




Lindsey Dao, BSN, RN, Anna Lee Rhea BSN, RN, Laura Gray, PhD, RN, David Phillippi, PhD, Asos Mahmood, MBChB, MPH, PhD, Satya Surbhi, PhD, MS, BPharm
Belmont University Doctor of Nursing Practice Program
• Residents of Shelby County, Tennessee experience disproportionate cardiovascular (CV) health risks and barriers to preventive care.
• Over half of adults in Shelby County are overweight or obese, significantly higher than the 37% state average.3
• 16% of adults in Shelby County have been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes and 41.5% live with hypertension.2
• Fewer than 30% of residents have seen a primary care provider in the past year, reflecting limited access to preventive services in this medically underserved area.1
• These disparities highlight the need for accessible, low-cost, community-based strategies to promote healthy behaviors and reduce preventable CV risks.



• 22 participants enrolled; 1 opt-out; 11 completed the survey (50% response rate)
• 100% (11/11 participants) read all or most MTMs


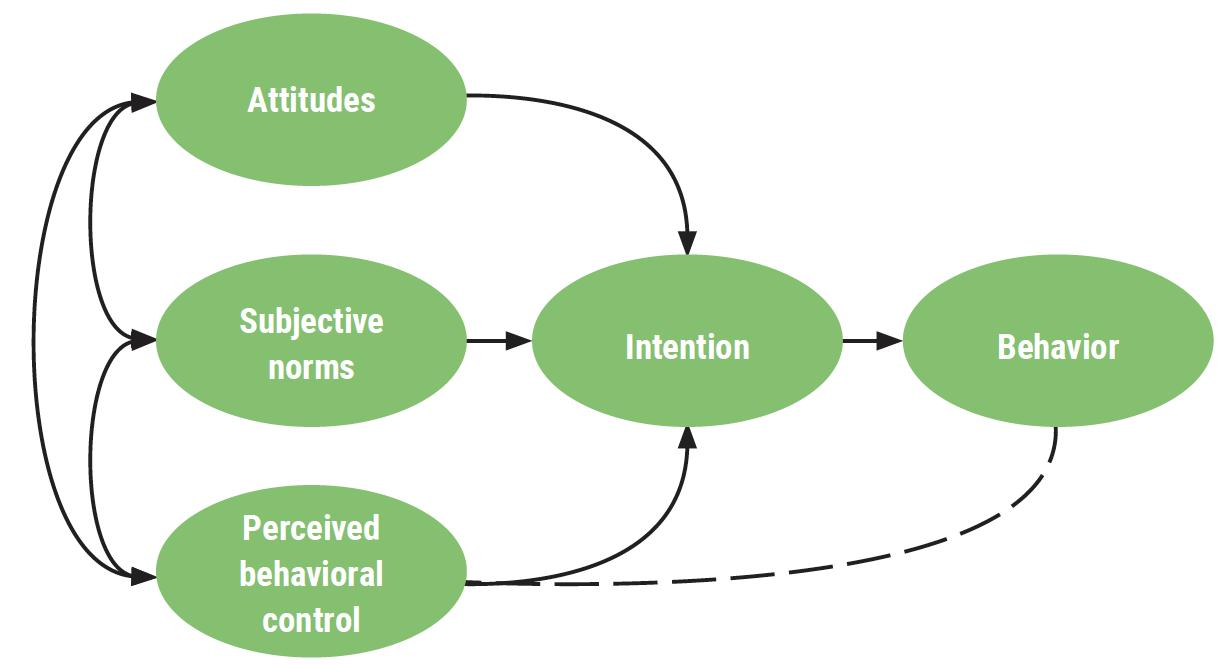
• Purpose: To evaluate the impact of a 3-week Motivational Text Messaging intervention on self-reported physical activity and dietary behaviors among adult participants at the University of Tennessee Heath Science Center (UTHSC) Shelby County Health Hubs.
• Aim: By October 2025, at least 20% of UTHSC Shelby County Health Hub participants who receive the motivational text messaging intervention will self-report a healthier diet and/or increased physical activity.
• Quality Improvement (QI) project using a post-intervention evaluation design
• Change Idea: Implement Motivational Text Messaging (MTM) to promote cardiovascular risk–reducing behaviors
• Setting & Population: A convenience sample of 22 African American adults (2 males, 20 females) was recruited from two UTHSC Shelby County Health Hubs, ShelbyCares and Uptown, which serve medically underserved communities in Memphis, Tennessee
• Intervention: Participants received three MTMs per week for three weeks via SMS, focused on promoting healthy eating, physical activity, and motivation for behavior change
• Message Content: MTMs were adapted from a previous UTHSC evidence-based message library (2016) and culturally tailored to reflect African American health beliefs and Memphis community context
• Post-intervention data were collected using an electronic survey assessing engagement, perceived behavior change, satisfaction, and message preferences
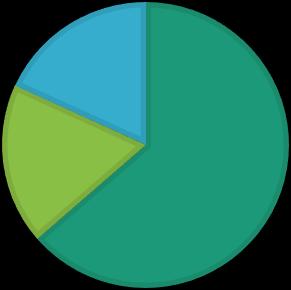
• 64% (7/11 participants) reported behavior change (increased activity/eating healthier)
• 18% (2/11 participants) reported not sure of behavior change but felt increased motivation
• 72% (8/11 participants) reported MTMs felt personal
• 91% (10/11 participants) wanted MTMs to continue
• Morning messages (8–11AM) preferred by most participants
• Mixed preference for message frequency



• MTMs increased motivation and supported healthy behavior change.
• High engagement indicates feasibility in underserved community settings.
• Participants already in Health Coaching also wanted MTMs to continue, showing MTMs can complement existing wellness services.
• Written feedback came only from participants who reported no or uncertain behavior change. Participants expressed interest in receiving more varied and educational content, such as healthy recipes, information on Blue Zones and healthy aging, and nutrition or macronutrient guidance.
• Overall, MTMs were well received, but expanding message variety may enhance future engagement and strengthen longterm sustainability.
Motivational text messaging is a feasible, low-cost strategy to support and encourage healthy behaviors in underserved communities. It can be integrated into existing Health Hub services as a supplemental tool that reinforces health education and promotes ongoing engagement between visits. Expansion to additional UTHSC Health Hubs is realistic and sustainable with minimal staff support. Future implementation should include 2-way messaging and greater variety in message topics, including recipes, aging wellness, and nutrition education, to maintain engagement. MTMs represent a scalable digital health strategy to promote health and reduce CV risk in community settings.