the global high-end sector, and demonstrates robust international competitiveness and growth potential.

CTSP’s contact: General Manager Lee


























































































































英輝三款轉接扳手新上市,用戶體驗全面革新!
With over 40 years of craftsmanship and a commitment to high quality, Ing-Hwei Implements Mfg Corp has become a trusted leader brand in Taiwan's tool industry. Originally focused on manufacturing DIY hand tools, it later transformed to specialize in professional-grade hand tools, particularly developing and producing double socket wrenches and punches. Today, its products fully comply with German DIN standards and have gained recognition in the European professional automotive repair market, with products marketed globally. Moreover, it listens to user feedback, optimizing its products to better match user feel and performance needs.




Continuously evolving, Ing-Hwei has addressed long-standing market issues such as limited size options and high prices by expanding its product lineup to include:
• Torque Wrench Spanner Adapter
• Crows Foot Spanner
• Flare Nut Torque Adapter
These new products cover a wide range of sizes, including 3/8" (4-square drive) 12-point star adapters from 6mm to 22mm, 3/8" (4-square drive) crows foot spanners from 8mm to 22mm, 1/2" (4-square drive) crows foot spanners spanning 23mm to 32mm, and 3/8" (4-square drive) flare nut torque adapters fitting 10mm to 22mm dimensions. Through production line expansion and technological upgrades, these products offer users richer size selection and competitive pricing — delivering high performance professional tools at competitive prices.
The torque wrench spanner adapter set is designed with dual functions as a wrench and extension, securely fitting nuts to avoid slippage. In tight spaces where regular sockets and wrenches cannot operate, this adapter set enables users to easily apply sufficient torque for nut removal. The key lies in its adjustable length that compensates for existing tool length limitations, greatly improving operational convenience and efficiency. Made from chrome vanadium steel with corrosion-resistant chrome plating, these tools guarantee long-lasting durability and stable performance, delivering excellent performance even in harsh environments. The market has welcomed these products with enthusiastic response, with customers highly praising IngHwei’s competitive pricing, quality, and nut-holding stability.
Strategically targeting professional automotive repair and maintenance industry customers, Ing-Hwei aims to expand both domestic and overseas markets. It also offers custom packaging, labeling, and tailored manufacturing services, supports urgent orders, and provides fast delivery with 24-hour response times to ensure customers receive superior service experience.
Looking ahead, Ing-Hwei will continue listening closely to customer needs, developing further product improvements aligned with expectations, and uphold its mission to provide enhanced user experience and diverse supply platforms. This commitment will further consolidate its market leadership position as the most trusted professional hand tool expert.
Ing-Hwei’s contact: Mr. An-Szu Chen (Andy)
Email: inghwei@inghweitools.com.tw
Copyright owned by Fastener World / Article by Dean Tseng



































五金零組件全球新聞
Mr. Wu-Zhi Hsieh Takes Helm
謝武志接掌台灣手工具公會 引領產業數位與綠色轉型
compiled by Fastener World

On September 5, 2025, Taiwan Hand Tool Manufacturers' Association (THTMA) held its 17th General Meeting in Taichung City, electing Wu-Zhi Hsieh, President of Jun Kaung Industries, as the new association Chairman. Hsieh will lead a team focused on driving digital transformation, green manufacturing, and international expansion to meet evolving industry challenges. Hsieh expressed gratitude for members’ trust and highlighted the responsibility of his role. Taiwan’s hand tool industry is globally recognized for high quality and flexible manufacturing, providing a strong market position. However, fast-changing global affairs like U.S. tariffs, supply chain restructuring, environmental trends, AI, and digital technology are reshaping competition. Hsieh stressed that digital transformation is no longer exclusive to large firms; ERP systems, smart machinery, automation, AI, and big data are key to boosting efficiency. The association will seek government resources to support members’ digital adoption toward high-value manufacturing. Green sustainability is now imperative. The association will assist companies in obtaining international environmental certifications to enhance competitiveness in global procurement. Hsieh also emphasized the importance of international market development, partnering with trade and economic ministries to promote overseas exhibitions and digital marketing, shifting from price to value-based competition. Talent cultivation and industry succession remain vital. The association plans to strengthen industry-academia collaboration and training programs, underscoring the promising future of conventional industries and calling for united innovation and value creation.

美國關稅對中國手工具衝擊, 台灣競爭力或可提升
Secretary-General of the Executive Yuan, Ming-hsin Kung, stated in a press conference that Taiwan’s main competitors in hand tools for the U.S. market are Vietnam and China. Vietnam’s current temporary tariffs match Taiwan’s at about 23.3%, while China faces much higher tariffs totaling 58.3%. Kung noted China’s exports have sharply declined due to tariffs, creating market opportunities for Taiwan. He emphasized Taiwan’s competitors are not South Korea or Japan, as South Korea mainly supplies spray guns and Europe and Japan have their own brands. U.S. brands are unlikely to shift sourcing to South Korea, Japan, or Europe despite higher Taiwanese tariffs.
According to Kung, China’s hand tool exports to the U.S. dropped by 25%, 34%, and 16% in April, May, and June respectively, indicating market contraction. This provides Taiwan with space to compete more aggressively. If Taiwan expands efforts, it can capitalize on this market shift. Government support toward industrial upgrading is essential to seize this opportunity and grow Taiwan’s presence in the U.S. hand tools market.
墨西哥擬提高中國進口關稅
The Mexican government plans to raise tariffs on Chinese imports in its 2026 budget to protect domestic industries from cheap imports and meet U.S. demands. These higher tariffs are expected on goods like cars, steel products, textiles, and plastics to reduce dependency on China and other Asian countries. Mexico’s trade deficit with China has grown, and increased tariffs could boost revenue and ease the budget deficit while improving relations in the USMCA trade agreement with the U.S. and Canada. Chinese cars have gained popularity in Mexico, making it the top global market for these vehicles, but higher tariffs may increase prices and reduce affordability. Industry experts suggest quotas for lowtariff Chinese cars to balance consumer access and international pressure. Mexico currently imposes tariffs ranging from 5% to 50% on many Chinese goods, and the planned tariffs aim to further shield its domestic industries.


德國汽車業遭美國關稅衝擊 裁員超過5萬人

Germany’s automotive industry faces severe challenges due to U.S. tariffs and other factors. A recent report by consulting firm Ernst & Young Global shows that approximately 51,500 jobs were lost in Germany’s auto sector over the past year, accounting for nearly 7% of total positions, making it the hardest-hit industrial sector. Major manufacturers like Mercedes-Benz and Volkswagen, along with suppliers such as Bosch, Continental, and ZF, have announced costcutting plans, while Porsche plans to significantly reduce its batterypowered vehicle business. As of June 30, 2025, total industrial employment in Germany fell by 2.1%, equivalent to about 114,000 jobs, with industrial sales declining for eight consecutive quarters, dropping 2.1% year-on-year in Q2. Ernst & Young Global predicts this downward trend in industrial employment will continue. Industry insiders cite U.S. tariffs, high energy costs, and weak domestic demand as major pressures. Ernst & Young Global’s Germany managing partner Jan Bruecher highlights a steep decline in exports to the U.S., posing clear risks to Germany’s industrial sector and underscoring the need for caution amid ongoing challenges.
澳洲終止對華可互換夾緊螺栓夾頭反補貼調查

On August 11, 2025, the Australian Anti-Dumping Commission announced the termination of the anti-subsidy investigation on Chinese imports of interchangeable bolted clipping system clip heads. The decision was based on the negligible subsidy margins found for Ningbo Fenghui Metal Products and other Chinese exporters, making the subsidy impact insignificant. The investigation began in June 2024 following a complaint by Australian company Abey Australia Pty Ltd. It covered imports from April 1, 2023, to March 31, 2024, with the injury period starting April 1, 2020. In March 2025, the Commission issued a preliminary affirmative anti-dumping determination, imposing provisional dumping duties which calculated ad valorem at 31.5% for Ningbo Fenghui and 76.8% for other exporters. However, due to insufficient evidence for subsidies, the anti-subsidy probe continued until now. The product’s Australian customs code is 7326.90.90.60. The termination of the anti-subsidy investigation provides short-term relief to Chinese exporters, improving their competitive position in the Australian market.
現代汽車第二季因美國關稅損失6億美元
英國汽車產量創1953年以來新低

Hyundai Motor reported a 16% drop in operating profit for Q2 2025, reaching 3.6 trillion KRW (about USD 2.64 billion), down from 4.28 trillion KRW in the same period last year. U.S. tariffs on vehicles and parts negatively impacted profits, causing a loss of approximately 828 billion KRW (USD 606 million) in Q2. The company expects even greater impact in the third quarter. The CFO noted the U.S. tariff rate on South Korean cars might slightly decrease from the current 25%, though the extent is uncertain. This tariff challenge highlights ongoing trade policy risks for the automotive sector, with Hyundai actively adjusting strategies to sustain competitiveness.
UK car and van production in the first half of 2025 has hit its lowest level since 1953 (excluding Covid lockdowns). Car output fell 7.3%, while van production dropped 45% due to Vauxhall’s Luton plant closure. Uncertainty over US tariffs caused some manufacturers to slow or halt production. A US-UK tariff deal reducing automotive tariffs from 27.5% to 10% took effect at the end of June, boosting June production slightly. Electric vehicle production grew 1.8%, reaching a record 25% of total output. The UK government reinstated EV grants of up to £3,750, but unclear eligibility criteria have confused manufacturers and consumers. SMMT CEO Mike Hawes described the period as “depressing” but hopes it marks the industry’s bottom. He noted that to meet the government’s target of 1.3 million vehicles per year by 2035, the UK needs one or two new carmakers. While EV grants aim to support the market, qualification depends on carbon emissions and verified targets, with details yet unclear. The UK automotive sector is tackling challenges from US tariffs and growing Chinese competition.


