@aestheticsgroup
@aestheticsjournaluk
Aesthetics
aestheticsjournal.com
occur when incorrect injection sites are used, with doses that are too high and/or inappropriate patient selection; commonly occurring with inexperienced practitioners.4 No medication has been found to effectively reverse the effects of botulinum toxin. There are various methods, physical and medical, which may provide some improvement prior to normal muscle function returning.
Treatments to improve eyelid and eyebrow ptosis
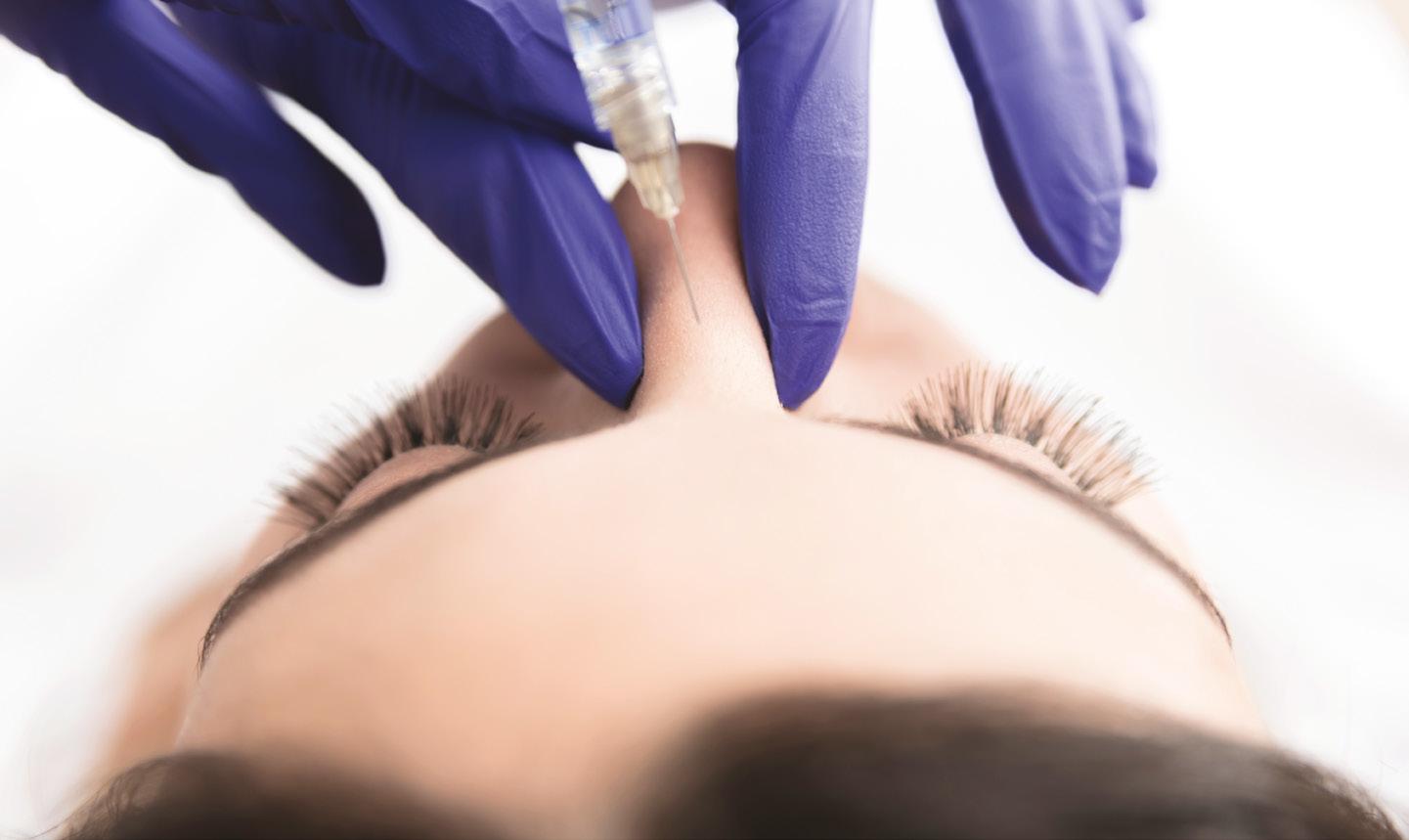
Understanding Ptosis Dr Aileen McPhillips introduces ptosis following toxin treatment and the relevant options for management Ptosis is derived from the Greek word for ‘falling’ and refers to the drooping of a body part.1 The term is commonly associated with drooping of the eyelid – more specifically called blepharoptosis. Ptosis can occur in all age groups and may be caused by various factors. With relevance to aesthetic practitioners, ptosis may occur as an adverse reaction following botulinum toxin treatment, and therefore is an important issue to be aware of. Botulinum toxin is administered to provide facial rejuvenation, which might result in muscle weakness and potentially lead to eyelid or eyebrow droop.
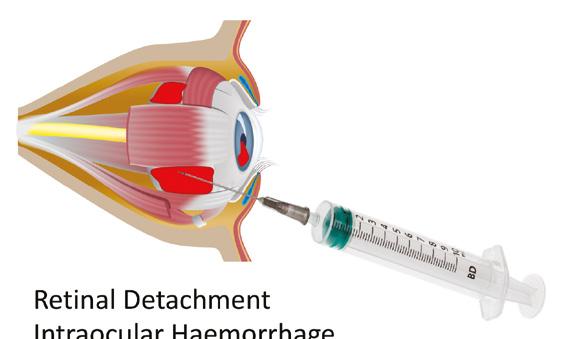
Where does ptosis occur? Upper eyelid ptosis may occur when treating the glabellar complex. Botulinum toxin diffuses through the orbital septum, affecting the lid elevator muscle as it transverses the pre-periosteal plane, or the toxin may track along the tributaries of the superior ophthalmic vein.2 Drooping of the upper eyelid causes a poor cosmetic appearance and can significantly impair vision. Various studies suggest an incidence of 1-5%, with
the lower incidence occurring when treatment is carried out by experienced practitioners.3,4 Therefore, injection technique and medical experience play a key role in the occurrence of this complication. Eyebrow ptosis is an adverse effect of treatment in which the forehead containing botulinum toxin causes reduced activity in the frontalis muscle.4 It tends to
Careful patient selection is key in avoiding complications post-treatment with botulinum toxin. Following a thorough consultation and full medical history, the practitioner should assess the face and patient’s anatomy noting in particular the brow position and pre-treatment asymmetry. Facial muscle tone should also be assessed and noted. Pre-treatment photography is important for future reference.5 Physical stimulation Physical stimulation including manual or electrical, such as using an electric toothbrush for several minutes daily has been shown to accelerate the return of muscle function in the region. It is anecdotally reported that this improves ptosis hastily and is commonly suggested by experienced practitioners as a useful ritual to follow, however, no formal studies have been conducted to assess this. Medication Anticholinesterase or alpha-adrenergic eye drops enhance cholinergic transmission by indirectly inhibiting the destruction of
Ptosis tends to occur when incorrect injection sites are used, with doses that are too high and/or inappropriate patient selection; therefore more commonly occurring with inexperienced practitioners
Reproduced from Aesthetics | Volume 8/Issue 8 - July 2021