Arrow®擴展產品線推出新系列手工具
Arrow Tool Group, a trusted name in fastening solutions for nearly 100 years, has expanded its product range by launching its first line of Arrow-branded hand tools. Known primarily for the iconic T50® staple gun, this new collection caters to DIY enthusiasts, homeowners, and the growing community of thrift-store treasure hunters. The hand tools are designed to make home improvement, quick repairs, and creative upcycling projects easier and more accessible. CEO Roberto Izaguirre highlights that these tools deliver the durability professionals expect while being friendly and easy to use for DIYers. The collection showcases a variety of essential tools: adjustable wrenches and lock pliers, multi-bit screwdrivers in various sets, and more. In partnership with a DIY influencer of a blog called Thrift Diving, Arrow promotes the hand tools through engaging tutorials and challenges designed to inspire confident and enjoyable projects. This new line represents Arrow's commitment to quality, innovation, and broadening accessibility for home improvement enthusiasts.
UF-Tools推出全球批量訂 購螺絲起子的方案

UF-Tools, a professional precision screwdriver manufacturer, announced new bulk order solutions to support international retailers, distributors, and e-commerce sellers worldwide. The well-received products highlight UF-Tools’ reputation as a reliable Chinese manufacturer offering high-quality tools at competitive prices. To meet growing global demand, UF-Tools now offers large-volume orders with customized services, including logo printing, packaging design, and private-label branding, providing OEM and ODM options that enable partners to build their brands. All screwdriver kits comply with international standards such as CE certification for Europe and North America, ensuring product safety and market readiness. With streamlined production and global shipping, UF-Tools facilitates efficient bulk purchasing for overseas buyers. A company spokesperson emphasized that these bulk order solutions empower partners to access precise, durable, and market-ready tools, cementing UF-Tools’ position as a trusted partner in the global hardware market.
美國聖克萊爾技術教育中心獲贈價值7,800美 元工具及安全裝備

St. Clair TEC's Construction Trades program recently received a generous donation of tools and personal protection equipment (PPE) valued at over USD7,800 from the Marshall E. Campbell Company and its industry partners. This contribution will provide students with access to professional-grade equipment essential for their training and future careers.
The donation process started with a visit by a Marshall E. Campbell representative who toured the program’s tool storage area with instructor Ken Sygit to assess specific needs. Based on this assessment, the company supplied a variety of high-quality tools and PPE.
On September 10, Marshall E. Campbell staff delivered the initial donation valued at USD7,375, including items such as a saw, impact drill, sawhorses, hand tools, gloves, and other safety gear. Stanley Black & Decker’s industrial account manager Scott Schillag accompanied the delivery. The program’s key staff—Lesley Murphy (CTE Director Principal), Ken Sygit (Construction Trades Instructor), and Caleb Howell (Construction Trades Paraprofessional)— were present to receive the equipment. A follow-up donation of USD500 in tools and PPE was made possible through Milwaukee Tool, coordinated by Josh Richardson, with additional safety gear contributions from MCR Safety’s Terry Reed.
Lesley Murphy expressed gratitude for the support, emphasizing that these tools will allow students to train with the same professional-grade equipment they will encounter in the workforce. While the donation primarily benefits the Construction Trades program, the impact extends across TEC as students share resources between programs, enhancing overall career readiness and hands-on learning opportunities.




























Stanley Black & Decker任命
Christopher Nelson為新任執行長
Stanley Black & Decker announced Christopher Nelson as its president and CEO effective October 1, 2025. Nelson, who serveed as chief operating officer, executive vice president, and president of the Tools & Outdoor business, succeeds Donald Allan Jr., CEO since July 2022. Upon taking the CEO role, Nelson also joins the board of directors.


Grainger盈利和展望受宏觀經濟困境衝擊
As part of this transition, Allan becomes executive chair of the board from October 1, 2025, while current board chair Andrea Ayers becomes lead independent director and continue chairing the executive committee. Allan planned to retire October 1, 2026, after which the board would return to an independent chair governance structure.
Board chair Ayers praised Allan’s 26 years of leadership, emphasizing his vital role in transforming Stanley Black & Decker and stabilizing the business through tough times. Allan remains an important resource as executive chair to support Nelson and the board. Nelson expressed honor in leading the iconic American company, citing his deep understanding of customer needs and confidence in the company’s strong foundation for sustainable long-term growth. Since joining in 2023, Nelson has been instrumental in optimizing the company’s core businesses and strategic roadmap. He looks forward to driving growth and innovation globally.
Ingersoll Rand歡迎Aurobind Satpathy加入董事會
Ingersoll Rand, a global provider of mission-critical flow creation and life sciences and industrial solutions, announced the appointment of Aurobind Satpathy to its Board of Directors, effective immediately.

Satpathy currently serves as a senior partner at McKinsey & Company, a global management consulting firm. During his nearly 30-year career with McKinsey & Company, Satpathy led multibillion-dollar mergers, guided companies through public-to-private transitions, and architected growth strategies that resulted in increases in market capitalization. In addition, Satpathy led global technologyenablement efforts within McKinsey’s Operations practice and held leadership roles across several offices, practices, and global committees.
“Aurobind’s leadership in high-impact engagements across diverse industries demonstrates his deep expertise in aligning strategy with execution,” said Vicente Reynal, chairman and chief executive officer of Ingersoll Rand. “We look forward to leveraging his strategic mindset, and his ability to unlock value through bold, data-driven insights will be a welcome addition to our Board.”
This appointment underscores Ingersoll Rand’s ongoing commitment to maintaining a robust and dynamic Board of Directors focused on innovation, operational excellence, and sustainable growth.
Shares of tool company Grainger fell 12% in premarket trading after its second-quarter earnings missed Wall Street expectations, impacted by tariffs, and its fullyear forecast came in below consensus. Grainger posted earnings per share of USD 9.97 for the quarter, slightly below analysts’ average estimate of USD 10.06. Revenue rose to USD 4.55 billion, narrowly topping expectations of USD 4.53 billion. For the full year, Grainger expects earnings between USD 38.50 and USD 40.25 per share, below the consensus estimate of USD 40.54. It also forecasts revenue of USD 17.9 billion to USD 18.2 billion, compared with expectations of USD 17.94 billion. “Performance was impacted by some tariff-related factors which are also flowing into our updated outlook,” said CEO D.G. Macpherson, noting the ongoing macro backdrop remained challenging.

Fastenright, South Africa’s leading stainless steel fastener supplier, celebrates 15 years of steady growth and success. Founded with a vision to provide unmatched quality and service, Fastenright now stocks about 10,000 products across four warehouses, with a fifth under construction, ensuring swift delivery for diverse industries where even small fastener failures can cause costly downtime. Managing Director Rainer Lutz reflects on the challenges of building a specialized supplier and credits his team and key partners for their dedication. Fastenright’s products are vital in major projects, such as supplying over 15,000 fasteners for Milnerton’s historic wooden bridge restoration and securing the corrosionresistant MeerKAT radio telescope in Northern Cape. The company specializes in high-grade stainless steels including acid-resistant A4-80 and duplex grades 2205 and 904L, with select sizes stocked for urgent orders. Fastenright also supplies fasteners for water treatment, marine, and industrial applications. Looking ahead, Fastenright aims to expand in renewable energy sectors, particularly solar, by partnering with global leaders to offer a reliable local alternative with extensive inventory and fast delivery. Lutz reaffirms the company’s commitment to quality, service, and lasting customer relationships in South Africa and beyond.

Optimas推出QuickShip計劃 解決扣件庫存短 缺問題
Optimas Solutions launched its QuickShip program to solve inventory shortages affecting OEMs and distributors. Operating from their Wood Dale, Illinois facility, the program offers a rapid lead time of 1 to 4 weeks for externally threaded fasteners sized 2mm to 20mm diameter and 5mm to 220mm length. QuickShip integrates Optimas’ engineering, tooling, cold heading, threading, and local secondary processing—including heat treatment and plating—to dramatically reduce the usual 8 to 16-week lead times. Daniel Harms, CEO of Optimas Americas, said the program offers a seamless, efficient solution that prevents downtime from part shortages. Featuring over 40 thread styles and 6 licensed drive types with IATF and ISO certifications, QuickShip ensures high-quality parts. VP Chris Martens emphasized the program’s agility and costeffectiveness, enabling manufacturers to quickly access precision-engineered components to keep operations smooth. Ranked 8th in fasteners on MDM’s 2025 Top Distributors list, Optimas reported USD 635 million in 2024 revenue, reflecting its strong position in the market.
Zhengshan Intelligence Successfully Develops 718 Nickel-Based Alloy Bolts

正山智能成功研製718鎳基合金螺栓
Zhengshan Manufacturing Innovation recently announced successful product validation of 718 nickelbased alloy bolts, marking a significant breakthrough in domestic high-end fasteners and breaking long-term foreign monopolies. The bolts use high-temperature resistant alloy materials with carefully balanced iron, nickel, chromium, and molybdenum, offering excellent pressure and corrosion resistance suitable for aerospace, petrochemical, and other advanced sectors. Supported by a national laboratory and over 50 advanced testing devices, the company achieves over 99% product testing coverage. Their self-developed digital management platform ensures over 95% equipment connectivity, enhancing R&D efficiency and product quality. The company holds three intellectual property rights related to data and optimizes production costs through multi-process integration. It plans to continue advancing technological innovation, expand global competitiveness, and promote the domestic substitution of high-end fasteners.
Riverspan收購United Titanium 推動特殊合金扣件


Riverspan Partners has acquired United Titanium, a leading manufacturer of fasteners and components for aerospace, defense, and medical industries. Founded in 1962 and headquartered in Wooster, Ohio, United Titanium offers over 14,000 SKUs made from specialty metals like titanium, zirconium, and tantalum. Products include hex head bolts, socket head cap screws, and pipe fittings, used where corrosion resistance and strength are critical. Led by President Mike Reardon, United Titanium has built strong market positions and long-term customer relationships. Riverspans partner Dave Thomas expressed commitment to enhancing innovation and service to support continued growth. According to Verified Market Research, the global titanium fasteners market was valued at USD 4.3 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 7.2 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 7.5%. Growth is driven primarily by aerospace and defense demand for lightweight, strong, corrosion-resistant materials, along with expanding automotive, medical, and marine sectors. Founded in 2022 and based in Chicago, Riverspan focuses on lower middle-market industrial companies with EBITDA between USD 5 million and USD 35 million. This acquisition positions United Titanium for further expansion and strengthens Riverspan’s industrial portfolio in specialty alloy fasteners.


San Diego fastener distributor Mesa Fastener Inc. was acquired last month by investment firm Raymond Capital Management, according to a recent announcement from the company’s advisory firm Generational Group.
Generational Group stated that Mesa, founded in 1977 as a provider of tapping screws for mobile home awnings, now stocks over 10,000 unique products and supplies commercial threaded fasteners— including blind rivets, bolts, nuts, anchors, washers, and other specialty items—to various industries across the Southwest.
The announcement noted that Raymond Capital Management builds “resilient, high-performing industrial brands” through acquisitions and expertise. The St. Louis-based firm offers distribution, inventory management, custom manufacturing, and analytics capabilities.
The deal, which closed on August 11, did not disclose its terms.
TTX穩定桿連桿
Mevotech has released a new TTX stabilizer bar link, part number TXMS40836, enhancing its Terrain Tough Extreme (TTX) product line with full front-end coverage for both 12th and 13th generation Ford F-150 trucks (2009-2020 models). This new stabilizer bar link kit is engineered to provide superior durability, optimized compression control, and easier installation, making it ideal for demanding commercial and passenger vehicle use.

The TXMS40836 features advanced technologies including Repel-TEK™ surface treatment to resist rust and corrosion, and upgraded rubber bushings with knurling to secure the stabilizer bushing firmly in place. The design also includes a unique Labor Saver™ barrel nut that reduces installation time and effort. Mevotech’s in-house and third-party durability testing ensures the stabilizer bar link delivers reliable, long-lasting performance, meeting the high standards required for heavy-use vehicles.
With this release, professional technicians can now access a complete range of TTX suspension and steering components for Ford and Lincoln trucks and SUVs in North America, supporting over 9 million vehicles. Mevotech continues to lead in providing robust, high-performance aftermarket parts designed for longevity and ease of installation.

TONE Tool has introduced its new locking pliers series designed specifically to tackle rusted or damaged bolts and nuts. The three available models—VPN-100, VPN-175, and VPN-250—offer varied jaw opening sizes to accommodate different fastener dimensions, with cutting capabilities for diameters ranging from 1.2 mm to 2.3 mm.
These locking pliers feature a unique triple-point jaw design that securely grasps bolts and nuts, including small-diameter screws, preventing slippage even on worn or rounded fasteners. An integrated hexagonal adjustment screw allows the user to tighten the grip once the pliers are locked, ensuring superior holding power during mechanical operations. The tool is designed to provide durability and reliability, making it ideal for professional and industrial use.
TONE Tool emphasizes safety by advising users not to use the pliers for unintended purposes and not to modify the tool, such as extending the handle. Confirming the locked position before use is crucial for safe operation. This innovative tool aims to improve efficiency and safety in demanding mechanical tasks where traditional pliers struggle, offering a dependable solution for fastener rescue and handling.
Kyoto Tool Co., Ltd. (KTC) introduces a new 9.5sq Cordless Ratchet Wrench Set. The ultra-compact and lightweight cordless ratchet offers high rotation speed approximately 1.4 times faster than KTC’s previous model JAR353, significantly reducing operator fatigue and shortening work time.
Designed for ease of handling, the wrench features an LED light synchronized with the trigger switch to improve visibility on target workpieces. A battery charge indicator informs users of remaining power, while a reliable locking mechanism prevents accidental operation, enhancing safety.
The set provides a familiar user experience for those switching from air ratchets, combining portability with efficiency. With its innovative design, KTC aims to support faster and safer maintenance and mechanical operations across industries.



冷媒用可更換套筒頭扭力扳手
TONE Tool has introduced a new torque wrench model TCSP01 designed specifically for refrigerant flare nut fittings used in air conditioning and refrigeration systems. This innovative torque wrench features interchangeable spanner heads that cover four common sizes (17mm, 22mm, 26mm, 29mm), allowing users to work flexibly with various flare nut sizes using a single tool.
The TCSP01 ensures precise tightening by alerting the user with a distinct “click” sound and a light tactile shock once the preset torque value is reached. This feature helps prevent under-tightening and over-tightening, which can cause refrigerant leaks and damage system integrity. The torque is adjustable to four different levels, and the spanner heads can be quickly removed and replaced with a one-touch mechanism, improving efficiency on the job.
Constructed with durable materials and offering a torque accuracy of ±4%, the TCSP01 is designed with ease of use and reliability in mind. TONE also attaches a quality inspection certificate with each unit. The tool is ideal for technicians servicing HVAC equipment, helping ensure safe, leak-free refrigerant connections.
輪端軸承調整套筒
RevHD, a leading provider of wheel-end components, has introduced its new Rev-Socket product line designed to simplify and improve the accuracy of bearing adjustments on manually adjusted wheel hubs. These sockets are engineered to visually guide technicians through the 2-1-1 bearing adjustment procedure—an easy-to-remember and repeatable method that reduces human error and ensures consistent RP-618 accuracy on the wheel end.
The sockets feature etched hash marks that act as visual guides, helping technicians step through the 2-1-1 adjustment process with precision and speed. Compatible with a wide range of nuts on the market, these tools are ideal for small fleets and dedicated repair shops aiming to enhance maintenance efficiency. This new socket empowers technicians to perform precise manual bearing adjustments quickly and accurately. By improving bearing adjustment accuracy and speeding up the process, RevHD's new sockets are expected to elevate maintenance standards across the industry.


UF-Tools has launched a new 35-in-1 Electric Screwdriver, designed to combine versatility, convenience, and power in one compact tool. This latest innovation includes 35 different screwdriver bits, allowing users to handle a wide variety of screw types and sizes, making it an ideal tool for professionals and DIY enthusiasts alike.
The electric screwdriver boasts features such as variable speed control, ergonomic design for comfortable use, and a rechargeable battery providing long runtime. Its multifunctionality allows quick bit switching and precise torque control, enhancing efficiency on various tasks from electronics repair to home maintenance.









































Import

In descending order according to weights of 2024 Source: EU Trade Helpdesk

According to 2024 data, China, Taiwan, and India are the top three import sources. Import value from China rebounded to €278,267,568 in 2024, a significant increase from €217,331,182 in 2023, approaching 2022 levels. Import value from Taiwan decreased from €242,825,339 in 2023 to €226,265,804 in 2024, indicating a decline in imports. India saw a slight rebound, rising from €34,157,413 in 2023 to €36,011,473 in 2024, though still below the 2022 level. Among the top 3, China showed the most significant growth, while Taiwan exhibited a declining trend.
China, Taiwan, and India remain the primary import sources. Import value from China rebounded to €762,937,122 in 2024, up from €646,233,338 in 2023 but below the 2022 figure of €880,803,558. Import value from Taiwan increased slightly from €122,885,897 in 2023 to €126,591,992 in 2024, indicating Taiwan's stable export performance. Import value from India saw a significant increase, rising from €26,491,476 in 2023 to €35,798,825 in 2024, surpassing the 2022 figure of €34,241,916 and indicating strengthened import demand. Overall, import values from countries other than China either rebounded or remained stable.
HS 8207--Interchangeable Tools
China, the United Kingdom, and Turkey are the primary import sources. In 2024, import value from China value reached €1,072,623,886, remaining largely unchanged from 2023's €1,067,841,253, indicating China's stable export performance. Import value from the UK rebounded from €114,251,307 in 2023 to €122,009,822 in 2024, showing an upward trend. Import value from Turkey, however, declined significantly from €85,817,791 in 2023 to €76,428,003 in 2024, reflecting reduced demand. Overall, import weights in 2024 rebounded compared to 2023, primarily driven by increased demand from countries like the UK. However, declines from nations such as Turkey indicate market volatility.











HS 8204--Hand-Operated Spanners & Wrenches


The United States, the United Kingdom, and Switzerland remain the primary export markets. In 2024, exports of the 27 EU member states reached €284,854,931, demonstrating steady growth and an increase from €278,932,758 in 2023. Exports to the United States reached €62,843,610 in 2024, continuing their upward trend with a significant increase from €57,897,157 in 2023, reflecting robust market demand. Exports to the United Kingdom also maintained growth, rising from €41,212,322 in 2023 to €43,549,085, indicating market stability. On the other hand, exports to China amounted to €17,601,682 in 2024, showing a slight decrease compared to 2023, indicating reduced demand. Exports to Turkey, however, demonstrated a growth trend, rising from €9,791,615 in 2023 to €10,422,182, reflecting a relatively robust performance.
The United Kingdom and the United States are the primary export markets. Exports of the 27 EU member states reached €758,061,101 in 2024, demonstrating steady growth and an increase from €709,665,944 in 2023. Exports to the United States in 2024 totaled €162,826,415, a significant increase from €142,778,336 in 2023, reflecting a robust rebound in demand. Exports to the United Kingdom also grew steadily, rising from €89,852,087 in 2023 to €94,898,002 in 2024. In contrast, exports to Turkey saw a slight decline, falling from €22,256,632 in 2023 to €21,218,723, indicating a pullback in demand. Exports to China, however, increased from €29,561,654 in 2023 to €34,488,095 in 2024, reflecting a rebound in demand within that market.
The United States and China are the primary export markets. Exports of the 27 EU member states totaled €3,624,318,820 in 2024, a slight decrease from €3,645,172,043 in 2023, indicating a stable yet slightly declining trend. Exports to the United States decreased from €867,202,592 in 2023 to €854,462,449 in 2024, indicating a slight decline in demand. Meanwhile, exports to China remained stable, with 2024 exports totaling €365,536,758, a slight decrease from €369,265,116 in 2023. Exports to the United Kingdom saw significant growth, rising from €256,158,412 in 2023 to €286,378,935 in 2024, indicating strengthened demand. Exports to Turkey, however, decreased from €177,626,488 in 2023 to €162,888,263 in 2024, reflecting reduced market demand. Overall, demand in major markets like China remained stable, while demand in the US showed a slight decline and the UK demonstrated growth.


Copyright owned by Fastener World / Article by Shervin Shahidi Hamedani
Brazil’s fastener industry, already operating in a competitive global environment, now faces one of its biggest external challenges in decades. In mid-2025, the United States imposed a 50% tariff on a wide range of Brazilian imports. While certain commodities such as pulp and refined copper were exempted, industrial inputs like fasteners, specialty metal components, and their raw material base, steel, aluminum, and copperderived products, were left exposed.
For Brazil’s fastener sector, this development represents both a shock and an inflection point. On one hand, it risks undermining competitiveness in a core export market; on the other, it creates pressure for adaptation, innovation, and diversification. To understand the long-term implications, it is necessary to assess the cost dynamics, market share risks, and potential strategic responses of Brazilian fastener producers.
According to sectoral analysis, the Brazil industrial fasteners market was valued at USD 1.33 billion in 2024. Looking ahead, the industry is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.20% between 2025 and 2034, reaching USD 2.21 billion by 2034.
The growth trajectory is closely tied to Brazil’s robust agricultural machinery sector. As farm equipment producers increasingly demand durable and vibration-resistant fasteners for machinery operating in rugged field conditions, new opportunities are emerging for suppliers able to innovate in design and performance. This agricultural pull is complemented by demand from construction, automotive, and infrastructure projects, all of which are key pillars of Brazil’s industrial economy.
Table 1: Brazil Industrial Fasteners Market Projection (2024–2034, Pre-Tariffs)
To better illustrate the tariff effect, we've modeled two growth scenarios:
1. Baseline Projection (No Tariffs) – Based on market research, the sector is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.2%, expanding from USD 1.33 billion in 2024 to USD 2.21 billion by 2034.
2. Tariff-Adjusted Projection (Low Case) – Accounting for lost U.S. exports (~USD 30–35 million annually, ~2.5% of market) plus indirect effects on input costs and investment confidence, growth slows to ~4% CAGR, resulting in a market value of USD ~1.97 billion by 2034.









Although the fastener industry is not Brazil’s largest export sector, it is highly sensitive to global trade conditions. The 50% U.S. tariff affects not only finished fasteners but also key inputs like steel and aluminum, amplifying cost pressures throughout the supply chain.
1. Cost Pressures Across the Value Chain
Producers now face higher input costs and reduced export competitiveness in their second-largest destination market. The U.S. has historically absorbed a meaningful share of Brazil’s fastener exports, especially in automotive, construction, and machinery. Losing pricing power in this market undermines economies of scale.
2. Market Share Erosion
The tariffs are likely to accelerate sourcing shifts. Under USMCA, Mexican suppliers retain tariff-free access and benefit from short logistical chains into U.S. hubs. Asian producers also remain costcompetitive due to scale. Unless Brazilian suppliers differentiate on quality or specialty niches, market share losses are likely.
3. Investment Risks
For fastener producers, export stability is critical to justify investment in new technology. The tariff shock introduces uncertainty that could delay modernization and digitalization efforts. In an industry already transforming toward coated, lightweight, and smart fasteners, this poses a long-term competitiveness risk.
The repercussions of the 50% tariff extend well beyond Brazil’s core fastener manufacturers. Because fasteners are embedded across multiple industrial ecosystems, related sectors are directly affected by cost and competitiveness shifts.
1. Steel and Metalworking
Fasteners rely heavily on steel, aluminum, and copper. With tariffs also applied to these raw materials, Brazilian mills and processors face rising costs and tighter margins. This creates a double burden for fastener makers: higher input prices and reduced export competitiveness.
2. Automotive Sector
Brazil’s automotive industry is one of the largest consumers of engineered fasteners. The tariff shock weakens Brazil’s ability to export vehicles and components to the U.S., while also raising domestic production costs. For Tier-1 and Tier-2 suppliers, this compounds the pressure to find cost savings elsewhere in the supply chain.
A growth driver for the fastener market, agricultural machinery depends on vibration-resistant and durable fasteners. While domestic demand remains strong, tariffs increase the cost of producing equipment intended for export, potentially narrowing Brazil’s competitive edge in international agribusiness markets.
4. Construction and Energy Infrastructure
High-volume fastener applications in construction, renewable energy, and oil and gas also face knockon effects. If costs rise faster than global benchmarks, Brazilian firms risk losing bids for international projects, from wind turbine installation to offshore rigs.
Despite the headwinds, Brazil’s fastener industry retains several advantages:
• Specialization and Quality: Brazilian producers have strong capabilities in high-strength, engineered fasteners for mining, energy, and infrastructure. These niches are less price-sensitive.
• Domestic Growth Buffer: Rising agricultural and construction demand sustains baseline expansion.
• Currency Dynamics: A weaker Real can partially offset cost disadvantages abroad.
• Diversification Opportunities: Mercosur, Africa, and Southeast Asia provide alternative markets less affected by U.S. trade policy.
1. Government–Industry Coordination
Brazil’s response must be collaborative. The federal government has initiated both WTO consultations and domestic legal frameworks for reciprocal tariffs. For the fastener industry, engagement with government trade bodies is essential to ensure the sector’s needs are represented. Possible measures include export financing schemes, temporary rebates, or targeted relief for fastener producers integrated into global automotive and machinery supply chains.
2. Market Diversification
The U.S. will remain an important market, but producers must actively cultivate alternatives. Latin America represents a natural first tier, with cultural and logistical affinities. Africa and Southeast Asia, undergoing industrial and infrastructure expansion, represent second-tier opportunities. Developing B2B digital export channels can also expand reach to smaller industrial buyers beyond traditional distributors.
3. Process and Product Innovation
Rising tariffs increase the urgency of improving efficiency. Lean manufacturing, automation, and better energy utilization can compress production costs. At the same time, product innovation, such as corrosion-
resistant coatings, highprecision fasteners, or fastening systems integrated with digital monitoring, can create value-added niches where price is not the sole competitive lever.
Joint ventures with foreign partners, especially in markets less exposed to U.S. tariffs, could help Brazilian companies retain international relevance. Partnering with OEMs or Tier-1 suppliers in automotive, aerospace, or construction equipment could shift relationships from commodity supplier to strategic collaborator.
The U.S. tariffs are not just a Brazil-specific issue. They signal a shift in the global trade environment towards protectionism and supply chain nationalism. For fasteners, a sector that thrives on global integration, scale, and standardization— the implications are profound. Companies must prepare for a world where tariffs, non-tariff barriers, and geopolitical risk increasingly shape competitive dynamics.
Brazil’s experience will be closely watched by other emerging-market fastener producers. The ability, or inability, of its industry to adapt may provide lessons on how to safeguard competitiveness amid external shocks. The key lies not just in surviving short-term disruption but in repositioning for the long-term future of fasteners: high-performance, technology-enabled, and globally integrated products.
The imposition of a 50% U.S. tariff on Brazilian exports presents a formidable challenge to the country’s fastener-related industries. The shock threatens cost structures, market share, and investment confidence. Yet, within this challenge lies an opportunity: to accelerate diversification, deepen specialization, and strengthen innovation.
Brazil’s fastener industry has demonstrated resilience in the past, operating in cycles of currency volatility, raw material shortages, and shifting demand. The current tariff regime is more than another cycle; it is a structural challenge that requires strategic recalibration. If industry and government act in concert, Brazil can transform vulnerability into competitive renewal, ensuring its fastener sector remains a credible global player in the years ahead.
References: • Expert Market Research (EMR GLAIGHT), Brazil Industrial Fasteners Market Size and Share Outlook 2025–2034.
• Reuters, Reports on Brazil’s response to U.S. tariffs, August 2025.
• Fact.MR, Industrial Fasteners Market in Latin America, 2024.




























美歐關稅協議如何重塑汽車供應鏈與扣件產業格局

Data note: The data for this article is derived from the Eurostat trade statistics. Eurostat trade statistics analyze imports and exports on all modes of transportation. That value is calculated in USD FOB Value and Net Weight (kg.) for exports. The HS Codes used in this article are 8703 (motor cars and other motor vehicles designed to transport people other than public transportation type) and 7318 (screws, bolts, nuts, coach screws, screw hooks, rivets, cotters, cotter pins, washer and similar articles of iron or steel).
Anewtransatlantic trade deal is shaking up the cost of doing business in the auto world. Under the recently announced U.S.-EU trade framework, most European goods now face a 15% tariff floor, including cars. While tariffs on EU-built vehicles are conditionally being brought down to that level, steel and aluminum remain in limbo, with negotiations still unresolved. The spotlight, however, is squarely on the auto industry—the largest single export channel from Europe to the United States. In 2024 alone, nearly US$42 billion worth of EU-manufactured passenger cars rolled into the U.S. market. That flow is now subject to a new cost calculus. For automakers, the shift means tough choices about pricing, production strategies, and whether to bring more operations stateside. And for the fastener industry— tightly intertwined with automotive supply chains—the ripple effects are immediate: higher import costs, stronger incentives for localized sourcing, and fresh uncertainty over whether future quotas could sweep in steel and aluminum fasteners.
In a rapidly escalating trade standoff, the U.S. reignited tensions with Europe by raising tariffs on steel and aluminum imports to 25% on March 12, 2025, under Section 232 of U.S. trade law. This move triggered a swift global response, with the EU retaliating by announcing tariffs on US$23 billion worth of American goods, phased in from April through year’s end. Meanwhile, the current administration doubled down in April by implementing a sweeping 10% “reciprocal tariff” on most imports—though it faced immediate legal challenges. By early
June, the U.S. had expanded these tariffs to 50% on metals and extended them further to cover appliances and over 400 derivative products, despite EU warnings and growing industry unease. Talks intensified in June, but with no full deal in sight by the July 9 deadline, European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen pivoted to pursuing a more political “agreement in principle.”
That framework was unveiled on July 27, when President Trump and von der Leyen announced a compromise: most EU goods would now face a 15% U.S. tariff—down from a threatened 30%—while strategic goods like aircraft remained exempt. However, steel and aluminum were notably left out, remaining under a punishing 50% tariff. The following day, both sides revealed plans for a “metals alliance” to explore a quota-based system (TRQs) to address global overcapacity—particularly from China. A more formal “Agreement on Reciprocal, Fair, and Balanced Trade” was outlined on August 21, pledging deeper cooperation on tariff realignment and industrial investment. Yet by late August while the EU signaled willingness to eliminate some industrial tariffs to gain reduced car duties, no progress had been made on metals. European industry leaders—especially in steel—continued to criticize the deal’s ambiguity and burden, as critical details on quotas and tariff relief remained elusive.
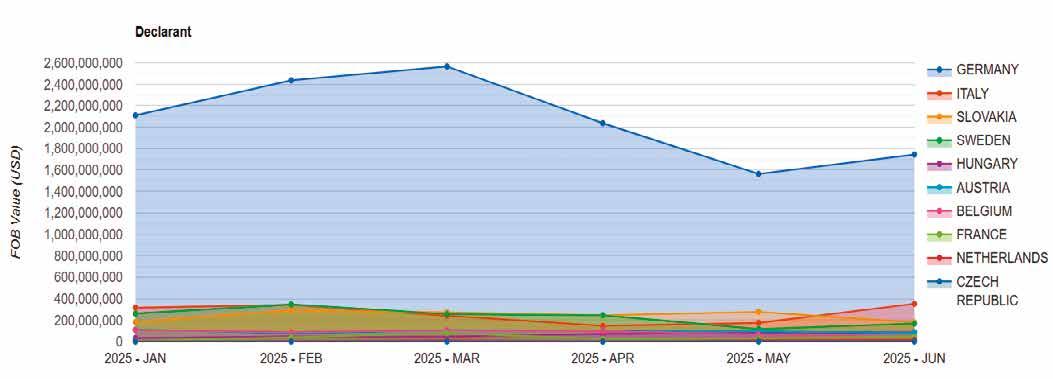
During the first half of 2025, the European Union exported US$18.6 billion worth of automobiles to the United States, with






Germany accounting for a dominant 67% of that total. Other major EU exporters included Italy (8.5%), Slovakia (7.7%), and Sweden (7.5%). Monthly figures show a strong start to the year: exports totaled US$3.1 billion in January, rising to US$3.6 billion in both February and March. However, shipments declined in the second quarter, dipping to US$2.9 billion in April, US$2.4 billion in May, and US$2.7 billion in June—a downward trend that analysts attribute in part to ongoing uncertainty surrounding transatlantic tariff negotiations. In a broader view, 2024 saw total EU auto exports to the U.S. reach US$42.2 billion, slightly below the US$43.8 billion posted in 2023. Among the top automotive export categories are HS Code 870323 (passenger vehicles with spark ignition), 870340 (hybrid vehicles), and 870324 (larger-capacity spark ignition vehicles), which remain the backbone of EU-to-U.S. trade in the automotive sector.
870323 - passenger motor vehicles with spark-ignition internal combustion reciprocating piston engine, cylinder capacity over 1,500 cc but not over 3,000 cc
870340 - passenger motor vehicles, with both spark-ig intrnl combust and electric motor, other than those charges by pluggin to external electric power
870324 - passenger motor vehicles with spark-ignition internal combustion
- motor
870360 - motor vehicles with both spark-ig and electric motor, capable
by plugging to extnl pwr
870322 - passenger motor vehicles with spark-ignition internal
870333 - passenger motor vehicles with compressionignition internal combustion piston engine (diesel), cylinder capacity over 2,500
870350 - motor vehicles, with both compres-ig internal combust piston engine (diesel/semi-diesel) and electric motor,not charged by plug
870332 - passenger motor vehicles with compressionignition internal combustion piston engine (diesel), cylinder capacity over 1,500 cc but not over 2,500 cc
870321 - passenger motor vehicles with spark-ignition internal combustion reciprocating piston engine, cylinder capacity not over 1,000 cc
870370 - motor vehicles, with both compression-ignition internal combustion (diesel/semi-diesel
870340
870333 -
870350 - motor vehicles, with both compres-ig internal combust piston engine (diesel/semi-diesel) and electric motor,not charged by plug








870332
870390 -
870370 - motor vehicles, with both compression-ignition internal combustion (diesel/semi-diesel and electric motor, capable of charged by plugging
Fastener exports from the EU to the U.S. also held steady through the first six months of 2025, totaling US$636 million. Germany once again led the pack, supplying 48% of that volume, followed by France and Italy, each contributing 15%. The remaining EU member states accounted for smaller shares ranging between 1% and 4%. While month-to-month fastener exports remained largely stable, February marked a minor dip to US$103 million, down from US$106 million in January, before rebounding to US$107 million in March. This steadiness contrasts with the volatility in automobile exports and underscores the strategic importance of fasteners as a more stable, albeit less headline-grabbing, component of the transatlantic trade equation.







Declarant



















































The U.S. automobile industry is facing an acute supply chain risk because of the 50% tariff imposed on steel fasteners imported from the European Union. These seemingly small components are vital to the structure and safety of every vehicle, playing an essential role in assembling engines, suspensions, electronics, and battery systems, especially in electric vehicles. Historically, many of these highgrade, precision-engineered fasteners have come from European suppliers, particularly in Germany and Italy, where manufacturers like Würth, Böllhoff, and Fontana have dominated the supply chain.
With no exemptions or relief mechanisms currently in place under the broader U.S.–EU trade framework, these fasteners now fall under the same elevated tariff burden applied to broader steel and aluminum categories. The result is a steep increase in production costs and potential delays as U.S. automakers and parts suppliers scramble to requalify new sources of supply. The just-in-time nature of automotive manufacturing leaves little room for error, and many of the fasteners subject to the tariffs must meet rigorous quality and safety standards, limiting the speed at which suppliers can pivot.
In response, companies are beginning to reconfigure their sourcing strategies. Mexico, which benefits from tariff-free access under the USMCA, is rapidly emerging as a preferred alternative, with some EU-based fastener producers already operating satellite facilities there.
Domestic U.S. producers stand to gain, but the ramp-up in certified production capacity is likely to take years, not months. While there is growing pressure from industry groups like the Industrial Fasteners Institute to include fasteners in any future tariff-rate quota system or exemption framework, no changes have been confirmed. Until then, fasteners remain a hidden but critical pressure point in an industry already contending with inflation, supply chain volatility, and the transition to electric mobility.
Unless meaningful adjustments are made either through new trade carveouts or accelerated investment in North American manufacturing, automakers may find themselves caught between rising costs and tighter margins, with
downstream effects rippling through vehicle pricing, competitiveness, and production stability well into 2026.
Taiwan being home to the world’s largest fastener export industry is also seeing increased demand. South Korean firms, particularly those tied to the Hyundai-Kia supply network, offer another viable option for advanced parts.






Fasteners may be small in size, but they are fundamental to modern manufacturing. They hold together the skeleton of a car, secure battery packs, keep washing machines and refrigerators intact, and join the complex structures of aircraft and engines. A single product can require thousands of fasteners, each playing a precise role.
While the cost of fasteners in an automobile represents only about 2–3% of the total body value, their impact goes far beyond their price tag. Production speed, defect rates, product reliability, and even warranty costs often depend on these components. As Fastener World Inc. points out, fasteners are practically invisible to consumers but indispensable to manufacturers’ efficiency and profitability.
Tariffs have two distinct channels of impact:
1. Direct: a 50% duty on fasteners (HS 7318) shipped from Mexico to the U.S.
2. Indirect: a 30% duty on everything that contains fasteners—cars, parts, appliances, aerospace components— assembled in Mexico and exported north.
Because Mexico is deeply integrated into U.S. supply chains, the indirect channel is by far the larger economic lever.
Copyright owned by Fastener World / Article by Behrooz Lotfian

Global context helps. The world traded about US$49.8 billion in iron fasteners in 2024; the United States was the largest importer (~US$7.05 billion). So the direct, Mexico-origin sliver of U.S. fastener supply is modest relative to total U.S. fastener imports, but it is highly tailored to North American manufacturing needs and standards (OEM prints, PPAP’d parts, just-in-time delivery). Disrupting that specialized flow would punch above its weight in terms of production headaches.
Let’s size the direct exposure first. In 2024, Mexico exported about US$315.5 million of iron & steel fasteners (HS 7318) worldwide, with roughly US$266.5 million going to the United States. In the same year, Mexico imported US$2.90 billion of iron & steel fasteners— making it the 3rd largest fastener importer globally—with the United States being its top supplier at US$1.40 billion. Mexico is, in other words, a net importer of fasteners to feed its factories.
• Price jump on Mexico-origin fasteners in the U.S.: Empirical work on the 2018 tariff wave found near-full passthrough of import tariffs to U.S. domestic prices, meaning most of the duty showed up as higher prices for U.S. buyers, not lower foreign prices. Expect a similar dynamic here: U.S. buyers would pay close to ~50% more for affected Mexico-origin fasteners until they re-source.
• Scramble to re-source: Mexican-tooled fasteners are often engineered, audited, and qualified for specific assembly steps. Switching to non-Mexican supply (U.S., Taiwan, China, EU) isn’t instantaneous—especially for critical fasteners and safetyrelated joints—inviting delays and premium freight.
However, because Mexico exports far fewer fasteners than it imports, the direct, tariff-on-fasteners channel is numerically smaller than the indirect, tariff-on-everythingwith-fasteners channel.

No industry in Mexico is more fastener-intensive (by value and complexity) than automotive. Mexico produced roughly 4.0–4.2 million vehicles in 2023–2024, among the top five producers globally, and exports the bulk to the U.S.
On the components side, estimates put Mexico’s auto-parts production value at ~US$122–127 billion in 2024, with the U.S. the destination for ~85–90% of exports. Through early 2025, Mexico shipped US$42.2 billion in auto parts just in the first five months (87% to the U.S.). Even with recent softness, H1 2025 auto exports to the U.S. were ~US$22.1 billion for finished vehicles and US$40.7 billion for parts.
A 30% tariff on Mexican autos and parts landing in the U.S. would therefore cover tens of billions of dollars of highly fastener-dense goods per year. Automakers have already warned that broad tariffs would ratchet up U.S. vehicle prices and disrupt integrated supply chains; a 30% rate would intensify that effect.
Mexico is a major exporter of refrigerators, freezers, washers, dryers, ovens, and related components to the U.S. In 2024, Mexico shipped about US$9.46 billion in home appliances to the U.S., second only to China. Refrigerators alone accounted for ~US$7.25 billion of Mexico’s 2023 exports (with US$6.38 billion to the U.S.) .
A 30% duty would thus sweep across an US$8–10 billion stream of fastener-intensive goods. Cabinet frames, compressors, doors, hinges, racks, and internal subassemblies rely on thousands of fasteners per product family, many bought on contract schedules months in advance.
• U.S. retail price pressure on mid-market fridge/freezer/washer/dryer lines built in Mexico.
• Production juggling by multinationals with plants in both Mexico and the U.S. (and sometimes Asia). Short-term, shifting production isn’t trivial due to tooling and supplier footprints; medium-term, companies can rebalance SKU.
Mexico’s aerospace industry—concentrated in Querétaro, Baja California, Sonora, Chihuahua, and Nuevo León—employs ~50–60k workers directly and has exports around the US$10.7 billion mark in 2025. It is highly fastener-intensive, governed by rigorous certification of every bolt and rivet.
A 30% tariff would bite in two places :
•Airframe subassemblies and machined components shipped to U.S. primes (higher landed cost, potential schedule slips if re-sourcing is required).






•Aerospace-grade fasteners (if Mexico-origin and exported to the U.S.)— a smaller dollar amount than autos/appliances but often zero-defect, qualificationheavy parts where switching suppliers is slow.
The 2018–2019 research record is instructive. Multiple studies found that U.S. import tariffs were largely passed through to domestic prices; foreign exporters did not significantly cut prices to offset duties, and U.S. consumers and downstream firms bore the cost. Using that empirical lens, a 30% tariff on Mexico-origin goods would, absent carve-outs, materially raise costs for U.S. buyers (OEMs, retailers, consumers) while compressing Mexican manufacturers’ volumes and margins as price elasticity bites. Short-run pass-through is typically highest where qualification and tooling are specific (think: automotive safety-critical fasteners, aerospace hardware) and where inventory buffers are thin. Over 12–24 months, expect partial resourcing to the U.S., Canada, Asia, or Europe—though that introduces its own constraints (capacity, lead times, and new-supplier approvals).
• Direct exposure (fasteners themselves): Moderate. Mexico exports <US$200 million in fasteners to the U.S. annually, so the tariff’s direct hit to U.S. fastener supply is measurable but not system-sized. However, those parts are often highly engineered, and swapping sources quickly is hard.
• Indirect exposure (everything that uses fasteners): Very large. The tariff would fall on US$10s–US$100s of billions in Mexico-made vehicles, parts, appliances, and aerospace goods— sectors where fasteners are ubiquitous and switching costs are high. Expect price increases for U.S. buyers, volume pressure for Mexican plants, and a multi-year resourcing grind.
• Pass-through: History says the tariff cost largely lands on U.S. customers (consumers and downstream manufacturers), at least in the short run. Mexico’s factories take the hit via demand reductions and margin squeezes, especially in price-sensitive product tiers.







If a 30% tariff materialized and stayed broad, the most likely end-state is not a clean re-shoring of everything to the United States, but rather a patchwork: some dual-sourced fasteners, some SKU shifts among North American plants, higher inventory buffers, and incrementally higher prices for U.S. autos and appliances. For Mexico, the fastener-related economy would remain intertwined with U.S. demand but would be forced into defensive investments (qualification of more non-U.S. suppliers, added logistics, and working capital), trimming the very efficiency advantages that made North America’s integrated manufacturing so competitive in the first place.






























Vietnam is located on the eastern part of the Indochina Peninsula, bordered by the Gulf of Tonkin and the South China Sea to the east and south, adjacent to Yunnan and Guangxi Provinces of China to the north, and neighboring Laos and Cambodia to the west. It covers an area of 331,000 sq km with a coastline of over 3,200 km. Since the end of 2024, its population has exceeded 0.1 bn. Since implementing its Renovation policy in 1986 and establishing a socialist-oriented market economy in 2001, Vietnam's national economy has developed rapidly, becoming one of the fastest-growing economies in Asia and the world. Its annual GDP growth rate has consistently remained above 6%, propelling the country from one of the poorest in the world into the ranks of middle-income countries.
Vietnam has been in a state of prolonged war since the mid-20th century, and it was only after the reunification of North and South Vietnam that the country began to recover and rebuild. Due to the prolonged conflict and communist rule, Vietnam severely lacked the conditions necessary for developing its automotive industry, resulting in weak R&D capabilities and production technology in this sector. Before the reform and openingup, Vietnam's domestic demand for cars primarily relied on importing complete vehicles from the former Soviet Union or importing auto chassis from East Germany, which were then assembled into medium- and largesized passenger vehicles at factories in locations such as Tỉnh Hoà Bình, Ba Dinh, Nam Ha, Haiphong, and Da Nang. Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union and the reunification of East and West Germany, Vietnam lost its original import sources. To ensure the supply of the domestic car market, the Vietnamese government established policies allowing foreign investment to set up car assembly plants in Vietnam. In 1991, two jointventure (JV) car assembly plants were established: the Vietnam Mekong Automobile Company, a JV between S. Korea and Vietnam, and the
Vietnam Motors Corporation (VMC), a JV between Japan, S. Korea, and Vietnam. These JV assembly plants gradually laid the foundation for Vietnam's automotive industry.
In 2024 Vietnam's total vehicle ownership was estimated to reach approx. 900,000 units, with 48.4% being commercial vehicles and buses and 51.6% being small and medium-sized passenger vehicles and microcars. Vietnam's auto parts manufacturing, assembly, and production capabilities are insufficient, with most vehicles being assembled and sold locally by int’l brands. Most auto parts manufacturers are foreign-owned, and key components for passenger vehicles, commercial vehicles, or trucks are largely dependent on imports.
In recent years Vietnam's economy has grown rapidly, domestic demand has expanded, and it has signed tariff and trade agreements with many countries, making it the core of economic development among ASEAN. Its automotive industry has seen active investment and expansion. In addition to domestic carmakers (e.g., VinFast and Thaco) actively expanding their production, Korean Hyundai has partnered with Vietnamese carmakers to establish a JV for car production. Since Jan. 2018, ASEAN have abolished import and export tariffs on cars, which could pose risks of decline for Vietnam's car manufacturing and parts industries due to car and part imports from Thailand and other ASEAN. The Vietnamese government is actively cultivating strategic car models for the market,
developing supporting industries, and expanding resource integration plans for car manufacturers. Simultaneously, it is actively constructing steel mills required for the automotive industry and large-scale car factories, striving for industrial transformation.
Vietnam is actively integrating into the int’l community and has signed several FTAs with other countries. A recent report released by its Ministry of Industry and Trade (MIOT) points out that the new FTAs have not only brought Vietnam hundreds of millions of USD in export revenue each year, but also have helped Vietnam attract foreign investment.
Vietnam's exports to major FTA markets, such as the EVFTA, the CPTPP, and the UKVFTA, have all shown a growth trend. In terms of the CPTPP, Vietnam's trade value with CPTPP member countries in 2024 increased by 12.1% compared to 2023, reaching US$134.5 billion. Vietnam's exports to Canada grew by over 18.9%, and exports to Brunei grew by over 151.2%. With the signing of the EVFTA, Vietnam's trade value with the EU in 2024 increased by 7.8% compared to 2021; simultaneously, the value of goods imported by the EU from Vietnam reached 76.54 billion USD. Regarding the UKVFTA, Vietnam's trade surplus with the UK in 2024 exceeded 7.83 billion USD.
Although Vietnam's exports to the aforementioned markets have grown, the share of these markets in Vietnam's total exports remains relatively small (even less than 10% in some provinces). Notably, Vietnam's FTA utilization rate is lower than expected, with the EVFTA at 26.1%, the UKVFTA at 24.4%, and the CPTPP at just 5.0%. Vietnamese enterprises exporting products to FTA markets are relatively few in number, primarily due to the fact that most Vietnamese products fail to meet the quality, food safety, and manufacturing technology standards required by FTA markets. Currently, many FTA import markets are raising technical standards and imposing non-tariff barriers, while Vietnamese enterprises have not proactively enhanced their capabilities to meet the qualifications required for FTA preferential treatment.
The vast majority of Vietnam's export products are raw materials or products manufactured by foreign importers. Very few Vietnamese companies are able to export their own brand products to FTA markets, and there is still room for improvement in terms of brand building and positioning. In comparison, highyield products exported by European, US, and Japanese invested companies still account for the vast majority of Vietnam's export revenue, including footwear, mobiles & components, machinery & equipment, as well as motor vehicles such as cars, motorbikes, components, etc.
The Vietnamese MIOT believes that it is necessary to accelerate the compilation and publication of legal documents related to FTA commitments and conduct regular reviews. It hopes to collaborate with other ministries and local governments to build an ecosystem that fully leverages the opportunities presented by FTAs. Funding should be set aside to support enterprises in fully utilizing FTAs, especially new small and medium-sized enterprises, and to seek financing sources from int’l financial institutions.
Since joining the WTO in 2007, Vietnam has actively developed industrial parks through policy incentives and foreign investment, fostering an export-oriented economy and attracting global industrial supply chain shifts. It has emerged as a key destination for overseas investment and a rising manufacturing hub in Asia, transitioning from an agricultural nation to a major producer and exporter of electronic products. Since 2012, electronic products have become Vietnam's largest export commodity. Since 1991, Vietnam has established JV car assembly plants and now possesses its own domestically developed car brands.
Vietnam is the only country that has signed FTAs with major trading partners such as the US, Japan, China, the EU, S. Korea, and the UK. It has joined or is negotiating a total of 19 FTAs, of which 15 have taken effect, one has been negotiated and is awaiting signature, and three are currently under negotiation. Table 1 shows the countries/regions with which Vietnam has signed FTAs and their implementation schedules. The aforementioned 19 FTAs provide Vietnamese enterprises with
advantages, effectively promoting trade activities, business connections, and bringing Vietnamese products to end consumers in many major markets. Meanwhile, the number of goods eligible for preferential tariffs under FTAs has also increased. In 2024, the total export value under FTAs using preferential Certificates of Origin (C/O) reached US$108.4 billion, representing 33.8% of Vietnam's total export value of US$320.7 billion to FTA-signed markets.
ISTI(2025/08) Vietnam has reduced import tariffs on car components since Jan. 2008, cutting rates by 3–5% for components of small passenger vehicles with 5–7 seats and vehicles with 16+ seats. Import tariffs on components for small passenger vehicles with 5–7 seats in Vietnam range from
20–25%, while those for vehicles with 16+ seats range from 13–17%. In line with the development of Vietnam's automotive industry, import tariffs on cars will continue to decrease annually. In 2014, the import tariff on cars within ASEAN was 50%. It then reduced to 35% in 2015, 20% in 2016, 10% in 2017, and 0% in 2018. The import of cars has impacted Vietnam's domestically produced cars, making many car manufacturers hesitant to invest. To mitigate the risks associated with the gradual tariff reduction, the government has implemented industrial policies to increase the localization rate of car assembly and components in Vietnam.
The Vietnamese government insists on focusing on the automotive industry as the core of industrial development, hoping to increase the domestic production ratio of auto parts, assembly, and complete vehicle production. In response to requests from car manufacturers, Vietnam has repeatedly lowered import tariffs on complete vehicles in order to stimulate car assembly production. Meanwhile, in order to foster the development of the automotive industry, “automotive” has been designated as a highly protected industry and subject to high tariffs, including import tariffs and special

consumption taxes. According to the ASEAN FTA and Vietnam's trade liberalization commitments, the government is preparing countermeasures. The Vietnamese MIOT has recommended developing the automotive industry through tax policies, pointing out that large enterprises should be encouraged to develop the automotive industry on the basis of equal treatment for domestic and foreign manufacturers, and that car manufacturers and parts assemblers should develop peripheral industries to deepen their integration into the global automotive industry’s value chain.
Many car assembly manufacturers continue to request tax incentives from the government. The car manufacturing industry is eligible for tax incentives and preferential policies for acquiring land for factory construction. The Vietnamese Ministry of Finance, in cooperation with the Ministry of Commerce, has submitted a proposal to the Central Government for approval and has formulated preferential policies for automotive investment and production, including the implementation rules for the Special Consumption Tax Law on Cars. In 2018, Vietnam abolished import tariffs on ASEAN cars in accordance with the ATIGA, completely opening up its domestic car market. Coupled with the implementation of the ASEAN FTA and a significant amount of domestic demand, this has actively attracted more int’l car manufacturers to set up operations in Vietnam.
Vietnam encourages int’l leading car manufacturers to establish their presence in Vietnam. To enable the domestic industry to prepare early, the MOIT has introduced policies to assist the Vietnamese automotive industry in enhancing its competitiveness. Under these policies, Vietnam imposes high tariffs on imported luxury vehicles and incentivizes domestic enterprises or JV to engage in auto parts production or complete vehicle assembly (CBU) within the country. The government also reduces tariffs on exports. The Vietnamese government's adjustments to policies related to the automotive industry and components aim to promote reform, openness, and internationalization. The government is developing the automotive sector as a key industry, not only to meet domestic demand but also to enter ASEAN and the int’l market.
Copyright owned by Fastener World / Article by James Hsiao





Data note: The data for this article is derived from the US Census trade statistics. US Census trade statistics analyze imports and exports on all modes of transportation. That value is calculated in USD by general FOB for imports and FOB for exports. Fasteners in this article are defined as any product under HS Code 7318 (screws, bolts, nuts, coach screws, screw hooks, rivets, cotters, cotter pins, washers and similar articles, of iron or steel). The volume in terms of mass is recorded in Gross Weight (KG).
The ongoing trade tensions between the United States and China have sent ripple effects throughout the global fastener supply chain, fundamentally reshaping trade flows, manufacturing practice and strategic planning across multiple industries. These dynamics are beginning to be seen in the first few months of 2025 through statistical trade data and the shift in fastener trade between these two major economic powers. Additionally, the escalation of tariffs and regulatory measures are beginning to have immediate impacts on trade policies and international market strategies. Ultimately, the manufacturers and importers are managing operational pressures including rising costs and logistical disruptions deepening the economic divide between the U.S. and China.
Looking at the fastener supply chain on a holistic level, the U.S. primarily sources from Taiwan and China. Historically, Taiwan has maintained upwards of 30% of the market share of fastener trade to the U.S., followed by China that has maintained anywhere from 17% to 20% of the total market share in FOB value (Table 1-1 to 1-2). Countries such as Japan, Canada and Germany follow suit, accounting for upwards of 5% to 10% of the total market share. In February 2025, U.S. fastener imports from China totaled USD
Table 1-1. U.S. Import Origins of Fasteners (2022-2023)
95 million (Table 1-3), down from USD 121 million in January – a sharp 21% decline (Table 1-2). This stark decline in February 2025 can be attributed to the tariff threats of late 2024 following the presidential election results where U.S. importers may have begun to shift to a more conservative mindset. Overall, there was a near 11% decline in total fastener imports into the U.S. in February 2025 compared to January 2025.
Table 1-3. U.S. Import Origins of Fasteners (Feb. 2025)
Table 2-1. Fasteners Imported from China to the U.S. by Category (2022-2023)
731811 - Coach Screws, Threaded, Of Iron Or Steel
731814 - Self-Tapping Screws, Threaded, Of Iron Or Steel
731815 - Other Threaded Screws And Bolts, With Or Without Their Nuts Or Washers, Of Iron Or Steel
731816 - Nuts, Threaded, Of Iron Or Steel
731819 - Other Threaded Articles Of Iron Or Steel
731821 - Spring Washers And Other Lock Washers, Of Iron Or Steel
731822 - Washers, Other Than Lock Washers, Of Iron Or Steel
731823 - Rivets Of Iron Or Steel
731824 - Cotters And Cotter Pins, Of Iron Or Steel
731829 - Other Nonthreaded Articles (Fasteners), Of Iron Or Steel
Table 2-2. Fasteners Imported from China to the U.S. by Category (2024-Feb. 2025)
731811 - Coach Screws, Threaded, Of Iron Or Steel
731814 - Self-Tapping Screws, Threaded, Of Iron Or Steel
731815 - Other Threaded Screws And Bolts, With Or Without Their Nuts Or Washers, Of Iron Or Steel
731816 - Nuts, Threaded, Of Iron Or Steel
731819 - Other Threaded Articles Of Iron Or Steel
731821 - Spring Washers And Other Lock Washers, Of Iron Or Steel
731822 - Washers, Other Than Lock Washers, Of Iron Or Steel
731823 - Rivets Of Iron Or Steel
731824 - Cotters And Cotter Pins, Of Iron Or Steel
731829 - Other Nonthreaded Articles (Fasteners), Of Iron Or Steel
The U.S. primarily imports fasteners from China within HS 731815 (threaded screws and bolts), 731816 (threaded nuts), and 731814 (selftapping screws) ( Table 2-1 to 2-2). These are all common components in the automotive industry for engine assembly and suspension systems. However, these are also components used for manufacturing machinery equipment, electronics and appliances. In February 2025, U.S. imports from China fell by 21.6% for HS 731815, 17% for HS 731816, and nearly 27% for HS 731814. In addition to the decline in market share by value, February 2025 also saw a significant drop in fastener import volumes, with a 24% decrease recorded (Table 2-2).
Feb. 2025)
731812 - Wood Screws Other Than Coach Screws, Threaded, Of Iron Or Steel
731814 - Self-Tapping Screws, Threaded, Of Iron Or Steel
731815 - Other Threaded Screws And Bolts, With Or Without Their Nuts Or Washers, Of Iron Or Steel
731816 - Nuts, Threaded, Of Iron Or Steel
731819 - Other Threaded Articles Of Iron Or Steel
731821 - Spring Washers And Other Lock Washers, Of Iron Or Steel
731822 - Washers, Other Than Lock Washers, Of Iron Or Steel
731823 - Rivets Of Iron Or Steel
731824 - Cotters And Cotter Pins, Of Iron Or Steel
731829 - Other Nonthreaded Articles (Fasteners), Of Iron Or Steel
In relation to U.S. fastener exports, China has remained strong as its third largest trading partner accounting for 5% of the total market share. Ahead of China are Canada and Mexico which together account for over 50% of the total market share. Due to the USMCA trade agreement, U.S. trade with its immediate neighboring partners is beneficial for several reasons including advantages on tariffs. In February 2025, there was a slight decrease of 9% in total fastener exports from the U.S. to China ( Table 3-1 to 3-2). Amongst the fasteners exported from the U.S. to China were 731815, 731816, and 731829 (non-threaded articles of fasteners) (Table 4).
In 2025, the U.S.-China trade relationship intensified sharply, beginning in February when the United States imposed a 10% tariff on all Chinese imports of goods, citing national security concerns. This was quickly followed by a second increase in March which raised the tariff to 20%. By early April, a more aggressive stance was taken as the U.S. implemented an additional 34% tariff, bringing the cumulative rate to 54%, and immediately increased it further to 125% with a clarification pushing the effective rate to 145%. In response, China launched a series of retaliatory measures beginning in February with the imposed tariff ranging from 10-15% on key U.S. exports including commodities such as crude oil, LNG, agricultural machinery, and vehicles. In March, this expanded to agricultural goods such as soybeans, port and cotton. By mid-April, China escalated its retaliation, first raising tariffs on all U.S. goods to 84%, and then to 125%. It also suspended exports of critical minerals and magnets essential to high-tech manufacturing, signaling a strategic shift beyond tariffs. These actions combined marked a severe escalation in trade tensions, with profound implication for industries reliant on U.S.-China supply chains, including fasteners.
Higher tariffs sharply increase the price of Chinese fasteners leading to a higher landed cost for US Importers and consumers. This will more than likely cause a rise in production costs for U.S. manufacturers who rely on Chinese fasteners. Let alone the number of supply chain disruptions that will be seen considering how fasteners are a critical component. These disruptions could lead to delays or cost fluctuations, and ultimately cause inventory planning issues for companies relying on Chinese suppliers.
The 2025 escalation in U.S.-China trade tensions has had immediate, tangible effects on manufacturing and procurement operations across the fastener supply chain. With import costs rising sharply due to elevated tariffs, U.S. manufacturers face mounting pressure to manage tighter margins, especially in cost-sensitive sectors like automotive, electronics, and industrial equipment. Procurement teams are contending with increased lead times, limited availability of specific fastener types, and greater volatility in pricing. The uncertainty around future policy shifts has led many companies to adjust purchasing strategies such as placing earlier or larger orders, increasing safety stock levels, or renegotiating supplier contracts to include contingency clauses. Operationally, manufacturers are also absorbing the impact of supply delays from China, forcing adjustments to production schedules and occasionally leading to stalled assembly lines. These pressures are not only straining supplier relationships but also reshaping how manufacturers evaluate risk and resilience within their global sourcing strategies.
In summary, the 2025 tariff escalation has created a costlier, riskier and less predictable trade environment for fasteners moving between the U.S. and China, with consequences for both immediate operations and long-term supply planning.
Copyright
owned by Fastener World / Article by Sabrina Rodriguez

After President Trump took office, the U.S. promoted new tariff policies that had a significant impact on the global economic and trade structure. Against this backdrop, Indonesia became the first ASEAN country to complete an agreement with the U.S., securing a relatively favorable tariff rate of 19%. This phenomenon not only reflects the U.S.’s emphasis on the developmental potential of Indonesia’s industrial environment but also highlights Indonesia's unique potential position among ASEAN countries. Although the trade volume of machinery products between the U.S. and Indonesia is currently not high, Indonesia possesses abundant metal mineral resources, a large domestic market, and low labor costs, giving it a significant price competitiveness in machinery equipment and components. In recent years, the Indonesian government has actively promoted local processing of metal raw materials such as nickel, bauxite, and copper through its mineral policies. This has successfully made Indonesia the world's largest stainless steel exporter, with foreign investment in Indonesia's metal industry accounting for 23.4%. Therefore, Indonesia still has the opportunity to attract metal processing industries as well as procurement or assembly processes for related machinery parts to the local area. Indonesia provides abundant raw materials, policy support, and huge market linkage opportunities for the metal products industry, driving notable development advantages in related machinery products.
印尼機械產業在美國關稅
Countries from Which the
Table 1 shows the major countries from which the U.S. imported machinery products from 2020 to 2024. U.S. imports of machinery products increased from 311 million USD in 2020 to 441 million USD in 2024, with a CAGR of 9.1%, indicating stable growth in demand. The top 15 import sources accounted for a 94.5% market share, demonstrating high concentration. Germany ranked first with 107 million USD, accounting for 24.3%, with a CAGR of 18.5%; Italy ranked second with 68 million USD, accounting for 15.3%, with a CAGR of 14.7%, making both countries the main sources of machinery imports. China held about 7.0% market share with a CAGR of 24.5%, showing rapid expansion of its influence. Taiwan ranked 12th, with a smaller scale but a potential growth rate of 23.6%. Currently,
Table 1. Major Countries from Which the U.S. Imported Machinery
Germany and Italy still dominate the U.S. import market, but U.S. imports are becoming more diversified, with rapidly increasing market shares from the two sides of the Taiwan Strait and emerging countries.
Table 2 shows categories of U.S. imported machinery from the world from 2020 to 2024. The main machinery category was "Machinery for Working Metal" (Tariff Code: 847981), which increased from 155 million USD in 2020 to 258 million USD in 2024, holding a 58.5% market share and a CAGR of 13.6%, becoming the main import driver. This reflects strong demand in the U.S. infrastructure, automotive, and electronics industries for metalworking and wire-winding machinery. The second category was "Injection Molding or Shaping Machinery" (Tariff Code: 847759), which increased from 156 million USD to 183 million USD by 2024, with a 41.5% market share but only a 4.0% CAGR. The U.S. import focus is shifting from molding machinery to metalworking machinery, indicating deeper reliance on precision metalworking equipment due to reshoring and industrial chain strengthening.
Table 3 shows the major countries from which Indonesia imported machinery products from 2020 to 2024. Indonesia’s machinery imports increased rapidly from 54.93 million USD in 2020 to 155 million USD in 2024, with a CAGR of 29.5%. The top 10 importing countries accounted for a highly concentrated market share of 98.5%. China jumped from 16.977 million USD to 120 million USD, capturing a 77.7% market share and a CAGR of 63.1%, effectively forming a monopoly. Italy, although small with 8.119 million USD, showed a high CAGR of 78.0%, demonstrating the advantage of European high-end equipment entering the Indonesian market. Indonesia's imports from the U.S. rose from 1.759 million USD to 7.376 million USD, with a market share of 4.8% but a rapid CAGR of 43.1%, showing quickly growing influence. In contrast, Japan, Taiwan, Germany, and Singapore all experienced declines in their market shares. Overall, China’s dominant position in Indonesia’s machinery product market is expanding rapidly, compressing the share held by other countries. Non-China suppliers will need to rely on technological differentiation and high-end markets to maintain competitiveness in the future.
Table 4 shows the categories of machinery products imported by Indonesia globally from 2020 to 2024. The main imported machinery product category was "Machinery for Working Metal" (Tariff Code: 847981), which surged from 37.324 million USD to 137 million USD, accounting for 88.4% of imports with a CAGR of 38.3%. This category is the main growth driver for machinery products, reflecting strong demand in the Indonesian market for metalworking and wire-winding machinery. In contrast, "Injection Molding or Shaping Machinery" (Tariff Code: 847759) only increased from 17.611 million USD to 17.909 million USD, making up 11.6% of imports but with a mere 0.4% CAGR, indicating a stagnant market. This shows that Indonesia’s infrastructure and manufacturing sectors still maintain a demand primarily for metalworking machinery imports.
Table 4. Categories of Machinery Products Imported by Indonesia Globally from 2020 to 2024
Table 5 shows the major export destinations for Indonesia's machinery products from 2020 to 2024. Indonesia’s machinery exports increased from 282,000 USD in 2020 to 3.742 million USD in 2024, with a CAGR of 90.9%. Although the total export amount remains modest, the growth momentum is strong. Vietnam is Indonesia’s largest export destinations, reaching 3.36 million USD in 2024 and accounting for 89.8% of exports, with a CAGR of 95.3%, demonstrating a highly dominant position. Malaysia, India, and Thailand have also emerged as important export destinations for Indonesia in recent years. Despite the rapid export growth, Indonesia’s machinery exports are overly reliant on the Vietnamese market, presenting a clear structural risk. Moving forward, Indonesia needs to expand into diversified markets such as other ASEAN countries and regions like Europe and the U.S. to enhance resilience.
5. Major Export Destinations for Indonesia's Machinery Products from 2020 to 2024
Table 6 shows the categories of Indonesia’s machinery exports to the world from 2020 to 2024. Indonesia’s main exported machinery product category is "Machinery for Working Metal" (Tariff Code: 847981), which surged from 76,000 USD to 3.363 million USD, capturing an 89.9% market share with a CAGR of 157.9%, becoming the main export driver. In contrast, "Injection Molding or Shaping Machinery" (Tariff Code: 847759) only increased from 206,000 USD to 379,000 USD, with a 10.1% market share and a limited CAGR of 16.5%. Overall, while Indonesia’s machinery exports are rapidly expanding, the scale remains small and overly concentrated on a single product category, representing structural risk. Going forward, measures such as product diversification, export market diversification, and technology upgrades are necessary to improve industry resilience and strengthen competitiveness.
In 2024, the U.S. GDP was approximately 29.2 trillion USD. The manufacturing sector primarily exports civil aircraft and engine parts and imports motor vehicles, data processing machines, etc. The U.S. machinery industry covers civil aircraft, non-electronic machinery, machine tools, precision machinery, medical equipment, biotechnology, agricultural/mining/transport machinery, as well as electric vehicle battery assembly and semiconductor processing equipment.
The development of machinery industries in various U.S. states is closely linked to high-tech trends such as electric vehicles, semiconductors, aerospace, and advanced manufacturing. Key states include:
• New York (industrial machine tools production center, semiconductor development)
• Pennsylvania (focus on advanced manufacturing and 3D metal printing)
• Arizona (semiconductor manufacturing core, driving related processing machinery and battery equipment)
• Kentucky (hub for automotive and electric vehicle battery manufacturing)
• North Carolina (significant investments in industrial machinery and electric vehicle battery assembly)
• Tennessee (major transportation equipment, attracting forging equipment manufacturers)
• Ohio (leading U.S. engine production, advanced machinery manufacturing)
• Texas (increased electric vehicle productivity, large automotive parts industry)
Most U.S. states provide manufacturing machinery sales tax exemptions (e.g., Georgia), R&D and investment tax credits, and employment subsidies. The government also actively promotes workforce training to meet industry talent needs.
In 2024, Taiwanese companies' cumulative investment in the U.S. "machinery equipment manufacturing" sector reached 376 million USD, including metal cutting bandsaws, forging equipment, aircraft component technology, charging station/battery assembly, and semiconductor processing equipment. This serves as a reference for companies considering setting up factories in Indonesia for cross-national collaborations.
The U.S. machinery industry benefits from a large economy, high-tech development, industrial clusters by state, and active government policies. Rapid growth and investment potential come from electric vehicles, aerospace, semiconductors, and advanced manufacturing technologies.
Copyright owned by Fastener World /
Machinery products (Tariff Codes: 847981 and 847759) are not included in the U.S. steel and aluminum Section 232 tariff list or its derivatives, so rates apply equally to all countries. For example, the U.S. tariff rate on machinery goods is 15% for Japan and South Korea; ASEAN countries have 19% for Malaysia and Thailand, 20% for Vietnam. Currently, Indonesia’s market share in U.S. machinery imports is very low (no related imports from Indonesia in 2024). Therefore, Indonesian competitiveness in the U.S. depends on fundamentals such as mineral resources, location, cost, capacity, technology, regulations, as well as the capacities of investors planning local production.
After the U.S.-China trade war, international investment strategies tend to spread risk by establishing a "China-Taiwan Plus One" approach, finding suitable production bases beyond Taiwan. Indonesia is considered a promising Southeast Asian option, leading many Taiwanese firms to shift production lines from increasingly saturated countries like Vietnam to Indonesia. This supply chain restructuring trend offers Indonesia a strategic opportunity to develop as an export-oriented manufacturing base for machinery products.
In 2024, Indonesia had about 279 million people, making it the fourth largest country globally and the largest in ASEAN. It possesses a vast domestic market and demographic dividend foundations. This provides local sales opportunities and a stable base for export production. The workforce is abundant and young, with 40 million workers aged 20 to 39.
Indonesia has actively improved its investment environment in recent years, launching comprehensive employment creation laws and loosening restrictions on foreign investment. The number of industries with foreign ownership limits was drastically reduced from 350 to 41 conditional industries, reducing many investment barriers and increasing incentives.
1. Tax Holiday: Machinery and key components manufacturing industries are classified as "pioneer industries" and along with upstream basic metal industries enjoy tax holidays. Depending on investment amount, companies can receive up to 20 years of full corporate income tax exemption, followed by 2 additional years of 50% tax reduction.
2. Tax Deductions: Qualified investments can deduct 30% of taxable income within 6 years, i.e., 5% of total investment yearly.
3. Two-Year Import Duty Exemption: New or expanded companies can apply for exemption from import duties on production machinery and raw materials for two years.
4. Super Tax Deduction Scheme: Certain metal processing industries (e.g., nails, screws, metal fasteners) can receive additional corporate income tax deductions for expenditures on R&D and talent training.

In 2018 and again in the 2020s, the U.S. administration has applied tariffs on steel and aluminium imports using Section 232 (national security) and other trade tools. The 2018 measures (25% on many steel products, 10% on aluminium) produced immediate upstream price effects; more recent reinstatements and announced increases (e.g., moves to 25% and later up to 50% for all origins excluding the UK) have renewed uncertainty across North American supply chains. The U.S. government has explicitly framed these actions as protecting domestic metals production, with fact sheets and executive actions issued in 2025 reiterating and expanding such tariffs.
Many fasteners use commodity steel coil or bar stock as primary inputs and are either produced domestically in Canada or imported finished products from the U.S., Mexico, Europe and Asia. Even when final fastener goods are Canadian-made, their raw material inputs and price competitiveness are sensitive to cross-border tariffs on steel and aluminium.
There are multiple transmission channels through which U.S. tariffs on metals affect Canadian fastener firms.
Tariffs on steel and aluminium raise the landed cost of raw materials that either come indirectly through U.S. supply chains or through broader global price ripples. Even if Canadian fastener manufacturers source steel domestically, market prices for plate, coil and bar stock are internationally linked. The United States is a major metals market; policy-driven price changes there affect global spreads and the cost basis for Canadian mills and service centres. The USITC (United States International Trade Commission) and other modelling studies show downstream industries face higher production costs when upstream tariffs increase.1
1 https://www.usitc.gov/publications/332/pub5405.pdf?utm_source=chatgpt.com
2. Trade Diversion and Competitive Displacement
Tariffs distort trade flows. When the U.S. erects tariffs, suppliers redirect exports elsewhere or source alternative suppliers. That can mean U.S. buyers—formerly purchasing Canadian finished fasteners—seek different sources, or Canadian fastener exporters find markets more constrained. Conversely, tariff differentials can make imported finished fasteners from third countries relatively more or less attractive compared to domestic production, changing competitive dynamics for Canadian plants and distributors.2&3
3. Supply-chain Friction and Lead-time Volatility
Tariffs often come with sudden compliance, paperwork and certification changes. Firms respond with altered inventories, port congestion, and greater demand for domestic supplier qualification — all of which add cost and slow production cycles.4
4. Demand Shock and Project Delays
Higher component costs cascade into higher construction, automotive and equipment prices — sectors that consume fasteners heavily. When metal price pressures appear, customers may delay capital projects or seek lower-specification alternatives, suppressing demand for higher-value or specialty fasteners. Broad macro analyses and surveys of Canadian businesses show rising uncertainty and anticipated impacts on sales when tariffs are in play.5
• Number of Businesses
As of 2025, there are 822 fastener suppliers (distributors + wholesalers + service providers + manufacturers) operating across Canada—including manufacturing and distribution—highlighting the sector’s breadth. Major concentrations are found in Ontario (about 335 suppliers), Alberta (132), British Columbia (118), and Quebec (100)6
• Domestic Manufacturing Scale
The screw, nut, and bolt manufacturing generates approximately USD 1.1 billion in annual revenue as of 2024–2025, with about 107 manufacturing businesses and an employment base of roughly 3,587 people.7
• Broader Fastener Market
Considering industrial fasteners—including plastic and other categories—the market is even larger: Canada’s fastener market reached USD 1.983 billion in revenue in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.4%, reaching USD 2.561 billion by 2030.8 One forecast report is even more bullish: it projects the market growing from USD 3.33 billion in 2024 to USD 5.09 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 5.45%.9
• Export Activity
In 2024, exports of screws, bolts, nuts, and similar steel articles (HS 7318) totalled USD 635 million, up from USD 644 million in 2023. This category accounted for roughly 0.09% of Canada’s total merchandise exports (valued at USD 721 billion).8
2 https://atlasmfg.com/blog/2025-tariff-update-steel-aluminum-tariffs-rise-to-25-andglobal-trade-tensions-mount/?utm_source=chatgpt.com
3 https://www.rbc.com/en/thought-leadership/economics/featured-insights/how-u-ssteel-and-aluminum-tariffs-would-impact-canadas-economy/?utm_source=chatgpt.com
4 https://www.endries.com/blog/navigating-the-tariffs-endries-philosophy-andapproach/?utm_source=chatgpt.com
5 https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/pub/11-621-m/11-621-m2025007-eng.htm?utm_ source=chatgpt.com
6 https://www.poidata.io/report/fastener-supplier/canada/?utm_source=chatgpt.com
The Government of Canada is working to reduce harm and protect competitiveness in the fastener sector. Ottawa is negotiating exemptions and quota arrangements with the United States, continuing to use diplomacy to ease the burden on industries dependent on steel and aluminum. It is providing temporary relief by offering tax measures, credit lines, and short-term grants, helping SMEs manage working capital pressures as costs are rising. At the same time, the government is supporting domestic capacity by encouraging investment in steel and aluminum production, while strengthening customs enforcement to prevent tariff circumvention and unfair imports. It is also funding programs that are helping manufacturers move into higher-value fastener production through certification, R&D, and automation. By consulting industry and applying countermeasures, Ottawa is showing that it is actively shaping conditions for resilience, even as political will and budget limits are setting the pace.10
Industry commentaries from distributors and trade associations underscore adaptive behaviors: suppliers building buffer inventories, re-negotiating supplier contracts, and prioritizing qualifying high-margin OEM relationships. Retailers and infrastructure OEMs — careful about total lifecycle cost — have signalled willingness to pay modestly higher prices for reliable, certified Canadian-made fasteners if delivery and quality are guaranteed. Yet smaller contract manufacturers remain vulnerable. These on-the-ground accounts mirror the broader warnings published in financial and trade press about potential “catastrophic” impacts on jobs and steel sector health if tariffs escalate dramatically.11
Trump-era tariff measures — and their reappearance and intensification in the 2020s — are a reminder that trade policy can change rapidly and have outsized impacts on even seemingly small sectors like fasteners. For Canadian fastener manufacturers, the twin challenges are managing immediate input-cost shocks and positioning themselves for a potentially re-regionalized, higher-cost industrial landscape. Companies that proactively diversify supply, capture more value, shore up liquidity, and engage with government and industry peers will be best placed to weather tariff cycles.
The fastener industry’s future in Canada will depend less on the next headline and more on which firms anticipate policy volatility and adapt their structures and strategies accordingly. Given the central role of steel and aluminum inputs, any durable solution will also require a smart public policy — negotiated trade arrangements where possible, targeted temporary support, and programs that help firms move up the value chain. In short: plan, adapt, and upgrade.
7 https://www.ibisworld.com/canada/industry/screw-nut-bolt-manufacturing/646/?utm_ source=chatgpt.com
8 https://www.grandviewresearch.com/horizon/outlook/industrial-fasteners-market/ canada?utm_source=chatgpt.com
9 https://www.credenceresearch.com/report/canada-industrial-fasteners-market?utm_ source=chatgpt.com
10 https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/pub/11-621-m/11-621-m2025007-eng.htm?utm_ source=chatgpt.com
11 https://www.endries.com/blog/navigating-the-tariffs-endries-philosophy-andapproach/?utm_source=chatgpt.com


































